AP Econ Test
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
What is economics
behavior science concerned with how scarce resources are allocated among unlimited wants, needs, and desires
What does it mean to be scarce
Limited and wanted
What does scarcity lead to
trade-offs
What is the opposite of scarcity
abundance
What are decisions at the individual level and then the aggregate level called
microeconomics and macroeconomics
What are positive economics
How things actually are (his shirt is red)
What are normative economics
How things should be done (that shirt is a good material)
What are resources
Things used to make something else
What are the four categories resources are classified into called
The factors of production
What are the 4 factors of production
Land (natural resources + rent) Labor (workers and + wages) Capital (physical capital like machines and tools + human capital like experience and education + financial capital like money and interest) entrepreneurship (ability to combine resources to satisfy society, take risks, make decisions + profit)
What is opportunity cost
What you could have done (the next best thing)
What does the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) represent
A simplified model of an economy producing only 2 goods
What does the PPC curve prove
How an economy is doing (dot on curve=good)
What does a dot to the right of the PPC curve show
An impossible scenario
What does a dot to the left of the PPC curve show
What would happen if the economy is not producing goods efficiently
What is absolute advantage
Producer 1 can make more than producer 2
What is comparative advantage
Producer 1 can make it while giving up less than producer 2
How to calculate opportunity cost
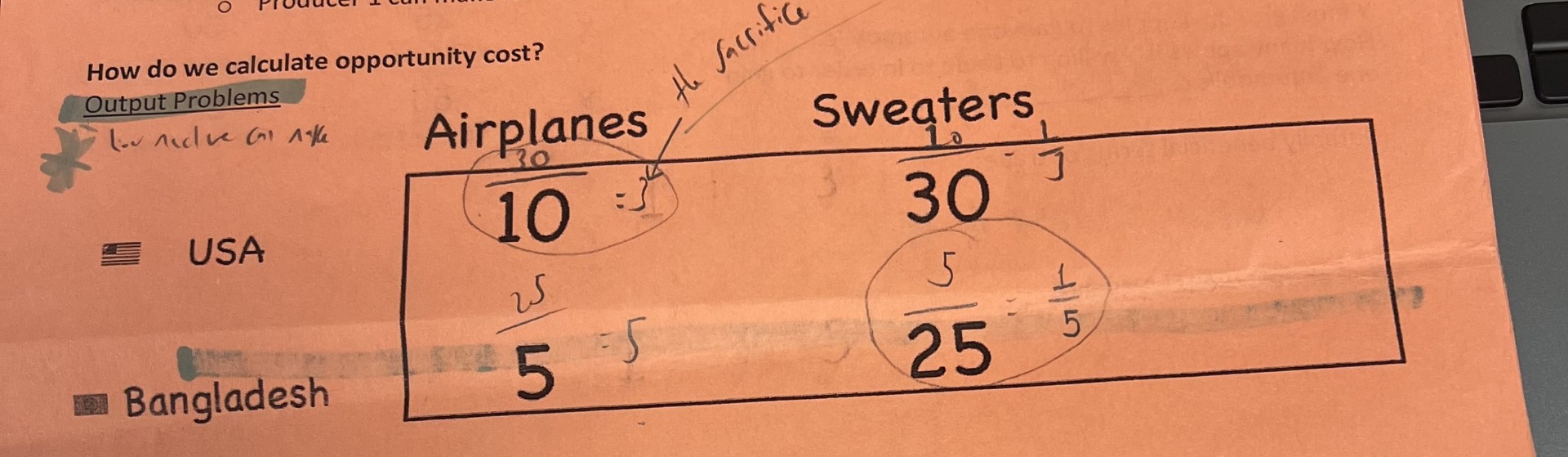
What are terms of trade
An agreed upon exchange rate of two goods between two producers (typically between nations)
-If X gives up one automobile, it gains 2 apples. If X trades one automobile, how many apples does it need to acquire in order for it to gain from trade?
-Y must give up 4 apples to gain one automobile. How many apples is Y willing to trade in order to gain 1 automobile?
