Cardiovascular Registry Review-MIDTERM, module 4 exam
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
The increased stretch on cardiac muscle fibers at end-diastole caused by increased venous return is called?
A. Afterload
B. Automaticity
C. Preload
D. Inotrophy
C. Preload
The preferred fuel for ATP production by the myocardium is?
A. Citric Acid
B. Cholesterol
C. Glucose
D. Fatty acids
D. Fatty acids
How many weeks approximately does it take for the heart to be completely developed?
A. 5wks
B. 7wks
C. 6wks
D. 4wks
C. 6wks
The atria are physically separated and electrically insulated from the ventricles by the?
A. Fossa ovalis
B. Fibrous skeleton
C. Annulius/fibrous skeleton
D. SA node
C. Annulius/fibrous skeleton
What part of the IVS form last?
A. Outlet region
B. Inlet region
C. Apical region
D. Perimembranous region
D. Perimembranous region
What is the first thing that occurs when the interatrial septum is developing?
A. The ostium primum develops
B. The septum primum develops
C. The septum secundum develops
D. The ostium secundum develops
B. The septum primum develops
The structure within the myocyte where ATP production occurs is the?
A. Sarcomere
B. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
C. Mitochondria
D. Transverse tubules
C. Mitochondria
Which layer of the primitive, single heart tube will give rise to the myocardium and epicardium?
A. Truncus arteriousus
B. Sinus venosus
C. Bulbus conus
D. Mesoderm
D. Mesoderm
The pulmonary artery and aorta split due to spiraling of the?
A. Bulbus cordis
B. Atrioventricular canal
C. Aorticopulmonary septum
D. Perimembranous septum
C. Aorticopulmonary septum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum:
A. Is a storehouse for Na+
B. Connects one myocyte to the next
C. Helps spread the action potential
D. Is a storehouse for Ca++
D. Is a storehouse for Ca++
Where do the atrioventricular valves originate?
A. Sinus venous region
B. Endocardial cushion region
C. Bulbus cordis region
D. Inlet region
B. Endocardial cushion region
The phase where no stimulus is capable of resulting in another wave of depolarization is called the?
A. Recovery phase
B. Absolute refractory phase
C. Relative refractory phase
D. Repolarization phase
B. Absolute refractory phase
Which structures carry the electrical signal through the septum downward separately into each ventricle?
A. Purkinje fibers
B. Internodal tracts
C. Bundle of HIS
D. Bundle branches
D. Bundle branches
The middle layer of the original heart tube is made up of:
A. Cardiac mantle
B. Endothelial jelly
C. Cardiac Jelly
D. Endothelial layer
C. Cardiac Jelly
In order for the action potential to initiate ventricular contraction,which happens first?
A. Na+ rushes into the cell
B. K+ leaves the cel
C. The SA node is stimulated
D. The sympathetic nervous system releases norepinephrine
A. Na+ rushes into the cell
When Na+ first rushes into the myocyte, which statement is accurate?
A. It is about -30 mVolts on the inside of the cell
B. It is about +30 mVolts on the inside of the cell
C. It is about +90 mVolts on the inside of the cell
D. It is about -90 mVolts on the inside of the cell
D. It is about -90 mVolts on the inside of the cell
What part of the IVS forms first?
A. Outlet region
B. Inlet region
C. Apical region
D. Perimembranous region
B. Inlet region
The pair of arches that will give rise to the right and left pulmonary arteries are the?
A. 6th pair of arches
B. 5th pair of arches
C. 3rd pair of arches
D. 4th pair of arches
A. 6th pair of arches
The entire array of thick and thin filaments between Z lines is called a(n)?
A. Actin filament
B. Sarcomere
C. Sarcolemma
D. Myosin filament
B. Sarcomere
Which chamber of the heart is the smallest with the lowest pressure?
A. Left Ventricle
B. Left atrium
C. Right atrium
D. Right Ventricle
C. Right atrium
The coronary sinus is covered by the Eustachian valve?
