Biology midterm
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Parts of a controlled experiment
control group, experimental group, independent variable, dependent variable, constants
dependent vs. independent
independent- variable being changed
dependent- variable responding to change
experimental vs. control groups
control group- all variables are same as experimental except no independent variable
experimental group- all same as control except their is independent variable
what makes a controlled experiment a controlled experiment
only 1 variable being changed
Know the steps of the scientific method
make observation, form hypothesis, designed control exp, collect data, analyze data
Know the characteristics of life
reproduces
respond to environment
homeostasis
evolution
grow and develop
Quantitative vs. qualitative data
quantitative- descriptive
qualitative- numbers
Hypothesis vs. theory
hypothesis- testable observation
theory- explains why/how something happens
Importance of peer review
fact checking, make sure paper is unbiased
why scientists use metric system
every scientist worldwide use it
the units of metric system
meters, liters, grams
how to convert metric system
kilo- 1000
hecta- 100
deka- 10
base- 0
deci- .1
centi- .01
mili- .001
subatomic parts of the atom and their charges
protons- positive
electrons- negative
neutrons- neutral
what is the top number on the image and what does it mean
atomic number- number of protons

what is bottom number and what does it mean
atomic mass- # protons + # neutrons

how many neutrons in carbon
6

how isotopes differ
in neutrons
Covalent vs. Ionic bonds
covalent- shares electron
ionic- electrons transfer
Properties of water
polarity, hydrogen bonding, cohesion, adhesion, high heat capacity
solute vs. solvent
solute dissolves in solvent
pH scale
basic- 8-14
acidic- 0-6
neutral- 7
the different macromolecules
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
The monomers for carbohydrates
monosacharrides
Functions of the carbohydrates
fast short term energy
monomers for proteins
amino acids
monomers for lipids
