Chapter 8-10 Bones, Joints and Muscles -Lecture
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
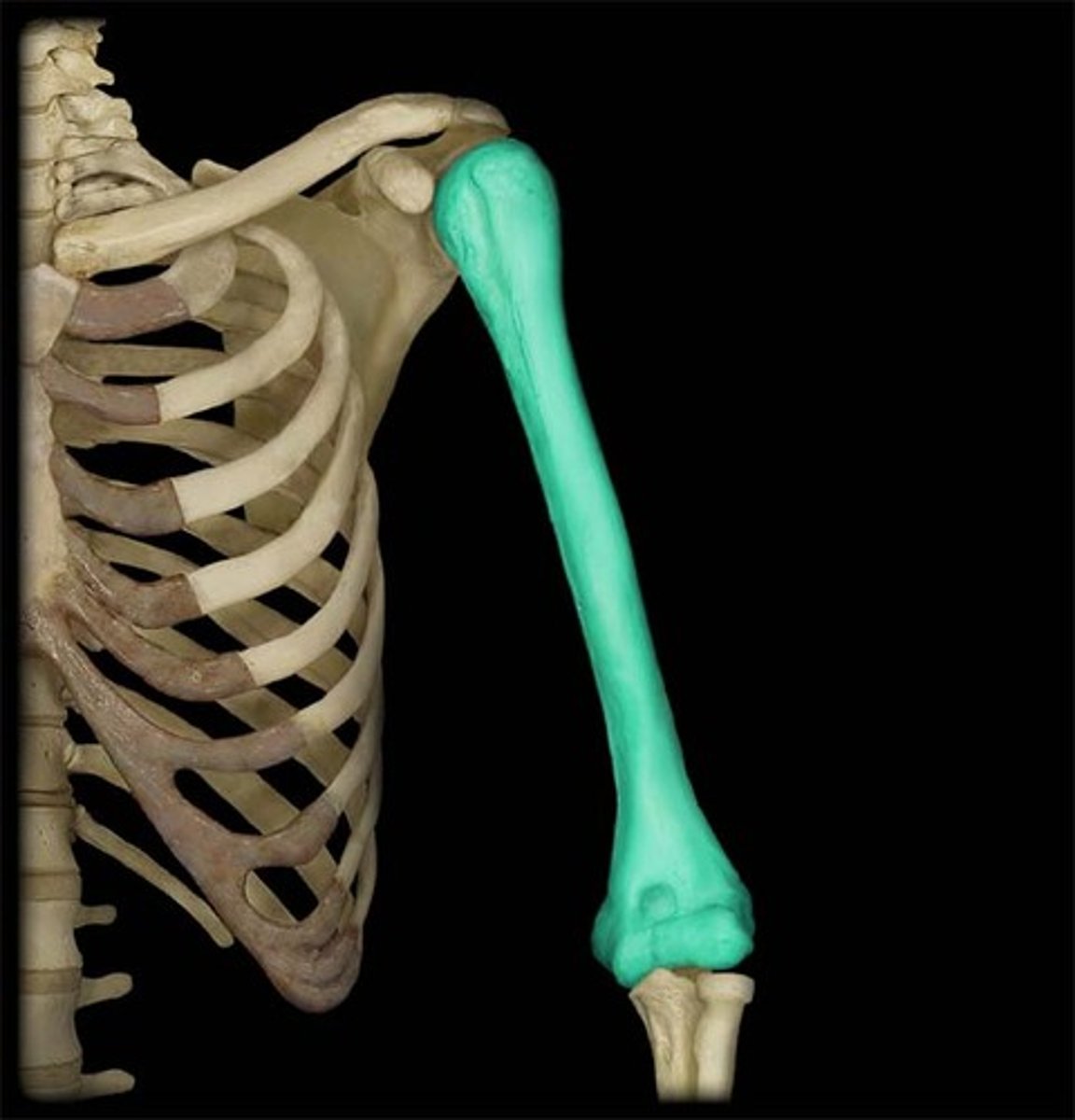
Humerus
Brachial bone, also known as "funny bone"
Upper arm bone
Radius
One of the antebrachial bones
Attaches to thumb
This one is bigger
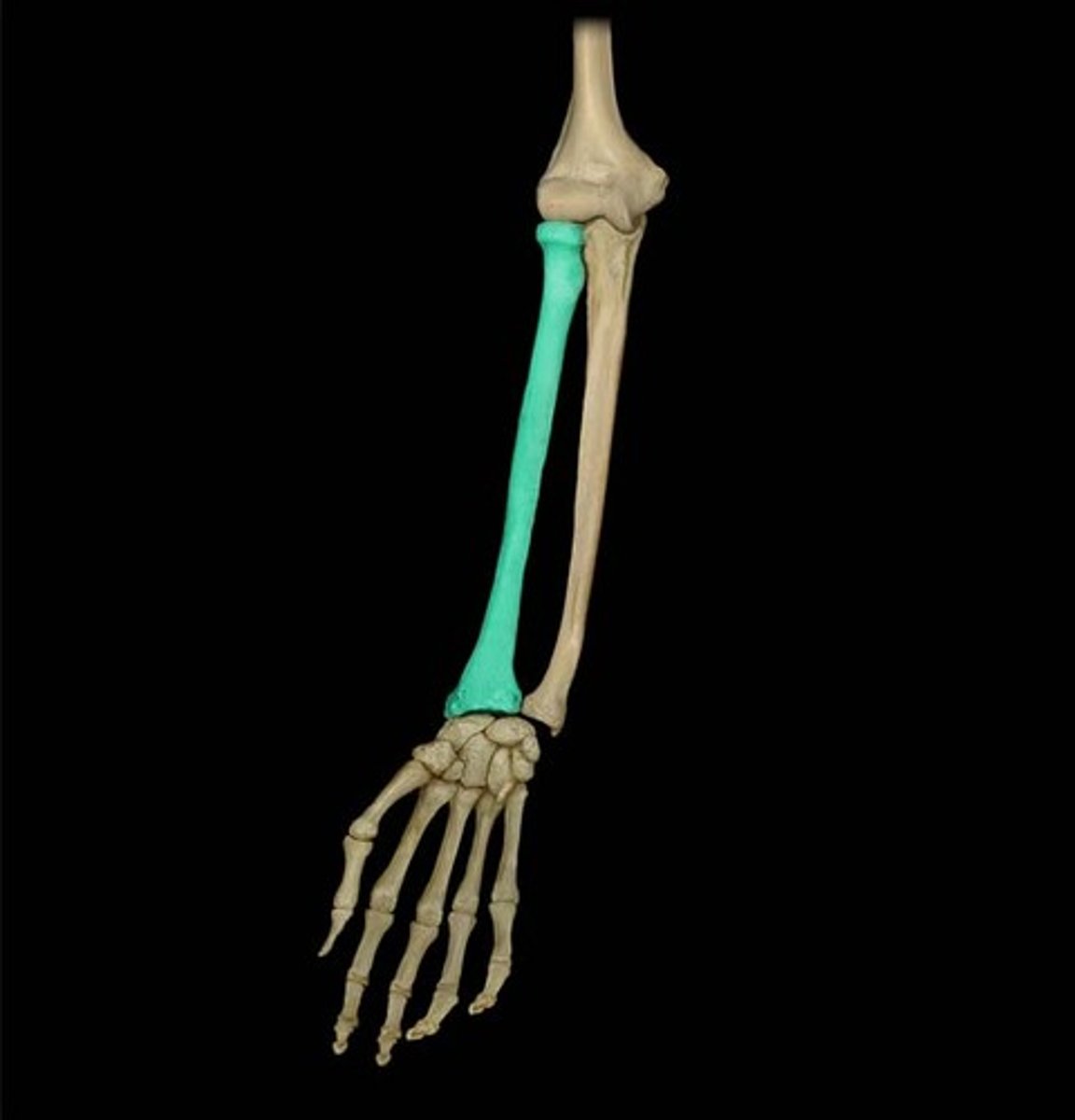
Ulna
One of the ante brachial bones
Other side
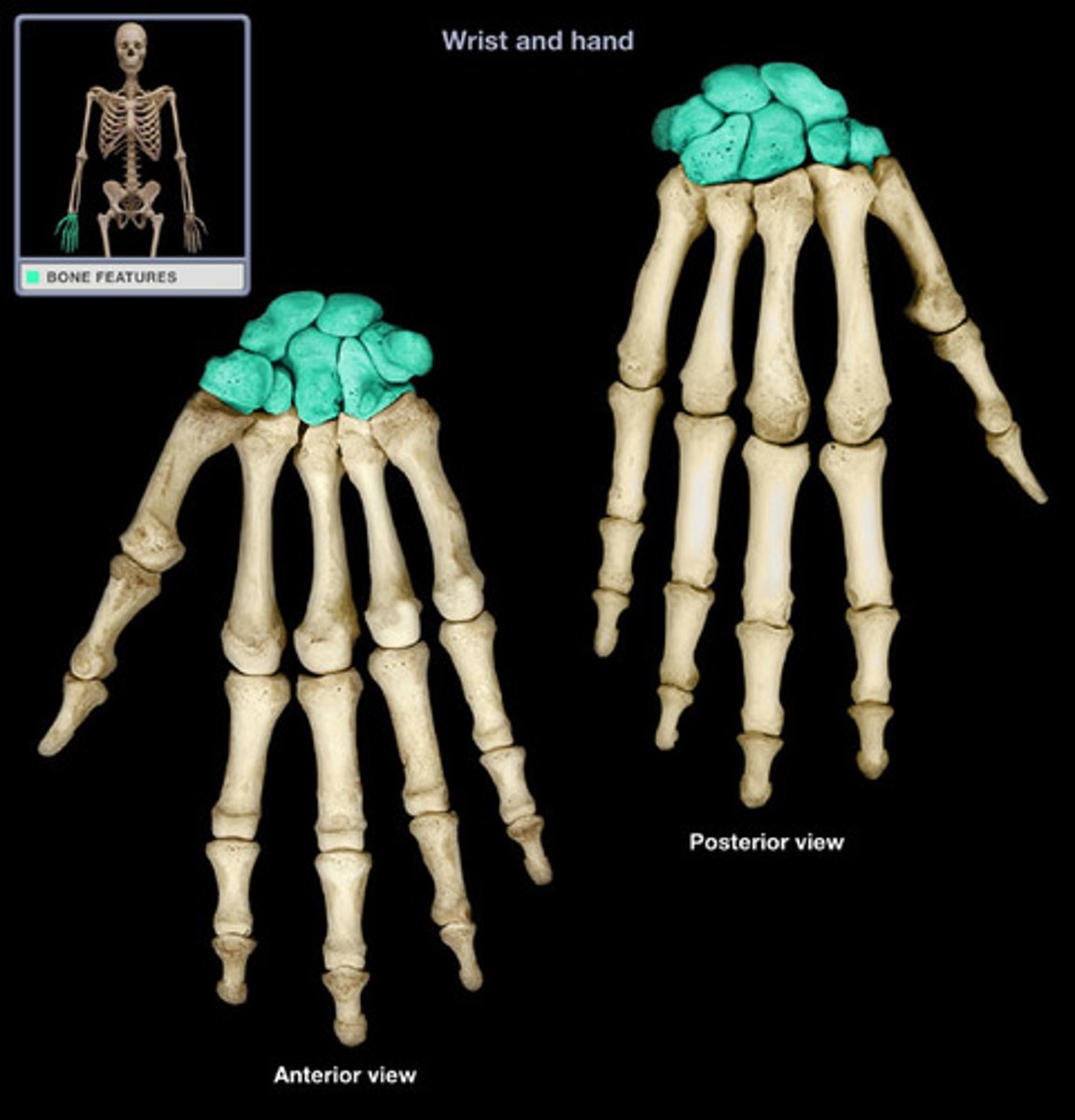
Bones in carpal
Lat to Med
Proximal: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform Distal :Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
*Some Lovers Tri Positions That They Cant Handle
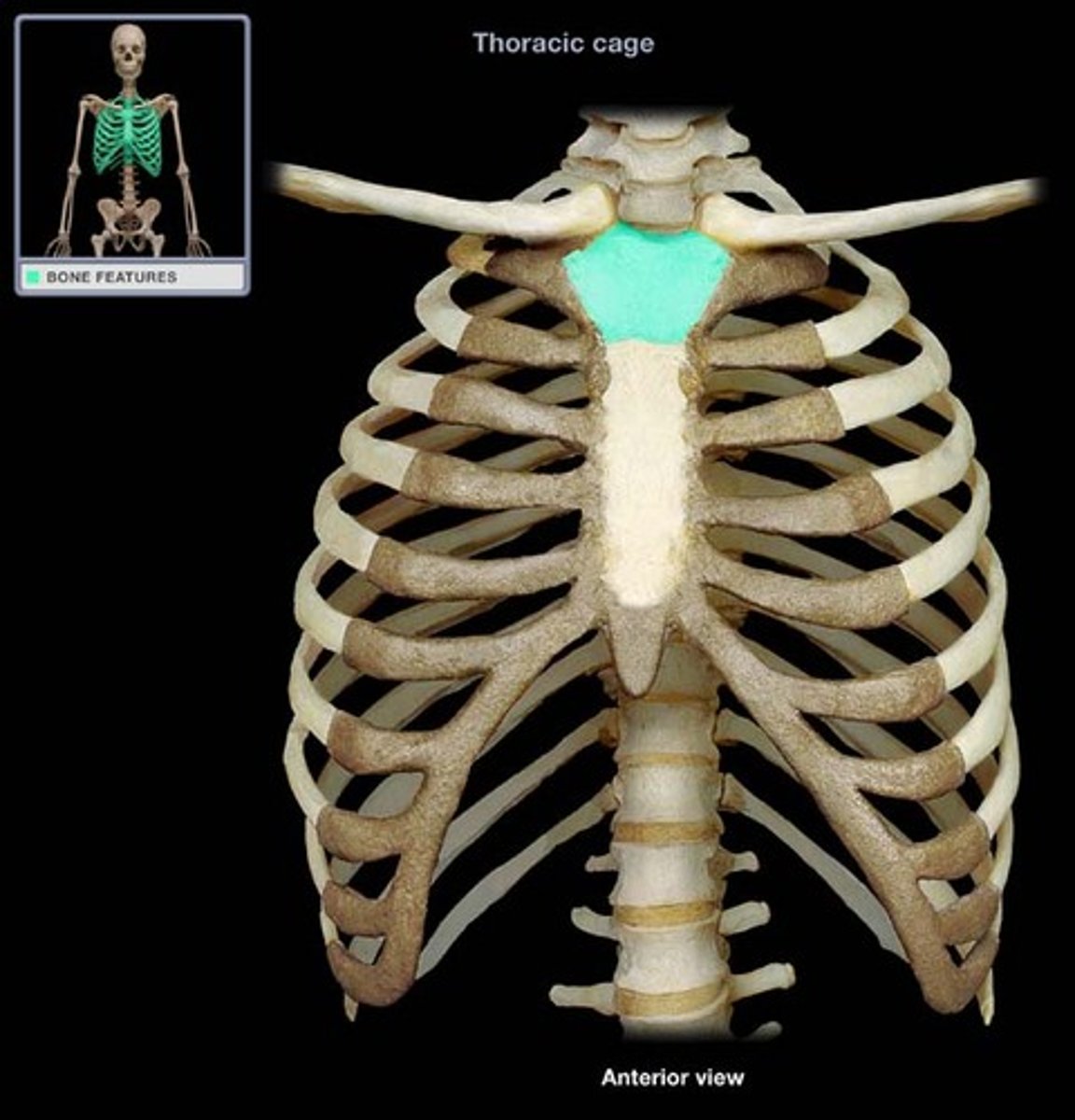
Sternum
CHEST BONE
Has three parts:
-Manubrium: top
-Body: middle
-Xiphoid process: end
Manus
Hand
Scapula
In between the humerus and calvic bone(collar bone)
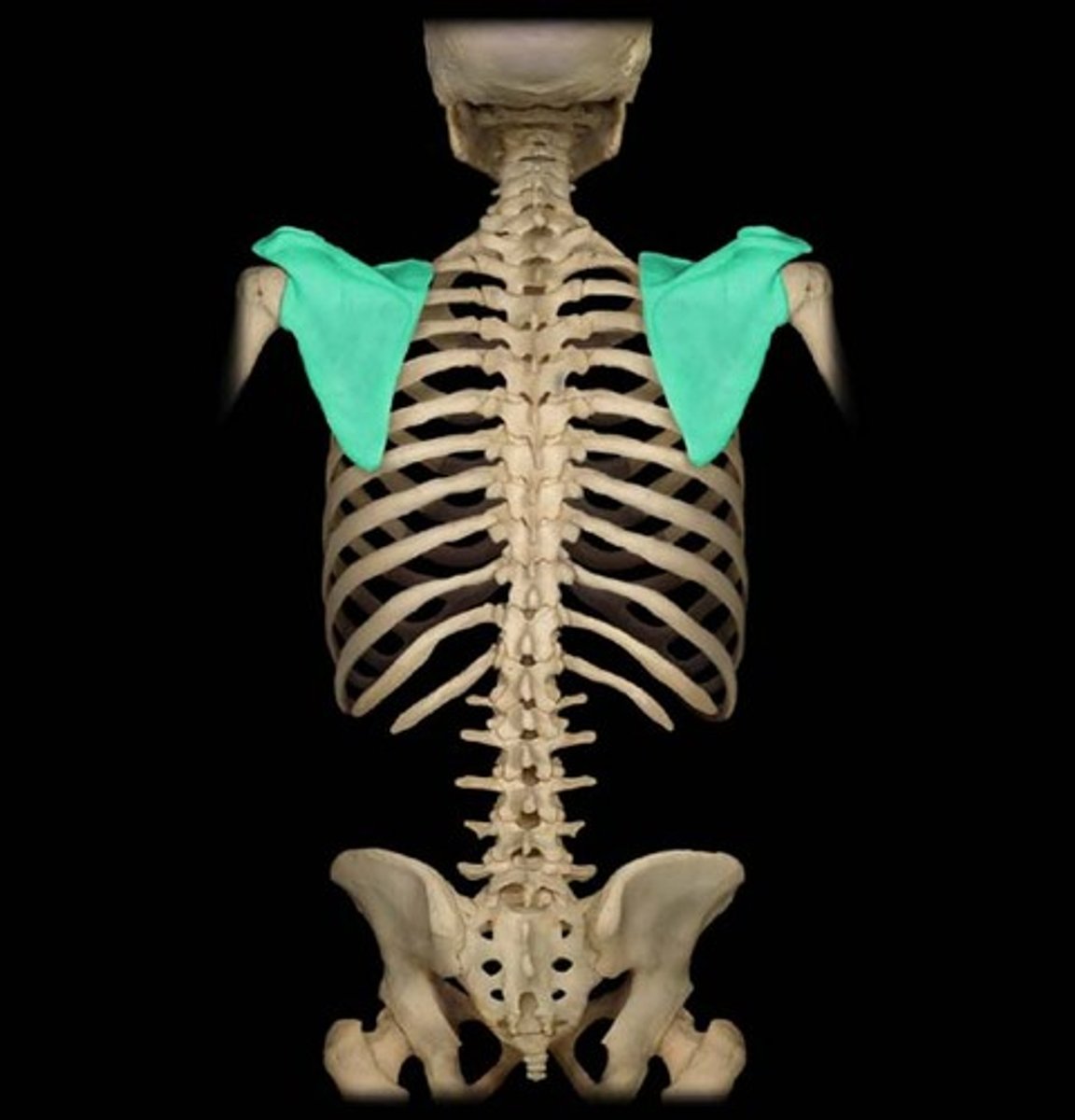
Organization
humerus > scapula > clavicle > sternum
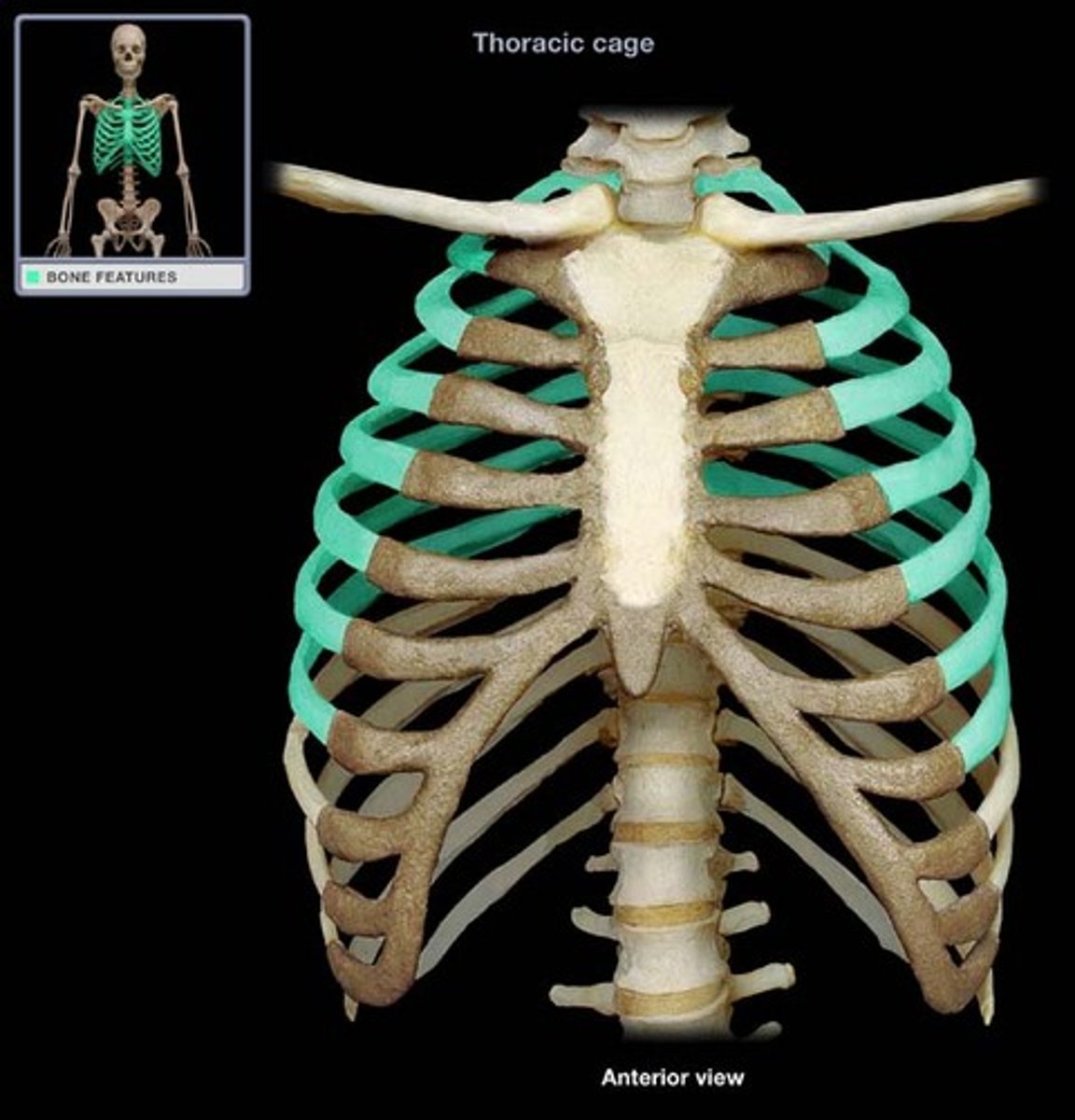
Ribs
-First 7: "true ribs" because they have Independent articulation(meaning they attach to the sternum via costal cartilage)
-8-10: "false ribs" -they fuse together, lack independent articulation
-11 & 12: "floating ribs" because they attach don't attach anteriorly just posteriorly.
