Skeletal Muscle Biomechanics
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what are the behavioral properties of musculotendinous units?
Extensibility
Elasticity
Irritability
Ability to develop tension
these properties are common to all muscle, including the cardiac, smooth and skeletal muscle of human beings, as well as the muscles of other mammals, reptiles, amphibians, birds, and insects
what extensibility?
ability to stretch or to increase in length
what is elasticity?
ability to return to normal length after stretch
Muscle’s elasticity returns it to normal resting length following s stretch and provides for the smooth transmission of tension from muscle to bone
what is PEC?
parallel elastic component
what is the purpose of PEC?
provided by the muscle membranes
supplies resistance when a muscle is passively stretched
what is SEC?
Series elastics component
what is the purpose of SEC?
residing in the tendons
acts as a spring to store elastic energy when a tensed muscle is stretched
what is CC?
Contractile component
what is the purpose of CC?
muscle property enabling tension by stimulated muscle fibers
PEC, SEC, CC, these components of muscle elasticity are so named because?
because the membranes and tendons are respectively parallel to and in series (or in line) with the muscle fibers (muscle cells) which provide the contractile component
The parallel elastic component is suggested to consist of?
consist of the membranes surrounding the contractile components which includes the sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, the perimysium and the epimysium. Act most effectively against high loads
SEC is most effective as?
most effective against low elastic loads
what is irritability?
ability to respond to a stimulus
electrochemical (actin potential)
mechanical (external blow)
Stimuli affecting muscles are either electrochemical, such as an action potential from the attaching nerve, or mechanical, such as external blow to a portion of a muscle. When activated by a stimulus, muscle responds by developing tension
what is one behavioral characteristics unique to muscle tissue
the ability to develop tension
historically, the development of tension by muscle has been referred to as contraction, or the contractile component of muscle function
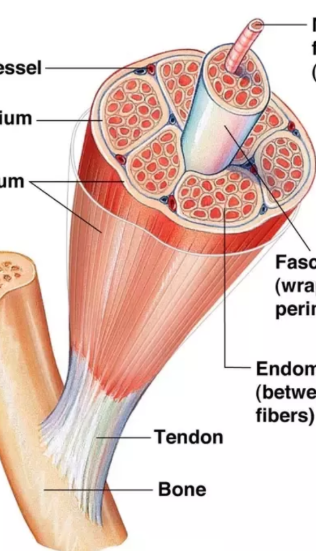
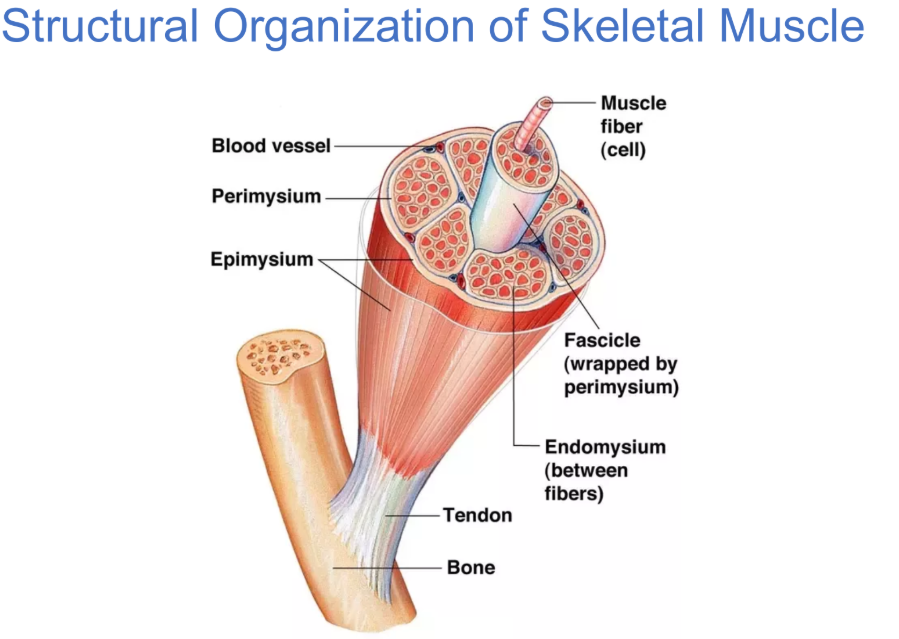
a whole skeletal muscle is considered an organ of the muscular system. Each or muscle consist of?
skeletal muscle tissue
connective tissue
nerve tissue
and blood or vascular tissue
what is epimysium?
the outermost sheath of connective tissue covering each muscle
in the epimysium, each muscle is made up of groups of muscle fibers called??