fatty acids, glycerol
monomers for nucleic acids
nucleotide
functions for proteins
speeding up chemical reactions- cell transport
function for lipids
long term energy storage- structure cell membrane
function for nucleic acid
contains genetic information
What is occurring when a chemical reaction happens
one set of chemicals is changing into another
which are the reactants in a reaction
molecules before reactions
which are the products in a reaction
molecules after the reaction
energy-releasing reaction
exothermic
energy-absorbing reaction
endothermic
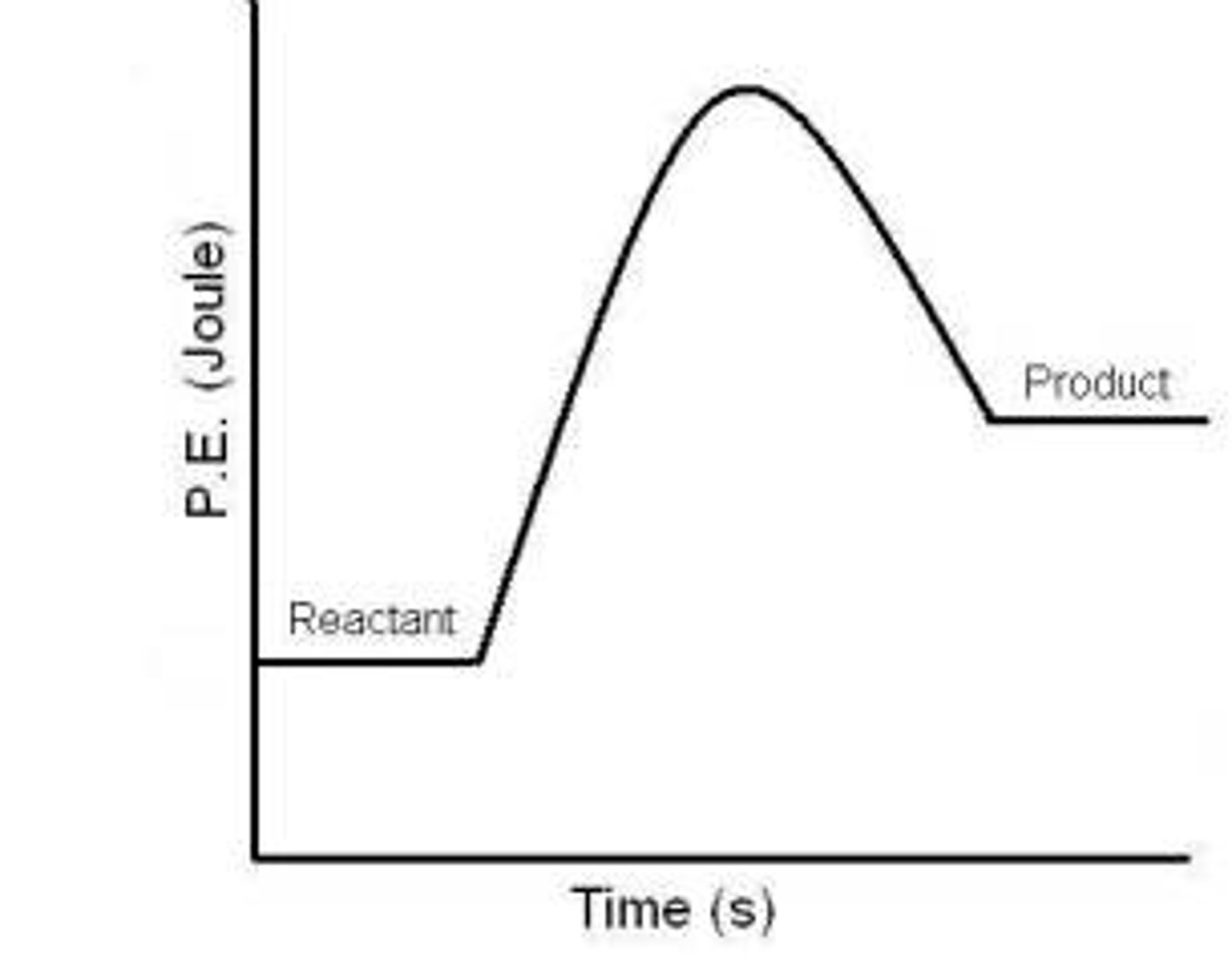
what kind of reaction is this
enothermic
what kind of reaction is this
exothermic
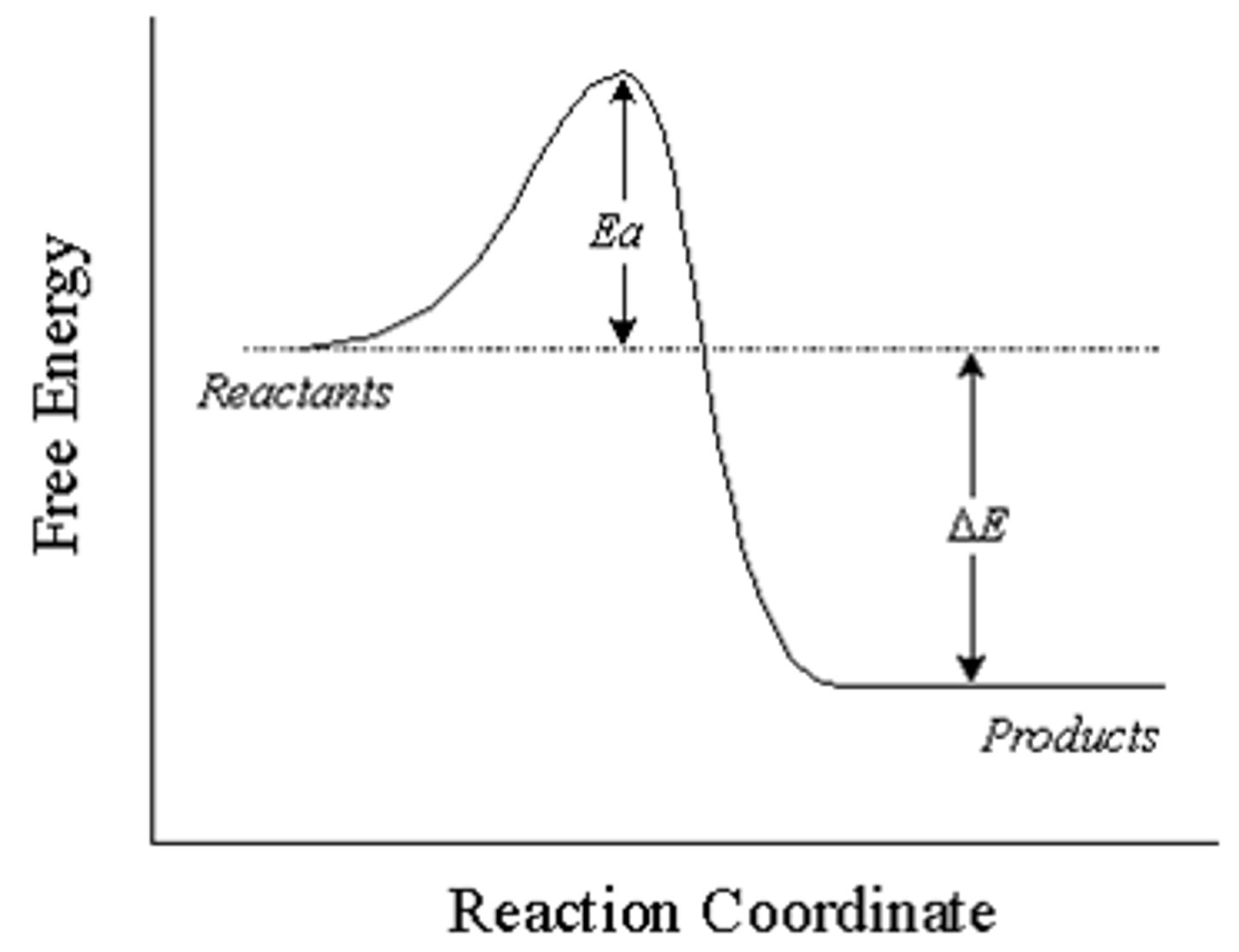