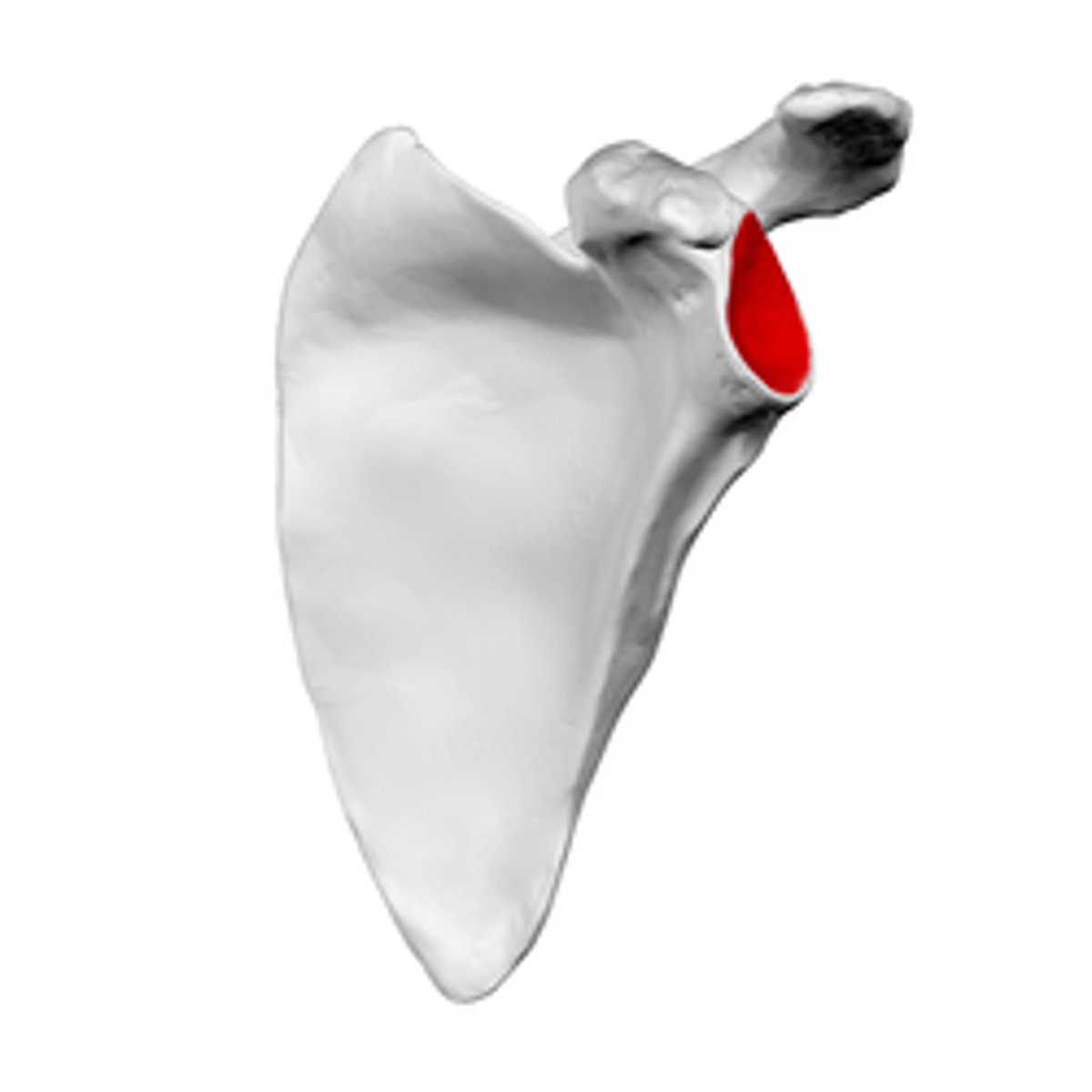
Why do you get more movement from the shoulder joint than any other?
1. Glemoid cavity is shallow
2. Scapula can move
3. Shoulder only attaches to sternum clavicular joint
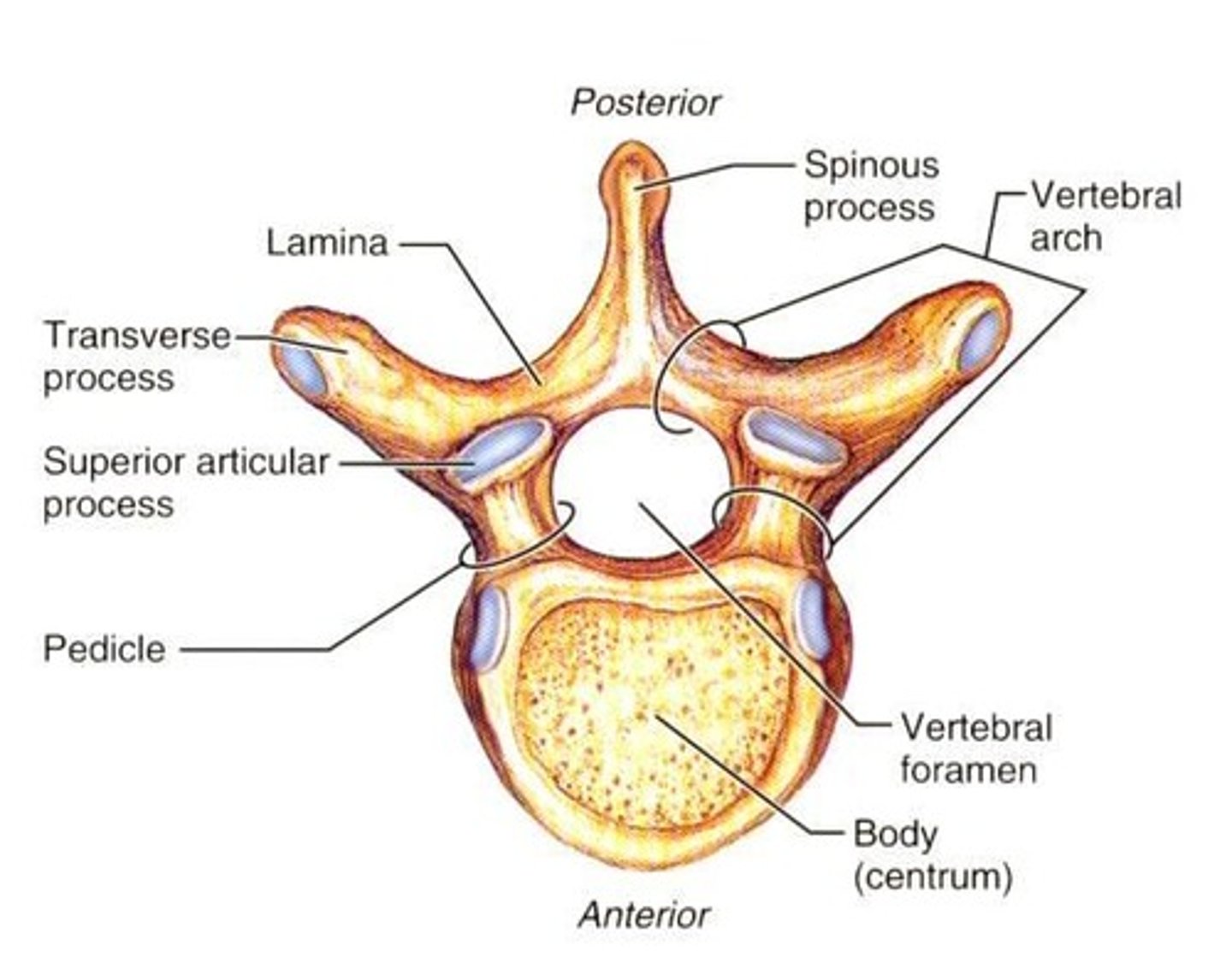
General structure of vertebrae
traverse > lamina > spinous
traverse > pedicle > body
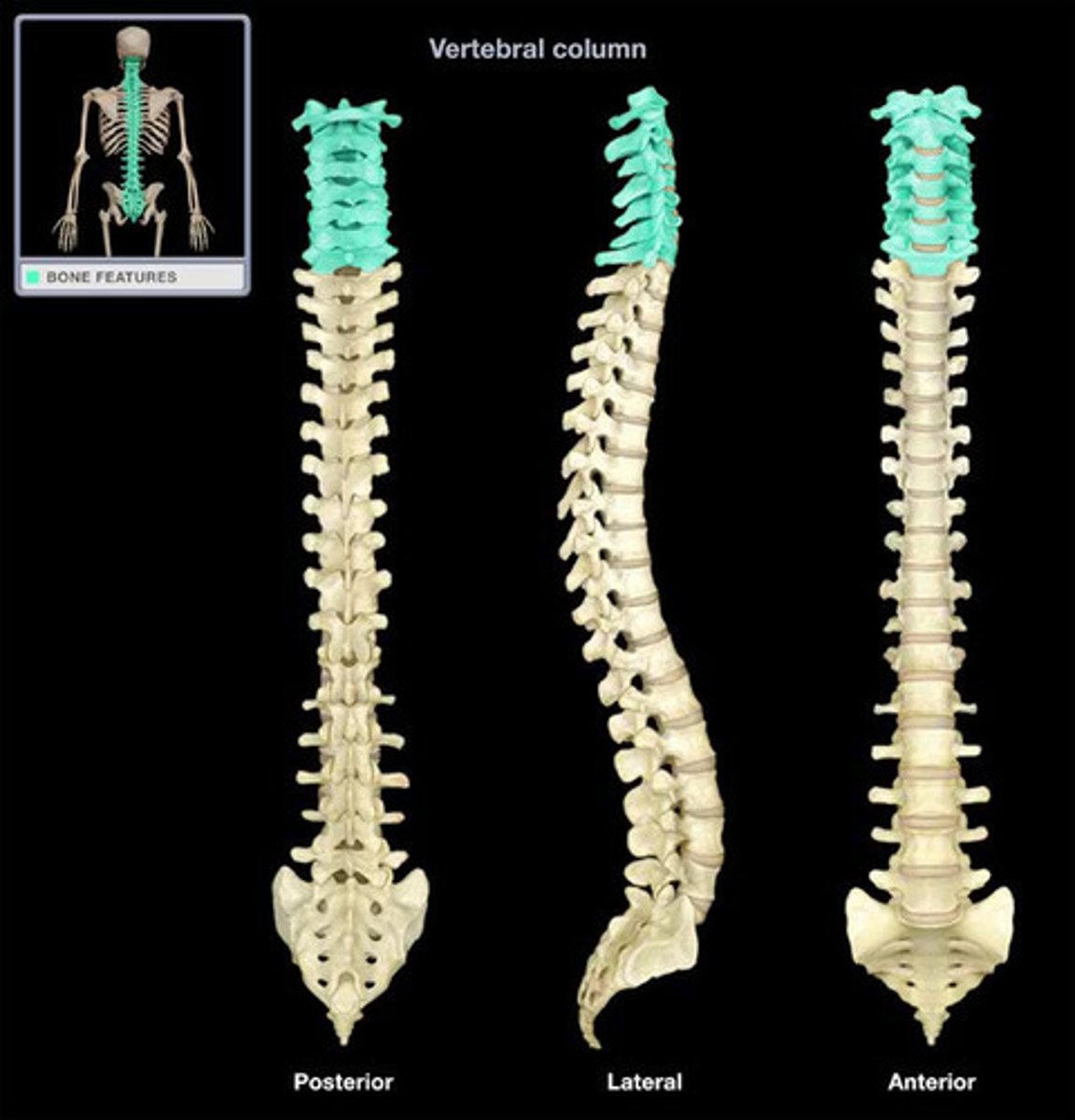
C1
C1 - Atlas
More superior to the head; in contact with the occipital bone (#1)
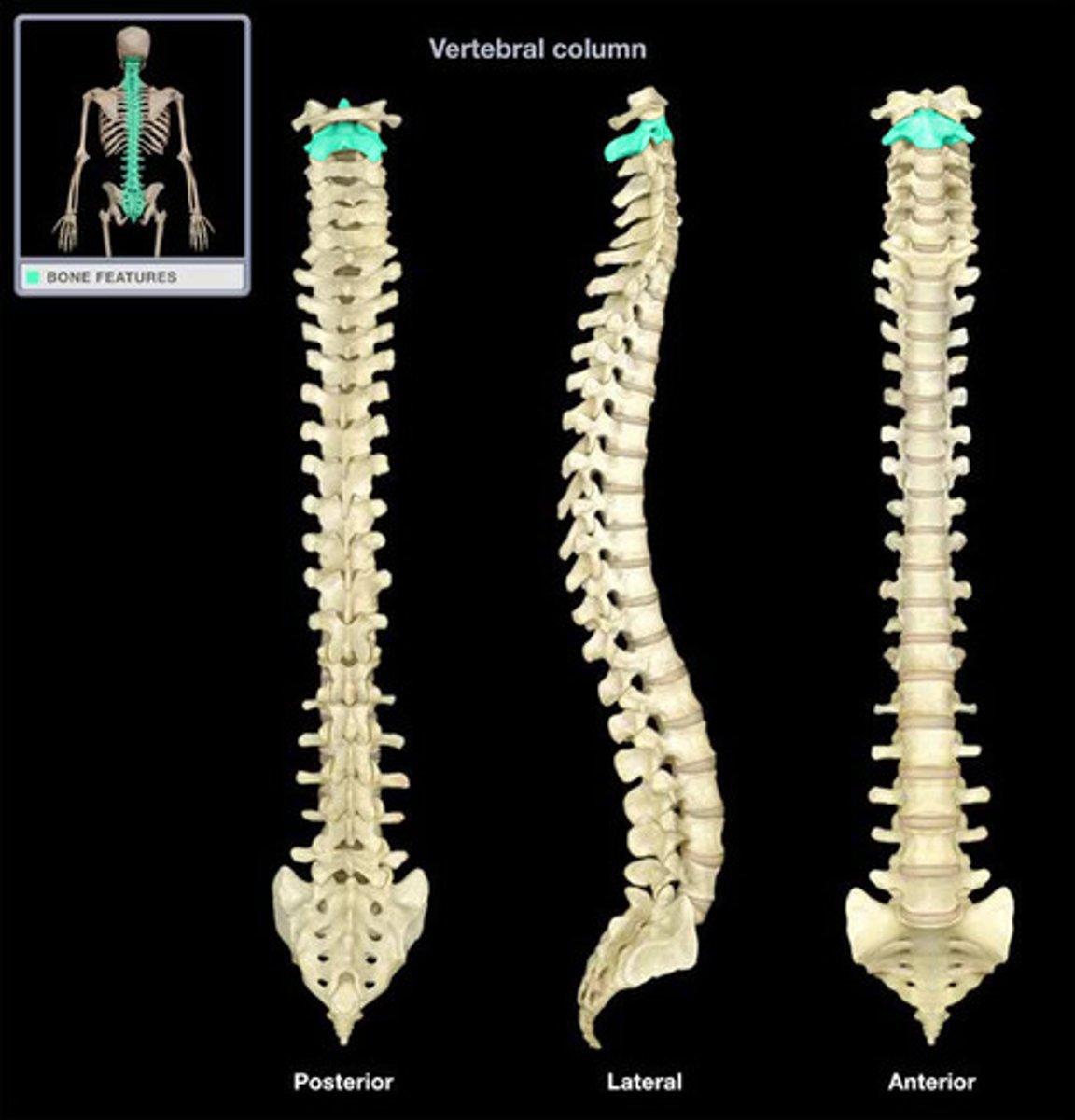
C2
C2 - Axis
second cervical vertebra
Atlanto occipital joint
Allows you to shake your head "yes"
-articulation between the atlas and the occipital bone
Atlanto axial joint
Allows you to shake your head "no"
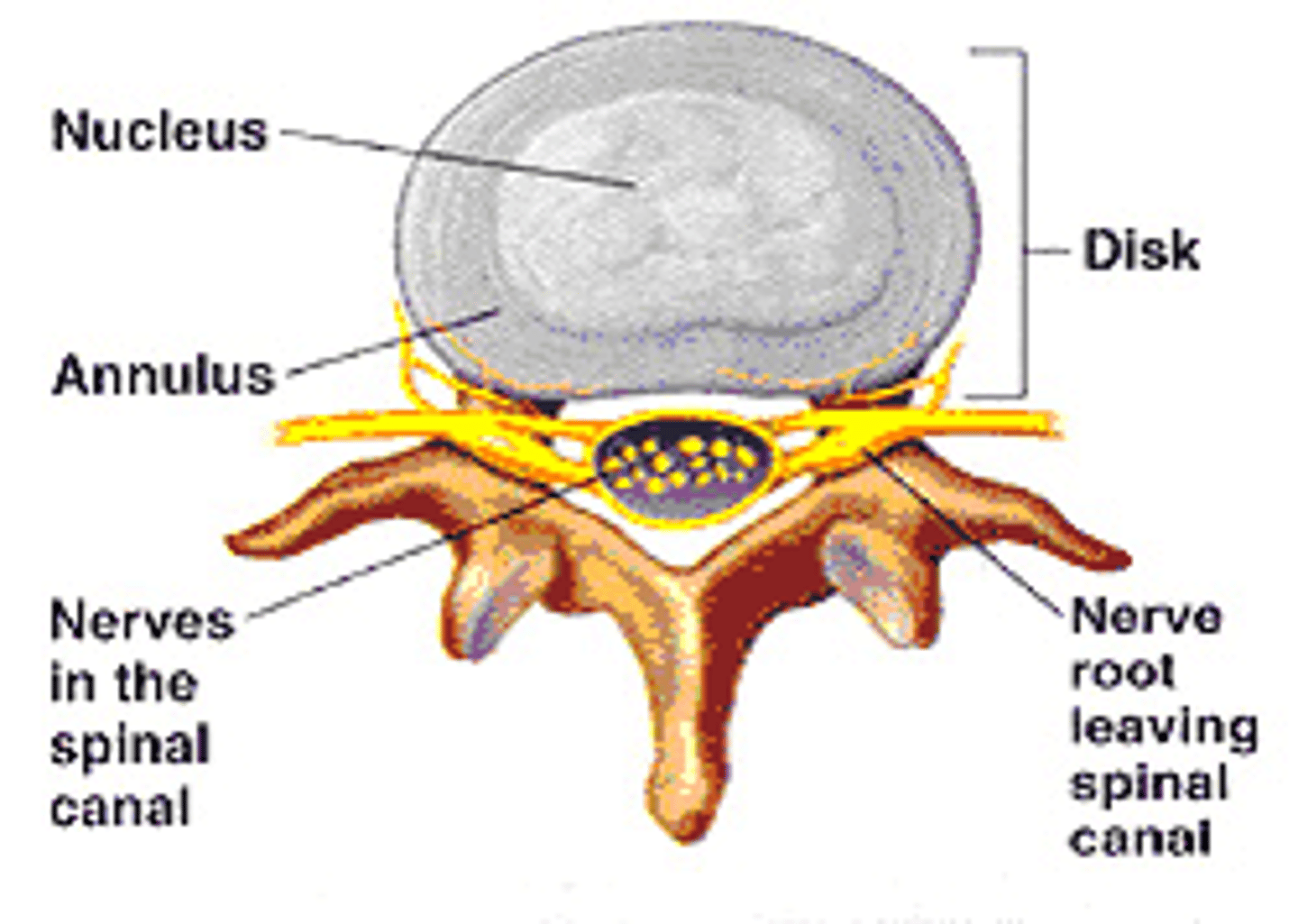
Disc in spine
Outside ring: Annulus Fibrosis
Inside (jelly like): Nucleus Pulpous
Head of rib
Attaches to body of vertebrae
Tubercle
Attaches to transverse process
Cervicle vertebrae
