Organic Chemistry Prelab Quizzes
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GU SP2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
During this experiment you will collect an FTIR spectrum of your unknown compound and annotate stretching absorbances consistent with various functional groups. Which region of the spectrum will you annotate?
1500 - 3500 wavenumbers
What is the "selection rule" for IR absorption?
The vibration must result in a change to the molecular dipole.
Which type of NMR spectrometer will we use to collect magnetic resonance spectra this week?
Pulsed (Fourier Transform) NMR
What types of NMR peaks must be annotated on your NMR spectrum? Choose all that apply
Peaks associated with your compound of interest, TMS (if present), The residual protochloroform peak, Peaks associated with solvent impurities
Which technique this week is commonly used to detect nanograms of material?
Mass Spectrometry
Which of the following is/are true regarding annotation of your mass spectrum this week?
the molecular ion peak must be labeled, one reasonable fragment must be labeled
In which solvent will you dissolve your NMR sample?
deuterated chloroform
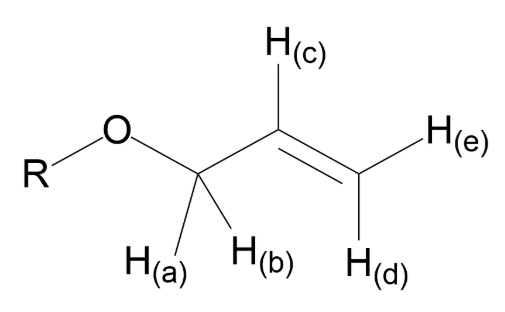
Shown below is a generic allyl ether. Which of the labeled hydrogens on this group will produce 1H-NMR resonances that do NOT conform to the n+1 rule?
H(c), H(d) and H(e) only
Which of the following best describes the role of potassium carbonate in this week's reaction (Protecting Groups)?
It generates a phenoxide nucleophile
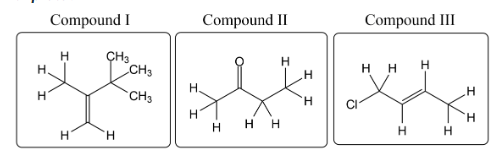
Which of the compounds shown below is expected to produce a 1H-NMR spectrum that contains a doublet of triplets?
Compound III Only
Which of the following best describes why it is particularly important to perform a water drop test on your extraction mixture this week (Protecting Groups)?
Concentrated aqueous solutions of potassium carbonate can be extremely dense, and may appear below dichloromethane in the separatory funnel
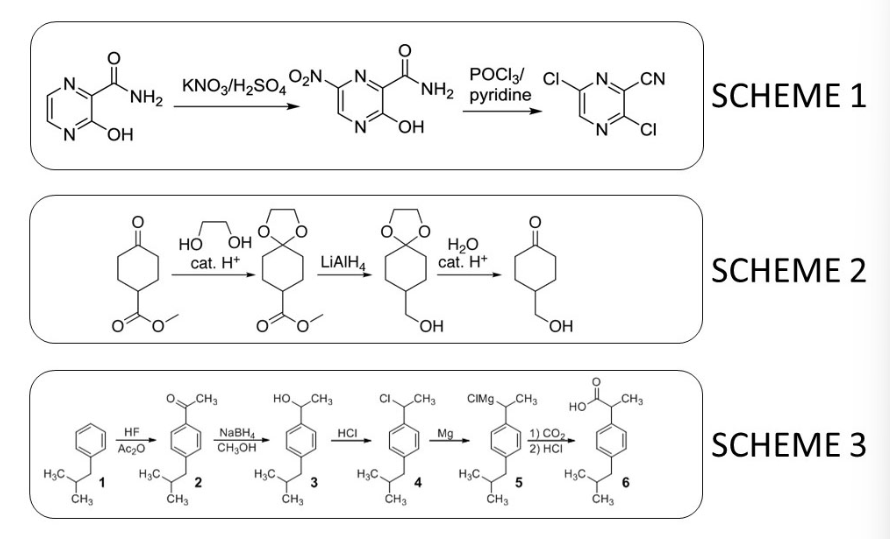
Shown below are three synthesis schemes. Which of these schemes contains a depiction the complete execution of a protecting group synthesis strategy?
Scheme 2 only
Under which set of conditions is a reaction most likely to be under thermodynamic control?
High temperatures over a long period of time
Which of the following materials from this week's experiment has a particularly bad odor, and so must be transported through the lab with great care?
Dicyclopentadiene and cyclopentadiene
Which of the following best describes the thermodynamic driving force behind the Diels Alder reaction?
The reaction is enthalpically driven because two pi bonds are lost and two sigma bonds are created.
Why must cyclopentadiene be used shortly after distillation?
Two molecules of cyclic dienes can undergo a Diels Alder reaction between themselves.
Why is it not necessary to distill the dicyclopentadiene before use in this week's HOT (thermodynamic control) reaction?
The dimer will 'crack' into monomers during the reaction itself, eliminating the need to do so before the reaction is run.
Which of the following statements best describes the role of sulfuric acid in this week's reaction (Regiospecific Reactions)?
It protonates the nitric acid, promoting the formation of a nitronium electrophile.
