Human Anatomy Chapter 6 The Skeletal System 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Calcium and phosphate
raw materials for calcified ground substance
vitamin A
promotes formation of glycosaminoglycans (protein-carb fibers)
vitamin C
promotes collagen cross-linking adding stiffness
vitamin D
necessary for calcium absorption by small intestine and reduces urinary calcium loss
Calcitonin
secreted by thyroid gland and stimulates osteoblasts in children and pregnant women
Parathyroid hormone
secreted by parathyroid glands and stimulates bone reabsorption to boost level of calcium in blood
acromegaly
features of bones start to get bigger due to adult growth hormone hypersecretion
osteitis deformans
excessive osteoclast proliferation and bone resorption
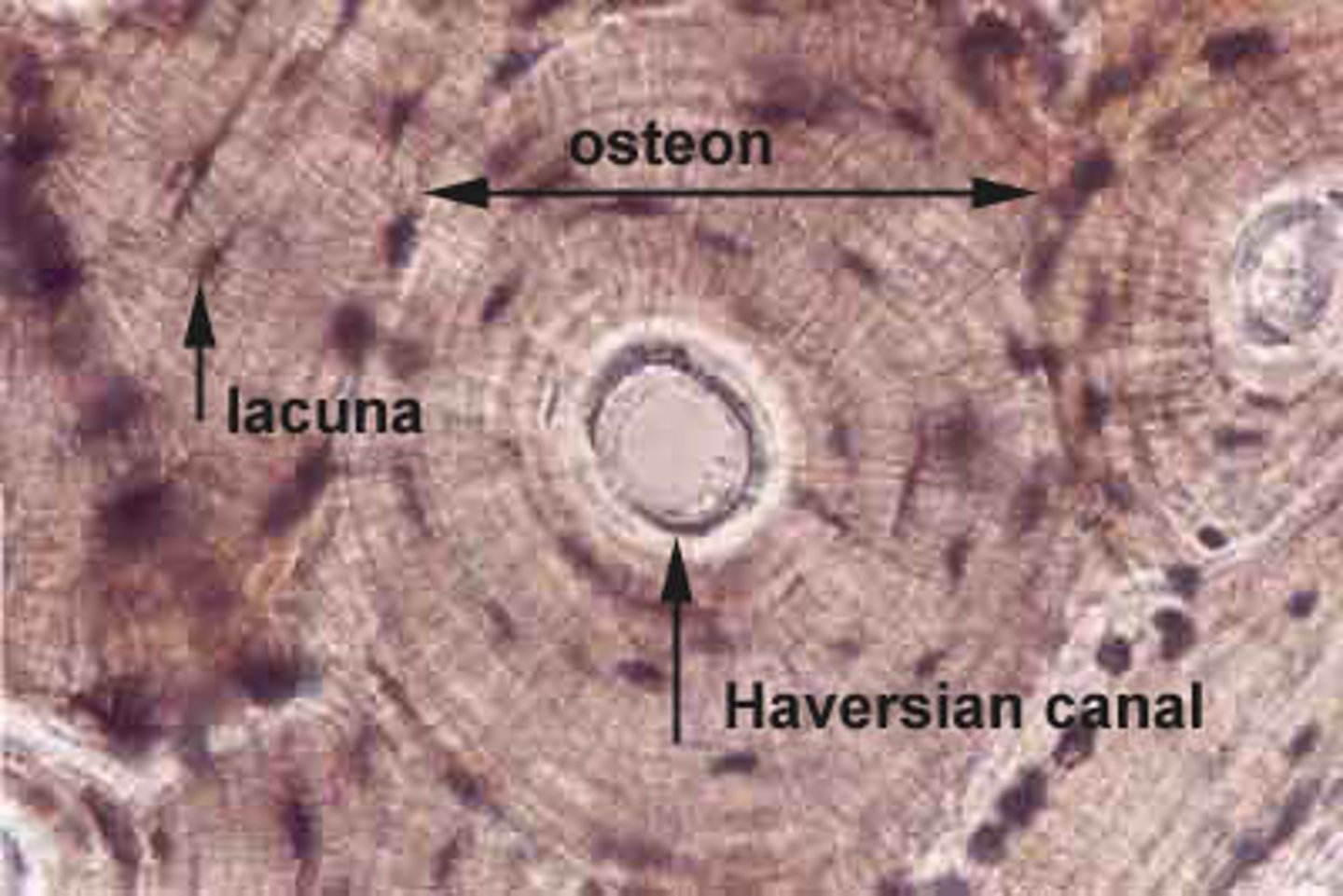
Lacunae
cavities that house osteocytes
Canaliculi
small canals that connect lacunae
Osteon
-basic unit
-concentric lamellae
-central canal
growth hormone
promotes intestinal absorption of calcium and stimulates growth plates and bone elongation
estrogen and testosterone
stimulate long bone growth during adolescence
Osteopenia
loss of bone
complete fracture
bone is broken into two or more pieces
impacted fracture
one bone fragment is driven into the marrow cavity or spongy bone of the other
Osteoporosis
-bone lose mass and become subject to pathological fractures
-treatment: bis-phosphonates and parathyroid hormone
-Prevention: weight-bearing exercise, adequate calcium and protein
osteosarcoma
bone cancer
Cartilage
embryonic precursor of most bones and covers many joint surfaces
Ligaments
hold bone to bone at joint
Tendons
attach muscle to bone
Functions of the skeleton
support, protection, movement, electrolyte balance, acid-base balance, blood formation
What is bone?
