Lesson 2: Cell membrane Differentiations and Interactions and Communication
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Where are cells joined together and what is the composition
In tissues
-formed by Extracellular matrix and cells
Microvilli
-On apical surface of epithelial tissues
-Increased absorption
-physical barrier
-maintain their shape thank to cytoskeleton
Lateral interdigitations
-increase cell adhesion between cells
-with Ca2+ and Cytoskeleton
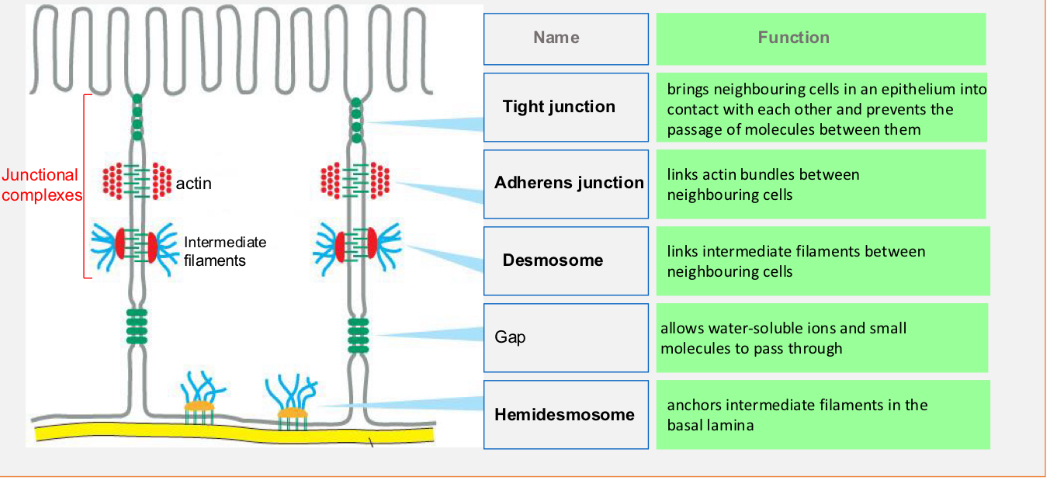
Cell junctions
Contact points between the plasma membranes of cells or between
cells and extracellular matrix.
Types of cell junctions
1. Occluding or Tight junctions
2. Anchoring Junctions to the cytoskeleton:
