Cell Biology Exam 1
1/298
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
299 Terms
Stem cells
unspecialized cells that have self renewal abilities and can differentiate into any cell an organism possess
Totipotent
develop into any cell and present in early development
Pluripotent
develop into any cell within the 3 germ cells but cannot form an organism by itself
Multipotent
develop into any cell in the body derived from a certain germ layer
Unipotent
develop into one type of cell or tissue
Cell Theory (Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow)
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function for an organism
Cells only come from pre-existing cells
20th Century Biology
Reductionistic approach—understands by breaking down a complex system into smaller pieces
DNA sequence
raw DNA sequence with computational tools to identify open reading frames
Gene circuits
regulatory networks of genes and their products that control where and how much a product is made
Modern High-Throughput Technologies Pathway
DNA sequence→ Genes → Gene product → gene circuits
21st century Biology
integrative approach—looking at the whole system by combing parts together
Phenomics
the study between phenotypes and genotypes
Mass and Energy GC
metabolism and transport
Information Transfer GC
transcription, translation, and signal transduction
Cell Fate GC
cell motion divisions, adhesion, differentiation
Macro cell components
proteins (~50–60% of dry mass), nucleic acids (~15%), polysaccharides (~10%), lipids (~5–10%)
Micro cell components
organic molecules, inorganic ions (salts)
Crowding
the idea that due to multiple processes the components within a cell have limited space
Eukaryote water percentage (AC)
70%
Integrated functions
the meshing of multiple gene products due to a crowded cell environment
Eukaryote protein percentage (AC)
15%
Eukaryote metabolite percentage (AC)
1-3%
Eukaryote DNA percentage (AC)
1%
Eukaryote volume (AC)
4000 microns 3
Cell diffusion speed
often fast, milliseconds
cell metabolism speed
often slower
Numerical Aperture
a measure if a lens ability to gather light and resolve fine specimen detail
higher NA= better detail
Light microscope
uses visible light passed through or reflected from a sample ; magnified by lenses for visualization and sharpened by phase contrast
Fluorescent Microscope
high intensity light to excite fluorescent dyes or proteins, only tagged parts of the cells emit visible light
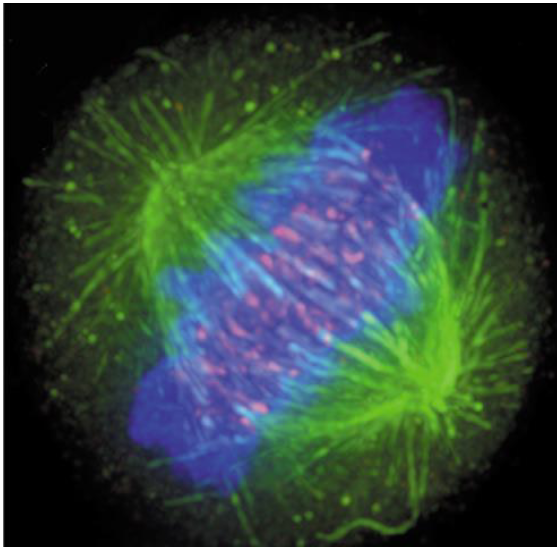
FM excitation
= light absorbed
FM emission
= longer wavelength light released
Atomic Force Microscope
measures surface topography with a probe, the tip
is repelled by or attracted to the surface, the cantilever beam deflects, the magnitude of the deflection is captured by a laser that reflects at an oblique angle from the very end of the cantilever
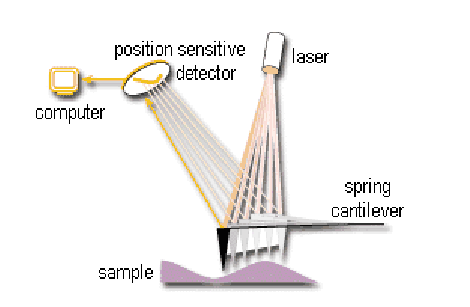
AFM Contact mode
tip is in continuous physical contact with the sample surface while scanning, measuring forces directly
AFM Tapping mode
