Lecture 8: The Axial Skeleton 🩻💀
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major terms and structures discussed in Lecture 8 on the axial skeleton.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
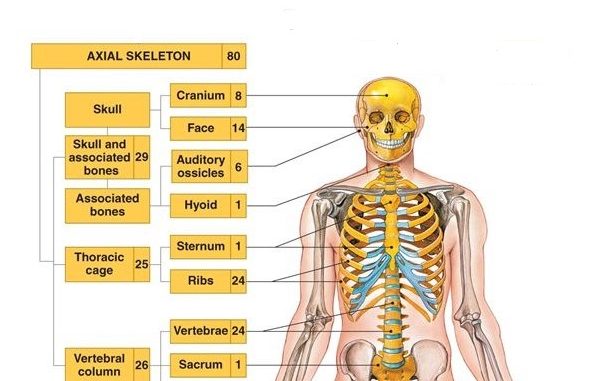
Axial Skeleton
80-bone division forming the body’s axis; skull, vertebral column, sternum, 12 pairs of ribs, and hyoid; supports/protects organs and provides muscle attachments.
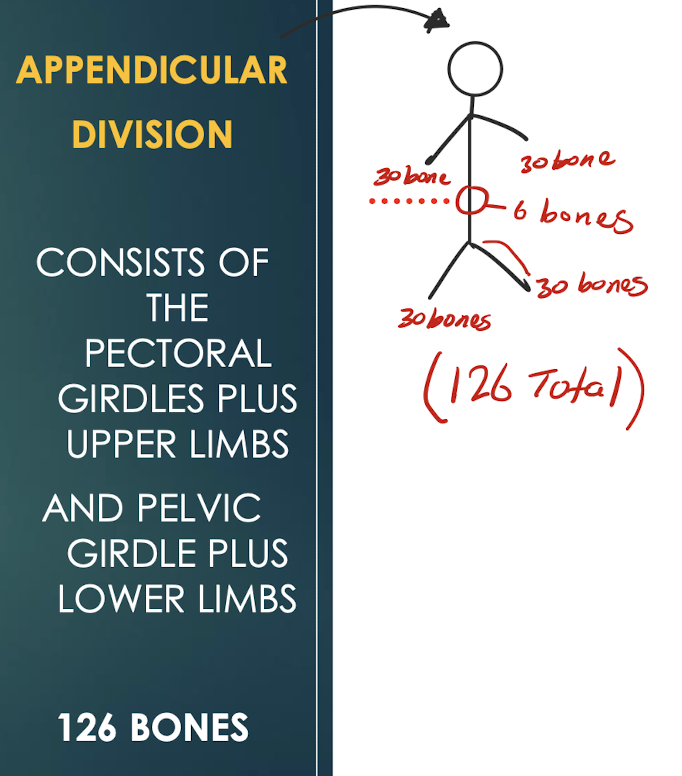
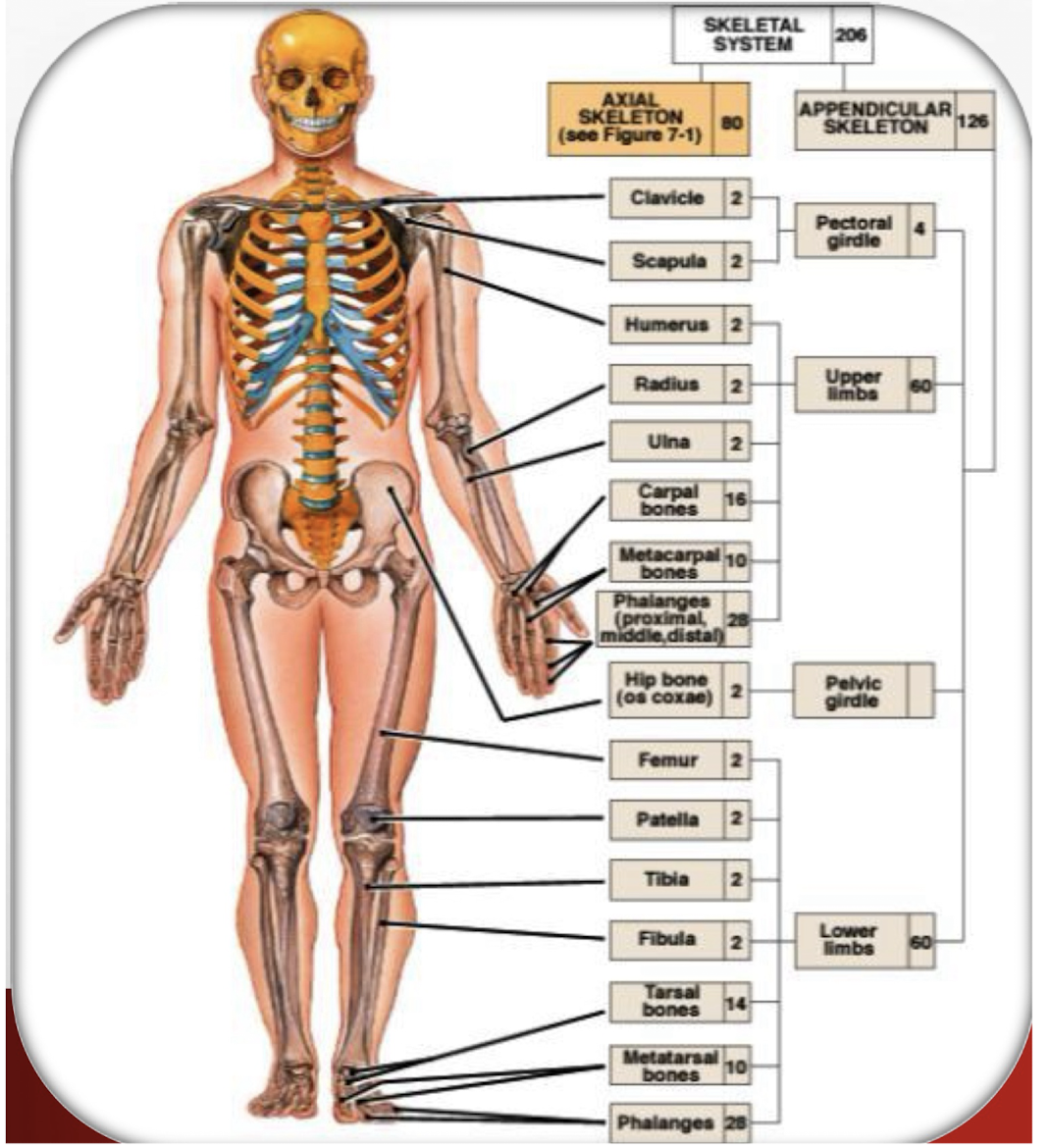
Appendicular Skeleton
126-bone division; pectoral girdles & upper limbs plus pelvic girdle & lower limbs.
