PSY 101 exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
1
New cards
what is psychology?
psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior
\
(mind: internal experiences of self and the world
behavior: actions and responses that are observable and measurable)
\
(mind: internal experiences of self and the world
behavior: actions and responses that are observable and measurable)
2
New cards
wundt
they call me the father of scientific psychology; i established the first psychology research laboratory in germany in 1879
3
New cards
james
i wrote the *Principles of Psychology* in 1890 and established functionalism, the first school of psychology in the united states. I am also considered the father of american psychology
4
New cards
freud
i was most controversial in my day for I wrote about unconscious conflicts, sex, and the importance of early childhood experiences
5
New cards
watson
i believe if you’re going to study behavior you have to be able to observe it and measure it. you cannot observe a thought
6
New cards
mary calkins
first female psychologist
7
New cards
metacognition
understanding how we think and learn and reflecting on that process
8
New cards
humanistic-positive perspective
emphasizes working toward reaching our full potential and finding happiness
9
New cards
behavioral perspective
the study of observable behavior
10
New cards
neuro/genetic perspective
influences of biological factors, including genotypes and the nervous system
11
New cards
cognitive perspective
how mental processes work
12
New cards
social/cross-cultural perspective
how the environment we are currently in and are raised in influence behavior
13
New cards
evolutionary perspective
studying how the psychological traits we posses were early adaptive mechanisms
14
New cards
psychoanalytic/ psychodynamic approach
the unconscious, early childhood experiences (freud)
15
New cards
is psychology more nature of nurture?
equally important
16
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- cognitive psychologist
the study of how we perceive information, how we learn and remember, how we acquire and use language, and how we solve problems
\
* A *cognitive psychologist* asks people to do a driving simulation task and measures delays to different distractions.
\
* A *cognitive psychologist* asks people to do a driving simulation task and measures delays to different distractions.
17
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- developmental psychology
explores how thought and behavior change and show stability across the life span
\
* A *developmental psychologist* measures how many words a two-year-old says when with their parent compared to when with a stranger.
\
* A *developmental psychologist* measures how many words a two-year-old says when with their parent compared to when with a stranger.
18
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- behavioral neuroscience
studies the links among brain, mind, and behavior. neuroscience cuts across various disciplines and subdisciplines of psychology. one can study the brain functions involved in leaning, emotion, social behavior, mental illness, etc.
\
* A *behavioral neuroscientist* examines fMRI scans while people recount negative memories.
\
* A *behavioral neuroscientist* examines fMRI scans while people recount negative memories.
19
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- personality psychology
considers what makes people unique, as well as the consistencies in people’s behavior across time and situations
\
* A *personality psychologist* administers intelligence tests to anxious and secure fraternal and identical twins.
\
* A *personality psychologist* administers intelligence tests to anxious and secure fraternal and identical twins.
20
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- social psychology
considers how the real or imagines presence of others influences thought, feeling, and behavior
\
* A *social psychologist* examines stereotype conformity when surrounded by peers, compared to authority figures.
\
* A *social psychologist* examines stereotype conformity when surrounded by peers, compared to authority figures.
21
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- clinical psychology
focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders and ways to promote psychological health
* A *clinical psychologist* has just completed an intake (initial or background-gathering)interview with an apparently depressed gentleman who lost his job on month ago
* A *clinical psychologist* has just completed an intake (initial or background-gathering)interview with an apparently depressed gentleman who lost his job on month ago
22
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- health psychology
examines the role of psychological factors in physical health and illness
\
* A *health psychologist* measures men’s body dysmorphia.
\
* A *health psychologist* measures men’s body dysmorphia.
23
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- school psychology
studies how students learn, the effectiveness of particular teaching techniques, the dynamics of school populations, and the psychology of teaching
\
* An educational psychologist designs a new standardized math test for the state, while a *school*
*psychologist* goes over test results with the parents of a child who appears to have a reading disability.
\
* An educational psychologist designs a new standardized math test for the state, while a *school*
*psychologist* goes over test results with the parents of a child who appears to have a reading disability.