A. True
B. False
B. False
All of the following are actions that the atria perform except:
A. Conduit
B. Pump
C. Reservoir
D. Regulator
D. Regulator
Which of the following is not a name for the aortic valve cusps?
A. Right coronary cusp
B. Left coronary cusp
C. Anterior coronary cusp
D. Non-coronary cusp
C. Anterior coronary cusp
The moderator band is located within the left ventricle.
A. True
B. False
B. False
Which vessel is the first to branch off of the aortic arch?
A. Innominate
B. Left subclavian
C. Right subclavian
D. Left common carotid
A. Innominate
The thick round fibrous skeleton that acts as a support for valve attachment is called the:
A. Oracle
B. Chordae tendineae
C. Annulus
D. Papillary muscle
C. Annulus
What are the string-like structures that are attached to the MV leaflets and the papillary muscles?
A. Annulus
B. Nodules
C. Chordae tendineae
D. Pectinate
C. Chordae tendineae
The right ventricle is lined with more muscular ridges called trabeculations than the left ventricle.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which of the following is not a name for the TV leaflets?
A. Inferior
B. Posterior
C. Medial
D. Anterior
A. Inferior
Which of the following views would be best to visualize a dissection?
A. Bicaval view
B. Transgastric short axis
C. LV outflow view
D. Descending thoracic aorta
D. Descending thoracic aorta
TEE is very helpful at visualizing what posterior structure?
A. Interventricular septum
B. All of the above
C. LV apex
D. Interatrial septum
D. Interatrial septum
Which study gives a better assessment of the left atrial appendage?
A. TEE
B. TTE
A. TEE
Which of the following would be an appropriate standard transducer frequency range for a transesophageal echocardiogram?
A. 8-10 MHz
B. 4-7 MHz
C. 1-2.5 MHz
D. 2-3 MHz
B. 4-7 MHz
Which of the following physiologic factors is fundamentally associated with improved image resolution when performing a TEE?
A. Faster sound pulse travel
B. Better pulse penetration
C. Reduced tissue attenuation
D. Less artifact production
C. Reduced tissue attenuation
What does the Omni indicator signify on the imaging screen when performing a TEE?
A. Probe temp warning
B. Automatic gain controls
C. Electronic image plane rotation
D. Image frequency adjustment
C. Electronic image plane rotation
TEE has improved image quality because of what factors?
A. Better signal to noise ratio
B. Decreased imaging depth
C. Higher frequency transducers
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
Which of the following is a relative contraindication to performing a TEE exam?
A. Uncooperative patient
B. Active upper GI bleed
C. Esophageal varices
D. Hypotension
C. Esophageal varices
What percentage of transesophageal cases have complications serious enough to interrupt the exam procedure?
A. 2%
B. 4%
C. 7%
D. <1%
D. <1%
Name 3 pathologies that can be seen better by TEE.
LAA Thrombi, Endocarditis, Aortic dissection
While measuring dP/dT in the presence of MR, what value is normal for systolic function?
A. >1000 mm Hg/sec
B. 500-1000 m/sec
C. <1000 mm Hg/sec
D. < or equal to 1000 mm Hg/sec
A. >1000 mm Hg/sec
What is the normal range for LV fractional shortening?