-What are the mutually beneficial terms of trade
-Greater than 2 apples
-Less than 4 apples
-Between 2 and 4 apples
Define a competitive market
A market in which there are many buyers and sellers of the same good or service, none of whom can influence the price at which the good or service is sold
Define quantity demanded
The actual amount of a good or service consumers are willing and able to buy at some specific price
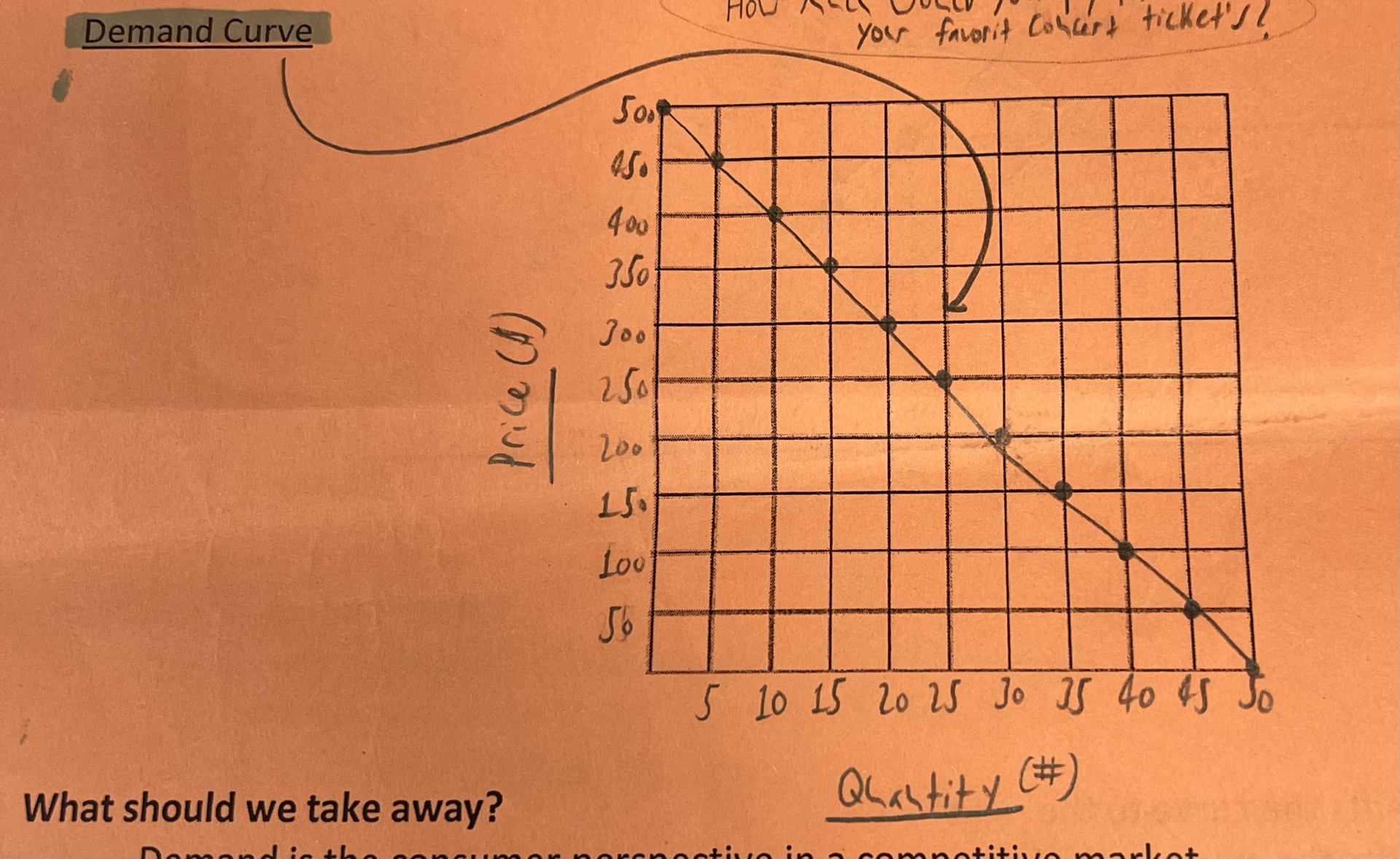
Define the law of demand
As the price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded decreases and vice versa
What does the demand curve look like
What shifts the demand curve
MERIT
Market size (number of consumers)
Expectations (expectation of a future change in price)
Related goods (Complements-goods/services purchased together Substitutes-goods/services purchased in place of other goods)
Income (normal good- if income increases, so does demand inferior good- if income increases, demand decreases)
Tastes (changes in style, trends, and/or popularity)
Define quantity supplied
The actual amount of a good or service producers/sellers are willing and able to sell at some specific price
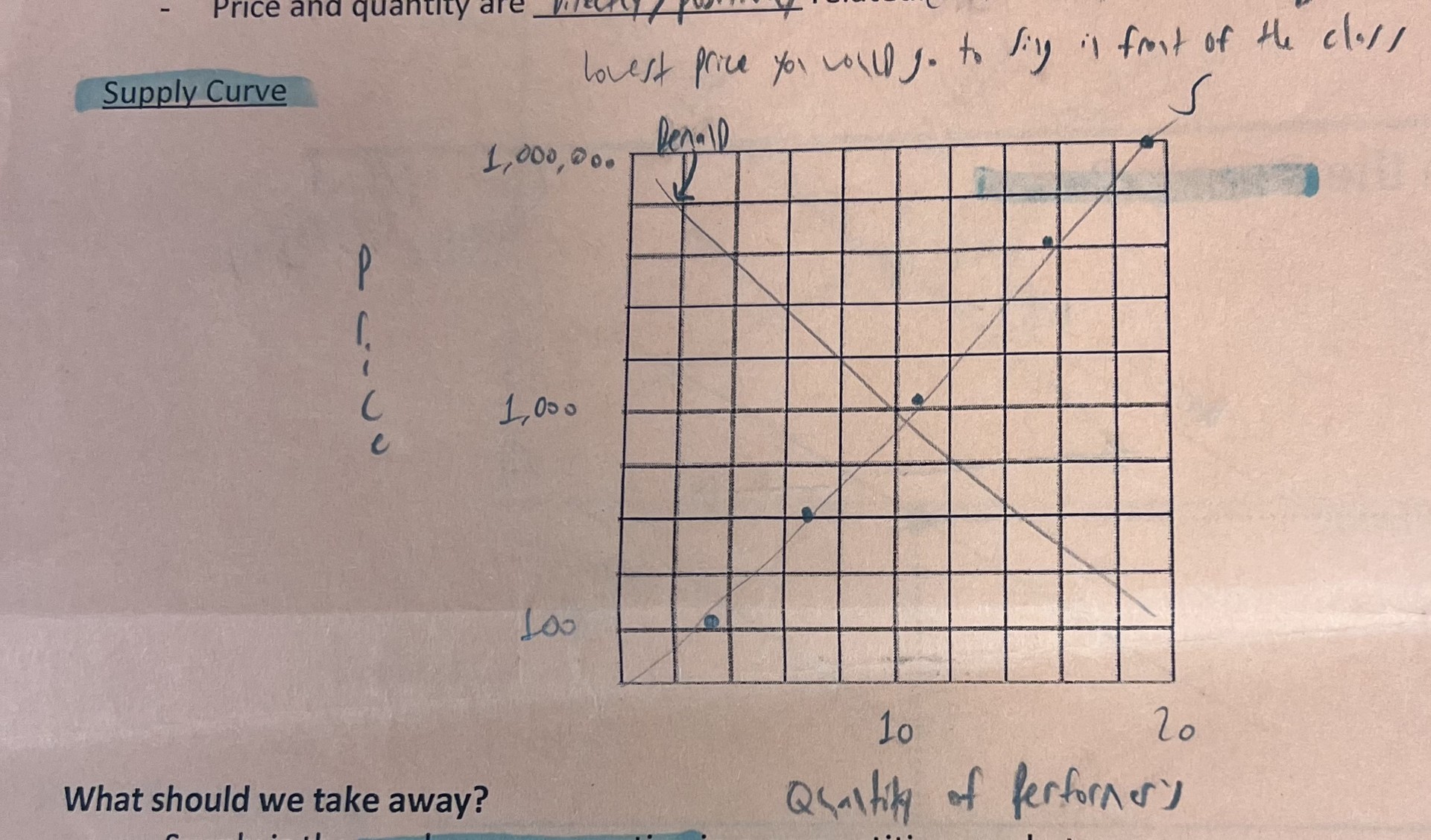
What is the law of supply
As price increases, the corresponding quantity supplied increases
What does the supply curve look like
What shifts the supply curve
TRICE
Technology (new technology increases supply)
Related prices (complement products)
Substitutes (Products produced in place of other products)
Input prices
Competition (Increased competition increases supply)
Expectations (If producers expect prices to increase, they produce more)
Where does a market equilibrium point occur
at a point where the supply curve and the demand curve intersect
What is a subsidy
Government paying for a company to make things (ex. paying a company to keep producing solar panels)
What is a transfer payment
