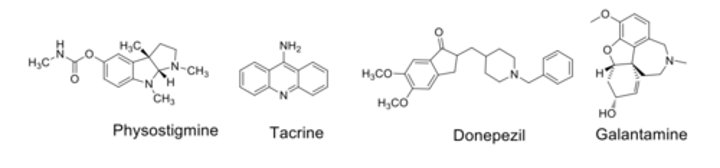
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
name the two types of enzymes that hydrolyse ACh
AChE and BChE (Butyrylcholinesterase)
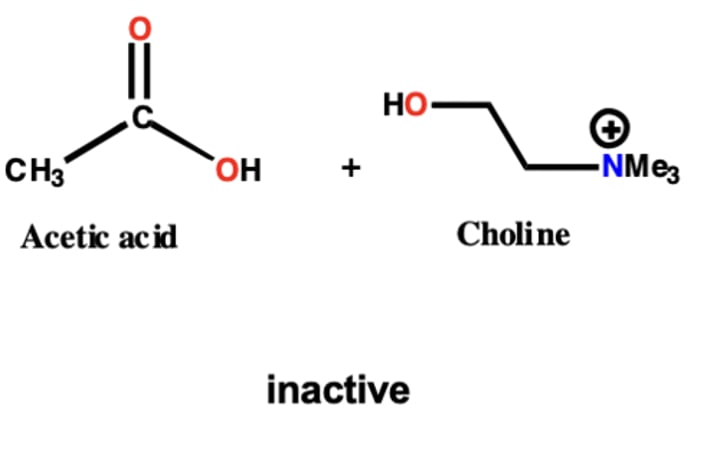
ACh is inactivated to give what 2 molecules?
acetic acid and choline
how does the structure of AChE allow the hydrolysis of ACh?
• Anionic binding region similar to cholinergic receptor site
• Binding and induced fit strains Ach and weakens bonds
• Molecule positioned for reaction with His and Ser
in ACh mechanism, what is the role of Ser?
nucleophile- attacks C=O on ACh so it is available to act on substrate
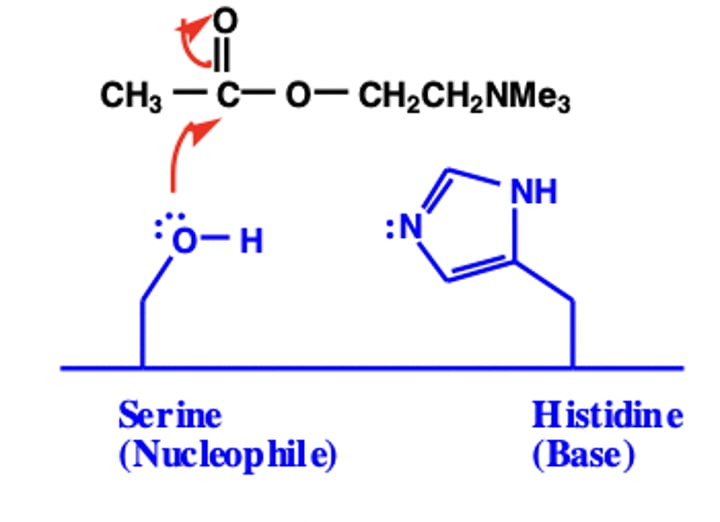
in ACh mechanism, what is the role of His?
acts as both acid and base catalyst (H donor/acceptor)
what 3 amino acids is targeted in cholinergic system?
Ser, His, Asp
Serine and water are _________ nucleophiles. What must be added to drive reaction?
poor- catalyst (basic)
Leaving groups are aided by which amino acid residue at cholinergic receptors ?
His- acts as acid catalyst
Why do organophosphates inhibit acetylcholinesterase for so long?
- binding covalently to a serine residue in the enzyme active site
- P-O bond is very stable
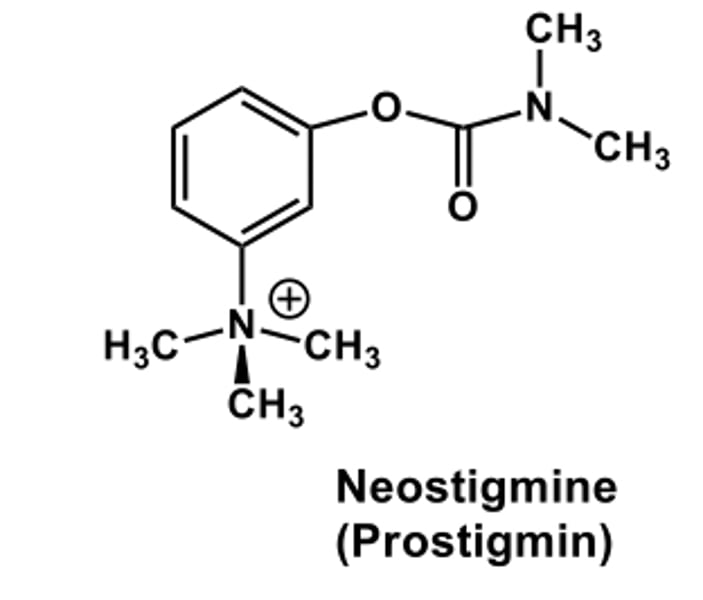
what class of AChE are the most important?
Carbamates
what group on carbamates blocks the activity of AChE?
carbamoyl group- undergoes slow hydrolysis- stops AChE acting on ACh
Neostigmine and Pyridostigmine are used in?
local anaesthetics
describe the action of DFP and Echothiophate
Long acting irreversible inhibitors of AChE
organophosphates lead to ?
permanent inhibition of AChE
organophosphates antidotes require what ideal properties (2)?
- Strong nucleophile required to cleave strong P-O bond i.e. Hydroxylamine
- Non-polar
what is Glaucoma?
increased pressure in the eye
how does AChEs treat glaucoma?
-Inhibition of AChE leads to enhanced effect of ACh in stimulation of ciliary body
-increases drainage of fluid from eye
relieves intra-ocular pressure
what is Myasthenia Gravis?
Auto-immune depletion of Acetylcholine (Ach) receptors- leads to flaccid muscles (weakness of face, tongue. double vision or drooping eyelids, difficulty chewing, swallowing and talking)
Alzheimer's disease is characterised by?
loss of neurons in cerebral cortex- reduced cholinergic activity
how to AChE inhibitors treat AD?
-used to prevent breakdown of ACh
-Increased ACh to compensate for loss of cholinergic neurones
-improves cognition (symptomatic relief)