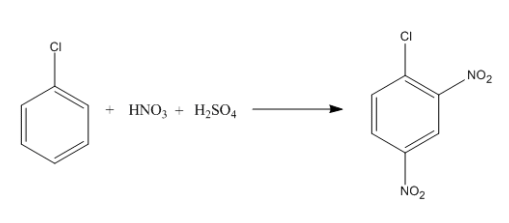
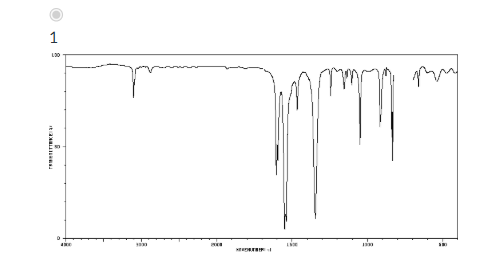
Which of the IR spectra below corresponds to that of the product depicted in the nitration of chlorobenzene below?
Which of the following solvent/reagent combinations are dangerously reactive and should never be mixed? Choose all that apply.
Acetone and nitric acid, Ethanol and nitric acid
Which of the following correctly describes the identity of the solution used to neutralize the toxic gases escaping the reaction vessel (Regiospecific Reactions)?
Aqueous sodium bicarbonate
When analyzing our product this week (Regiospecific Reactions), which spectroscopic technique will help us to demonstrate the locations that have been modified during our reaction?
1H-NMR spectroscopy
As an extra precaution against explosions in the chemical waste accumulation site, which special measure will we be taking?
leaving container lids loosely atop the container to allow containers to vent
The goal of the cold reaction is to avoid the occurrence of a second nitration. According to the procedure, what is the maximum temperature that the cold reaction can be allowed to reach before the second nitration begins to take place?
50 °C
Which of the following statements is/are true?
I. The acid in the Fischer esterification is catalytic
II. The acid in acidic ester hydrolysis is catalytic
III. Saponification takes place under basic conditions
I, II, and III
Guest Professor Tyler Durden chose to use lye as a reagent in his ester hydrolysis reaction as opposed to a strong mineral acid. Why did he make this choice?
Because basic hydrolysis of esters (saponification) is an irreversible reaction, and leads to high yields without having to carefully consider experimental design.
Assuming that you begin with exactly 5.0 g of benzoic acid, the theoretical yield of methyl benzoate from this week's Fischer esterification is:
5.7 g
Which is a common complication of refluxing basic aqueous solutions that can be prevented by liberally greasing the joint between the condenser and the boiling flask?
Fused glassware
Which water-miscible byproduct from the hydrolysis of methyl benzoate will make it necessary to pour your aqueous rinsings into the organic waste after performing a saponification?
methanol
Which proton NMR feature do you expect will be present in the product of part A (methyl benzoate) that will NOT be observed in its starting material for this step (benzoic acid)?
A sharp singlet near 3.0 ppm (-CH3 on -O-CH3)
Which best explains the reasoning behind the dropwise addition of one reagent to the other with vigorous stirring during this week's reaction?
It keeps the concentration of the second reagent (added dropwise) low as the reaction proceeds, leading to varying ratios of products.
Why will the reagents be dissolved in 3M sodium hydroxide this week (Stoichiometric Reaction Control)?
The sodium hydroxide will act as a catalytic base, generating the nucleophile needed to initiate the reaction.
Which best explains why benzaldehyde is not expected to act as a nucleophile in this week's reaction?
Benzaldehyde does not have any protons on its alpha carbon, so it cannot form an enolate ion that will act as a nucleophile in the aldol condensation. It can therefore only act as the electrophile in this type of reaction.
Which of the following best describes the rationale for synthesizing dibenzalacetone from benzaldehyde and acetone as a sunblock ingredient?
The HOMO-LUMO transition in dibenzalacetone is lower in energy than for starting materials, and should result in a longer wavelength absorption maximum.
Which of the following best explains why acetone cannot be used as a solvent when attempting to synthesize dibenzalacetone by a crossed aldol reaction?
The stoichiometry of the reaction predicts that the desired product (dibenzalacetone) will not form when large excess of acetone is used.
How will you dispose of your solid product obtained from the reaction workup (Stoichiometric Reaction Control)?
Dissolve it in acetone and add it to the Nonhalogenated Organic waste
Which method of moisture-exclusion will we be using in this week's experiment (Air and Water Exclusion)?
Attachment of the system to a drying tube filled with dessicant.
Which of the following atmospheric gases can promiscuously react in certain systems and so must sometimes be excluded when those reactions are carried out?
water, nitrogen, oxygen
Which of the following best explains why water must be excluded from a Grignard reaction?
Water is a weak acid (will react with Grignard reagent)
Which best describes the reason for using addition funnels instead of separatory funnels to introduce reagent solutions to the reaction flask this week?
Addition funnels allow the reagent solution to flow easily within a closed system.
Which of the following best describes why we are generally limited to using alkyl ethers as solvents for Grignard reactions?
Ether forms a stabilizing complex with the metal center on the Grignard reagent, helping it to form.
Which of the following statements is true?
Even though this week's starting material is an organic halide, its conversion to a Grignard and ultimately its inorganic byproduct will be quantitative, so there will be no halogenated waste from the reaction mixture this week (assuming your Grignard reaction runs).
Which statement best describes how molecular sieves are able to remove water from ether?
3 angstrom sieves contain pores large enough for water to fit in and become trapped, but too small for ether to do the same.
Which best describes how a Schlenk line establishes an inert atmosphere in a flask?
Sequentially evacuating and refilling a flask with inert gas removes all traces of atmospheric gases.