3 - Wheelchairs & Accessibility
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Which parts of the wheelchair serve as postural support?
come into direct contact w the patient
seat, back, armrest, front rigging
Which parts of the wheelchair serve as the mobility base?
help support system move around
wheels, tires, locks, frame
What landmark should a wheelchair seat back go up to?
inferior angle of scapula
When should a seatback be reclined less than 90 degrees?
for patients with poor trunk control, to prevent them from falling forward
Describe the difference between a wheelchair that reclines and a wheelchair that tilts in space
recline - only the seat back moves
tilt in space - the whole chair and all rigging moves together and rotates
What is the seat back angle in a standard wheelchair?
90 degrees
What are desk length armrests?
shortened armrests that allow the wheelchair to be wheeled closer to a desk or table without interference from the armrest
What components are part of a wheelchair's front rigging?
foot plate, leg rest (calf pad), heel strap
What is the function of front rigging?
support the lower extremity
Describe front rigging in a standard wheelchair
has foot plate, no leg rest (calfpad), no heel strap
is removable
Describe the inner rim of the drive wheel
the tire, can be solid rubber or air filled (pneumatic)
Which type of tire is preferred? Which is better for outdoor use? Indoor use?
pneumatic tires preferred, best for outdoor use
solid rubber preferred for indoor use
Describe the outer rim of a drive wheel
rim that the patient pushes on to move
typically smooth, may have projections
What is a wheel camber?
angle of a wheel's tilt inwards
What is the camber of a standard wheelchair?
0-8 degrees
Would a higher camber provide less or more stability? Explain
higher camber = more side to side stability
increases base of support
What is a wheelchair caster?
tiny wheel at the front or back of the wheelchair
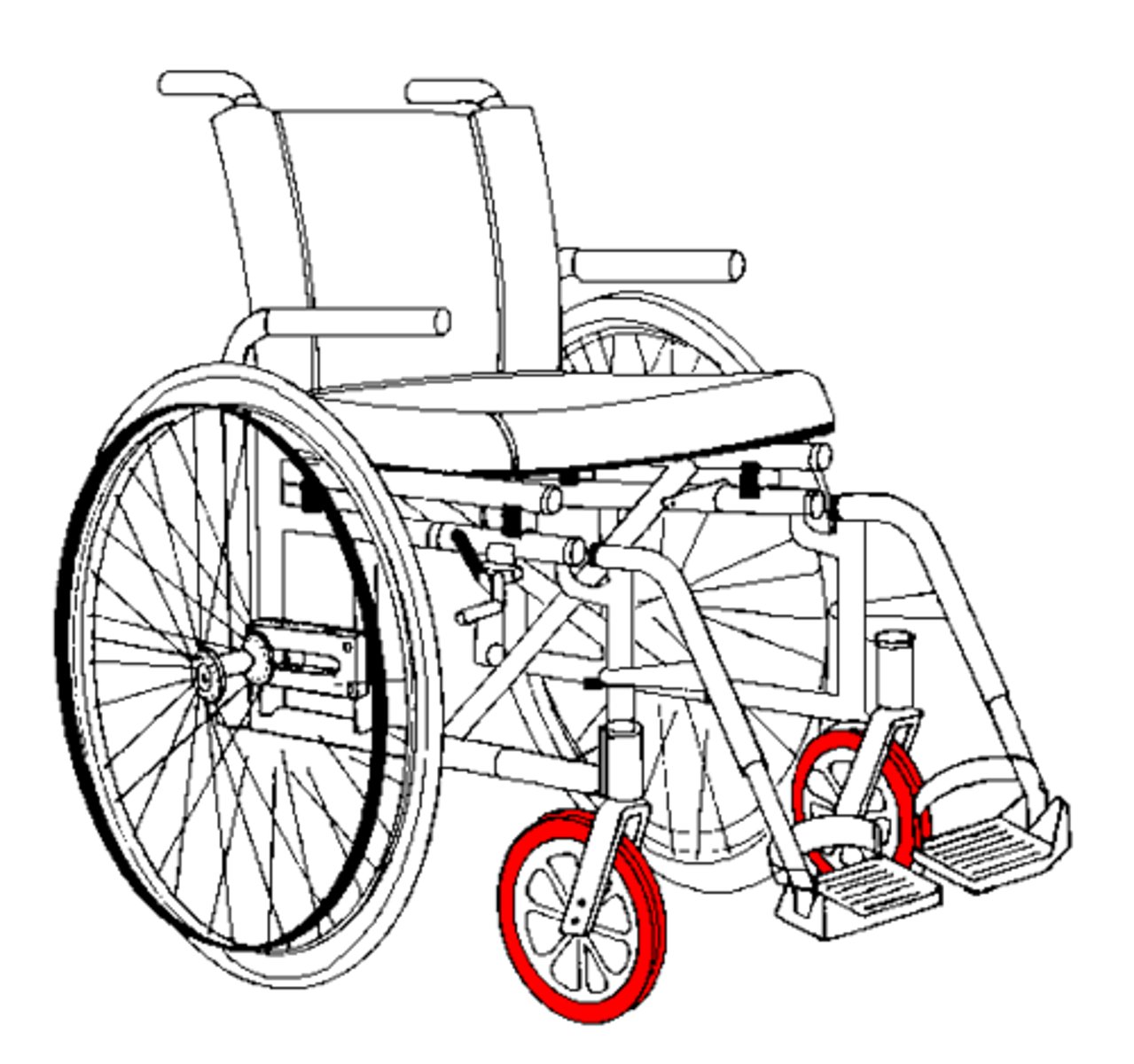
What is the caster size on a standard wheelchair?