24
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- industrial/organizational (IO) psychology
an applied science, meaning it requires understanding the real-world rather than a laboratory behavior. involved matching employees to their jobs and aims to make workers more productive and satisfied with work environments
\
* A *I/O psychologist* has been hired as a consultant for a company that has had a dramatically high
employee turnover rate for the past 2 years.
\
* A *I/O psychologist* has been hired as a consultant for a company that has had a dramatically high
employee turnover rate for the past 2 years.
25
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- sports psychology
examines the psychological factors that affect performance and participation in sports and exercise
\
* A *sports psychologist* has been hired to work with a minor league baseball team that has had two losing seasons.
\
* A *sports psychologist* has been hired to work with a minor league baseball team that has had two losing seasons.
26
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- community psychology
focuses on how individuals are connected to and part of their communities
\
* A *community psychologist* meets with community members, groups, and organizations to address local houselessness.
\
* A *community psychologist* meets with community members, groups, and organizations to address local houselessness.
27
New cards
subdiscipline of psych- forensic psychology
blend of psychology, law, and criminal justice
\
* A *forensic psychologist* testifies in court to the mental state of a woman claiming workers compensation for an alleged Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) she received falling off a ladder at work.
\
* A *forensic psychologist* testifies in court to the mental state of a woman claiming workers compensation for an alleged Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) she received falling off a ladder at work.
28
New cards
empiricism
philosopher john locke established a view that knowledge and thoughts come from experience and observations, a point of view known as _____
29
New cards
steps of the scientific method
o **Observe**
o **Predict** (make a specific hypothesis)
o **Test** (design a study and collect data)
o **Interpret** (analyze results and interpret findings, (risk of overinterpretation))
o **Communicate** (publish/present findings)
o **Replicate** (why? - question again, again, and again)
o **Predict** (make a specific hypothesis)
o **Test** (design a study and collect data)
o **Interpret** (analyze results and interpret findings, (risk of overinterpretation))
o **Communicate** (publish/present findings)
o **Replicate** (why? - question again, again, and again)
30
New cards
validity
measuring all of what you actually need to measure, measuring all aspects of what you need to measure
31
New cards
reliability
must experience the same result many times to be considered reliable
32
New cards
independent variable
variable manipulated by the researcher
33
New cards
dependent variable
changes due to the effect of the manipulated variable
34
New cards
*___* variable affects change in the ___ variable
independent, dependent
35
New cards
identify the dependent & independent variables
\
a cognitive psychologist would like to find out whether more extensive education might protect individuals from dementia and related disorders later in life
\
a cognitive psychologist would like to find out whether more extensive education might protect individuals from dementia and related disorders later in life
independent variable: education
dependent variable: dementia/related disorders \`
