Ch 18: DNA Mutation: Types, Causes, and Repair Mechanisms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the role of mutations in biology?
Mutations are the source of all genetic variation, provide raw material for evolution, and are associated with many diseases and disorders.
What are the two main categories of mutations?
Somatic mutations and germ-line mutations.
What are the three basic types of gene mutations?
Base substitutions, insertions, and deletions.
What distinguishes a transition from a transversion mutation?
A transition is the substitution of a purine for a purine or a pyrimidine for a pyrimidine, while a transversion is the substitution of a purine for a pyrimidine or vice versa.
What is an expanding nucleotide repeat?
An increase in the number of copies of a set of nucleotides.
What is a missense mutation?
A mutation that results in an amino acid being replaced by a different amino acid.
What is a nonsense mutation?
A mutation that changes a sense codon into a stop codon.
What is a silent mutation?
A mutation that changes a codon to a synonymous codon, resulting in no change in the amino acid sequence.
What is a suppressor mutation?
A mutation that hides or suppresses the effect of another mutation.
What are the two types of suppressor mutations?
Intragenic suppressor mutations and intergenic suppressor mutations.
What is a loss-of-function mutation?
A mutation that results in the loss of some function.
What is a gain-of-function mutation?
A mutation that results in the gain of some function.
What is a lethal mutation?
A mutation that results in the death of the organism.
What factors affect mutation rates?
The frequency of changes in DNA, the probability of repair when changes occur, and the probability of detection of mutations.
What is the Ames test used for?
To identify chemical mutagens.
What is mismatch repair?
A DNA repair mechanism that corrects mismatched bases and other DNA lesions.
What is direct repair?
A repair mechanism that restores the correct structures of altered nucleotides.
What is base-excision repair?
A repair process where glycosylase enzymes recognize and remove specific modified bases, followed by the replacement of the entire nucleotide.
What is nucleotide-excision repair?
A repair mechanism that removes and replaces damaged DNA that distorts the DNA structure.
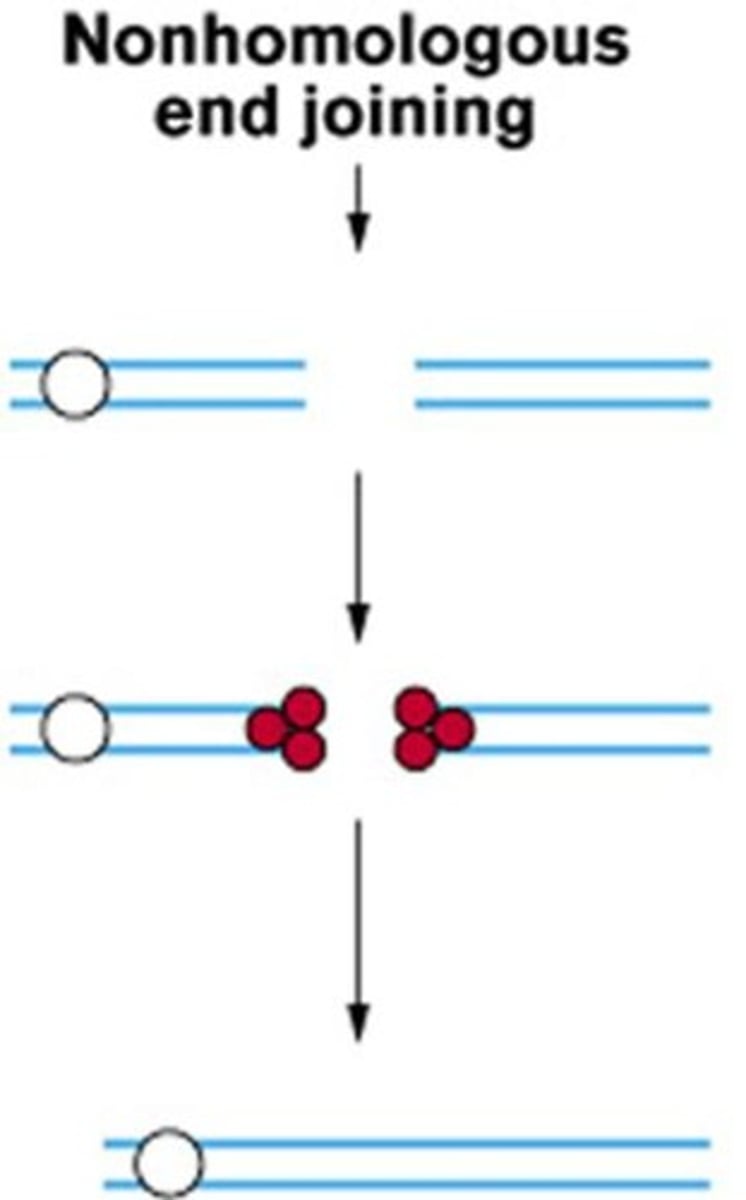
What is the difference between homology directed repair and nonhomologous end joining?
Homology directed repair uses a sister chromatid for repair, while nonhomologous end joining joins any DNA ends together and is error-prone.
What are transposable elements?
Sequences that can move about the genome, also known as 'jumping genes'.
How do transposable elements affect the genome?
They can cause mutations and contribute to genetic diversity.
What is the significance of variegated maize kernels?
They are caused by mobile genes resulting from transposition.
What is the role of chemicals in DNA mutations?
Chemicals can alter DNA bases, leading to mutations.
How does radiation affect mutation rates?
Radiation greatly increases mutation rates in all organisms, often causing thymine dimers.
What is a thymine dimer?
A mutation caused by two thymine bases dimerizing, blocking replication.
What is the relationship between mutations and cancer?
Defects in DNA repair are often associated with increases in cancer.