APES Unit 4 Test
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Japan 2011 Earthquake
Tohoku Earthquake → Tsunami → Flooding of nuclear power plant → Meltdown
Components of Earth’s Crust
Oxygen
Silicon
Aluminum
Components of Air
Nitrogen 78%
Oxygen 21%
Other 1%
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Radioisotopes
Radioactive isotopes - their chemical identity changes as they shed subatomic particles and emit high-energy radiation
Half-Life
The amount of time it takes for one-half of something’s atoms to decay
Radioactive
The quality by which some isotopes decay, changing their chemical identity as they shed atomic particles and emit high-energy radiation
Water Properties: Cohesion
How water droplets stick together
Water Properties: High Heat Capacity
Requires a large amount of energy to change its temperature
Water Properties: Adhesion
How water sticks to other things
Water Properties: Universal Solvent
Can dissolve most substances
Water Properties: Density
Solid form is LESS dense than liquid form
Bond within H2O molecules
Covalent Bond
Bond between H2O molecules
Hydrogen Bond
Hydrocarbons
Chains of C & H molecules ONLY
- Crude Oil
- Petroleum Products
- Natural Gas
- Coal
Benefits of Carbon
-Carbon has created wealth and modern lifestyle
- Heating living things or fossil fuels breaks Carbon
- Broken Carbon connects with 2 Oxygens and creates CO2
What happens to CO2 when it enters the atmosphere?
Some CO2 gets dissolved in ocean (and makes carbonic acid), some is taken in by trees to make tree tissue (called sequestration), but most stays in atmosphere and traps heat = warmer planet
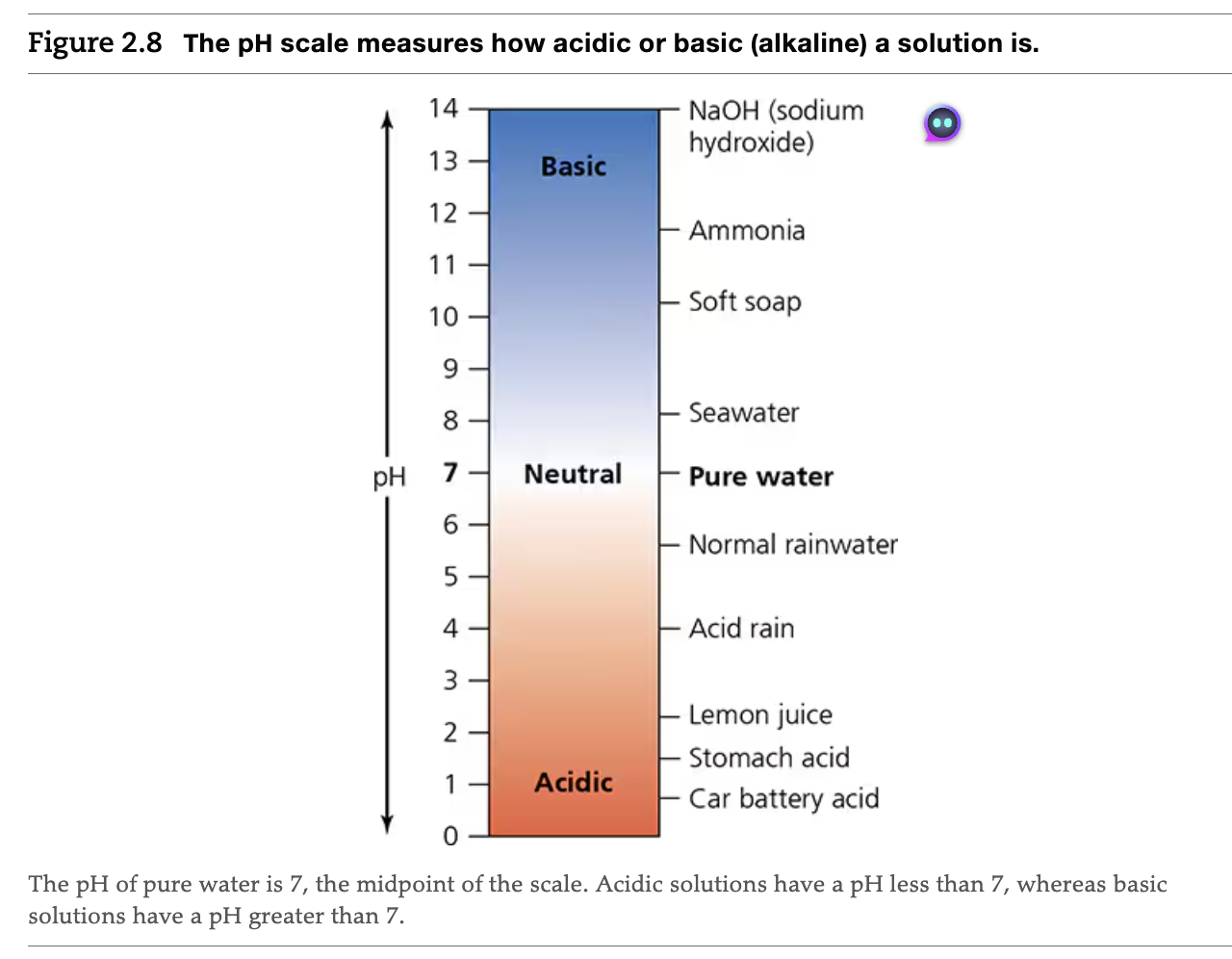
pH Scale
Each # = 10x H+ ion concentration (from 5-7, 100x increase in H+ concentration
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can change from one form to another but it cannot be created nor destroyed
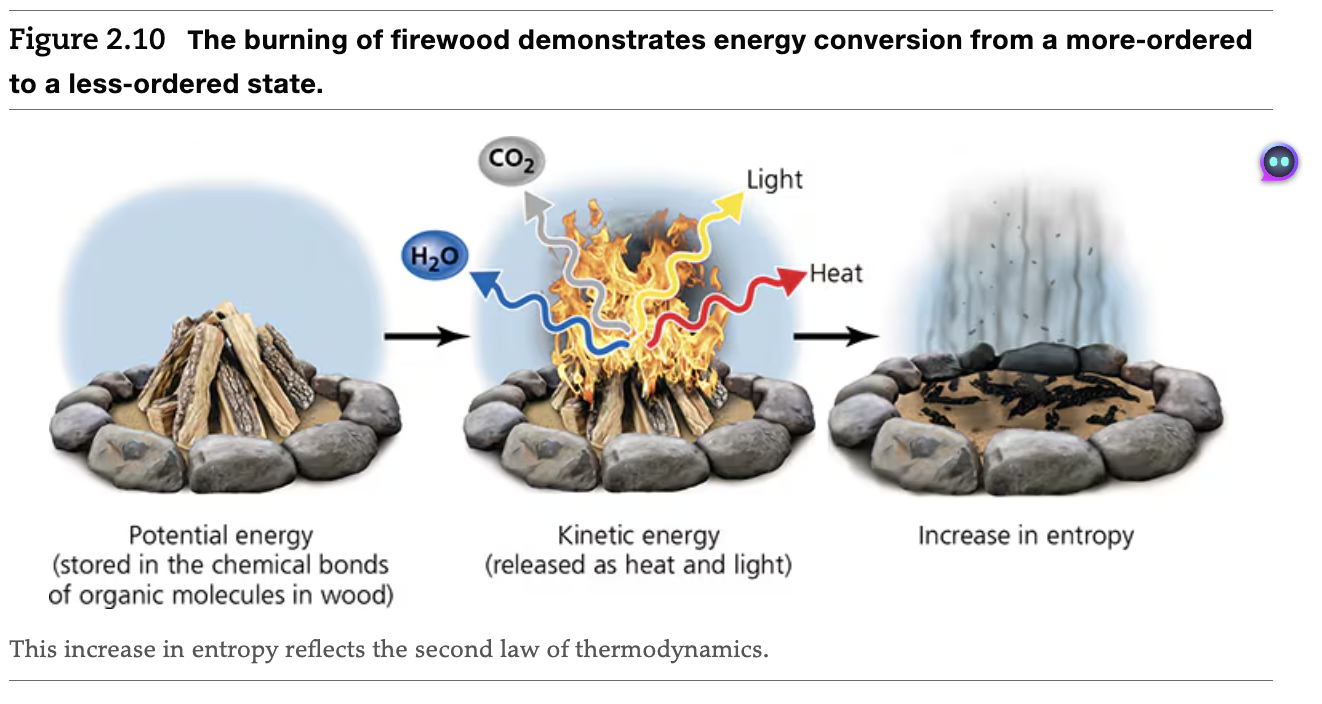
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
The nature of energy will change from a more-ordered state to a less-ordered state as long as no force counteracts this tendency (systems tend to move toward increasing disorder or entropy)
