Bacterial growth and nutrition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What happens in the ‘cell growth phase’ of the bacterial cell cycle?
Cell mass and size increase
Special enzymes break wall to allow expansion
What happens in the ‘DNA replication phase’ of the bacterial cell cycle?
Chromosome is copied in preparation for division
How does binary fission differ to mitosis/meiosis?
• Cytoskeleton aids separation of chromosomes
• No requirement for microtubular spindle apparatus or complex
patterns of arrangement
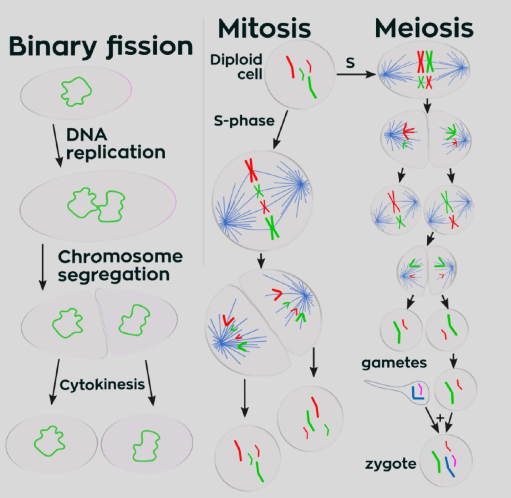
What happens during the ‘binary fission phase’ of the bacterial cell cycle?
• Asexual reproduction
• Septum divides enlarged cell into two identical daughter
cells.
Describe the process of binary fission:
• Replicating chromosomes attach to cell membrane in separate locations
• Cell continues to elongate pulling two identical chromosomes further apart
• Invagination of cell wall and membrane as new material is laid down
• Pulled together by fission ring
• Completion of new cell membrane and cell wall
• Septum material can dissolve slowly
• Daughter cells may not separate straight away
• Forms characteristic pairs, chains or clusters
• Each daughter cell then enters cell cycle
What is ‘generation time’?
Generation time = amount of time to complete one cell cycle
• Generation times are typically fast under ideal conditions.
• E. coli could cover the Earth one foot deep in 36 hours.
• Other bacteria grow very slowly, doubling time more than one day.
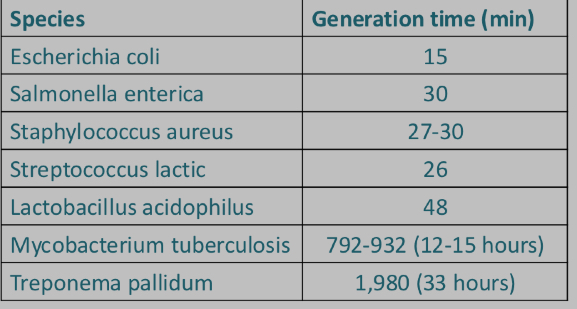
What are oligotrophs?
• Spend majority of life in nutrient-limited state
• Infrequent division
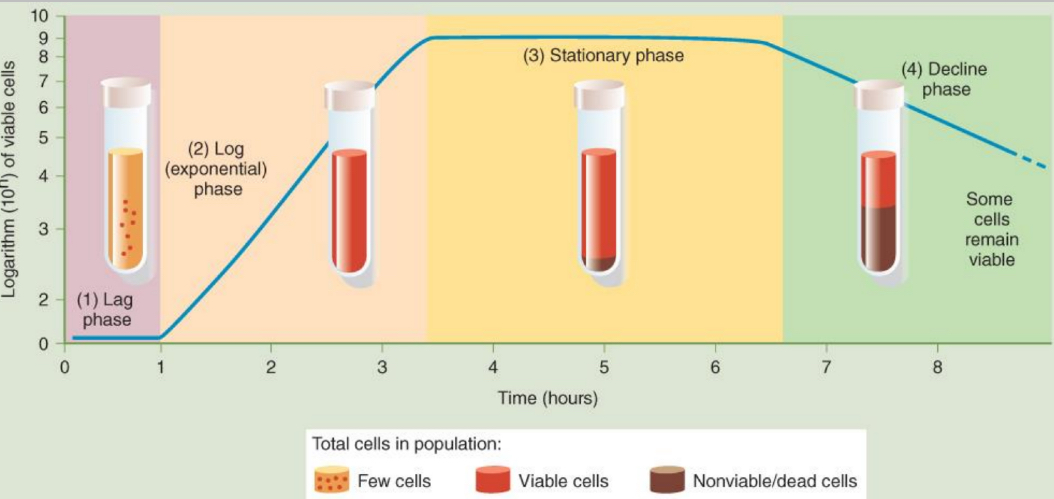
What happens during the ‘lag phase’ of bacterial growth?
- Adapting to new environment
- Cell growth processes
- Preparation for binary fission
- Length will depend on metabolic activity of the
population
B
What happens during the ‘log phase’ of bacterial growth?
