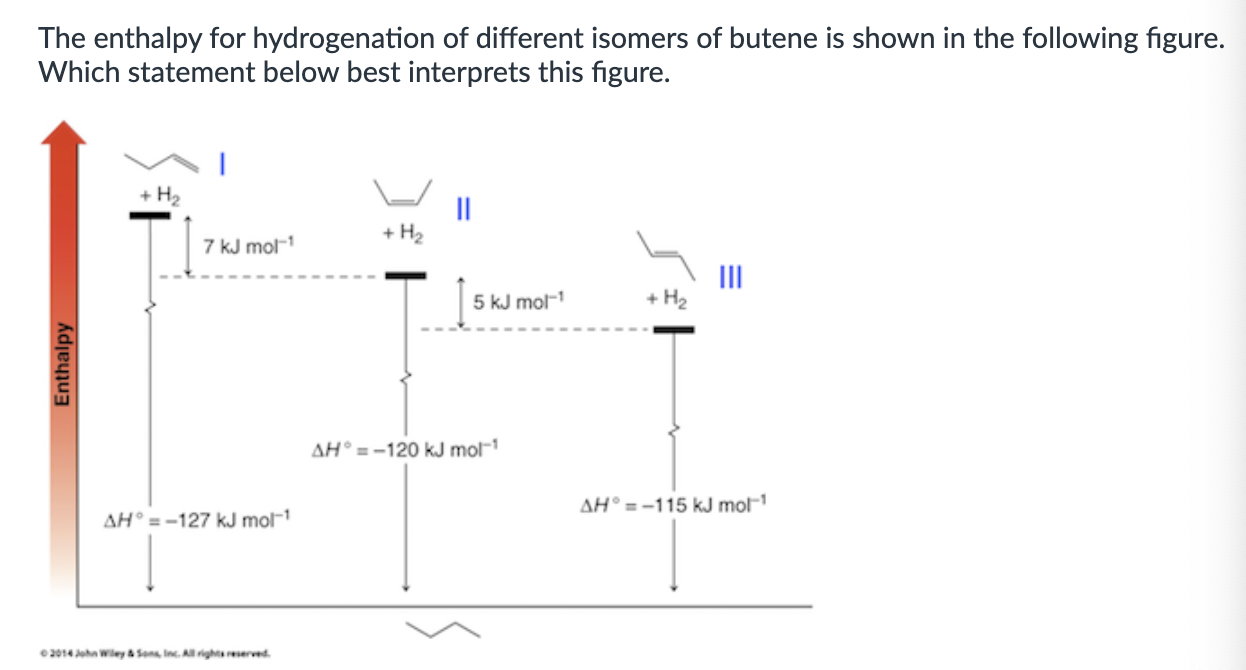
Orgo Exam 3
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the rate-determining step of an E1 or SN1 reactions?
Formation of the carbocation
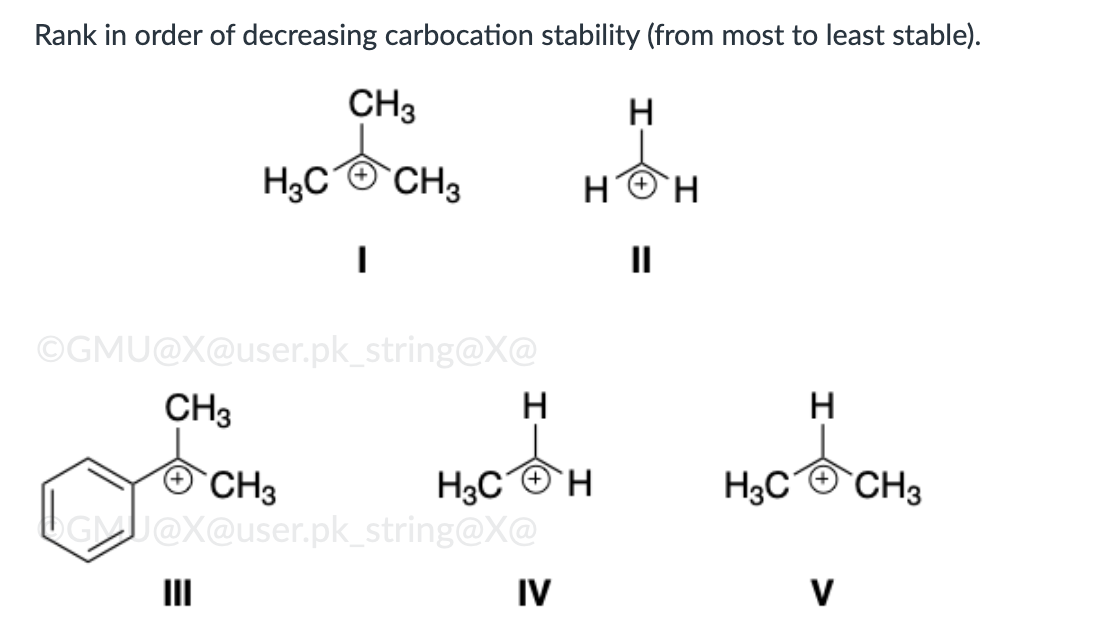
III, I, V, IV, II
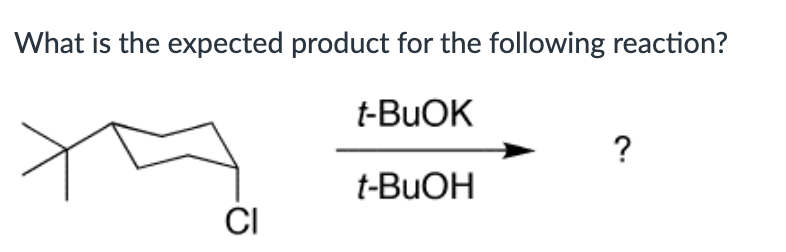
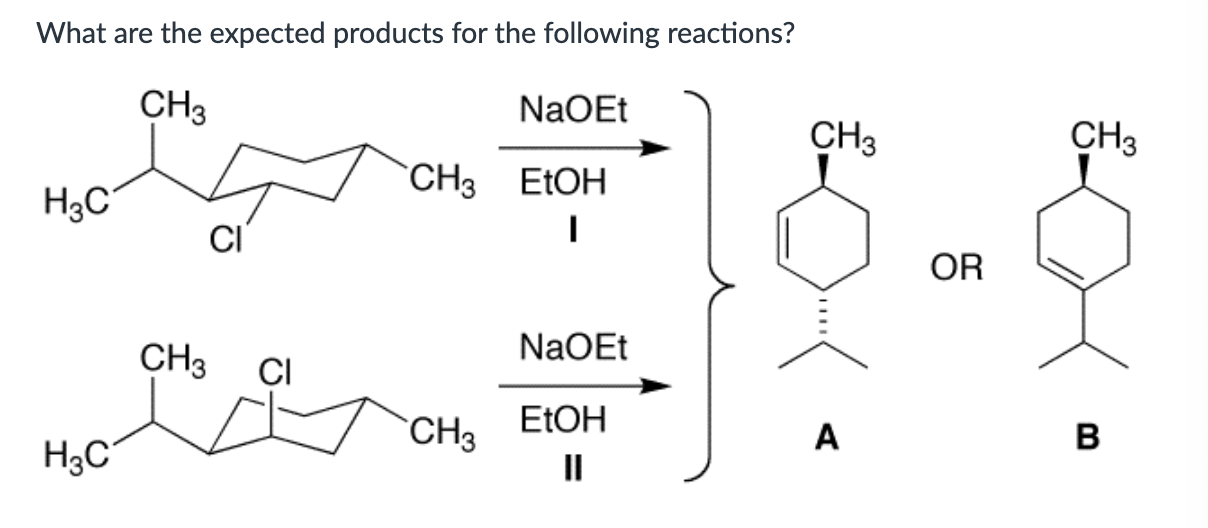
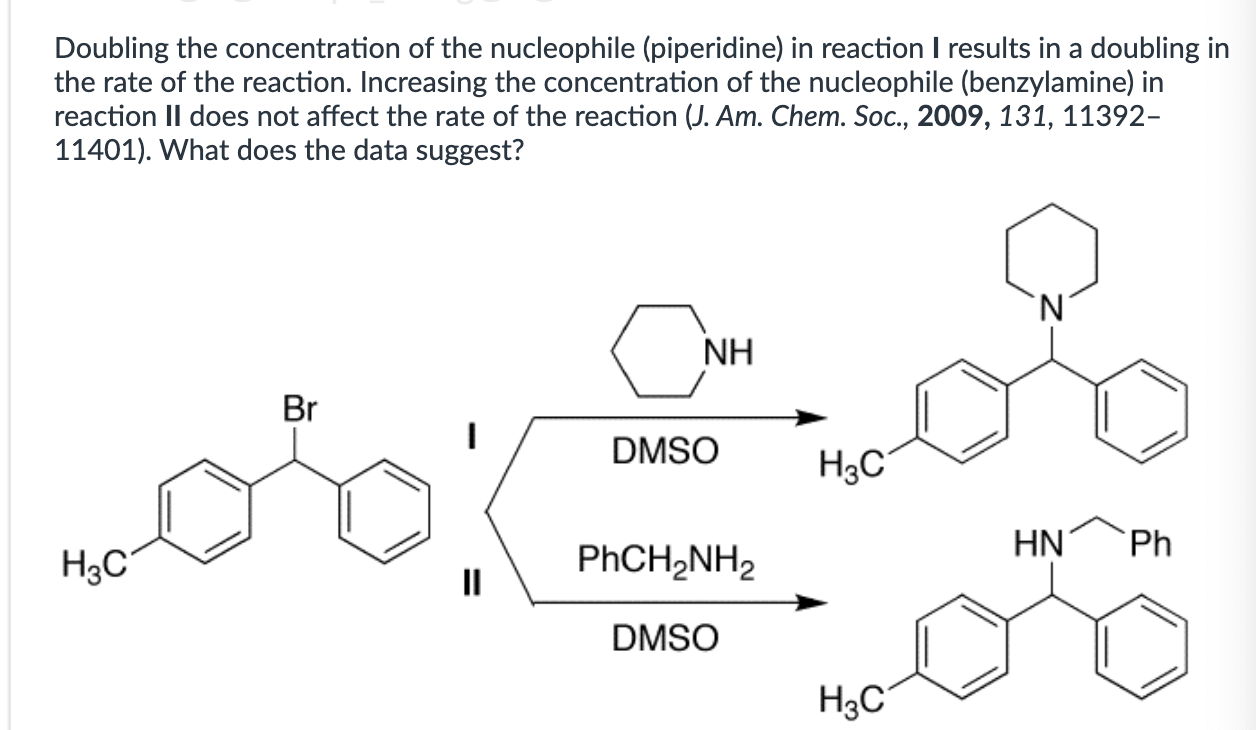
Product A for reaction I, and a mixture of products A and B for reaction II.
