Bio U1 AOS 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
1
New cards
Living Things
Anything that can move, respire, sense, grow, reproduce, maintain equilibrium, excrete waste, and take up nutrients.
2
New cards
Homeostasis
the maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment in the body despite changes in the external environment.
3
New cards
Organism
A living thing made up of one or more cells.
4
New cards
Cell Theory
The idea that all living things are made of cells, cells are the smallest functional unit of living things, and all cells come from pre-existing cells
5
New cards
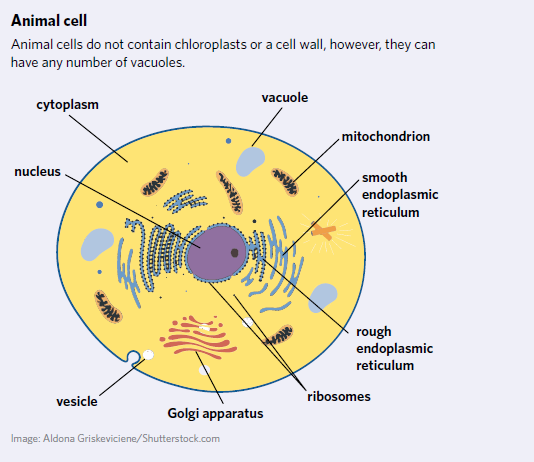
Prokaryotes
A group of single-celled organisms with no nucleus and a circular loop of DNA. Bacteria and archaea are both prokaryotic.
6
New cards
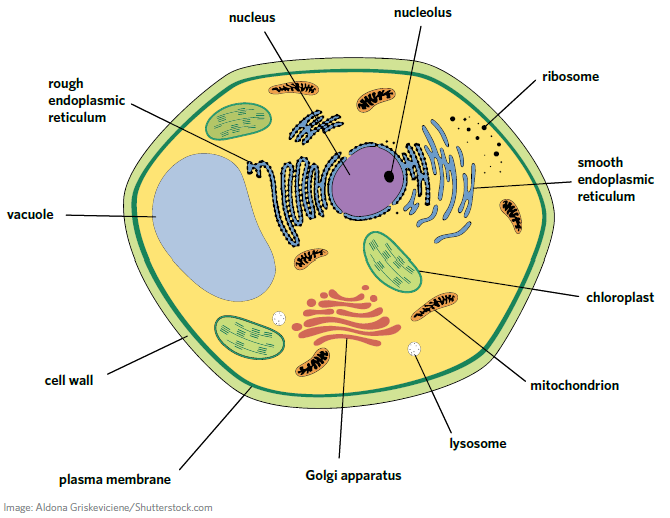
Eukaryotes
A group of single and multi-celled organisms with a nucleus and linear strands of DNA. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic.
7
New cards
Plasma/Cell membrane
The phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins which separate the intracellular environment from the extracellular environment. Also known as the cell membrane.
8
New cards
Cytosol
The aqueous fluid that surrounds the organelles inside a cell.
9
New cards
Ribosomes
Small RNA-protein structures that are the site of protein synthesis. They either float freely in the cytoplasm or are attached to the RER.
10
New cards
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid)
A double-stranded nucleic acid chain made up of nucleotides. DNA carries the instructions for proteins which are required for cell and organism survival.
11
New cards
Membrane bound organelle
Structure within a cell that is enclosed by a phospholipid bilayer.
12
New cards
Chromosome
The structure made of protein and nucleic acids (DNA) that carries genetic information.
13
New cards
Nucleus
A double membrane-bound organelle that protects and confines the genetic information (DNA) of a cell.
14
New cards
Nucleolus
Inside the nucleus is a smaller structure known as the nucleolus which is the site of ribosome production.
15
New cards
Plasmid
A small, circular loop of DNA that is separate from a chromosome, typically found in bacteria
16
New cards
Somatic Cell
Any cell that is not a reproductive cell (such as sperm and egg cells). Somatic cells are diploid, meaning they contain two sets of chromosomes – one inherited from each parent.
17
New cards
Mitosis
The cell division phase which involves the complete separation of sister chromatids and nuclei.
18
New cards
Germline Cells
Cells that are involved in the generation of gametes in eukaryotes.
19
New cards
Gametes
Reproductive cells that arise from germline cells that contain half the genetic material of a somatic cell. In humans, gametes are sperm and eggs.
20
New cards
Meiosis
A specialised form of cell division used to produce gametes in sexually-reproducing organisms.
21
New cards
Binary Fission
The method of cell replication used by prokaryotes.
22
New cards
Micrometres (μm)
Unit of measurement where 1 mm = 1 000 μm.
23
New cards
Organelle
A cellular structure that performs specific functions.
