chem 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
1
New cards
Heat is the________________________________
transfer of thermal energy between two bodies that are at different temperatures.
2
New cards
Heat will always flow from the _________substance towards the__ ______________ substance.
hotter, cooler
3
New cards
Fast moving particles are associated with having more _______________, while _____moving particles are associated with having less energy.
energy, slow
4
New cards
Temperature is the measurement of_____________________
thermal energy
5
New cards
When fast moving molecules hit the sides of a thermometer, they transfer energy to the ___________________
thermometer
6
New cards
As this energy is ______________to the liquid within the thermometer, the liquid will go up inside the thermometer.
transferred
7
New cards
does temperature equal thermal energy?
no
8
New cards
Temperature measures__________________________________
how fast particles are moving
9
New cards
Energy measures ____________and is given in the units of _________
heat , Joules (J).
10
New cards
________________________ is the study of heat changes in chemical reactions.
Thermochemistry
11
New cards
_________________ describes the energy lost or gained within the system of the reaction.
Enthalpy
12
New cards
enthalpy (ΔH) you will do as follows
ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants
13
New cards
As enthalpy is a measurement involving __________its units will be based in Joules (J).
energy
14
New cards
Enthalpy units will be ______________
kJ/mol
15
New cards
alternate equation for enthalpy:
\
\
ΔH=−Q/mol
16
New cards
Since enthalpy is a finite, measurable amount it can be either a ______________value or a ___________value
positive , **negative**
17
New cards
**________________________**processes are any processes that give off heat
**Exothermic**
18
New cards
**__________________** processes are any processes where heat has to be absorbed
Endothermic
19
New cards
supplied to the system from the surroundings
**Endothermic**
20
New cards
that is to say, that they transfer thermal energy from the system into the surroundings.
**Exothermic**
21
New cards
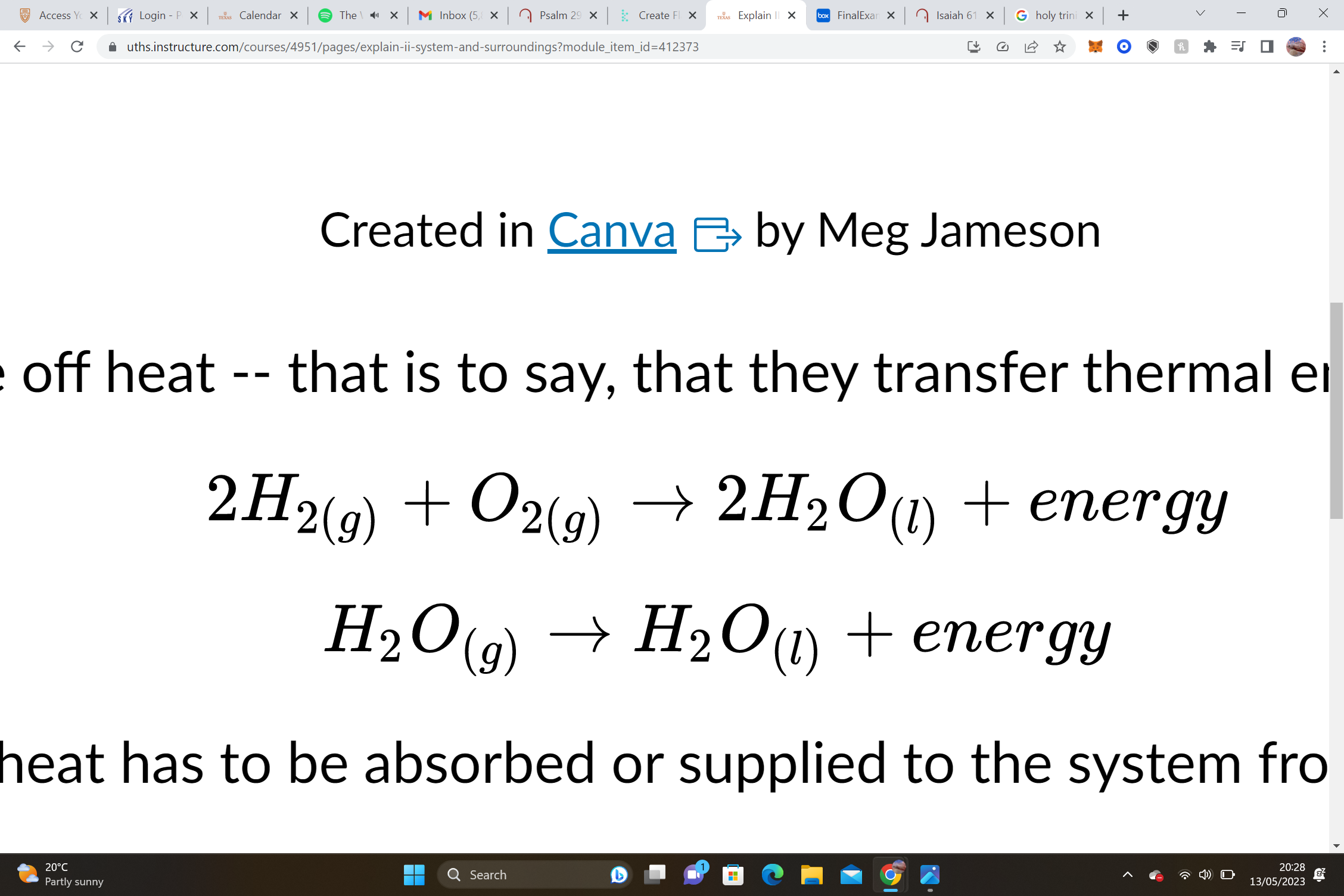
endo or exo
exo
22
New cards

endo or exo
endo
23
New cards
_______________ processes have less energy in the reactants than in the products
endothermic
24
New cards
_______________ processes have less energy in the products than the reactants
exothermic
25
New cards
the amount energy it takes to get beyond the activated complex and complete the reaction