The government giving money back (like social security checks)
What does circular flow look like
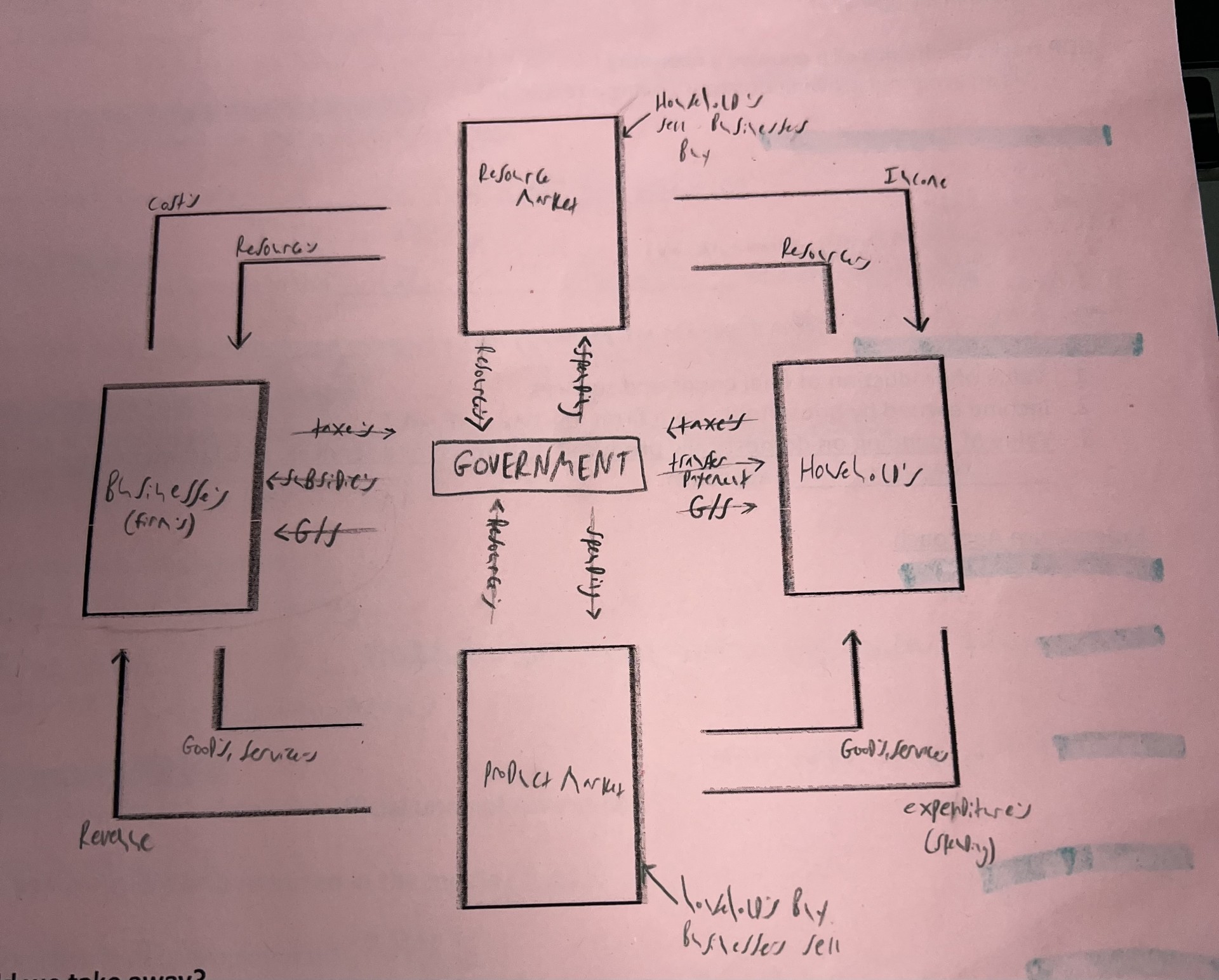
Define gross domestic product (GDP)
Total value of all FINAL goods and services produced in the economy in a given year
What is a final good
A product you pull right off the shelf
What is a intermediate good
Goods that go into the production of other goods
What does GDP track
the health of a country’s economy
What are some things that are not included in the GDP
-used goods
-stocks and bonds
-non-market goods (like mowing someones lawn
-foreign made goods
-black market activities
-transfer payments (like social welfare programs)
What are the three ways you can measure GDP
Value of production of final goods and service
Income approach= income earned by households from firms
Expenditure approach= value of spending on domestically produced final goods and services
What is the expenditure approach equation
GDP=C+I+G(X-M)
Consumption (what households spend on final goods)
Investment (by businesses in capital goods)
Government spending
eXports sold
iMports bought
Define employed
currently holding a full or part-time job
Define unemployed
People who are not currently employed but are actively looking for work
What is the labor force
Employed + Unemployed
How to calculate the labor force participation rate
(labor force/16+ total population)x100
What is the unemployment rate
the percent of the total number of people in the labor force who are unemployed
What is the unemployment rate equation
(Number of unemployed workers/labor force)x100
Define discouraged workers
Capable workers who have given up looking due to job market
Define marginally attached workers
would like to work, but gave up looking
Define underemployed workers
part-time workers who want full-time positions
Who are the limitations to the unemployment rate and therefore not included in it
Discouraged, marginally attached, and under-employed workers