fascicles surrounded by a connective tissue layer called perimysium
multiple units of individual muscle fibers within each fascicle are surrounded by_______, a connective tissue sheath
endomysium
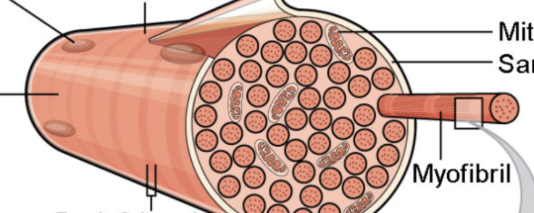
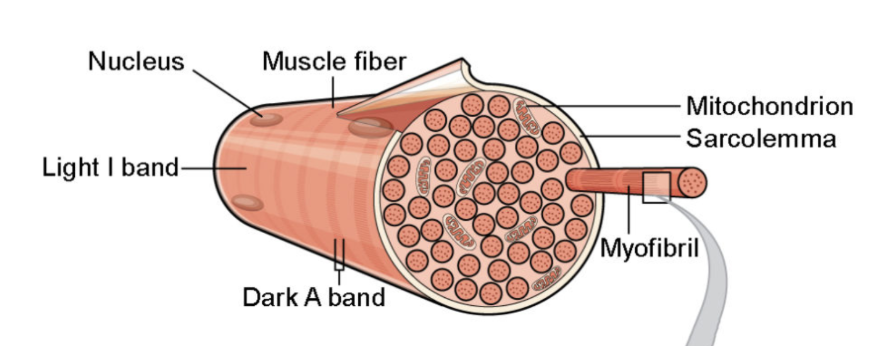
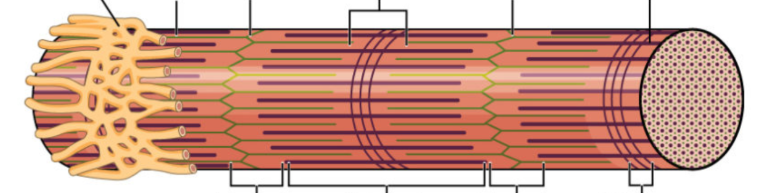
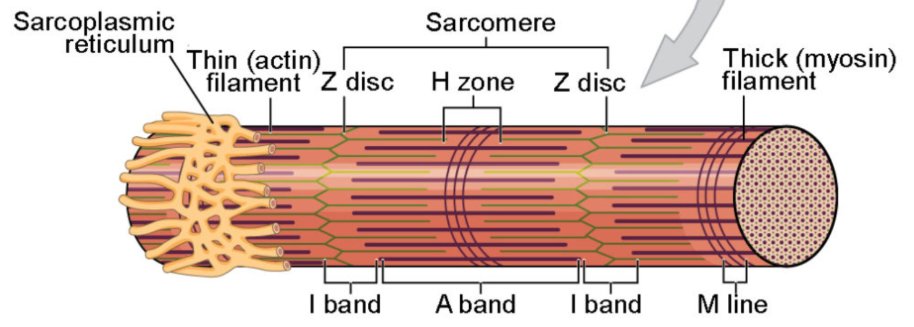
what is a muscle fiber?
muscle cell
threadlike shape
single muscle cell surrounded by a membrane called the sarcolemma and containing specialized cytoplasm called sarcoplasm
what are myofibrils?
special organelle, made of myofilaments (actin and myosin)
the two most essential myofilaments that make up the contractile elements of the muscle fiber are?
actin and myosin
they are arranged distinctively in a striated pattern to form the dark A band, the light I band, and the fundamental unit of contraction, also referred to as a sarcomere
what forms the dark A band?
the sarcomere consists of a central M line, and attached to it on either side are the thick myofilaments of myosin. This forms the dark A band
the sarcomere is bordered by the ?
by the Z-line which serves as the site of origin of the thin myofilaments of actin that project towards each other as they partially overlap the myosin filaments
the regulatory proteins, namely troponin____ and tropomyosin, play a key role in the myofilaments sliding mechanism leading to contraction
troponin C, I, T
what are the other major proteins that contribute to the mechanical properties of the muscle?
Titin and nebulin
what is a unique T-tubule?
There is a unique T-tubule system in place for the conduction of neuronal action potential to the interior of the muscle cell via invaginations of the sarcolemma to enhance coordination and uniform muscle contraction
what are the summary of events in muscle contraction and relaxation
Acetylcholine released from the axon terminal binds to receptors on the sarcolemma
An action potential is generated and travels down the T tubule
Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in response to change in voltage
Ca2+ binds troponin; cross-bridges form between actin and myosin
Acetylcholinesterase removes acetylcholine from the synaptic cleft
Ca2+ is transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Tropomyosin binds active sites on actin causing the cross-bridge to detach
what are some structural organization of skeletal muscle
some fibers run the entire length of a muscle; other are shorter
skeletal muscle fibers grow in both length and diameter from birth through adulthood
fiber diameter can be increased through resistance training
what is a motor unit?
single motor neuron and all fibers it innervates
considered the functional unit of neuromuscular system
the activation of one motor neuron will result in?
in a weak muscle contraction
the activation of more motor neurons will result in more muscle fibers being activated, and therefore?
and therefore a stronger muscle contraction
the higher the motor unit recruitment
the stronger the muscle contraction
what are the two types of motor unit?
Fast twitch (FT)
Slow twitch (ST)
what is fast-twitch fiber?
a fiber that reaches peak tension relatively quickly
what is slow-twitch fiber?
a fiber that reaches peak tension relatively slowly
what is recruited first?
ST fibers are always recruited first
slow twitch (ST) fibers are easier to activate than fast twitch (FT) fibers
increasing speed, force, or duration of movement involves progressive recruitment of motor units with higher and higher activation thresholds
what are the 2 types of fiber architecture?
parallel fiber arrangement
pennate fiber arrangement
what is parallel fiber arrangement?
fibers are roughly parallel to the longitudinal axis of the muscle
facilitates muscle shortening (muscle become shorten due to fiber shortening)
ex: sartorius, rectus abdominis, biceps brachii
what is pennate fiber arrangement?
shorth fibers attach to one or more tendons within the muscle
promotes muscle force production
ex: tibialis posterior, rectus femoris, deltoid
in pennate fiber arrangement, when muscle shorten they rotate about their?
their tendon attachment
this will increase the angle of pennation
greater angle of pennation will induce smaller amount of effective force
what is concentric contraction?
causes muscles to shorten, thereby generating force
Work against gravity to raise the body or objects
muscle contracts
what is eccentric contraction
cause muscles to elongate in response to a greater opposing force
work with gravity to lower the body or objects
what is isometric contractions?
generate force without changing the length of the muscle