Entropy (z)
The degree of disorder or uncertainty in a system
Energy Conservation
The decision and practice of using less energy (Efficiency - l)
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion
Potential Energy
Energy of position or composition
Cellular Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Energy other than from the Sun
-Gravitational pull of the moon (tidal energy)
- Radiation inside of Earth, which powers plate tectonics, volcanos, geothermal, hydrothermal vents
Chemosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + 3H2S → C6H12O6 + 3H2SO4
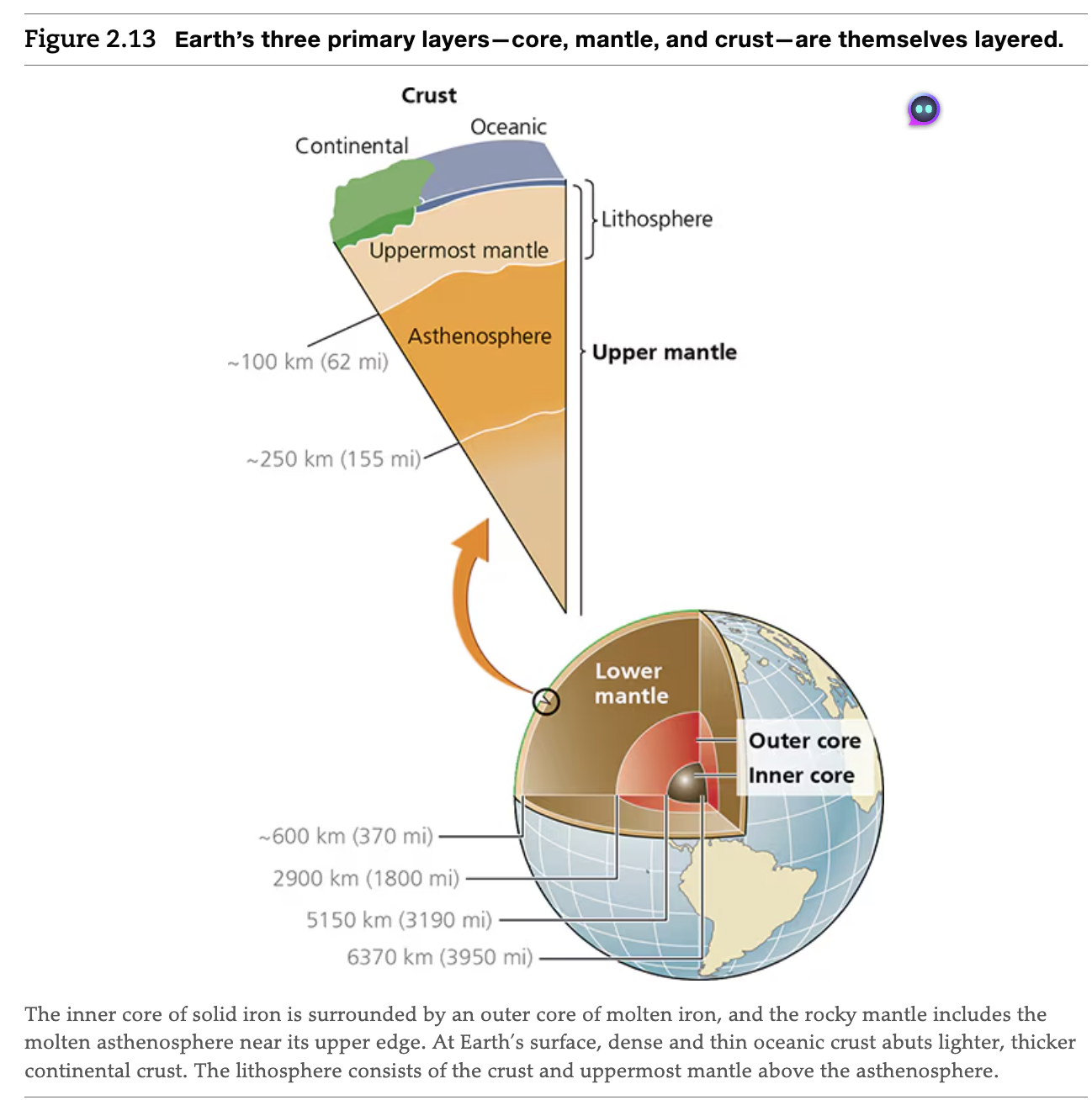
Layers of the Earth
Inner Core → Outer Core → Mantle (Asthenosphere) → Crust (Lithosphere)
Convection
Cool magma falls (its more dense) → Warmer magma rises (its less dense)
Breaks lithosphere into plates and moves them
Occurs in the upper mantle in a slow, creeping motion
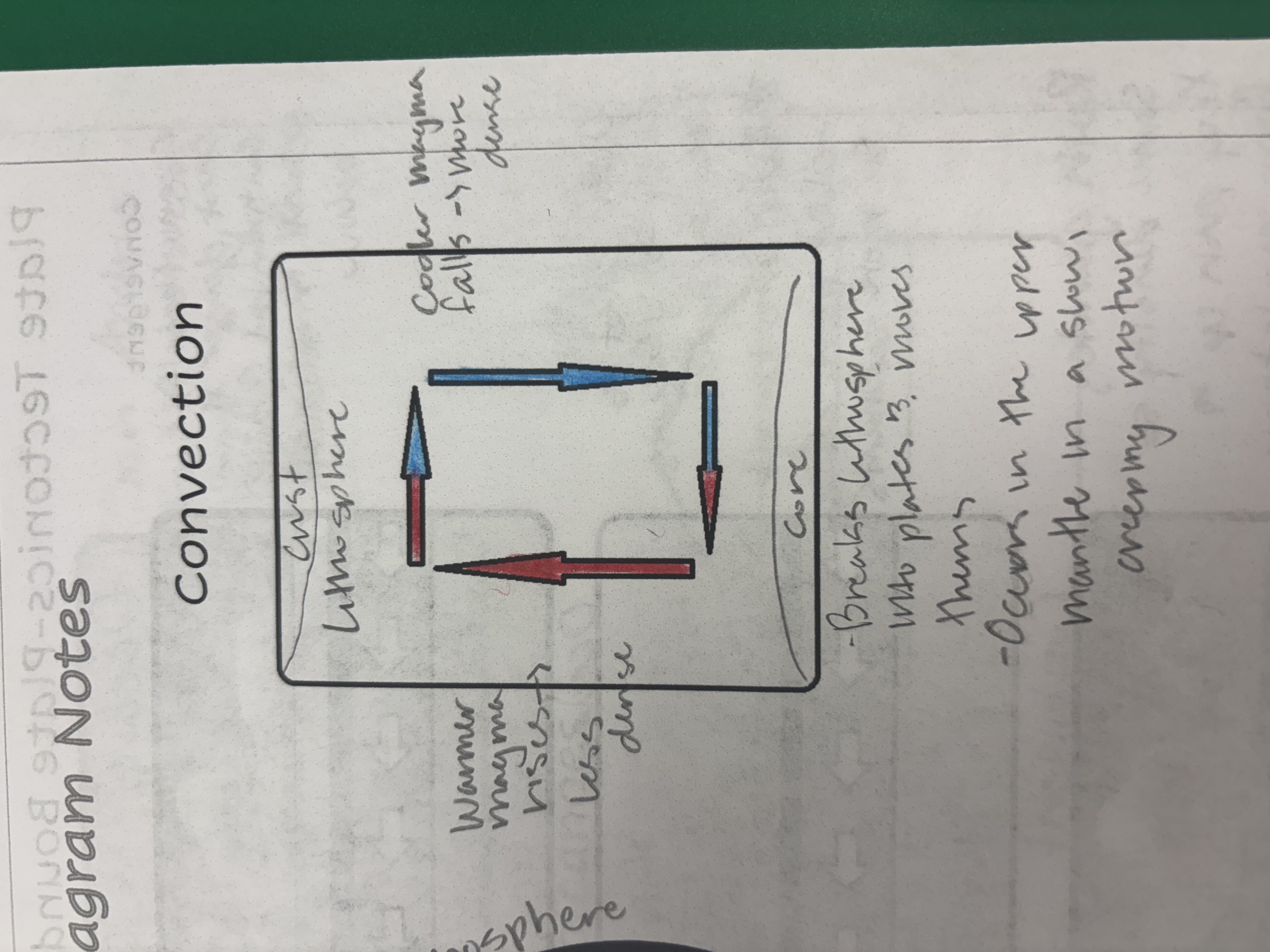
What drives convection?
The core of the Earth is radioactive and hot
What are the Earth’s 3 primary layers?
