APES Unit 4 Study Guide
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Total Fertility Rate
The average number of children per woman
Replacement Rate
Replacement level fertility is the level of fertility at which a population exactly replaces itself from one generation to the next.
In developed countries, replacement level fertility can be taken as required an average of 2.1 children.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths occurring during the year, per 1,000 people in the population
Infant Mortality / Infant Mortality Rate
The death of an infant before their first birthday. Infant mortality rate is the number of infant deaths for every 1,000 live births.
Child Mortality / Child Mortality Rate
The death of a child before their 5th birthday. Child mortality rate is the number of child deaths for every 1,000 live births.
Factors that influence birth and fertility rates
-age of marriage and first child
-educational and employment opportunities for women
-access to family planning
-government acts and policies
Demographic Transition model
The model of population change due to a shift in growth over time from rapid → slow → decline.
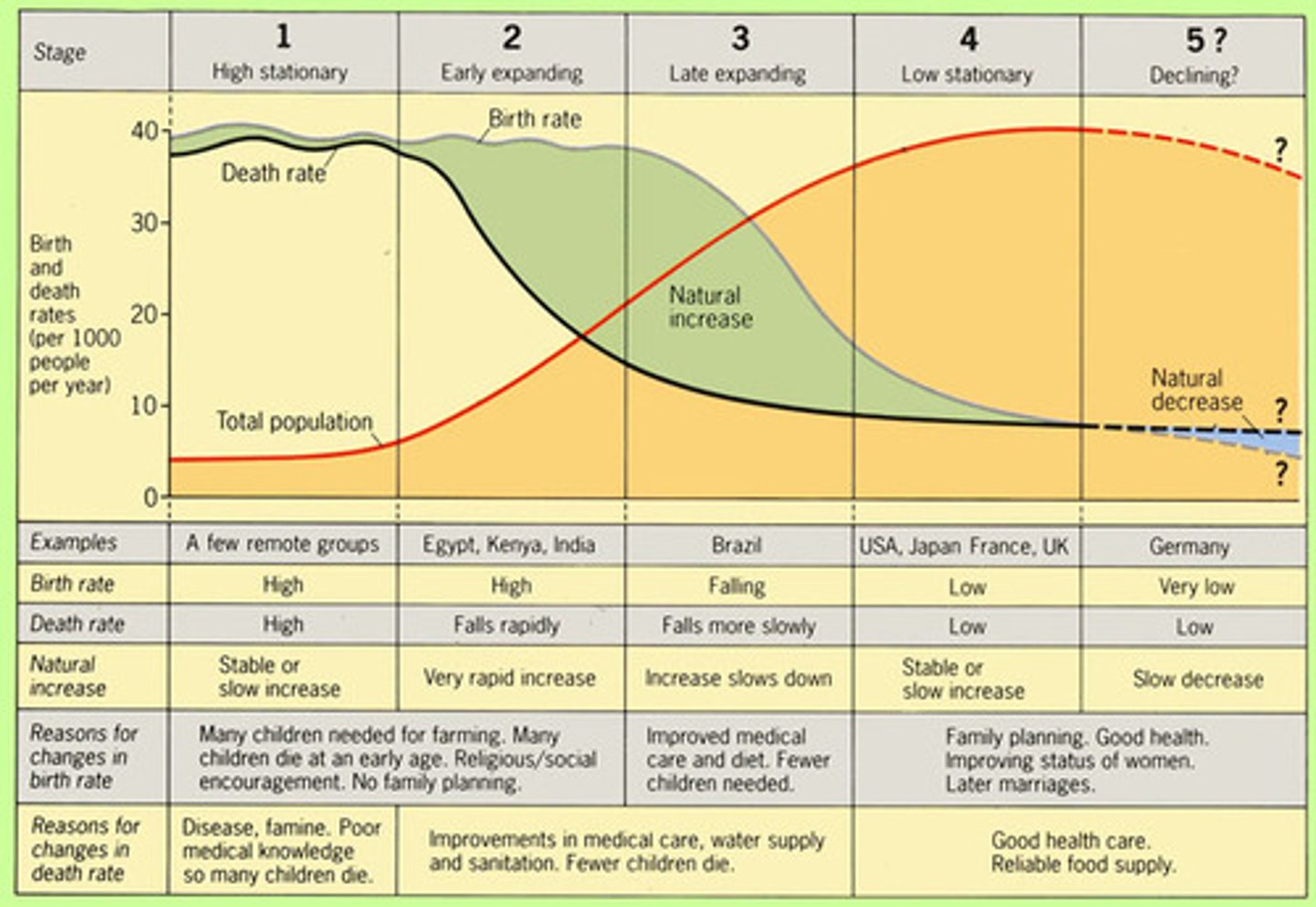
stage 1 of demographic transition
High stationary: Low growth; Very high birth and death rates; Hunting & gathering, agricultural societies.
stage 2 of demographic transition
Early expanding: High growth; Rapidly declining death rates and very high birth rates; Industrial societies or societies that benefit from the medical revolution. (Egypt, Kenya, India)
stage 3 of demographic transition
Late expanding: Decreasing growth; Birth rates rapidly decline; death rates continue to decline; Highly urban societies. (Brazil)
stage 4 of demographic transition
Low stationary: Low growth; Very low birth and death rates = zero population growth (USA, UK)
stage 5 of demographic transition
declining population: very low birth rates, low death rates, slow decrease (Germany)
Type I Survivorship Curves
Low death rate, many live to old age. K-selected species. (Humans)
Type II Survivorship Curve
Constant loss. Moderate death rate, individuals die at all ages. (Songbirds, lizards, jellyfish)
Type III Survivorship Curve
High death rate, many individuals die young and few live to old age. r-selected species. (Rats, insects, trees)
Life Expectancy (LE)
Average age of death in a population
Density dependent factors
competition for food/water, parasitism, predation
Density independent factors
natural disasters (wildfires, hurricanes, severe weather)
Urban sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land. Impacts: loss of ecosystems, farmland, natural cover.