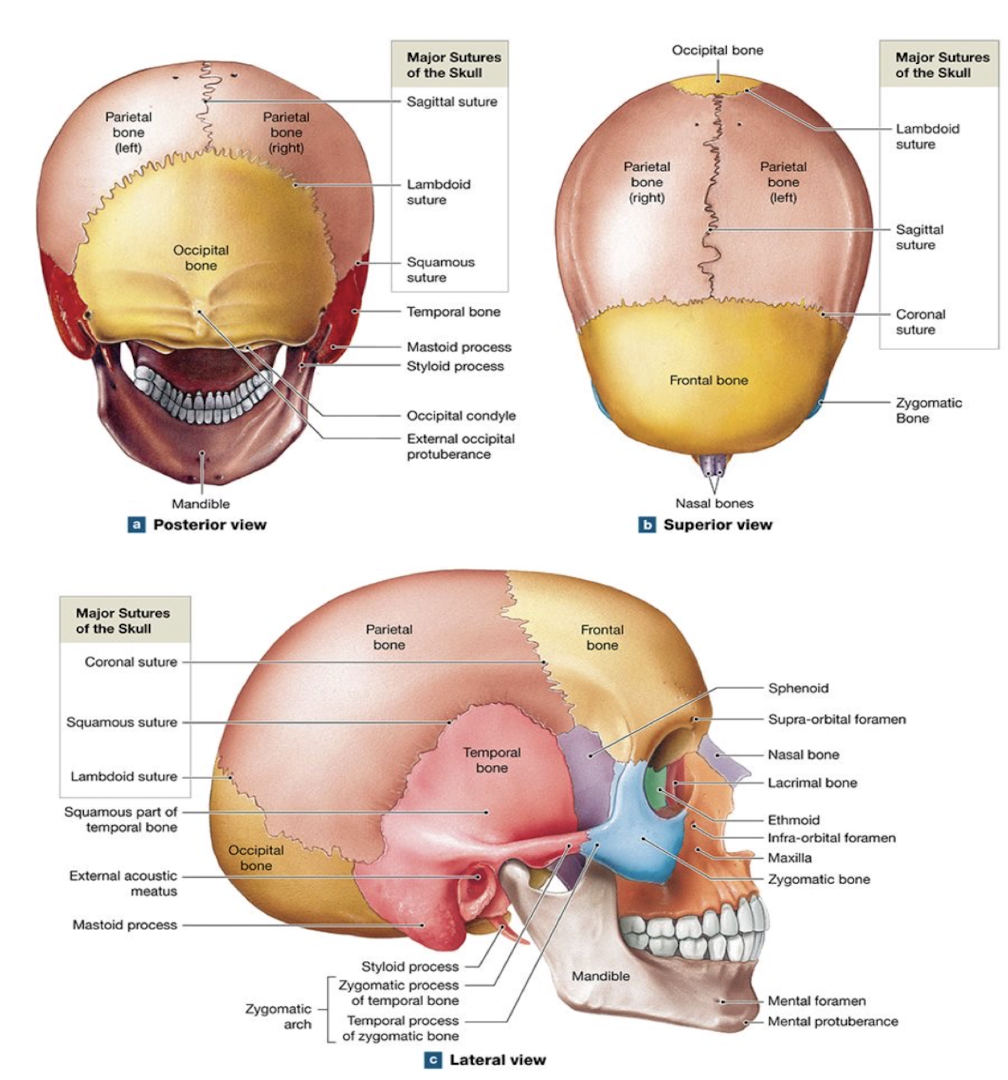
Suture
Immovable fibrous joint that unites skull bones (except the mandible).