Core, Mantle, Crust
Each have layers within them:
Inner Core → Outer Core → Lower Mantle → Upper Mantle → Crust
San Andres Fault
Fault line in Southern California, Pacific Plate and North American Plate slide past one another and cause lots of earthquakes (transform)
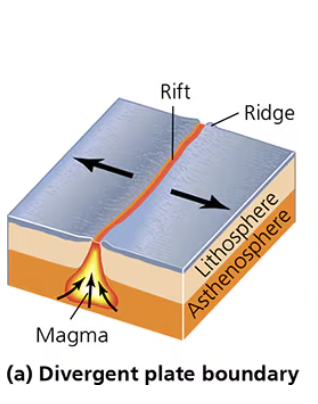
Divergent Plate Boundary
Crusts pull apart and magma rises up, hardens when cooled by water, and creates underwater mountain ranges
Ex: Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Sea Floor Spreading
*on land: Rift Valley in Iceland and African Rift Valley
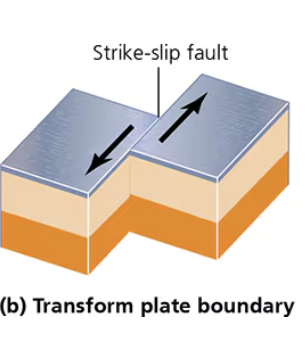
Transform Plate Boundary
Two plates slide past each other in opposite directions
- Strike → ship fault
Ex: San Andres Fault between Pacific and North American Plates
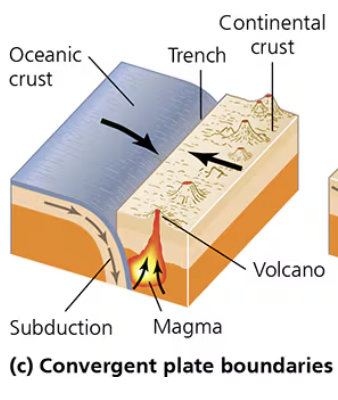
Convergent Plate Boundary (Oceanic + Continental)
Oceanic (basalt) crust is denser than continental (granite) crust and subducts below
- Creates deep ocean trenches and cracks in the continental plate → magma seeps up and creates volcanoes
*Plates can get stuck and suddenly release energy → earthquakes and tsunamis
Ex: trenches and volcanic arcs
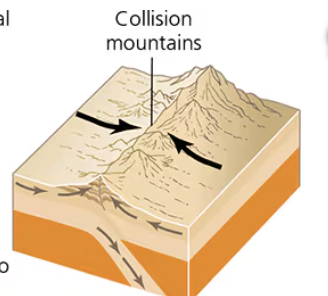
Convergent Plate Boundary (Continental + Continental)
Both granite, have same density, so they push up and form mountains
- small amount of subduction
Ex: Himalaya Mountains between India and Nepal
Convergent Plate Boundary (Oceanic + Oceanic)
Older crust is denser → subducts and creates trench
(both are basalt but the older one is more dense because it has more sediments)
- Cracks occur in this plate → magma seeps up; volcanic island arcs
Ex: Japan, Aleutian (Alaska), Tsunamis and Earthquakes
