2.3 aggregate supply
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
The AS curve
the entire quantity of goods and services within an economy
-curve is sloping upwards as at a higher price level, producers are willing to supply more so they can make more profits.
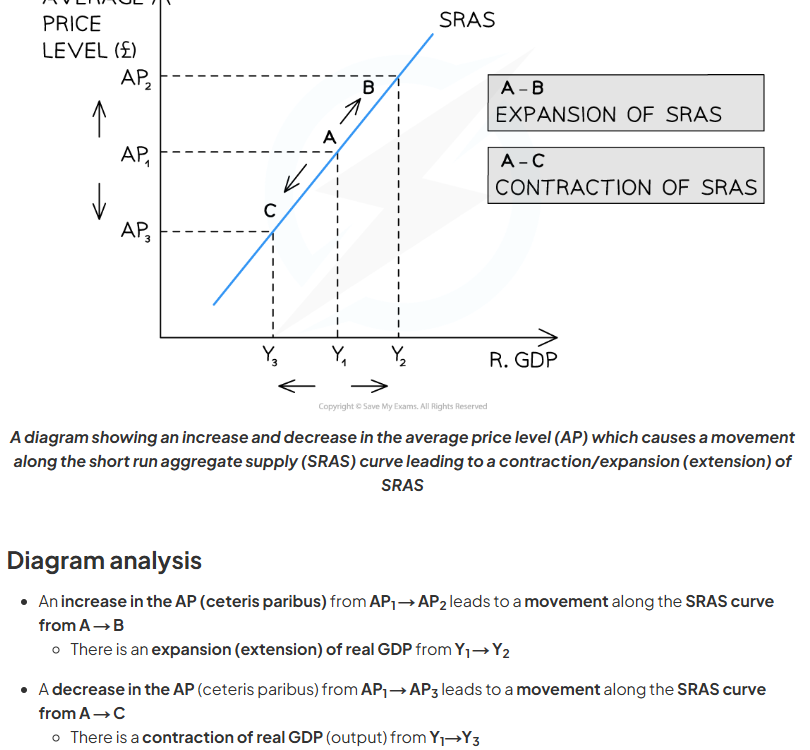
movement in aggregate supply curve
if price level increases, then there is an expansion in real GDP and leads to a movement in along the SRAS curve
if price level decreases, there is a contraction in real GDP and leads to a movement along the SRAS curve.
shift in the SRAS curve
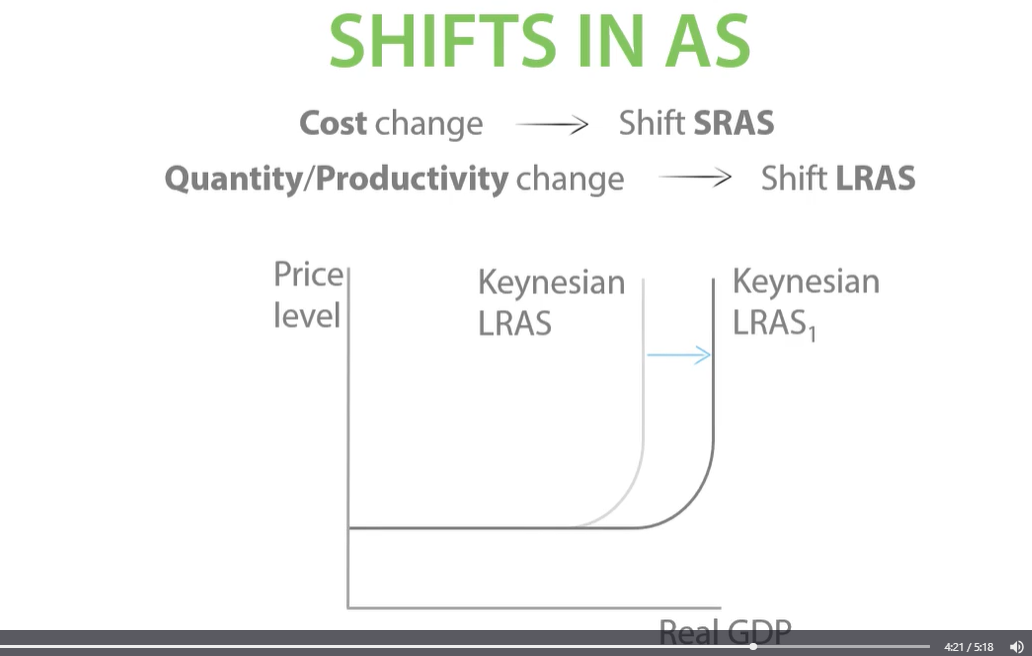
whenever their is a change in the conditions of supply in an economy, such as costs of production there is a shift in the entire SRAS curve.
-when costs change we shift SRAS. when quantity/ productivity shift we shift LRAS.
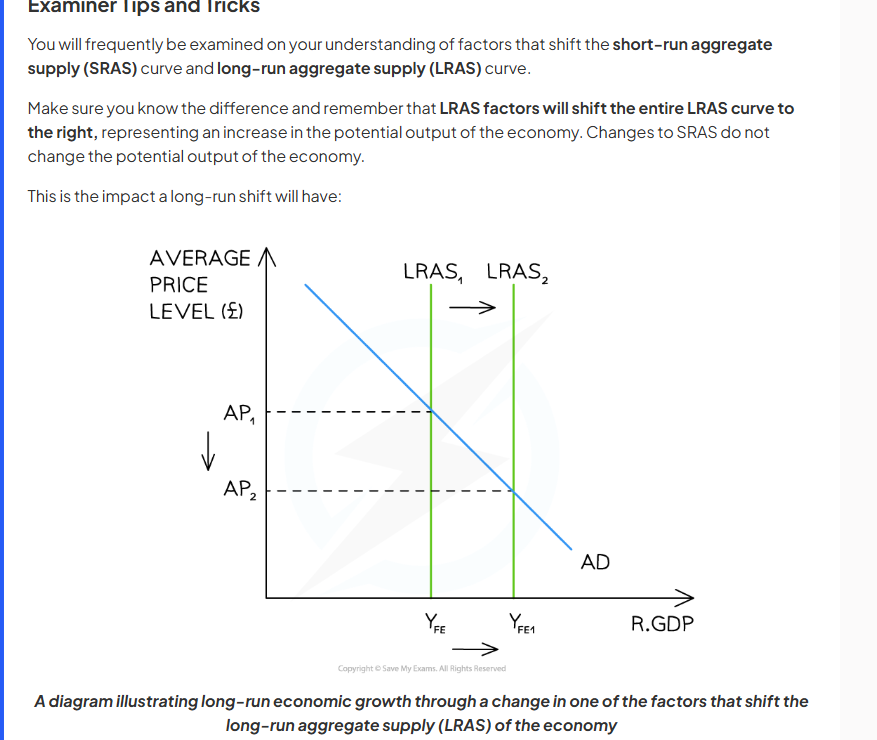
quantity/factors of production increases, LRAS shifts to the right
LRAS will shift if there is a change in the quantity or productivity in the factors of production.
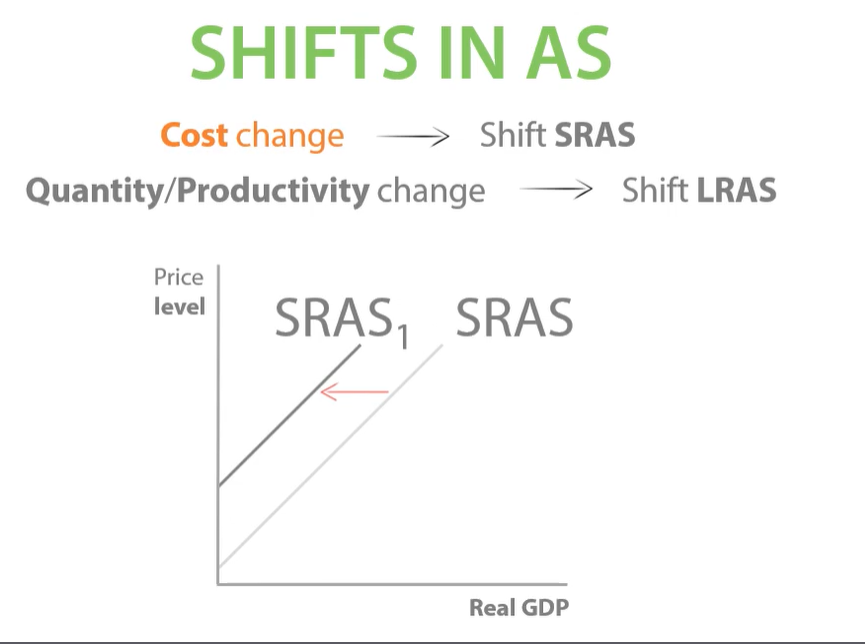
shift in SRAS. costs increases.
increase in costs means producers cant afford to produce as much so sras will shift to the left, output will decrease.
SRAS is influenced by
costs of production. where at least one factor of production is fixed.
LRAS is influenced by
the productive capacity in the economy. productive capacity is changed by the quality or quantity of the factors of production.
factors influencing short run AS- increase and decrease in costs of raw materials and energy
as the rise of input costs increases, fewer goods can be produced with the same amount of money. sras shift left
as the rise of input costs decreases, more goods can be produced with the same amount of money. sras shift right
factors influencing short run AS- increase and decrease in exchange rates
-producers often import raw materials
-stronger currency leads to cheaper exports and cheaper imports lead to decrease in input costs. lower costs equals more output