have transverse formania(holes)
Thoracic vertebrae
have articular facet for ribs
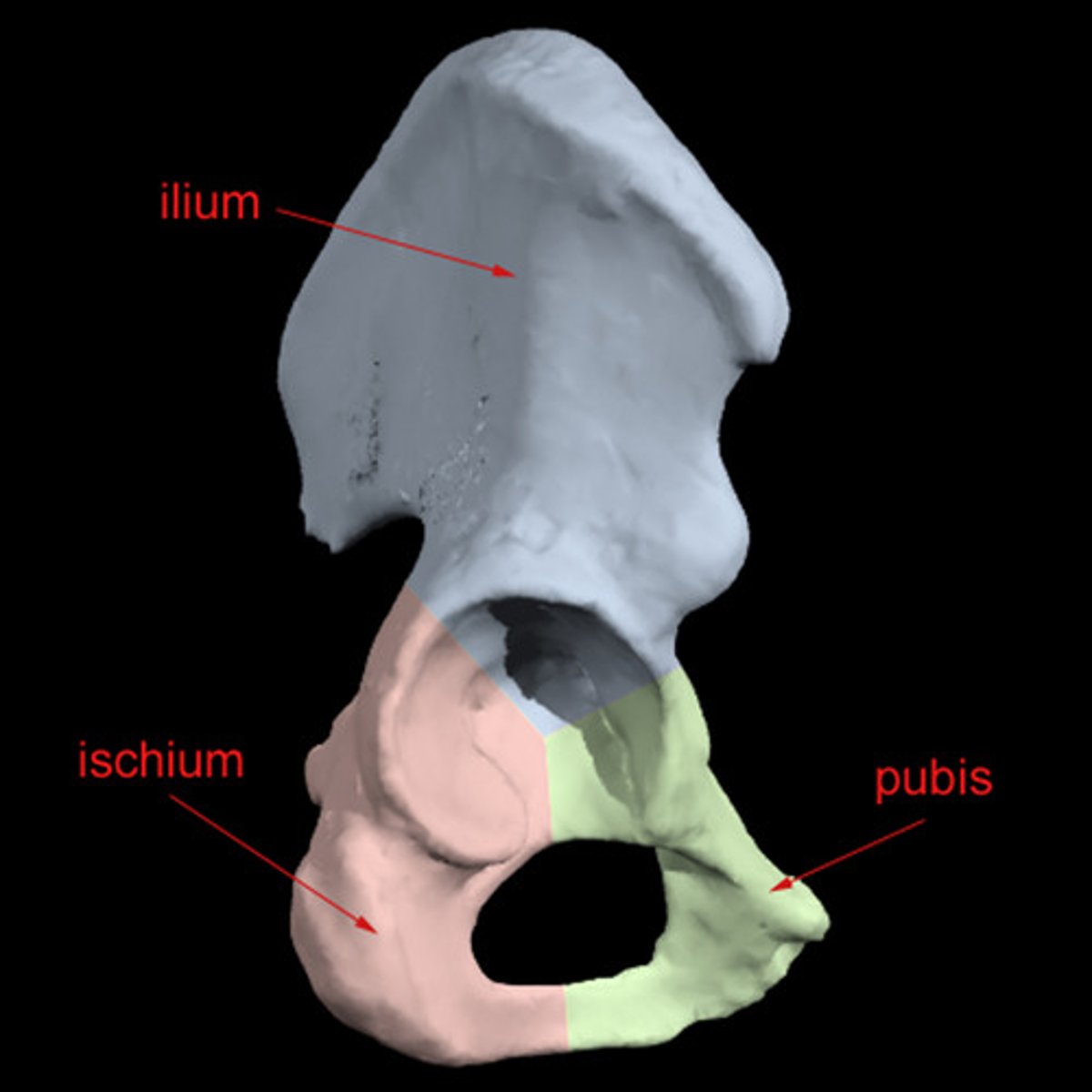
os coxae
Also known as Innomate bone
Made up of three bones:
1. Illium
2. Ischium
3. Pubis bones
hip bone
They unite and fuse at the acetabulum which is where the head of the femur inserts
Medial malleolus
Tibia + Talus
(Inside ankle knot)
Lateral malleolus
Fibula + Talus
(outside ankle knot)

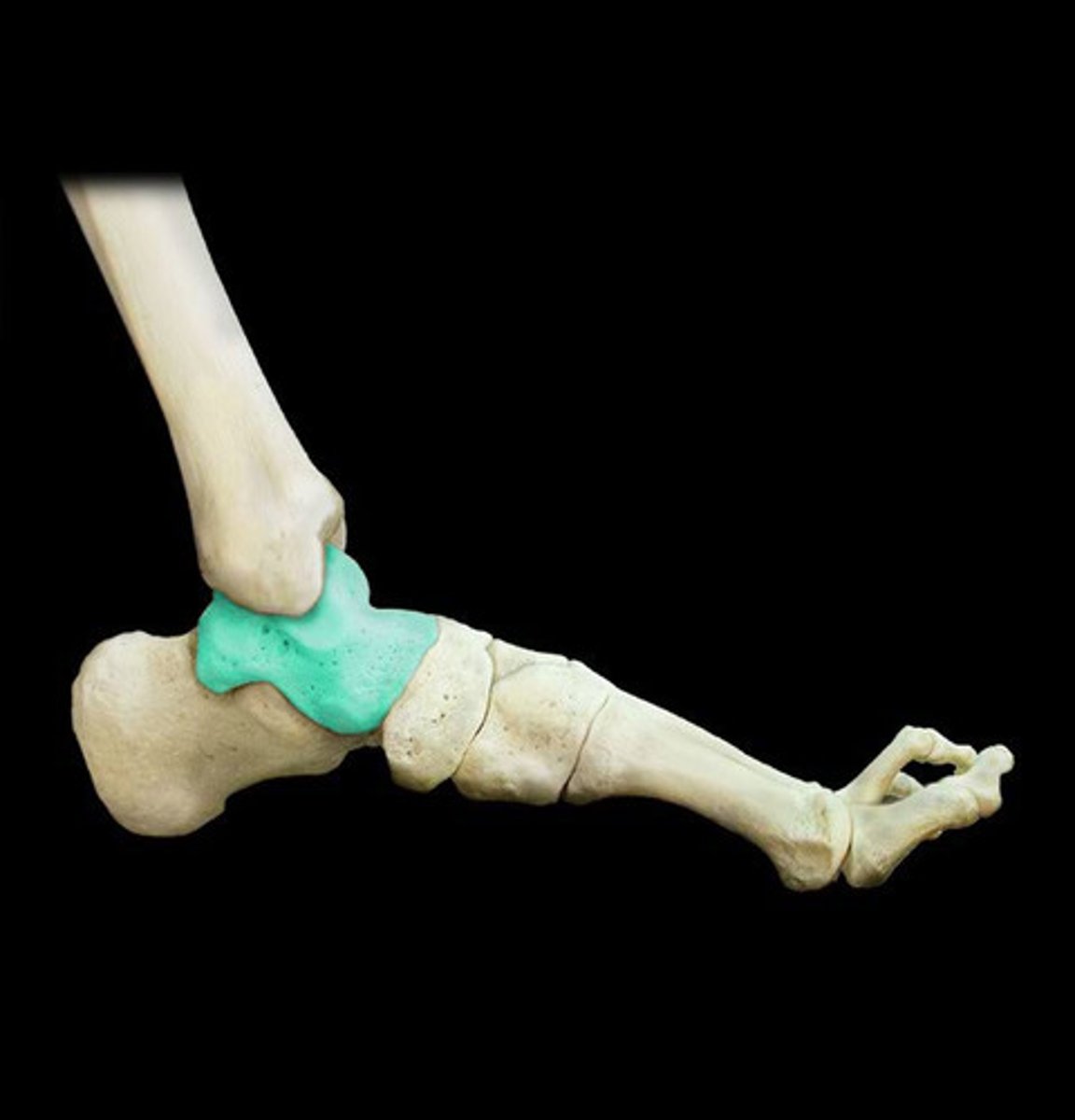
Heel bone
Calcaneus
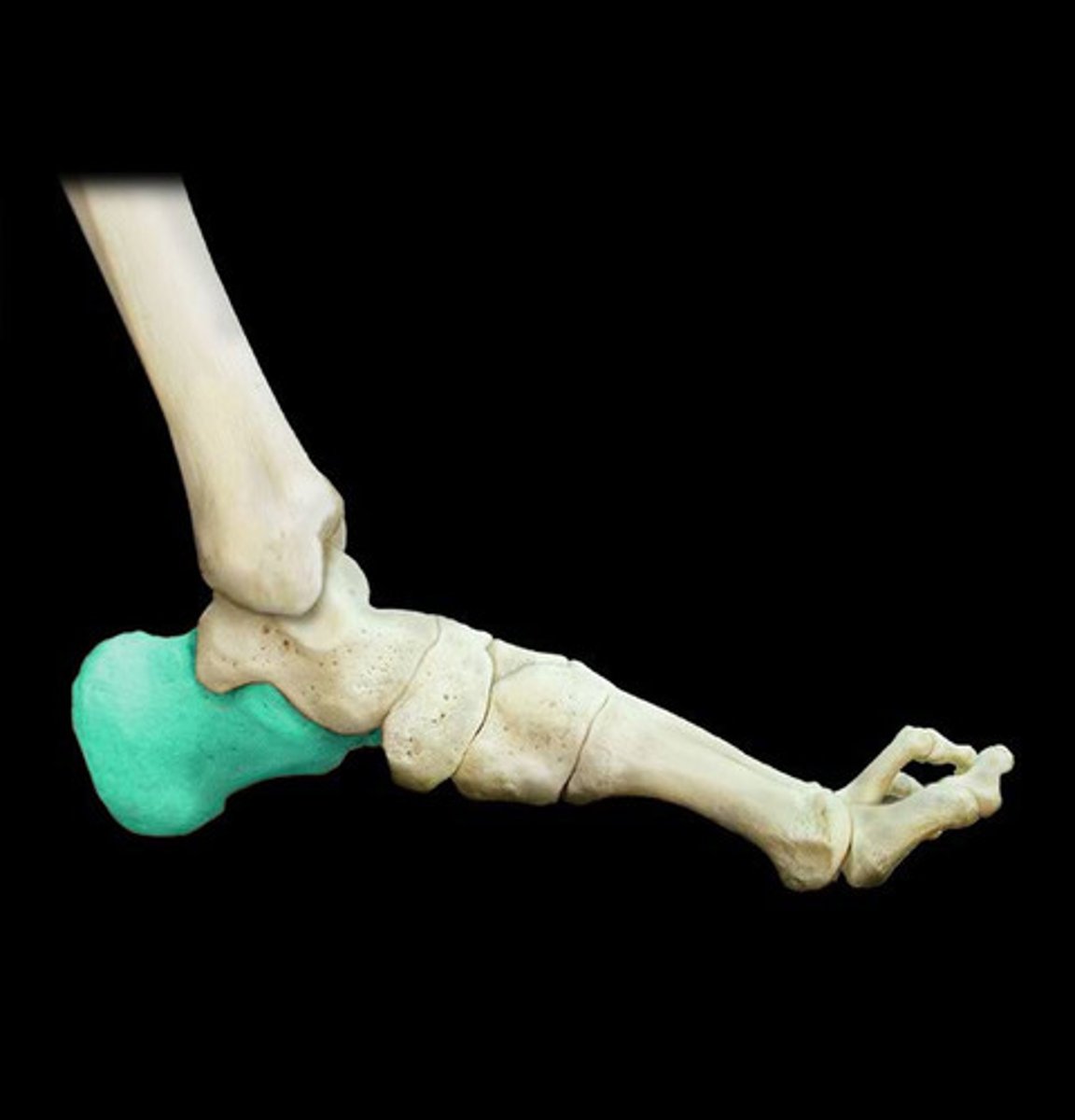
Talus
Makes up ankle joint
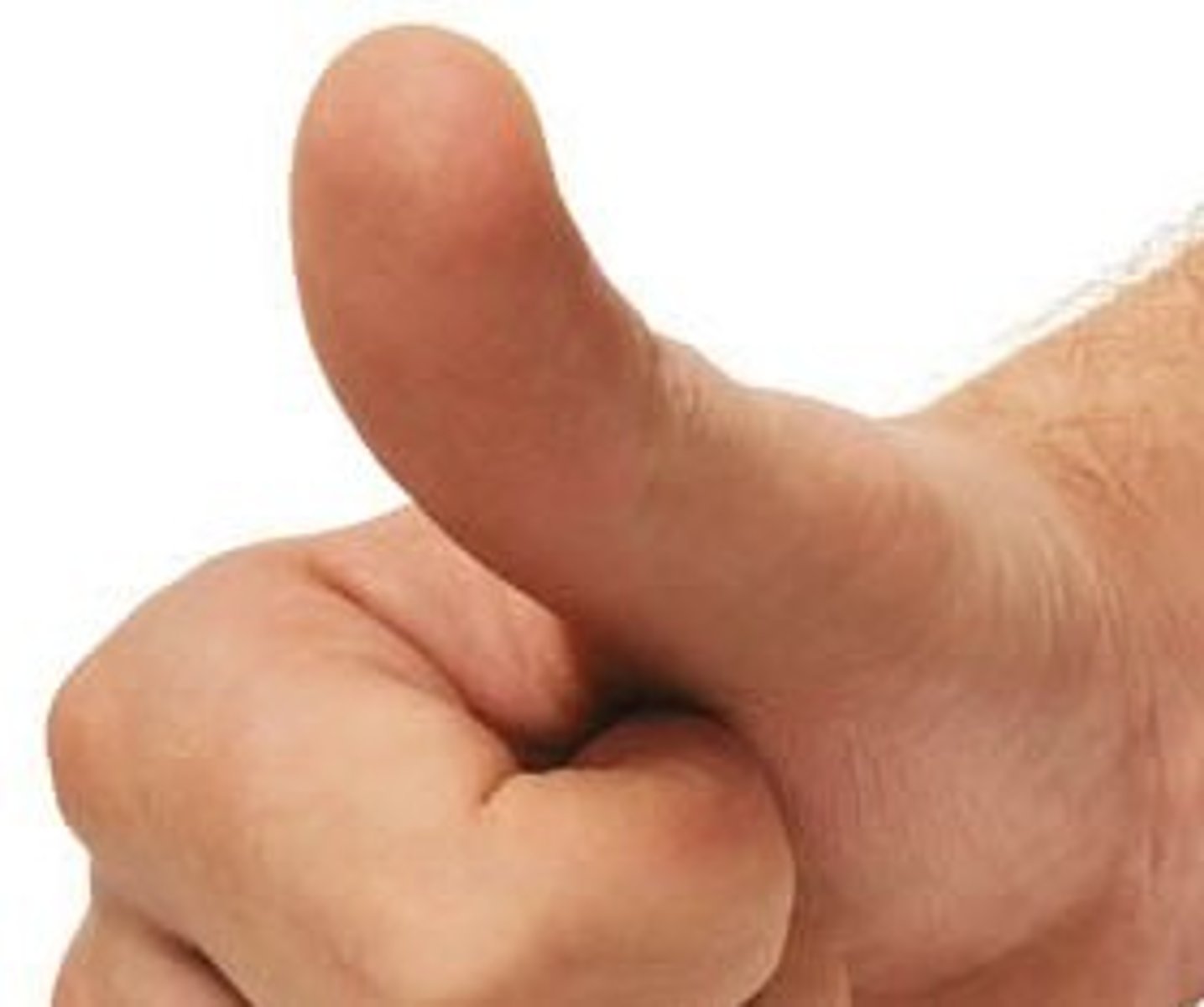
Pollux
Thumb

Hallux
Big toe
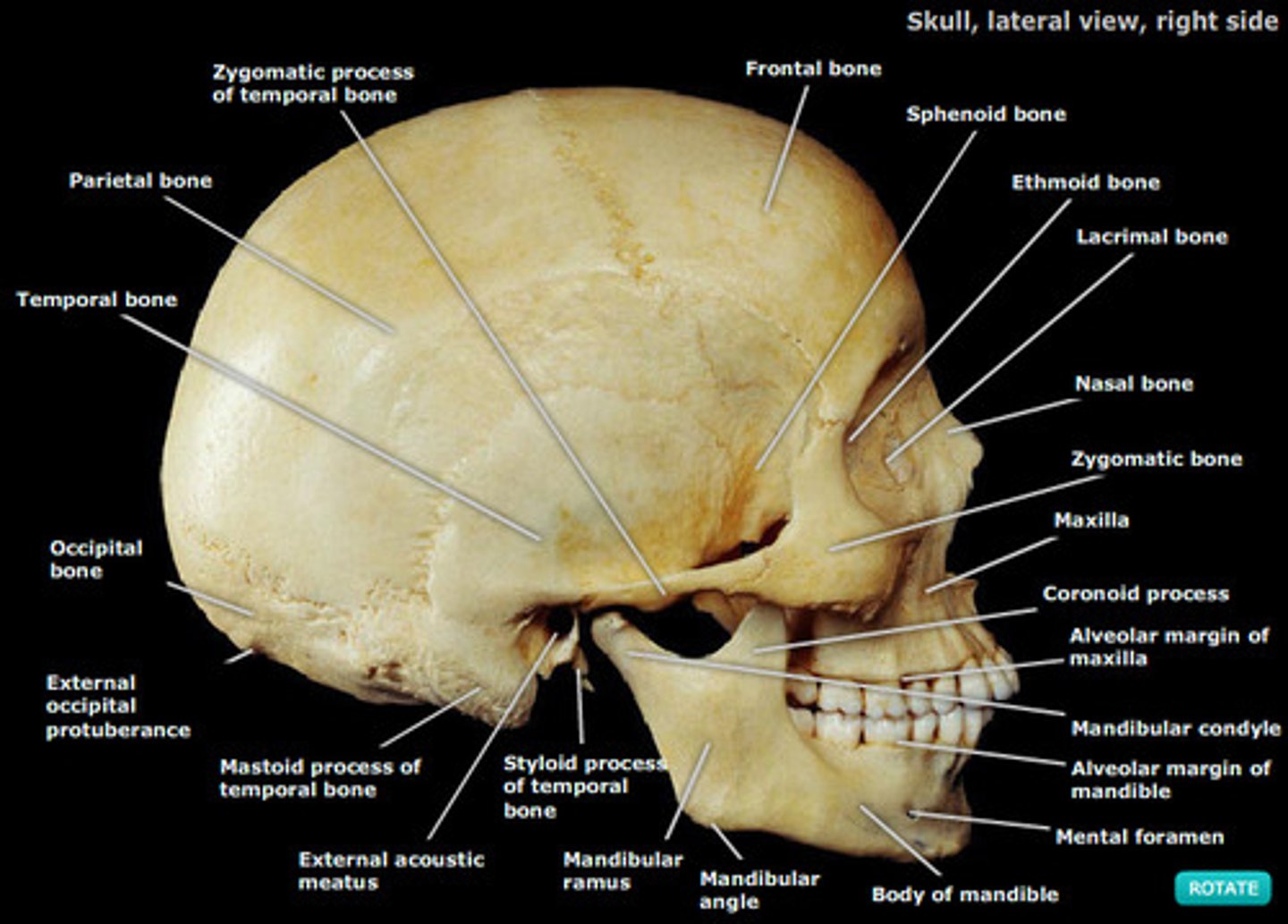
Lateral view of skull
From the side
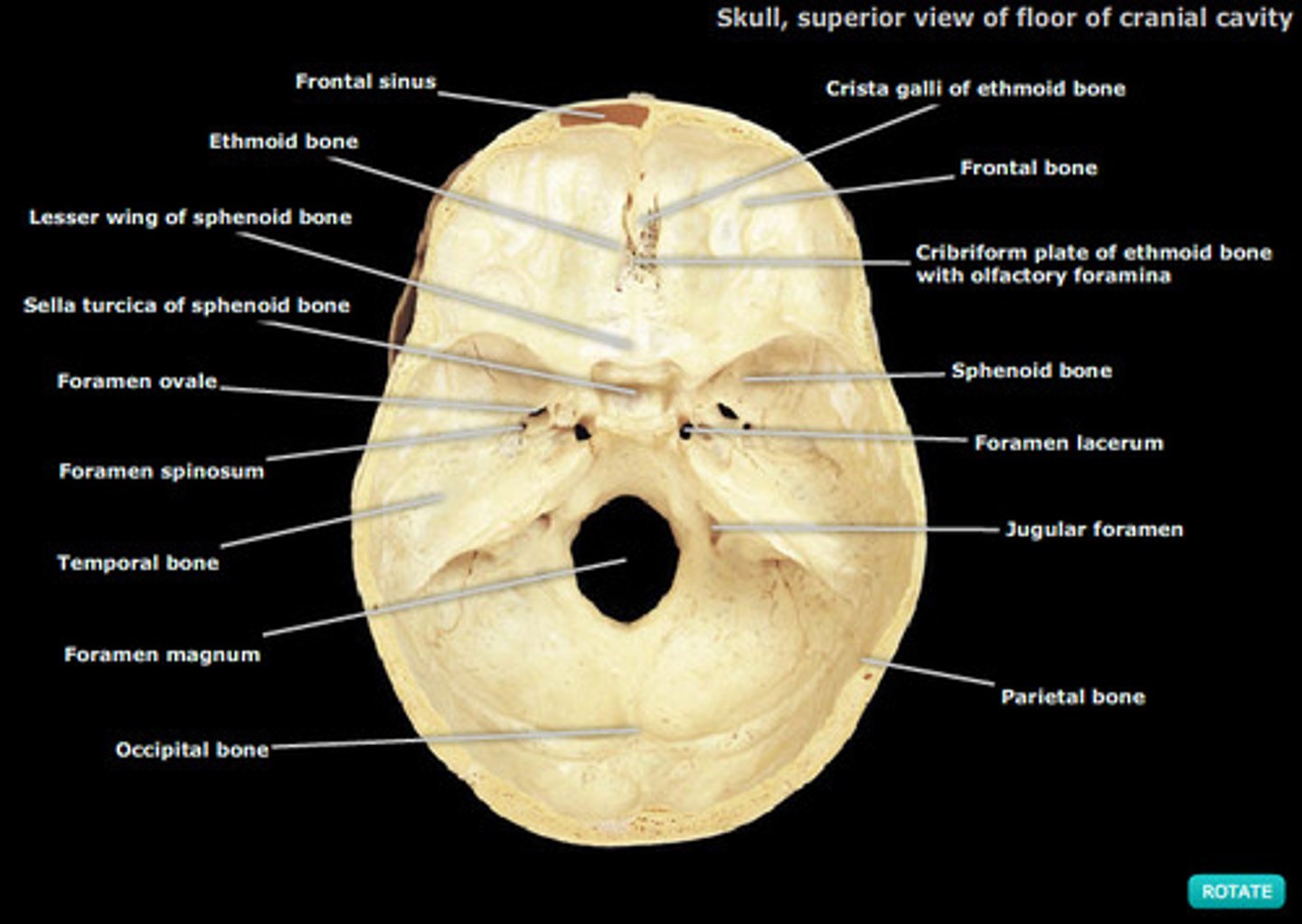
Superior view of cranial floor
On top, inside of skull
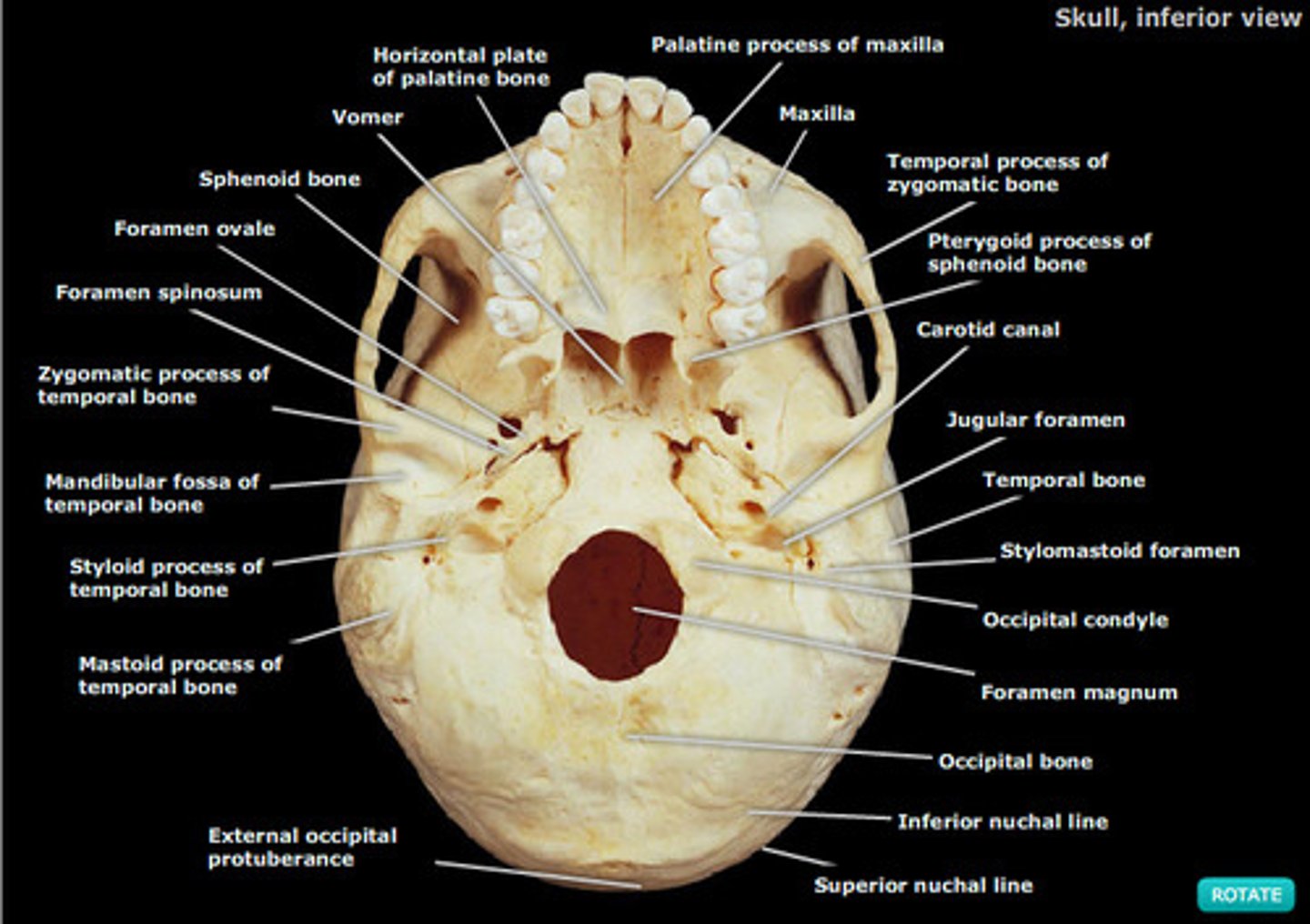
Inferior view of skull
Under the skull
Frontal
Forehead
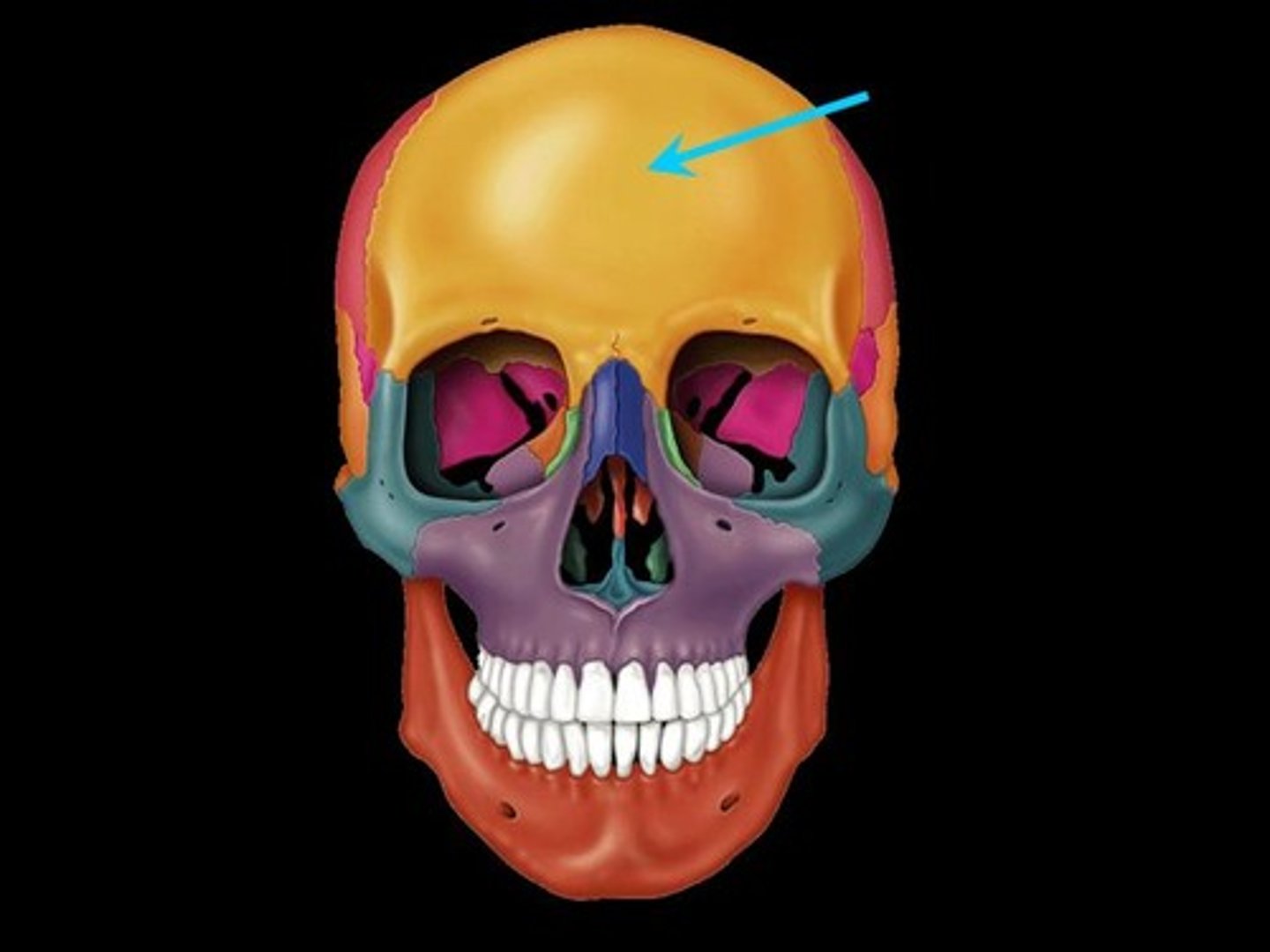