A. 25-45%
B. 50-75%
C. 75-100%
D. 0-20%
A. 25-45%
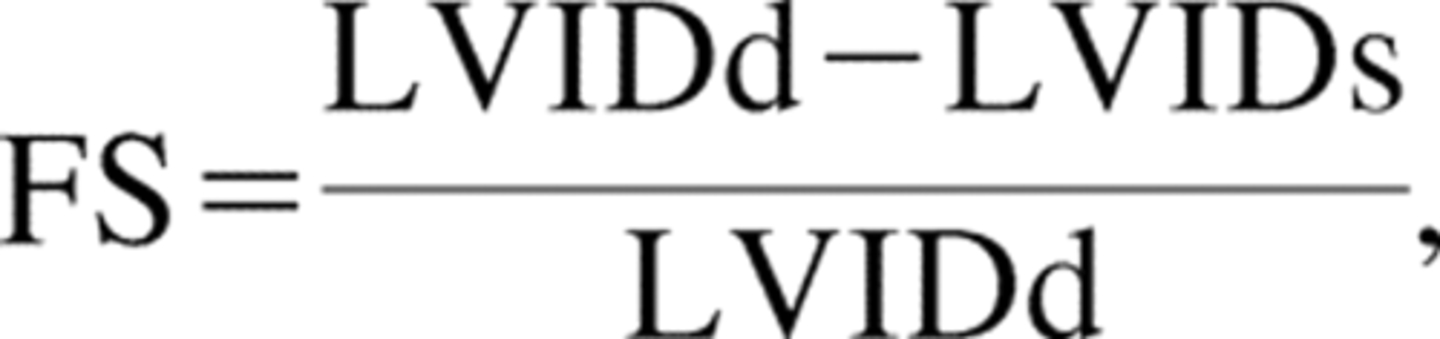
What is a normal E/A ratio?
A. < 1.0
B. > 2.0
C. 1.0 - 2.0
D. 1.0
C. 1.0 - 2.0

A MV PHT of 220 msec is consistent with a MVA of?
A. 1.0 cm^2
B. 0.6 cm^2
C. 0.75 cm^2
D. 0.5 cm^2
A. 1.0 cm^2
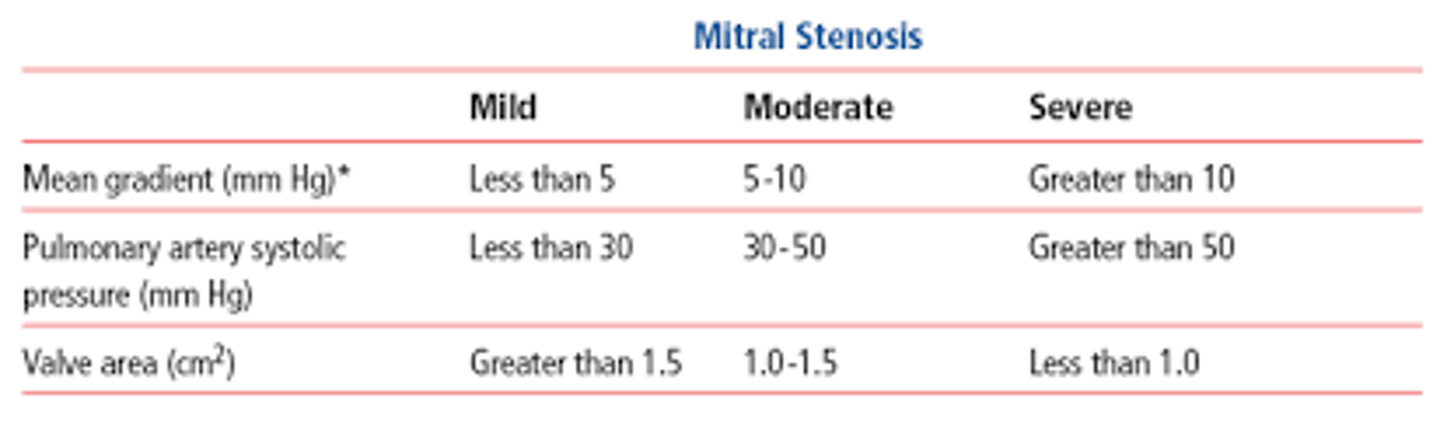
Severe MS is considered with which mean gradient and MVA?