What happens at convergent boundaries when it is one continental crust and one oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is denser and will go below (subduct) continental crust and oceanic
- Make a trench
What happens at convergent boundaries when it is two continental crusts
Two continental crusts have the same density and therefore push each other up
- Make mountains
Volcanic Arcs
One oceanic plate subducts beneath another → pushes magma up and makes islands
- Water is displaced and causes tsunami
Ex: Japan and Aleutians in Alaska
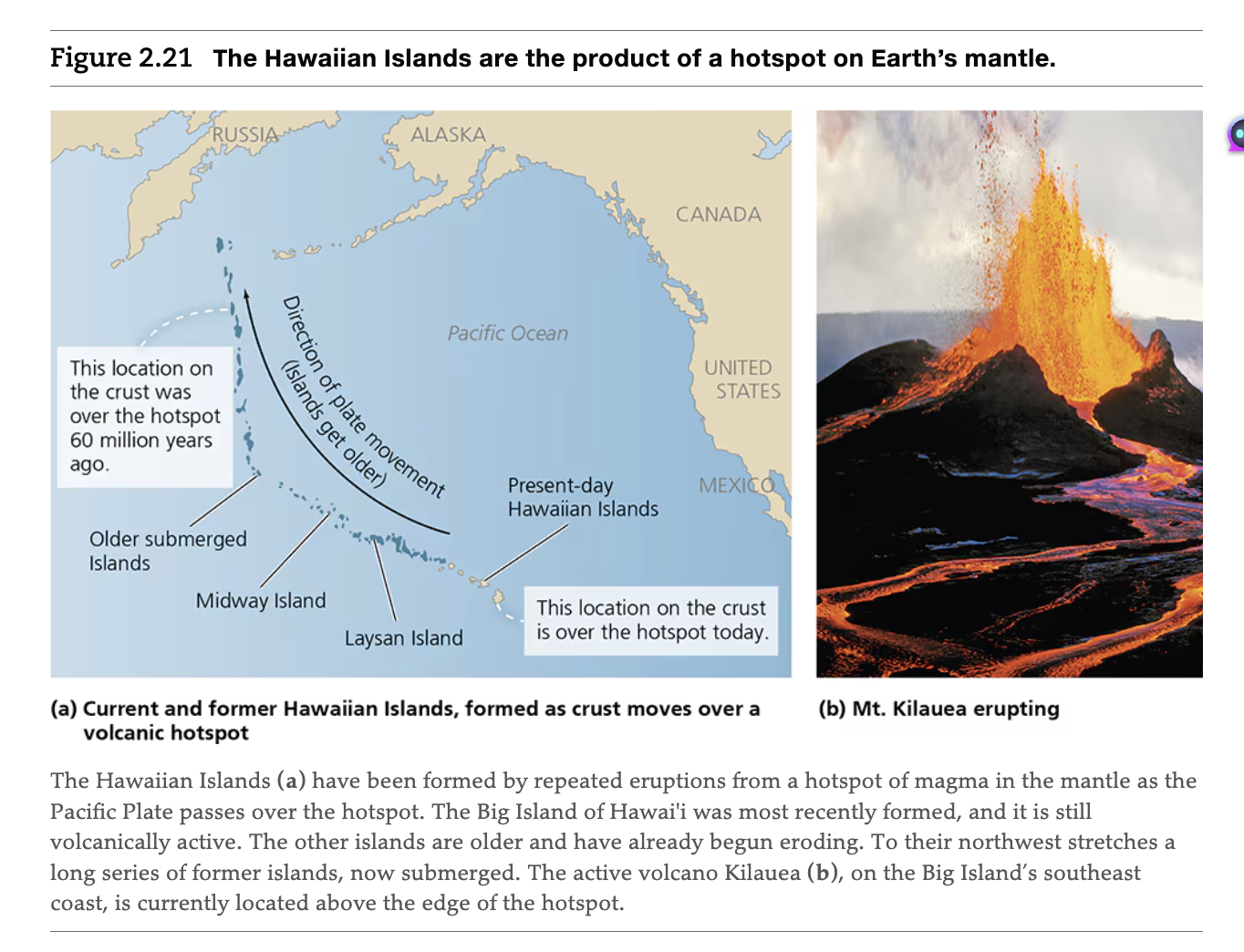
Hot Spot Volcanoes
Occur in the middle of plates where the curst has cracks and magma seeps up
Ex: Yellowstone- North American Plate (Flat volcano)
Igneas Rock
Rock that forms when magma or lava cools
Ex: granate, basalt
Metamorphic Rock
When any type of rock is subjected to great heat or pressure, it may alter to become metamorphic rock
Ex: magma and slate
Sedimentary Rock
Formed as sediments are physically pressed together and as dissolved minerals seep through sediments and act as a kind of glue, bonding the sediment particles together
Ex: Shale, Limestone, Coal
Lithification
the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock
Ring of Fire
A string of volcanoes and sites of seismic activity, or earthquakes, around the edges of the Pacific Ocean
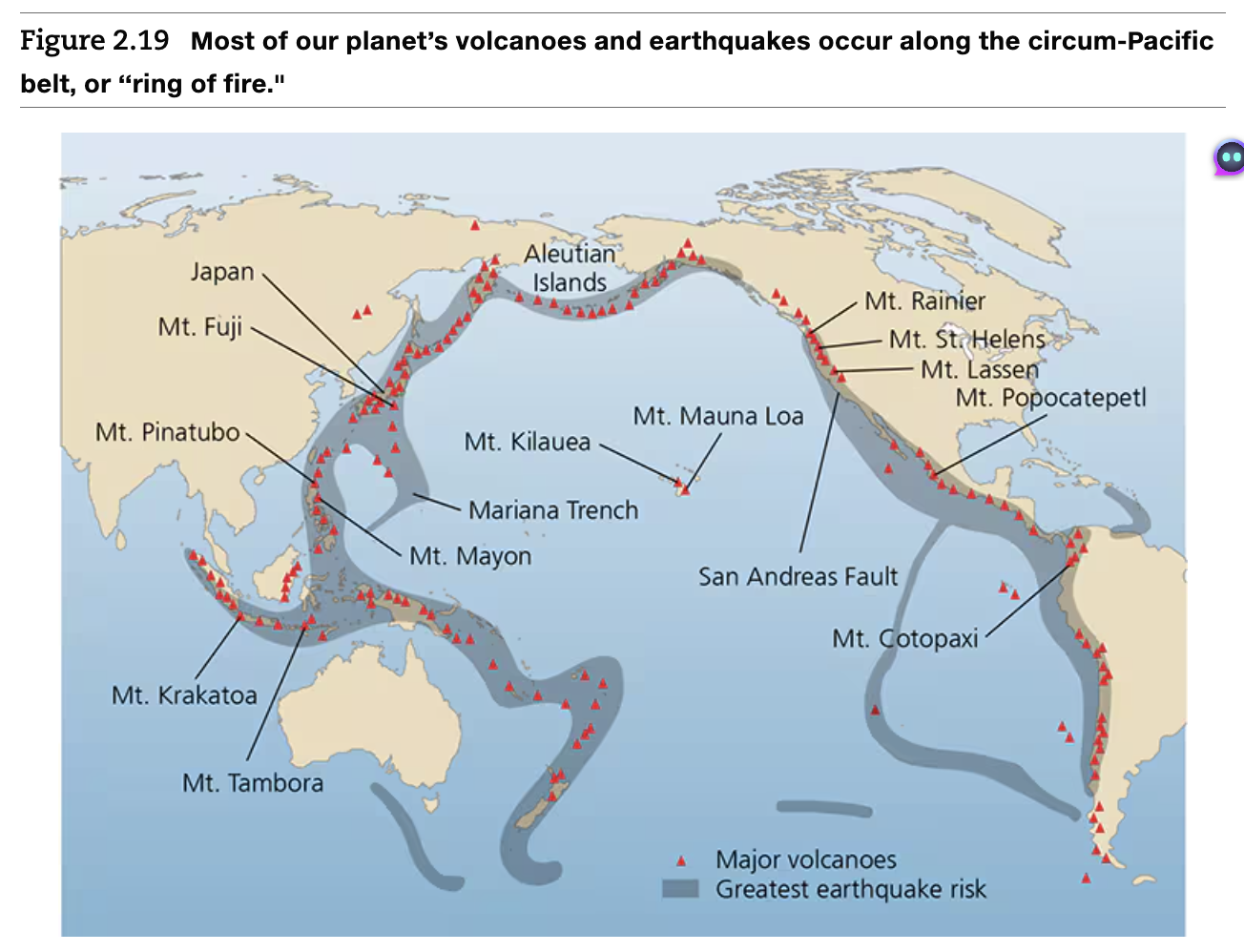
Hotspot Volcanos
An area of the Earth's mantle from which hot plumes rise upward, forming volcanoes on the overlying crust
Landslide
Occurs when large amounts of rock or soil collapse and flow downhill
- Sudden manifestation of the phenomenon Mass Wasting
Mass Wasting
The downslope movement of soil and rock due to gravity
Physical Weathering
