C14 - Chemical Kinetics (Gen. Chem 2)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

12 Terms
rate law
equation relation concentrations to reaction speed (in molarity/s))
reaction rate
(d[A]/dt)(1/a)
[A] = concentration of A
a = # mols
k
rate constant (varies by temperature)
1st order
∆M is directly proportional to reaction speed
ln[M]t = -kt + ln[M]0
t1/2 = 0.693/k
2nd order
∆M is proportional to reaction speed by the square
1/[A]t = kt + 1/[A]0
t1/2 = 1/2[A]0
0 order
∆M does not affect rate
[A]t = -kt + [A]0
t1/2 = [A]0/2k
Arrhenius equation
k = Ae-E/RT
E = activation energy
ln(k1/k2) = (E/R)(1/T2 - 1/T1)
f = e-E/RT
f = fraction of molecules where E ≥ Ea
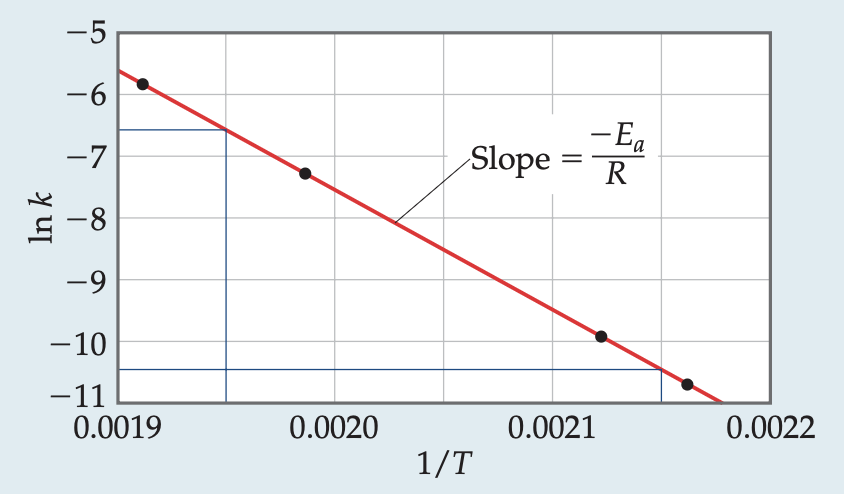
activation energy graph
ln(k) = -E/RT + ln(A)
molecularity
unimolecular
bimolecular
termolecular
elementary step
1 part in an entire chemical process
rate law for e-step = # of molecules
slow initial e-step
rate = k1[reactant1][reactant2]
fast initial e-step
rate k2(k1/k-1)[step 1 constituents][step 2 non-intermediate]