Match the Carbon-halogen bond strengths for methyl halides
H3C-F
H3C-Cl
H3C-Br
H3C-I
472 kJ/mol, 239 kJ/mol, 350 kJ/mol, 293 kJ/mol
H3C-F —> 472 kJ/mol
H3C-Cl —> 350 kJ/mol
H3C-Br —> 293 kJ/mol
H3C-I —> 239 kJ/mol
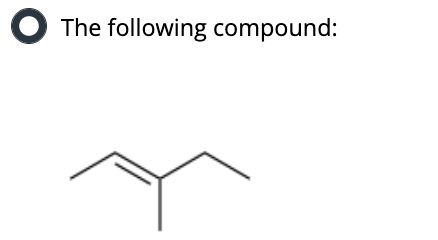
What dihedral angle does an anti-coplanar transition state refer to
180 degrees
Match the carbon-halogen bond lengths for the methyl halides
H3C-F
H3C-Cl
H3C-Br
H3C-I
1.39 Å, 214 Å, 1.78 Å, 1.93 Å
H3C-F —> 1.39 Å
H3C-Cl —> 1.78 Å
H3C-Br —> 1.93 Å
H3C-I —> 2.14 Å
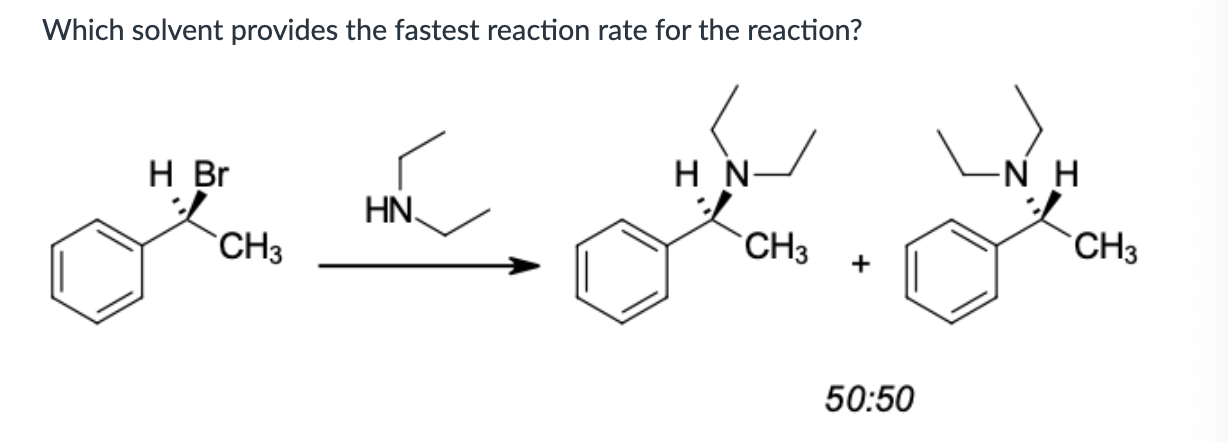
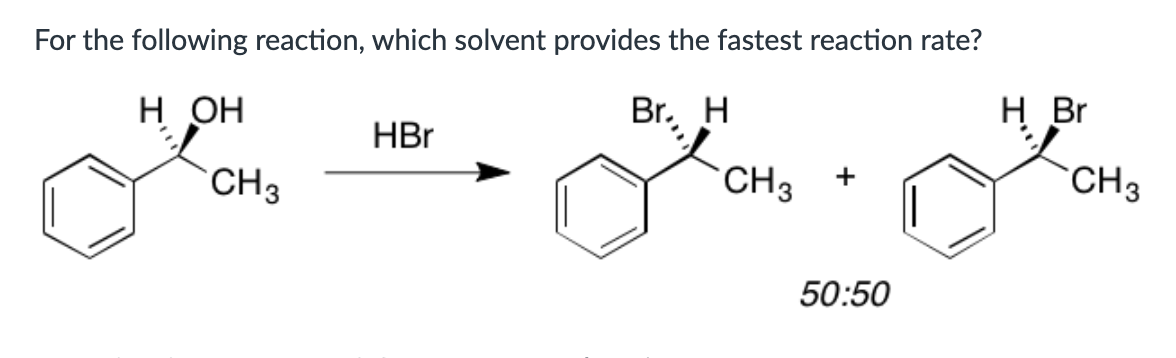
water
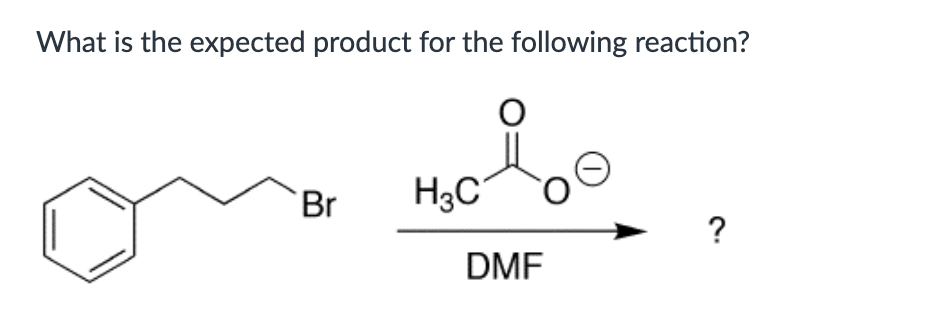
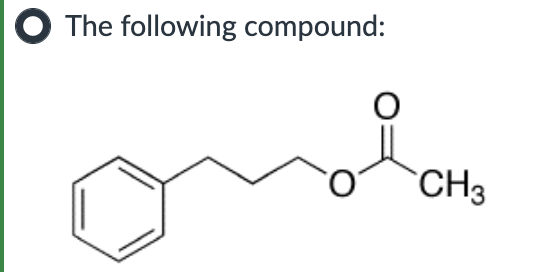

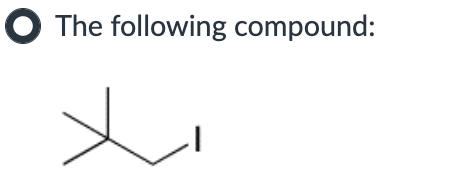
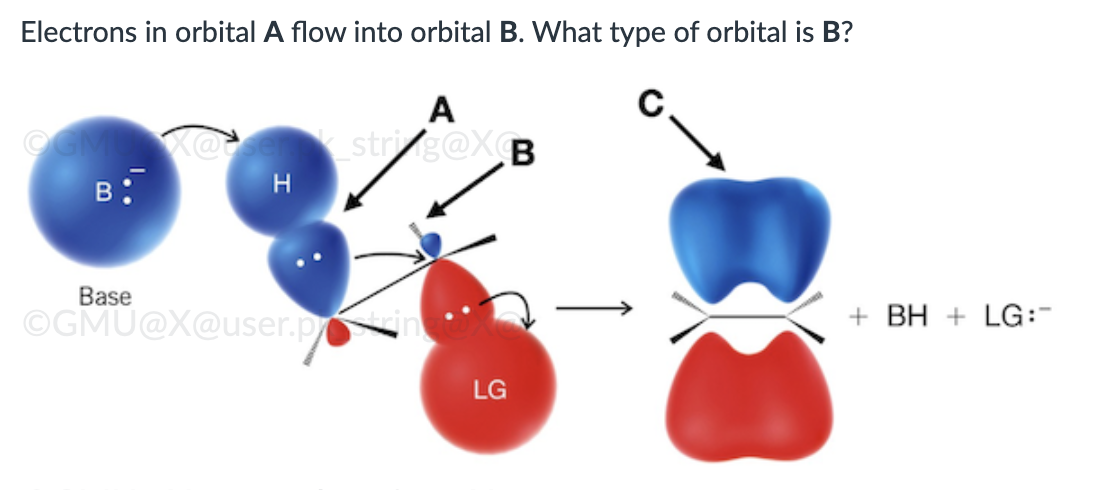
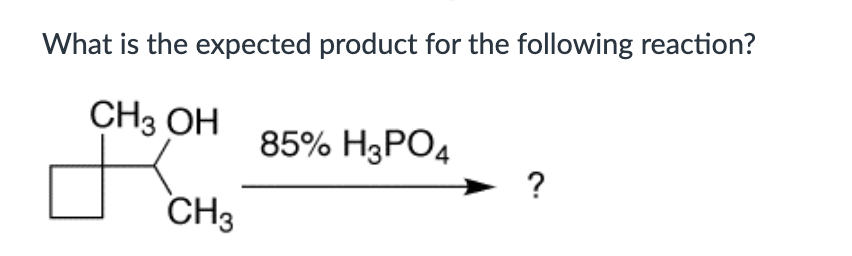
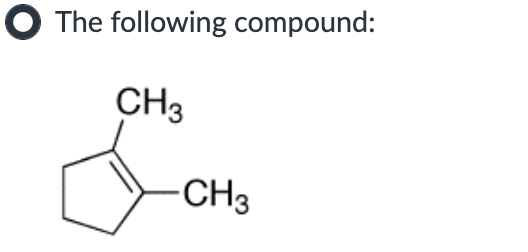
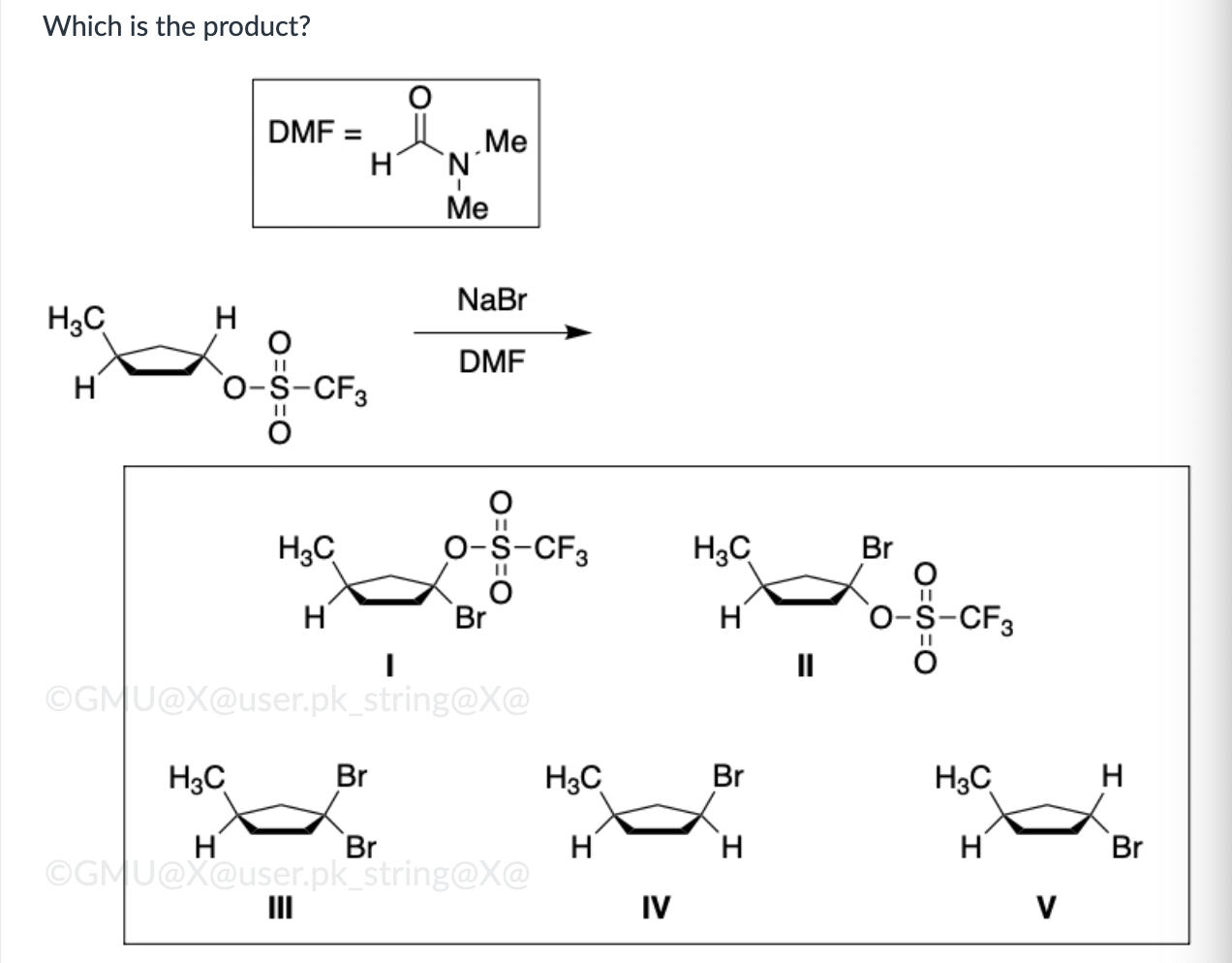
IV
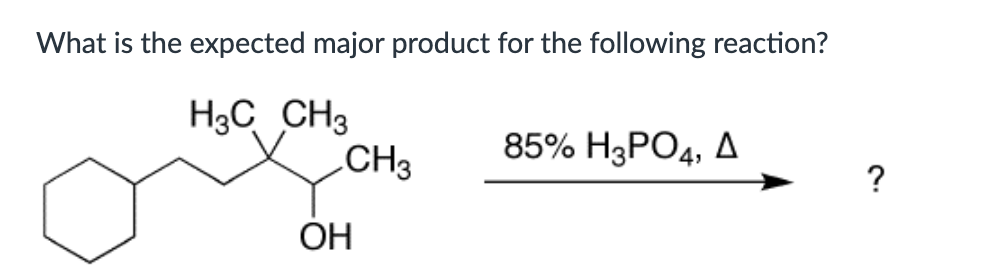