activation energy
26
New cards
______________ reactions have a small reaction energy
exothermic
27
New cards
___________________________________reactions have a large activation energy
endothermic
28
New cards
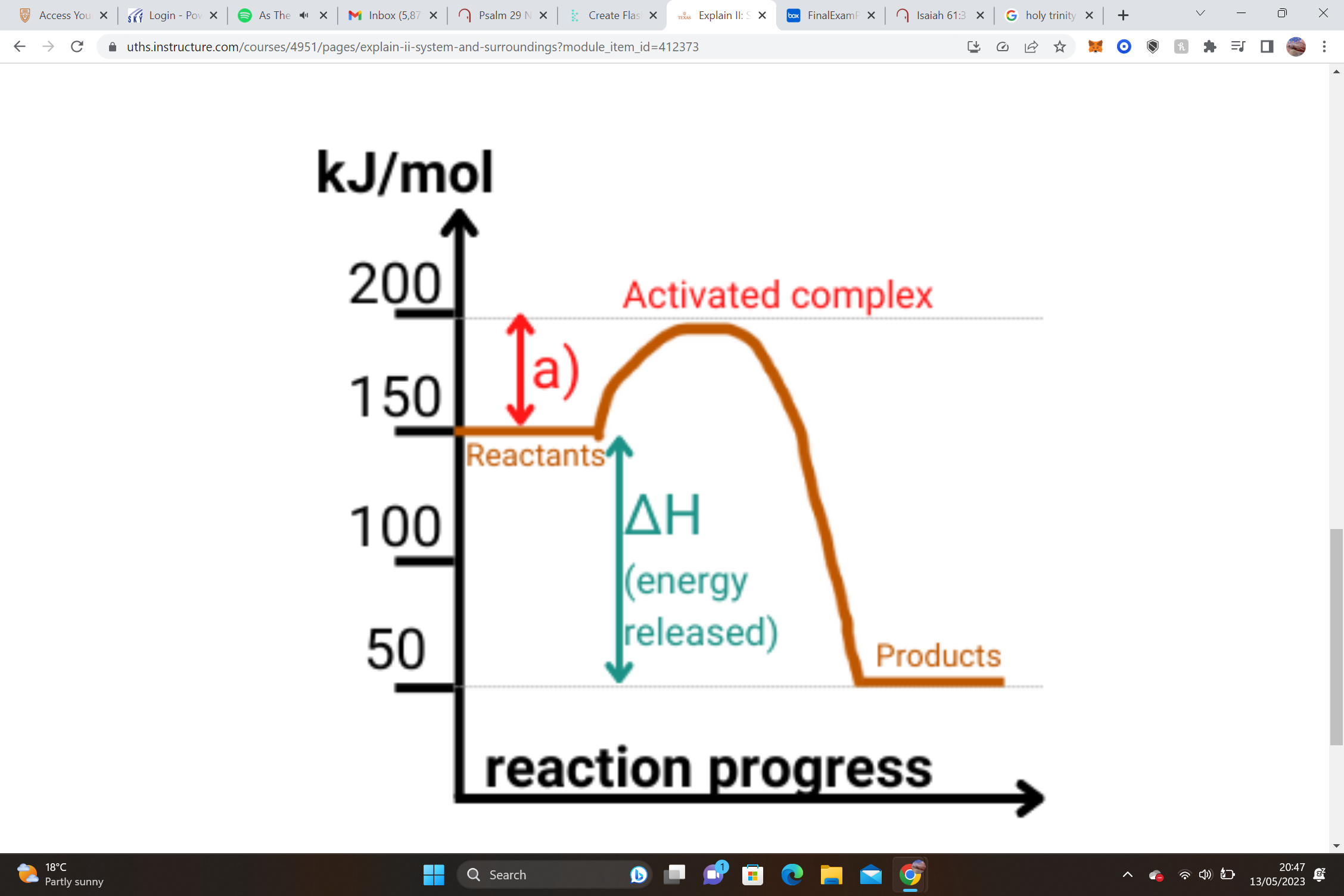
endo or exo and why
exo, ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants= ΔH = 50 - 150= -100kJ(negative)
29
New cards
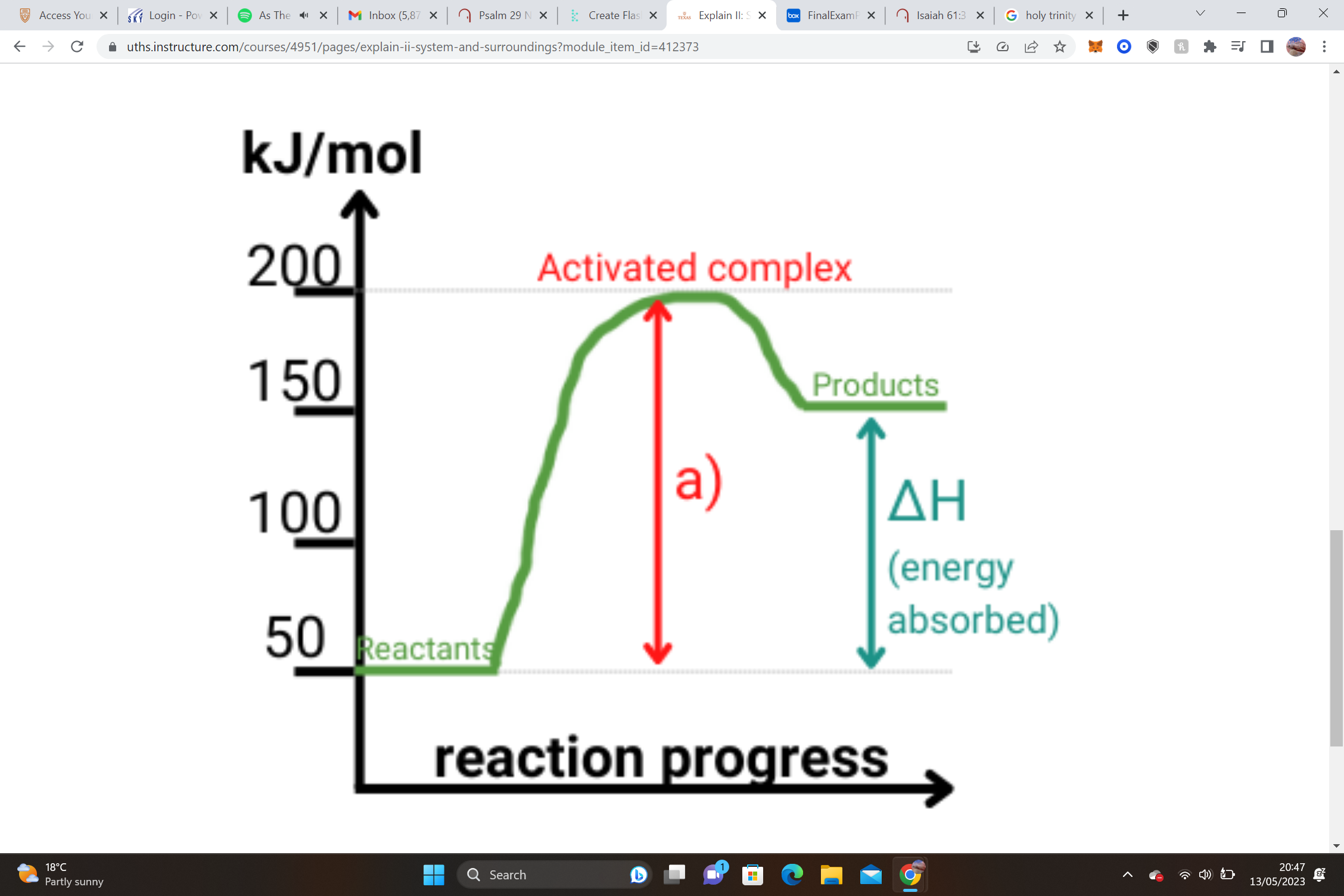
endo or exo
endo, ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants= ΔH = 150 - 50= +100kJ(postive)
30
New cards
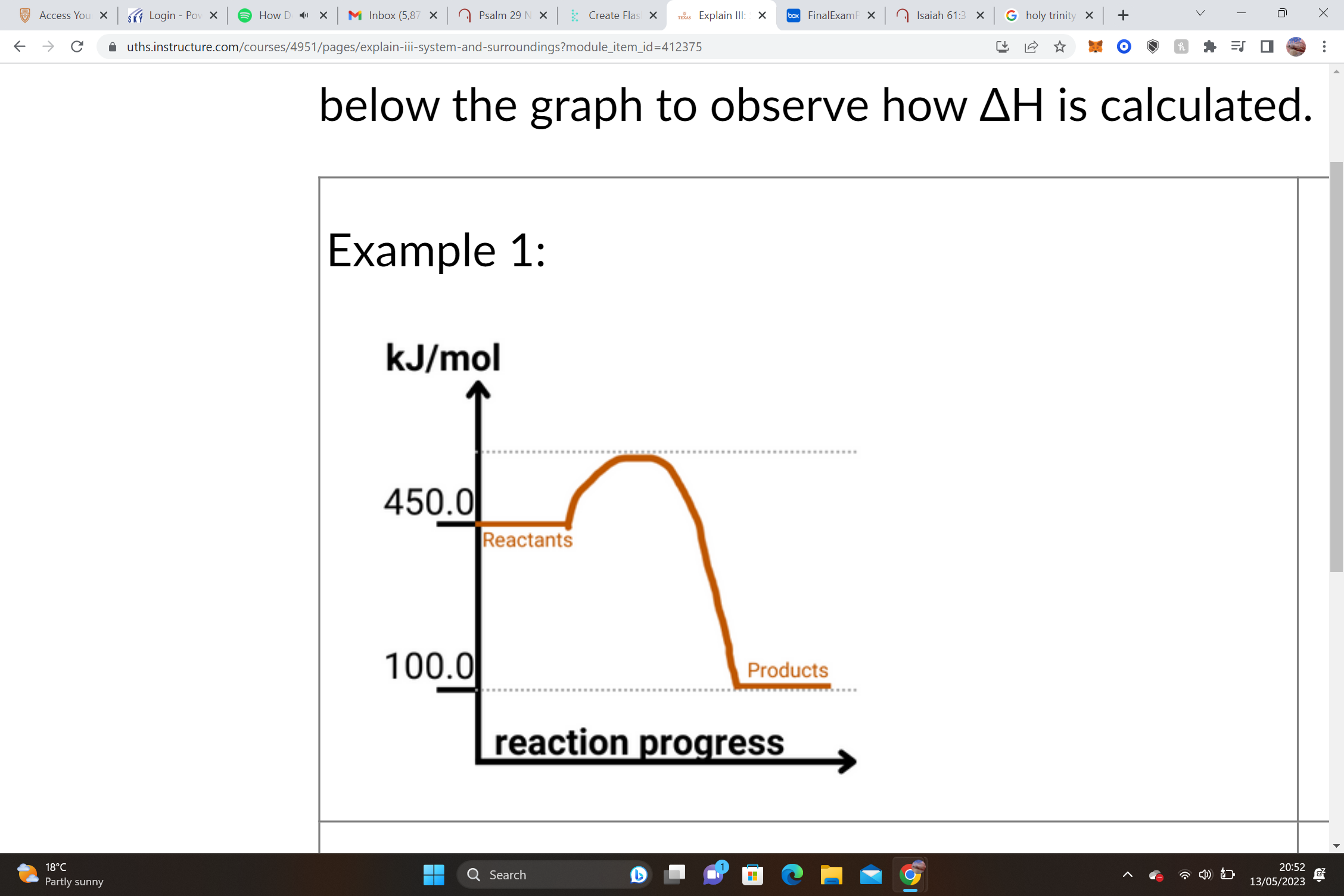
1. Reactants =______________ Products = 100.0 kJ/mol
ΔH = Products – Reactants= _____________ __–__ __________ __=__ _____________
1. – ΔH values are _______________, and we know that this shape of graph is an ________________graph.
450.0 kJ/mol, 100.0 kJ/molΔH , 100.0 kJ/mol, 450.0 kJ/mol, -350.0 kJ/mole, exothermic
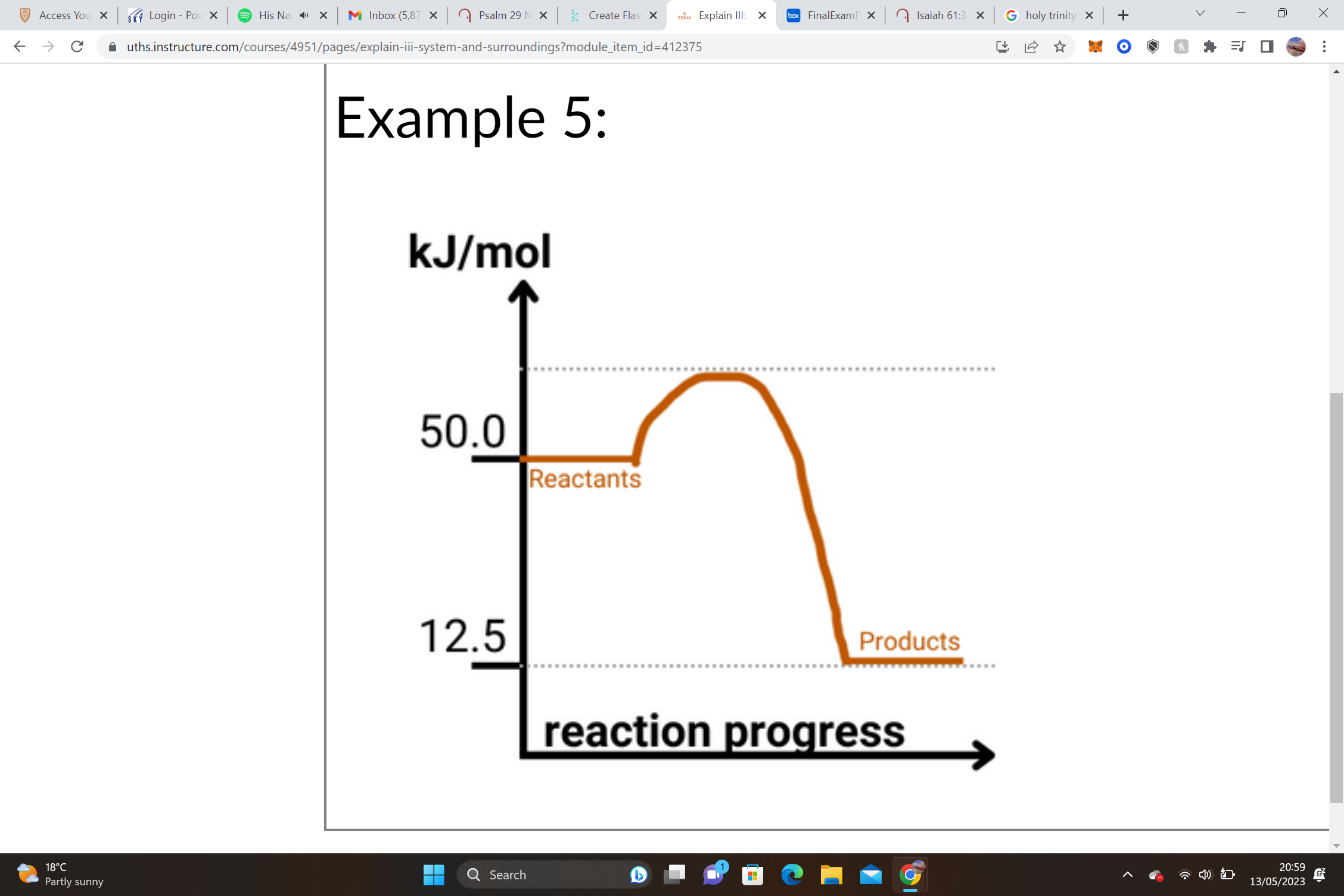
31
New cards
1. Reactants = __________________ Products = __________________ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __________________– __________________= __________________ kJ/mole
3. ______ΔH values are __________________, and we know that this shape of graph is an __________________ graph.