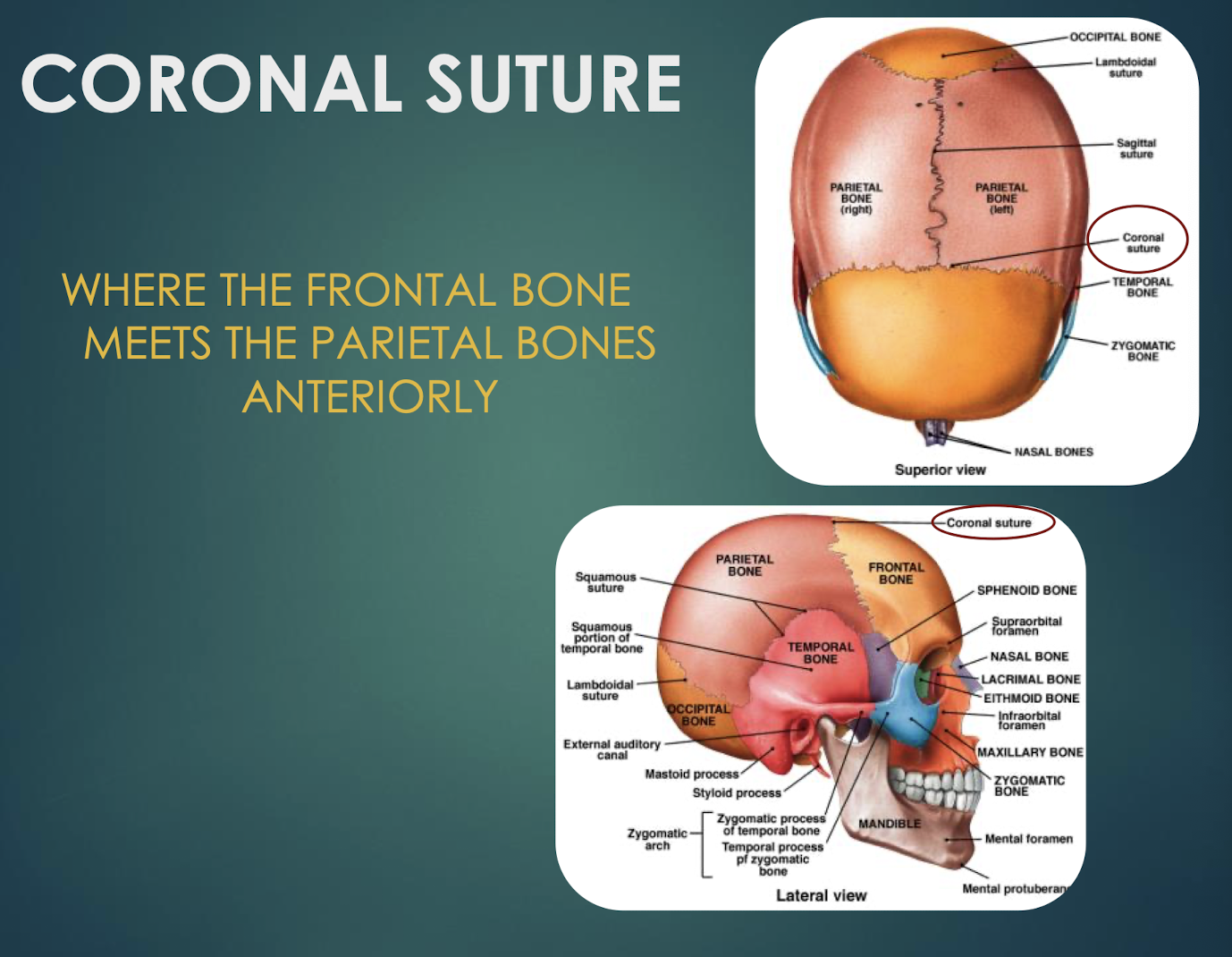
Coronal Suture
Junction where frontal bone meets parietal bones anteriorly.
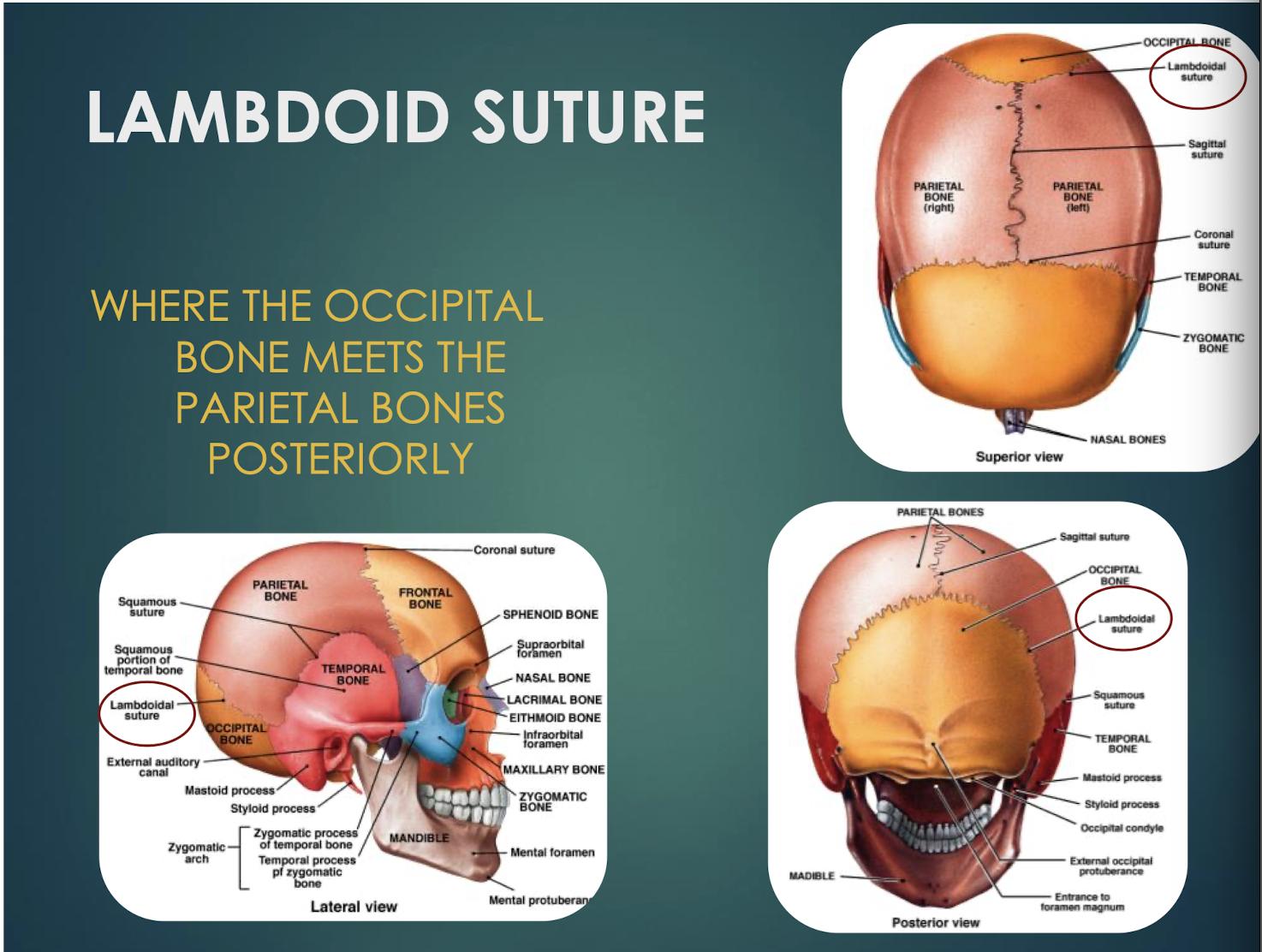
Lambdoid Suture
Junction where occipital bone meets parietal bones posteriorly.