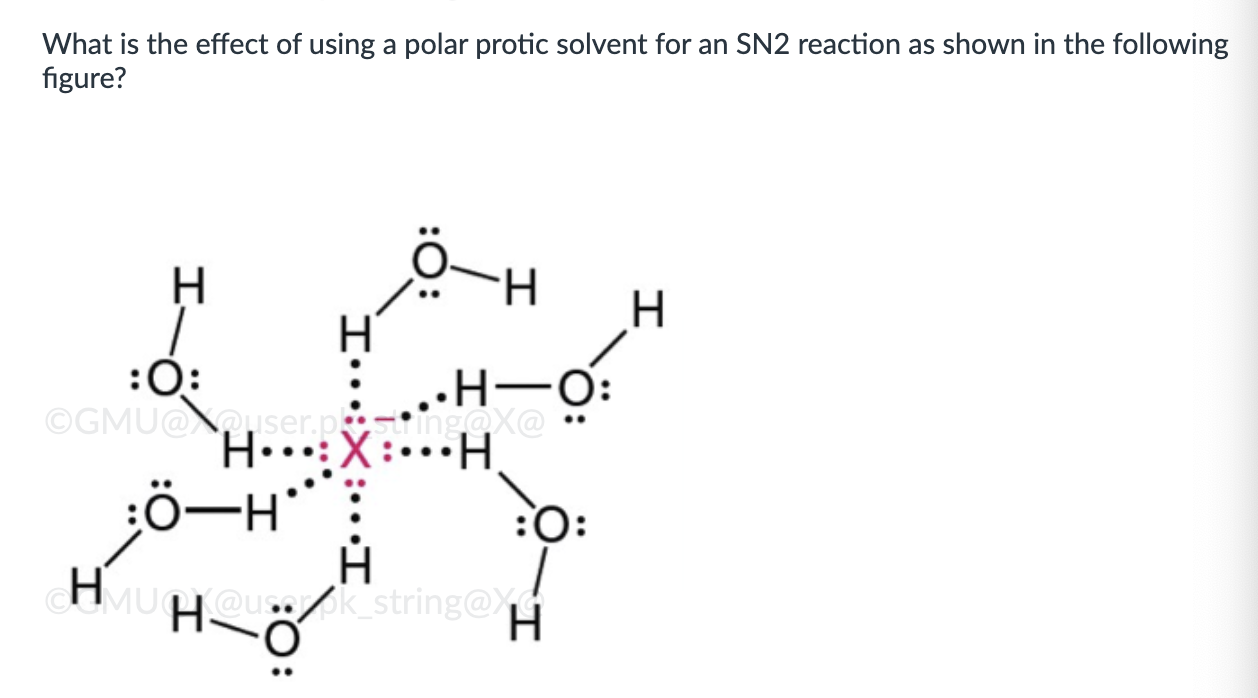
Reaction rate is slowed by solvation of the anion
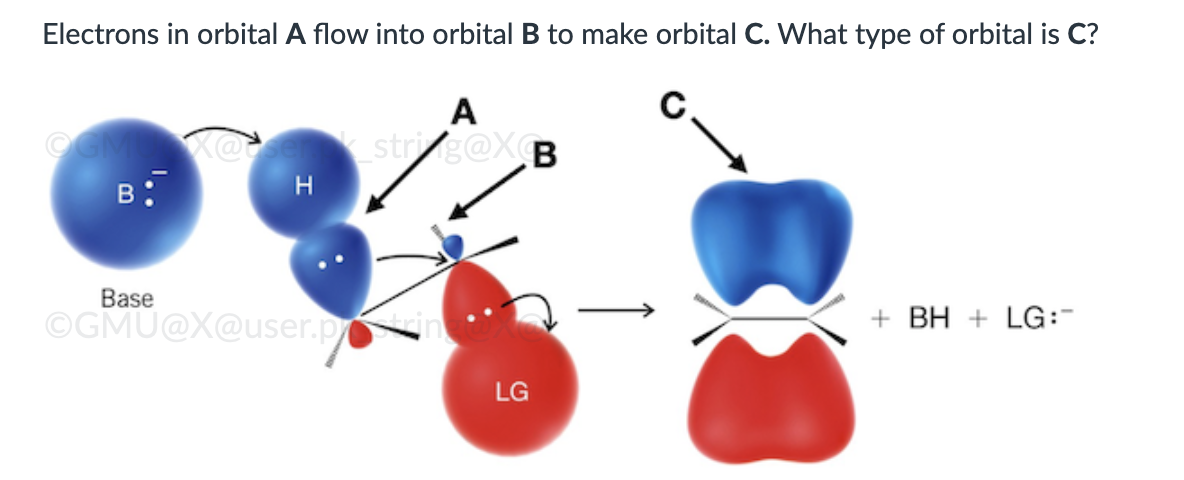
π

What does racemization refer to?
loss of optical activity
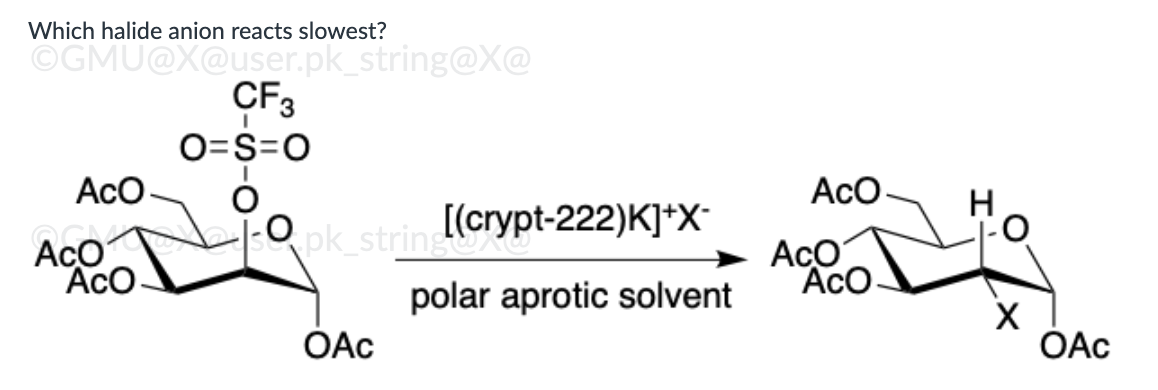
I-
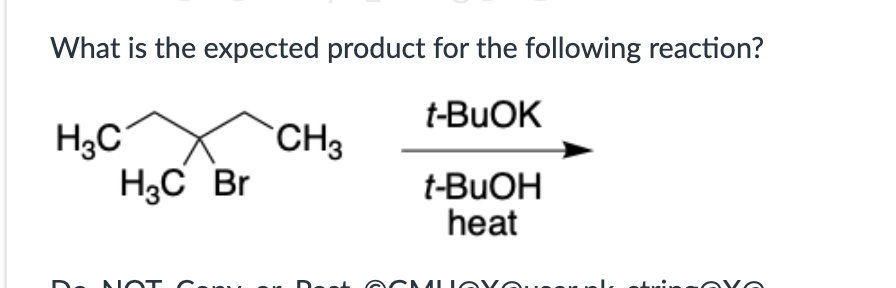
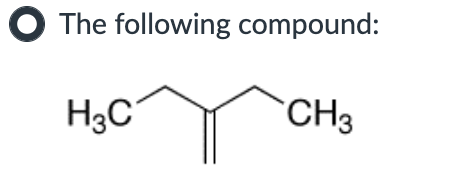
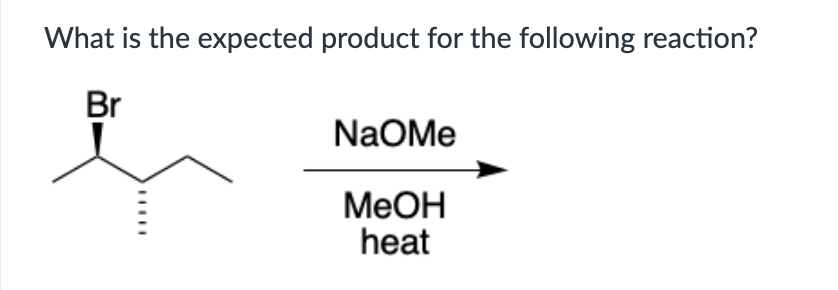
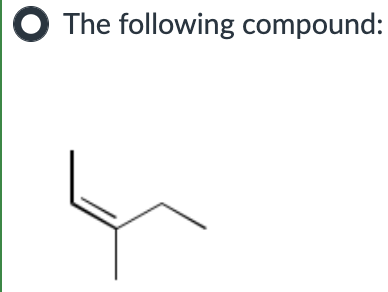
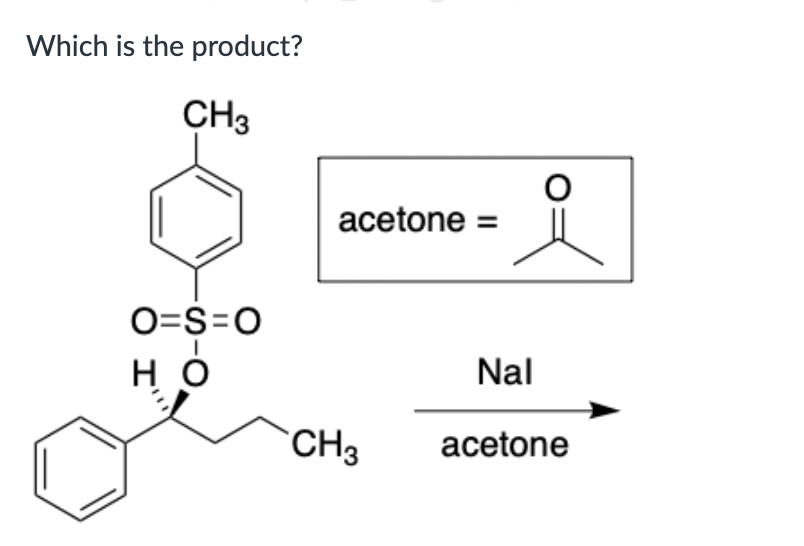