intermittent contact, tip oscillates and lightly “taps” the surface at the end of each swing, reducing damage to soft samples and minimizing lateral forces
Confocal Microscope
uses lasers and a pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light, produces sharp, thin “optical sections” that can be stacked into 3D images
Electron microscope
uses an electron beam of light to a much higher resolution (nm range)
TEM
transmission electron microscope, internal structures
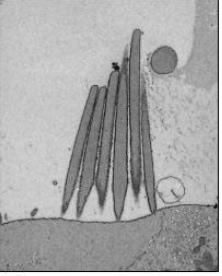
SEM
scanning electron microscope, surface detail
Molecular beacon
recognition based on fluorescent energy transfer, hairpin DNA with fluorophore + quencher → fluorescence only when bound to target
FRET
energy transfer between donor and acceptor fluorophores, when close → measures protein interactions
Cytoplasm
contents of a cell excluding the nucleus
cytosol
the fluid portion of the cytoplasm suspends the organelles
centriole
a cylinder of 9 triplets of microtubules held together by supporting proteins (9+0 array)
microtubules
hollow tubes made out of tubulin that provide strength and support, movement of cellular structures
microfilaments
double helix polymer of actin that possesses directionality and aids in cell movement
cell membrane
a barrier that encases the cell comprised of proteins, cholesterol and lipids
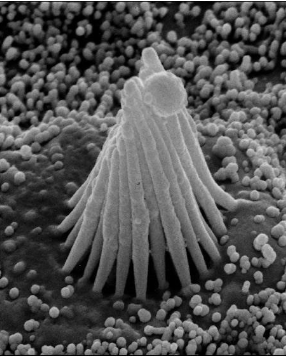
cilia
long extensions containing microtubule doublets in a 9 + 2 array to move material over the surface
proteasomes
hollow cylinders that contain proteolytic enzymes and regulatory proteins to break down and recycle damaged proteins
ribosomes
RNA + proteins that function in protein synthesis
Golgi apparatus
flattened cisternae that stores, alters, and packages secretory vesicles
mitochondria
double membrane with inner folds enclosing enzymes (95% of ATP synthesis )
ER
network of membranous channels that synthesis secretory products and carry out transport/ storage
peroxisomes
vesicles with degradative enzymes to neutralize toxic compounds generated in catabolism
lysosomes
vesicle that contains digestive enzymes that removes damaged organelles and pathogens
integral proteins
proteins that span the entire membrane while corresponding to the differing polar/nonpolar regions
peripheral proteins
proteins found on the outside of the membrane used for communication and support
anchoring proteins
attach the inside/outside structures to stabilize
receptor proteins
bind and respond to ligands
carrier proteins
transport specific solutes through the membrane that normally couldn’t cross
channel proteins
regulate water flow and solutes through the membrane (ions+ polar molecules) w/ the concentration gradient
glycocalyx
sticky sugar coat, Lubrication and Protection, Anchoring and Locomotion, Specificity in Binding (receptors), Recognition (immune response)
Endocrine signaling
hormones secreted and carried through the circulation system to act on distant body sites
Paracrine signaling
signaling molecules with RNA + DNA fragments in the exosomes that are released by one cell to act on neighboring target cells