The jobs of enzymes in a chemical reaction
speed up the reaction
what is activation energy
minimum amoutn of energy for reaction to occur
do enzymes increase or decrease the activation energy in a graph
decrease
what effects the enzymes ability to work
pH, temp, salinity
the affects if enzyme put in an environment not optimum
enzyme will no longer work
what did scientist Hooke contribute to cells
first person to identify/observe cells- cells are basic unit of life
what did scientist Leeuwenhoek contribute to cell theory
first to observe microorganisms- cells are basic unit of life
what did Schleiden contribute to cell theory
all plants composed of cells- all living things made of cells
what did schwann contribute to cell theory
all animals composed of cells- all living things made of cells
what did virchow contribute to cell theory
all cells come from existing cells- new cells produce from existing cells
what is cell theory
All living things are made up of cells, cells are the basic units of life, new cells are produced from existing cells
Know the two different microscopes
light microscope, electron microscope
Prokaryotic cell
- no nucleus
- no organelles
- cytoplasm
- oldest form of life
Eukaryotic cell
- have nucleus for DNA
- membrane bound organelles
- ribosomes
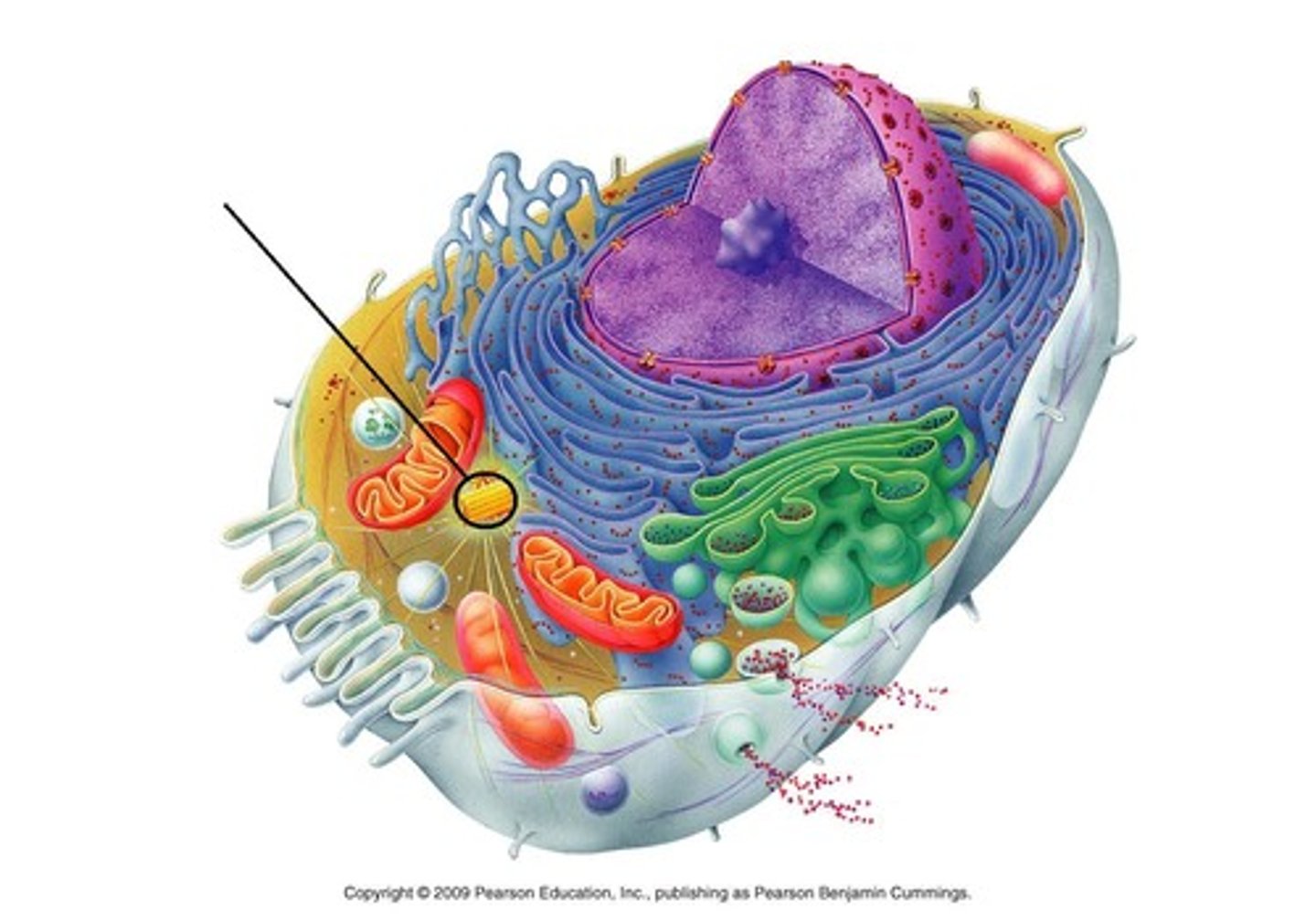
Mitochandria
convert chemical energy from food into compounds cell can use- cellular respiration