A. >10 mmHg, MVA <1.0 cm^2
B. 2-4 mmHg, MVA = 3.0 cm^2
C. >5 mmHg, MVA >1.0 cm^2
D. >20 mmHg, MVA <1.0 cm^2
A. >10 mmHg, MVA <1.0 cm^2
All of the following are part of Diastole except:
A. Isovolumic contraction
B. Diastasis
C. Rapid filling
D. Isovolumic relaxation
A. Isovolumic contraction
The LVOT velocity should be measured in the Apical 5C using:
A. CW doppler with the sample placed at the base of the AV on theLV side just before pre-valvular acceleration parallel to flow
B. PW doppler with the sample placed at the base of the AV on theLV side just before pre-valvular acceleration parallel to flow
C. PW doppler when the velocity is 100cm/sec with a 60 degreeangle and turbulent flow
D. CW doppler with the sample volume exactly 1cm before thecalcified AV
B. PW doppler with the sample placed at the base of the AV on the LV side just before pre-valvular acceleration parallel to flow
The vena contracta is?
A. The narrowest width of the regurgitant jet
B. The widest width of the regurgitant jet
C. Part of the IVC
D. The valve orafice
A. The narrowest width of the regurgitant jet
Which of the following is least consistent with severe MR?
A. Regurgitant orifice area .5cm^2
B. Max regurgitant velocity 5.2 m/sec
C. Mitral vena contracta .8cm
D. Mitral E wave velocity 2.5 m/sec
A. Regurgitant orifice area .5cm^2
The TV opens when?
A. The velocity of blood flow in the RV exceeds the velocity in the RV.
B. The RV pressure drops below the RA pressure
C. The LV pressure rises above the LA pressure
D. The RV pressure rises above the RA pressure
B. The RV pressure drops below the RA pressure
Barlow's syndrome is another term for?
A. Parachute MV
B. Cleft MV
C. Myxomatous MV prolapse
D. MV stenosis
C. Myxomatous MV prolapse
What is normal Cardiac output?
A. 4-8 L/min
B. 40,000 - 80,000 mL/min
C. 10,000 - 15,000 mL/min
D. 1-5 L/min
A. 4-8 L/min
The hockey stick valvular appearance is associated with?
A. Congential malformation of the semilunar valves
B. Doming
C. Prolapse
D. Regurgitation
B. Doming
The largest size of the LA is measured at?
A. Ventricular diastole
B. Atrial diastole
C. End ventricular systole
D. Mid diastole
C. End ventricular systole
When the MV leaflets are tethered together, the color doppler may be termed?
A. B notch bump
B. Candle flame
C. W sign
D. Flying hockey stick
B. Candle flame
A small fibro-elastic protrusion seen on the AV in older patients may represent.
A. Lambl's excrescence
B. Perforation of the aortic cusp
C. Chiari network
D. Endocarditis
A. Lambl's excrescence
Which window generally yields the highest accuracy for obtaining the peak aortic systolic velocity?
A. Left sternal border
B. SSN
C. Right sternal border
D. Apical 3C
C. Right sternal border
A 22 yo male patient has an E/A ratio of 1.3 decel time of190msec, and a pulm vein S/D ratio of .70. What is the patient grade of diastolic dysfunction?
A. Normal
B. Grade 2
C. Grade 4
D. Grade 3
E. Grade 1
A. Normal

A tumor "plop" observed by echo is usually the result of this most common intracardiac tumor?
A. Atrial myxoma
B. Sarcoma
C. Rhabdomyoma
D. Teratoma
A. Atrial myxoma
A subcostal 4C is generally best to interrogate which pathology?
A. Eccentric motion of the pulmonic annulus
B. PFO or septal defects
C. Raphe
D. Mitral stenosis
B. PFO or septal defects
The common cause of a flail leaflet is:
A. MAC (mitral annular calcification)
B. Rupture of the chordae tendineae
C. Endocarditis
D. Parachute MV
B. Rupture of the chordae tendineae
To calculate the AVA cm^2 use the:
A. Continuity equation
B. Modified simpsons
C. PHT
D. Simplified Bernolli equation
A. Continuity equation
Doming is a result of?