1. Reactants = __210.0 kJ/mol__ Products = __150.0 kJ/mol__ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __150.0 kJ/mol__– __210.0 kJ/mol__= __-60.0__ kJ/mole
3. __-__ΔH values are __exothermic__, and we know that this shape of graph is an __exothermic__ graph.
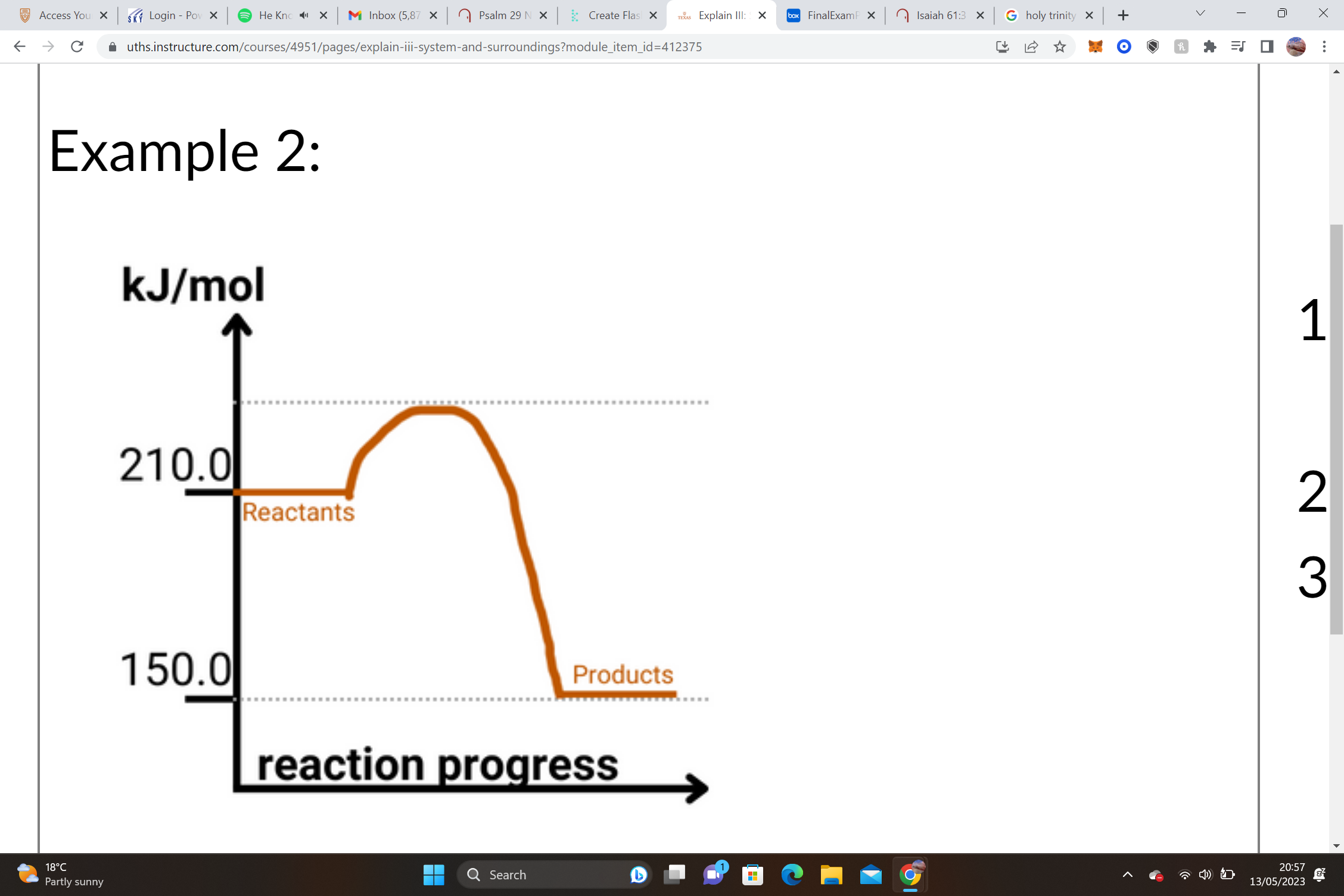
32
New cards
1. Reactants = __________________ Products = __________________ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __________________– __________________= __________________ kJ/mole
3. ______ΔH values are __________________, and we know that this shape of graph is an __________________ graph.
1. Reactants = __12.5 kJ/mol__ Products = __50.0 kJ/mol__ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __50.0 kJ/mol__– __12.5 kJ/mol__= +__37.5__ kJ/mole
3. __+__ΔH values are __endothermic__, and we know that this shape of graph is an __endothermic__ graph.
