Scientists quiz 10/30/25
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Democritus
Developed the concept of the atom
John Dalton
Developed the atomic theory & law of multiple proportions
- atomic theory: all matter is made of atoms
- law of multiple proportions: when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers. For example, carbon and oxygen form both carbon dioxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2)
Benjamin Franklin
electricity, coined battery (positive, neg charge)
William Crookes
made the cathode ray tubes, discovery of the element thallium and fundamental in the development of atomic physics
J.J. Thomson
through his experiments with cathode rays, charge to mass ratio of an electron, plum pudding model
Robert Millikan
charge and mass of an electron, oil drop experiment
Eugen Goldstein
discovered canal rays (positive ions) (found proton's charge, but not the actual proton)
William Roentgen
discovered X-rays in 1895 while experimenting with cathode rays, experiemented w/ uranium
Antoine Becquerel
BIG RADIATION GUY (uranium), discovering spontaneous radioactivity, uranium compound could expose a photographic plate through black paper, even in the dark. This led to his conclusion that the material was emitting its own radiation spontaneously.
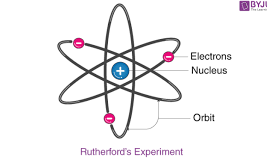
Ernest Rutherford
OVERSAW gold foil experiment, alpha beta gamma radiation, (his model is also known at nuclear model)
James Chadwick
discovering the neutron in 1932
Henry Moseley
the atomic number is the correct basis for the periodic table, rather than atomic mass
Johann Balmer
discovering a formula in 1885 that accurately predicts the wavelengths of the spectral lines of hydrogen, known as the ______ series
Max Planck
the father of quantum theory, which he developed in 1900 by proposing that energy is emitted and absorbed in discrete packets called "quanta", _____'s constant
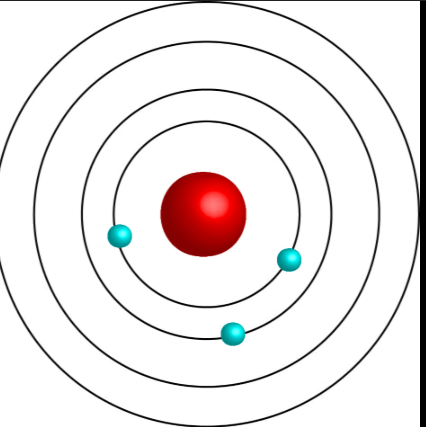
Neils Bohr
planetary model/develped the ___ model of the atom/electrons exist in specific, fixed orbits around the nucleus and jump between these orbits, releasing or absorbing energy as light
Albert Einstein
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT (light is a particle, electrons jump energy levels), developing the theory of relativity, which revolutionized the understanding of space, time, and gravity
Louis DeBroglie
wave-particle duality, all matter exhibits both wave and particle properties.
Werner Heisenberg
uncertainty principle: that there are inherent limits to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as a particle's position and momentum, can be simultaneously known
Erwin Schrodinger
______ equation: In 1926, he developed a differential equation that provides a mathematical model for the wave-like behavior of electrons and other particles
Wave function: The equation uses a mathematical function called the wave function, represented by the Greek letter psi (Ψcap psiΨ), to describe the probability of finding a particle in a specific location.