OCR Chemistry A: Module 5 - Buffers and Neutralisation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Define buffer solution
A system that minimises pH changes on addition of small amounts of an acid or a base
What are two ways to make a buffer solution?
- By combining a weak acid with its salt
- By combining an alkali with an excess of weak acid
How is a buffer created from a weak acid and its salt?
The salt provides a source of the conjugate base, as it dissociates in water completely.
How is a buffer created from an alkali and an excess of weak acid?
The weak acid is partially neutralised by the alkali, forming the conjugate base, and some is left over. The resulting solution is a mixture of the weak acid and the salt of the weak acid
Explain how a buffer acts to maintain the pH when a small amount of acid is added?
- The concentration of H+ ions increases
- The H+ ions react with the conjugate base
- The position of equilibrium shifts to the left, which decreases the concentration of H+ ions
Explain how a buffer acts to maintain the pH when a small amount of alkali is added?
- The concentration of OH- ions increases
- The OH- ions react with the H+ ions, making water
- Therefore the concentration of H+ ions decreases
- The position of equilibrium shifts to the right in order to restore the concentration of H+ ions
A buffer is most effective at removing either acid or alkali when the concentrations of the weak acid and the conjugate base are....
equal
When the concentration of the weak acid and the concentration of the conjugate base are equal, the pH of the buffer is equal to the
pKa of the acid
Write the equilibrium equation for a weak acid, HA
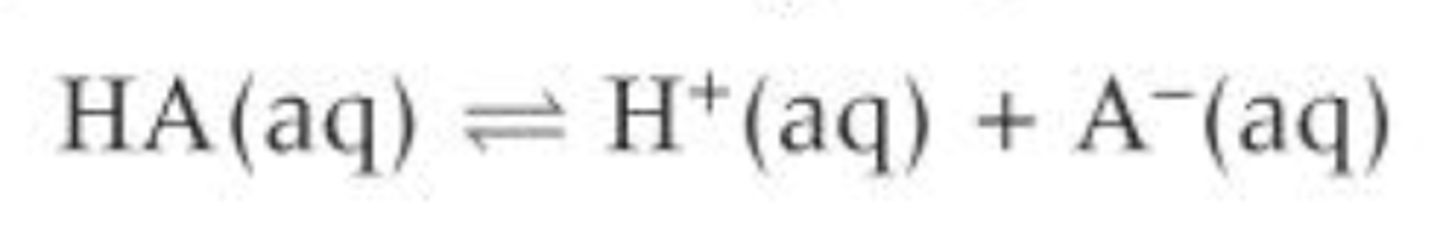
Write the Ka expression for a weak acid, HA
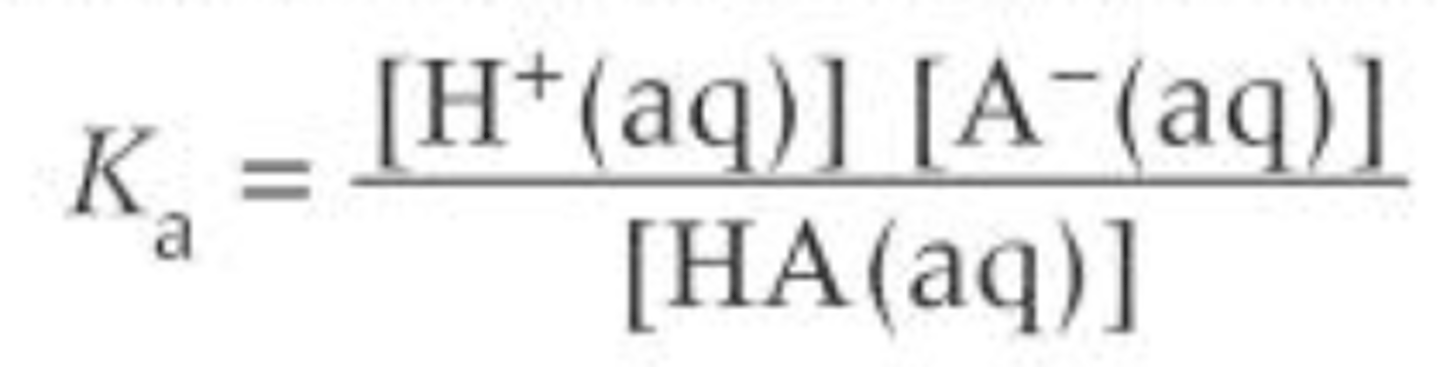
Why must the pH of the blood plasma be kept constant?