A. Elongated MV leaflets
B. MAC
C. Tenting of the anterior MV leaflet
D. Fused commissures
D. Fused commissures
If a physician suspects Carcinoid heart disease, you should pay attention to this structure , which may have thickening and rigidity causing severe regurgitation?
A. MV
B. TV
C. IVS
D. IVC and hepatic veins
B. TV
Joes HR is 100 bpm, his end-systolic volume is 70 mL and end-diastolic volume is 140 mL. What is his Cardiac output?
A. 8 L/min
B. 80,000 mL/min
C. 7 L/min
D. 4900 mL/min
C. 7 L/min

Which of the following is a sign of pulmonary HTN?
A. Flattened e-f slope of TV
B. Mid-systolic notch "early closure" pulmonic valve, aka flying W
C. Systolic anterior motion of the anterior mitral valve leaflet
D. IVC collapse >50% with respiration
B. Mid-systolic notch "early closure" pulmonic valve, aka flying W
An M-mode finding of fine diastolic flutter of the anterior mitral valve leaflet is consistent with?
A. Aortic stenosis
B. Mitral stenosis
C. Atrial fibrillation
D. Aortic regurgitation
D. Aortic regurgitation
A tricuspid regurgitant velocity of 4 m/sec indicates the presence of?
A. Severe tricuspid regurgitation
B. A flail tricuspid leaflet
C. Pulmonary HTN
D. Tricuspid stenosis
C. Pulmonary HTN
Severe AS is when the mean pressure gradient is higher than?
A. 50mmHG
B. 40mmHG
C. 30mmHG
D. 20mmHG
B. 40mmHG
Doming of the anterior MV leaflet in diastole suggests?
A. Flail MV leaflet
B. Cleft MV
C. Mitral valve prolapse
D. Mitral stenosis
D. Mitral stenosis
Severe AR is suggested when:
A. Holosystolic flow reversal in the descending aorta is present and a PHT of<200 msec
B. Holosystolic flow reversal in the descending aorta is present and a PHT of>500 msec
C. PHT of AR is >500 msec with a flat slope
D. PHT of AR is >75 msec
A. Holosystolic flow reversal in the descending aorta is present and a PHT of<200 msec
The best clinical indication for the classic finding of MV prolapse is:
A. A systolic ejection murmur
B. A mid systolic click
C. Systolic doming of the anterior leaflet
D. Diastolic fluttering of the MV
B. A mid systolic click
Vegetations are more commonly associated with?
A. Lupus
B. Abcesses
C. Myxomatous valve disease
D. Endocarditis
D. Endocarditis
To obtain the true circumference of the MV, the most accurate measurement is obtained at the short-axis view at the level of?
A. Commissures
B. Mitral annulus
C. Chordae Tendineae
D. Tip of the mitral leaflets
D. Tip of the mitral leaflets
Which flow velocity can be used to calculate pulmonary artery systolic pressure?
A. MR
B. AR
C. Pulmonic stenosis
D. TR
D. TR
What is the normal percent systolic thickening of the posterior wall and septum?
A. Less than 33%
B. Greater than 33%
C. Greater than 15%
D. Greater than 80%
B. Greater than 33%

In order to confirm that a tumor is a myxoma, you want to look for?
A. Involvement of a valve
B. Involvement of the myocardium
C. A stalk
D. Obstruction of flow
C. A stalk
In a patient that has HOCM, amyl nitrate should never be given to a patient when his outflow gradient/velocity exceeds which of the following?
A. 70 mm Hg
B. 2.7 m/sec
C. Both 50 mm Hg and 3.5 m/sec
D. 50 mm Hg
E. 3.5 m/sec
C. Both 50 mm Hg and 3.5 m/sec
If a patient is expected of having an aortic dissection, what should be interrogated for an echo?
A. Aortic regurgitation
B. Dilated aorta
C. Aortic flap
D. Dilated sinuses
C. Aortic flap
Which Cardiomyopathy is the most prevalent genetic primary cardiac disease?
