7.3 Pathology of Forestomach and Abomasum of Ruminants
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What conditions can affect the forestomach and abomasum?
Rumenal tympany - bloat
Rumenal acidosis
Left and right displaced abomasum (LDA, RDA)
Tramatic reticuloperitonitis
Clostridial disease
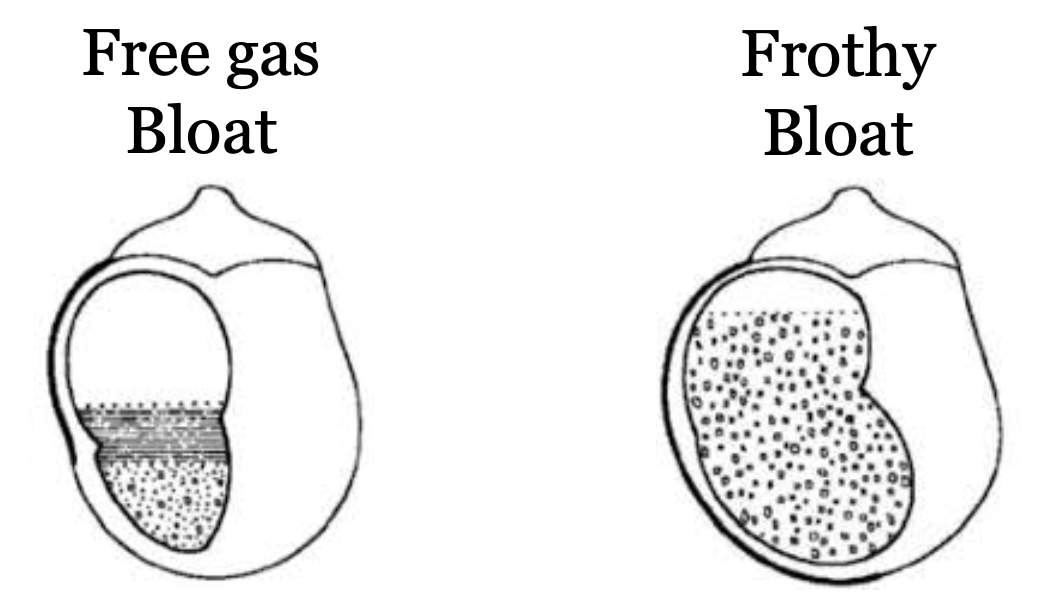
What is frothy bloat?
Gas entrapment within froth in rumen
Legume feeding
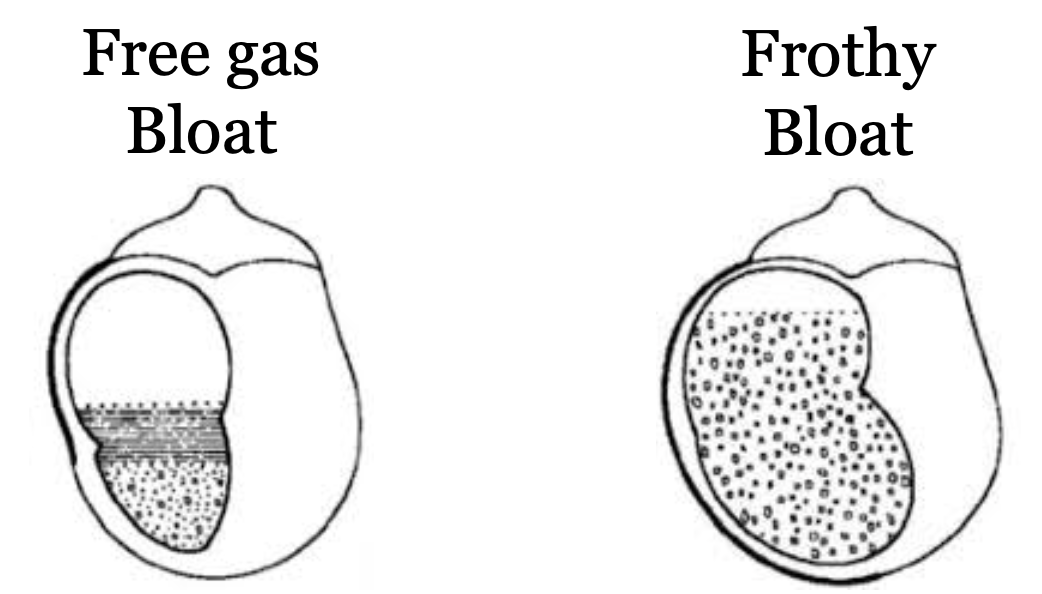
What is free gas bloat?
Inability to eliminate free gas from rumen
Overproduction of free gas - carbohydrate overlaod
Failure to eructation - oesophageal obstruction, recumbency
Functional disruption to rumen - nerve dysfunction. hypocalcaemia
What are clinical signs of rumenal tympany (bloat)?
Abdominal distension
Rumenal hypo motility
Pain, discomfort and vocalisation
Tachypnoea
Recumbency and death
What is rumenal acidosis?
Normal rumen function - pH 6-7. buffered by saliva
Consistent diet
High levels of cellulose and hemicellulose
Slow passage of ingest through GIT
Need time to chew cud
What risk factors can cause rumenal acidosis?
Size of conc. feeds
Feeding frequency
Overall starch levels
Forage access
Ration sorting
Transition
Cow comfort
What can cause rumenal acidosis?