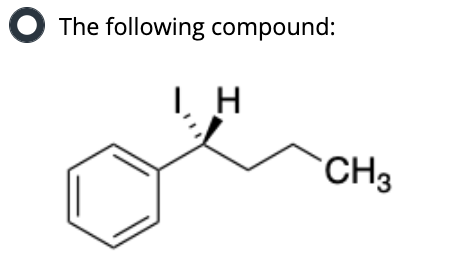
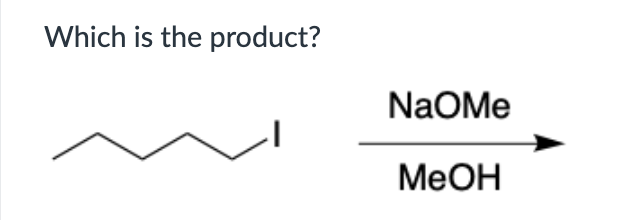
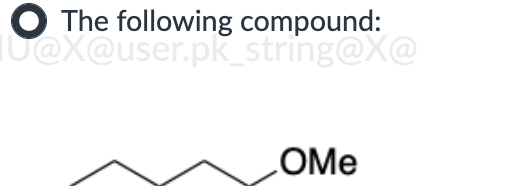
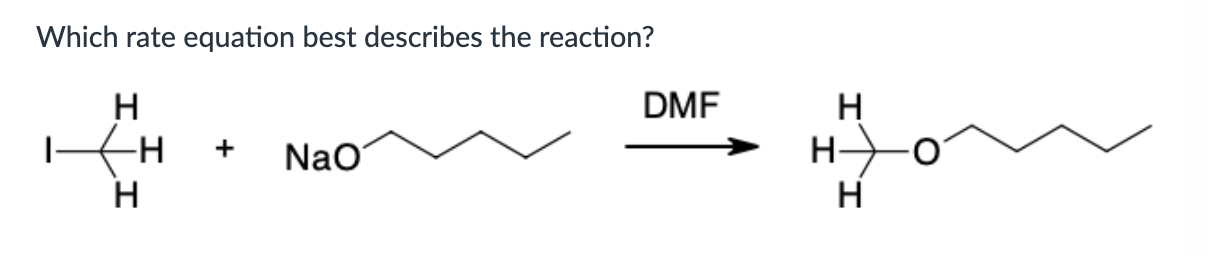

Put in order of INCREASING polarizability (1 being the least polarizable and 4 being the most polarizable)
H3C-F
H3C- I
H3C-Cl
H3C-Br
H3C-F
H3C- Cl
H3C-Br
H3C-I
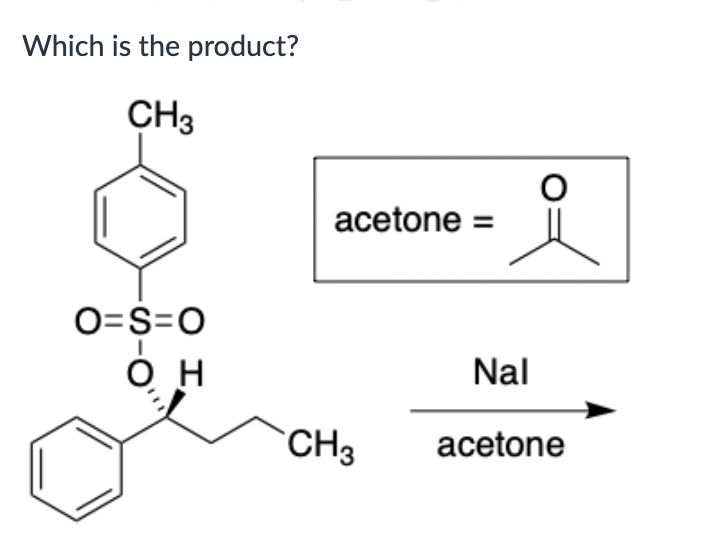
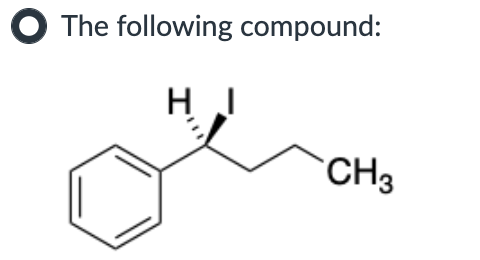
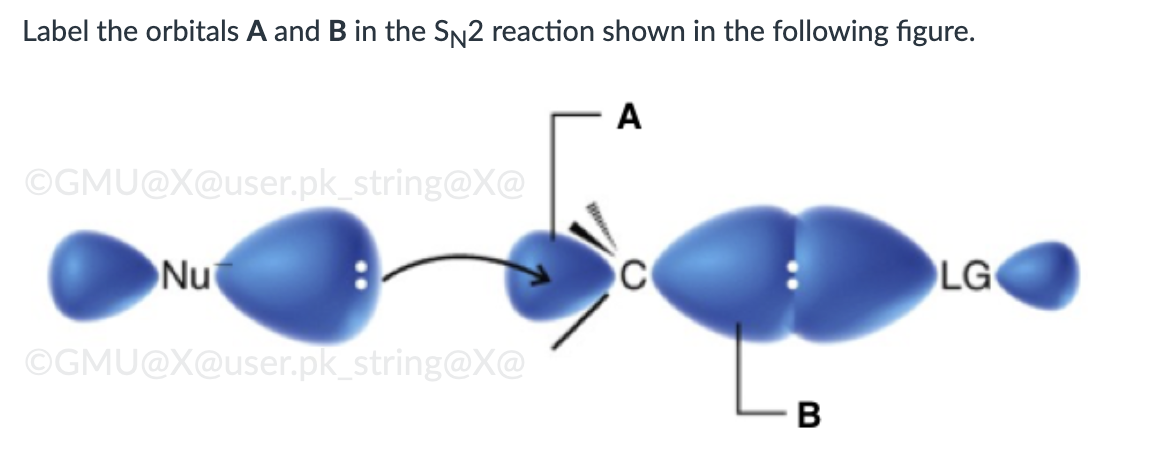
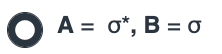