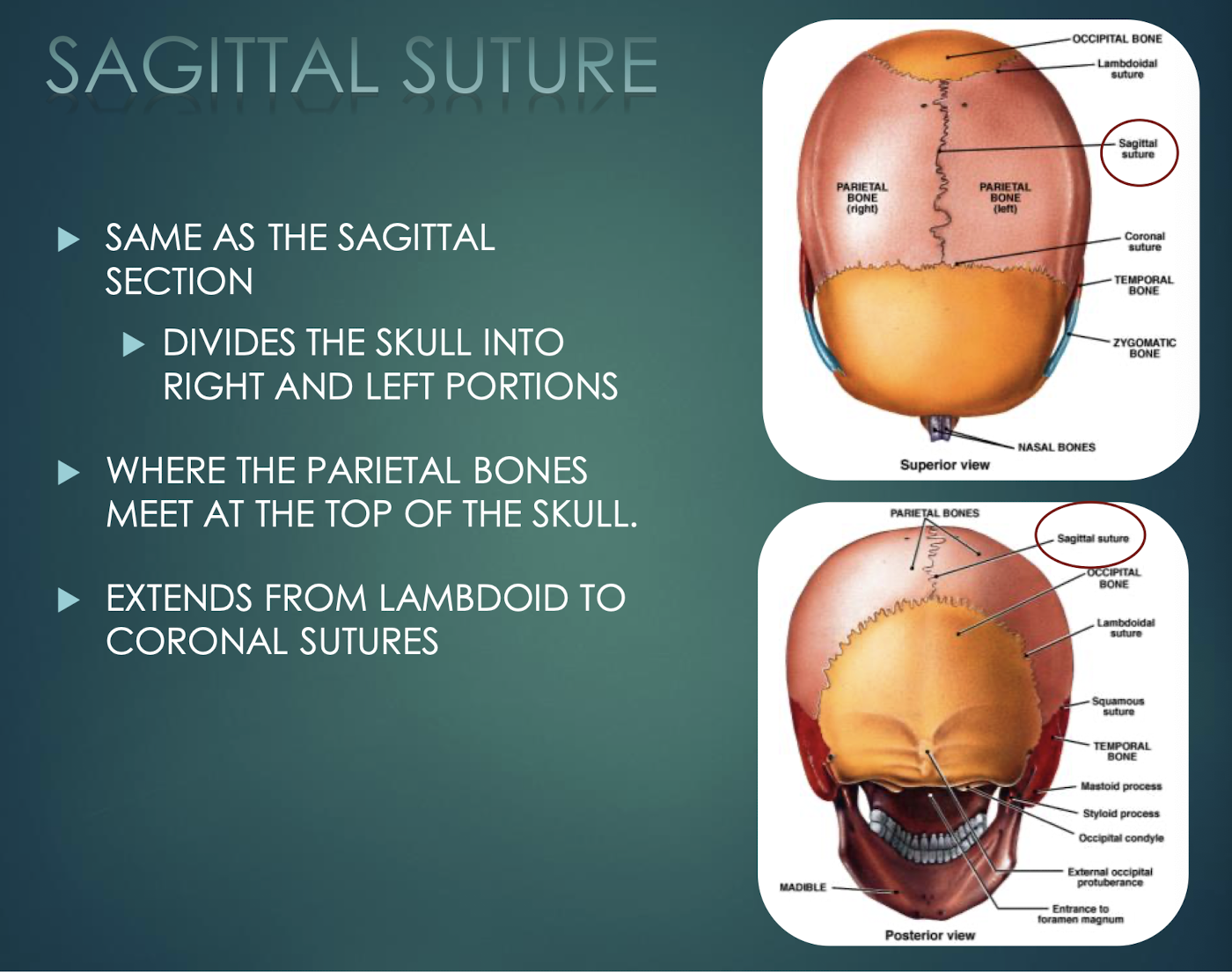
Sagittal Suture
Midline joint where the two parietal bones meet; runs coronal to lambdoid sutures.
