Electrophilic Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Give examples of hydrogen halides.
H-Cl
H-Br
H-I
Are hydrogen halides polar molecules?
Yes.
Halogen atoms are more electronegative than hydrogen.
Hydrogen will have a slight positive (δ+) charge; a halogen molecule will have a slight negative (δ-) charge.
Describe what happens when a hydrogen halide (H-Br) approaches the C=C double bond in an alkene molecule(ethene).
The delta positive hydrogen atom is attracted to the high electron density of the C=C double bond.
The hydrogen atom acts as an electrophile.
The positive charge on the hydrogen atom attracts the electron pair in the pi bond of the ethene. This causes a bond to form between the hydrogen atom and one of the carbon atom in the double bond.
Describe what happens when a bond is formed between the delta positive hydrogen atom and one of the carbon atoms in the double bond.
A carbocation intermediate is formed as the other carbon atom loses its share of the pair of electrons that was in the pi bond.
Also, the pair of electrons in the H-Br bond move to the delta negative bromine atom leaving a bromide ion with a lone pair of electrons.
This is an example of heterolytic bond fission.
Describe what happens after a carbocation is formed.
The electron pair on the bromide ion are attracted to the positively charged carbon atom in the carbocation.
A covalent bond forms between the bromide ion and the positively charged carbon atom.
The product formed is bromoethane.
Ethene is a…
Symmetrical alkene.
How many products can be formed when a symmetrical alkene is reacted with a hydrogen halide?
1 product.
What is hydrogenation?
The reaction between an alkene and hydrogen.
Describe what happens in an hydrogenation reaction.
The double bond of an alkene e.g. ethene, undergoes the addition of hydrogen in the presence of a metal catalyst.
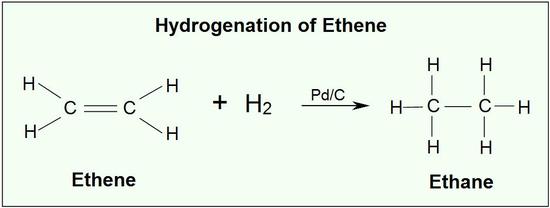
What are the conditions needed for an hydrogenation reaction?
The reaction takes place in the presence of a metal catalyst.
A transition metal is usually used, such as platinum and palladium, although nickel is more commonly used.
Give one important application of the hydrogenation reaction of alkenes.
One important application of this reaction is the production of margarine from vegetable oils.
Vegetable oils contain many double bonds (polyunsaturated); they are hydrogenated (hydrogen is added) to make margarine.