MIDTERM: Lesson 2.1: Proteins and Amino Acids
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Proteins
Comes from the Greek word, meaning “first rank of importance”.
Antibody
Exposure to proteins will stimulate ________ production.
Proteins > polysaccharides > nucleic acids > lipids
Degree of immunogenicity:
Proteins
These are macromolecules composed of polymers of covalently linked amino acids that are involved in every cellular process.
Amphoteric
Proteins that can bear positive and negative charges.
High dielectric properties
Their solubility is due to?
12% - 20%
They provide _______ of the total daily body energy requirement.
50% - 70%
Proteins is composed of ________ of cells’ dry weight.
Structural
Proteins that provide structural components
Collagen
What example of structural proteins is the tendons and cartilage?
Keratin
What example of structural proteins is the hair, skin, wools, and nails?
Contractile
Proteins that is responsible in the movement of muscles?
Myosin and Actin
Examples of contractile proteins.
Transport
Proteins that carry essential substances throughout the body?
Hemoglobin
What example of transport protein is responsible in transport of oxygen?
Lipoproteins
What example of transport protein is responsible in transport of lipid?
Albumin
What example of transport protein is responsible in transport of hormones?
Storage
Proteins that store nutrients
Casein
Storage proteins that stores proteins in milk
Ferritin
Storage proteins that store iron in the spleen and liver
Hormone
Proteins that regulate body metabolism and nervous system
Enzymes
Propteins that catalyze biochemical reaction in the cells
Sucrase
What enzymes catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose?
Trypsin
Proteins that catalyzes the hydrolysis of proteins?
Protection
Type of proteins that recognize and destroy foreign substances
Immunoglobulins
Example of protection proteins
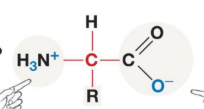
Non-Ionized form of Amino Acid
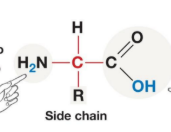
Ionized form of Amino Acid
Proline
______ is for the flexibility of the hinge region of immunoglobulins
Amino Acids
The monomer unit of proteins.
Polymers
Since amino acids are the monomer units of proteins. Therefore proteins are?
Linking together monomers unit
Polymers are made by ___________________?
Condensation
Polymers are made by linking together monomer units.
This process is known as?
Hydrolysis
Breaks polymers apart.
The final product has a lower potential energy bond than the reactant.
Polypeptide Structure
A chain of peptide bonds is considered the backbone or structural framework or the protein.
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary
Levels of Proteins Structure
Primary Sturcture
Linear order of amino acids
Every protein has a unique sequence or order of amino acids.
Secondary Structure
Alpha helix and beta sheets, not likely to contain proline.
Local folding of residues into regular patterns.
Created by interactions of the polypeptide backbone.
Tertiary Structure
3 dimensional folded shape of the protein
Global folding of a protein chain
Quaternary Structure
More than one polypeptide chain interacting to form a single structure
Higher-order assembly of proteins.
Non-Essential Amino Acids
The body can synthesize these for itself.
Food usually delivers these to the body but it is not essential for food to deliver these amino acids usually.
Essential Amino Acids
Cannot make on its own or cannot make sufficient amounts of these amino acids.
Therefore, they are required in the diet.
Conditionally Essential Amino Acids
Sometimes a non-essential amino acid becomes essential.
Protein Denaturation
If change in protein structure causes it to lose function.
Peptidases
Split most of the dipeptides and tripeptides into single amino acids.
Histones
strongly basic proteins that are insoluble in ammonium hydroxide but soluble in water.
Globins
sometimes classed as histones but appear to be a separate group as they are not basic nor are they precipitated by ammonium hydroxide.
Biuret test
Violet, general test for proteins/peptides
Xanthoproteic test
Tests tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine
Concentrated nitric acid, tests aromatic amino acids
Millon’s test
Detects tyrosine in the phenolic group
Composed of mercuric nitrate color red
Hopkins-Cole test
Detects tryptophan
Ninhydrin test
Detects the free amino group
Rheuman’s purple