Occurs with wind, rain, thermal expansion and contraction, and water freezing
Chemical Weathering
Changes the mineral makeup of the rock
Ex: Acid Precipitation dissolves some minerals in rocks
Biological Weathering
Occurs when roots of plants break apart rocks or when lichen secrete chemicals that dissolve parts of rocks
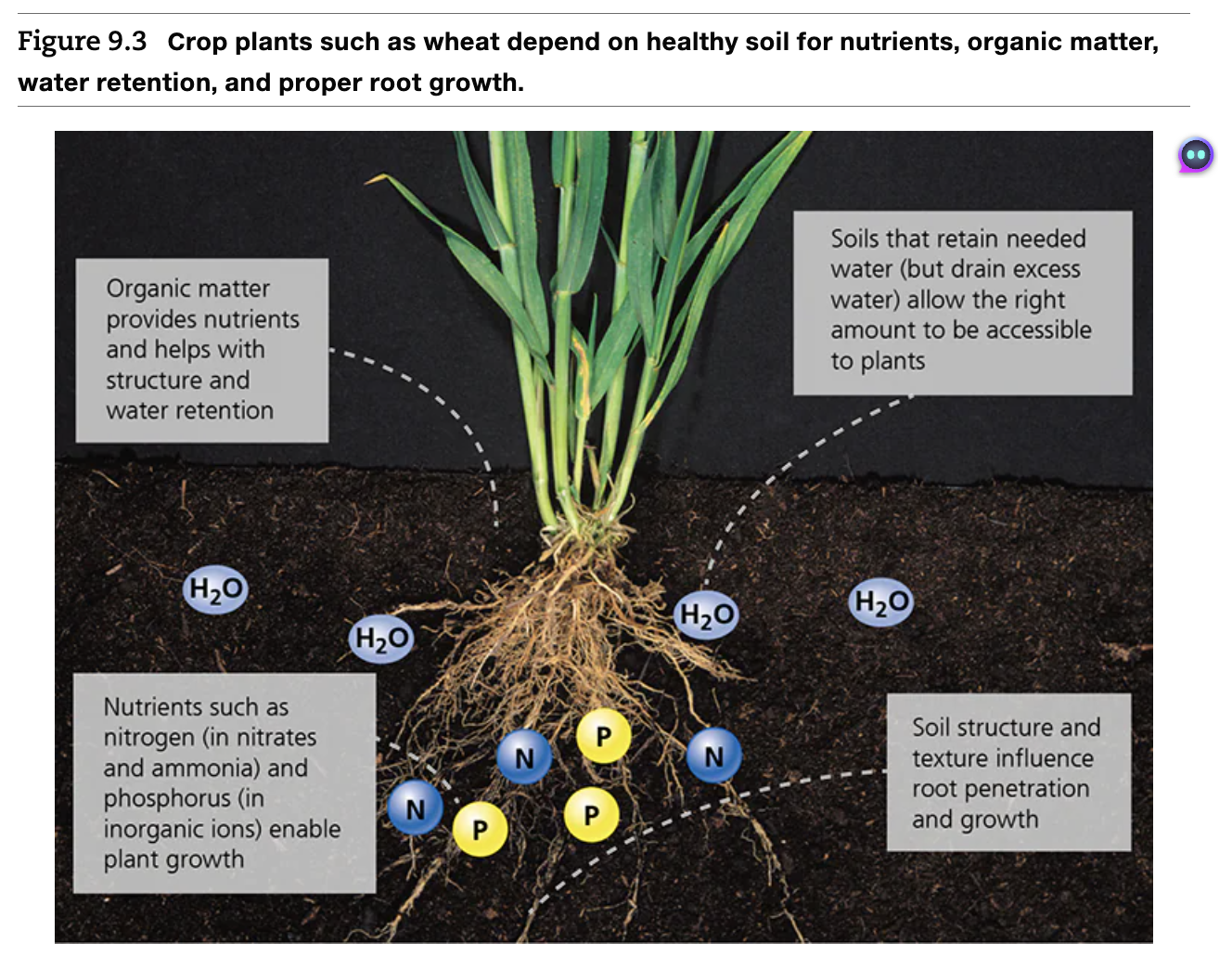
What do plants benefit from healthy soil?
Crop plants such as wheat depend on healthy soil for nutrients, organic matter, water retention, and proper root growth
Leaching
The process whereby soil particles suspended or dissolved in liquid are transported to another location
Soil Profile
The cross section as a whole, from the surface to the bedrock, of soil
Order of Soil Horizons
Only Apes Eat Bread Crumbs
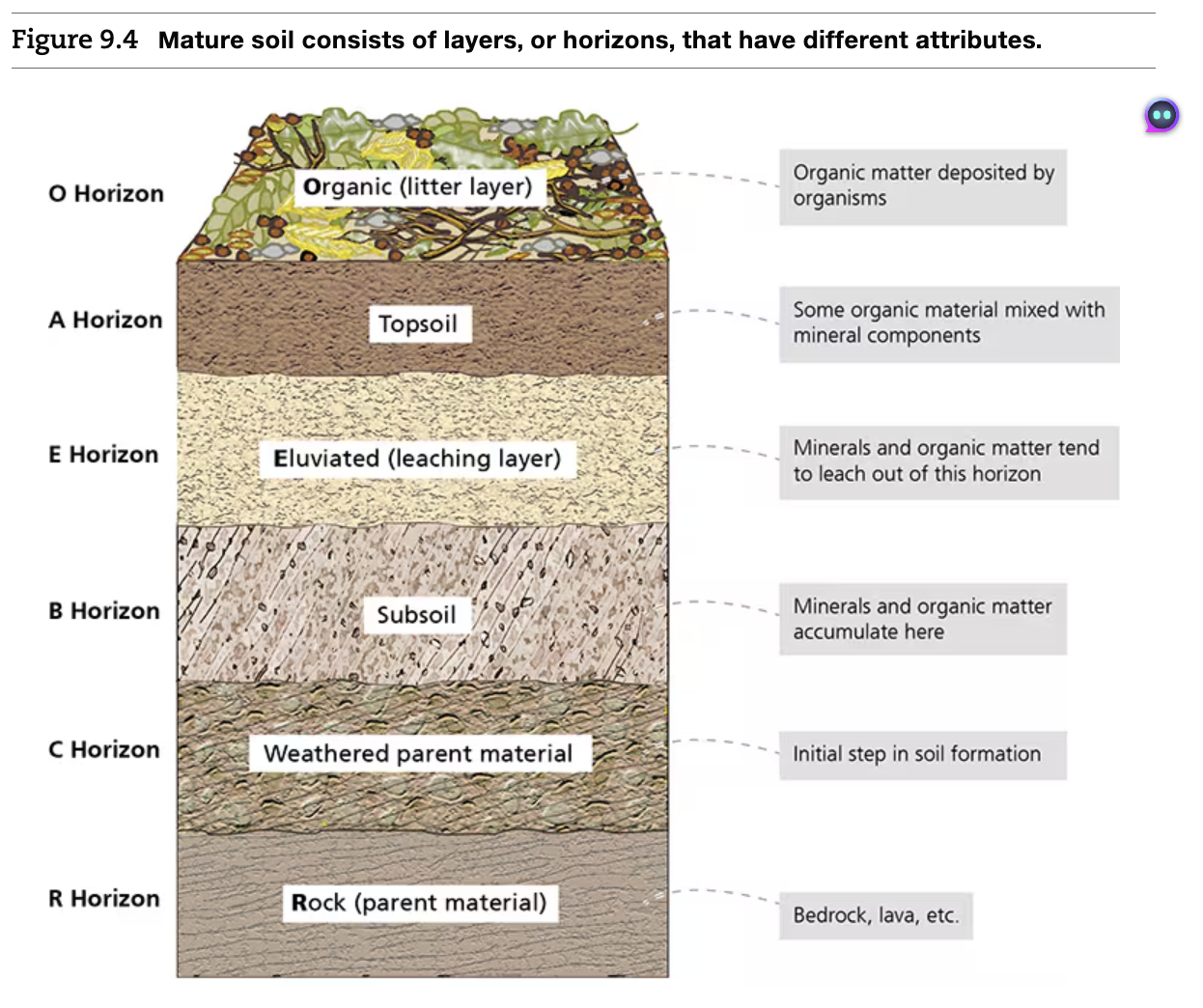
O Horizon
Organic layer
- the top layer, which consists of organic matter like decomposing leaves, twigs, animals, etc
A Horizon
Topsoil
- consists of some organic matter mixed with mineral components. It is the zone where most agriculture takes place
E Horizon
Eluvation or Leaching Layer
- Minerals leach into the B horizon
B Horizon
Subsoil where minerals accumulate
C Horizon
Weathered Parent Material
R Horizon
Rock → Pure parent material
Carbon Exchange Capacity
Indicator of soil fertility- shows plant’s ability to supply important nutrients
- Ca2+ , Mg2+ , K1+
Cations are held by negatively charged particles of clay and humus (colloids)
- Thin, flat plates with large surface areas
→ acts as storage for nutrients for plant roots
Best for this is Humus, then clay, then silt, then sand is the worst
Humus
Mature compost- very important for healthy soil
- Buffer for pH
