Social Learning Theory and Criminal Behavior
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What does the Social Learning Theory suggest about behavior?
Individuals model behavior they witness, particularly from role models or significant figures in their lives.
Who developed the Social Learning Theory and when?
Albert Bandura in 1977.
What are the three aspects of aggression that Bandura's theory explains?
1. How aggressive patterns of behavior are developed. 2. What provokes people to behave aggressively. 3. What determines whether they will continue aggressive behavior.
How does Bandura relate aggression to social behavior, status, and power?
Aggression can gain approval and status within social groups, suggesting that crime is learned through the desire for social acceptance.
What is the role of attention in observational learning?
Attention involves closely watching a model's behavior and its consequences, which is influenced by the observer's capabilities, motivation, and the model's characteristics.
What is retention in the context of observational learning?
Retention is the process of storing learned behavior in memory as a mental representation for later use.
What does reproduction refer to in observational learning?
Reproduction is the ability to perform the observed behavior, requiring both physical and psychological capacity.
What is motivation in the context of learning by observation?
Motivation is the desire to imitate learned behavior, influenced by the expectation of desirable consequences.
What is reinforcement in observational learning?
Reinforcement is the perceived reward for repeating observed behavior, which encourages the learner to repeat the action.
What historical examples illustrate the negative impact of social learning?
Examples include slavery, Nazism, sexism, and issues related to cultural diversity and education.
What does the Biological Theory claim about criminals?
Criminals are pre-programmed through their DNA, suggesting a genetic predisposition to criminal behavior.
What role does the pre-frontal cortex play in criminal behavior?
The pre-frontal cortex is responsible for decision-making and rational thinking; its underdevelopment may lead to impulsive and irrational decisions.
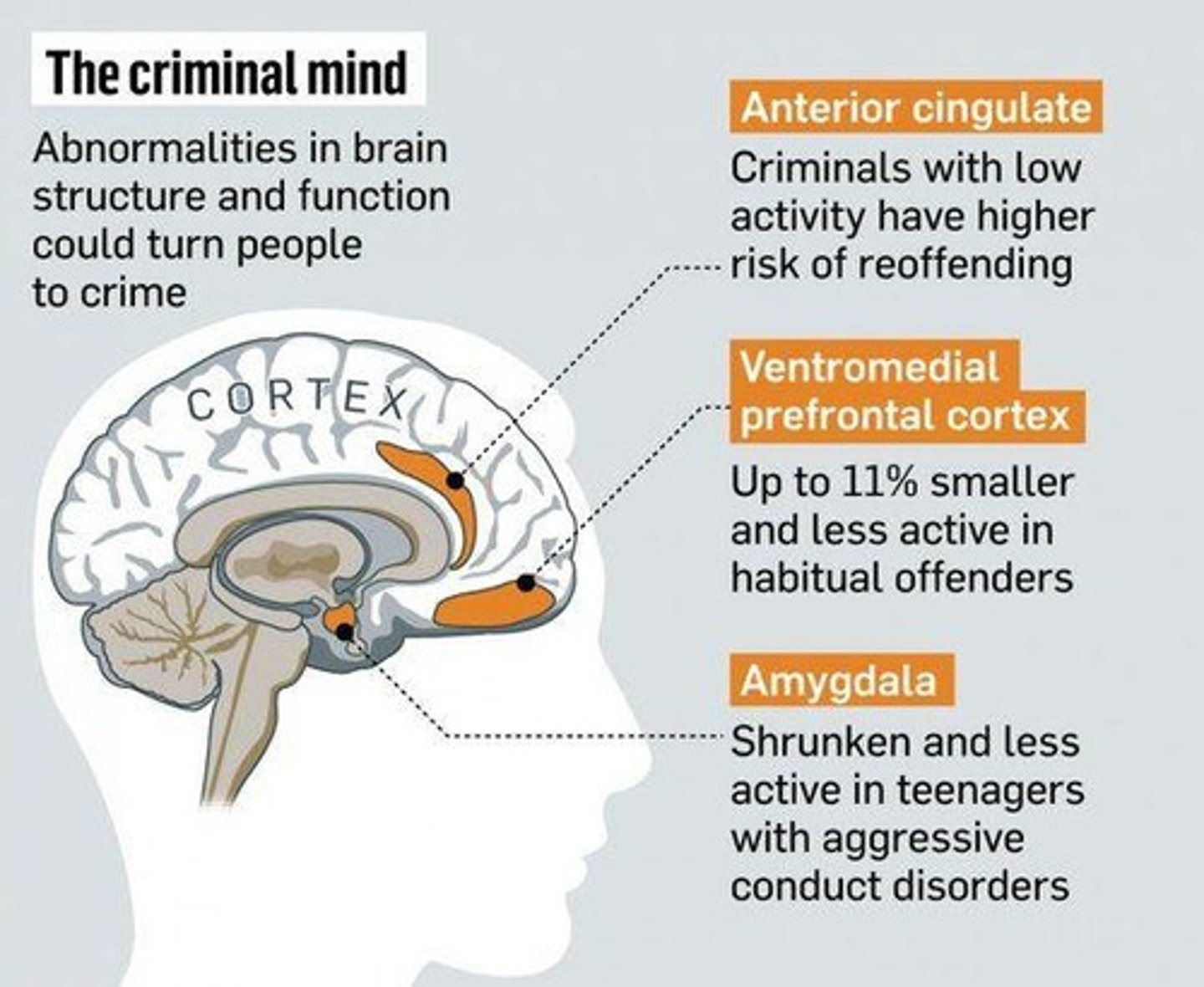
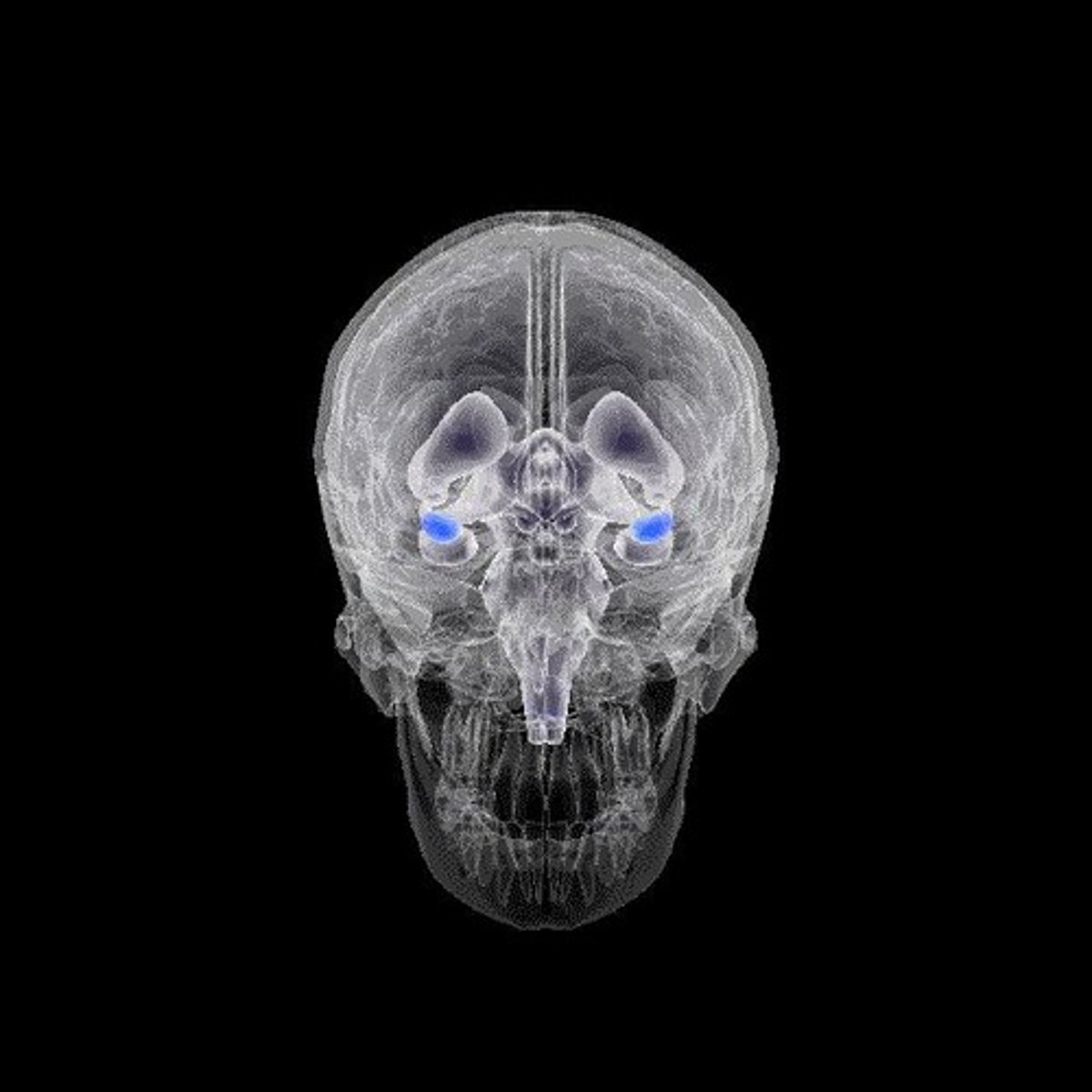
How does the amygdala function in relation to criminal behavior?
