Chem 1A midterm 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
types of degrees of freedom
rotations
vibrations
translations
what do each of the motions relate to?
more rotations and vibrations = higher specific heat
translations: only one that increases T
how does heat of the surroundings relate to heat of the system
qsurr = - qsys
when using a calorimeter, how do you find the heat of the surroundings vs. system
surroundings: qwater = mwater x cwater x Delta T
system: qsys = -qwater
what is q in exo vs. endothermic reactions
exo: q<0 (feels HOT)
endo: q>0 (feels COLD)
how does PE change in exo vs. endo reactions
exo: high to low PE
endo: low to high PE
PE for attraction and repulsion
attraction: low PE
repulsion: high PE
bond length and strength graph
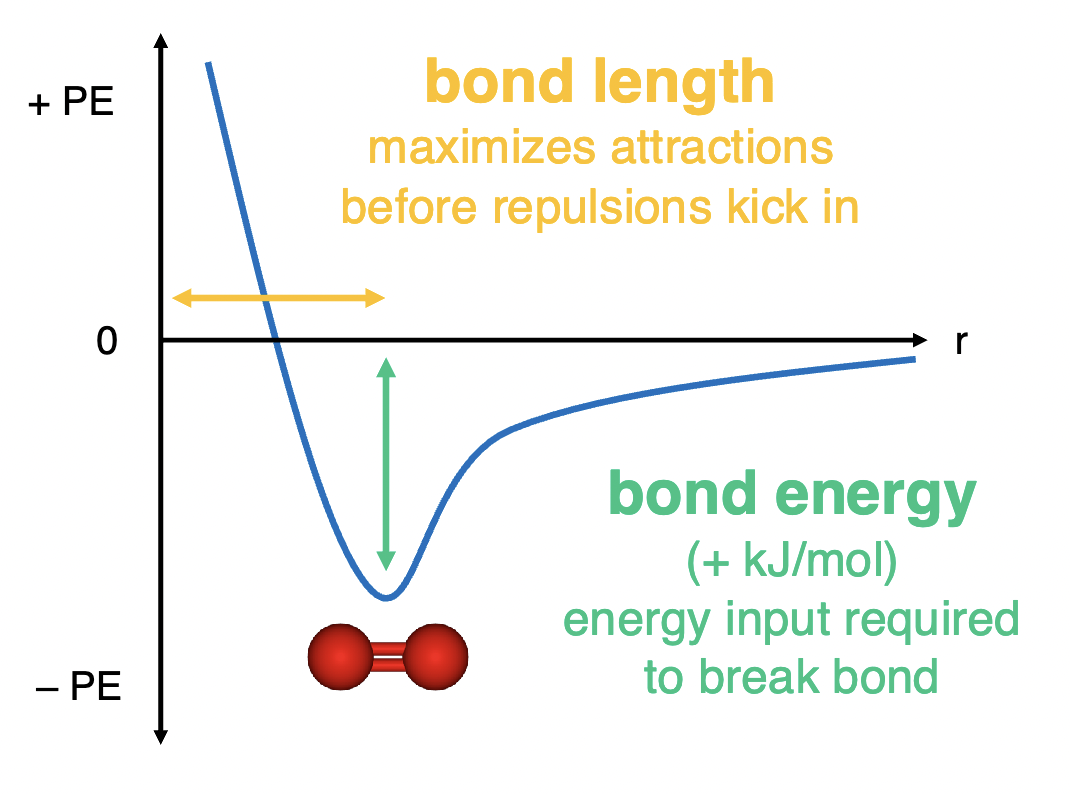
what type of reaction is bond making
endothermic
only way to release energy w/ bonds
to create a stronger bond
relationship of ΔS-surr to ΔH-sys
ΔS-surr always opposite sign to ΔH-sys
how does entropy relate to changes?
changes occur so that entropy increases
when is a reaction spontaneous
when ΔS>0
when is a reaction favorable?
when ΔG<0
when ΔS>0 and ΔH<0, when is the reaction favorable?
favorable at all T
when ΔS<0 and ΔH<0, when is the reaction favorable?
favorable at low T
when ΔS>0 and ΔH>0, when is the reaction favorable?
favorable at high T
when ΔS<0 and ΔH>0, when is the reaction favorable?
favorable at no T
the two things a system favors
lower energy
greater dispersion
what does ΔG° assume?
occurs at standard conditions
mixture of reactants and products
all solutions at 1 M = 1 mol / 1 L
composition of the equilibrium mixture
when is ΔG=0
at equilibrium
when is E° favorable
when E°>0
In what direction does electron transfer occur
so that ΔG°<0 and E°cell>0 (product favored)
how to know if atom is magnetic
if it has any unpaired electrons in orbital
oxidation
losing electrons
reduction
gaining electrons
ΔG° in redox
who is better at attracting the e-
E°cell
= E°red - E°ox
cathode
where reduction takes place
anode
where oxidation takes place
how does E° compare in cathode vs. anode
cathode: higher E°
anode: lower E°