Topic 7
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
True/False all human embryos undergo a hermaphroditic period
True
In what week of gestation do gonadal primordia arise
week 5
Primordial germ cells become what which become what
Primordail germ cells become cortex/inner medulla
– Cortex – develop into ovary
– Medulla – develop into testis
When is chromosomal sex determined
Conception
At what stage of gestation do undifferentiated gonads develop into phenotypic male or female gonads
7 weeks
(sexually bipotential until then)
Precursor of female internal sex organs
Mullerian system
Precursor of male internal sex organs
Wolffian system
Tjio and Levan (1956) contribution to genetics
Discovered 46 diploid for humans; 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes
X and Y Chromosomes are Easily Distinguishable Using a Technique Called _________
Karyotyping
Karyotyping
analysis of chromosomes using a light microscope
Karyotype
A pictorial display of metaphase chromosomes from a mitotic cell
Cytogenetics
The study of chromosome
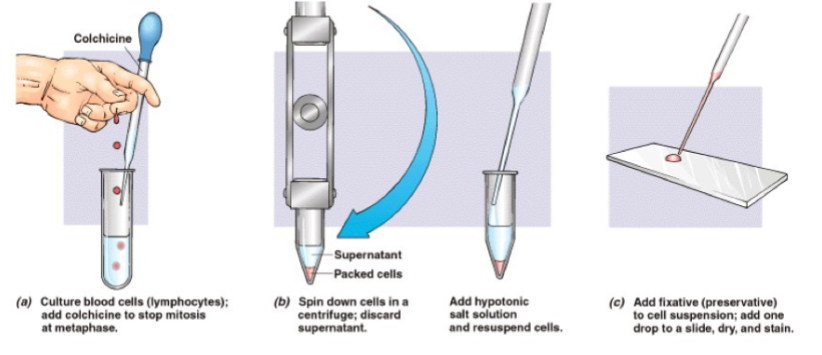
Karyotyping steps
Treat with colchicine which arrests the cells in metaphase
Stain to observe the chromosomes – Giemsa Stains
Photograph or visualize using a computer
Analysis of Chromosomes (Size, position of the centromere, banding and staining regions)
Fluorescent dyes can also be used in karyotyping. For what?
Bind to Specific Regions of Chromosomes
Variations in Color Detected by Computer Program - Result in Digital Image
Pairing of the Chromosomes is easier - Homologous Pairs Identical Colors
Aberrations and Crossovers Easily Recognized
Detect Translocations not Previously Recognizable
Karyotypes are often prepared using what cells
Lymphocytes
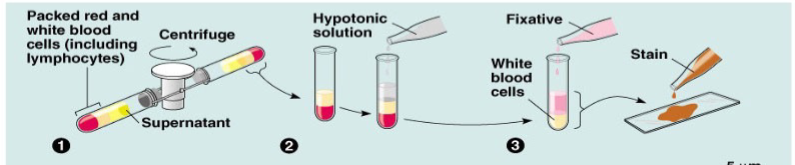
The Y chromosome structure in includes 2 main regions with 1 sub-region. Name all 3
PAR - Pseudoautososmal region
MSY - Male specific region
SRY - sex-determining region
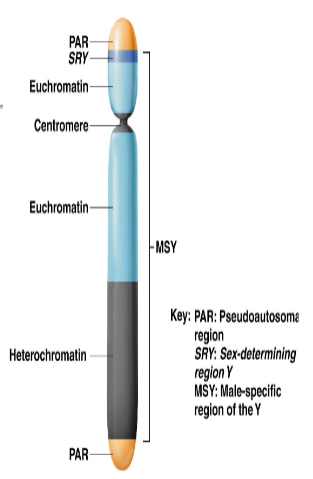
What regions on the Y chromosome that share homology with regions on the X chromosome
Pseudoautosomal Regions (PARs)
What is the function of PARs during meiosis
They synapse and recombine with the X chromosome
Why are PARs important for male gametogenesis
They ensure proper segregation of X and Y chromosomes
How can an XY female be possible
Deletion of the SRY region on Y Chromosome
How can an XX male be possible
Translocation of the SRY Region of Y to the X chromosome
If the SRY gene was given to a female mouse, what would happen
Converts Chromsomal Female Mouse to Phenotypic Male
At what stage of development does expression of SRY begin (by what cells along with development of what)
Sertoli Cells at Time of Testes Development
Where is SRY transcribed that it leads to Male specific Neural Properties
Hypothalamus & midbrain
What chromosome is SF1 gene on
Chromosome 9
Where is SF1 initially expressed & where does it remain expressed
Genital Ridges of both Sexes
Remains Solely in Developing Testes
What happens to SOX9 expression after SRY is expressed
SOX9 is upregulated in Sertoli cells just after SRY expression
What phenotype results from altered SOX9 expression in an XY individual
The individual is phenotypically female despite having an XY genotype
What leads to the regression of female ducts (what hormone by what cells)
Activation of Genes Endcoding Anti Mullerian Hormone secreted by Sertoli Cells
What is DAX1
Gonad Determining Genes
A lack of DAX1 (NR0B1) can lead to absent or underdeveloped gonads
What role does the DAX1 gene play in XY females
DAX1 region on the Y chromosome can interfere with testis development, even in individuals who have the SRY gene
What is DAX1 generally repressed by
SRY
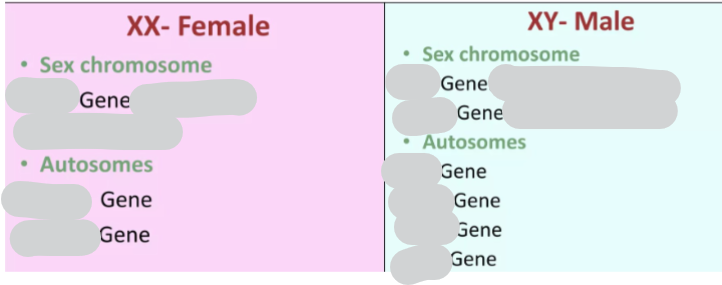
What genes are located on the sex chromosomes & autosomes in females vs males

Effect of SRY on a Y chromosome on Sox9
SRY binds to & elevates the enhancer Sox9 gene in the testis determining pathway
How does Sox9 block development of female phenotype?