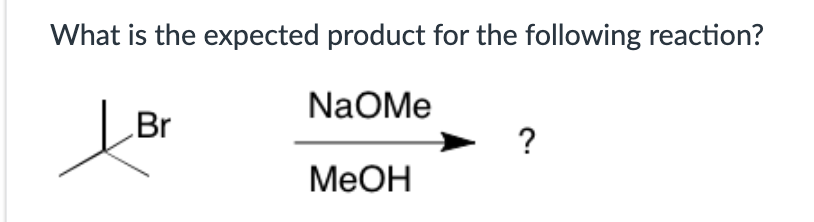

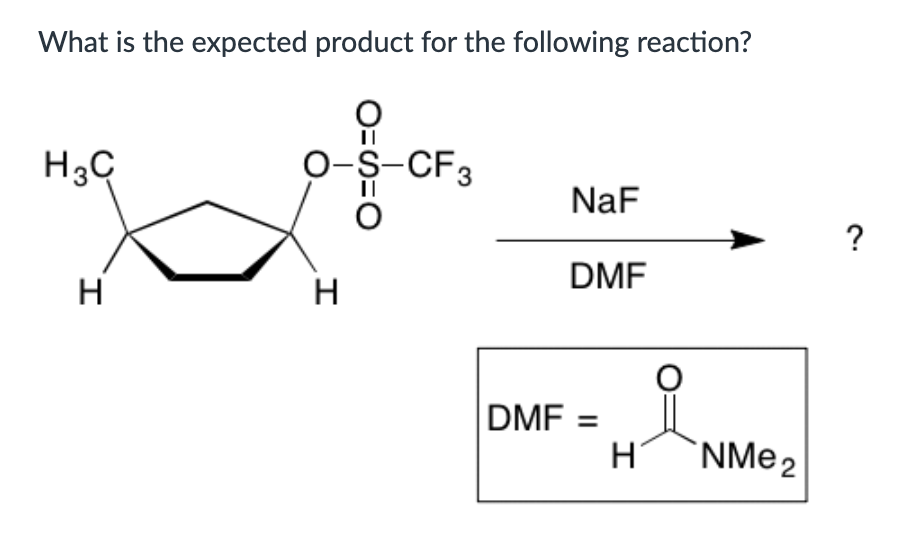
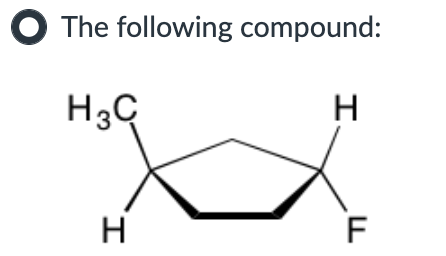
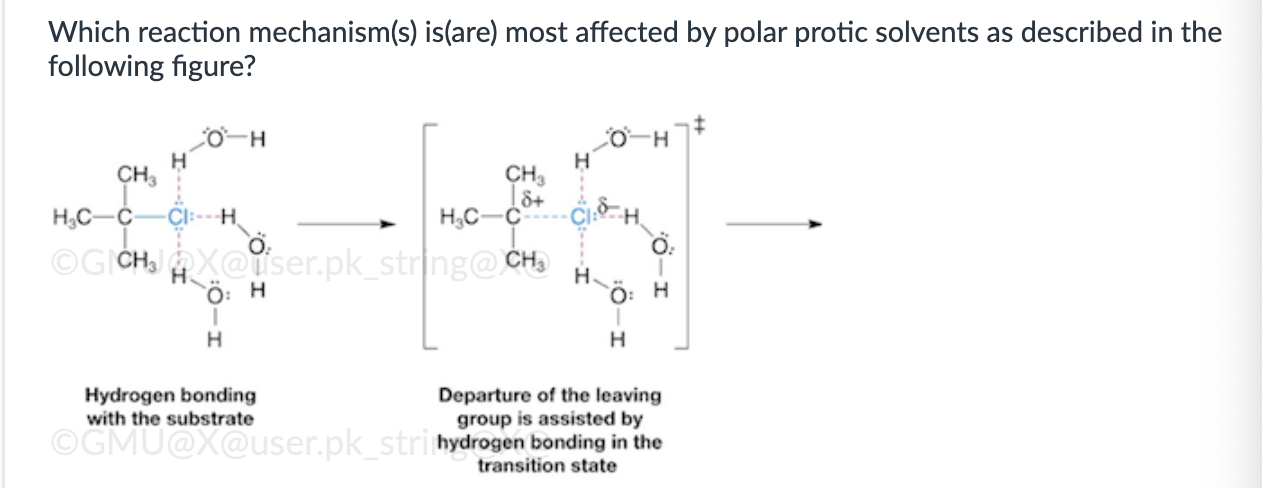
Both SN1 and E1
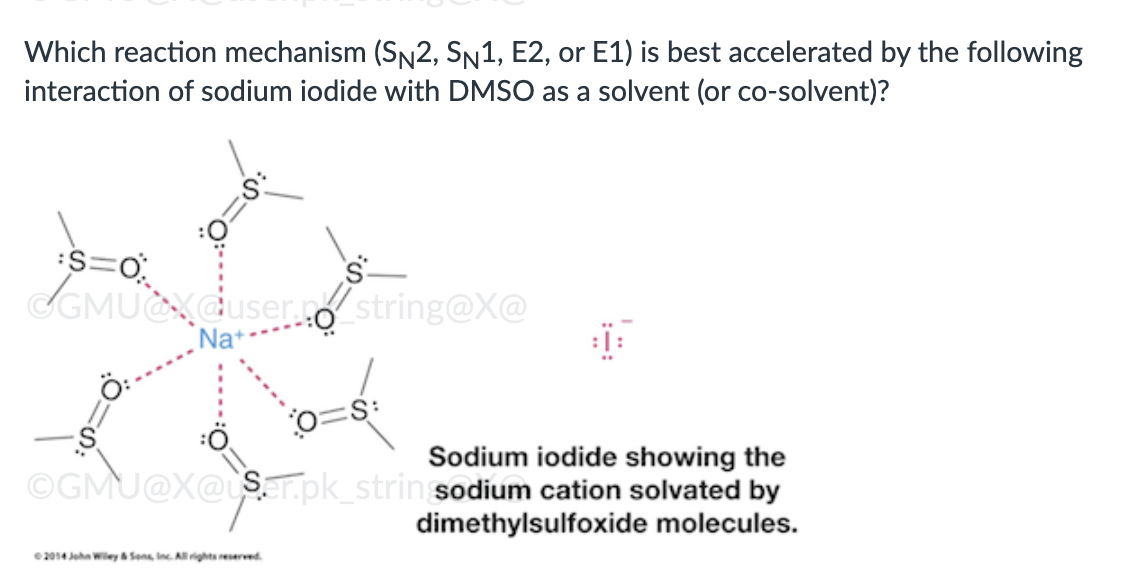
SN2
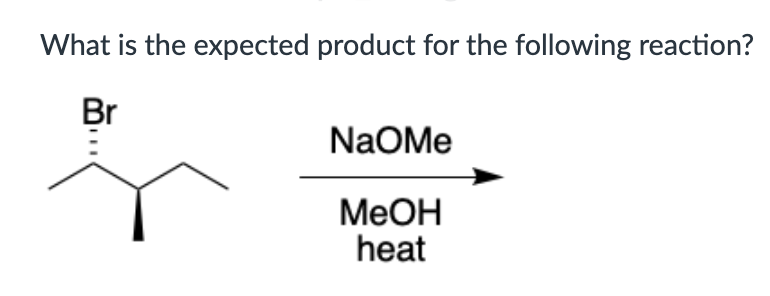
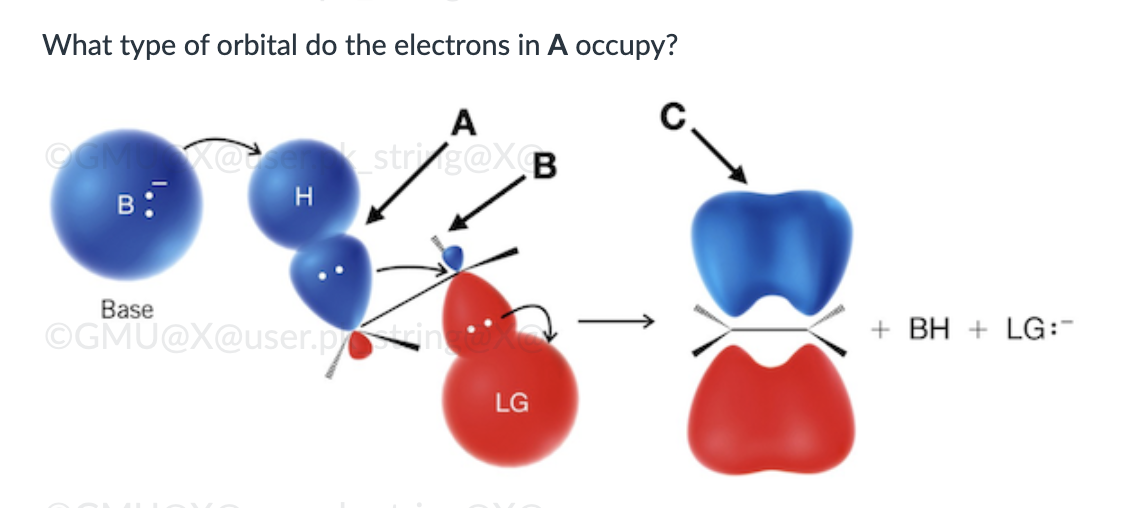
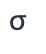
endergonic, shown by the blue line
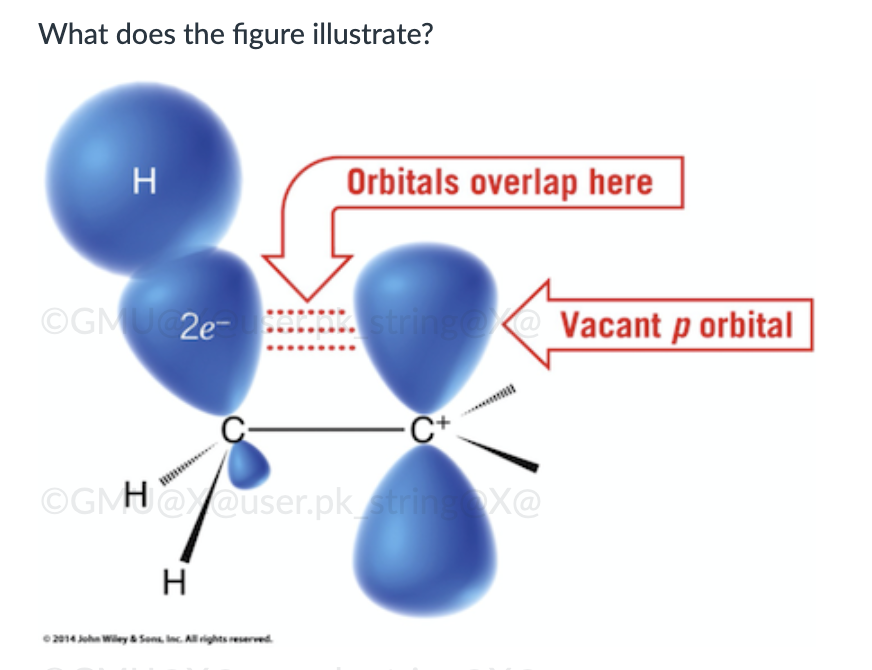
hyperconjugation