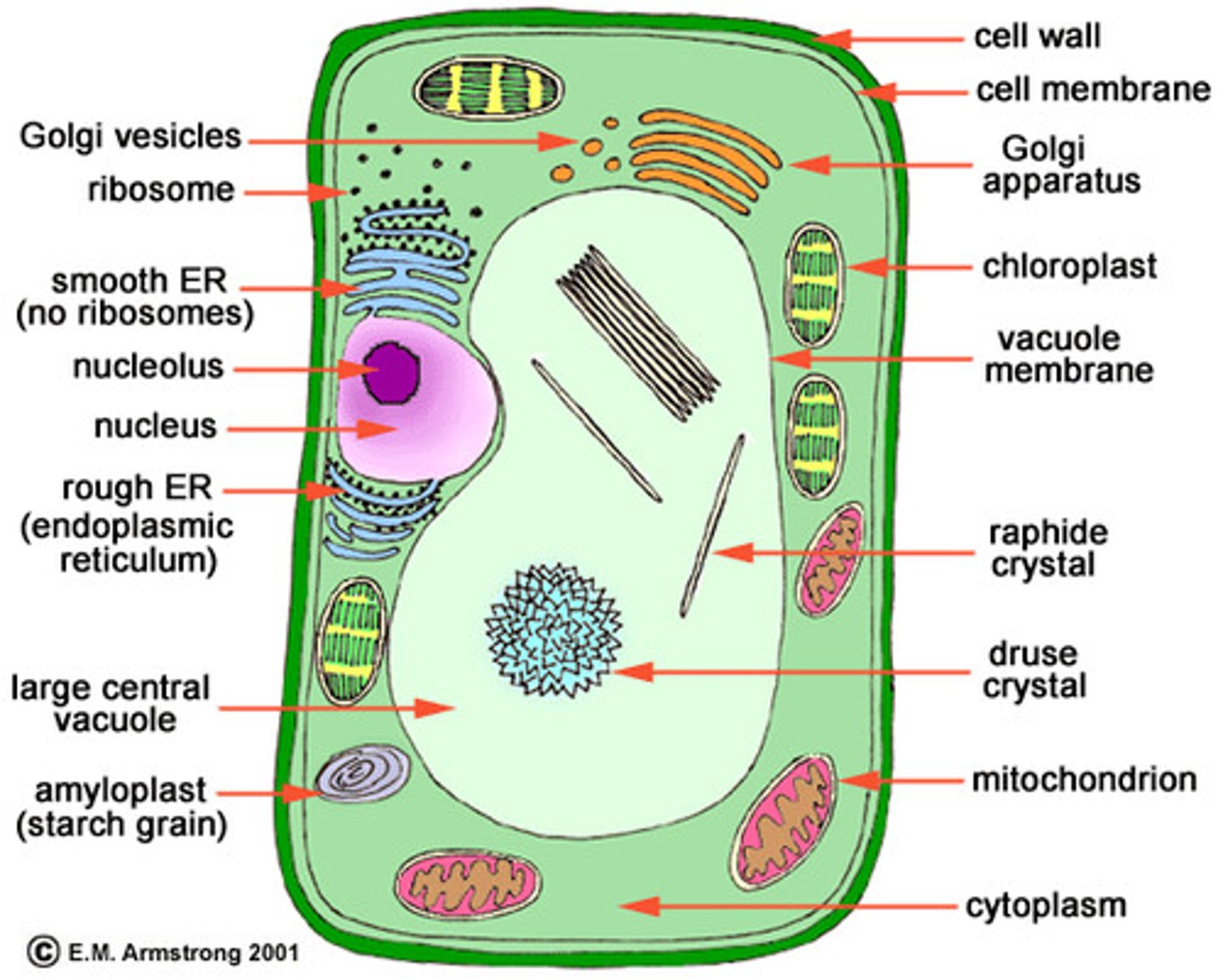
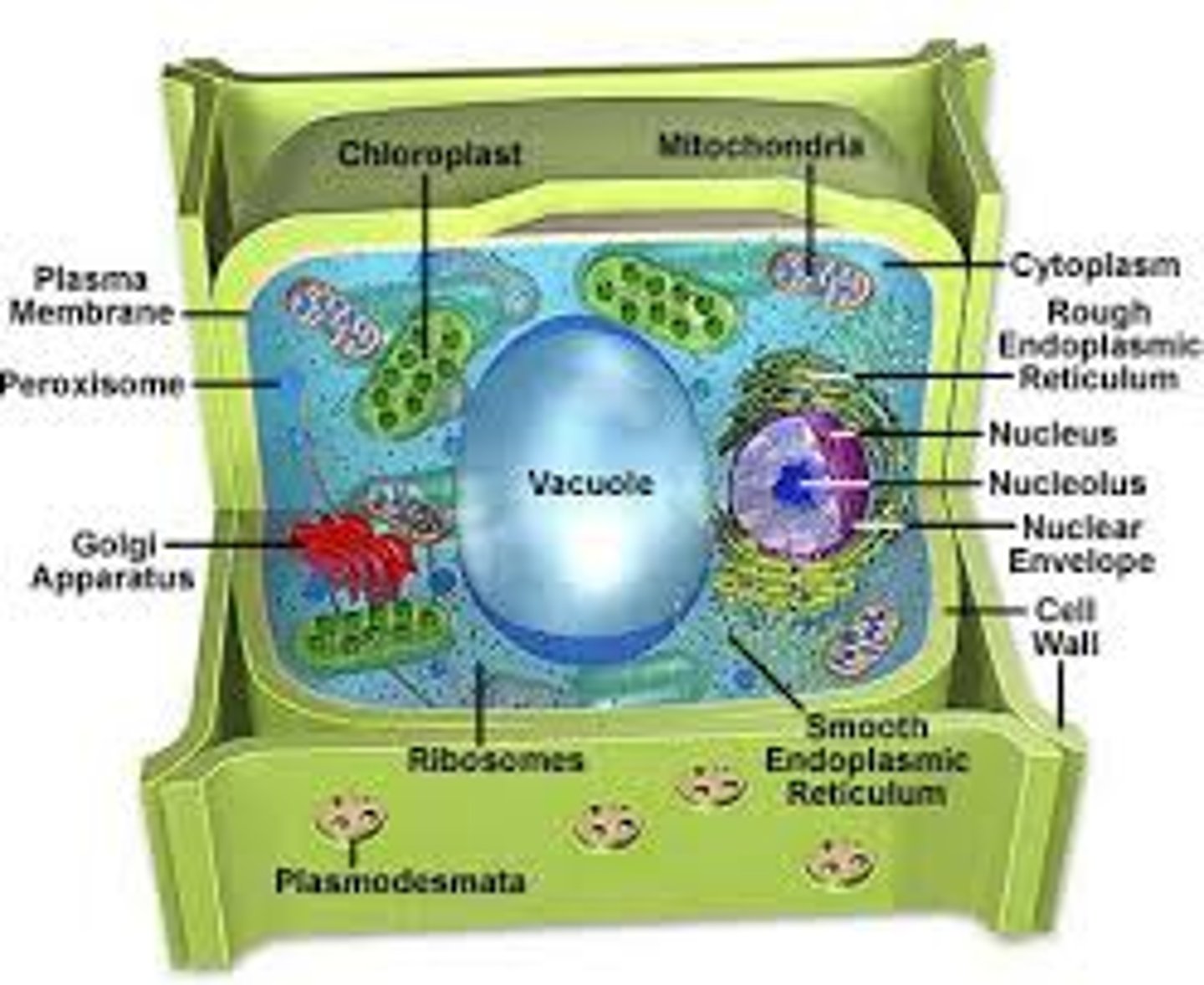
Chloroplast
contain chlorophyl that absorbs light energy- photosynthesis
Centrioles
do mitosis
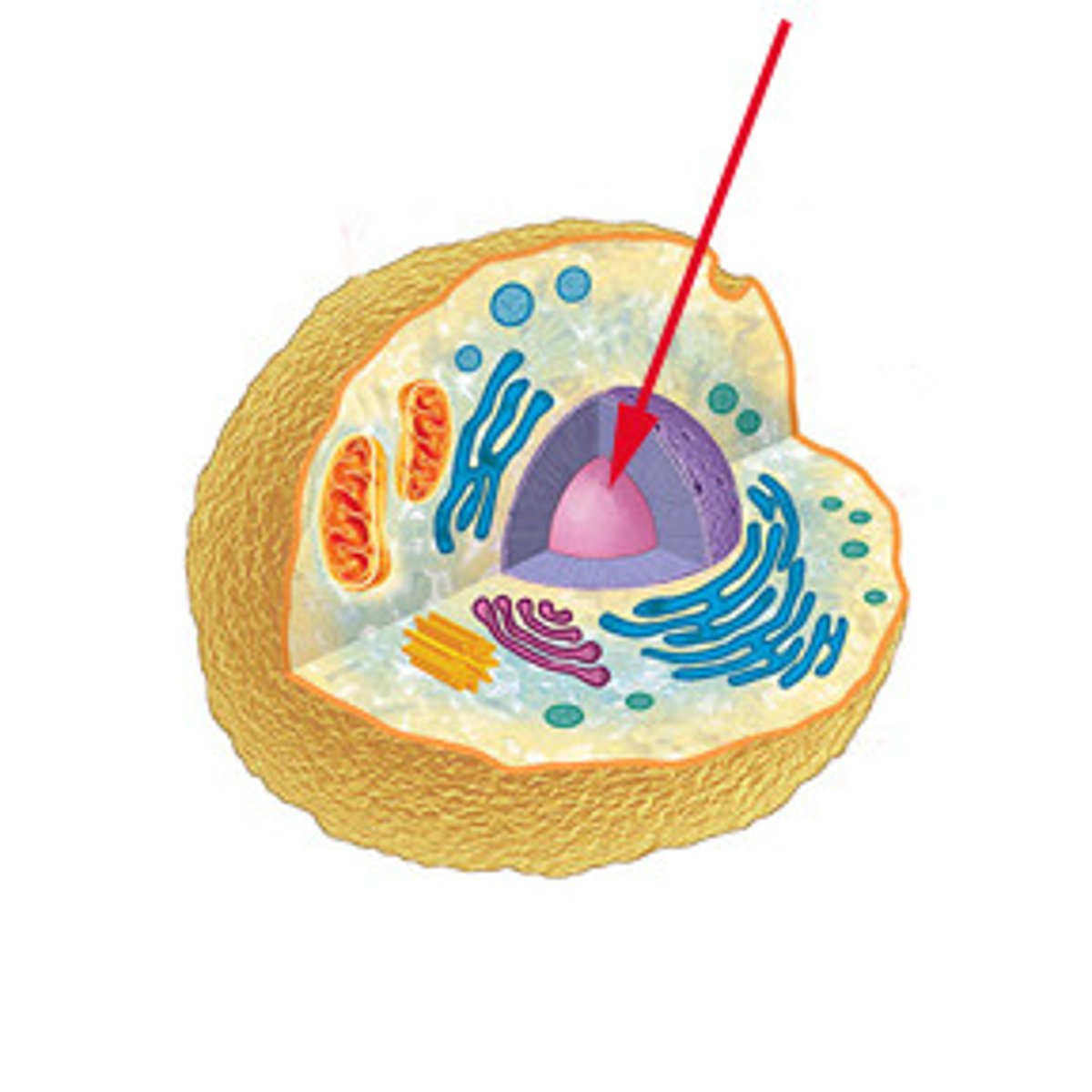
Nucleus
holds DNA/RNA
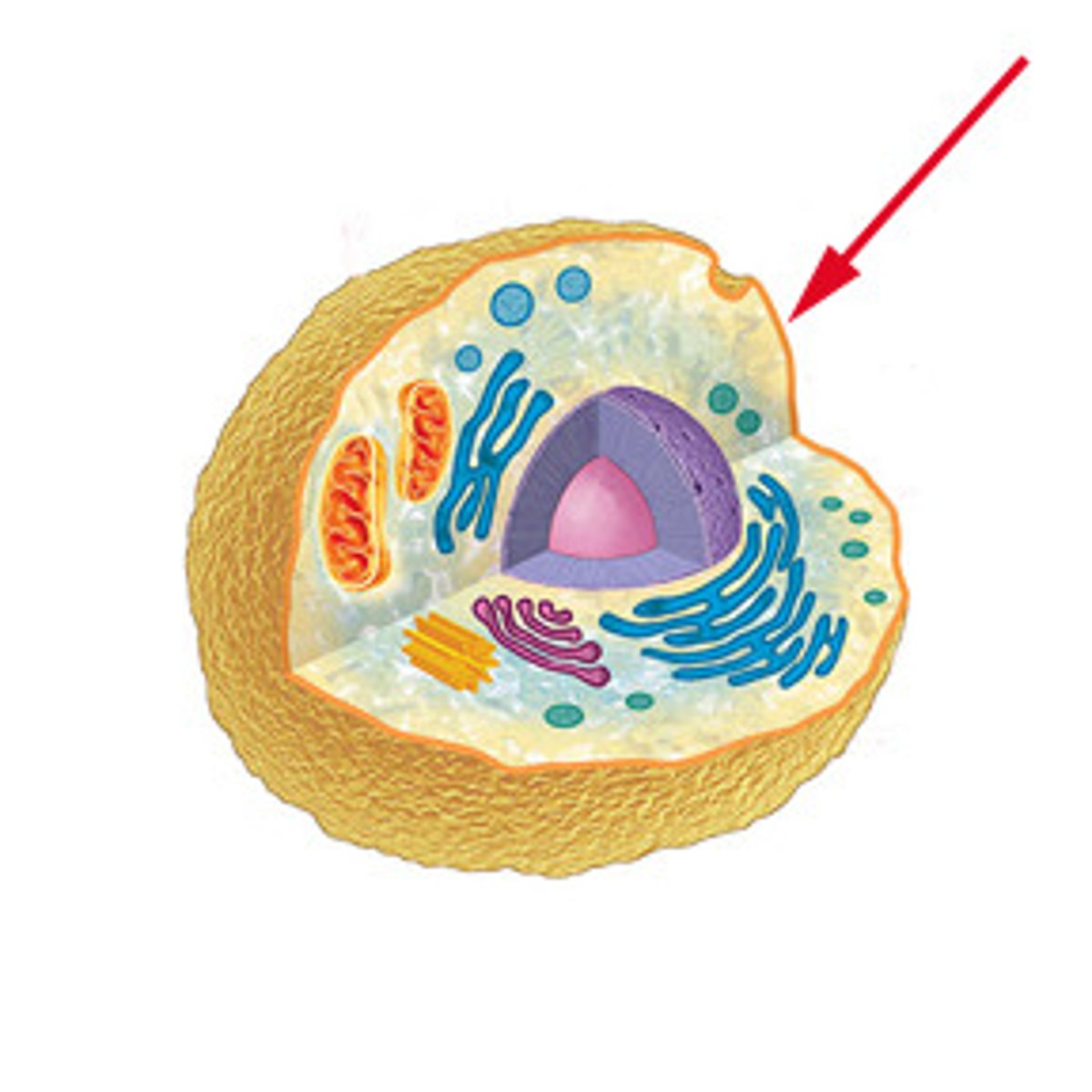
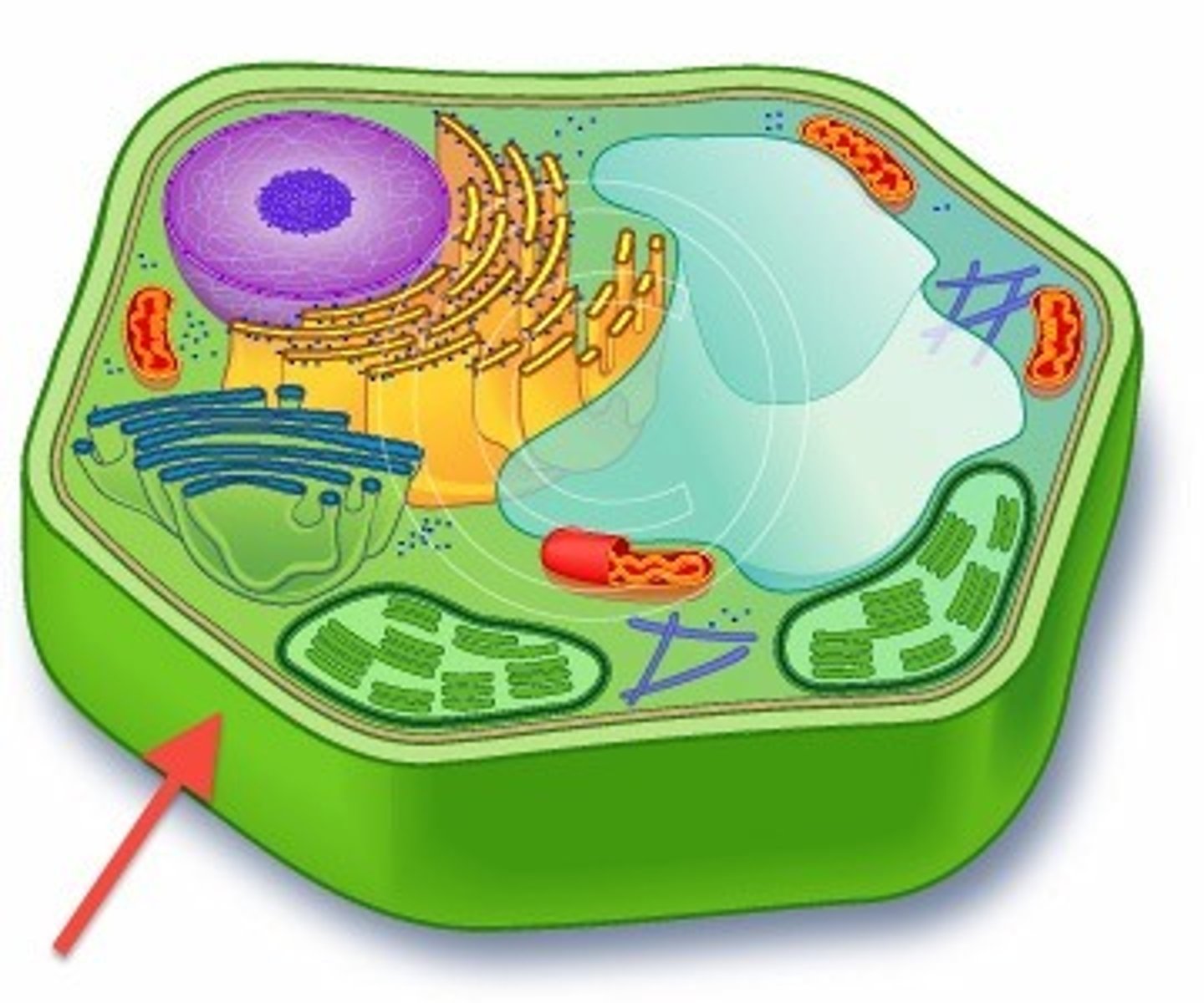
plasma membrane
cell membrane
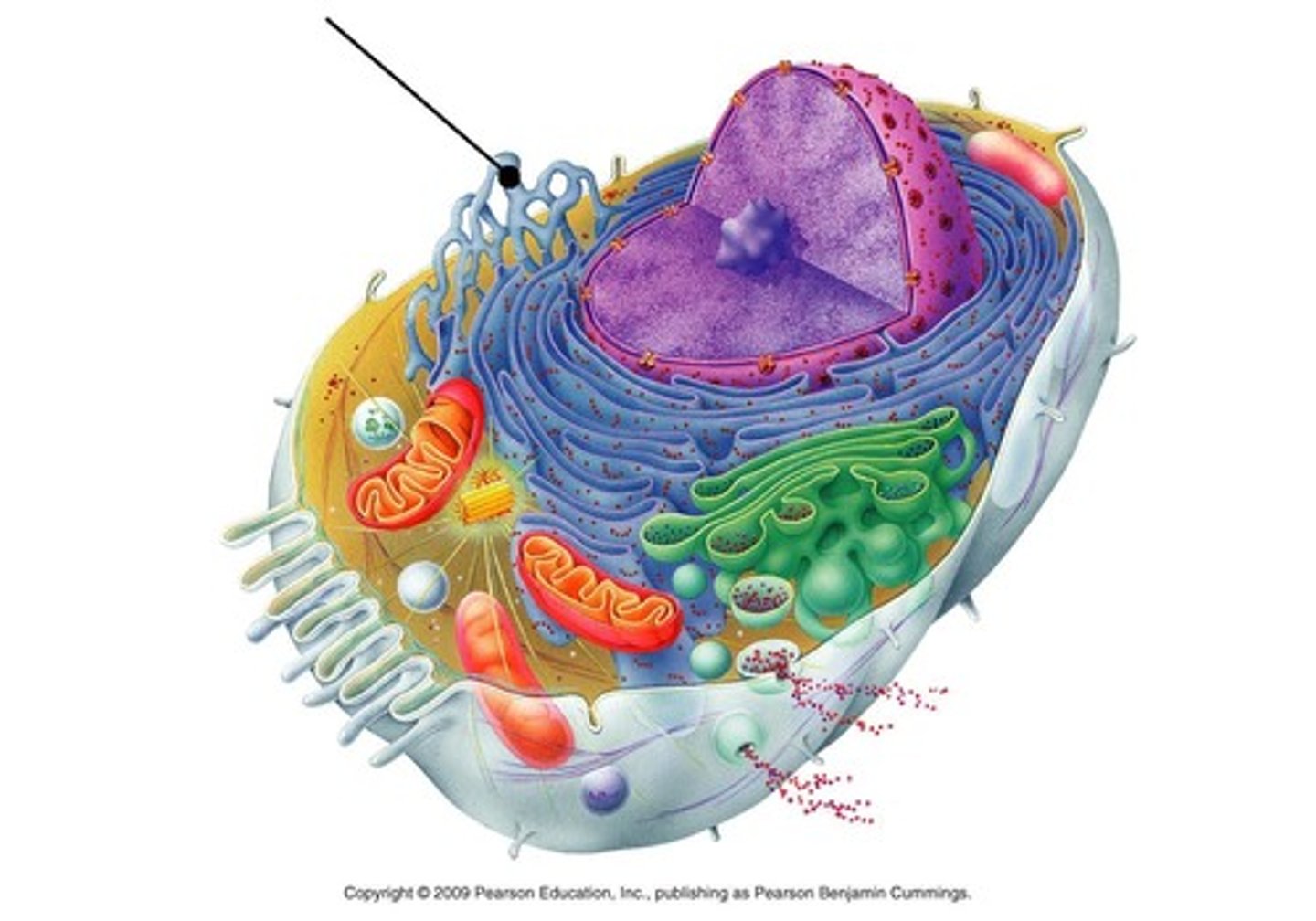
rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
makes protiens
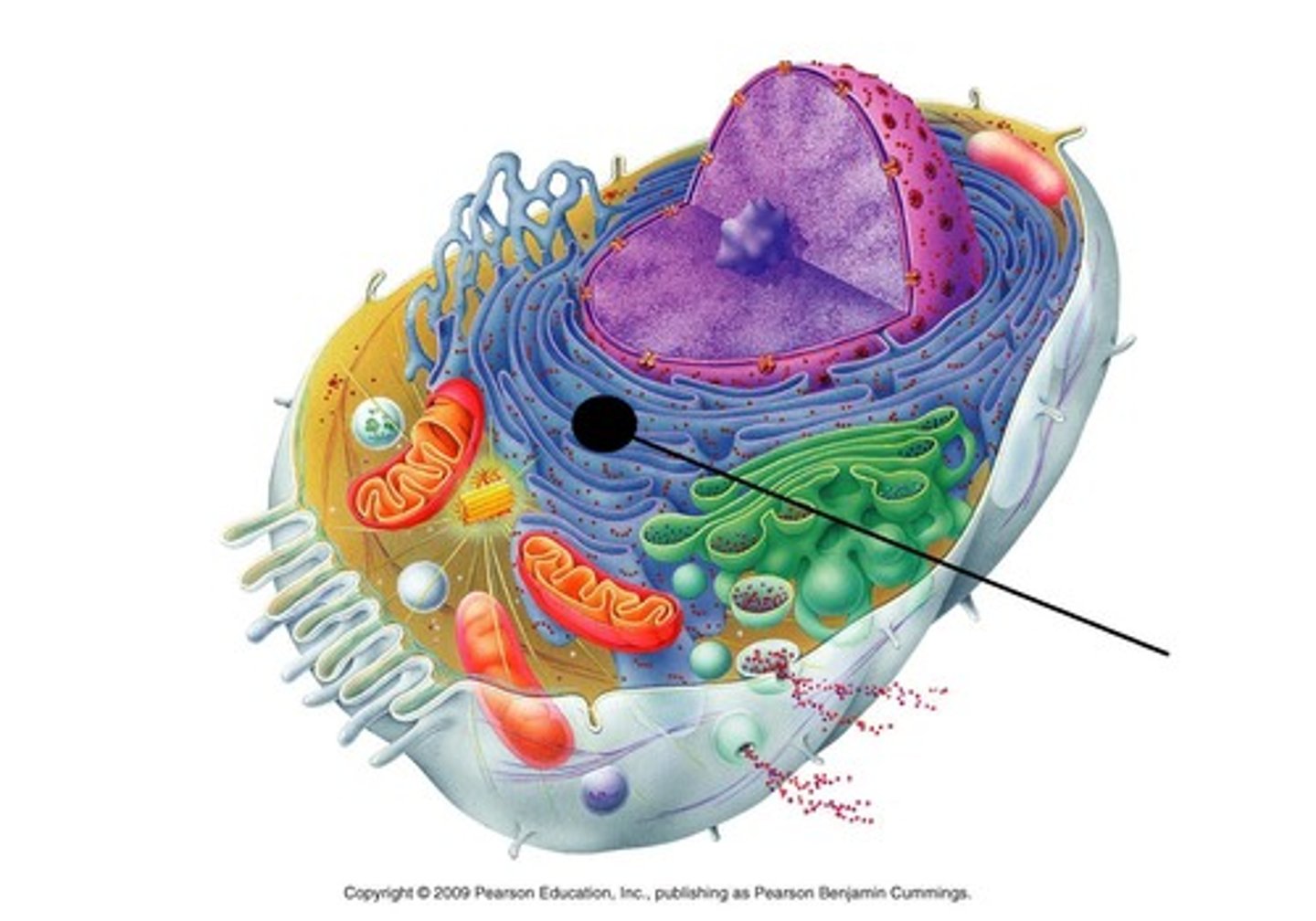
ribosomes
make proteins
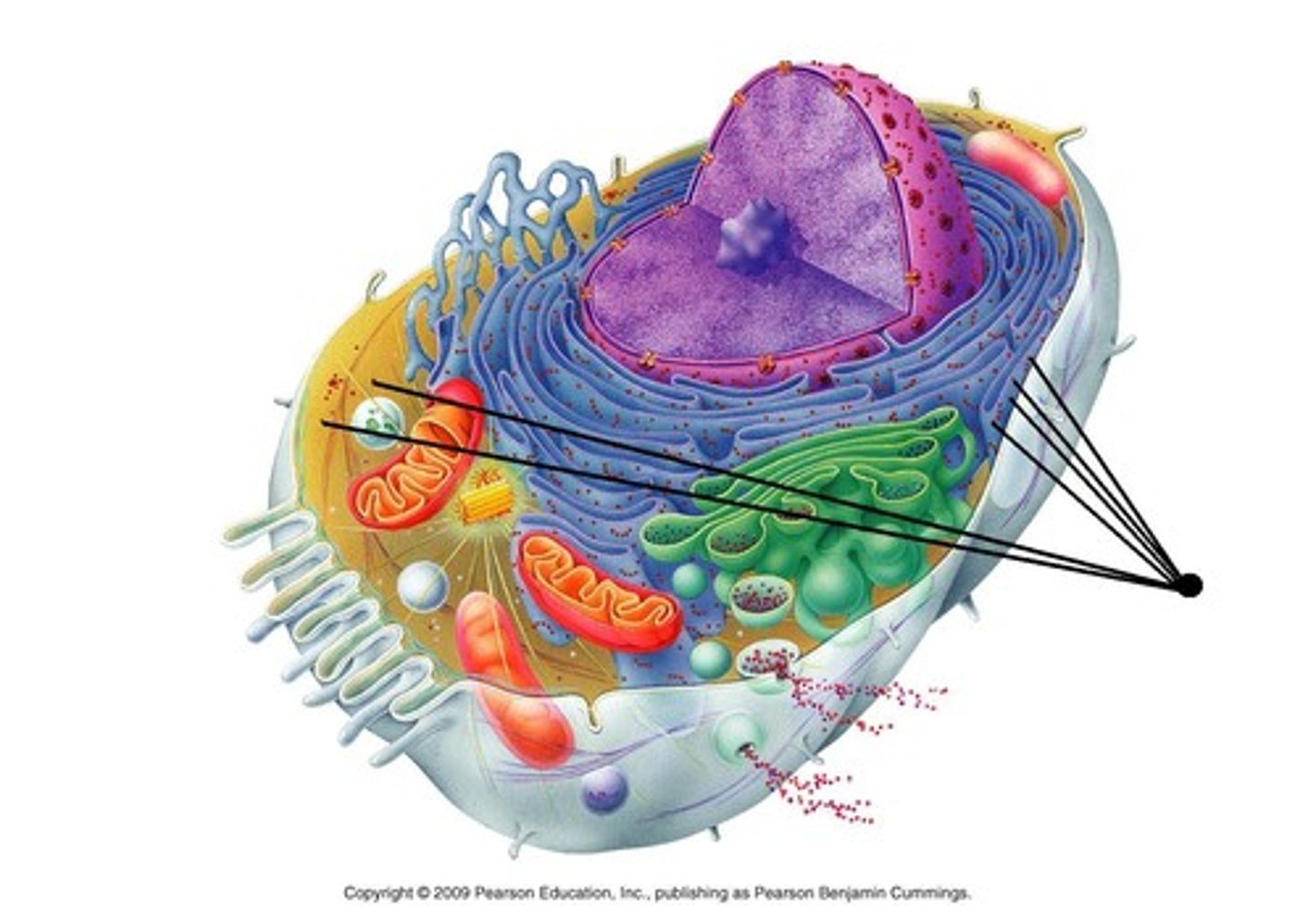
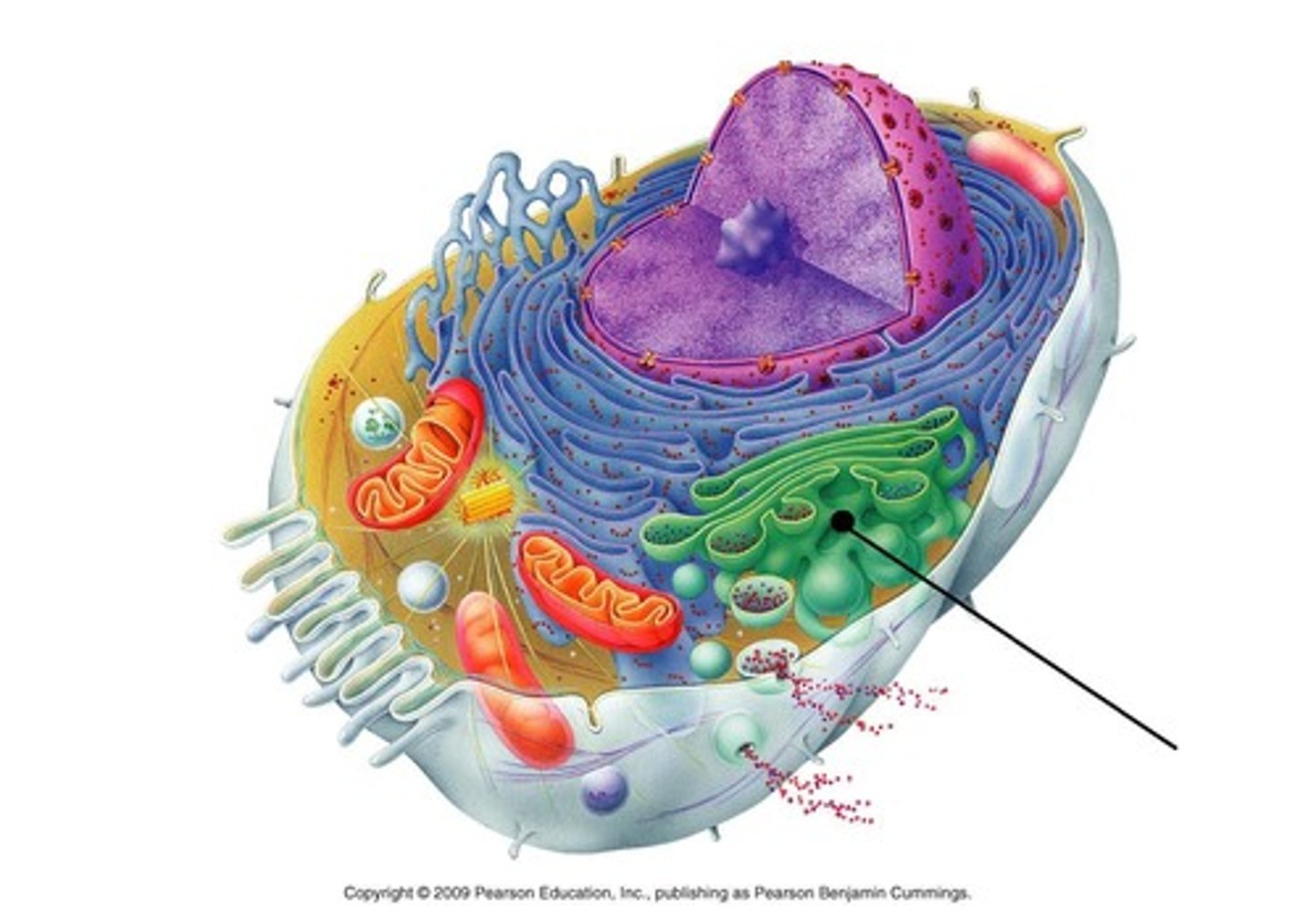
golgi apparatus
packages molecules from ER