Block the ovary-forming pathway by blocking β catenin
Binds to the promotor site on the gene for anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) - can’t be produced without SRY
What does Sox9 activate that stimulates testis development
Sox9 activates Fgf9 synthesis
Effect of Sox9 on Sertoli cells
Sox9 activates other genes that help generate Sertoli cells
How is the Wnt pathway stimulated in females
Absence of the Y chromosome allows Rspo1 to bind to its cell membrane receptor & stimulate the Wnt pathway (Wnt4)
What is β catenin and how is it produced
It is a transcriptional regulator produced by the Wnt pathway
How does β catenin contribute to positive feedback
Activates genes for Rspo1 & Wnt4
How does β catenin contribute to female phenotype development
Initiates the ovarian pathway of development
Prevents the production of Sox9
Activates other genes in the ovary → production of granulosa cells
How, if there are 2 X chromosomes, is there not an overloading of the genes on those chromosomes
Dosage compensation by inactivation of 1 X chromosome
What is a Barr Body
An inactivated X chromosome
(XX females & XXY males have a Barr body)
Where & when does x inactivation occur
X inactivation occurs outside the ovary around day 12 in utero
What is XIST
X-inactive specific transcript
Plays role in X chromosome activation
True/False XIST is present on both X chromosomes
Kinda True - Initially, XIST is transcribed from both X chromosomes
The X-inactivation center (Xic) is only active on the inactive X..
Only one X will continue to produce XIST – Inactive.
Inactive X is condensed/decondensed
highly condensed
In what phase can you stain a cell and see the inactive X (Barr bodies)
Stained interphase cells
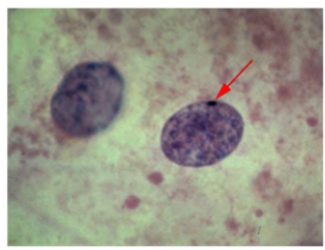
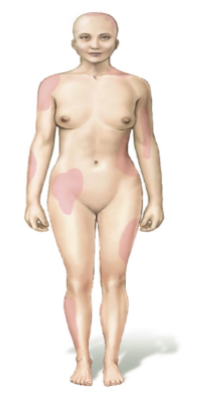
Give an example of anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Depiction of the absence of sweat glands in the shaded regions in a female due to them being Heterozygous for the X-linked condition
The locations vary from female to female, based on the random pattern of X chromosome inactivation during early development, resulting in unique mosaic distributions of sweat glands in heterozygotes.
Why do males with Androgen insensitivity syndrome develop phenotypically female
Males who inherit this condition produce testosterone and DHT but are unable to respond to either hormone due to a mutation in the gene encoding the androgen receptor.
These individuals have normal male chromosomes
The low level of estrogen that is produced by the adrenal glands is enough to stimulate female secondary sex characteristics
Summary slide
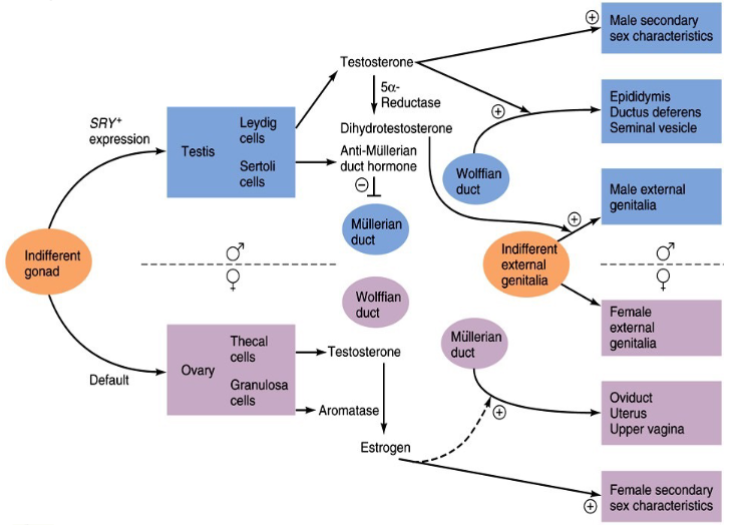
Does development of gonads in males & females begin at the same time
Male development of gonads occurs about 2 weeks before female gonadal development
When preparing a karyotype, why can’t we use RBCs
They don’t have a nucleus
In what stages of the cell cycle can FISH be done
Interphase & Metaphase