Parietal
right behind frontal (forehead)
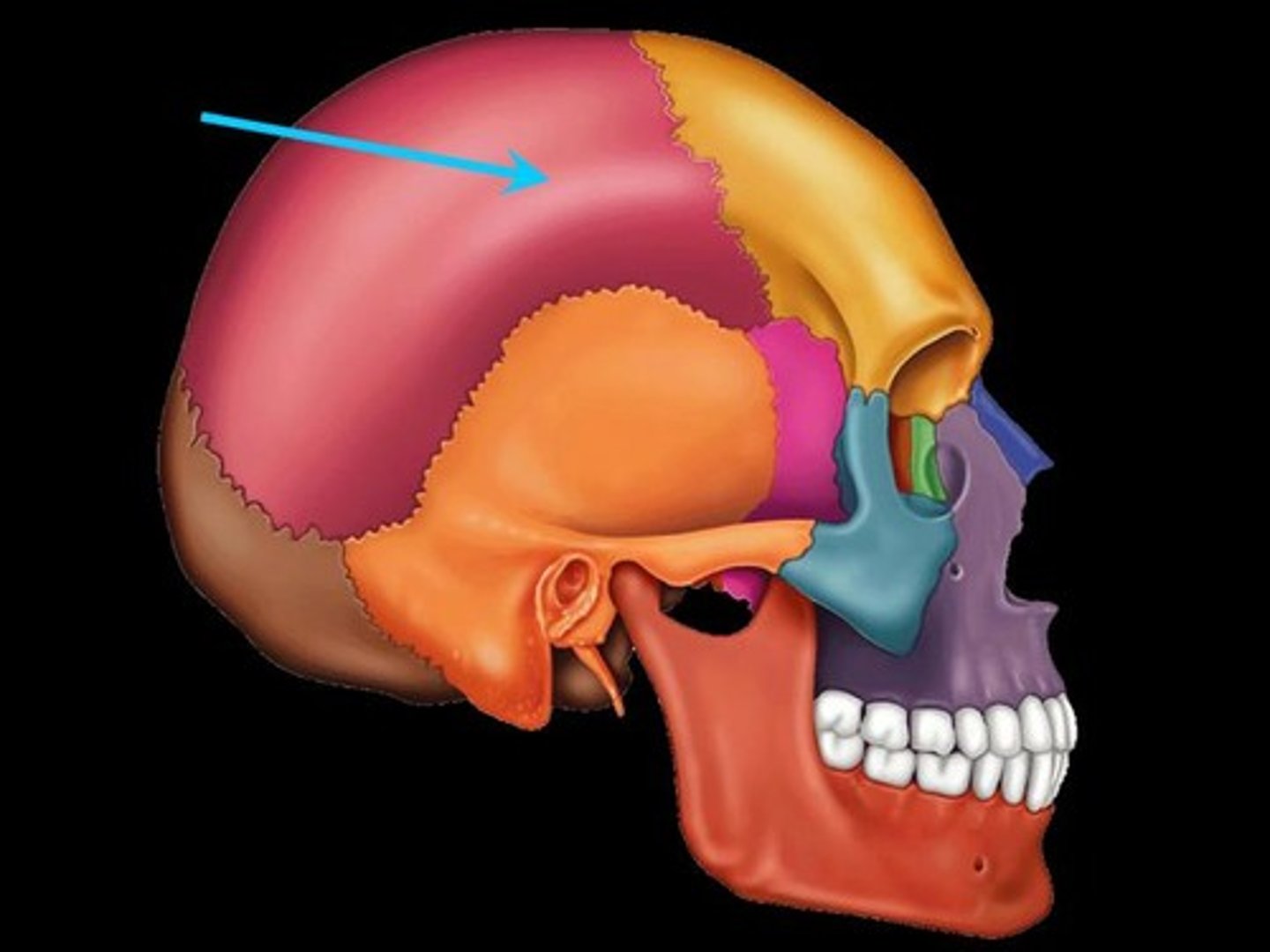
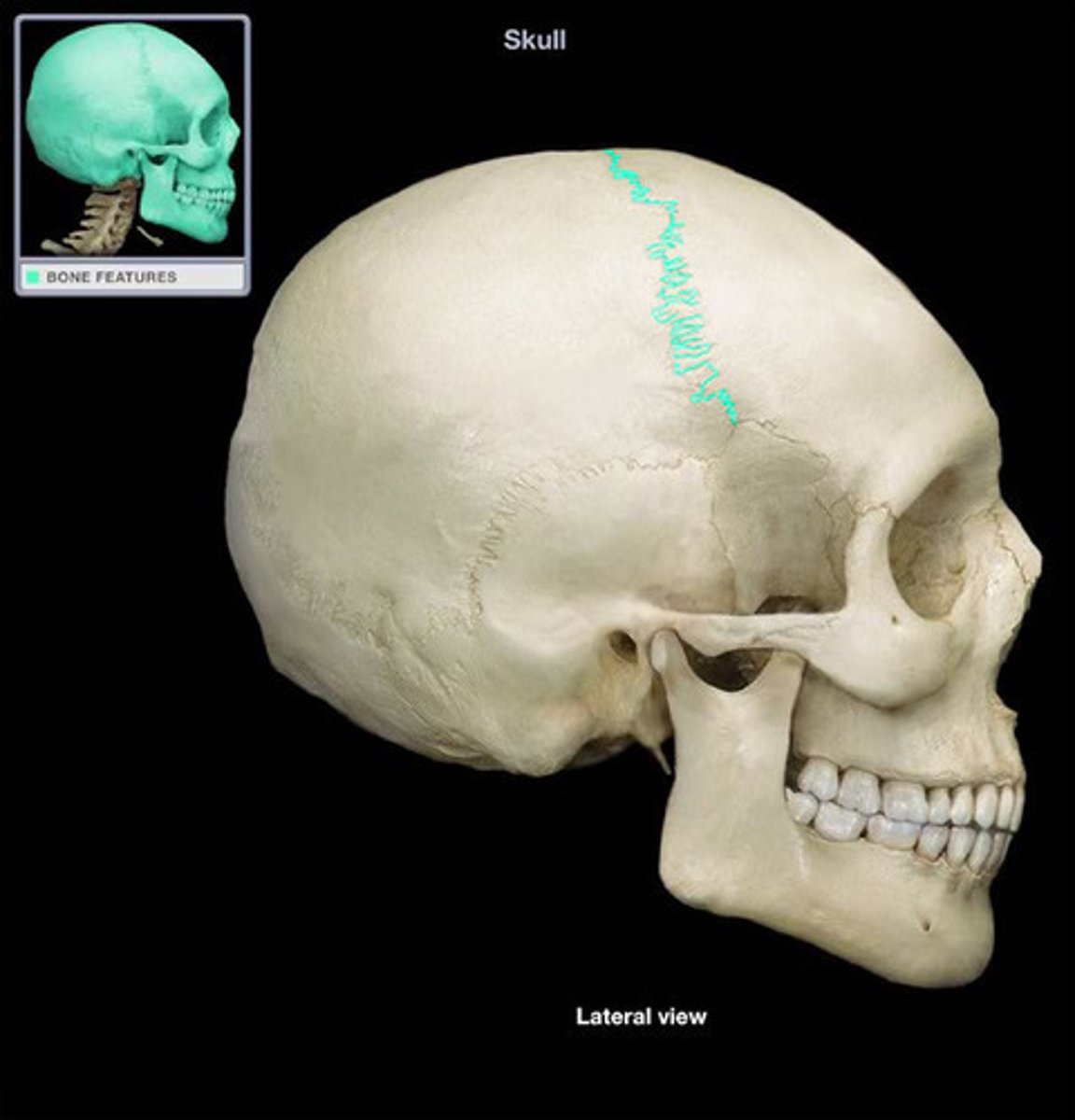
Cornal suture
Line in between frontal and parietal
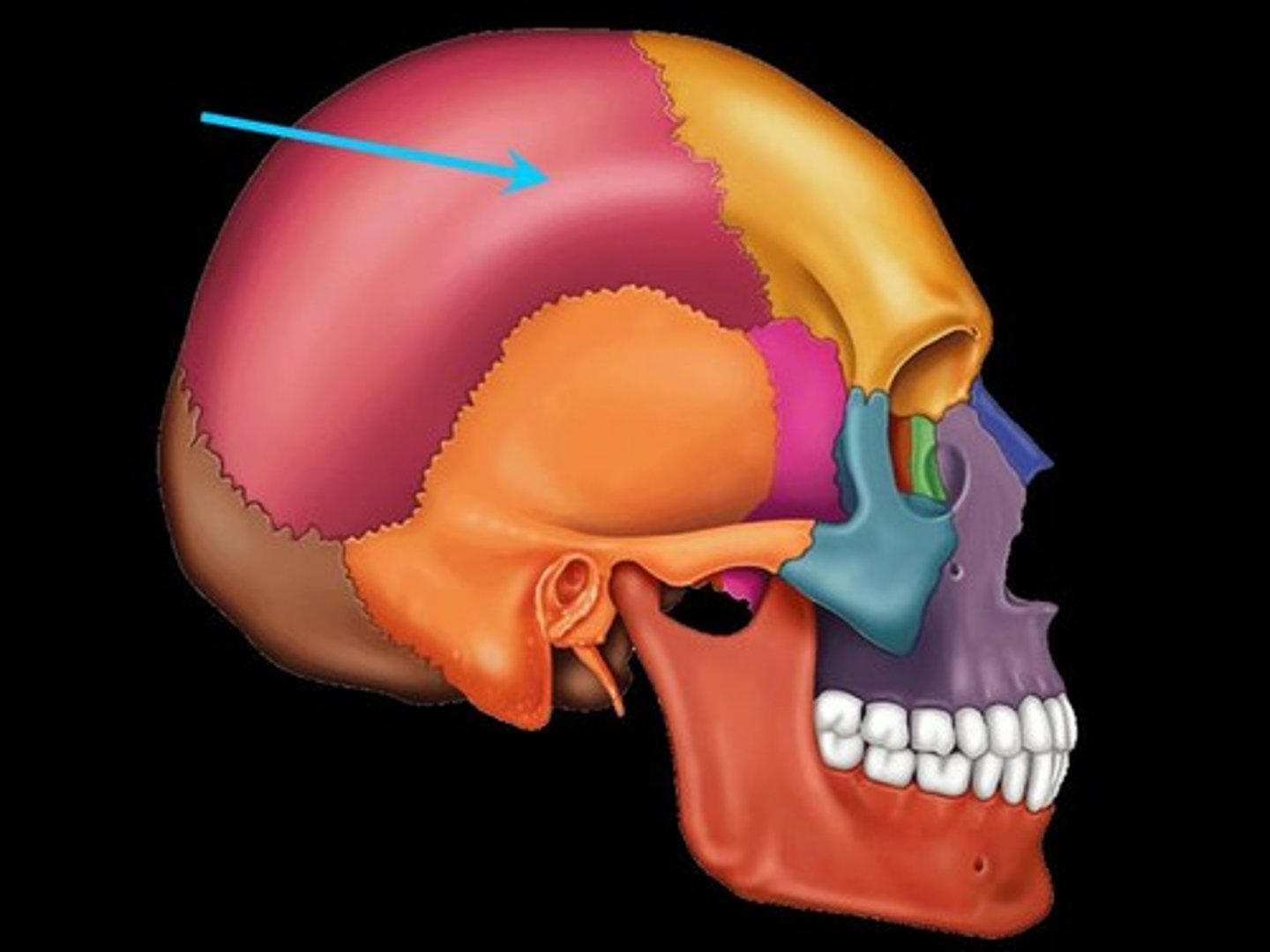
Parietal Bone(2)
Superior lateral bone of skull
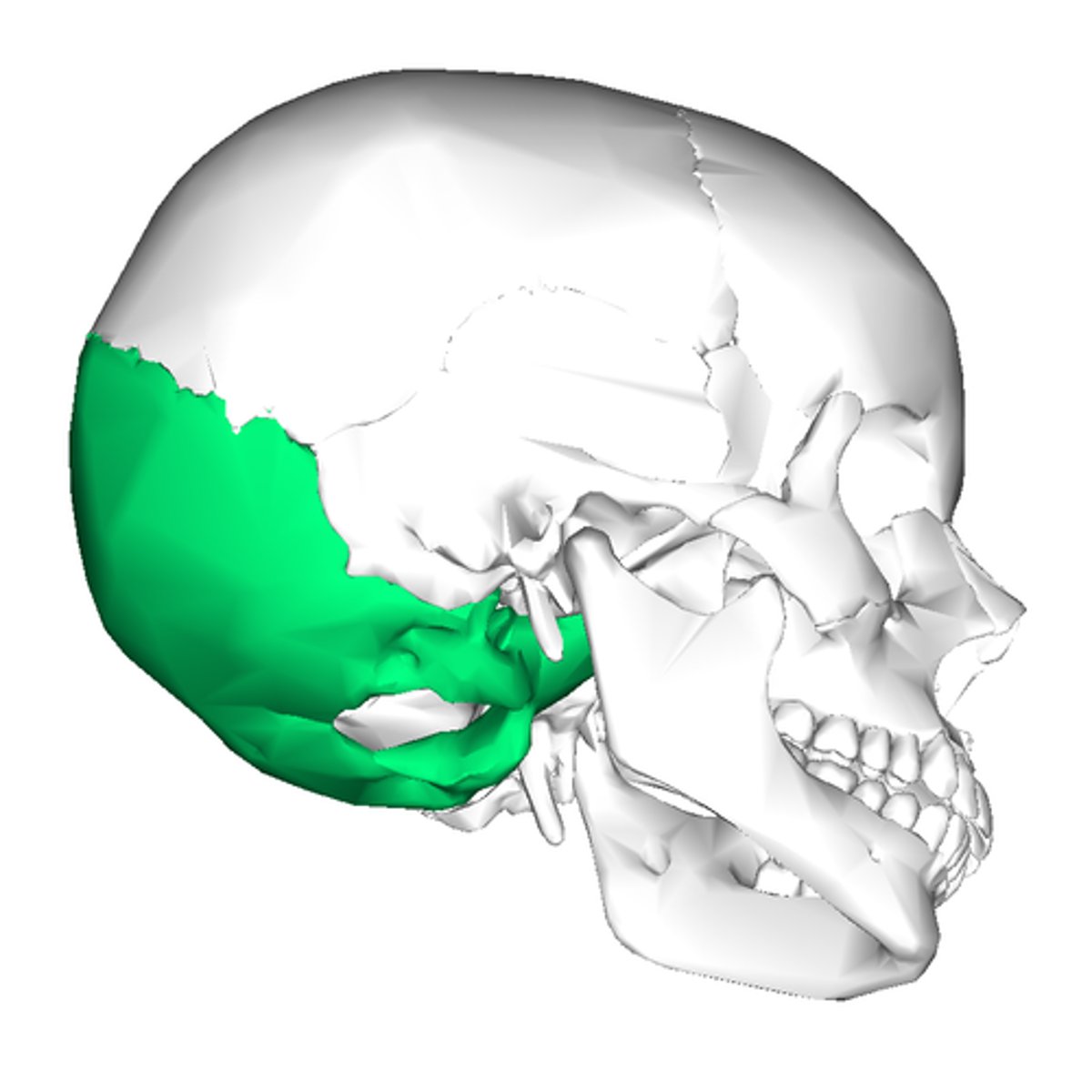
Occupital Bone
All the way to the back
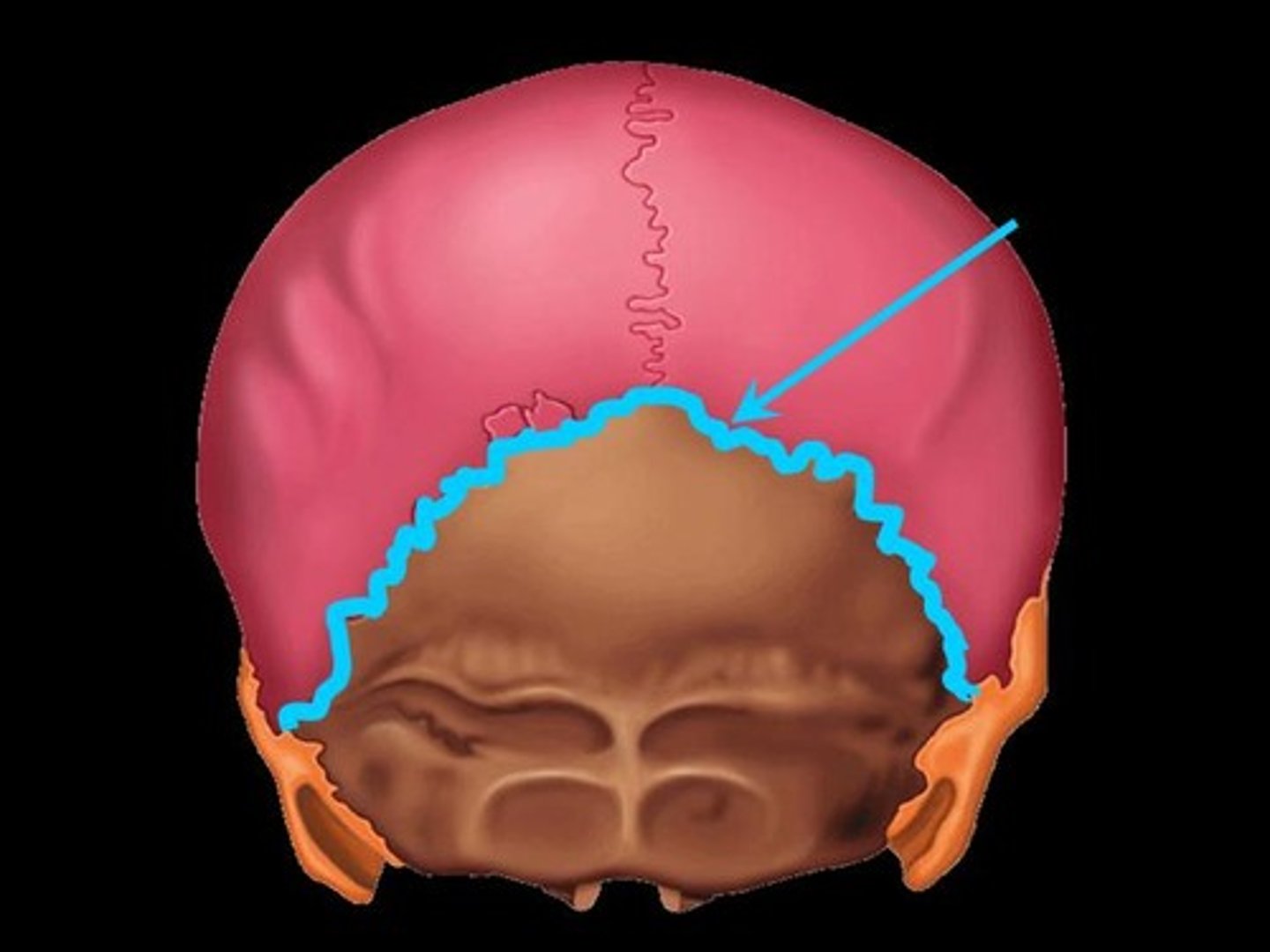
Lambdoid suture
between occipital and parietal
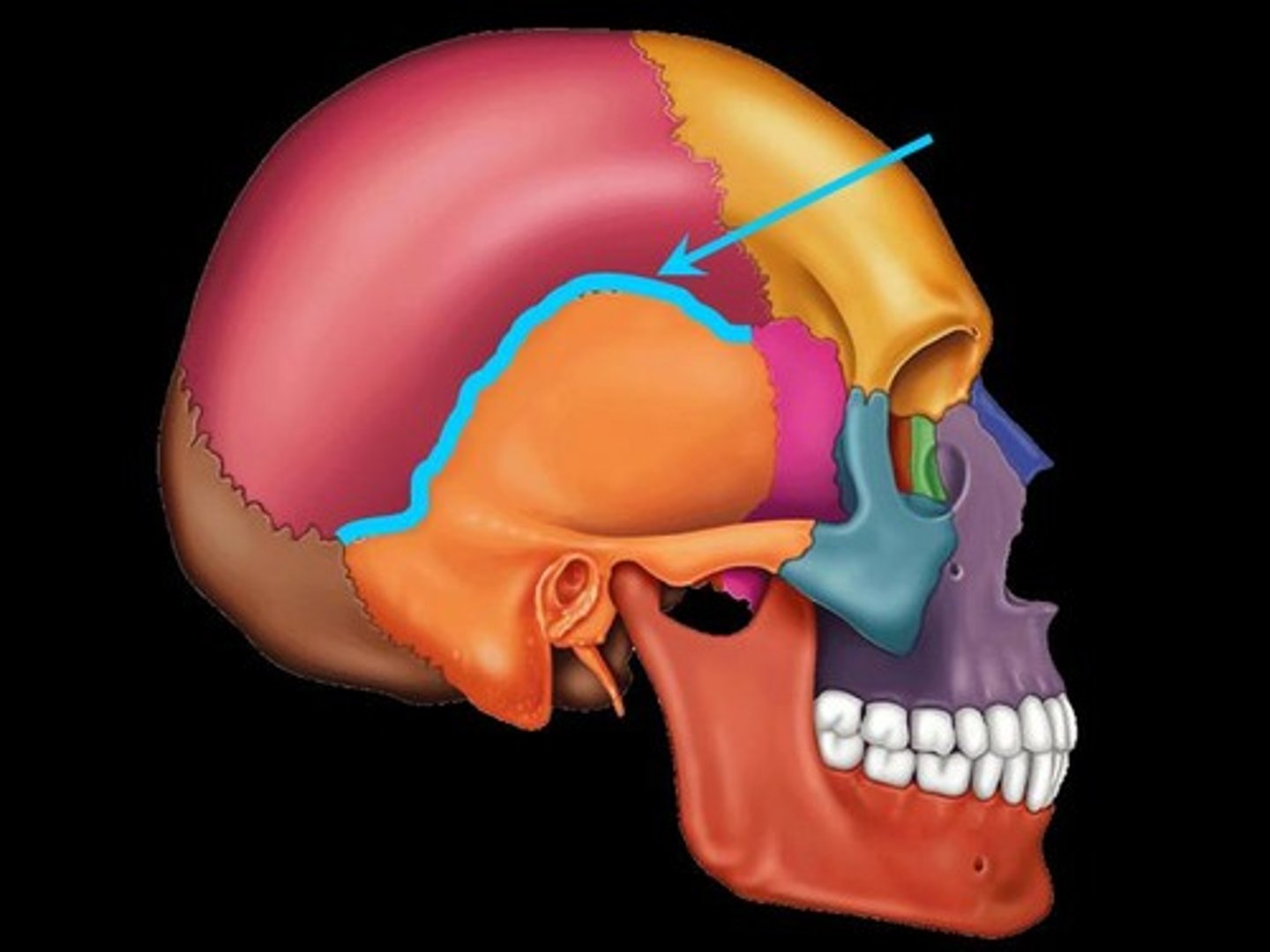
Squamous suture
between temporal and parietal
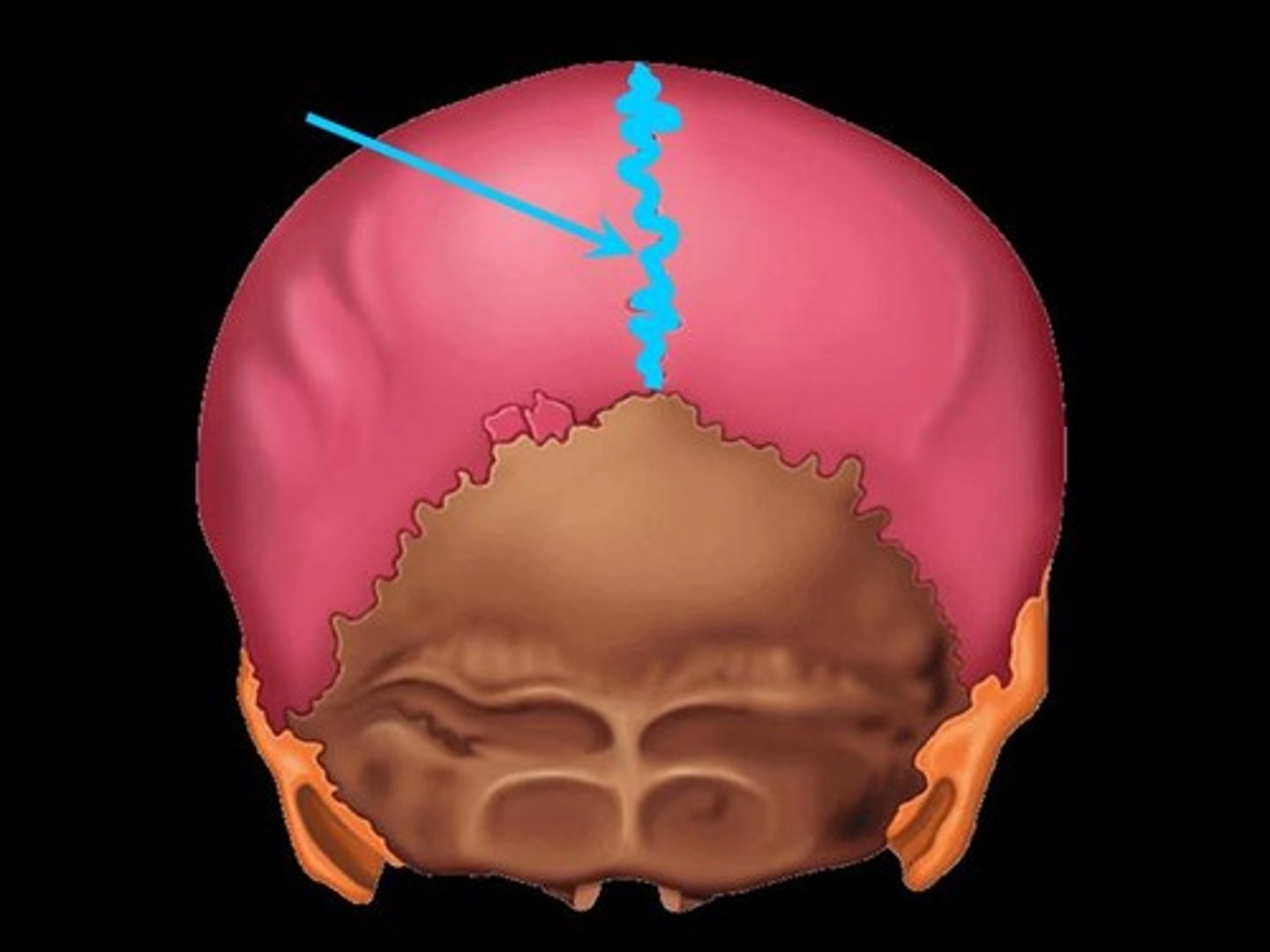
Sagittal suture
between the two parietal bones
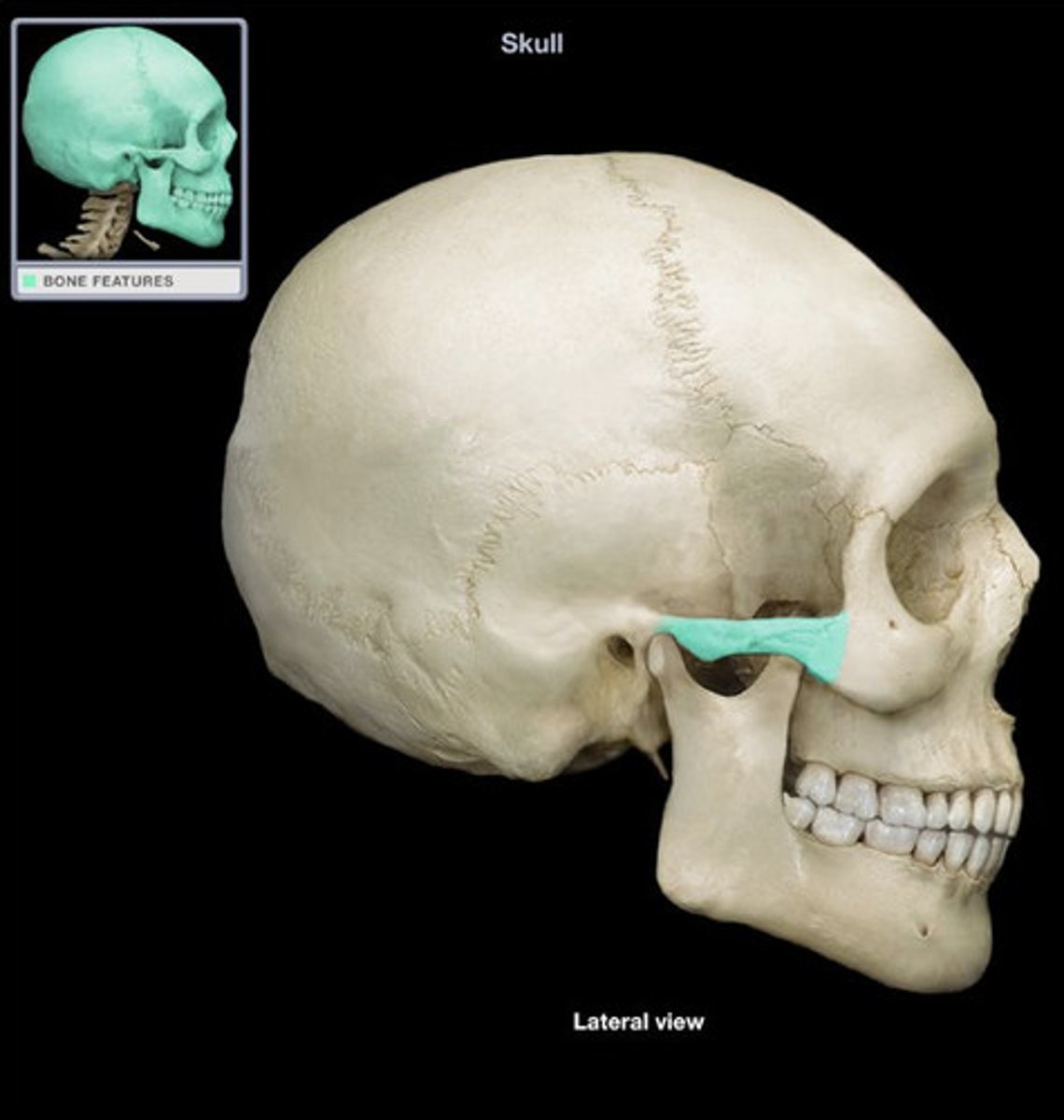
Zygomatic arch
Made up of zygomatic process of the temporal bone and temporal process of the zygomatic bone
Process
bone growing away from main bone
Faramin
Hole (a opening)
Primary curves
Born with these -thoracic and sacrum
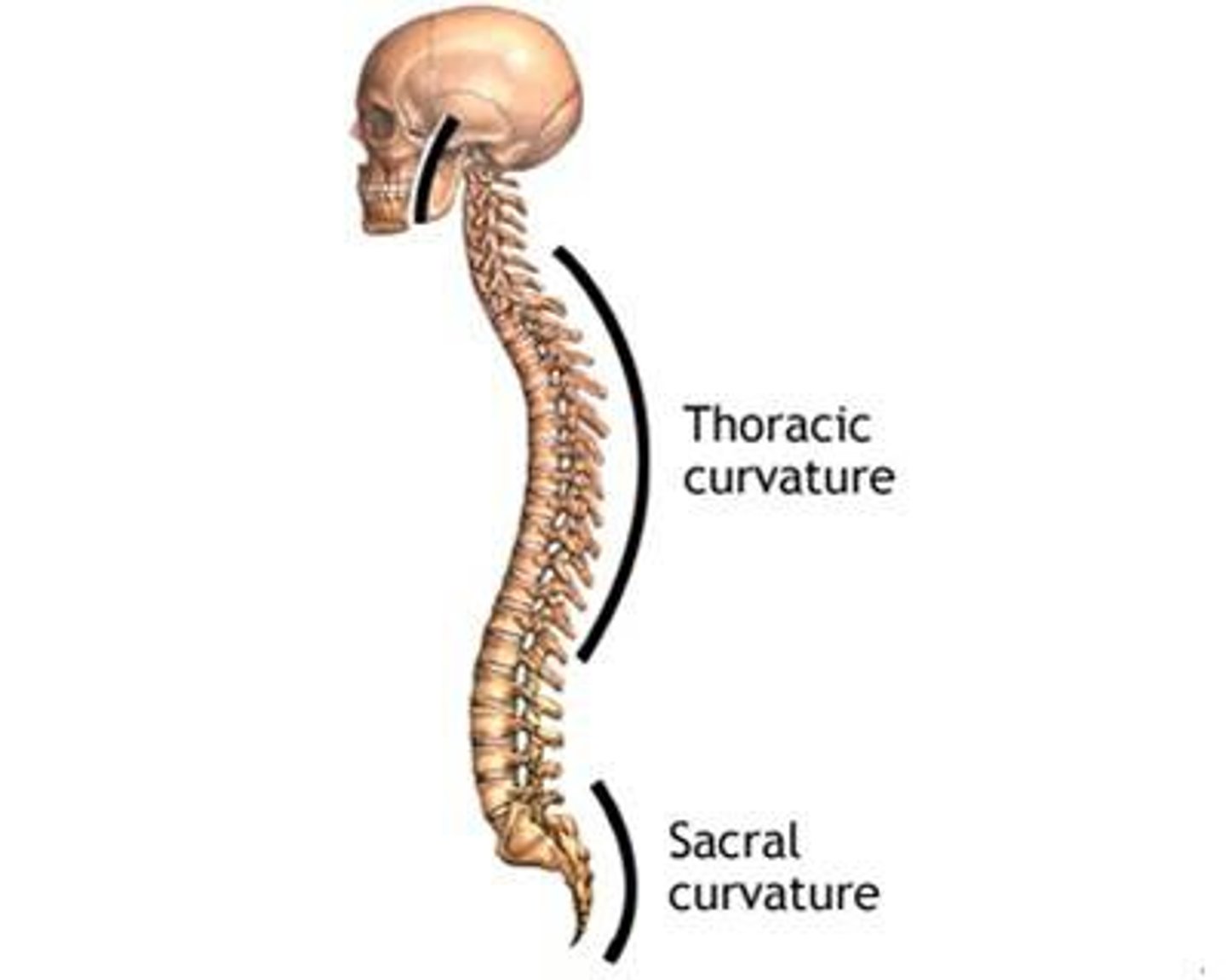
Secondary curves