connective tissue with a hard matrix
What are the other tissues present in bone?
blood, bone marrow, cartilage, adipose tissue, nervous tissue, and fibrous CT
What are the bone shapes?
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
Flat bones
-thin, often curved
Long bones
-rigid levers for movement
-compact and spongy bone tissue
-two epiphyses at ends of diaphysis
-marrow cavity
Short bones
-glide within joints
-composed of spongy bone sandwiched between plates of compact bone
Irregular bones
complex (weird) shapes
Sesamoid bones
oval, generally within tendon
Epiphysial line
remnant of growth plate
Periosteum
covering of bone
Nutrient foramina (long bone)
tubes/holes in bone for vessel
Endosteum
lining
trabeculae
honey comb like structure
Osteogenic cells
bone stem cells
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells
Osteocytes
mature bone cells, contribute to bone maintenance/homeostasis
Osteoclasts
bone-dissolving macrophages
Bone matrix
1/3 organic (collagen and large protein-carbohydrate complexes), 2/3 inorganic (85% hydroxyapatite, 10% calcium carbonate, and 5% other inorganic minerals)
spongy bone contains
-spicules and trabeculae
-porous appearance where the spaces filled with bone marrow
spicules
rods and spines of bone
bone marrow
A soft tissue inside medullary cavities of long bones, spaces within spongy bone, and large central canals within osteons.
red marrow
hematopoietic tissue, both red and white blood cells are made here
yellow marrow
mainly fat
red marrow location
skull, vertebrae, sternum, ribs, parts of pelvic girdle, and proximal heads of humerus and femur
yellow marrow location
long bones of limbs
ossification
bone formation, begins with mesenchyme
two methods of ossification
intramembranous and endochondral
Intramembranous ossification
-produces flat bones of skull and most of clavicle
-bone develops in a fibrous sheet resembling the dermis
endochondral ossification
-most bones develop this way
-bone develops from hyaline cartilage model
Bone elongation
bones grow longer at epiphysial plates
metaphysis
area of transition from cartilage to bone at each end of marrow cavity
Appositional growth
growth in diameter and thickness
stress fracture
caused by abnormal trauma
pathological fracture
occurs in bone weakened by a disease such as osteoporosis
closed reduction
nonsurgical realignment of broken bone ends and splinting of bone
open reduction
surgical realignment of broken bone ends
closed fracture
broken bone with no open wound
open fracture
skin is broken, bone protrudes through skin or wound extends to fractured bone
nondisplaced fracture
the portions of the bone are still in correct anatomical alignment
displaced fractures
the portions of the bone are out of anatomical alignment
comminuted fracture
bone is broken into three or more pieces
greenstick fracture
bone is bent toward one side and has incomplete fracture on opposite side
hairline fracture
fine crack in which sections of bone remain aligned
depressed fracture
broken portion of bone forms a concavity
linear fracture
fracture parallel to long axis of bone
transverse fracture
fracture perpendicular to long axis of bone
oblique fracture
diagonal fracture, between linear and tranverse
spiral fracture
fracture spirals around axis of long bone as the result of twisting stress