To maintain function of enzymes
What forms the buffer system in blood?
Carbonic acid and hydrogencarbonate
Write the equilibrium equation for the buffer system in the blood
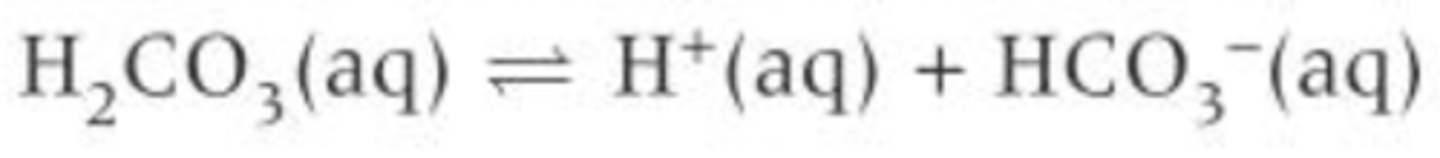
How does the buffer system in the blood remove excess acid?
- H+ ions react with the HCO₃⁻ ions
- The position of equilibrium shifts to the left, removing H+ ions from the system
What is the vertical section of a pH titration curve called?
The equivalence point
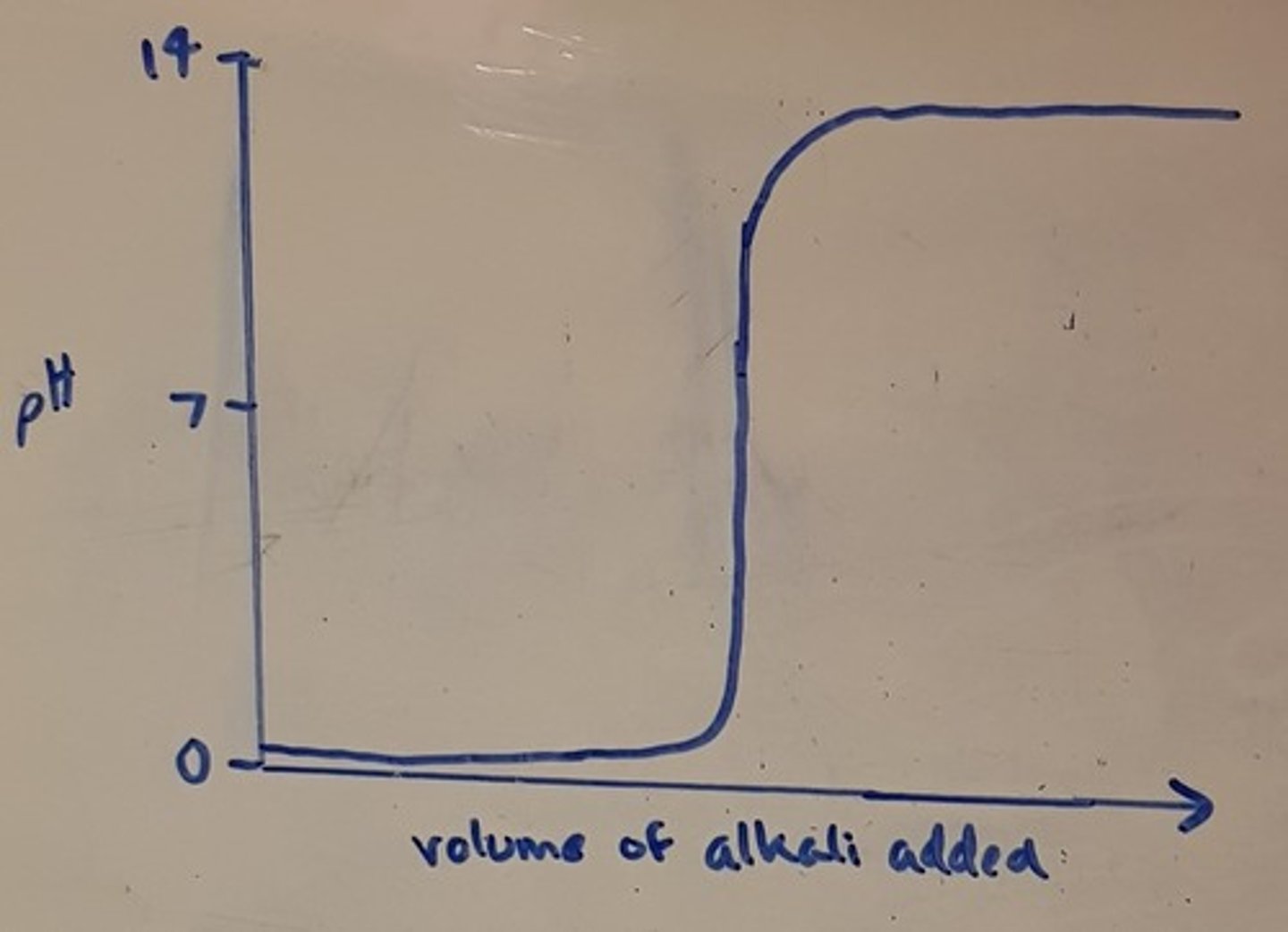
Draw a pH titration curve for a strong base added to a strong acid
Draw a pH titration curve for a strong acid added to a strong base