dependent variable: dementia/related disorders \`
36
New cards
correlation
a mutual relationship/connection between two or more things
\
example: height and weight
\
example: height and weight
37
New cards
causation
the act of causing something
\
example: how many hours you work and how much money you get paid
\
example: how many hours you work and how much money you get paid
38
New cards
3 examples of “correlational language”
* related to
* linked with
* associated with
* linked with
* associated with
39
New cards
examples of “casual language”
* affects
* causes
* makes
* leads to
* helps
* impacts
* “you should…”
* causes
* makes
* leads to
* helps
* impacts
* “you should…”
40
New cards
hypothesis
a specific, informed, and testable prediction of what kind of outcome should occur under a particular condition
41
New cards
pseudoscience
refers to practices that appear to be and claim to be science but do not use scientific method to reach their conclusions
42
New cards
replication
the repetition of a study that either confirms or disconfirms the original result
43
New cards
descriptive designs
researcher makes no prediction and does not try to control any variables. they simply defines a problem or interest and describes as carefully as possible the variable of interest
\
* naturalistic observations
* case studies
* surveys
\
* naturalistic observations
* case studies
* surveys
44
New cards
case studies
gathered by observing one person, often over a long period of time
45
New cards
qualitative research
data gathered from open-ended and unstructured answers, rather than quantitative or numeric answers
46
New cards
quantitative research
research that collects information using any kind of numeric and quantifiable scale and often has limited response options
47
New cards
correlational studies
measurer two or more variables and their relationship to one another
\
* survey
* observational
\
* survey
* observational
48
New cards
experimental studies
experimental manipulation of a predicted cause, the independent variable
\
random assignment of participants to control and experimental groups or conditions, meaning that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in a group
\
\
\
random assignment of participants to control and experimental groups or conditions, meaning that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in a group
\
\
49
New cards
longitudinal studies
make observations of the same people over time, ranging from months to decades. useful for studying change over time and can be used to study how specific causes affect specific outcomes
50
New cards
twin studies
observing the effects of genetics and environment is to study twins who are adopted or not and compare them to other siblings who are adopted or not
51
New cards
self-report measure
people’s written or oral accounts of their feelings, thoughts, or actions
52
New cards
behavioral measures
involve the systematic observation of people’s actions either in their normal environment (naturalistic observation) or in a lab setting
53
New cards
physiological measures
provide data on bodily responses
54
New cards
confirmation bias
the tendency to selectively attend to information that confirms one’s general beliefs while ignoring information or evidence that contradicts one’s beliefs
55
New cards
social desirability bias
people present themselves more favorably than they really are, not wanting to reveal what they are really thinking or feeling to others for fear of looking bad
56
New cards
effect size
a measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables
57
New cards
informed consent
