Chapter 4, Lesson 4: Chromosomes and Heredity
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 1, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Heredity
The transmission of genetic characteristics from parent to offspring
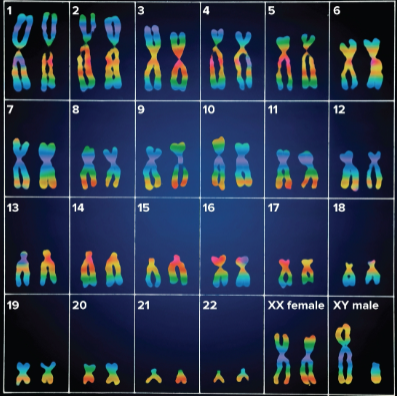
Karyotype
The chart of all 46 chromosomes by sides; shows 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
Same chromosomes in pairs with one inherited from each parent
Autosomes
Chromosomes that look alike and carry the same genes
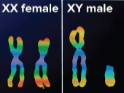
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine gender; men have one X and one Y chromosomes while women have homologous X chromosomes
Diploid
Any cell with 23 pairs of chromosomes; somatic (non-reproductive) cells are an example
Haploid
Cells with half as many chromosomes as somatic cells; ones in humans contain 23 unpaired chromosomes such as sperm and egg cells to restore regular pairing
Locus
The location of a particular gene on a chromosome
Allele
Different form of a particular gene; found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes
Dominant allele
An allele that expresses a protein in an individual
Recessive allele
An allele that does not express in an individual if it is paired with a dominant allele; only appears when recessive on both homologous chromosomes
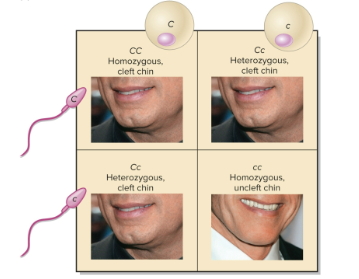
Genotype
The allele an individual possesses for a particular gene; visualized using Punnet square
Phenotype
An observable trait
Genetic counselors
Perform genetic testing and advise couples on genetic diseases
Gene pool
The genetic makeup of the whole population
Multiple alleles
More than two allelic forms of a gene; seen in A, B, and O blood types
Codominance
Both alleles equally dominant and phenotypically expressed; seen in AB blood types
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygous individual shows phenotype between traits each allele would have produced alone
Polygenic inheritance
Genes at two or more loci contribute to a single trait
Pleiotropy
One gene produces multiple phenotypic effects
Sex-linked traits
Traits carried on the X or Y chromosomes; men inherit more than the other due to having only one X chromosome
Penetrance of allele
Percentage of population exhibiting expected phenotype; allele may not fully express in population or can be modified by the environment
Epigenetics
Field examining nongenetic changes that alter gene expression and can be passed to offspring
Carcinogens
Environmental cancer-causing agents that can damage DNA; they can be found in radiation, chemicals, and viruses and cause uncontrolled cell growth