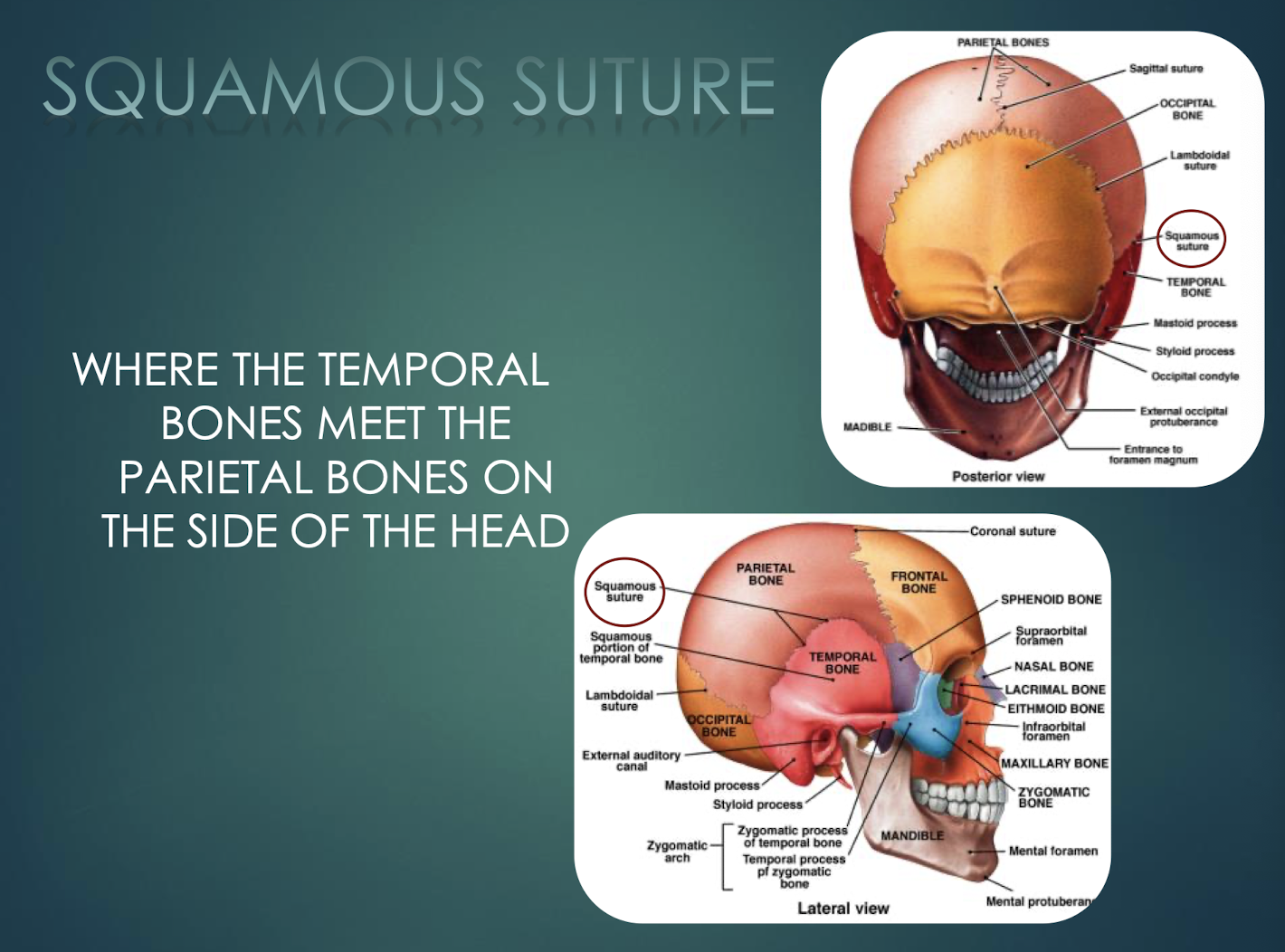
Squamous Suture
Joint where each temporal bone meets the parietal bone laterally.
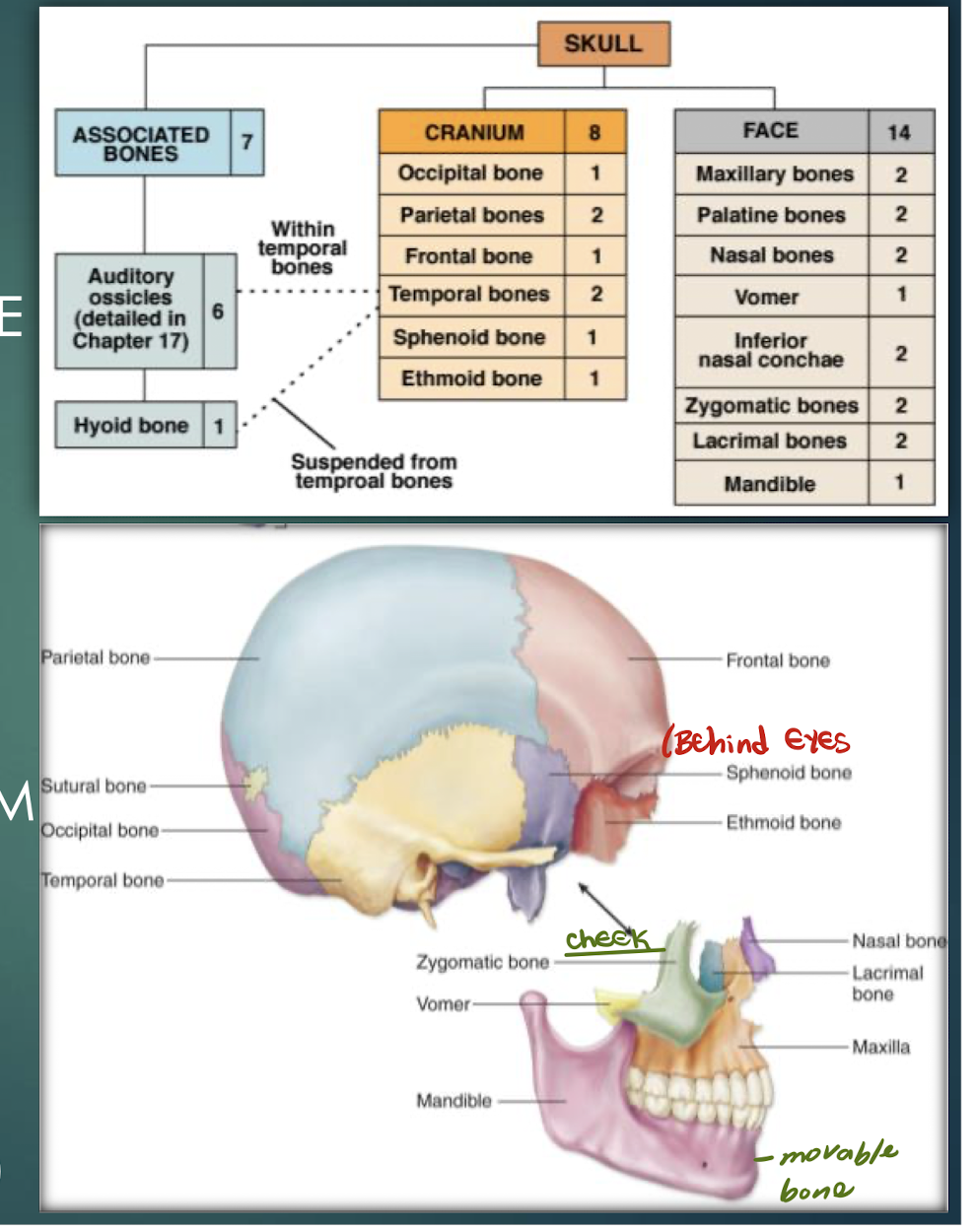
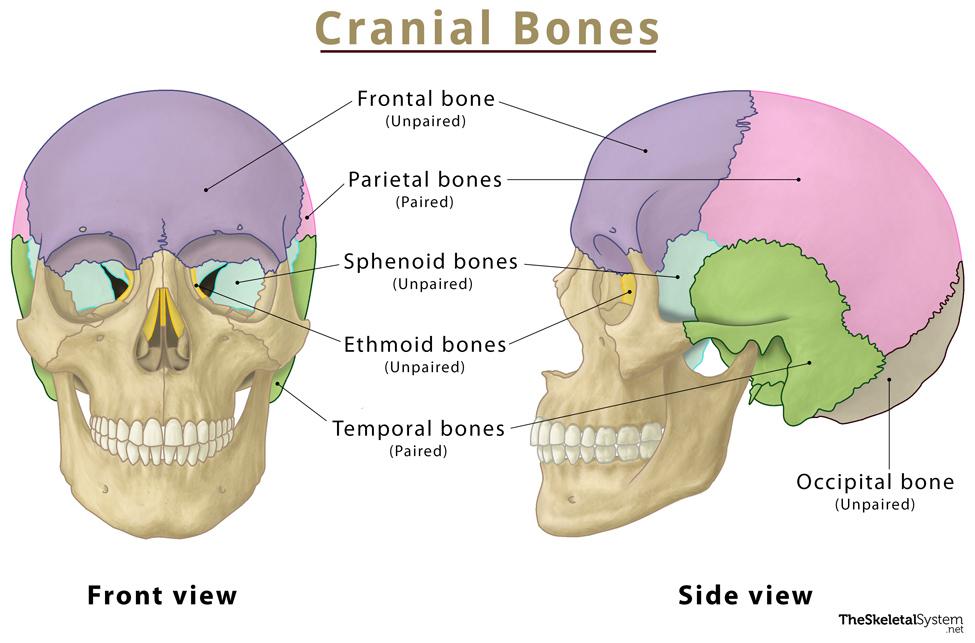
Cranial Bones