Disruptions to the water cycle due to urbanization
Addition of impermeable/impervious surfaces (cement, pavement) Decreased infiltration, (groundwater recharge), Increased runoff, Increased pollutants in water ways
Advantages of city life
Employment opportunities, better education, better amenities (hospitals, transportation)
Disadvantages of city life
Cost of living (rent, utilities, food, taxes), pollution, competition for resources, less natural environments
Urban runoff
Urban runoff is the flow of water from precipitation and outdoor water use that travels over surfaces in cities and does not soak into the ground. This water collects pollutants like motor oil, pesticides, and trash as it flows over roads, rooftops, and driveways, often ending up in storm drains that lead directly into rivers and lakes.
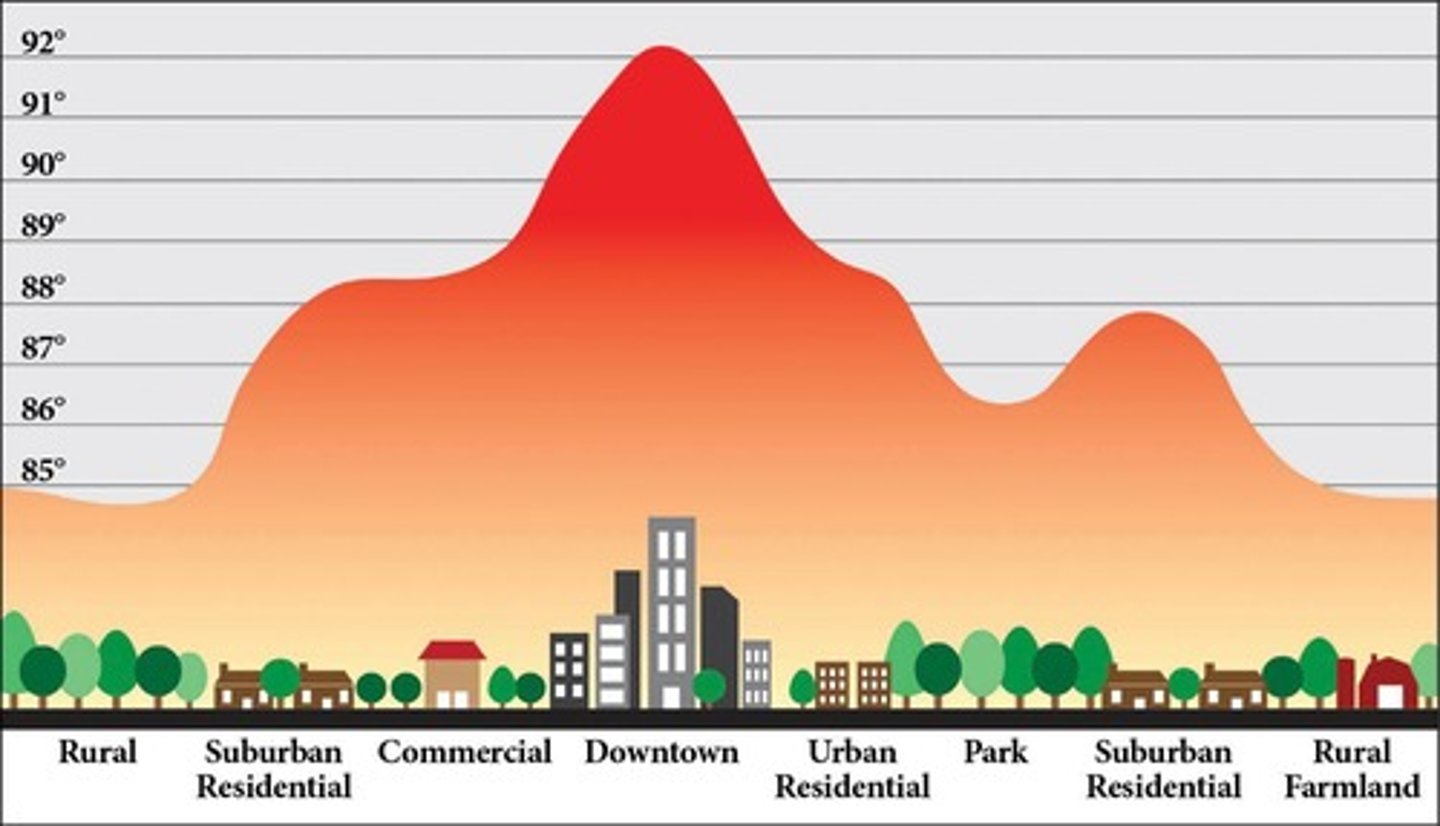
Urban heat island effect
the heat that cities generate as a result of having many buildings and few trees or other vegetation
Ecological Footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
Ecological assets
what a given pop. requires to produce the natural resources it consumes and to absorb its waste, especially carbon emissions.
Ecological deficit
An ecological deficit happens when a population consumes natural resources faster than the Earth (or a specific region) can regenerate them
Earth overshoot day
Marks the day when humanity's demand for ecological resources in a given year exceeds what Earth can regenerate in one year
Tragedy of the Commons
Suggests that individuals will use shared resources in their own self interest rather than in keeping with the common good, thereby depleting the resources.
Examples of tragedy of the commons
Overfishing, Water use, Deforestation - agriculture, Public parks or facilities