24
New cards
Cytoplasm
The cytosol and organelles inside the plasma membrane, excluding the nucleus
25
New cards
Vacuole
A membrane-bound sac that is used for water and solute storage. Vacuoles can also play a role in maintaining plant cell structure.
26
New cards
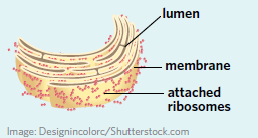
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
A membranous chain of connected and flattened sacs which are coated with ribosomes. This allows the rough endoplasmic reticulum to synthesise and modify proteins. The rough endoplasmic reticulum typically surrounds, or is close to, the nucleus.
27
New cards
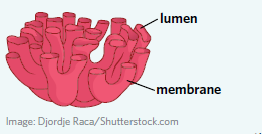
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
A membranous chain of connected and flattened sacs which are not coated with ribosomes. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the production of lipids in a cell.
28
New cards
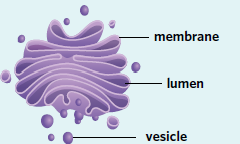
Golgi Apparatus
Stacked flattened sacs that are the sites of protein sorting, packaging, and modification for use in the cell or export. Protein-filled vesicles often fuse with or bud off from the Golgi apparatus. Also known as the Golgi body.
29
New cards
Lysosome
A membrane-bound vesicle that contains digestive enzymes. It is responsible for breaking down cell waste and toxins, acting like a garbage disposal.
30
New cards
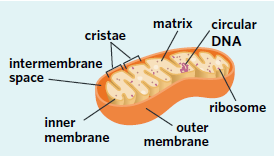
Mitochondrion
An organelle with a highly folded inner membrane surrounded by a second outer membrane. Mitochondria are the site of aerobic cellular respiration, a chemical reaction that produces the ATP required to power cellular processes. They also contain their own DNA and ribosomes. They are the primary site of energy production from aerobic cellular respiration
31
New cards
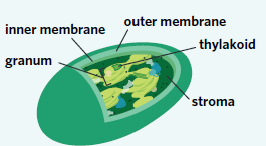
Chloroplast
A double membrane-bound organelle that contains flattened, fluid-filled sacs that are the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts also contain their own DNA and ribosomes.
32
New cards
Cell wall
A sturdy border outside the plasma membrane that provides strength and structure to plant, bacterial, and fungal cells. (Eukaryotes)
33
New cards
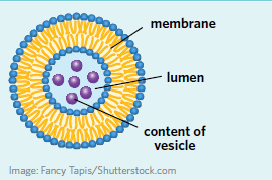
Vesicle
A small, membrane-bound sac that transports substances into or out of a cell, or stores substances within a cell.
34
New cards
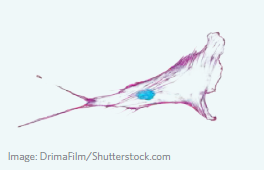
Cytoskeleton
A large network of protein filaments that start at the nucleus and reach out to the plasma membrane. The cytoskeleton is critical for maintaining shape and transporting vesicles around the cell. In the given fluorescence microscopy photo, the purple represents the cytoskeleton.
35
New cards
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
A type of nucleic acid that is a key structural component of ribosomes.
36
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The biochemical process in all living things that converts glucose into ATP. Can be aerobic or anaerobic respiration.
37
New cards
Crista
The fold of the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
38
New cards
Aerobic
Requiring oxygen.
39
New cards
Anaerobic
Requiring no oxygen.
40
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process of converting light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen.
41
New cards
Red blood cells
Cells that transport oxygen through the bloodstream and do not contain a nucleus.
42
New cards
Volume
The amount of space inside an object. Measured in (units of length)3 (i.e. mm3, cm3, m3).
43
New cards
Surface Area
The sum of the area of all exposed sides of a three-dimensional shape. Measured in (units of length)2 (i.e. mm2, cm2, m2).
44
New cards
Surface area : volume ratio (SA:V)
A comparison of the amount of surface area per unit of volume. In Biology, SA:V influences temperature regulation, and a high SA:V leads to more effective transport into and out of cells.
45
New cards
Intracellular
Inside a cell
46
New cards
Extracellular
outside a cell
47
New cards
Selective permeability
Property of cell membranes that ensures only specific substances pass across them. Also known as semipermeable.
48
New cards
Phospholipid
The main molecule of which membranes are composed. They have a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails.
49
New cards
Phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of amphiphilic molecules that forms the primary component of cell membranes.
50
New cards
Phosphate Head
The hydrophilic (water loving) subunit of a phospholipid
51
New cards
Fatty acid tail
The hydrophobic (water hating) lipid subunit of a phospholipid.
52
New cards
Polar
Describes a molecule with both a positive end and negative end. These tend to be hydrophilic.