Bones that encase and protect the brain (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid).
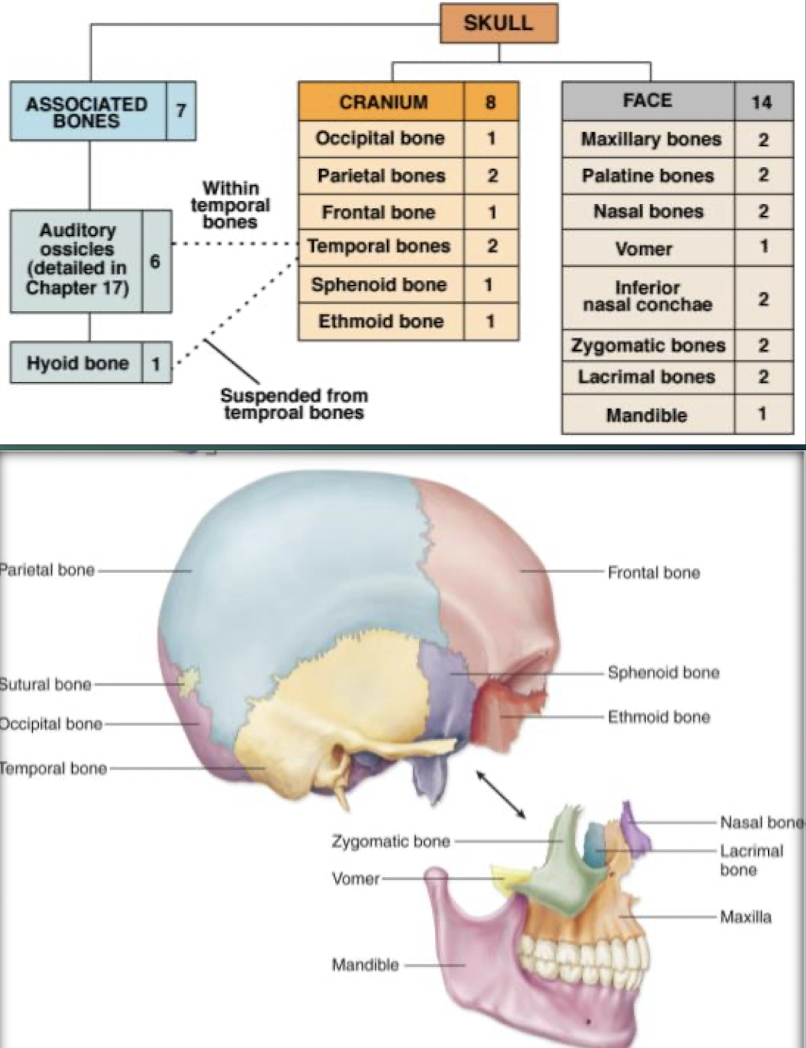
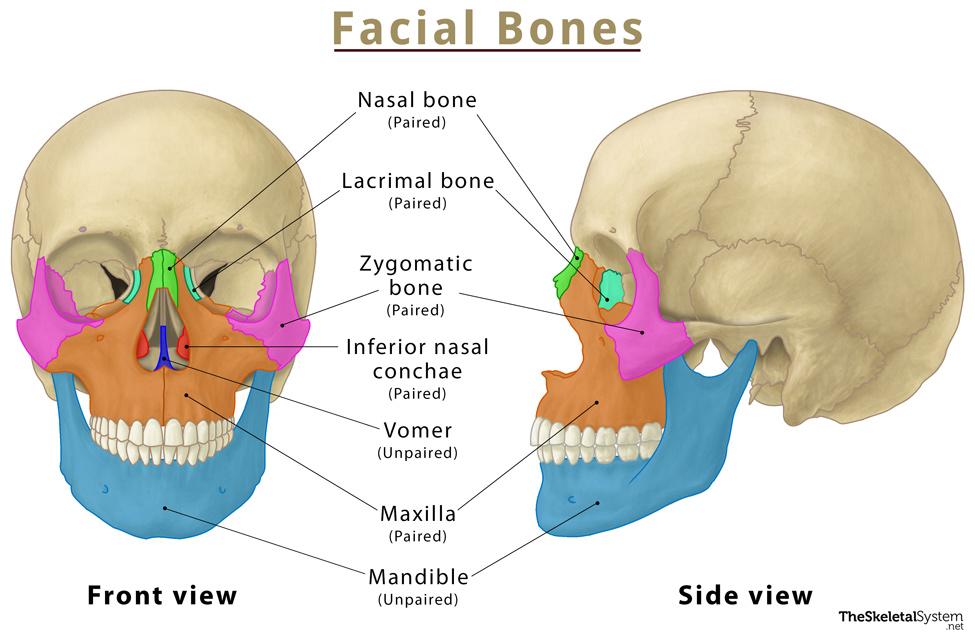
Facial Bones
Bones forming facial structure; 13 fused plus the movable mandible.