• Actin filament attachment:
2A-Adherens junction (cell-cell)
2B-Focal adhesions (cell-extracellular matrix)
• Intermediate filaments attachment:
2C-Desmosomes (cell-cell)
2D-Hemidesmosomes (cell-extracellular matrix)
3. Gap or communicating junctions (Channel-forming junctions)
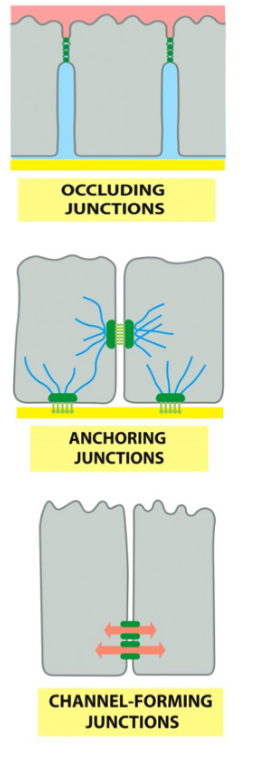
Functions of cell junctions
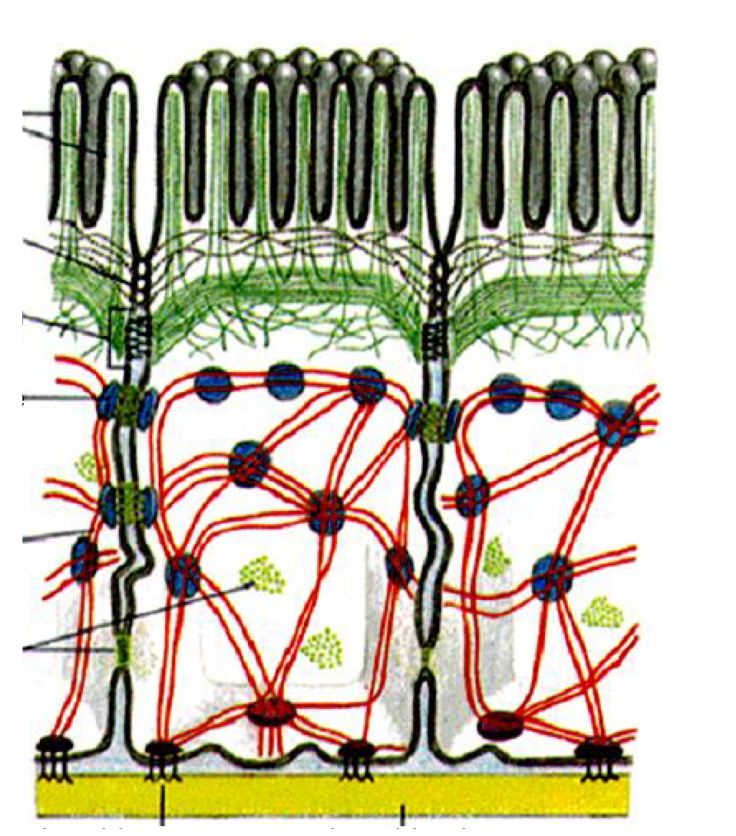
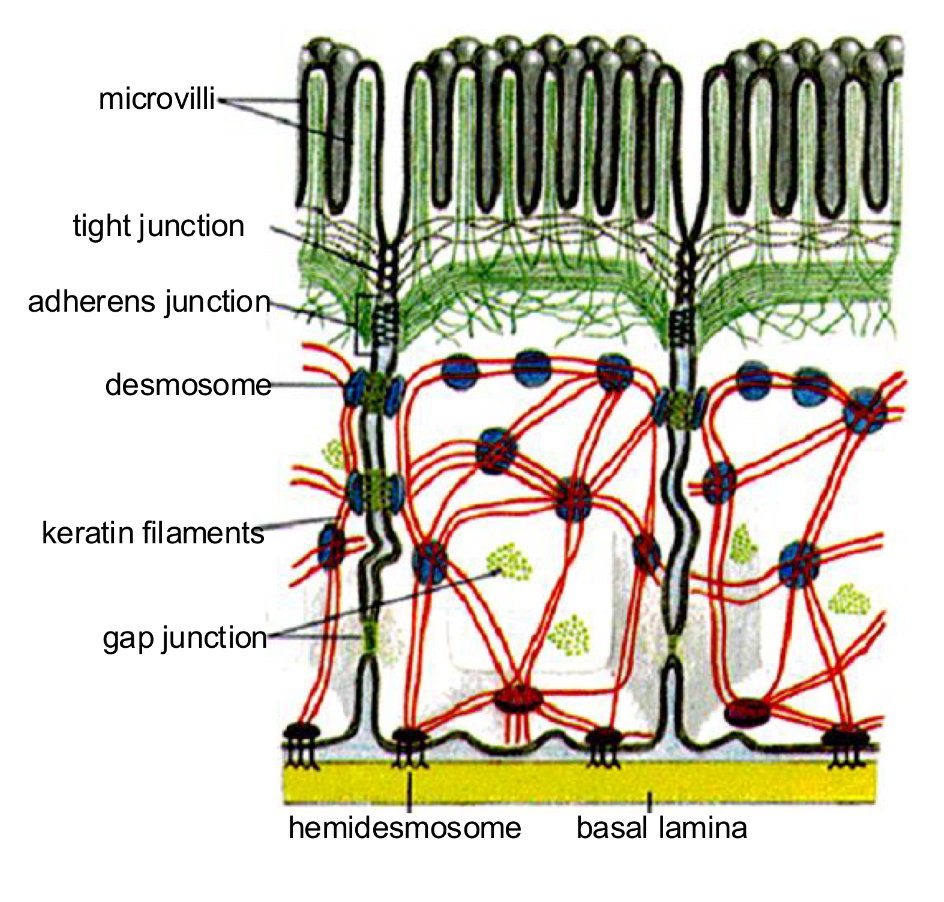
Interaction between cell and its environment
Membrane adhesion molecules
Membrane adhesion molecules Classification
• Ca2+-dependent:
• CADHERINS
• SELECTINS
• INTEGRINS
• Non- Ca2+ dependent:
• IMMUNOGLOBULINS
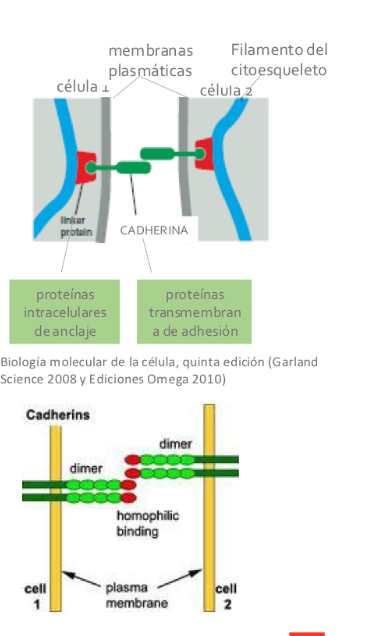
Cadherins
-adhesion between cells