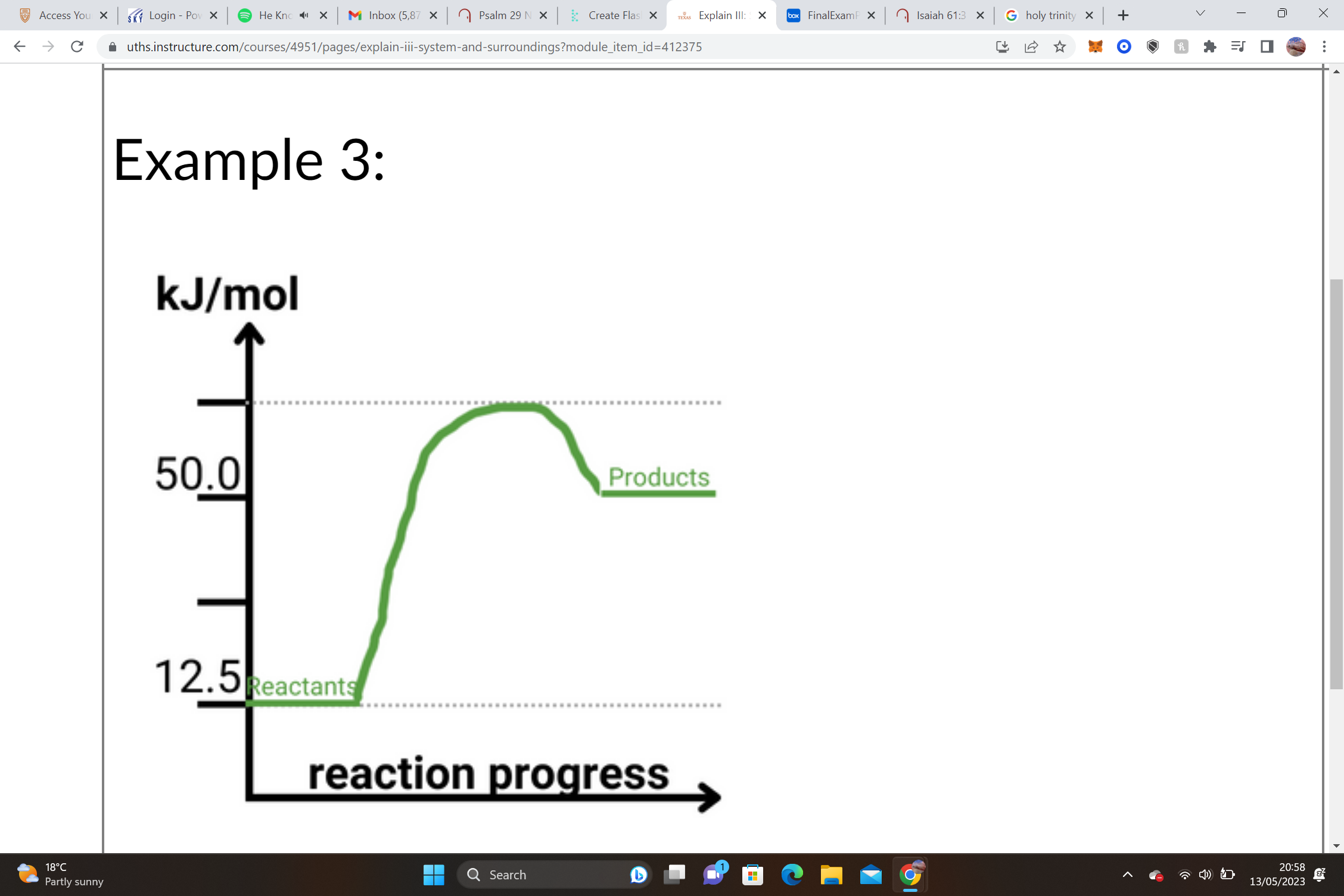
33
New cards
1. Reactants = __________________ Products = __________________ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __________________– __________________= __________________ kJ/mole
3. ______ΔH values are __________________, and we know that this shape of graph is an __________________ graph.
1. Reactants = __125.0 kJ/mol__ Products = __950.0 kJ/mol__ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __950.0 kJ/mol__– __125.0 kJ/mol__= +__825.0__ kJ/mole
3. __+__ΔH values are __endothermic__, and we know that this shape of graph is an __endothermic__ graph.
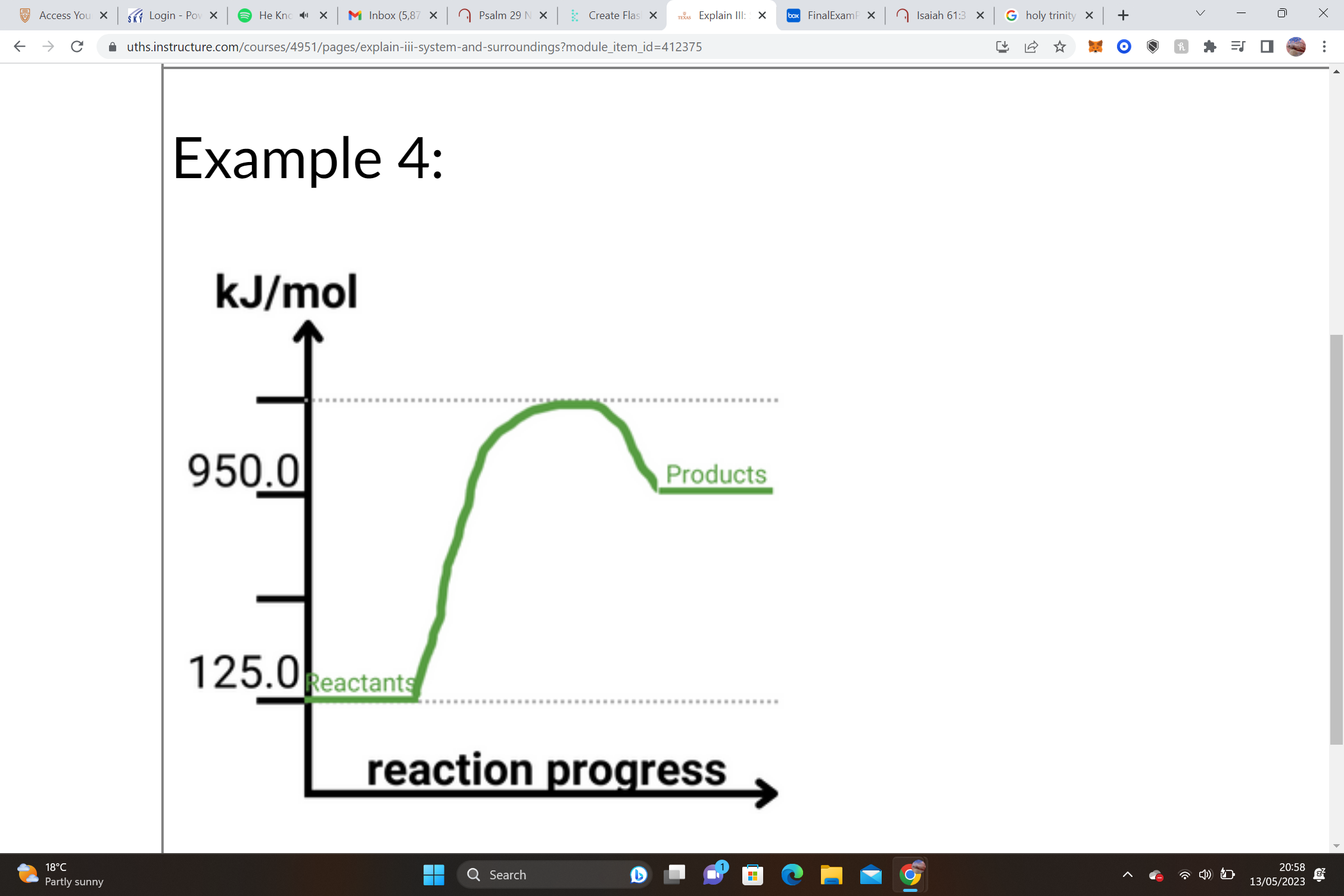
34
New cards
1. Reactants = __________________ Products = __________________ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __________________– __________________= __________________ kJ/mole
3. ______ΔH values are __________________, and we know that this shape of graph is an __________________ graph.