The amygdala is the emotional center of the brain; increased activity in this area is associated with impulsiveness and aggression in violent criminals.
What criticisms exist regarding the biological approach to crime?
Critics argue that crime is too varied to be attributed to a single gene, that brain dysfunction may not be present in all criminals, and that social environment plays a significant role.
What is the significance of observational learning in social contexts?
Observational learning highlights how individuals learn behaviors, including social norms and rules, from their environment without formal instruction.
What factors influence attention during observational learning?
Factors include the observer's capabilities, motivation, interest levels, the situation, distracters present, and the model's characteristics.
What is the importance of the cognitive aspect of retention in observational learning?
Retention involves storing the observed behavior in memory, which is crucial for later retrieval and reproduction of the behavior.
How does motivation affect the likelihood of behavior reproduction?
If the learner believes there will be a desirable consequence for imitating the behavior, they are more likely to reproduce it.
What happens if the modeled behavior is not reinforced?
If the behavior is not reinforced, it is less likely to be repeated by the observer.
How can social learning impact cultural diversity?
Social learning can perpetuate or challenge cultural norms and behaviors, influencing societal attitudes and practices.
What is the relationship between nature and nurture in the context of criminal behavior?
The debate centers on whether criminal behavior is inherited (nature) or learned from the environment (nurture).
What are some examples of learned behaviors in a school setting?
Examples include how to line up for the canteen, appropriate dress codes, and social interactions among peers.
What is the significance of role models in social learning?
Role models provide examples of behavior that individuals may choose to imitate based on perceived status and ability to replicate the behavior.
How does Bandura's BoBo doll experiment relate to social learning?
The experiment demonstrated that children imitate aggressive behavior observed in adults, highlighting the impact of modeling in learning.
What is the impact of social learning on deviant behavior?
Social learning suggests that deviant behavior can be learned through observation and the desire for social approval.