Come later in life -cervicle and lumbar
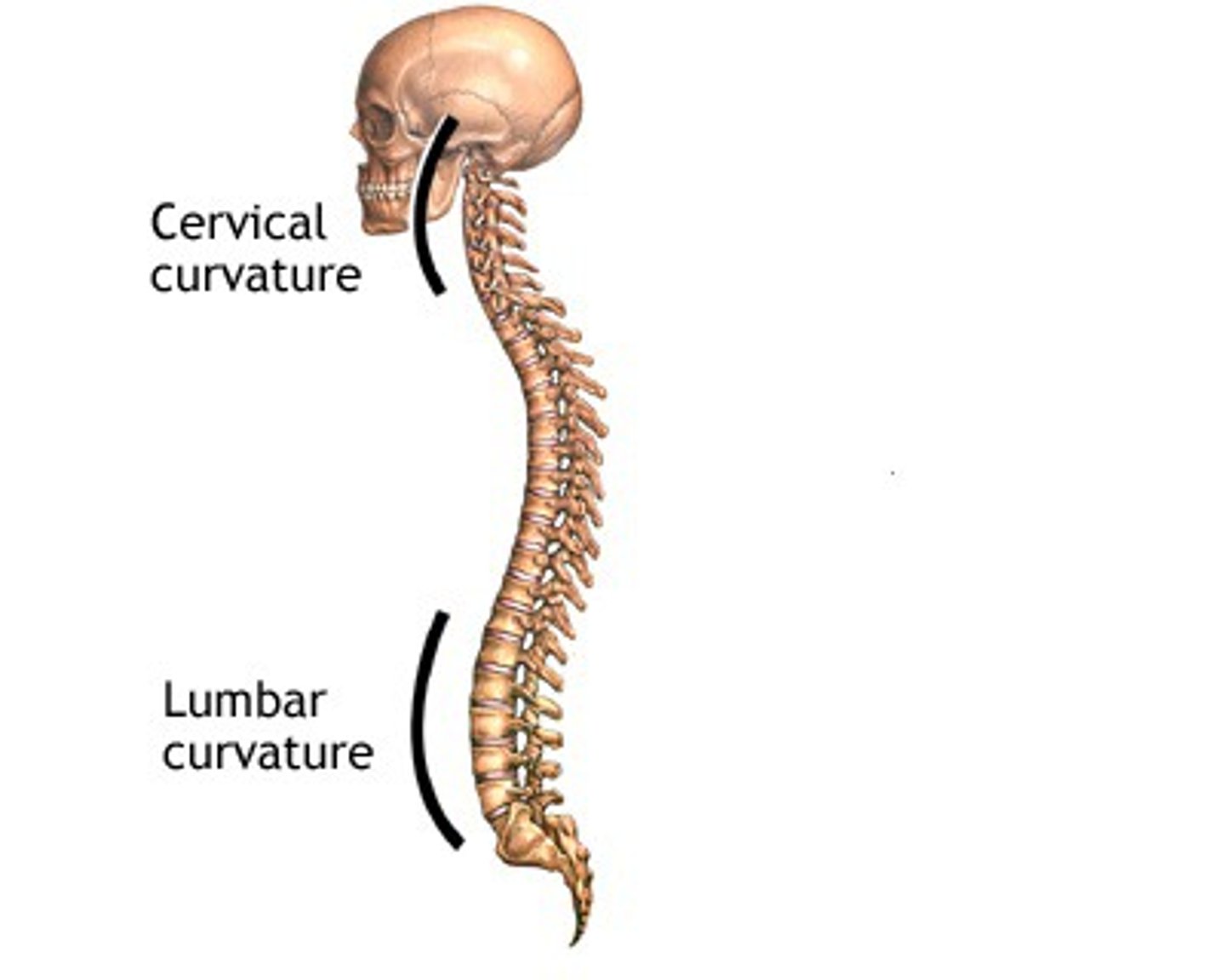
Joint
also known as "articulation", where two bones meet
Sutures
Skull -type of fibrous joint, synarthrosis (little to no movement)
*OUR SKULL DOESNT MOVE
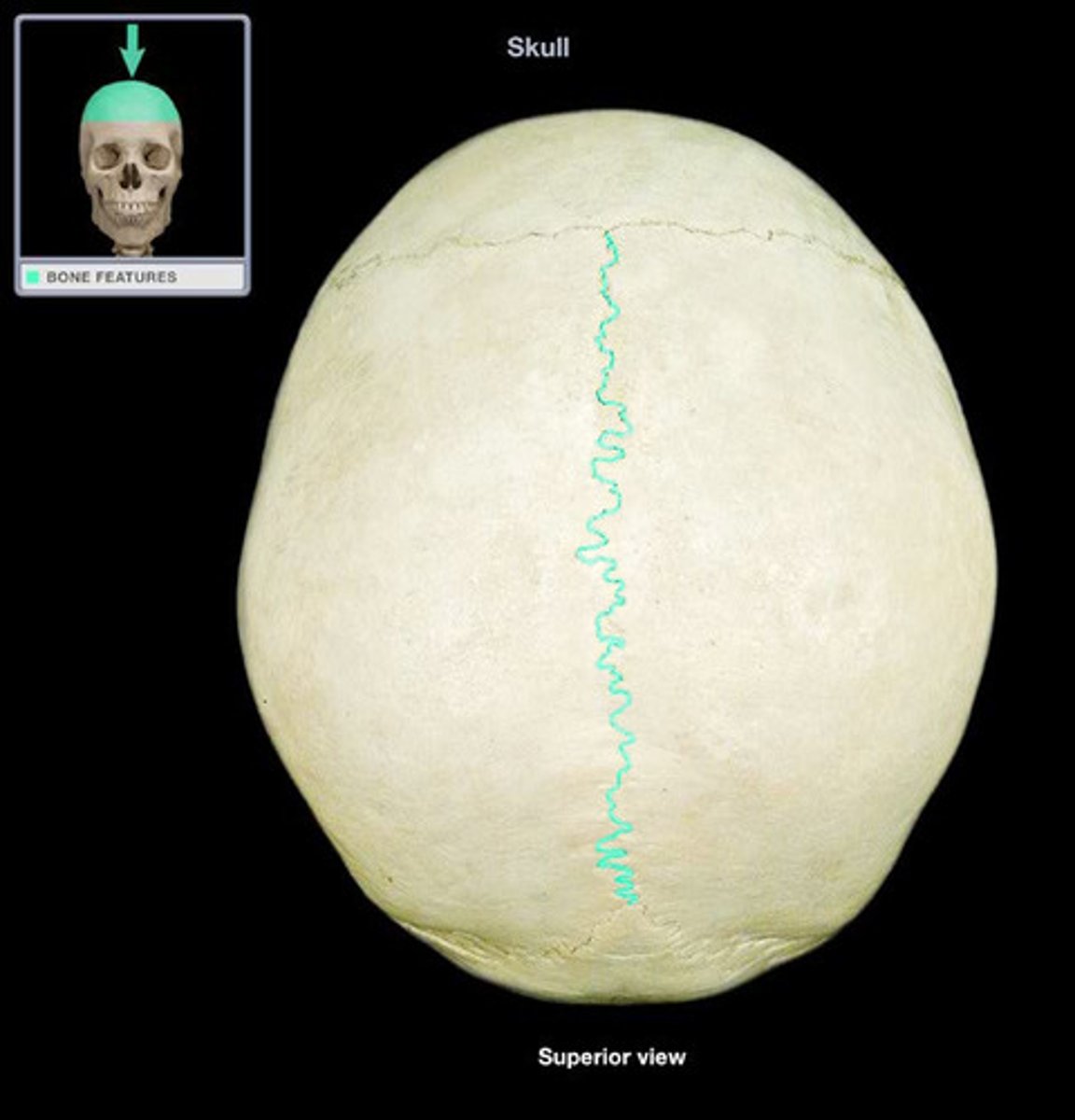
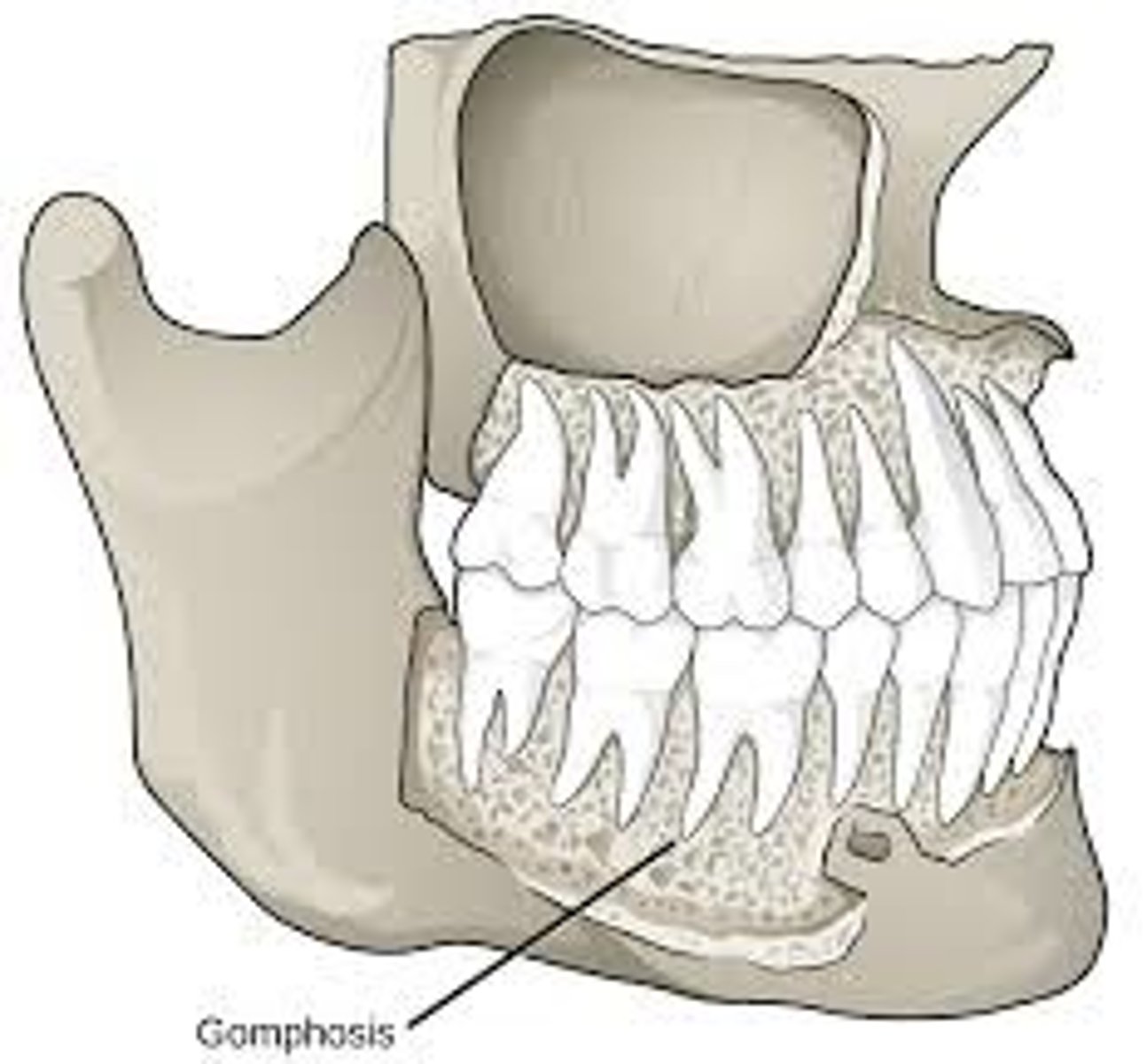
Gomphoses
teeth-type of fibrous joint, synarthrosis (little to no movement)
think of "gum"
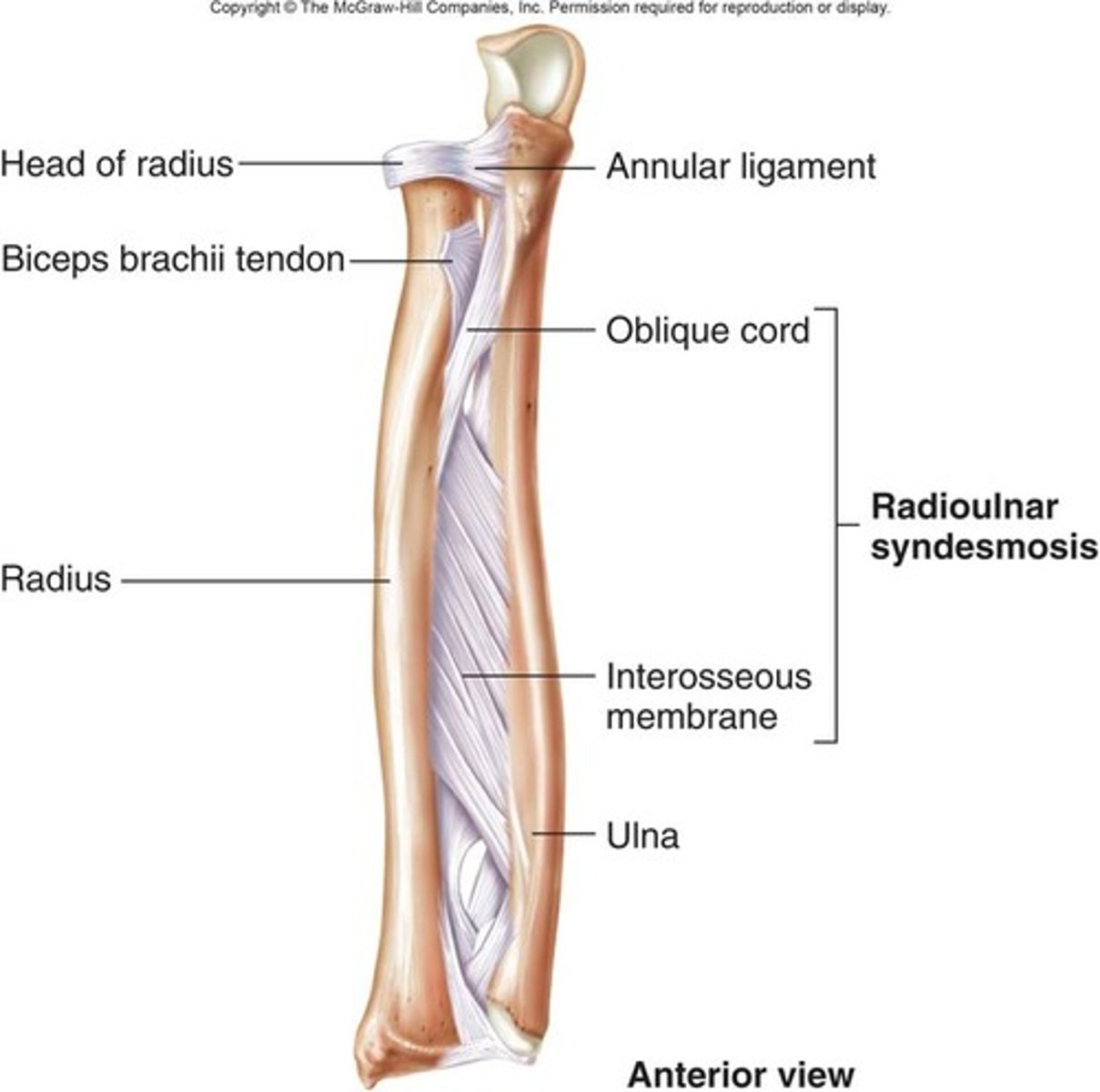
Syndesmoses
tibia/fibula and radius/ulna type of fibrous joint, synarthrosis (little to no movement)
Synchondroses
epiphyseal plate and 1st rib
joined by cartilage
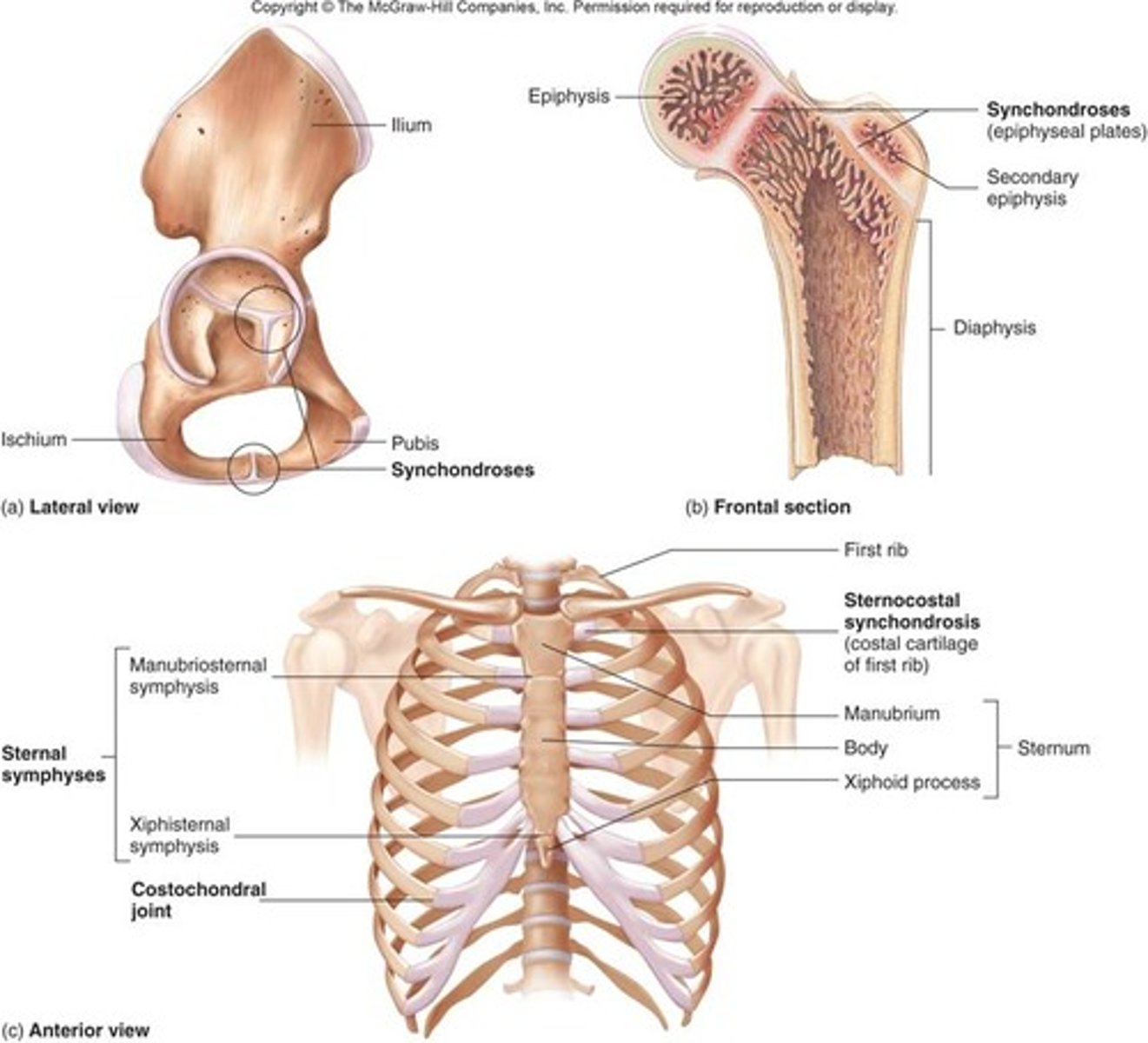
Symphyses
Intervertebrae disc and pubic bones
Meniscus
1. Absorb shock
2. Improves stability to the joint
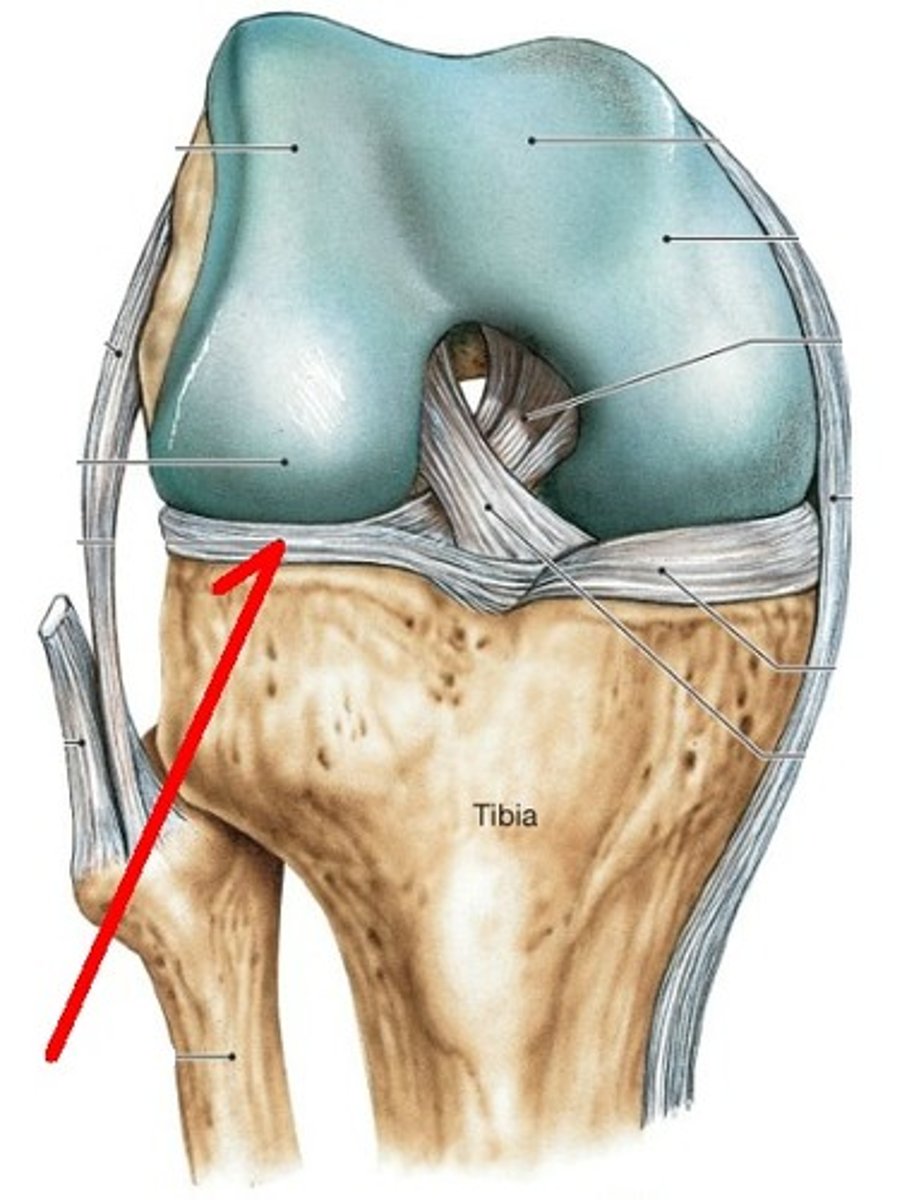
Tendon
Attaches muscle to bone
Ligament
Attaches two bones of a joint together
First class joint
Fulcrum in the middle (EFR) effort, fulcrum, resistance