A. Restrictive
B. Dilated
C. Infiltrative
D. Hypertrophic
D. Hypertrophic
If a patient has severe aortic regurgitation due to a dilated aorta, C closure would be visualized on which M-mode trace?
A. LV
B. RV
C. Aorta/ LA
D. Mitral
D. Mitral
A tumor that is usually found in the ventricular walls is a(n):
A. Myxoma
B. Fibroelastoma
C. Angiosarcoma
D. Fibroma
D. Fibroma
What is the most common primary, benign cardiac tumor?
A. Rhabdomyoma
B. Angiosarcoma
C. Lipoma
D. Myxoma
D. Myxoma
What causes the dip and plateau seen on cath with constrictive pericarditis?
A. Equalization of RV and LV pressures during systole
B. Equalization of RA and LA pressures during systole
C. Equalization of RV and LV pressures during diastole
D. Equalization of RA and LA pressures during diastole
C. Equalization of RV and LV pressures during diastole
A sinus of valsalva aneurysm usually involves the left coronary artery?
A. True
B. False
B. False
What type of tumor demonstrates a dumbell appearance of the IAS due to hypertrophy?
A. Myxoma
B. Lipoma
C. Fibroma
D. Angiosarcoma
B. Lipoma
In a patient with Marfan's syndrome, all of the following could be visualized on the PLAX except:
A. Aortic Insufficiency
B. Dilated aorta
C. TV prolapse
D. MV prolapse
C. TV prolapse
What type of pulse will a patient have with most pericardial disease?
A. Pulsus bisferiens
B. Pulsus parvus
C. Pulsus paradoxus
D. Pulsus alternans
C. Pulsus paradoxus
If a patient is in tamponade you will see the following:
A. RV late systolic collapse and/or RA early systolic collapse
B. RA late systolic collapse and/or RV early diastolic collapse
C. RA early diastolic collapse and/or RV systolic collapse
D. RV diastolic collapse and/or RA systolic collapse
D. RV diastolic collapse and/or RA systolic collapse
Beck's triad consists of:
A. Hypotension, decreased venous pressures, palpitations
B. Hypotension, elevated venous pressures, quiet heart sounds
C. Hypertension, decreased venous pressures, quiet heart sounds
D. Hypertension, elevated venous pressures, palpitations
B. Hypotension, elevated venous pressures, quiet heart sounds
At what size of the aorta will a patient with an aortic aneurysm be suggested to have surgery?
A. 7 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 4 cm
D. 6 cm
D. 6 cm
All of the following are part of the clinical diagnosis or triad commonly seen in patients with pericarditis except:
A. ECG changes
B. Fever and chills
C. Friction rub with paradoxical pulse
D. Substernal left sided chest pain
B. Fever and chills
What is the most common cause of tamponade?
A. Idiopathic
B. Viral infection
C. Post cardiac surgery
D. Cancer
D. Cancer
What heart sound is heard with a pericardial effusion?
A. Frictional knock
B. Friction rub
C. Soft heart sounds
D. Pericardial knock
B. Friction rub
Most right-sided thrombi are caused by pacemaker wires.
A. True
B. False
B. False
What treatment is used for constrictive pericarditis?
A. Pericardiocentesis
B. IV fluids
C. Pericardiectomy
D. ain relievers
C. Pericardiectomy
An aortic dissection is a tear between which two layers?
A. Intima and medial
B. Adventitia and medial
C. Adventitia and intima
D. Parietal and intimal
A. Intima and medial
Most cardiac thrombi appear spontaneously:
A. True
B. False
A. True
All of the following are physical signs or symptoms that a patient with a cardiac missile could present with except:
A. An ASD
B. A fever
C. Tamponade
D. A new murmur
B. A fever
The strain pattern known as the "cherry on top" is often associated with which Cardiomyopathy?
A. Amylodosis
B. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
C. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
D. AS
A. Amylodosis
2D imaging is better at diagnosing the presence of a pericardial effusion
A. True
B. False
A. True