-Embryogenesis: hold cells together of embryo
-Homophilic binding: same type (E and E cadherin)
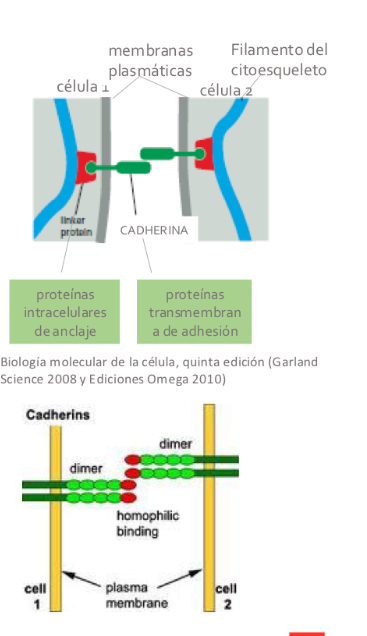
CadherinS types
-Adherence junctions
indirectly bind the actin cytoskeleton of neighboring cells.
Desmosomes
-bind intermediate filaments of neighboring cells.
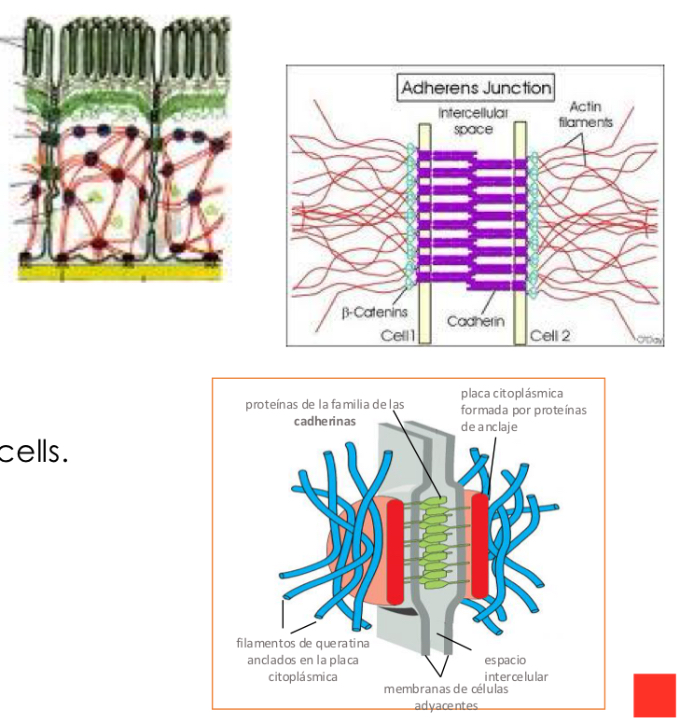
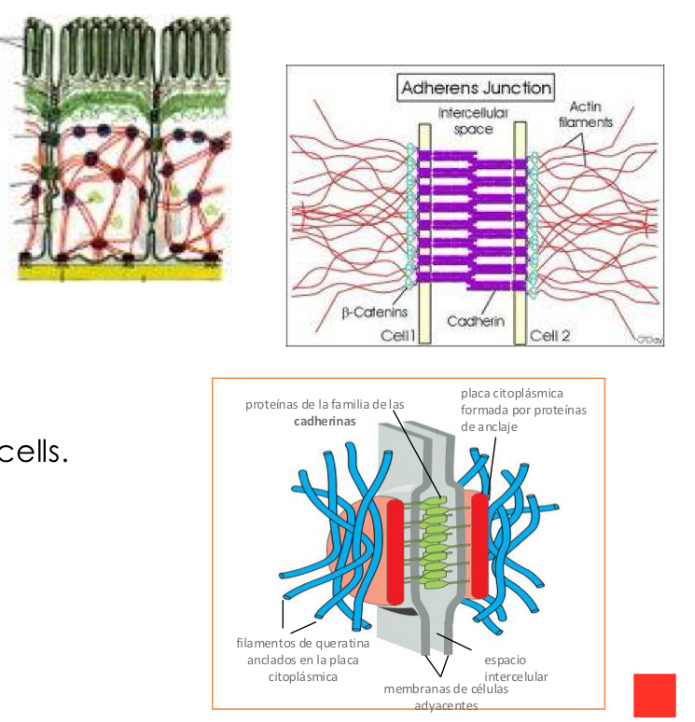
Cadherin classification
Classical cadherins:
-E-Cadherin (Epitehial cells)
-N-Cadherin (nerve)
-P-cadherin (placenta, epidermis)
Non classical cadherin:
-with adhesion function: desmosomal
-without adhesion function: T-cadherin (signaling)
Integrins
• Adhesion proteins that connect components of the extracellular
matrix to the cell cytoskeleton.