5in
What are the pros/cons of a larger or smaller caster?
smaller - better maneuverability but doesn't run as smooth
larger - rides smoother, less maneuverability
How do wheel locks differentiate from car brakes?
car brakes stop a vehicle already in motion
wheel locks prevent motion in a stationary wheelchair
When might anti rollback brakes be used?
to prevent wheelchair from going backwards, such as driving uphill
How can push locks be modified?
use an extension arm to make it easier to engage and disengage the lock
Describe the characteristics of a sport wheelchair
fixed frame, small caster wheels, high camber angle, short seat back height, fixed front rigging (if needed)
When might an individual need a power wheelchair?
if they have insufficient UE strength (can't self propel a wheelchair), need to conserve energy, have enough cognition to operate power wheelchair
Describe the differences between front wheel, rear wheel, and mid wheel power wheelchairs
front - drive wheel is in front of caster
rear - drive wheel is behind caster
mid - drive wheel is between two pairs of caster
Which type of power wheelchair is the easier to learn how to drive?
rear wheel drive
Which type of power wheelchair has the largest turn radius?
rear wheel drive
Which type of power wheelchair has the greatest stability?
rear wheel drive
Which type of power wheelchair has the least stability?
mid wheel drive
Which type of wheelchair has the smallest turn radius?
mid wheel drive
Which type of wheelchair is better suited for indoor use?
mid wheel drive
Describe some modifications in a wheelchair for an amputee
no leg rest on amputation side, drive wheels set further behind the back support
Why should a drive wheel be set further back in an amputee's wheelchair?
due to change in COG; ensure COG is still within BOS if they tilt back in their wheelchair
What is a bariatric wheelchair?
wheelchair capable of holding wider and heavier individuals
What is the weight capacity difference in a standard vs a bariatric wheelchair?
standard - 250-300lbs
bariatric - up to 500lbs
Describe some features that are characteristic of a bariatric wheelchair
wider seat, rear axle is shifted forward
Why should the rear axle of a bariatric wheelchair be further forward?
for better stability, ensures 80% of Pt's BW falls on the rear axle
How much of a patient's weight should fall on the rear axle of their wheelchair?
80%
How is upper leg length calculated?
back of hips to popliteal fold
How is seat depth calculated for a wheelchair?
upper leg length - 2in
Why might supine be a better position to take upper leg length?
controls pelvic position, more accurate measurement
What can result from a seat depth that is too long? Too short?
long - increased risk of pressure injury
short - knee will be flexed more than 90*
How is seat width calculated?
distance of widest part of Pt's hips + 2 in
What is the seat width of a standard wheelchair?
25-28in
What can result from a seat width that is too narrow or too wide?
narrow - increased pressure on both sides of hip
wide - Pt more likely to lean, increased pressure on one side, risk of scoliosis
How is lower leg length measured?
from sole of shoe (or bottom of foot) to popliteal fold
How is seat-to-floor height calculated?
lower leg length + 2in
What should the wheelchair seat height be if the patient uses their legs for propulsion?
same as lower leg length
What may happen if the seat height is too low?
may be harder to propel with feet, foot rests will drag on ground
What may happen if the seat height is too high?
feet will not reach the ground, will not be able to propel with feet
What may happen if the foot rests are too long?
feet will dangle, will not be adequately supported by the foot plates
What may happen if the foot rests are too short?
hips and knees will be in more flexed position, which can cause a flexion contracture and impact circulation
How is armrest height calculated?
length of underside of arm, from seat to olecranon process, plus 1 in
Describe some characteristics of accessible parking
1 accessible parking space every 25 parking spaces; 1 van accessible parking space every 6 accessible spaces
Describe some characteristics of accessible pathways of travel
curb cuts, clear of obstacles
Describe some characteristics of accessible entrances and doorways
beveled thresholds in doorways, large vestibules (space between doorways) that can allow navigation of a wheelchair, doors that are not super heavy
Describe some characteristics of accessible elevators, stairs, and railings
rails extend at least one foot beyond top step, elevator buttons within reach, braille buttons
Describe some characteristics of accessible common areas
service counter height should be low enough to be accessible