-weaker currency leads to expensive outputs and and expensive output lead to increase in input costs. higher costs equals less output.
factors influencing SRAS
exchange rates, costs in materials/ raw energy, and increase in tax rates
factor influencing SRAS -tax
taxes represent additional costs for the firms.
-higher taxes increases in costs which leads to less output. sras shifts left
lower taxes lower costs which leads to more output SRAS shifts right.
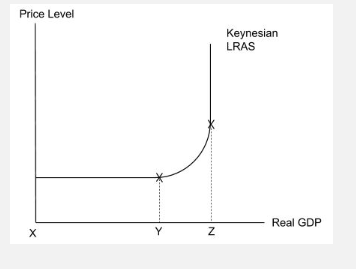
Keynesian LRAS
SICK BACK FLIP

In context of Keynesian LRAS what is spare capacity
when economy is producing below its potential output
neoclassical LRAS


Keynesian LRAS

factors influencing LRAS
factors influencing LRAS: technology advances
if more money is spent on technology the economy can produce goods in larger volume of goods or improve the quality of goods and services produced.
factors influencing LRAS: productivity
more productive labour and capital input will produce a larger quantity of output with the same quantity of input.
factors influencing LRAS: education and skills
-improves quality of human capital so it is more productive and more able to produce a wider variety of goods and services. become more innovative and able to contribute to technological advances.
factors influencing LRAS
technology, education and skills, productivity
factors influencing LRAS: government regulation
government regulation could limit how productive and efficient a firm can be if it is excessive.
factors influencing LRAS: changes and migration
net inward immigration and majority of population of working age, increase size of labour force which means economy can increase output.
factors influencing LRAS: competition policy
more competitive market encourages firms to be more efficient and more productive so not competed out of business. government can use effective competition policy to stimulate efficiency in the economy.
factors influencing LRAS
technology, migration, competition, government regulation, relative productivity . education and skills