What is U3
The official unemployment rate reported in the media
What is U6
The broadcast measure of unemployment (includes discouraged, marginally attached, and underemployed workers)
What is frictional unemployment
Unemployment due to the time workers spend in the job search (new graduates and if you have new opportunities so you voluntarily leave)
What is structural unemployment
More job seekers than available jobs (or someone who lacks the skills needed for a job)(like if robots take over your job)
What is cyclical unemployment
This is considered the most serious- happens during recessions it means the economy is bad and there is nothing you can do about it you just have to wait it out
What are the three types of unemployment
Frictional, Strutural, and Cyclical
Define what the natural rate of unemployment is
Some degree of unemployment is inevitable
What is the natural rate of unemployment equation
frictional + structural (since there will always be these 2 types of unemployment)
Define the consumer price index (CPI)
A measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by consumers for a FIXED market basket of goods and services (tracked monthly)
Define market basket
The goods and services bought by consumers
What does the CPI show
The purchasing power of the average American family
When CPI rises, what is occurring
Inflation
What does inflation erode
The purchasing power of a given income
What 2 things do you multiply together to find market basket
Price x ORIGINAL quantity
What is the equation for the CPI using market basket values
(market basket in current year/market basket in base year)x100
What is the equation to calculate the inflation rate using the CPI
((New CPI - old CPI) / (old CPI))x100
What does nominal mean
Not adjusted for inflation
What does real mean
Has been adjusted for inflation
Deflating salary equation
Real value= nominal value / (price index/100)