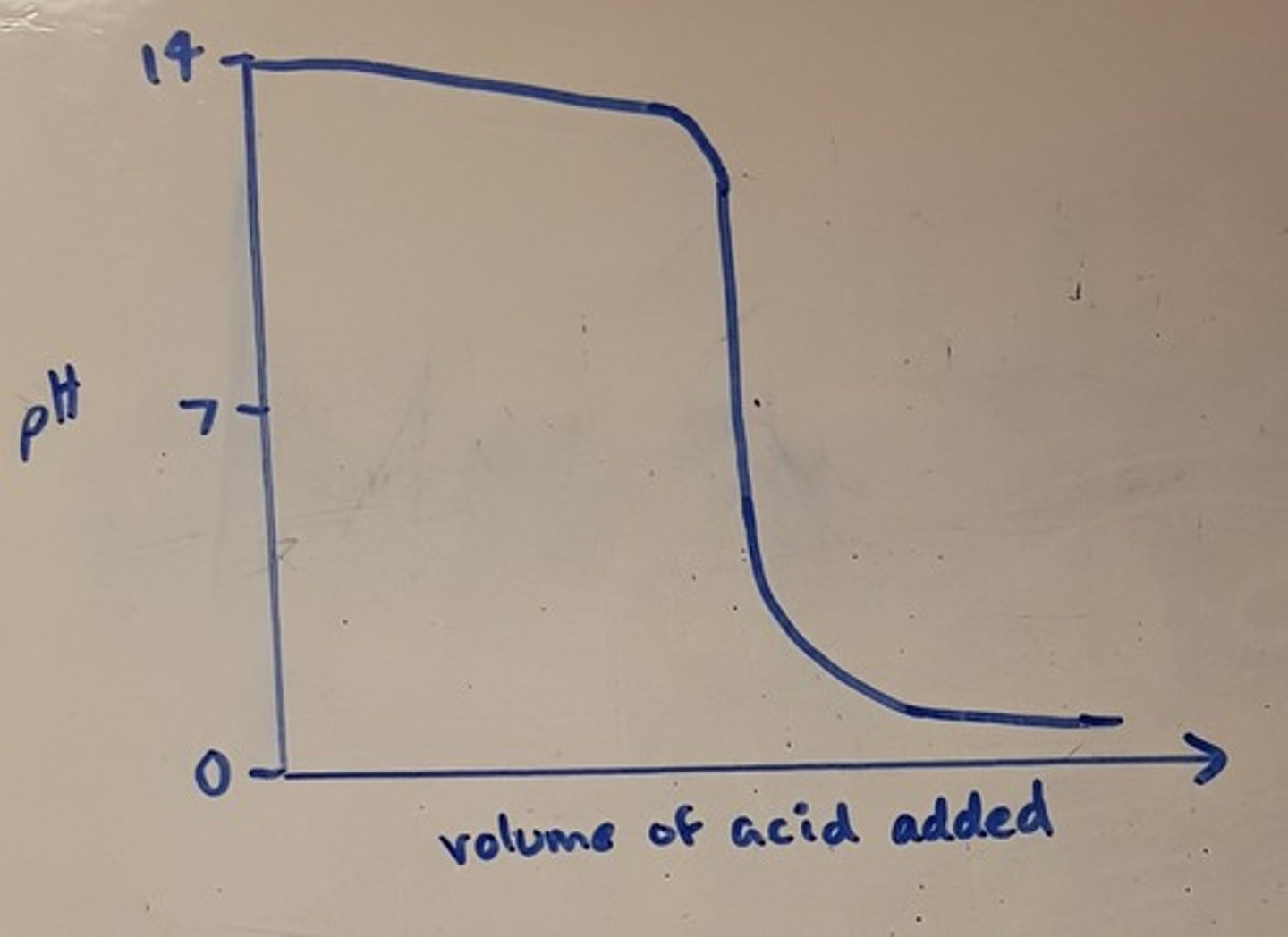
Draw a pH titration curve for a strong acid added to a weak base
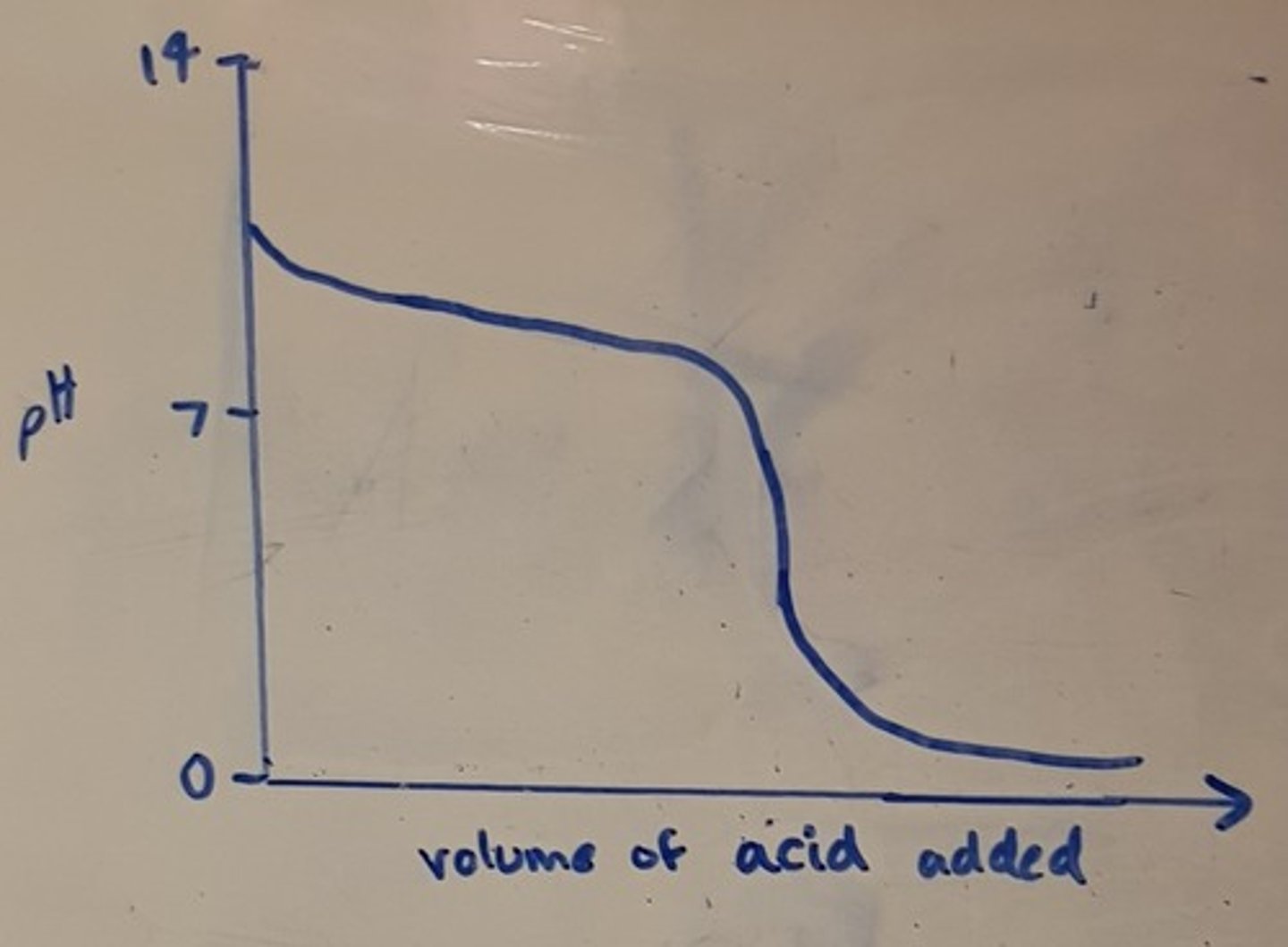
Draw a pH titration curve for a weak acid added to a strong base
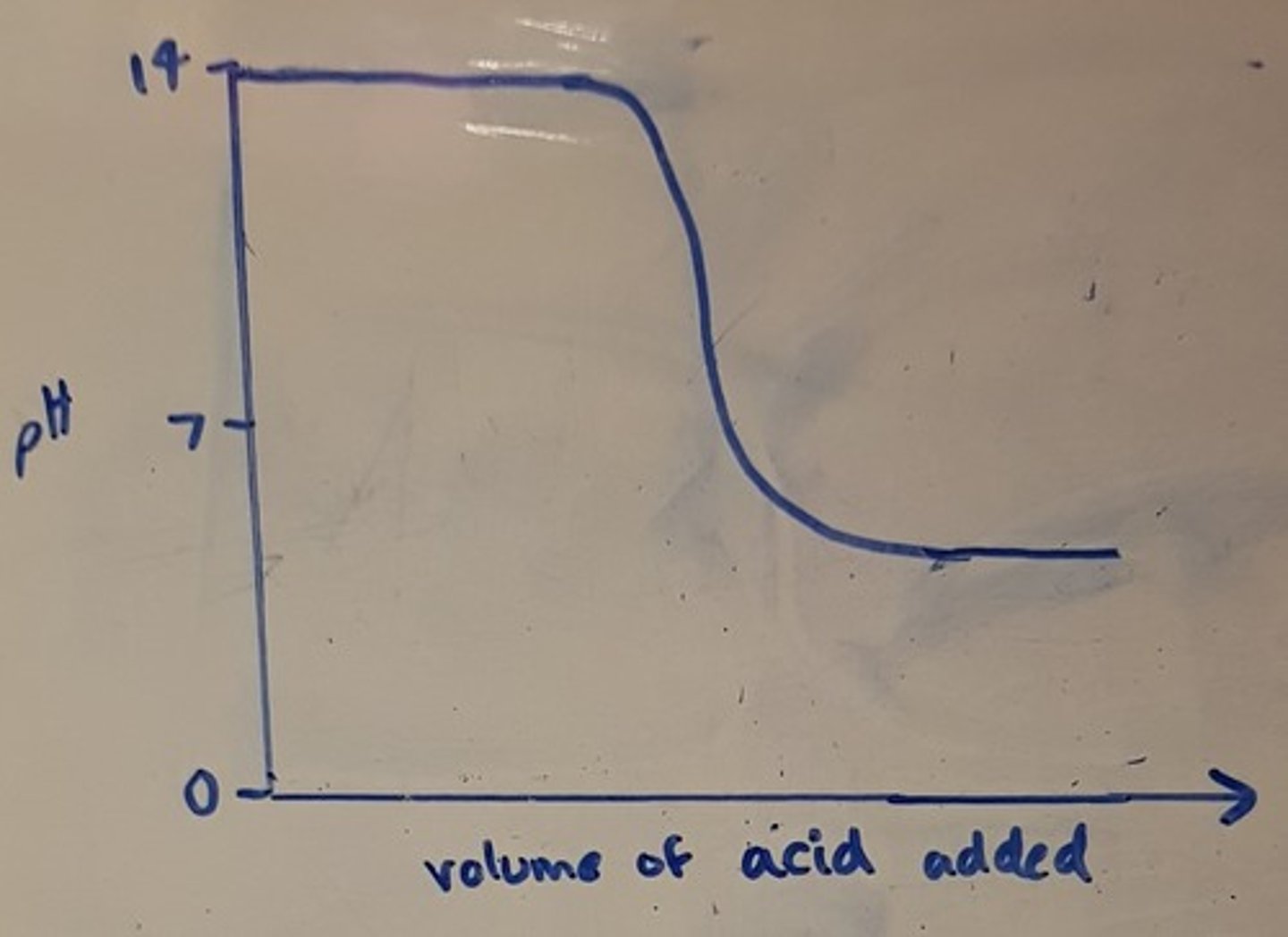