- Exponential growth
- Requires optimal metabolic and
physiological conditions
- Rapid increase in number of cells
What happens during the ‘stationary phase’ of bacterial growth?
- Population growth is arrested
- Limited by nutrient availability
What happens during the ‘decline phase’ of bacterial growth?
- Limited nutrients in closed system
- Cells start to die off
- Balanced state of cell death
The bacterial growth curve:
What is quorum sensing?
Chemical communication between bacterial cells in the
biofilm
Influences behaviour to enhance survival
Why does dormancy occur?
Response to unfavourable environmental conditions
• Limited nutrients
• Presence of toxins
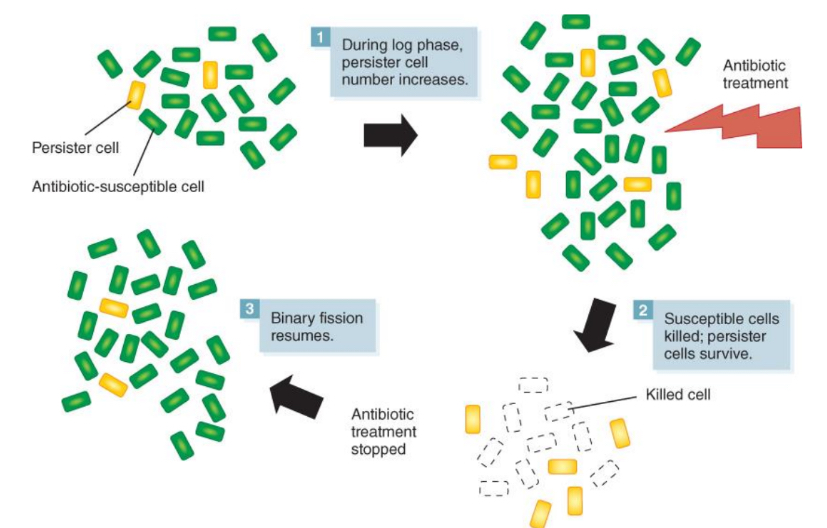
What are persister cells?
Persister cells are a small subset of bacteria that are genetically identical to the rest of the population but enter a dormant, non-growing state to survive harsh conditions, including antibiotics.
What are endospores?
• Produced in response to nutrient limitation (starvation)
• Complex program of gene expression
• Single endospore created by mother cell
• Represents growth-arrested stage
• Favourable conditions induces germination of endospore
• Spore coat breaks down (90 minutes)
• Immediately capable of asexual reproduction
• Thick peptidoglycan layer protects spore from outside environment
• Survives desiccation, extreme temperatures, chemical treatments and radiation
What are different conditions that optimal growth is dependent on?
• Temperature
• pH
• Osmotic pressure
• Carbon
• Oxygen
What are the 5 different groups of organisms related to temperature?
• Psychrophiles: range 0°C to 20°C
• Psychrotrophs: range 4°C to 39°C
• Mesophiles: range 10°C to 45°C
• Thermophiles: range 40°C to 70°C
• Hyperthermophiles: range 80°C to 115°C
What is minimum growth temperature?
Lowest temperature at which slow growth still possible.
What is maximum growth temperature?
Must stay below this or death results.
What are the different groups of organisms related to pH?
Acidophiles:
• Grow best at pH below 5
• Valuable in food/dairy industries
Neutrophiles:
• Majority of species, including most
bacterial pathogens
• Narrow range toleration
Alkaliphiles:
• Grow best at pH above 8
What does osmotic pressure mean?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure created by water moving across a membrane due to osmosis. The more water moving across the membrane, the higher the osmotic pressure.
What are the different groups of organisms related to osmotic pressure?
Extreme halophiles
• Require 20–30% salt
Halophiles
• Some grow in 2–5% salt
• Others grow in 5–20% salt
Halotolerant
• Can grow in ≤8% salt
Non-halophiles
• Grow optimally <2% salt
What are the conditions for growth related to carbon?
• Carbon is required to build organic molecules necessary for life
• Growth media must contain a carbon source
What are the conditions for growth related to oxygen?
• Many bacteria require oxygen for growth- obligate aerobes
• Some can survive in very low oxygen- microaerophiles
• Some are killed by oxygen- obligate anaerobes
• Some can grow with and without oxygen- facultative anaerobes
What other elements related to growth conditions?
Nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphate
• Needed for growth and reproduction
• Proteins contain nitrogen and sulfur.
• Amino acids contain nitrogen and phosphorus.
Most nitrogen and sulfur from breaking down proteins into amino acids;
Some species get ammonium or nitrate ions from soils.
How do bacteria get growth factors?
Growth factors must be obtained from the diet because they cannot be made by the organism
•Often includes essential vitamins and amino acids