What are the shortcomings of the CPI
Substitution bias-(when prices get too high, find an alternative, don’t buy expensive thing anymore)
Introduction of new goods- (greater variety, need for fewer dollars to maintain lifestyle)
Unmeasured quality changes- (the CPI doesn’t account for improvements of goods like cars getting seatbelts)
Volatile product prices- (goods like gas can misrepresent inflation)
Why does it matter if the CPI overstates or understates the true inflation rate
Many government programs use the CPI to adjust for changes in the overall level of prices (aka cost-of-living adjustments)
When inflation is higher what is lower
The purchasing power of a given amount of money
Who are winners of inflation
Anyone paying money at a FIXED amount, like borrowers
Who are losers of inflation
Anyone receiving money at a FIXED amount, like lenders or individuals on fixed incomes
What is the equation for nominal GDP
Price level x national income
Define nominal GDP
A measure of how much is spent on output in a given period (not adjusted for inflation)
What is real GDP
A measure of how much output is produced in a given period (adjusted for inflation)
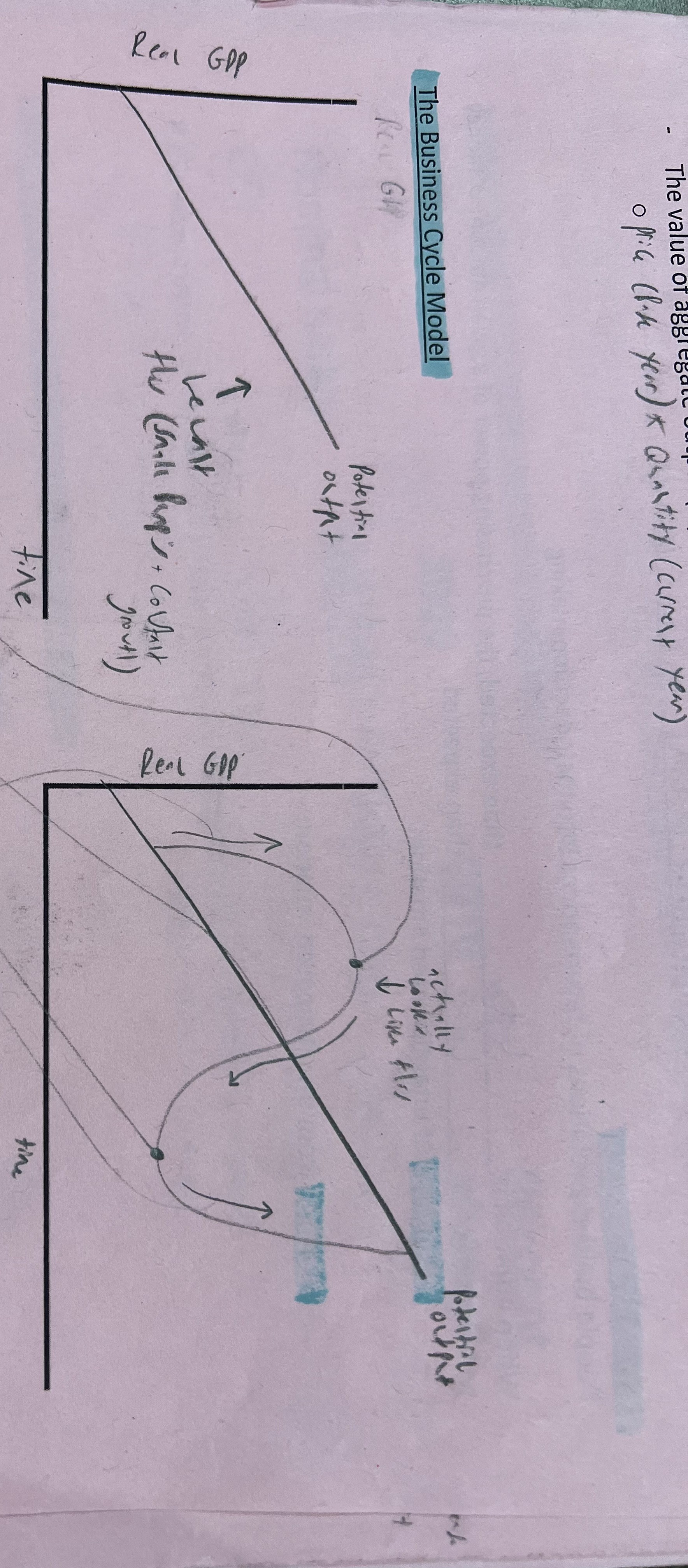
Define peak on a graph
A turning point (increasing to decreasing)
Define recession on a graph
Output decreasing, employment falls
Define trough on a graph
Turning point (decreasing to increasing)
Define expansion on a graph
Output increases, employment rises
What does the business cycle model look like
What is aggregate demand
The quantity demanded of all goods and services
What is the one thing that doesn’t shift the demand curve
price
What happens to aggregate output demanded when the price level falls
It increases
What is the real wealth effect
A change in price level causes the purchasing power of a given amount of wealth to change
What is the interest rate effect
