anaerobic respiration
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
how can cells produce some some atp in low oxygen conditions via anaerobic pathways
cells can oxidise reduced NAD, produced in glycolysis, use this foe hydrogen transport - glycolysis continues
2 pathways used by cells to respire anaerobically in low oxygen conditions
ethanol fermentation and lactate fermentations
what types of organisms use ethanol fermentation to respire anaerobically
yeast and plants
what types of organisms/cells use lactate fermentation when respiring anaerobically
muscle cells and microorganisms
explain the process of ethanol fermentation (3)
pyruvate is converted to ethanal by the enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase - co2 is a by product
ethanal is reduced to ethanol and catalysed by ethanol dehydrogenase - NADH oxidised to NAD
explain the process of lactate fermentation ()
pyruvate is reduced to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase - NADH oxidised to NAD
ethanol dehydrogenase
enzyme that catalyses the reduction of ethanal to ethanol
pyruvate decarboxylase
enzyme that catalyses the conversion of pyruvate to ethanal
in anaerobic respiration in animals, pyruvate is reduced to
lactate
what 2 things can happen after lactate is produced
oxidised back to pyruvate- used in krebs cycle or converted into glycogen for storage in the liver
oxygen debt
oxidation of lactate back to pyruvate needs extra oxygen - breathe deeper to make up
what is a redox indicator
substance that changes colour when reduced or oxidised
2 examples of redox indicators
DCPIP and methylene blue
what are redox indicators such as DCPIP and methylene blue used to investigate in rqp 9
effects of temperature and substrate concentration on the rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast
where can the oxidised NAD produced in anaerobic respiration be used