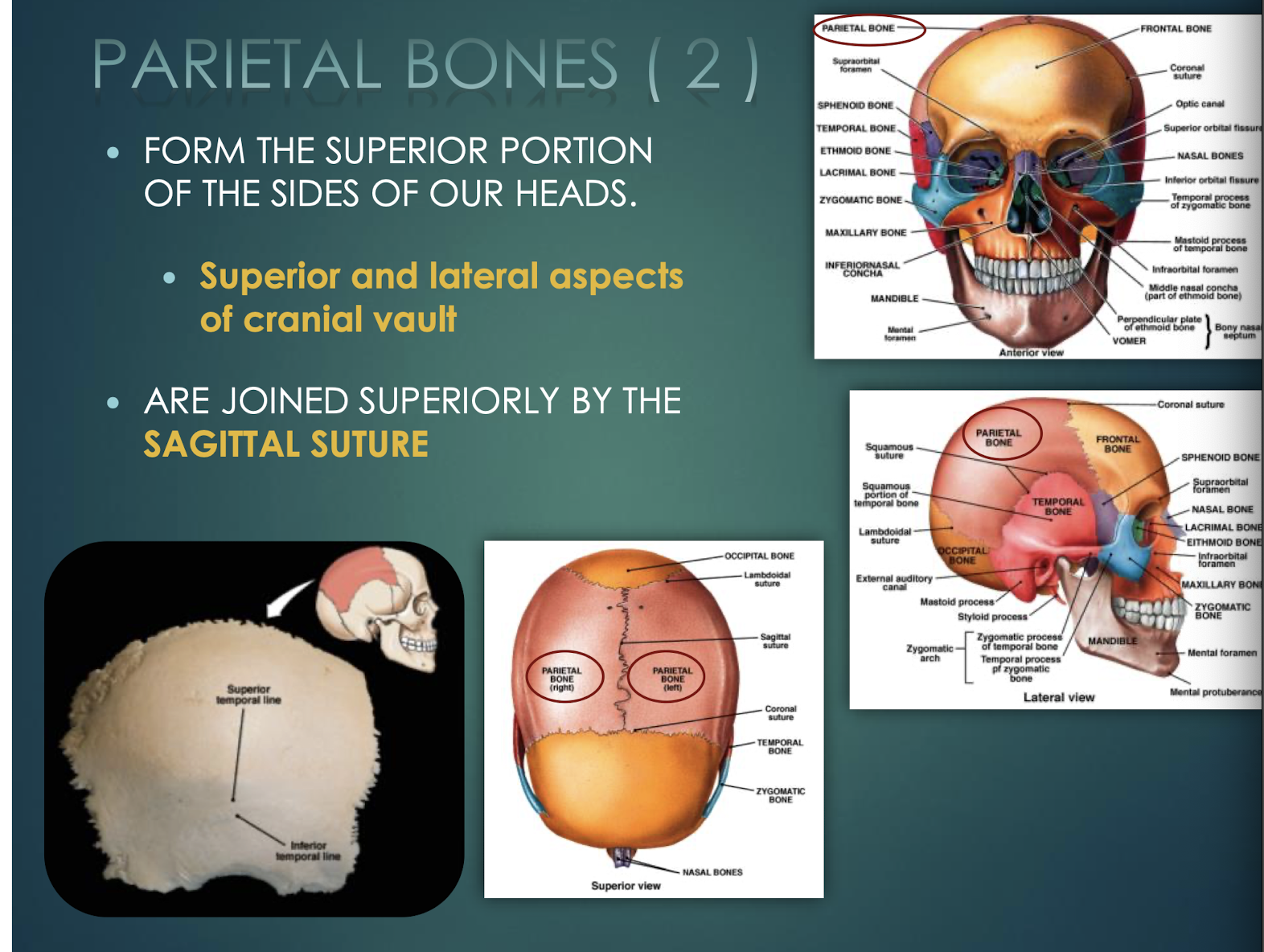
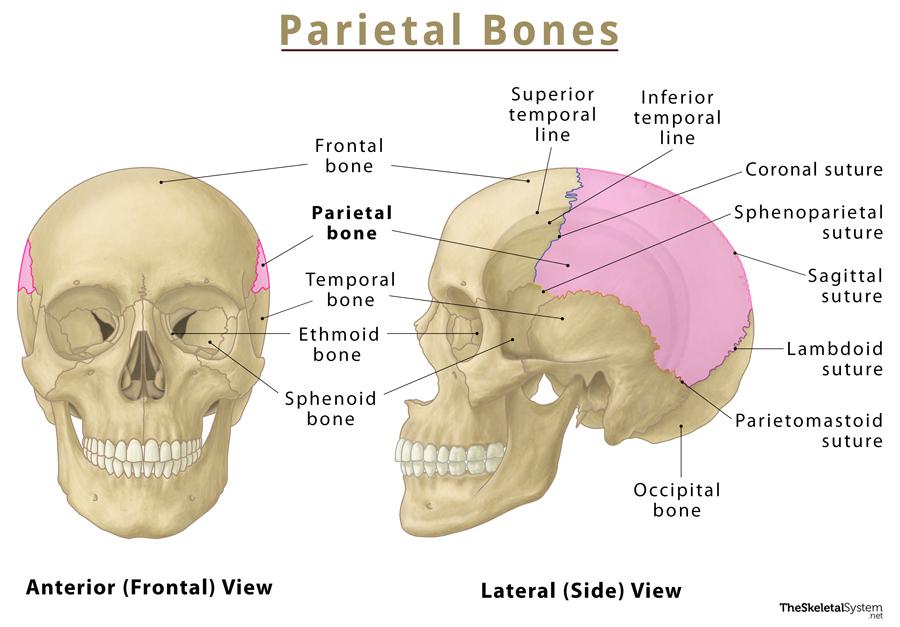
Parietal Bones
Paired bones forming superior & lateral skull walls; joined by sagittal suture.