A change in the price level causes a change in the demand for money. This impacts interest rates, which causes a change in the cost of goods and services purchased with borrowed money
What is the exchange rate effect
A change in the price level will make a foreign country’s goods/services more or less expensive to foreign buyers. This impacts the quantity demanded for these goods/services
What 5 things will cause a change in aggregate demand
Wealth, expectations, changes in physical capital, fiscal policy (government spending and taxes), and monetary policy (the central bank’s ability to change the quantity of money)
What is the multiplier effect
The multiplier effect refers to the phenomenon where an initial change in spending leads to a larger overall impact on aggregate demand and economic output. This occurs as increased income leads to further consumption and investment, amplifying the initial stimulus
What is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
The proportion of any extra income that’s spent by consumers
What is the marginal propensity to save MPS
Measures the proportion of extra income that is saved on consumption
What will MPC+MPS always equal
1
What is the equation for the multiplier effect
1/MPS
If a business invests 100$ into the economy determine how much money will be added to the GDP if the MPC is .80
1-.80=.20 which is the MPS then 1/.20 is 5 and take that and multiply it by the original 100 so 500$ in new money will be injected into our GDP
What does the short run aggregate supply curve show
The relationship between aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied by all sellers within an economy
Define aggregate
Total, whole
Define sticky wages
In the short term, many input costs tend to be fixed, meaning suppliers of products are locked into contracts for a period of time
Do wages stay sticky forever
No
What 4 factors impact aggregate supply
-Changes in productivity
-changes in input costs
-government action
-price