Chemistry-Fuels
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is Density?
The mass of a material per unit of volume.
How do you calculate density?
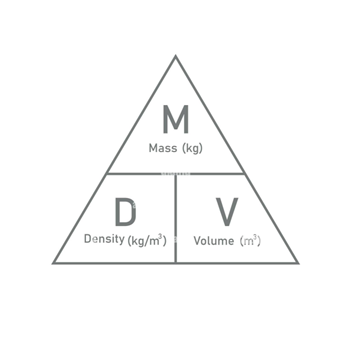
What is viscosity?
The ability of a fluid (liquid or gas) to flow. The higher the viscosity, the less easily it flows.
What is limewater?
A colourless liquid which turns cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it.
What is Complete Combustion?
A reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce Carbon Dioxide and water. Also releasing thermal energy.
What is Incomplete Combustion?
A reaction of a substance with a little oxygen to produce Carbon Monoxide and water. If no oxygen is present then the product will be Carbon.
What is acid rain
When Sulphur impurities react with oxygen this produces Sulphur Dioxide. This Sulphur Dioxide reacts with water to produce Sulphuric Acid (acid rain). Acid rain damages plaint life and and buildings/statues.
What is Global Warming?
Certain gases in the atmosphere trap the radiant energy from the sun (stops it reflecting back into space). This causes the average global temperature to increase over time.
What is Global Dimming?
Particulates from un-burnt fossil fuels enter form the atmosphere and block the suns energy from reaching the surface. This means that plants can photosynthesise less causing a drop in global food production.
What is Crude oil?
A black thick substance extracted from under the sea floor. A mixture of a very large number of compounds, mostly hydrocarbons.
What is a Hydrocarbon?
A molecule made up of only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
What is a Fuel?
A material such as coal, gas or oil that is burned to produce heat or power.
What do these gases do: Carbon dioxide, Carbon Monoxide, Nitrous Oxides, Sulphur Dioxide and Particulates?
Carbon Dioxide- Causes climate change
Carbon Monoxide- Poisonous gas which you cannot see or smell
Nitrous Oxide- Poisonous
Sulphur Dioxide- Reacts with water in atmosphere to cause acid rain
Particulates- Causes global trimming
What percentage of gases are in the atmosphere?
78% Nitrogen
21% Oxygen
1% ‘other‘ gases including Argon, Carbon Dioxide (0.03%), Hydrogen etc.
What is Distillation?
The separating of a mixture of liquids by the boiling point. (Using boiling and condensation).
What is the boiling point of water?
100 Degrees Celsius
What is flammability?
A measure of how quickly a specific material is capable of catching fire and burning.
What properties do you want a fuel to have?
High Flammability
Low Viscosity
To be a Liquid
What is Efficiency?
Getting the job done without wasting energy.
What is the Independent variable?
The variable being changed.
What is the Dependent variable?
The variable being measured
What is the Control variable?
The variables you keep the same.
What is the Risk Assessment?
Careful examination of what could cause harm to people during an investigation.
What are the effects of Carbon Monoxide poisoning?

How are fossil fuels formed?
Organisms die and fall to the sea floor
Layers of sediment fall on top, millions of years of heat and pressure force water out
Organisms turn into hydrocarbons forming fossil fuels
What is the Carbon Cycle?
Carbon dioxide is constantly cycling between organisms and the environment. This is called the Carbon Cycle.
How to test for Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen and Hydrogen?
Carbon Dioxide- bubble through limewater
Oxygen- Put a glowing splint inside the tube
Hydrogen- Put a lighted splint inside the tube
What are Hydrocarbons?
Monomers joined together to form a long chain called Polymer.
What are the 3 Polymer types?
Styrene
Ethene
Propene
How do you make Polymer more flexible?
Add plasticizers (they break bonds)
Reduce cross-links (bonds)
Decrease density
How do you make Polymer tougher?
Pack tightly together
Use cross linking agents to join chains
Increase the cross-links (bonds)
Increase density
What are the Problems with Plastics?
Pollution
Kill animals
Non Biodegradable
Eyesore
Microplastics
Starve animals
What are the Solutions for Plastics?
Recycle properly
Clean up plastic
Reuse plastic
Education on plastics
Alternatives for plastics
How do you make Polymers?
Polymers are made by chemical reactions that join lots of small molecules together to make long molecules. This can be used to produce plastics.
What are the stages of the Carbon Cycle?
Fossilization
Photosynthesis
Eating
Decomposition
Respiration
Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere
Combustion