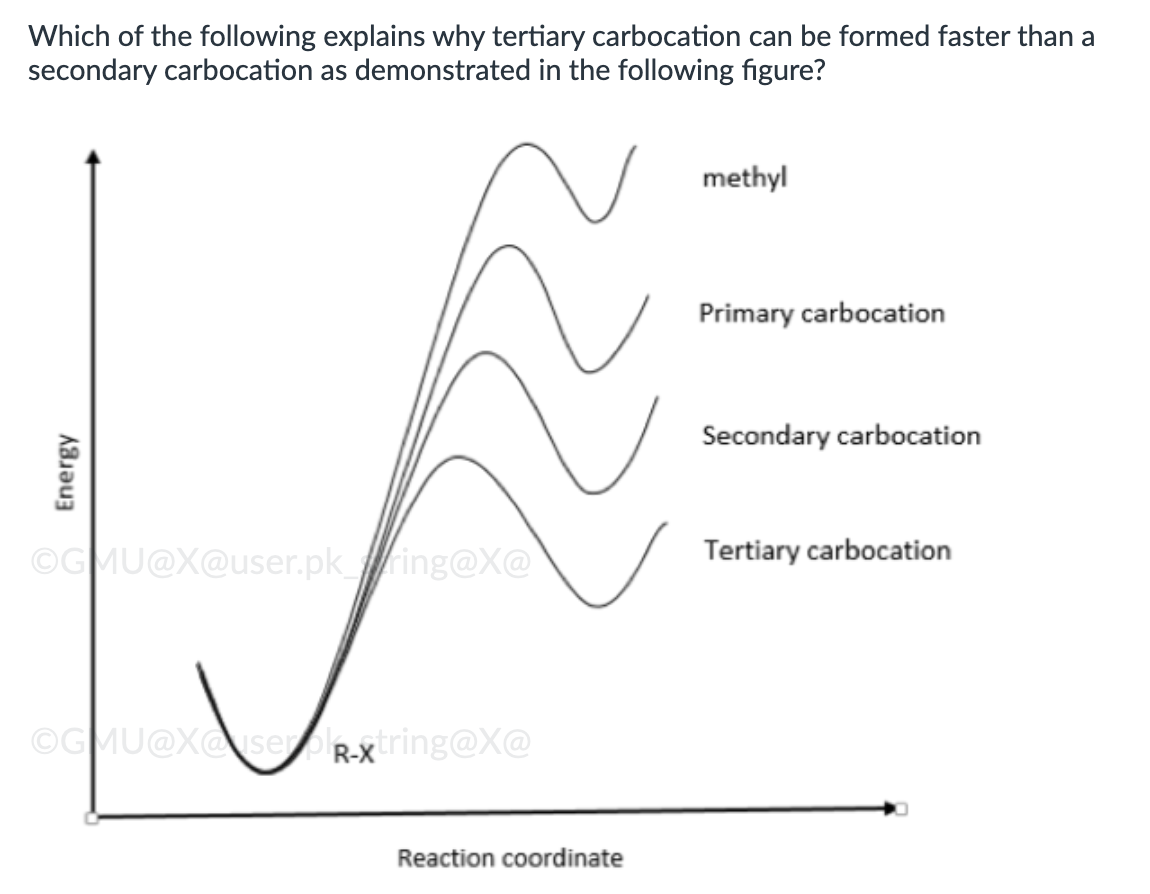
Hammond-Leffler postulate
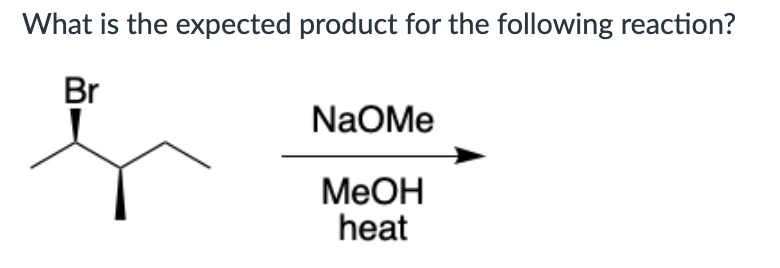
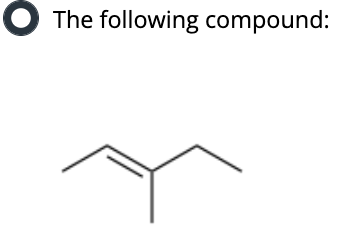
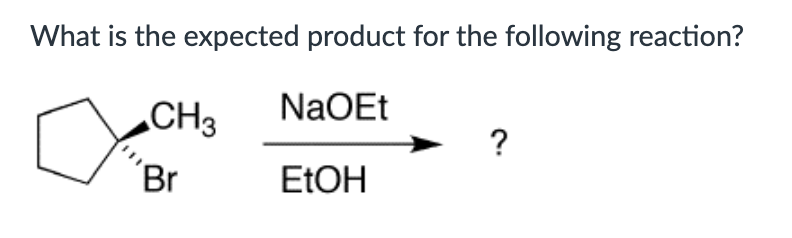
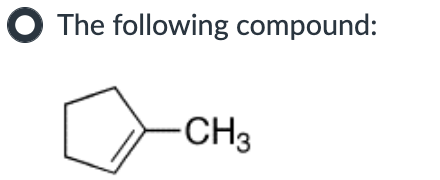
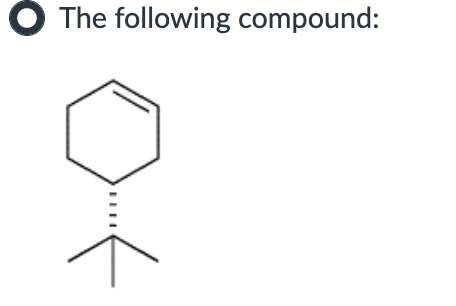
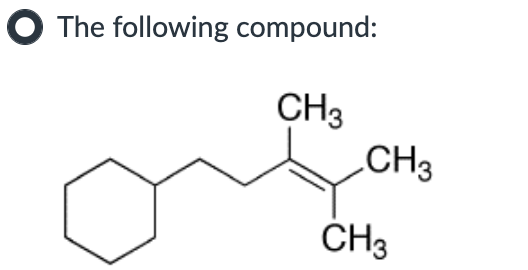
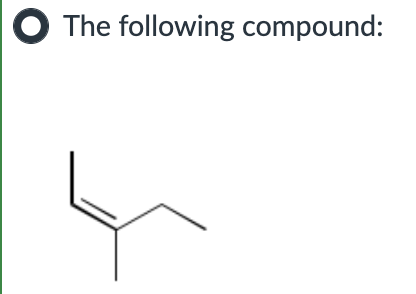
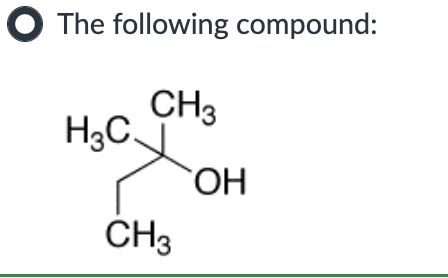
Which compound can undergo acid-mediated dehydration under the mildest conditions?