Acute rumenal acidosis - high quantity of CHO in short timeframe
Subacute rumenal acidosis (SARA) - chronic exposure to high starch levels. lack of physically effective NDF. herd level problem
What is the pathology (development) of rumenal acidosis?
Diarrhoea - osmotic draw from lactic acid. decreased gut transit time
Rumenitis - inflammation of rumen wall. liver abscessation. pulmonary thromboembolism
What are clinical signs of rumenal acidosis?
Acute rumenal acidosis - rumenal tympany and diarrhoea. tachypnoea. recumbency and death
SARA - decreased milk production, milk butterfat content, BCS, rumination. diarrhoea. undigested grains. faecal soiling. poor fertility
How can we diagnose SARA on farm observations?
Decrease/increase in faecal consistency and incomplete digestion
Poor cow cleanliness
Tail swishing
Decreased rumination and increase in dropped cuds
Ration assessment
How can we diagnose SARA?
Decreased herd performance
Decreased yields and bulk milk butterfat levels
Poor reproductive performance
Increased lameness and environmental mastitis
Rumenal pH monitoring boluses
What functional features can cause abomasal disorders?
Metabolic - hypocalcaemia. NEBAL. ketosis/fatty liver
Nutritional - concentrate to forage ration. physically effective fibre. rumen outflow
What physical features can cause abomasal disorders?
Reduced DMI and rumen fill
Pre-calving left shift
Post calving potential space
Genetics - abdominal contour
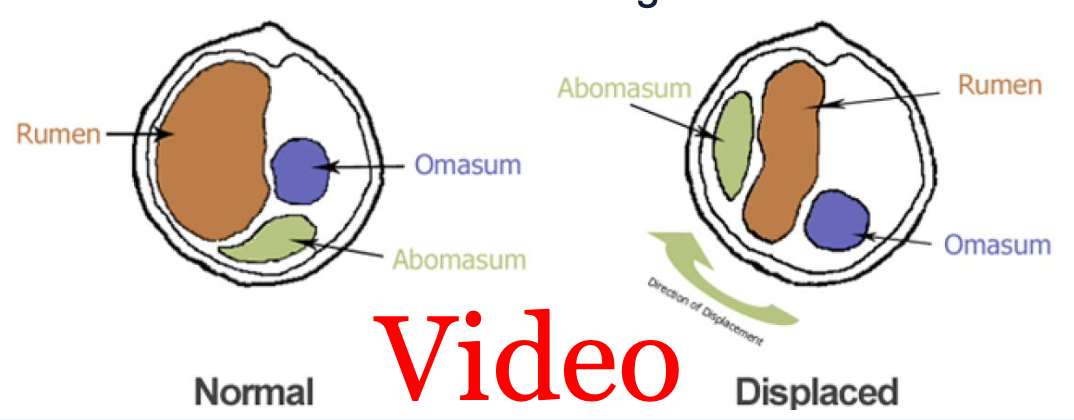
What is left displaced abomasum?
Most common form
Gas-distended abomasum displaced between left abdominal wall and rumen
Duodenum becomes compressed preventing outflow
Occasional intermittent/floating LDA
What are clinical signs of left displaced abomasum?
Selective anorexia - refuse concentrates
Decreased milk production
Decreased rumen fill and decreased faecal output
Extension of caudal part of ribcage
Ping on percussion - ventral half of abdomen between 9th and 12th intercostal space
What is right displaced abomasum (volvulus)?
Not most common form - 5% displacements
Abomasum floats up on RHS
Rotating over 90-180°
Volvulus/torsion
Obstruction of blood supply:
Sequestration of fluid and ions within lumen
Necrosis of abomasal mucosa and translocation of bacteria
Circulatory failure may superimpose metabolic acidosis due to hyper-lactatemaia
What clinical signs of right displaced abomasum are there?
Anorexia
Decreased milk production
Decreased rumen fill and motility
Extension of caudal part of ribcage
Ping on percussion on right flank - last 3 ribs and lumbar fossa
What is trauatic reticuloperitonitis (TRP)?
Ingestion of sharp penetrating object
Tyre wire syndrome
What is the pathogenesis of TRP?
Localised in reticulum
Trapped in honeycomb structure
Object penetrates reticulum wall due to luminal contractions
Peritonitis due to bacterial seeding - damage liver, heart, lungs
What are clinical signs of TRP?
Anorexia
Arched back/painful abdomen
Tachycardia
Pyrexia
Decreased GI stasis
Milk yield
How can we diagnose TRP?
Anterior abdominal pain tests
Auscultation
Diagnosis by exclusion
Abdominocentesis
Ultrasonography
Glutavac - fibrinogen test
What is abomasal ulceration?
Can occur in calves and adults
Caused by:
Stress
High starch/concentration ration
Concurrent disease
What is the pathogenesis of abomasal ulceration?
Ulcers on abomasal wall
Haemorrhage
Peritonitis
What are clinical signs of abomasal ulceration?
Foul smelling faeces
Melena
Anaemia
Tachycardia
Pale mucous membranes
What is clostridial disease?
Clostridium sordelli (abomasitis)- high milk intake in lambs 4-10 weeks. abomasal wall can be emphysematous, oedematous, hyperaemic
Clostridium septum (braxy) - abomasitis. ingestion of frosted forage. frosted feed damages mucosa of abomasum allowing bacteria to penetrate