1. Reactants = __50.0 kJ/mol__ Products = __12.5 kJ/mol__ΔH = Products – Reactants
2. __12.5 kJ/mol__– __50.0 kJ/mol__= -__37.5__ kJ/mole
3. __-__ΔH values are __exothermic__, and we know that this shape of graph is an __exothermic__ graph.
35
New cards
Temperature measures heat
False
36
New cards
temperature measures the _______________
kinetic energy of molecules
37
New cards
heat measures __________
energy
38
New cards
Which part of a reaction has more energy for an exothermic reaction?
Reactants
39
New cards
A thermometer works by directly measuring the amount of heat energy around it.
False
40
New cards
You light a campfire to cook s’mores. The system for this reaction is ___________, and the surroundings are ___________.
the logs burning on the fire; everything outside of the fire
41
New cards
Which part of a reaction has more energy for an endothermic reaction?
Products
42
New cards
Which of the statements below are true regarding systems and surroundings?
A system is where the reaction occurs, while the surroundings are where the reaction came from
Surroundings include the reaction itself
A system is where the reaction occurs, while the surroundings are everything outside of that reaction
A system is outside of the reaction itself
A system is where the reaction occurs, while the surroundings are where the reaction came from
Surroundings include the reaction itself
A system is where the reaction occurs, while the surroundings are everything outside of that reaction
A system is outside of the reaction itself
A system is where the reaction occurs, while the surroundings are everything outside of that reaction
43
New cards
An ice cube melts on your hand. This is an example of an ______________ reaction.
Endothermic
44
New cards
A campfire is an example of an _____________ reaction.
\
Exothermic
Exothermic
45
New cards
A sample of salt is placed within a Styrofoam cup filled with water. The salt dissolves rapidly. The water inside the cup gets colder, while the cup stays the same temperature. The salt is the _______, while the water is the ___________.
system, surroundings
46
New cards
Liquid water is placed into a freezer. Heat transfers from the __________ to the ________, resulting in an ___________ process.
water, freezer, exothermic
47
New cards
an exothermic reaction loses energy, so the products will have _______________ than the reactants.
less energy
48
New cards
a thermometer measures the amount of ______________ from molecules. This kinetic energy is transferred to the molecules inside of the thermometer.
kinetic energy
49
New cards
the system is where the ______________happens, the surroundings are ________________________
reaction, everything outside of that
50
New cards