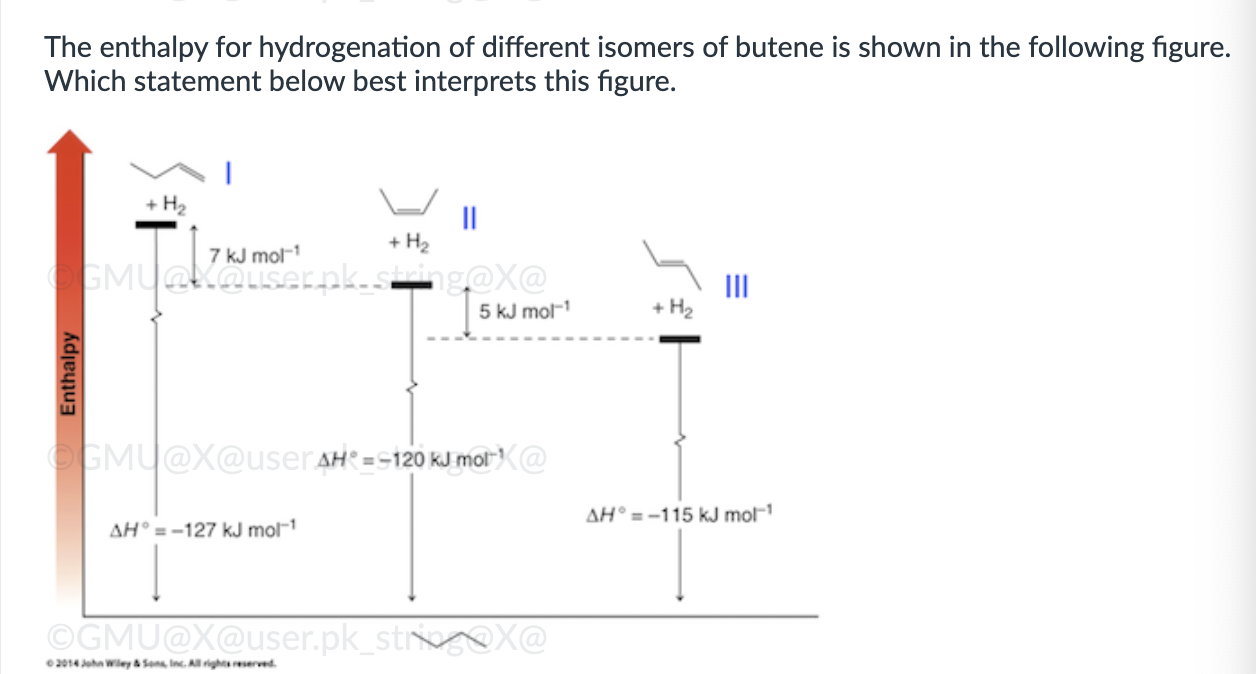

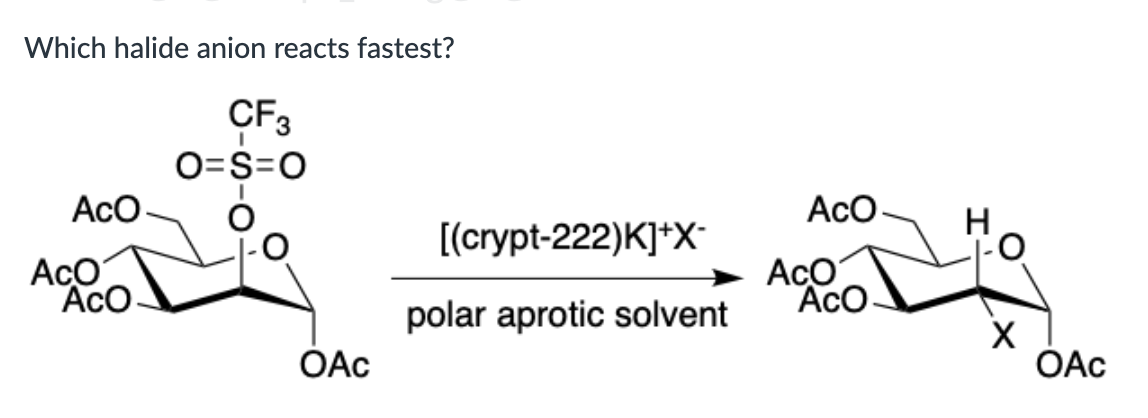
F-
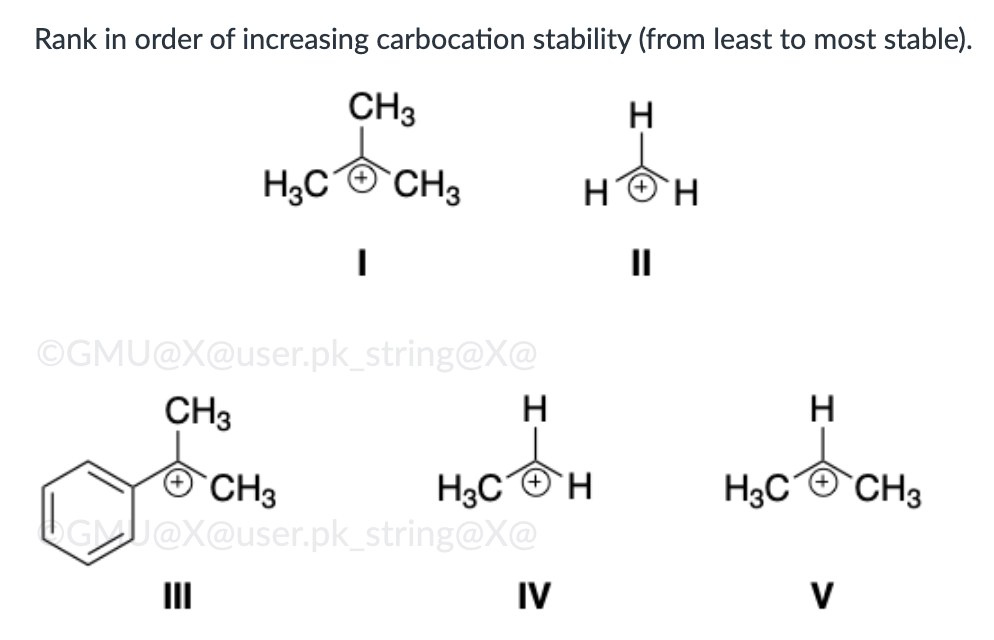
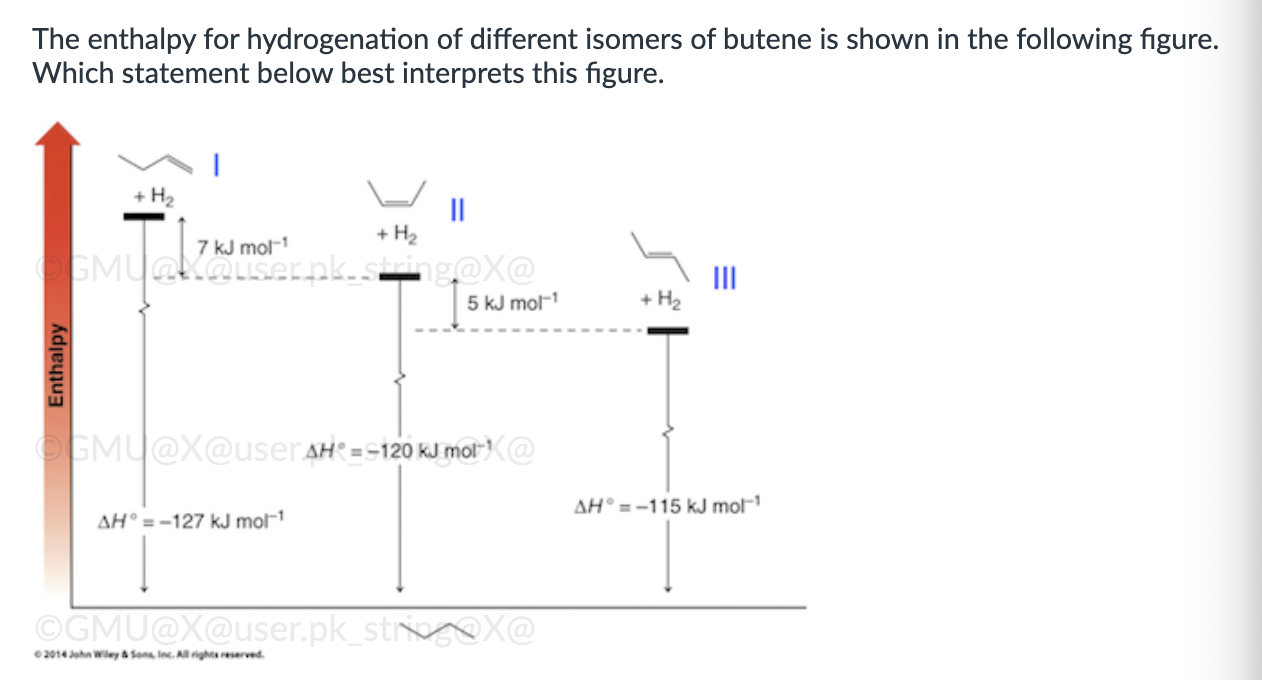
II, IV, V, I, III
Put in order of DECREASING polarizability (1 being the most polarizable and 4 being the least polarizable)
H3C-F
H3C- I
H3C-Cl
H3C-Br
H3C-I
H3C- Br
H3C-Cl
H3C-F