*Atlanto occipital joint bc its in between the neck muscles and weight of the face
Second class
Resistance in the middle (FRE)
*Openining your jaw or wheel barrow
Third class joint
Effort in the middle
*Elbow joint
Range of motion determined by
1. structure
2. strength and tautness of ligaments and joint capsule
3. action of muscles
Classes of synovial joint
1. Ball and socket -shoulder and hip joint
2. Condylar joint -radio carpal and MCP (metacarpal phylageal)
3. Saddle joint- trapezoimetalcarpal (base of thumb)
4. Palm(gliding)-carpal and tarsal
5. Hing joint-elbow and knee
6. Pivot joint-atlantoaxial joint (move side to side like saying "no"
Ranges of motion
1. Abduction- away from midline of body (kid being abducted-taken AWAY from parents)
2. Aduction- closer to mid-line of body (adding it)
Pronation
palm down or posterior
*"P"
Supination
palms UP
*handing someone a bowl of soup
Supine
Lying face up
*SOUP
Prone
lying face down (on stomach)
Dorsiflexion
toes towards shin
Plantar flexion
toes away from shin
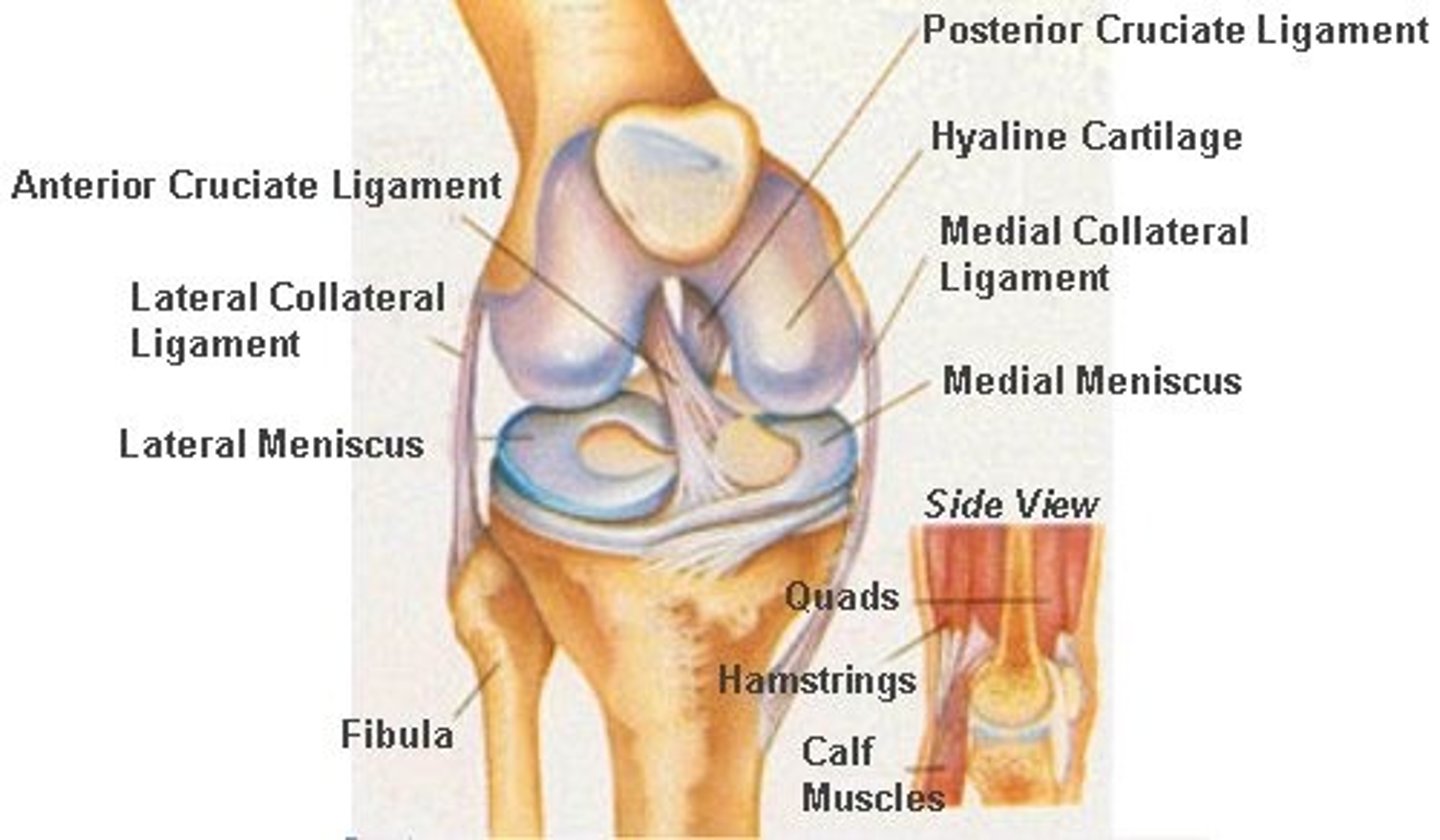
Knee joint
1. Lateral collateral ligament: femur to fibula
2. Medial collateral ligament: femur to tibia, also attached to medial meniscus
3. ACL (Anterior cruciate ligament)
4. PCL (Posterior cruciate ligament)
Functions of muscles
movement, stability, communication, control body openings heat productions and glycemic control
Aponeurosis
sheet like tendon seen in the palmaris longus
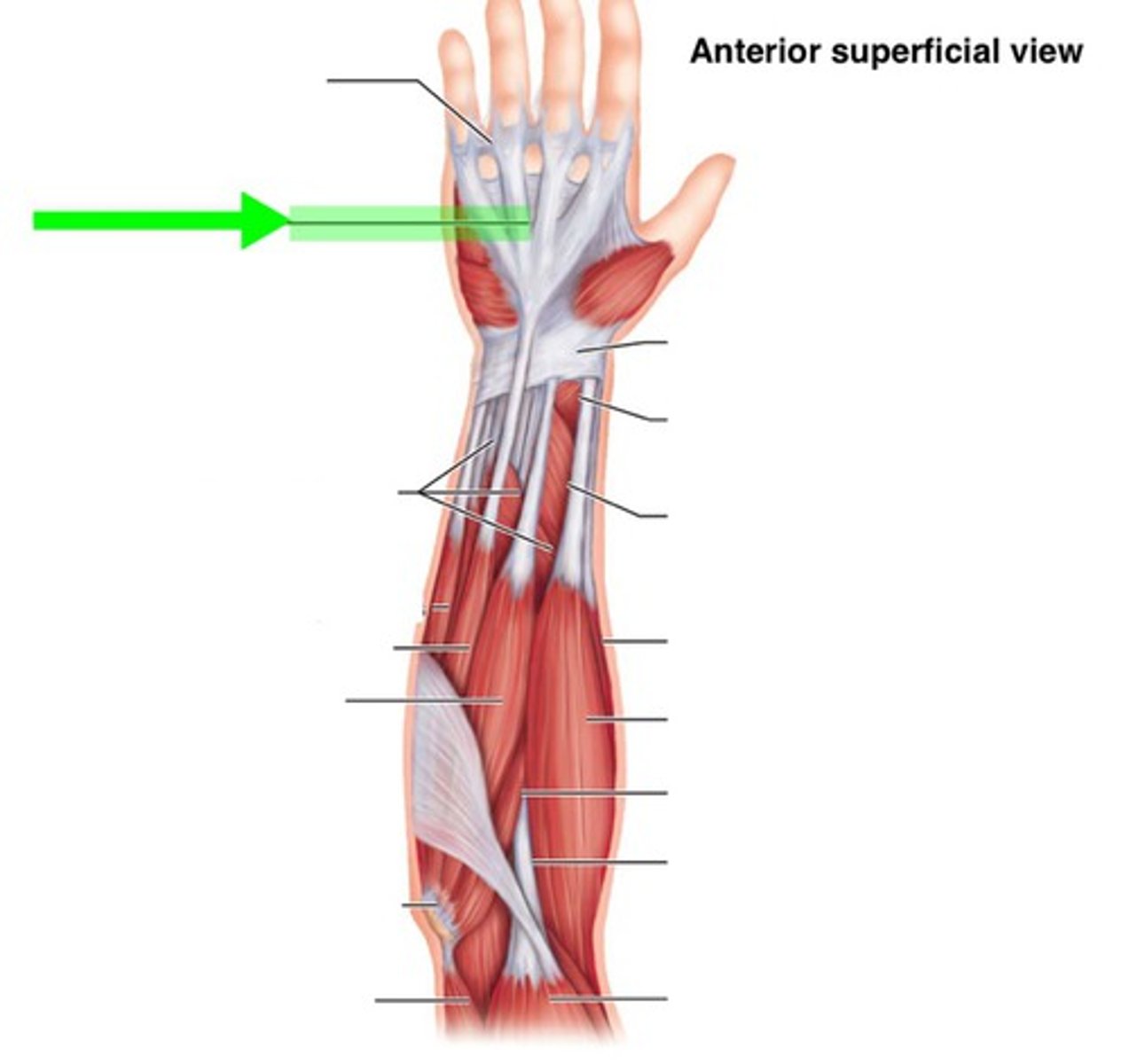
Retinacalum
a band of connective tissue around tendons
Muscle origin
end of the muscle that doesn't move, immovable end
Muscle insertion
end of muscle that moves, movable end
Agonist
primary mover of joint
Antagonist
opposes the agonist
synergistic muscles
contracts at the same time of the agonist to assist it
fixation