- Promotes microorganisms that maintain healthy soil
- Prevents nutrients from leaching out of the soil through water runoff
Physical Soil Tests
Soil Sieves: Separate soil into particle size (clay, silt, sand) and then use soil triangle to identify soil type
Soil Particle Sizes
Clay: grainest
Silt: middle
Sand: largest
Loam
Mix of all three soil particle sizes, the BEST soil
Swidden Agriculture
he traditional form of agriculture in tropical forested areas is swidden agriculture, in which the farmer cultivates a plot for one to a few years and then moves on to clear another plot, leaving the first to grow back to forest.

Porosity
Amount of water a soil can hold in its pore space between particles. Also determines how much room roots will have as they fill the pore space
Highest to lowest soil porosity
Highest: Loam
Clay
Silt
Lowest: Sand
*Opposite of particle size
Permeability or Drainage Rate
How fast soil drains
- Too high: roots don’t get enough water
- Too low: soil becomes waterlogged → root rot
*Adding sand increases drainage rates in soil
Highest to lowest soil drainage rate
Highest: Sand
Silt
Lowest: Clay
Chemical Properties of Soil: Nitrogen
Green leafy growth in plants
-Major component of chlorophyll which is used in photosynthesis
Chemical Properties of Soil: Phosphorus
-Plant Genetics
- Seed Development and Yield
- Fruit development
Chemical Properties of Soil: Potassium
-Strong Stems
- Aids in early growth
- Fights disease in bugs
Plant pH comfort zone
6.5-7 (slightly acidic)
- good for bacterial decomposition
- Works best with nutrient uptake
Effects of excessive acidity in plants
Causes Calcium, Phosphorus, and Magnesium to be changed into forms that plants can’t use, causing plants to suffer a deficiency.