-transmembrane glycoprotein
-are on the cell surface and switch from inactive to active when they bind to ligands
Exception: in blood cells, also cell-cell junction.
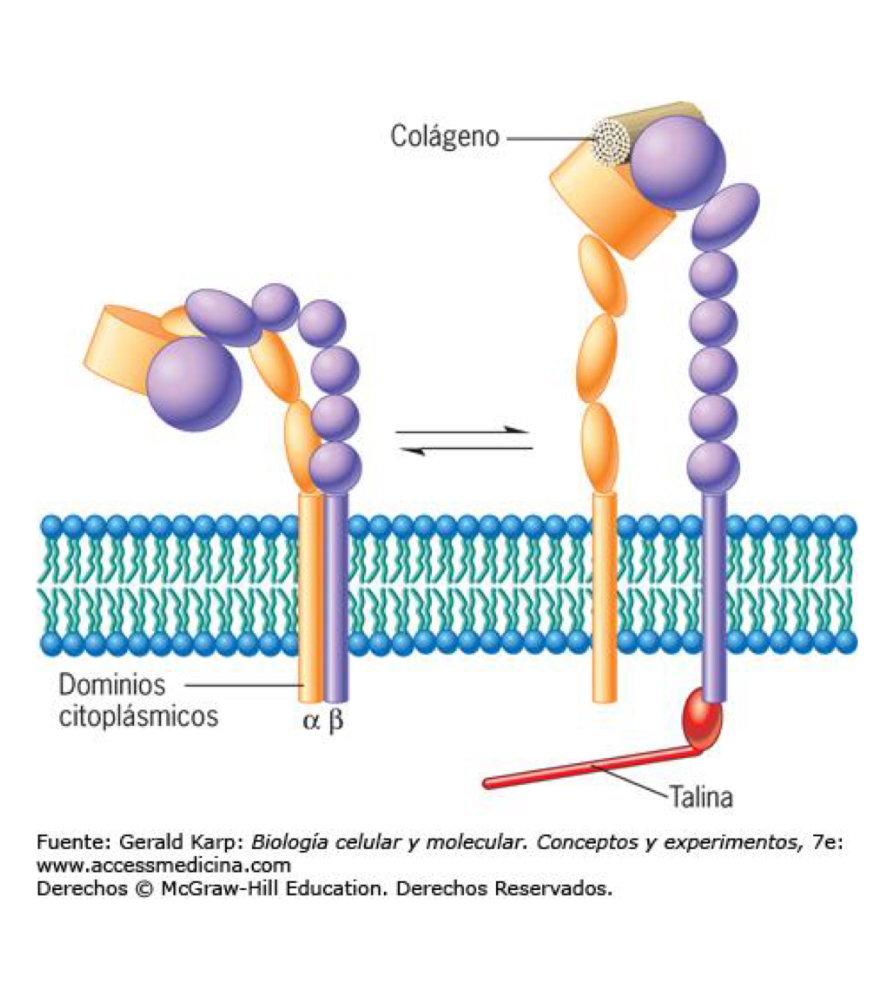
Structure
Consist of 2 subunits: heterodimer, 2 transmembrane glycoproteins
domains on extracellular side tat bind ions (Ca2+ or Mg2+)
Heterophobia binding: Integrins from one cell binding to different protein demo another cell or matrix
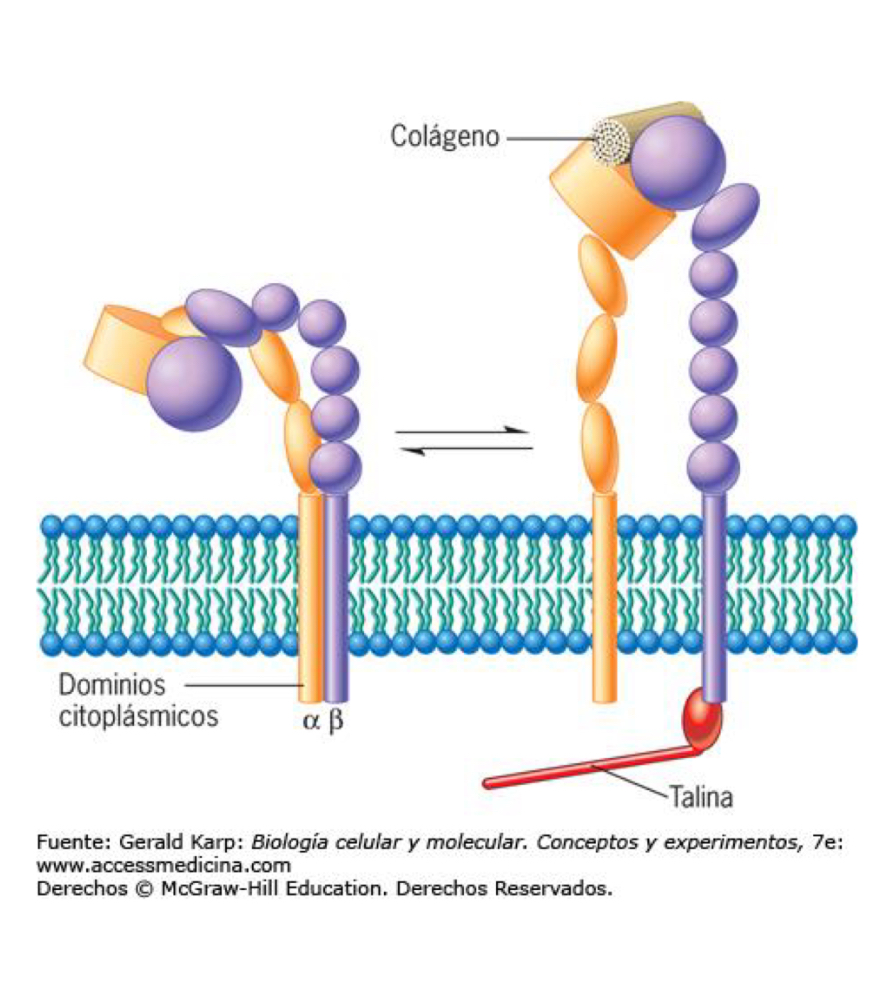
Integrins types
They are found in:
- Hemidesmosomes:
• They attach intermediate filaments to the matrix.
- Focal junctions:
• Bind the actin cytoskeleton to the matrix.
• On the extracellular side, integrins are connected to:
• the complex network of matrix filaments (collagen fibers, ....)
• the adhesion glycoproteins of the matrix (laminin, nidogen, ...)
Integrin functions
Functions:
• Adhesion
• Movement (fibroblast or macrophage)
• Form/Shape
• Growth
• Differentiation
• Signal transmission
Integrins Signalling from the outside to the inside
Important in platelets and white blood cells (leukocytes):
-these cells circulate in blood with integrins exposed but inactive.
• When they encounter the appropriate stimulus, the integrins are activated.
-integrin just changes its conformation
Selectins
-transmembrane proteins capable of recognising carbohydrates.
Types of selectin
• L-selectin in leukocytes (white blood cells).
• P-selectin on platelets and endothelial cells activated locally by
inflammation
• E-Selectin on endothelial cells
Selectin functions
Ca2+ dependent Leukocyte trafficking
Immunoglobulin
-most of the Ca2+-independent Intercellular adhesion
-weaker than Cadherins
-homophilic binding
Immunoglobulin functions
-Adhesion
-Signal transmission.
