Chemistry Unit Test 2/5/25
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
chemical bond
a mutal electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together
potential energy
this is what nature tries to minimize and is the reason behind he octet rule
ionic bonding
chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations(+) and anions(-); atoms completely give up electrons to other atoms
covalent bonding
the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms; the shared electrons are owned equally; atoms try to fill their s and p orbitals
electronegativity
a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons; the difference between this of two atoms determines if a bond is ionic or covalent
completely covalent
this is the bonding of two of the same molecules
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribtion of electrical charge
polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the bonded atoms have an unequal attraction for the shared electrons
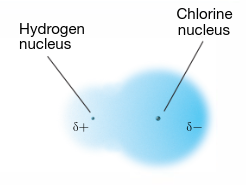
partial negative charge
δ-
partial positive charge
δ+
electron density
the more electronegative atom in a bond will have greater density around it
molecule
a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds; may consist of two or more atoms
molecular compound
a chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules; its composition is given by its chemical formula
stable covalent bond
a bond where there is balance between attraction and repulsion
bond length
the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy; the average distance between two bonded atoms measured in pm
bond dissociation energy
the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms; measured in kilojoules per more (kJ/mol)
octet rule
chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its highest occupied energy level
single bond
a covalent bond in which one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms; one sigma bond
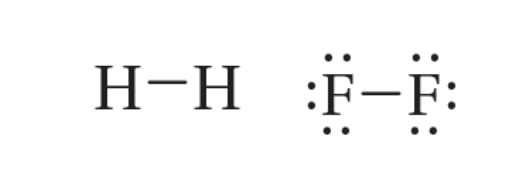
double bond
a covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms; one sigma and one pi bond; shorter and stronger
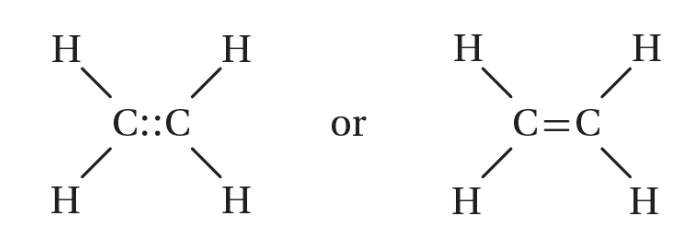
triple bond
a covalent bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms; one sigma and two pi bonds; shortest and strongest
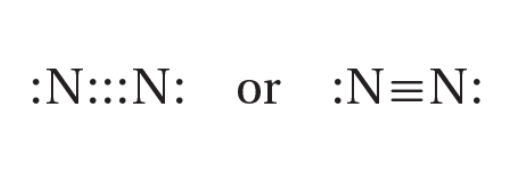
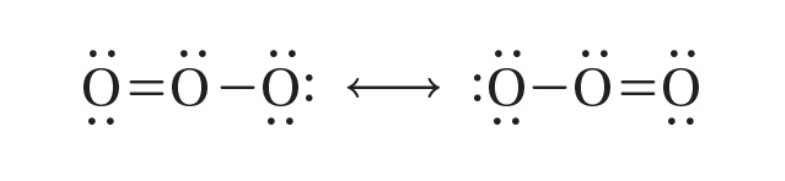
resonance
the bonding in molecules or Ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single Lewis structure; indicated by a double-headed arrow placed between the molecule’s resonance structures
ionic compound
a compound composed of positive and negative Ions that are combined so that the numbers of positive and negative charges are equal (electrical neutrality); most exist as crystalline solids
lattice energy
the energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions
attraction
the difference in the strength of __________ between the basic units of molecular and ionic compounds (ionic compounds are stronger) gives rise to different properties in the two types of compounds
ionic compound properties
high melting & boiling points
hard but brittle
solid = not conductor
molten = conductor
some water-soluble
polyatomic ion
a charged group of covalently bonded atoms; has molecular and ionic characteristics
metals
chemical bonding is different in ______ than it is in ionic, molecular, or covalent-network compounds; due to highly mobile valence electrons
delocalized electrons
electrons that do not belong to any one atom but move freely about the metal’s network of empty atomic orbitals; due to vacant orbitals in the atoms’ outer energy levels
metallic bonding
the chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons
molecular geometry
the 3D arrangement of a molecule’s atoms in space
molecular polarity
the uneven distribution of molecular charge; strongly influences the forces that act between molecules in liquids and solids; polar means unequal
VSEPR theory
repulsion between the sets of valence-level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be oriented as far apart as possible; lone pairs occupy space in the same way that bonded pairs do
hybridization
the mixing of two or more atomic orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to produce new hybrid atomic orbitals of equal energies
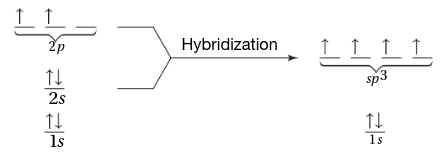
hybrid orbitals
orbitals of equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom; the number produced equals the number of orbitals that have combined
intermolecular forces
the forces of attraction between molecules; a good measure is boiling point because the higher the boiling point, the stronger the forces
dipole
created by equal but opposite charged that are separated by a short distance; strongest intermolecular forces
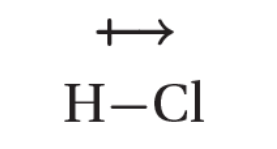
hydrogen bonding
the intermolecular force in which a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom is attracted to an unshared pair of electrons of an electronegative atom in a nearby molecule; high boiling points and strong dipole-dipole force
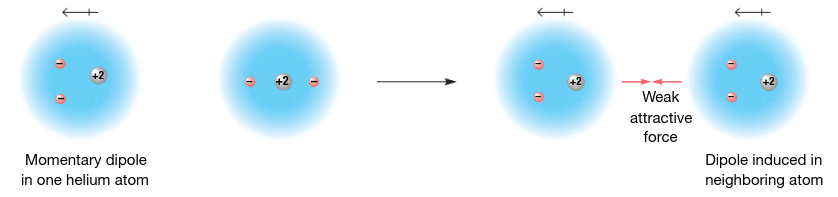
london dispersion forces
the intermolecular attractions resulting from the constant motion of electrons and the creation of instantaneous dipoles; increase with increasing atomic or molar mass
least
the _____ electronegative atom is the center of the lewis structure
binary molecular compounds
prefix indicates # of atoms of each element
last word suffix -ide
binary acids
1st word prefix -hydro
root of element suffix -ic
acid
oxyacids
contains both a hydrogen atom and an oxyanion
memorize Polyatomic ions
root of oxyanion
suffix -ate = -ic
suffix -ite = -ous
acid
suboctet
a few compounds form stable configurations with less than 8 electrons around the atom