tell participants in general terms what the study is about, what they will do and how long it will take, what the known risks and benefits are, and whom to contact with questions. they have the right to withdraw and must be signed by the participant (signed by guardian if under 18)
58
New cards
respect for persons
safeguard the dignity and autonomy of the individual and take extra precautions when dealing with study participants, such as children, who are less likely to understand that their participation is voluntary
59
New cards
beneficence
inform participants of costs and benefits of participation
60
New cards
privacy and confidentiality
protect the privacy of the participant, generally by keeping all responses confidential. confidentiality ensures that participants’ identities are never directly connected w the data they provide in the study
61
New cards
justice
benefits and costs must be distributed equally among participants
62
New cards
epigenetics
nature and nurture together influence who we are
63
New cards
3 major types of neurons
o **Sensory neurons:** Transmits impulses from sensory organs (example: skin, someone taps u on the shoulder so sensory neurons send the message to the brain and the brain tells u what that means) to brain & spinal cord
o **Motor Neurons:** Transmits impulses from brain & spinal cord to muscles and organs (example: taking in that someone is tapping you and your output from that information is caused by motor neurons)
o **Interneurons:** Perform connective or associative functions
o **Motor Neurons:** Transmits impulses from brain & spinal cord to muscles and organs (example: taking in that someone is tapping you and your output from that information is caused by motor neurons)
o **Interneurons:** Perform connective or associative functions
64
New cards
two cells of the nervous system
* **glial cells:** “glue”, surrounded neurons; hold them in place, makes myelin (myelin protects the neurons)
* **neurons:** building blocks of the nervous system, process & transmit information in the nervous system (through neurotransmitters)
* **neurons:** building blocks of the nervous system, process & transmit information in the nervous system (through neurotransmitters)
65
New cards
how do neurons communicate with each other?
neural communication, a two-step process including action potential and neurotransmission
66
New cards
dopamine
plays an important role in arousal, mood (especially positive mood); oversupply correlates with schizophrenia; voluntary muscle control
67
New cards
epinephrine
increases ANS activity; fight-or-flight response
68
New cards
norepinephrine
affects CNS activity; plays role in increasing alertness, attention
69
New cards
serotonin
plays role in mood, sleep, eating, temperature regulation; undersupply correlates with anxiety and depression
70
New cards
GABA
is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain; slows CNS function; correlates with anxiety and intoxication
71
New cards
frontal lobe function
speech, personality, problem solving, emotional processing, planning
72
New cards
parietal lobe function
sensory (temp and touch perception), reading, writing
73
New cards
temporal lobe function
language comprehension, behavior, hearing
74
New cards
occipital lobe function
vision
75
New cards
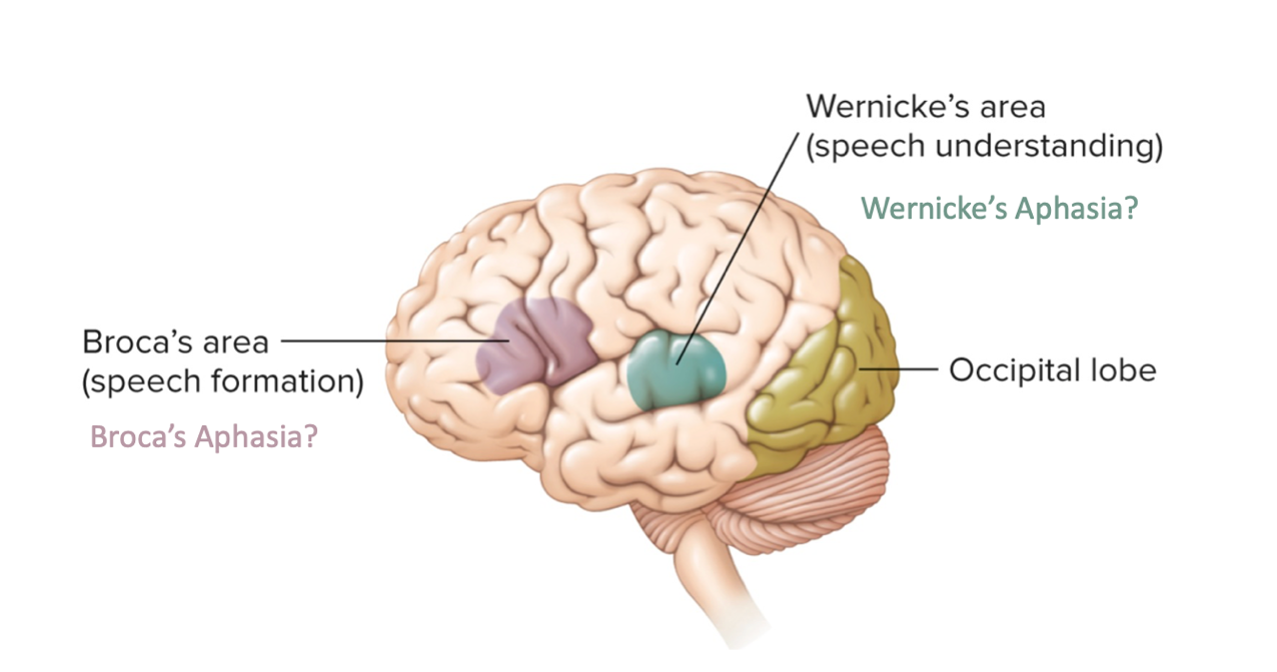
wernicke’s aphasia
can speak understood words, but cannot create a reasonable sentence with them. but can write correctly
76
New cards
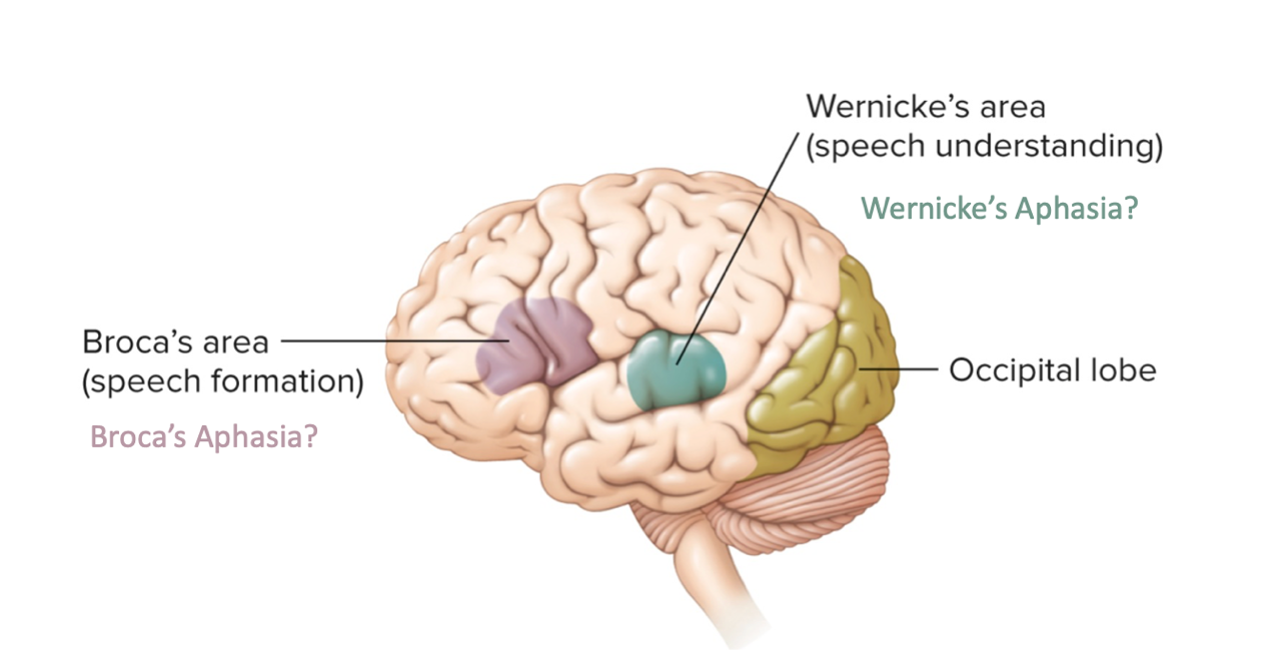
broca’s aphasia
cannot form the sounds of speech into normal words, but can write correctly
77
New cards
action potential triggers what?