contract to prevent the origin of another muscle from moving
muscle of the head and neck are supplied by cranial nerves
Diaphram
responsible for breathing
Rotator cuff
SITS
1. Supraspinatus
2. Infraspinatus
3. Tres minor
4. Subscapularis
IT Band (what forms it?)
Tensor facialata and glutes maximus
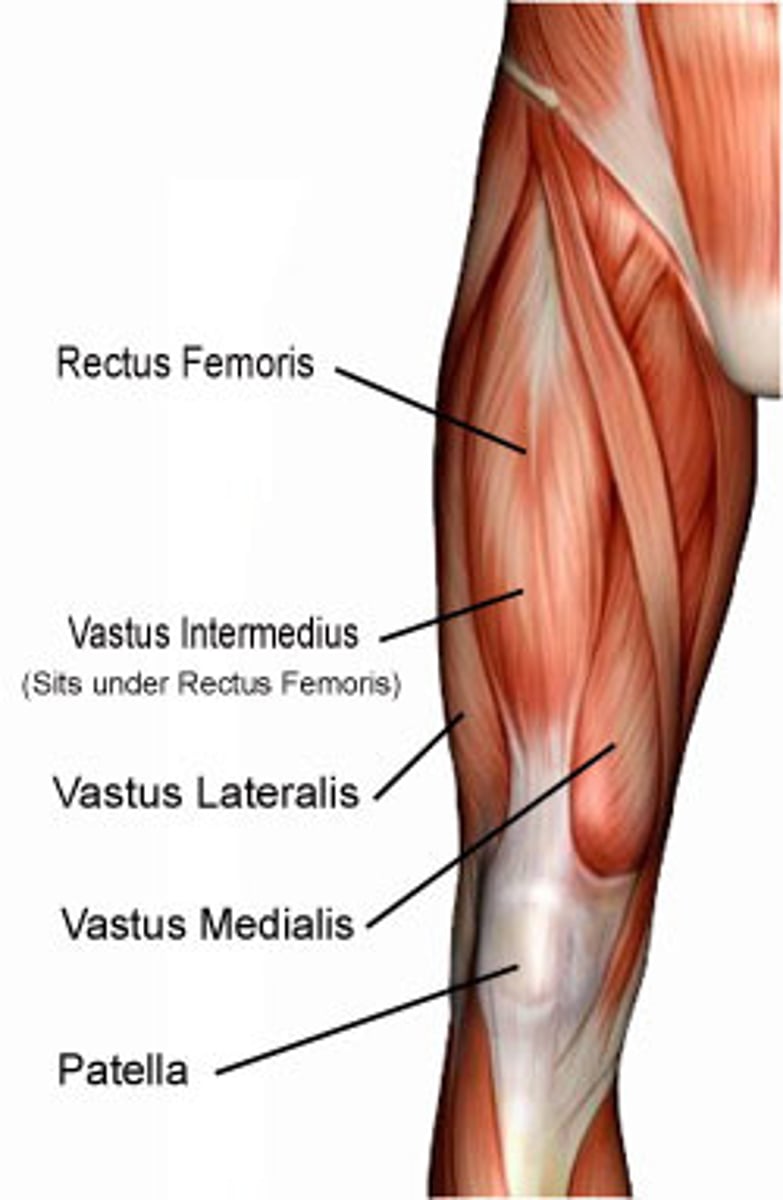
Quadriceps(Anterior)
Contains four muscles:
1. Rectus Femoris
2. Vastus lateralis
3. Vastus medialis
4. Vastus intermedialis
*Q,RV3
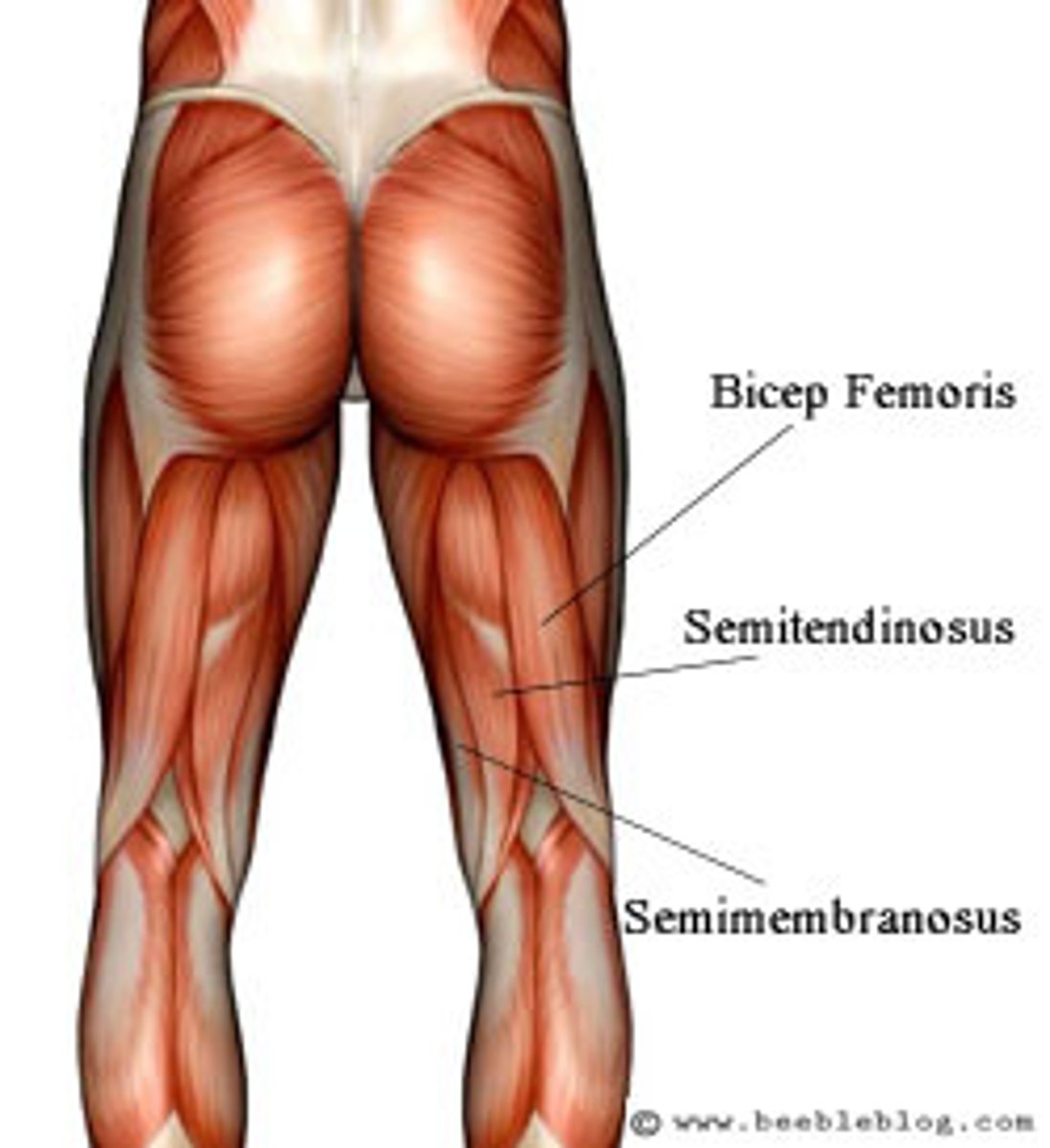
Hamstrings(Posterior)
Contains 3 muscles:
1. Biceps Femoris
2. Semimembraneous
3. Semitendonsus
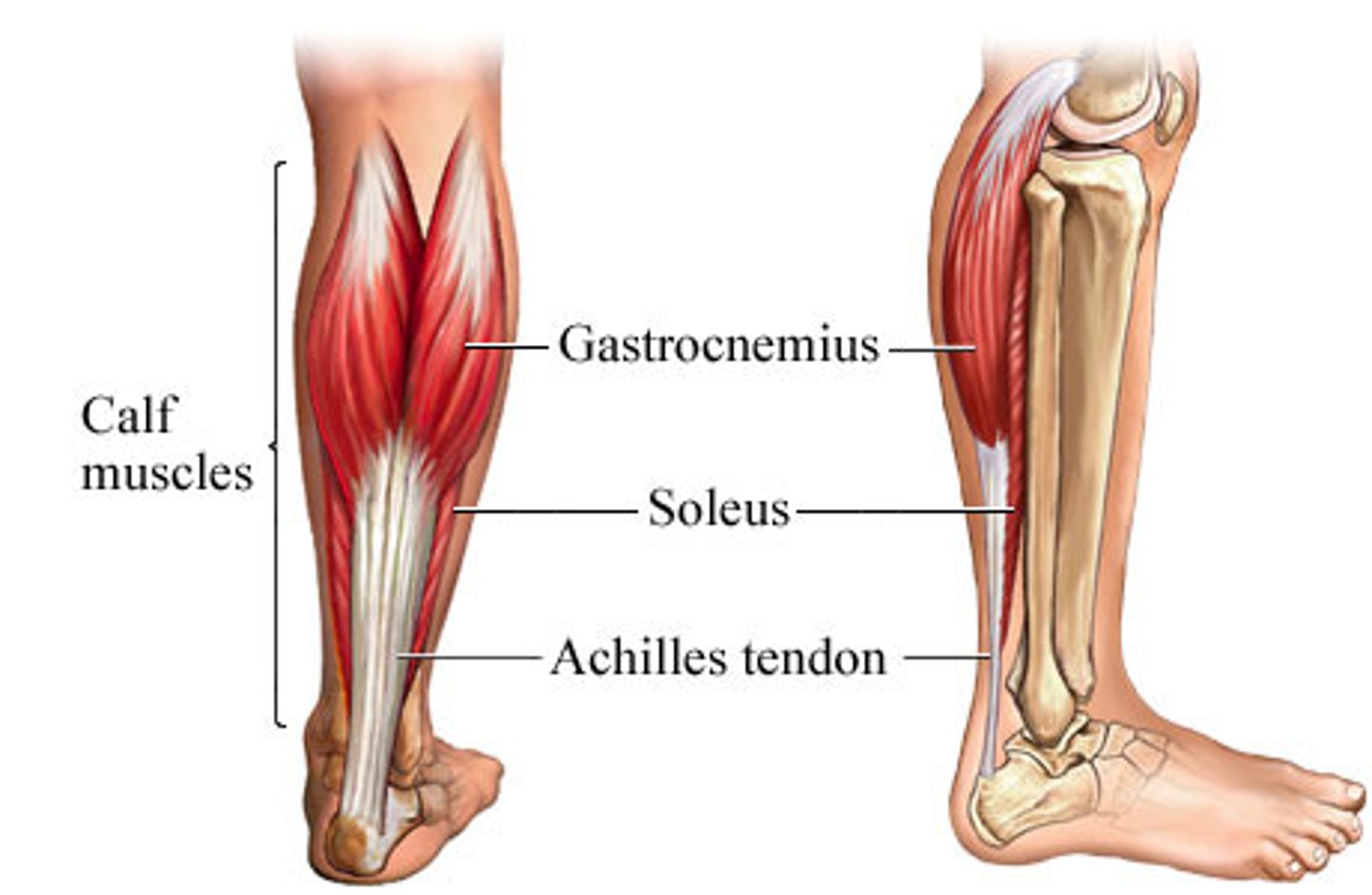
Calf
Gastrocrieums and soleus
Trick for 3 classes of jojnt
F-R-E
Fulcrum is a 1st class joint -atlantoaxial joint (pivot)
Resistance is a 2nd class joint -wheel barrow and jaw
Effort is a 3rd class joint - elbow
*only thing that changes is what's in the middle, but this is how you can remember!