Autocrine signaling
cells respond to molecules/signals that are produced by the cell
Signaling Pathway
Sensors→ Signaling pathway → Gene Expression (Nucleus) →Protein Expression → functions
Direct signaling
cell-cell or cell-matrix (integrins and cadherins)
Stages of signal transduction
Reception
Transduction
Cell response
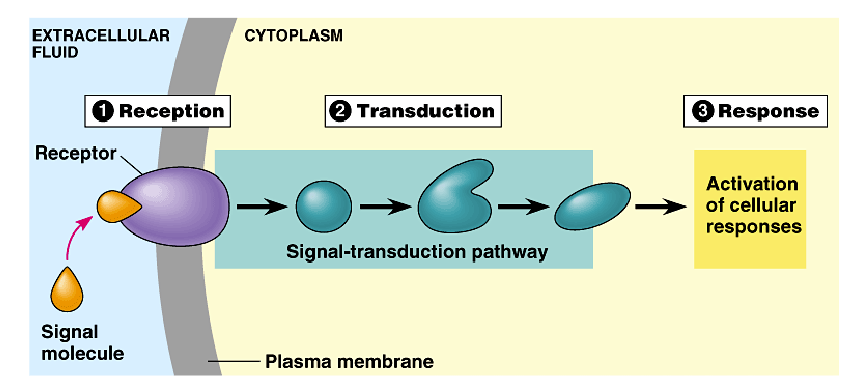
1.Reception
reception of an extracellular signal by cell
2.Transduction
processing of the signal from the outside to the inside of the cell (multi-stepped)
3.Response
cells response initiated with in the cell
Exosome Biogenesis
the inward budding of the membrane to form a vesicle and endosome, following another budding to create a multi-vesicular body that contains exosomes
exosomes
extracellular vesicles that contain mRNA,ncRNA, DNA fragments and proteins that can be degraded and transported
NO
a gas that signals to relax smooth muscle and vasodilation
CO
a gas the signals the brain at low levels
testosterone
a male sex hormone that regulates development of male reprod. tissues
estradiol
primary female estrogen control menstrual cycle and reprod. tissues
progesterone
prepares and maintains uterus for pregnancy
cortisol
stress hormone increase blood-glucose levels
aldosterone
increases sodium and water absorption in kidneys, raises BP
GCPRs
a large class of receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate an internal signal
GPCR steps
ligand binding → conformational change → G-protein activation (GDP→GTP) → effector enzyme → second messenger
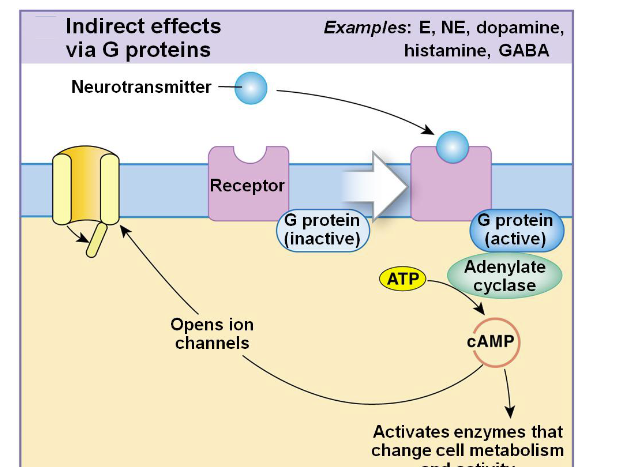
common GCPRs
cAMP, Ca²⁺, IP₃, DAG
cell development
the successive process of systematic gene-directed change through organisms life cycle (observable changes in structure/function)
Determination
cell fate committed (not reversible)
fertilization
the sperm and egg fuse together
cleavage
12-24 hour rapid division with no individual cell growth controlled by cyclins and Cdks
blastulation
mass of cells begin to form a hollow ball
differentiation
the cell begins to differentiate and form cavities
implantation
blastocyst implants into endometrium of uterus
Blastomere
a cell produced by division of zygote
blastocyst
a hollow ball, that is the new pluripotent cell that will become part of the embryo
inner cell mass
group of cells inside the blastocyst source of EBSC
hair, skin, nails, spinal cord, peripheral NS
ectoderm (5)
mesoderm (4)
muscle, bone, connective tissue, circulatory system
endoderm (5)
digestive tract, epithelium, stomach, colon, liver
cytoplasmic determinants
molecules that asymmetrically distributed in the egg cytoplasm, direct gene expression
ESC stages
zygote → morula → blastocyst → inner cell mass
Induction
to change the fate of a cell due to interaction with an adjacent cell
Somatic Nuclear Cell Transfer
a lab strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body and egg cell (micro-pipetting) (cloning)
Reproductive cloning
A process that creates a genetically identical organism by implanting a cloned embryo into a uterus to develop into a full organism