neurotransmission
78
New cards
brain hemispheres and functions
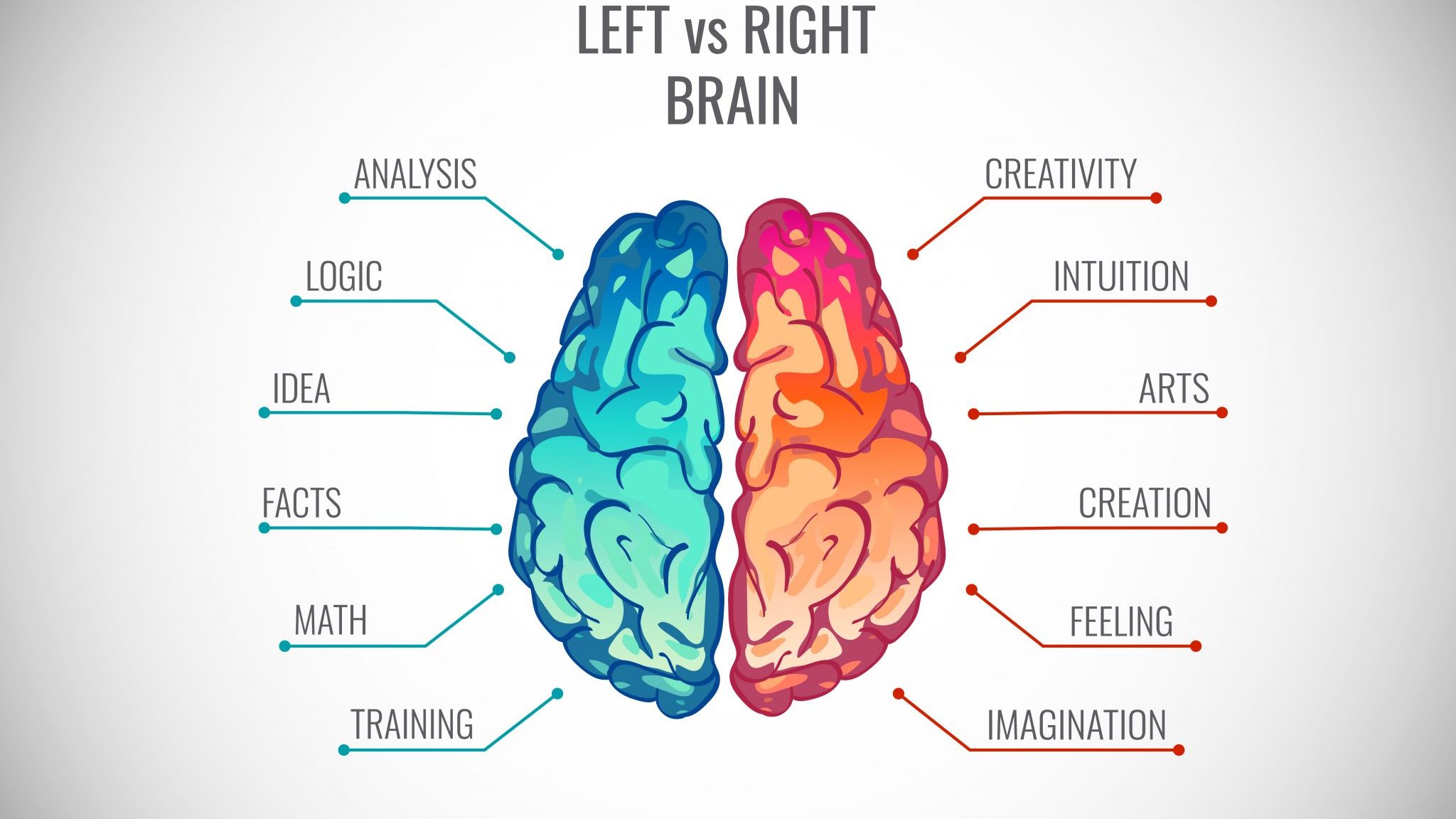
79
New cards
sensation
the stimulation of our sense organs by our outer world (example: eyes sensitive to light waves, ears to sound, skin to touch) “I see…hear…feel…smell…taste… something”
80
New cards
perception
the act of organizing and interpreting sensory experience “I see a cat” “i hear footsteps”
81
New cards
absolute threshold
the lowest intensity level of a stimulus we can detect 50% of the time
82
New cards
difference threshold
\- the smallest difference that can be detected 50% of the time
83
New cards
sensory adaption
sensitivity diminished when we experience constant stimulation (ex: sight (adapting to darkness/brightness), hearing (crickets outside, living in a big city))
84
New cards
Trichromatic Color Theory
perception of color comes from the combination of activating different cones
85
New cards
Opponent process Theory:
Cones are linked together (blue/yellow, red/green, black/white), activating one inhibits the other
86
New cards
rods
play a key role in night vision b/c they are most responsive to dark-and-light contrast
87
New cards
cones
responsible for color vision and are most functional in conditions of bright light
act much more quickly than rods
act much more quickly than rods
88
New cards
fusiform face area
viewing a face activates neurons in this area
89
New cards
what causes hearing loss?
* if hair cells in the inner ear become damaged
* when a person is exposes to very loud noises once or mederatlt loud noises over long periods of time
* when a person is exposes to very loud noises once or mederatlt loud noises over long periods of time
90
New cards
gestalt laws
* **similarity**: tendency to group like objects together
* **continuity**: we see points bro lines in such a way that they follow a continuous path
* **proximity**: we tend to group together objects that are near one another
* **closure**: occurs when e perceive a whole object in the absence of complete infomation