Cell communication
transmission of chemical extracellular signals between cells
-producing a response in the receiving cell
Signaling cell
Cell that produces the signal molecule
Types of signaling
-secrete signal molecules (by exocytosis or diffusion across the membrane)
-contact-dependent signalling: exposing signal molecules on their cell surface (influences cells that are in close contact)
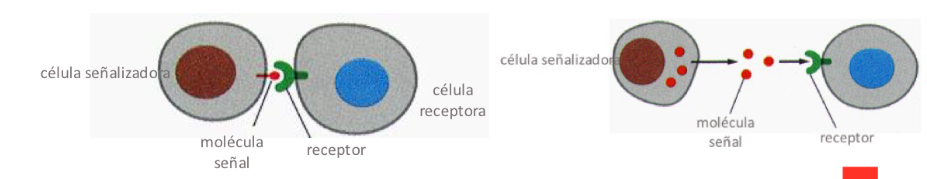
Type of signaling cells
Endocrine cells
-most common type of communication
-release ligands(hormones) into the bloodstream
-distributed throughout the body (long distances)
Type of signaling cells
Paracrine cells
-Inflammation and healing
-act over short distances → local communication
-signal molecule short half life → eliminated by enzymes or taken up
type of signaling cells
Autocrine / contact-dependent cells
-Embryonic developement
-secret hormone or chemical messenger → autocrine agent
-binds autocrine receptors to specific cell
type of signaling cells
Neuronal cells
-synaptic transmission
-Neurotransmitter released by neuron and activate receptors of postsynaptic cell
-long distances
-trigger membrane potential changes of postsynaptic cell
Receptor / target cell
Protein that recognises the ligand
Types of receptor / target cells
Surface receptor
-transmembrane proteins activated by ligands - transmit signal into cell
-3 types of surface receptors
Intracellular receptors
-intracellular proteins that bind small, hydrophobic ligands
-2 types of intracellular receptors
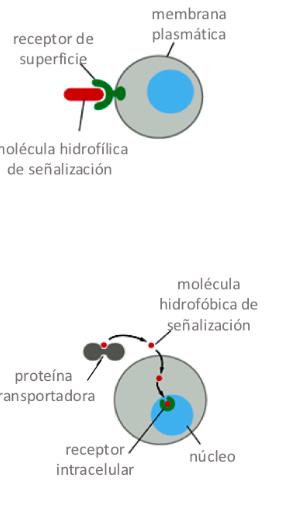
Surface receptors
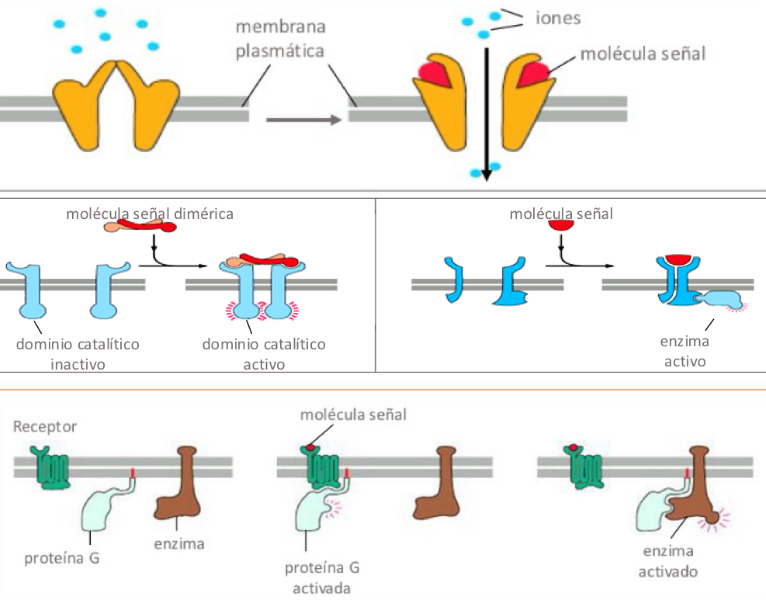
-Ion channel-gated receptors (Ligand opens channel, changing permeability of the membrane to some ions)
-Enzyme-linked receptors (receptors acts like enzymes or binds to enzyme and activates it.
-G protein-linked receptors (Ligand-receptor activates a G protein, which activates an enzyme or ion channel)
Intracellular receptors
Ligand-activated nuclear receptors (ligand binds and conformation changes which activates gene transcription
Cytoplasmic enzyme-linked receptors (cytoplasmic enzyme that activates signalling pathways, activate or inhibit responses)
Complexity
-each cell recognises only few
-same signal an generate different responses