SPTM314 Exam 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
NIKE
What is the largest sport-related company?
Financial Management
Using financial information to make the best decisions for your organization
Revenue
Money coming INTO an organization
Expenses
Costs that are incurred by an organization
Credit
Money owed to the business by others
Debt
Money owed to others by the business
Balance Sheet
The financial position of a business on a specific day
Assets=Liabilities+Owners Equity
Asset
Items of value such as cash, inventory, plant, property, equipment, accounts receivable, etc
Liabilities
Items of value owed to others
-Acc payable
-Notes payable
-Outstanding salaries/contracts
Owner's Equity
the amount remaining after the value of all liabilities is subtracted from the value of all assets
Income Statement
provides a financial summary of the firm's operating results during a specified period
Cash Flow Statement
Explains the inflows/outflows of cash only during a specific period of time
Current Ratio
Current Assets/Current Liabilities
Quick Ratio
(Current Assets - Inventory) / Current Liabilities
Net Working Capital
current assets - current liabilities
Total Asset Turnover Ratio
revenue/Total Assets (avg)
Debt Ratio
total liabilities/total assets
Debt-Equity Ratio
Total Debt/Total Equity
Net Profit Margin
Net Income/Revenue
Gross Profit Margin
EBIT/Revenue
Return on Assets
net income/average total assets
Return on Equity (ROE)
Net Income / Average Stockholders' Equity
Market Value
(Price per share of common stock) X (# of Outstanding shares)
Book Value
Total Assets-Total Liabilities
Earnings Per Share
(Net income)/(avg number of shares outstanding)
Price-Earnings Ratio
price per share/earnings per share
Sole Proprietorship
a business owned and managed by a single individual
-Owner keeps all profits
-unlimited liability
Partnership
a business owned by two or more people
Corporation
A distinct legal entity composed of one or more individuals/entities
-Most complicated to start
-Board of Directors
-Shareholders
-Easy to raise capital
Public Corporation
a corporation whose stock anyone may buy, sell, or trade
Private Corporation
business whose shares are not traded publicly on the stock market
S Corporation
a form of corporation that avoids double taxation by having its income taxed as if it were a partnership
Limited Liability Partnership
a type of partnership in which all partners are limited partners
Forecasting
Predicting future revenues and expenses
Budget
A tool used to predict the income and expenses of an organization on a long-term and short-term basis
Operational Budget
Day to day budget
Lists sales/revenues and expenditure for normal operations (Day-to-Day)
Capital Budget
Long term debt
Focuses on future expenditures such as new buildings, stadiums, and arenas (Long-Term)
Cash Flow Budget
examines the inflows and outflows of cash in a business on a day-to-day basis
Ability to pay bills with incoming cash
Zero Based Budgeting
A budgeting approach in which managers begin with a budget of zero and must justify every dollar put into the budget.
Incremental/Decremental Budgeting
Taking a prior budget and increasing or decreasing all items by some %
VERY EASY
Present Valuation
Measuring the present value of future cash flows
- (Cash Flow)/(1+r)
Annuity
A constant stream of payments that is received for a fixed number of periods
Revenue Sharing
Narrow revenue gap between large and small market teams by dividing funds equally amongst all teams
EBITDA
Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization
10-Q report
Quarterly report
10-K report
Required annual report filed with the SEC by publicly held firms
Uses of Ratio Analysis
- Comparing the performance of the business with previous years
- Comparing the performance of the business with its competitors'
- Comparing against other organizations of similar size and scope
Inventory Turnover Ratio
cost of goods sold/average inventory
Book value
Book value = Total assets - total liabilities
Present Value Formula
PV=FV/(1+r)^n
= Cash flow received in 1 year/(1 + the normal rate of return)
Our example:
Lets assume the current interest rate is 4%
PV = 105,000/1.04
PV=100,962
Future Value Formula
FV=PV(1+r)^n
Annuity Formula
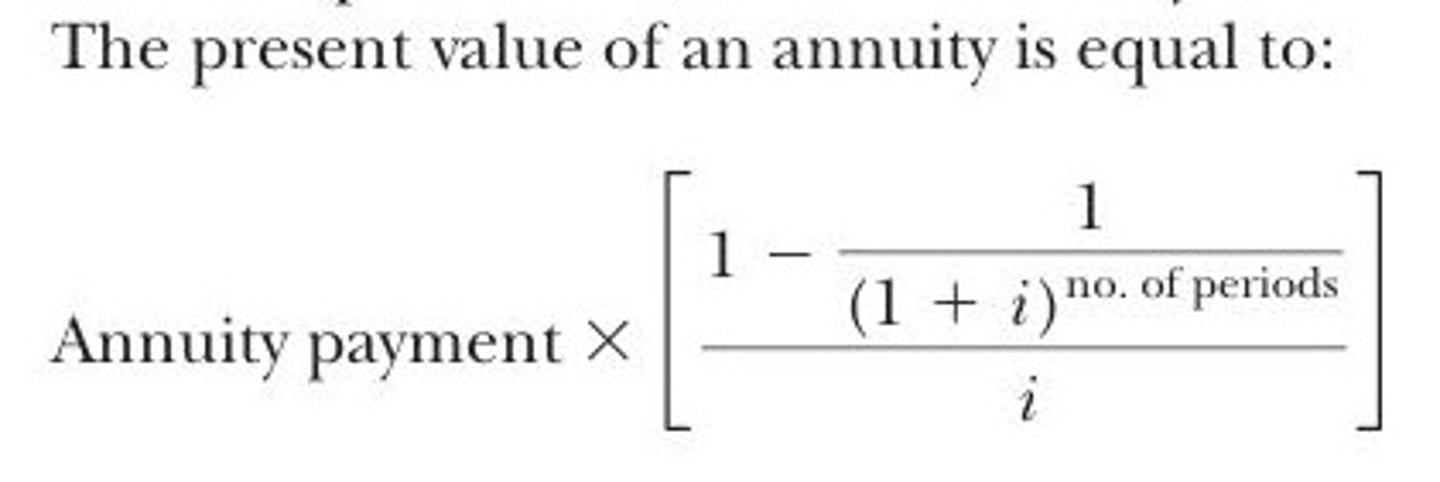
MLB National TV deal dates
ended 2021 new ones run 2022-2028
During covid what was MLB player prorated salary?
37%
MLB revenue sharing
-The goal is to narrow the revenue gap between large and small market teams
-Transfer money from the large market to small-market teams
Approximately 34% of net local revenue after ballpark expense. Funds divided equally amongst all teams
mlb revenue sharing supplemental plan
Approximately 14% of net local revenue after ballpark expenses
Funds are redistributed based on "performance factors" which measure financial performances of each team → need to hit certain revenue quotas etc
Top 13 Markets not permitted to receive $ from this plan
Luxury tax violators not permitted to be revenue sharing plan receivers (only pay in)
NEGATIVE of the system → the clubs can use the funds for anything even personal profit
MLB Salary Arbitration
Arbitrator must select either the player's salary proposal (after a couple years in the league) or the teams proposal
(based of performance)
can't split the difference or choose another figure
set up to drive compromise between the parties before trial
MLB Luxury Tax
funds paid to the tax is distributed to clubs, not over the tax
Tax % increased each time you have an additional offense
Put in place to limit large teams from buying everyone
Define finance
involves identifying current and future revenues and expenses and determining future budgets to help an organization succeed.
credit vs debit
Credit - $$ owed to the business by others
Debt - money owed to others by the business