in further glycolysis
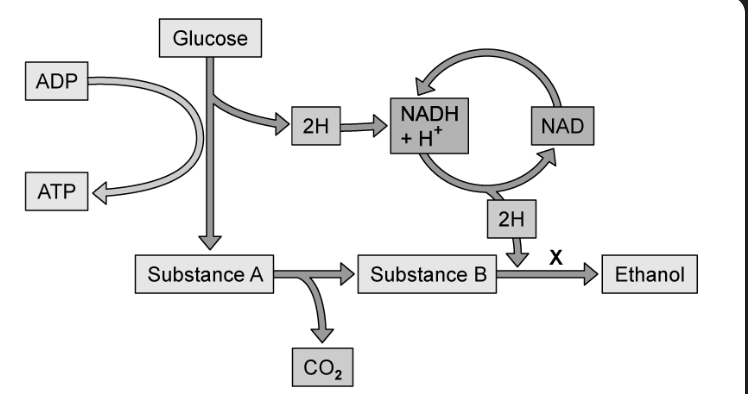
identify substance A
pyruvate
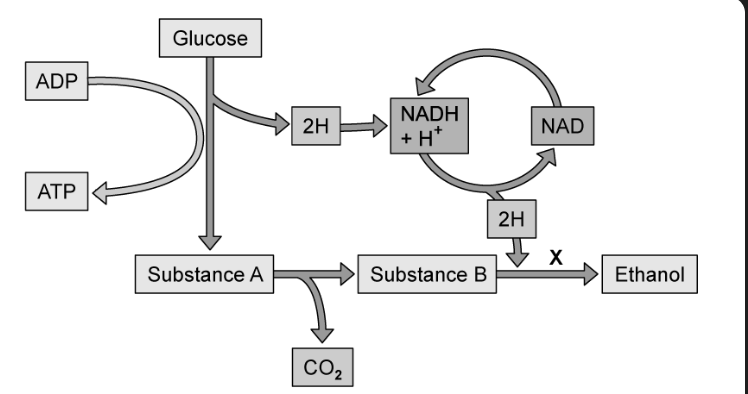
identify substance B
ethanal
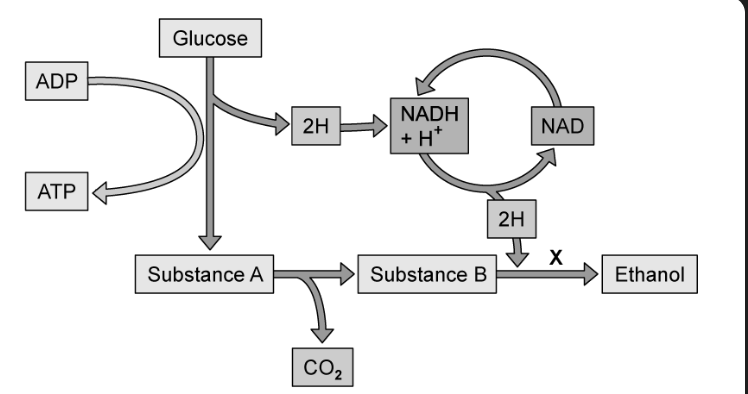
what reaction has occurred at point X, justify this (2)
reduction reaction
ethanal is the hydrogen acceptor
give 2 ways that lactate can be metabolised
oxidised to produce pyruvate
stored at glycogen
in an experiment to measure anaerobic respiration, a researcher uses an airtight container containing yeast. Why must the sealed container must be airtight (3)
no oxygen can enter
no co2 can escape
prevent entry of microorganisms
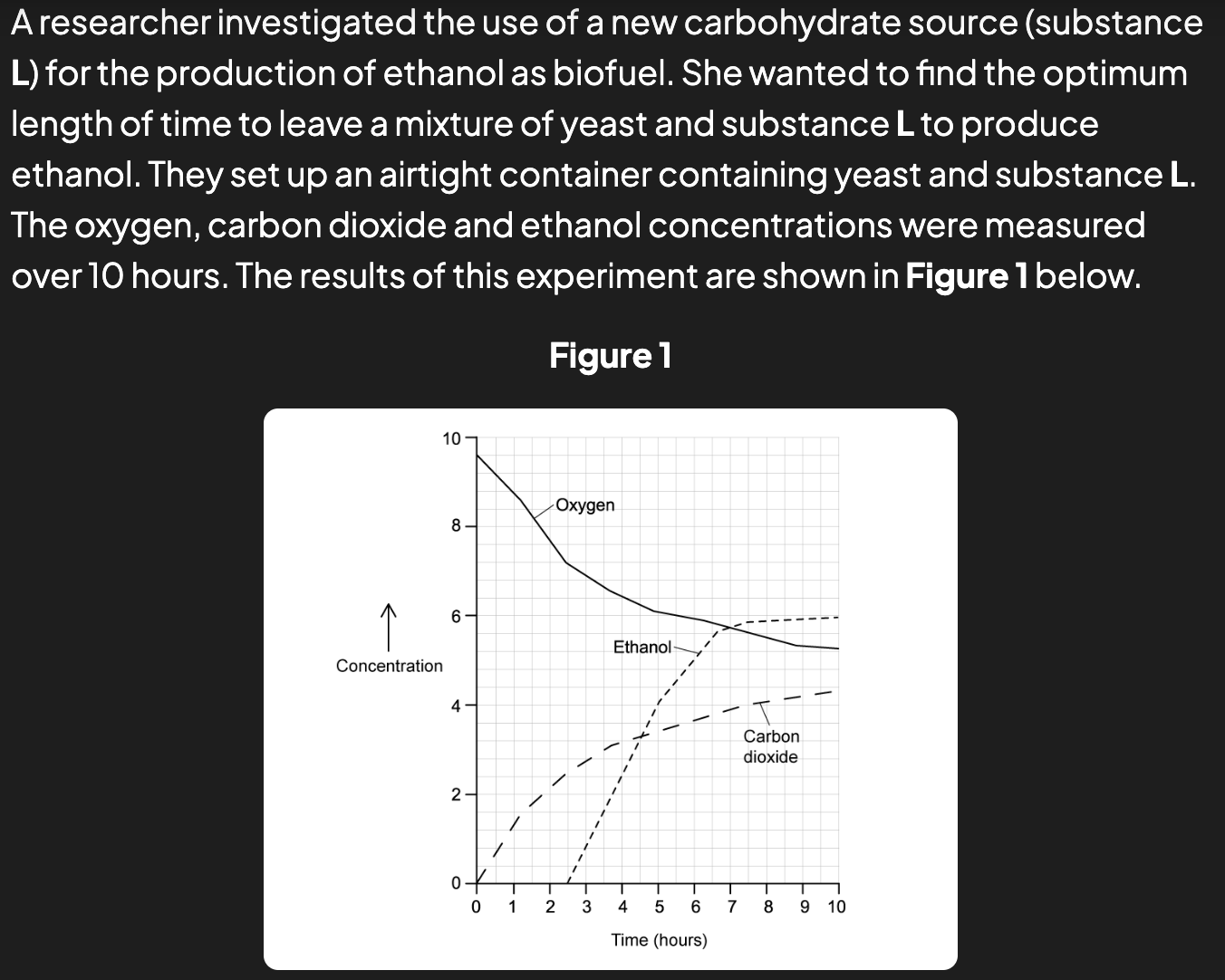
explain the relationship between the concentration of oxygen and co2 (2)
yeast are respiring aerobically
so oxygen used is equal to co2 produced
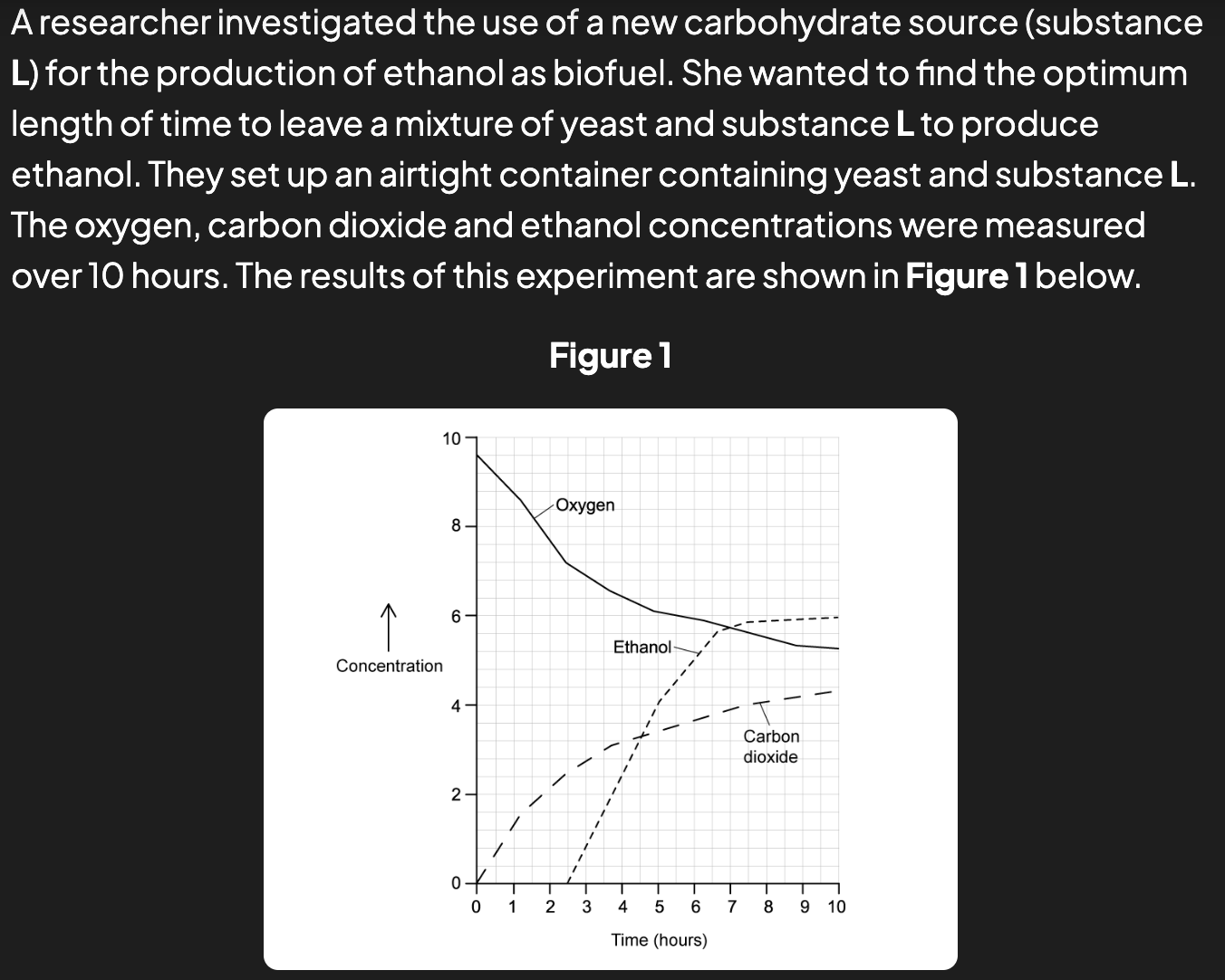
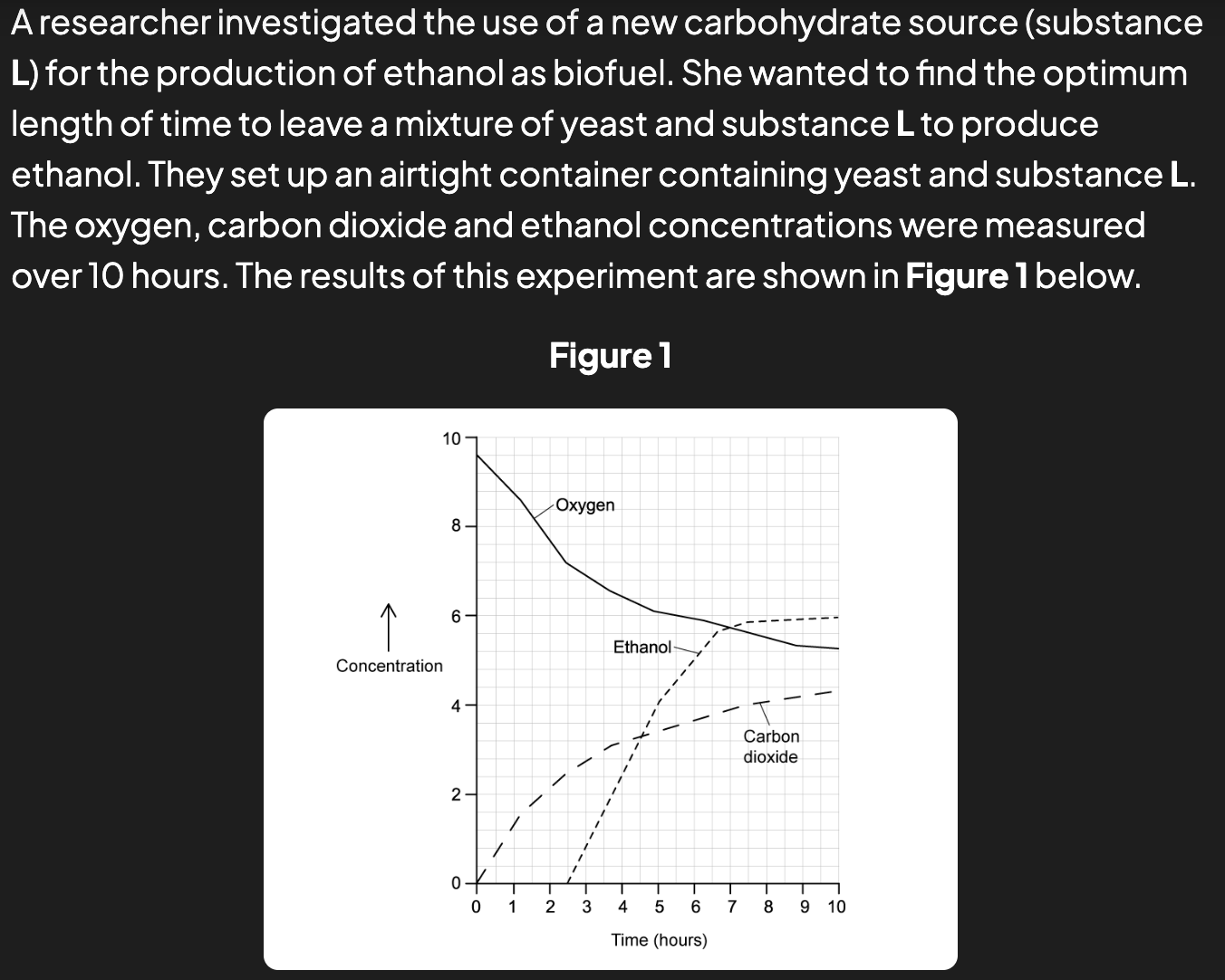
a bio fuel company want to know how long they should let the reaction go on for, when commercially producing ethanol for biofuels using substance L. use figure 1 to suggest a length of time - justify (3)
7 hours
curve starts levelling off
becomes less cost-effective
after exercise, explain why blood lactate begins to fall (2)
lactate converted to pyruvate
lactate reacts with oxygen
what happens when dcpip or methylene blue are present in anaerobic respiration (rqp 9)
they take up hydrogens from the organic compounds and are reduced instead of NAD - changing from blue to colourless
what does the rate of colour change correspond to in rqp 9, when investigating the rate of anaerobic respiration in yeast
the rate dehydrogenase is working at, therefore rate of respiration yeast
(rqp 9) rate of respiration(sec-1) =
1/time (sec)
6 control variables of the yeast practical (rqp9)
volume of dye added, volume of yeast suspension, type of substrate, concentration of substrate, temperature and pH