Slowdown of beneficial bacteria and increased toxicity from trace elements like Aluminum also occur
Effects of excessive alkalinity in plants
Disolves and disperses Humus
Plow Pan
A hard layer in soil that resists water
Seed Bank
Institutions that preserve seed types as a kind of living museum of genetic diversity. Keeps seed samples in cold, dry conditions to keep them viable, and they are planted and harvested periodically to renew the stocks
Causes of soil and land degredation
Erosion and Deposition
Erosion
The removal of material from one place and its transport to another by the action of wind or water
Deposition
When eroded material is deposited at a new location
Causes of Erosion
-Over Cultivating fields through poor planning or excessive plowing
- Overgrazing rangeland with more livestock than he land can support
- Clearing forests on steep slopes or with clear cuts
Ways to minimize erosion
Erect physical barriers that capture soil → growth of vegetation is what prevents soil loss
- Vegetation slows wind and water flow, while plant roots hold soil in place and take up water
Desertification
-Loss of 10% of the soil’s productivity
- Erosion
- Dust Storms
- Salinization
Dust Bowl
1800s: Thornestead Act gave 160 acres to farmers → 1900s-1920s: Farmers used all acres to grow wheat (cash crop that needs rain) → 1930s: rain stopped = drought → winds came and blew away tilled/loose topsoil
Soil Conservation Service
Works closely with farmers to develop conservation plans for individual farms, using science to assess the land’s resources and condition
Crop Rotation
Farmers alternate the type of crop grown in a given field from one season or year to the next
- many alternate with legumes to restore nutrients to the soil
- also helps to break disease cycles
Contour Farming
Plowing furrows sideways across a hillside, perpendicular to its slope and following the natural contours of the land
- The side of each furrow acts as a small dam that slows runoff and captures eroding soil
Terracing
Transforms slopes into a series of steps like a staircase, enabling farmers to cultivate hilly land without losing large amounts of soil to water erosion
Intercropping
Planting different crops in alternating bands or other spatially mixed arrangements
- helps slow erosion by providing more ground cover than does a single crop
- reduces vulnerability to insects and disease and can replenish the soil of nutrients
Shelterbelts
Rows of trees or tall shrubs planted along the edges of fields to slow the wind
- BEST AT PREVENTING WIND EROSION
No-Till Farming
Eliminates tilling altogether. Rather than plowing after each harvest, farmers leave crop residues atop their fields or plant cover crops, keeping the soil covered with plant material at all times to protect against erosion
Strip Cropping
A practice of growing field crops in narrow strips either at right angles to the direction of the prevailing wind, or following the natural contours of the terrain to prevent wind and water erosion of the soil
Benefits of No-Till Farming
Less labor, saves time, reduces wear on machines, lower fossil fuel use, higher soil productivity in the long term, enhances surface water quality, lower soil erosion, higher water filtration into soil
Rotational Farming
Regular rotation of livestock between different pastures in order to avoid overgrazing in a particular area
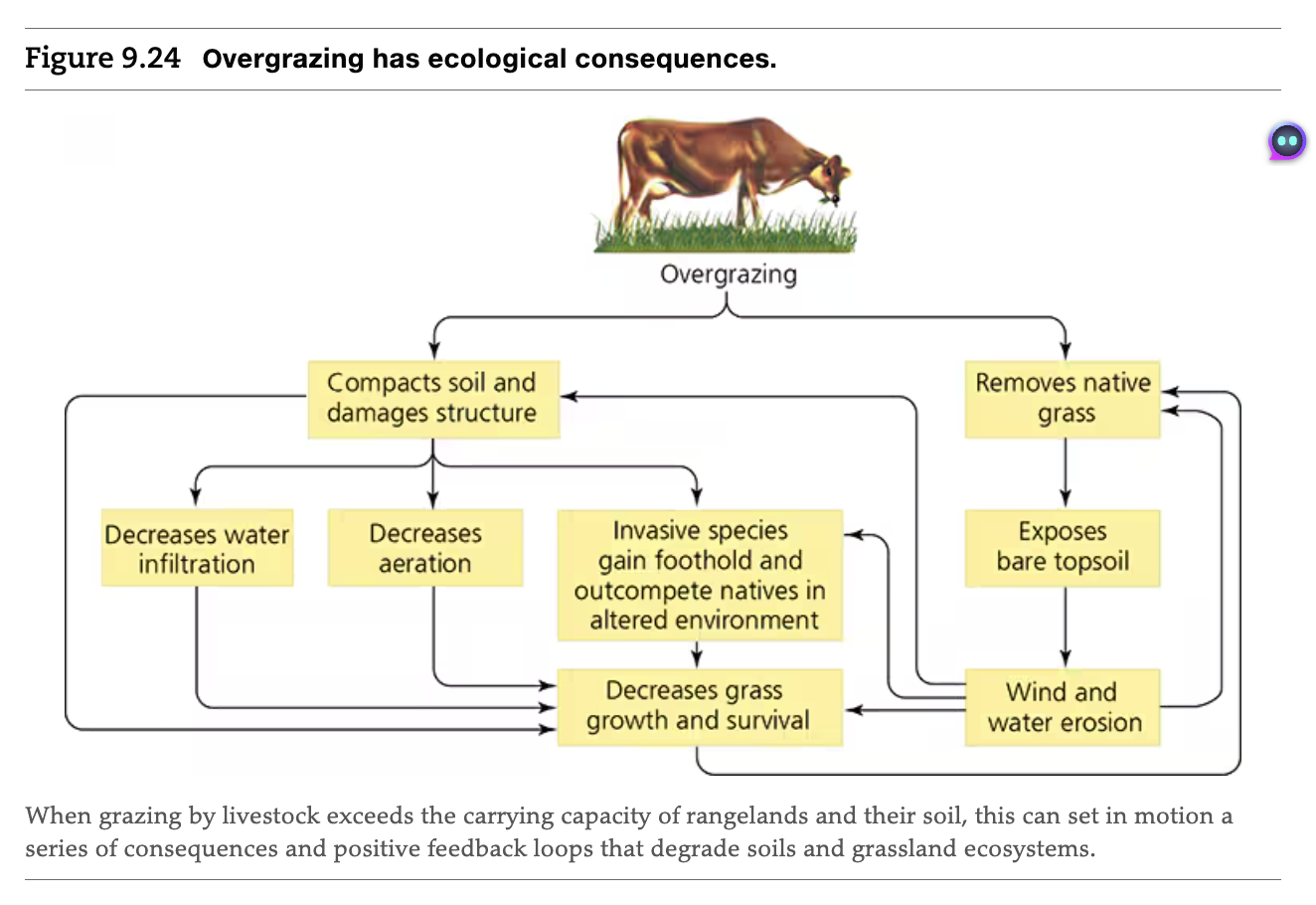
Ecological Consequences of Overgrazing
When grazing by livestock exceeds the carrying capacity of rangelands and their soil, this can set in motion a series of consequences and positive feedback loops that degrade soils and grassland ecosystems.
Swamplands Act
1850- Granted federal swamp and overflowed lands to states to reclaime and develop for agriculture