53
New cards
Nonpolar
Describes a molecule without a clearly positive or negative end. These tend to be hydrophobic.
54
New cards
Amphipathic
Describes molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. Also known as amphiphilic.
55
New cards
Protein
A class of biomacromolecule made of amino acid monomers folded into a 3D shape, consisting of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulphur.
56
New cards
Carbohydrate
A class of biomacromolecule made from monosaccharide monomers consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Also known as saccharides or sugars.
57
New cards
Cholesterol
A steroid-alcohol that regulates fluidity in plasma membranes.
58
New cards
Transmembrane protein
An integral protein that spans the entire plasma membrane.
59
New cards
Glycolipid
A phospholipid bound to a carbohydrate.
60
New cards
Glycoprotein
A protein bound to a carbohydrate.
61
New cards
Fluid mosaic model
The theory of how the plasma membrane is structured.
62
New cards
Passive transport
The movement of molecules through a semipermeable membrane and down the concentration gradient, without an input of energy.
63
New cards
Active Transport
Movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane that requires energy.
64
New cards
Diffusion
The passive movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration (down the concentration gradient).
65
New cards
Concentration Gradient
The difference in solute concentration between two adjacent areas.
66
New cards
Solute
A substance dissolved in the solvent.
67
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
A type of passive transport where molecules move through a phospholipid bilayer with the aid of a membrane protein.
68
New cards
Protein channel
A transmembrane protein pore in a phospholipid bilayer that selectively enables transport of large or polar molecules.
69
New cards
Carrier protein
A membrane protein that undergoes conformational change to transport molecules across a membrane.
70
New cards
Osmosis
The passive transport of a solvent (typically water) through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute (high solvent) to a region of high solute (low solvent).
71
New cards
Hypertonic
Describes a solution with a higher solute concentration when compared to another solution.
72
New cards
Isotonic
Describes a solution with the same solute concentration as another solution.
73
New cards
Hypotonic
Describes a solution with a lower solute concentration when compared to another solution
74
New cards
Turgid
Describes plant cells that are swollen and firm from water uptake.
75
New cards
Plasmolysed
Describes plant cells with weak and sagging plasma membranes from water loss.
76
New cards
Protein-mediated active transport
Describes plant cells with weak and sagging plasma membranes from water loss
77
New cards
Bulk transport/Cytosis
A type of active transport that uses vesicles to move large molecules or groups of molecules into or out of the cell.
78
New cards
Protein pump
A polypeptide that transports molecules across a membrane against its concentration gradient with the aid of ATP.
79
New cards
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
A high energy molecule that, when broken down, provides energy for cellular processes.
80
New cards
Carrier protein
A membrane based protein that undergoes conformational change to transport molecules across a membrane.
81
New cards
Exocytosis
A type of bulk transport that moves large substances out of the cell.
82
New cards
Endocytosis
A type of bulk transport that moves large substances into the cell.
83
New cards
Phagocytosis
Endocytosis of solid material or food particles.
84
New cards
Pinocytosis
Endocytosis of liquid or dissolved substances.
85
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
A method of reproduction that produces genetically identical cells without the fusion of gametes (sex cells).
86
New cards
Plasmid
A small, circular loop of DNA that is separate from a chromosome, typically found in bacteria.
87
New cards
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm and formation of two daughter cells.
88
New cards
Septum
A dividing wall formed during binary fission.
89
New cards
Interphase
The first stage of the eukaryotic cell cycle which involves cellular growth and duplication of chromosomes. Composed of three phases: G1, S, and G2.
90
New cards
Sister Chromatids
The two identical halves of a replicated chromosome.
91
New cards
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm and formation of two daughter cells.
92
New cards
Chromatin
Chromosomes (DNA and proteins) that have been unwound and loosely packed during interphase.
93
New cards
Terminally Differentiated
Cells that have fully specialised and no longer replicate.
94
New cards
Chromatid
One half of a double stranded chromosome.
95
New cards
Centromere
The structure that holds sister chromatid’s together.
96
New cards
Diploid
Cells or organisms that have two sets of chromosomes.
97
New cards
Daughter Cell
The formation of a new cell following cell replication.
98
New cards
Prophase
Prophase begins with the condensation of chromatin around histones into distinct chromosomes, so that they become visible under a microscope. Simultaneously, the centrioles migrate towards opposite ends (or poles) of the cell, and spindle fibres begin to form. The nuclear membrane breaks down and the nucleolus disappears.
99
New cards
Metaphase
In metaphase, the spindle fibres fully form and attach to the centromere of each chromosome. This allows the spindle fibres to guide the chromosomes towards the equator of the cell where they line up.
100
New cards
Anaphase
The spindle fibres contract, splitting the centromere and pulling sister chromatids to opposite ends of the cell.