an endothermic reaction __________energy, so it will have__ _________energy after it has reacted
gains, more
51
New cards
First, the ΔH values for the _______________must be found, and then the ΔH values for the _________must be found.
products , reactants
52
New cards
. First, the ΔH values for the products must be found, and then the ΔH values for the reactants must be found. After finding these values, solving _________minus __________________will give you the ΔH value.
products, reactants
53
New cards
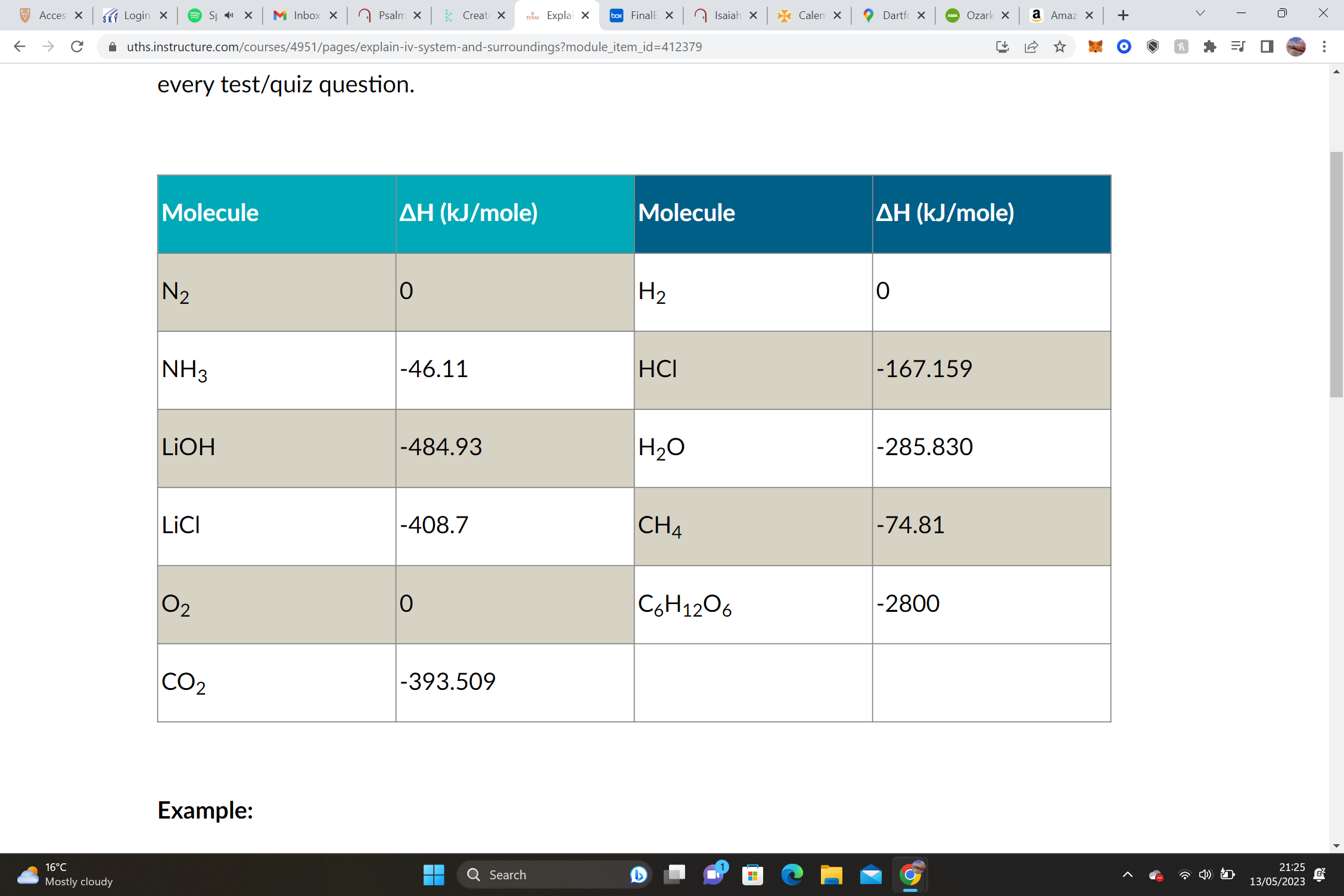
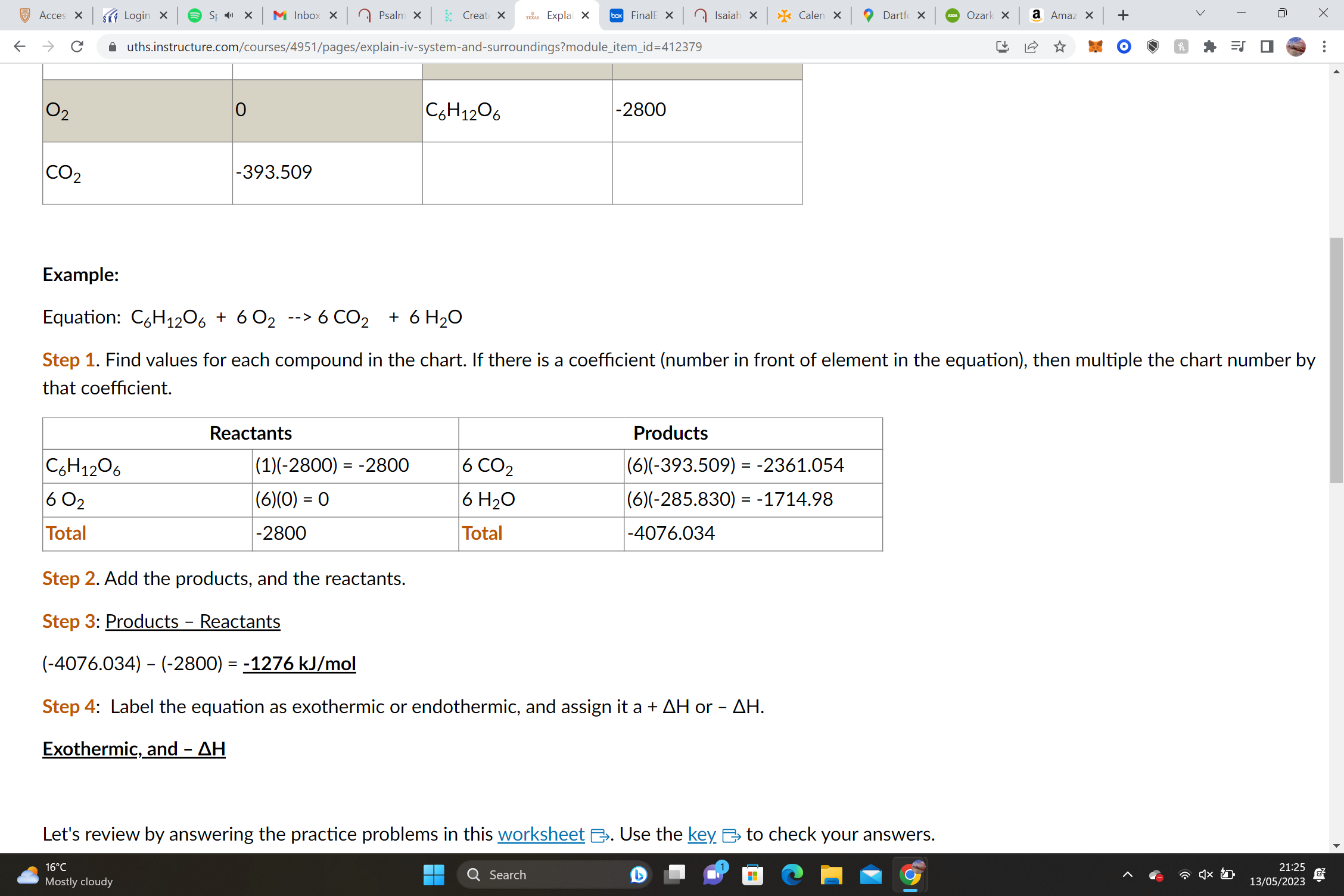
Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
(-4076.034) – (-2800) = **-1276 kJ/mol, Exothermic, and – ΔH**
54
New cards
**Exothermic ΔH values (-ΔH), are placed on the far ____________of an equation**.
right
55
New cards
Endothermic ΔH values (+ΔH), are placed on the far ___________of an equation
left
56
New cards
Exo = ________
exit
57
New cards
Endo = ______________
enter
58
New cards
H2 + Cl2 → 2 HCl + 185 kJ/mol
Information =
Information =
Exothermic, and -ΔH
\
\
59
New cards
H2 + F2 → 2 HF + 546 kJ/mol
Information =
Information =
Exothermic, and -ΔH
\
\
60
New cards
38\.0 kJ/mol + Fe3O4 + CO --> 3FeO + CO2
Information =
\
Information =
\
Endothermic and + ΔH
61
New cards
Equation: N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Equation: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
Step 1: N2 = 0, H2 = 0, NH3 = -46.11 \* 2 = -92.22
Step 2: Products = -92.22, Reactants = 0+0 = 0
Step 3: Products - Reactants; -92.22 - 0 = -92.22 kJ/mole
Step 4: Exothermic, -ΔH
\
Step 1: N2 = 0, H2 = 0, NH3 = -46.11 \* 2 = -92.22
Step 2: Products = -92.22, Reactants = 0+0 = 0
Step 3: Products - Reactants; -92.22 - 0 = -92.22 kJ/mole
Step 4: Exothermic, -ΔH
\
62
New cards
Equation: LiOH + HCl --> H2O + LiCl
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Equation: LiOH + HCl → H2O + LiCl
Step 1: LiOH = -481.93, HCl = -167.159, H2O = -285.830, LiCl = -408.7
Step 2. Products = -285.830 + -408.7 = -694.53; Reactants = -481.93 + -167.159 = -649.089
Step 3: Products - Reactants; (-694.53) - (-649.089) = -45.44 kJ/mole
Step 4: Exothermic, -ΔH
\
Step 1: LiOH = -481.93, HCl = -167.159, H2O = -285.830, LiCl = -408.7
Step 2. Products = -285.830 + -408.7 = -694.53; Reactants = -481.93 + -167.159 = -649.089
Step 3: Products - Reactants; (-694.53) - (-649.089) = -45.44 kJ/mole
Step 4: Exothermic, -ΔH
\
63
New cards
Energy from a reaction was determined to be 12552 J, when burning 16.3 grams of CH4. What is the total enthalpy of the reaction?
dive j by 1000 to kj, multiple by molar mass (12.011+ 4x1.008) divide by 16.3,
\
\-12.4 kJ/mole
\
\-12.4 kJ/mole
64
New cards
Energy from a reaction was determined to be 11563 J, when burning 15.0 grams of H2. What is the total enthalpy of the reaction?