Draw a pH titration curve for a weak base added to a strong acid
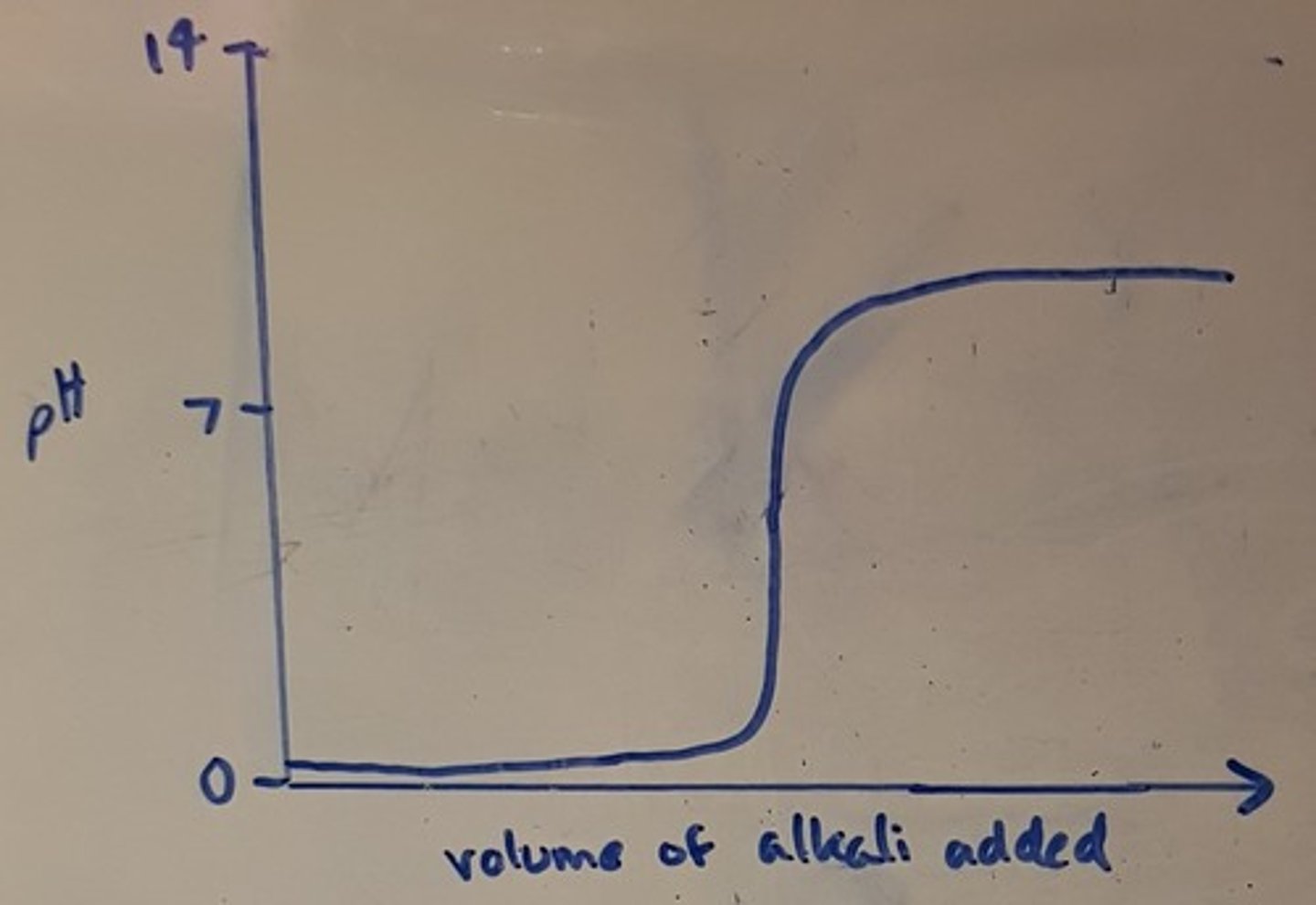
Draw a pH titration curve for a strong base added to a weak acid
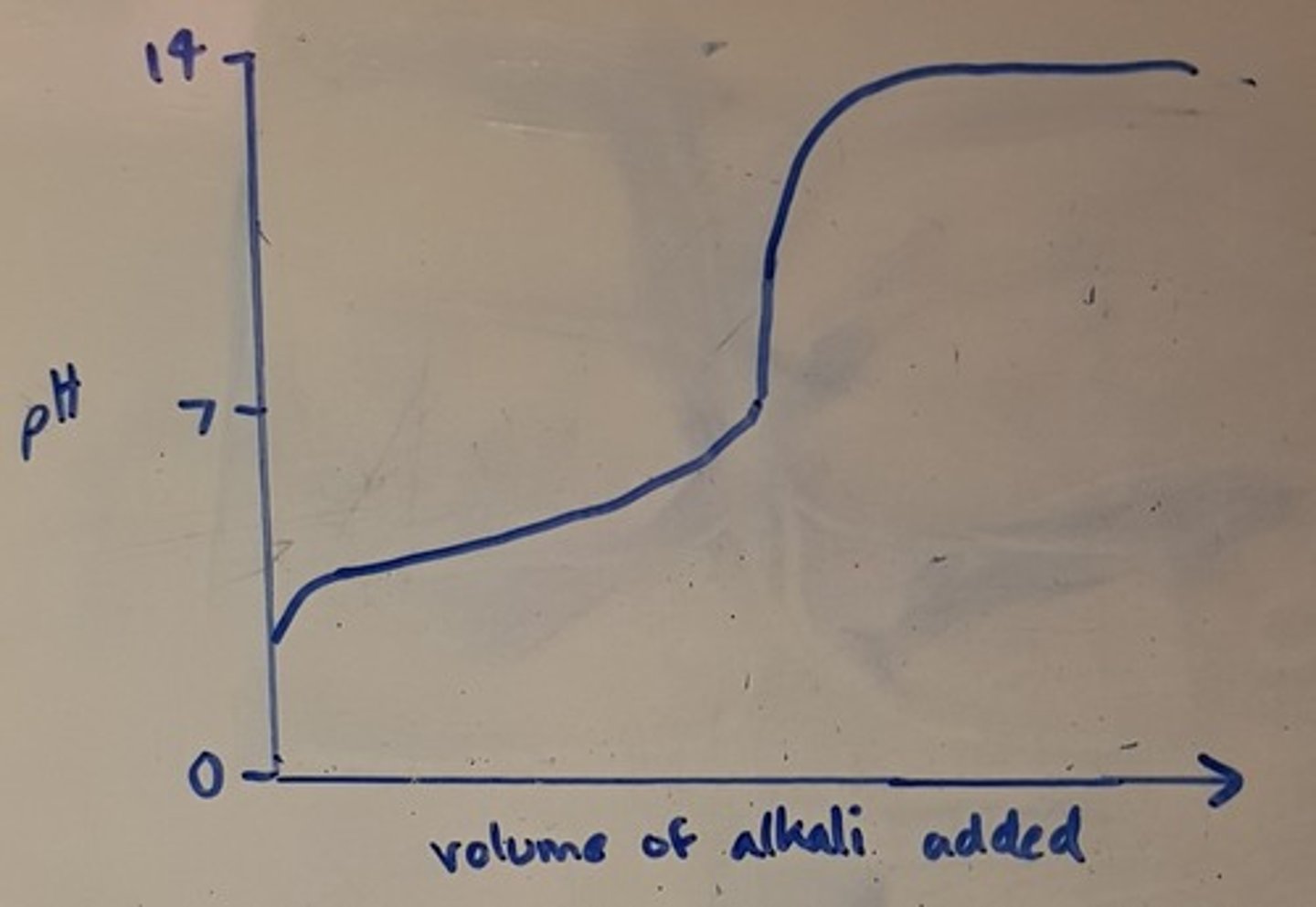
Define end point
The point in a titration where the indicator changes colour
Define equivalence point
The point in a titration at which the volume of one solution has reacted exactly with the volume of the second solution