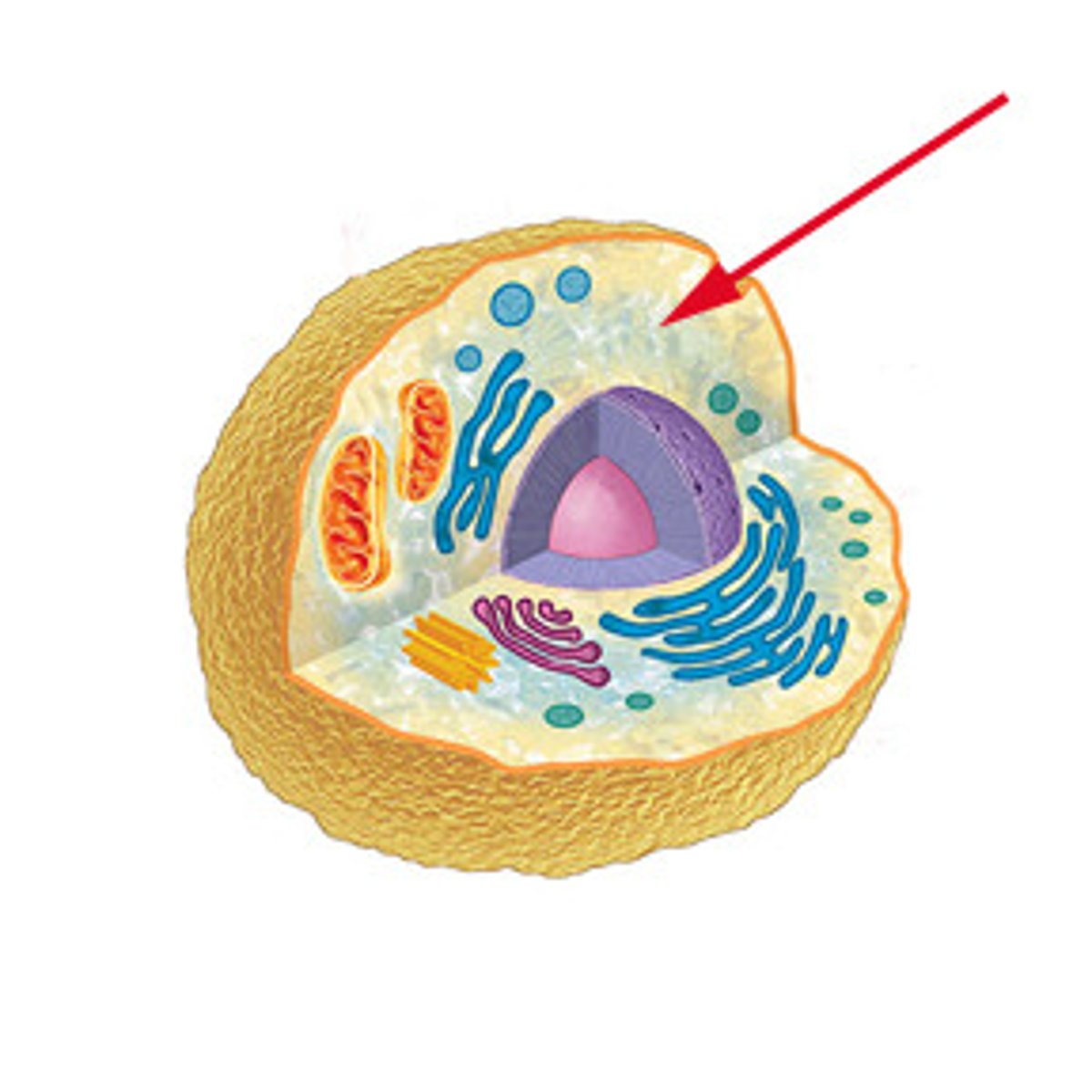
cytoplasm
liquid inside cell membrane
cilia
help movement
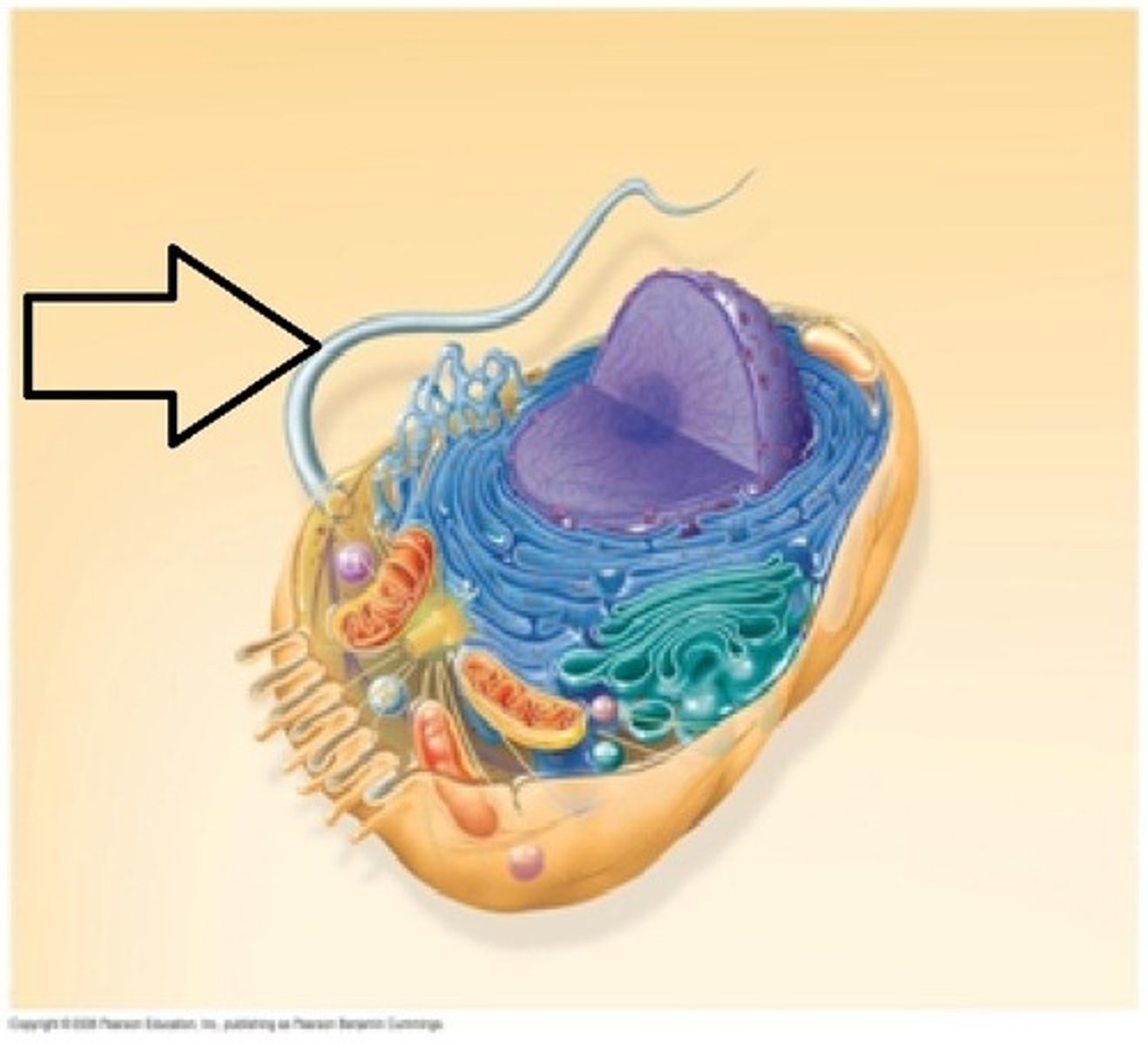
flagella
help move
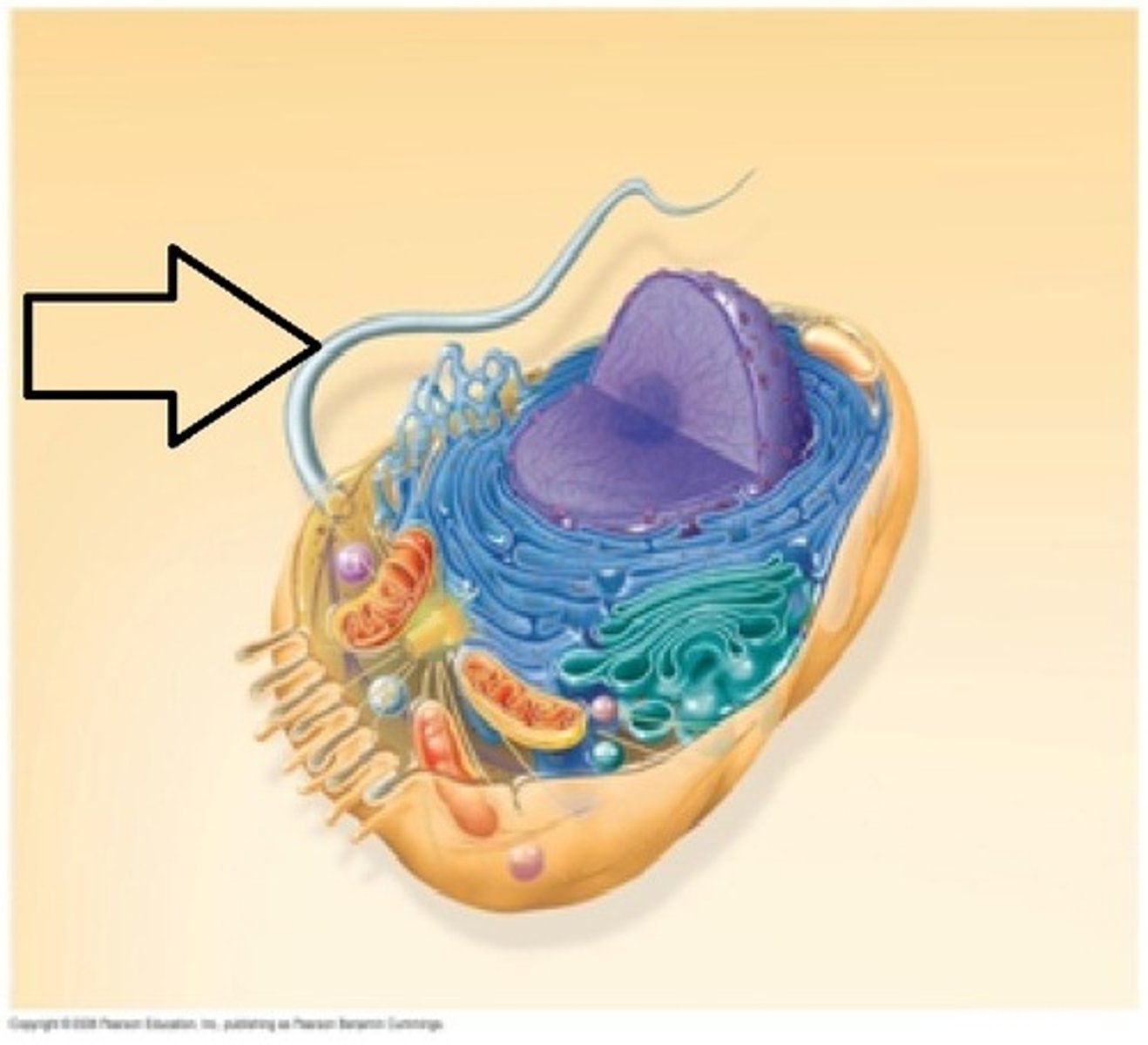
cell wall (found only in plant cells)
provides support and protection
smooth ER
make lipids and some carbs
cytoskeleton
give cells its shape and capacity for movement
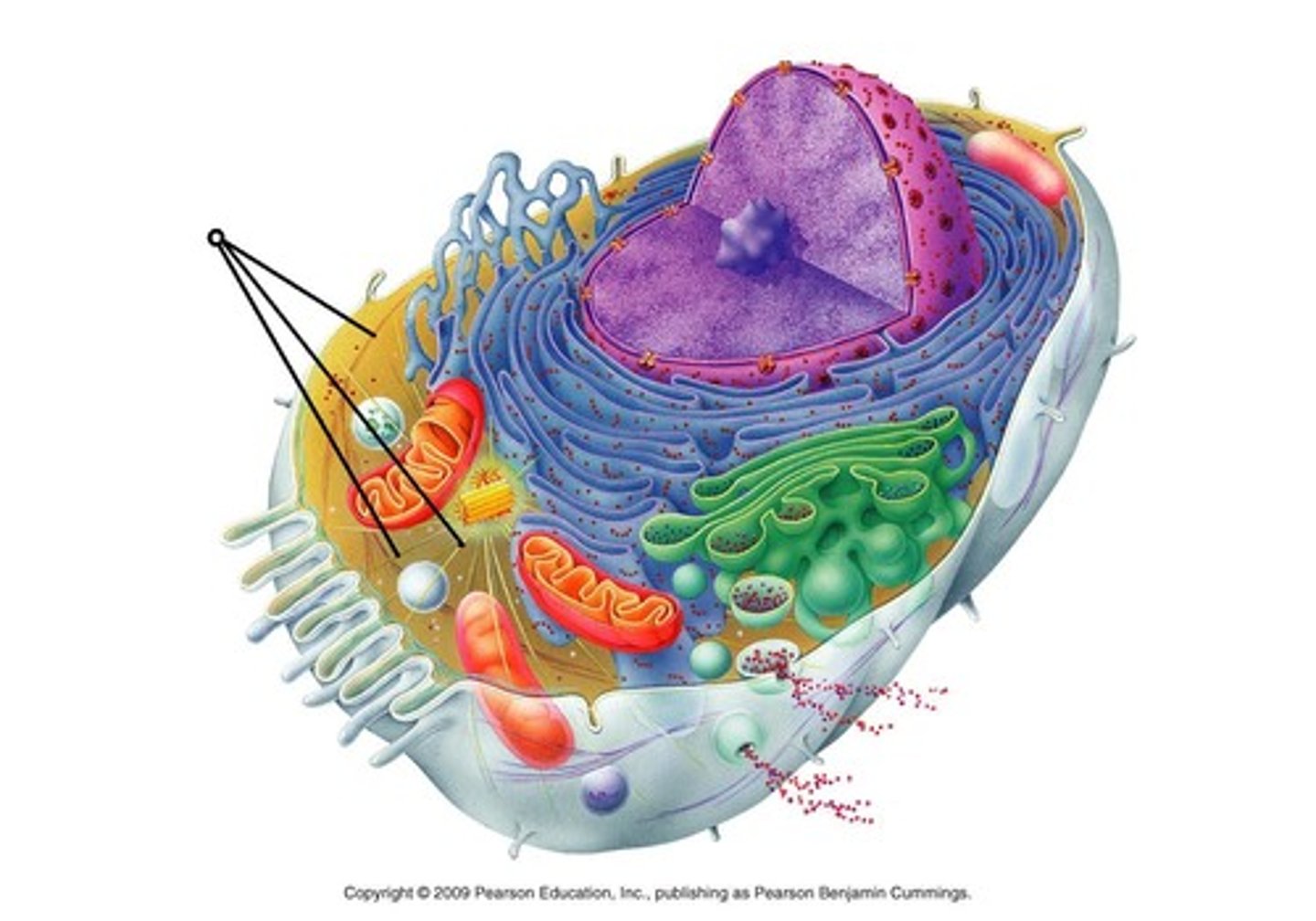
nuclear envelope
lets certain thing in and out of nucleus
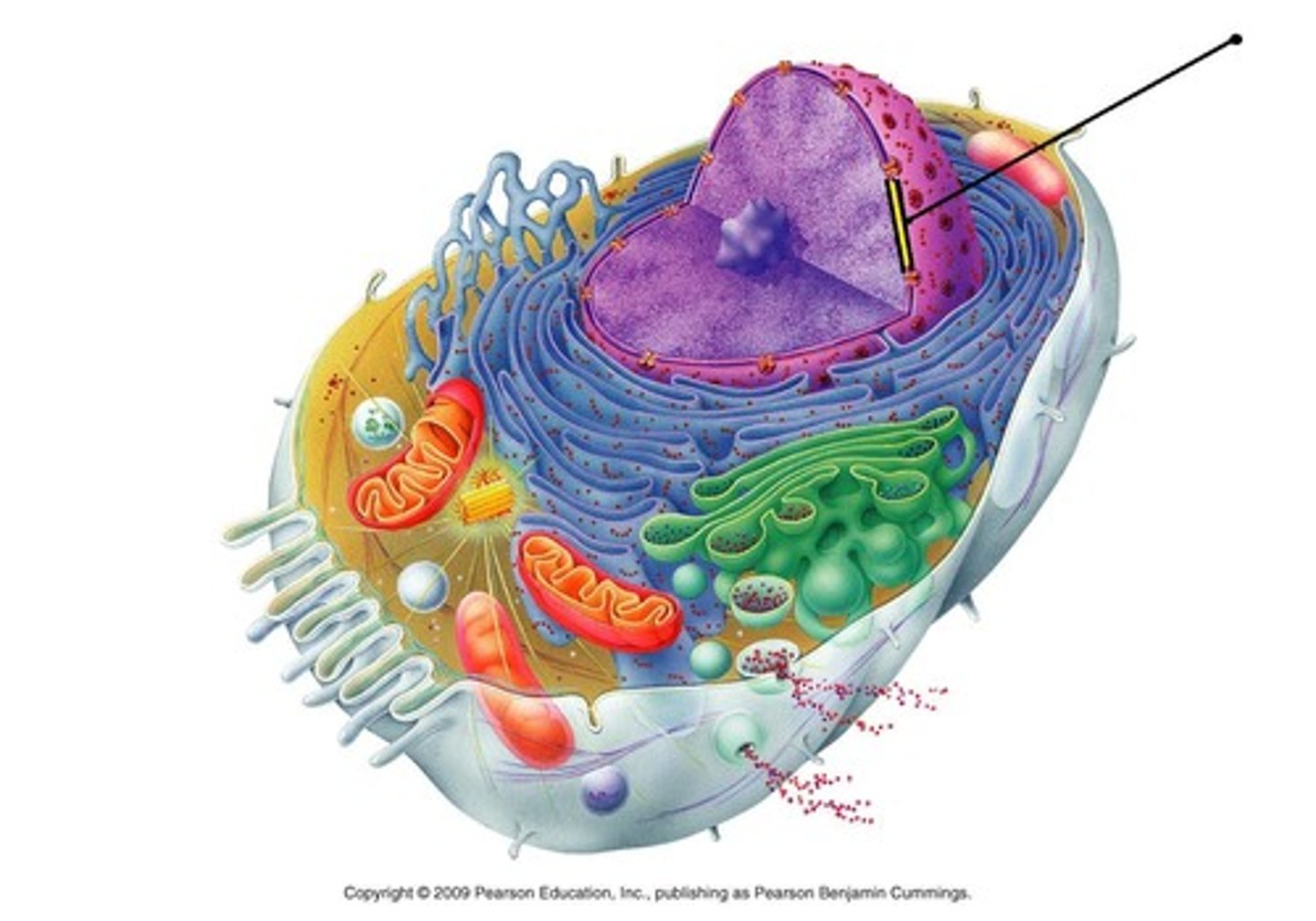
vacuoles (only plant cells)
store nutrients, holds and gets rid of waste- when filled with water holds structure
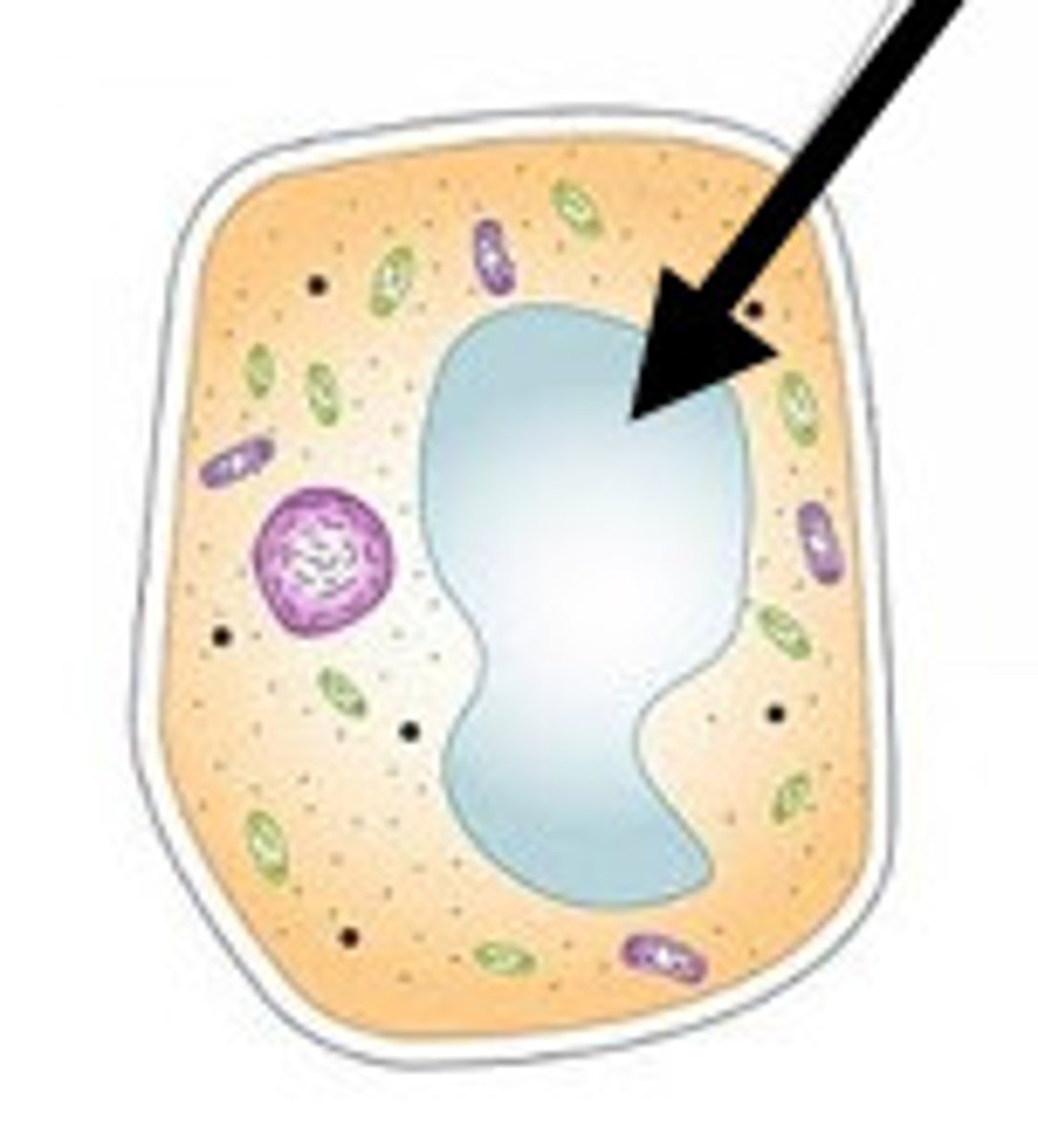
lysosomes (only animal cells)
break down waste