* **figure-ground**: the figure is the thing that stands in front of a somewhat unformed background
* **continuity**: we see points bro lines in such a way that they follow a continuous path
* **proximity**: we tend to group together objects that are near one another
* **closure**: occurs when e perceive a whole object in the absence of complete infomation
* **figure-ground**: the figure is the thing that stands in front of a somewhat unformed background
91
New cards
phantom limb syndrome
when people who have lost a limb feel pain in the missing arm or leg
92
New cards
synesthesia
occurs when a person experiences sensations in one sense when a different sense is stimulated
(senses get mixed up example: experience yellow or taste shapes)
(senses get mixed up example: experience yellow or taste shapes)
93
New cards
Who proposed a model of personality development with 8 stages, each defined by an identity crisis or conflict?
erik erickson
94
New cards
the ___ transmits electrical impulses toward the adjacent neuron
axon
95
New cards
___ says that the size of the just noticeable difference is a constant fraction of the intensity of the stimulus (E.G. 3% for weight perception)
weber’s law
96
New cards
what type of training can improve memory and attention?
mindfulness meditation
97
New cards
in the eye, ___ convert light energy into nerve energy
photoreceptors
98
New cards
zelda is a 2 year old and is mad her older cousin cason, got two cookies when she only got one, zelda’s mother breaks her cookie in half, giving her two halves. zelda is satisfied that things are even between her and cason because she has not yet acquired
low of conservation
99
New cards
in the forebrain, the ___ is responsible for forming new memories, while the ___ is responsible for processing emotions (especially fear)
hippocampus
amygdala
amygdala
100
New cards
who is credited with giving psychology independence from philosophy and physiology?
wundt