\-1.54 kJ/mole
65
New cards
amount of energy being present fortmula
Q = m・c・Δt
66
New cards
**Q meaning in Q = m・c・Δt** and unit
the amount of heat leaving or entering a substance, and is measured in Joules.
67
New cards
**m meaning in Q = m・c・Δt** and unit
mass of substance being heated. Mass is measured in grams.
68
New cards
**m in Q = m・c・Δt** This mass is not what is being ________, but the mass of the substance that is being heated or cooled because of the reaction. This substance is located in the ____, and not in the system.
reacted, surroundings
69
New cards
**c meaning in Q = m・c・Δt** and unit
**specific heat of substance being heated. Specific Heat is measured in J/g*°C**
70
New cards
Specific heat is defined as_________________________________________
the amount of heat that is required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius (or 1 kelvin).
71
New cards
Every __________________has its own specific heat.
molecule
72
New cards
**Δt =** change in temperature of substance being heated. Because temperature is measured in delta T, both Kelvin and Celsius can be put in. Since temperature is a delta, that means that in order to find it, you must take the Tfinal – Tinitial.
change in temperature of substance being heated.
\
Kelvin or Celsius
\
Tfinal – Tinitial.
\
Kelvin or Celsius
\
Tfinal – Tinitial.
73
New cards
A hot 5.00 gram piece of aluminum is placed into 75.0 mL of water. The water increases in temperature from 23.0°C to 28.0°C. The specific heat capacity of aluminum is 0.90, and water is 4.184. How much energy was lost by the aluminum?
**G:**mAl = 5.00 g Vwater = 75.0 mL t1 = 23.0 ℃ t2 = 28.0 ℃ \n cAl = 0.90 J/g・℃ cwater = 4.184 J/g・℃
**U**:Q = ?
**E:** Q = m・c・Δt Δt = tfinal - tinitial Dwater: 1 g = 1 mL
**S**:use water values since this is what is heating up
**S:(**75 g)(4.184 J/g・℃)(5℃) = 1569 → (sig figs) → **1570 J**
**U**:Q = ?
**E:** Q = m・c・Δt Δt = tfinal - tinitial Dwater: 1 g = 1 mL
**S**:use water values since this is what is heating up
**S:(**75 g)(4.184 J/g・℃)(5℃) = 1569 → (sig figs) → **1570 J**
74
New cards
_________________ is used to measure amounts of heat transferred to or from a substance
Calorimetry
75
New cards
A___________________________is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process
calorimeter
76
New cards
For example, when an ______________________reaction occurs in solution in a calorimeter, the heat produced by the reaction is absorbed by the solution, which increases its temperature
exothermic
77
New cards
When an ____________________reaction occurs, the heat required is absorbed from the thermal energy of the solution, which decreases its temperature.
endothermic
78
New cards
The temperature change, along with the specific heat and mass of the solution, can then be used to calculate the amount of __________________involved in either case.
**heat**
79
New cards
what is Q
the amount of heat being lost or gained
80
New cards
Calorimetry can find __ and _______ of a reaction.
Q and ΔH
81
New cards
3 things needed when solving for the amount of energy released or gained by a reaction
mass of the substance gaining or releasing the energy
\
specific heat of that substance.
\
the change of temperature for that substance.
\
specific heat of that substance.
\
the change of temperature for that substance.
82
New cards
ΔH is measured in ______________________
kJ/mole
83
New cards
while Q is measured in ___________
J
84
New cards
whebn solving for ΔH, 2 things to remember
convert Joules, into kilojoules (kJ)
convert grams into moles as well
convert grams into moles as well
85
New cards
*kinetic molecular theory* (KMT), a simple microscopic model that effectively explains ____________________
the behavior of gases
86
New cards
describe kmt in 5 rules
1. Gases are composed of molecules that are in continuous motion, traveling in straight lines and changing direction only when they collide with other molecules or with the walls of a container.
2. The molecules composing the gas are negligibly small compared to the distances between them.
3. The pressure exerted by a gas in a container results from collisions between the gas molecules and the container walls.
4. Gas molecules exert no attractive or repulsive forces on each other or the container walls; therefore, their collisions are *elastic* (do not involve a loss of energy).
5. The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas.
87
New cards
meaning of
Gases are composed of molecules that are in continuous motion, traveling in straight lines and changing direction only when they collide with other molecules or with the walls of a container.
Gases are composed of molecules that are in continuous motion, traveling in straight lines and changing direction only when they collide with other molecules or with the walls of a container.
as particles are always moving and bounce off of each other and their container.
88
New cards
meaning of the molecules composing the gas are negligibly small compared to the distances between them.
compared to how far apart gas particles are, the individual molecules themselves are relatively small
89
New cards
meaning of The pressure exerted by a gas in a container results from collisions between the gas molecules and the container walls.
gas pressure comes from gas particles hitting the walls of their container.
90
New cards
meaning of Gas molecules exert no attractive or repulsive forces on each other or the container walls; therefore, their collisions are *elastic* (do not involve a loss of energy).
they bounce off of each other perfectly, without sticking to or repelling one another, and no energy is lost when they do
91
New cards
meaning The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas.
gas particles gain more energy when they are heated, and lose energy when they are cooled. That energy is displayed through the speed of the gas particles, as they go faster and faster the hotter they get.
92
New cards
_______________is the result of gas molecules hitting the sides of their container
**Pressure**
93
New cards
As the energy of the molecules increases, the pressure exerted by those molecules will also increase as those molecules hit the walls of their “container,” both with more _________and more frequently.
force
94
New cards
**______________** can be thought of as the intensity of heat present in a substance, and it has a direct relationship with the kinetic energy of gas molecules (when the temperature of gas molecules increases, their kinetic energy does as well).
**Temperature** (T)
95
New cards
one mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 liters
96
New cards
The temperature of gases is always measured in degrees___________ (K), which can easily be converted from Celcius (C°) by adding ____________to any Celsius temperature.
Kelvin, 273
97
New cards
______________is caused by the force exerted by gas molecules colliding with the surfaces of objects
Gas pressure
98
New cards
**expansion -**
gases have no definite shape or volume
99
New cards
**low density -**
the particles of a substance in the gaseous state are about 1/1000th the density of the same substance in a solid or liquid state
100
New cards
**compressibility -**
the volume of a given sample of a gas can be greatly decreased