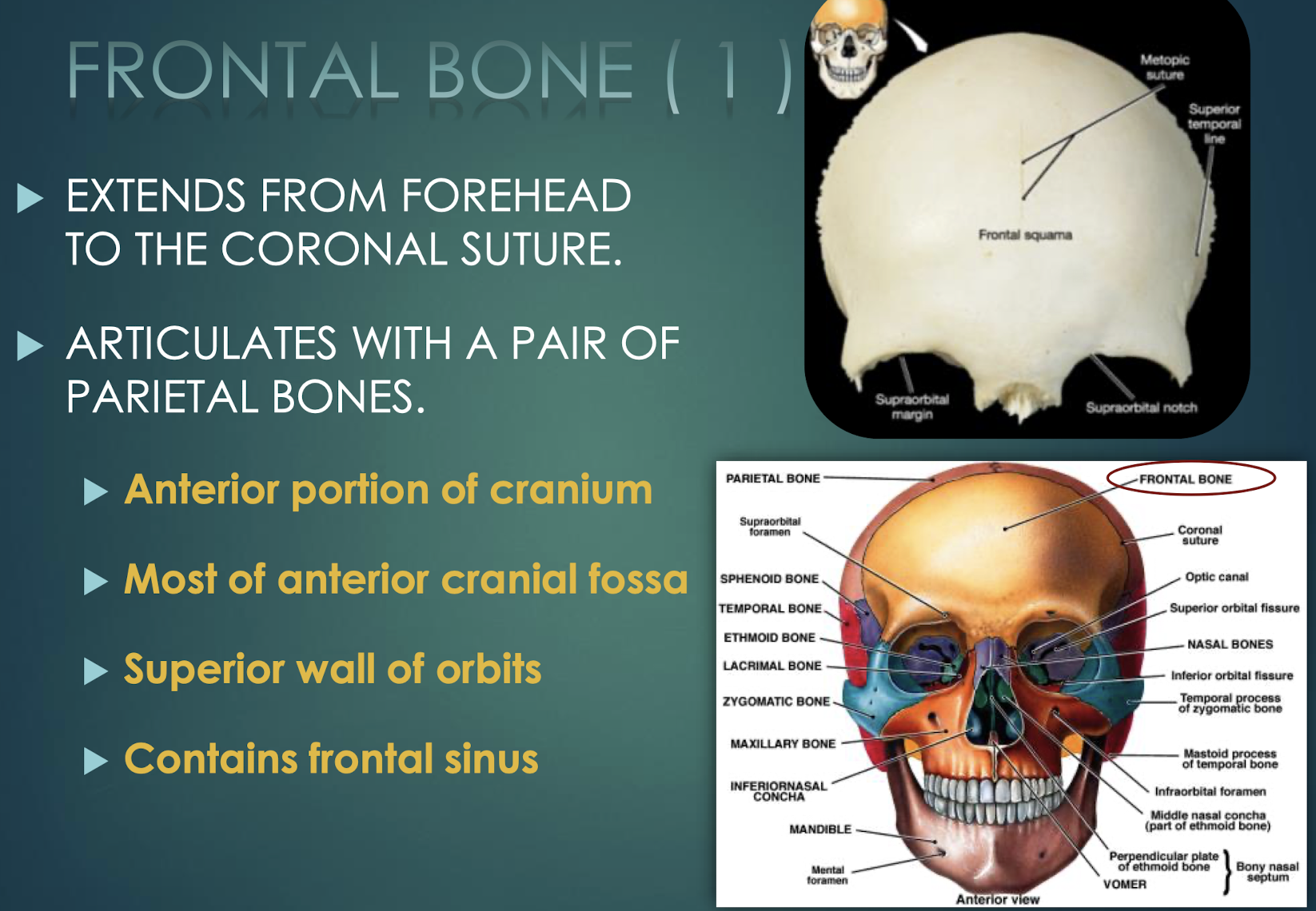
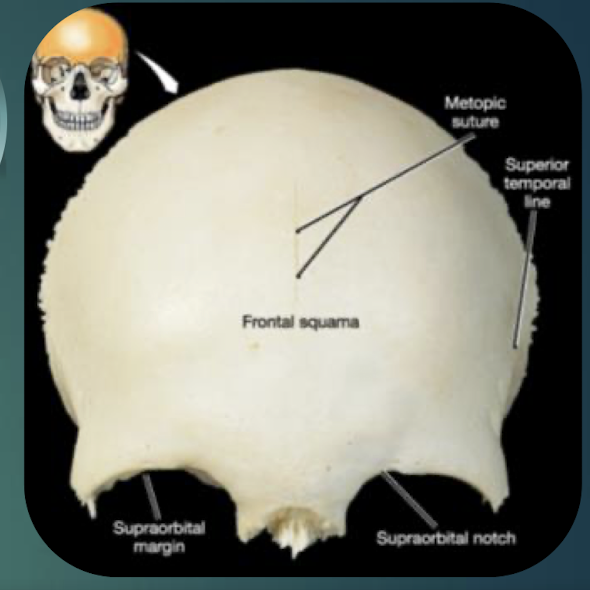
Frontal Bone
Single bone forming forehead, anterior cranial fossa, superior orbital walls; contains frontal sinus; meets parietals at coronal suture.
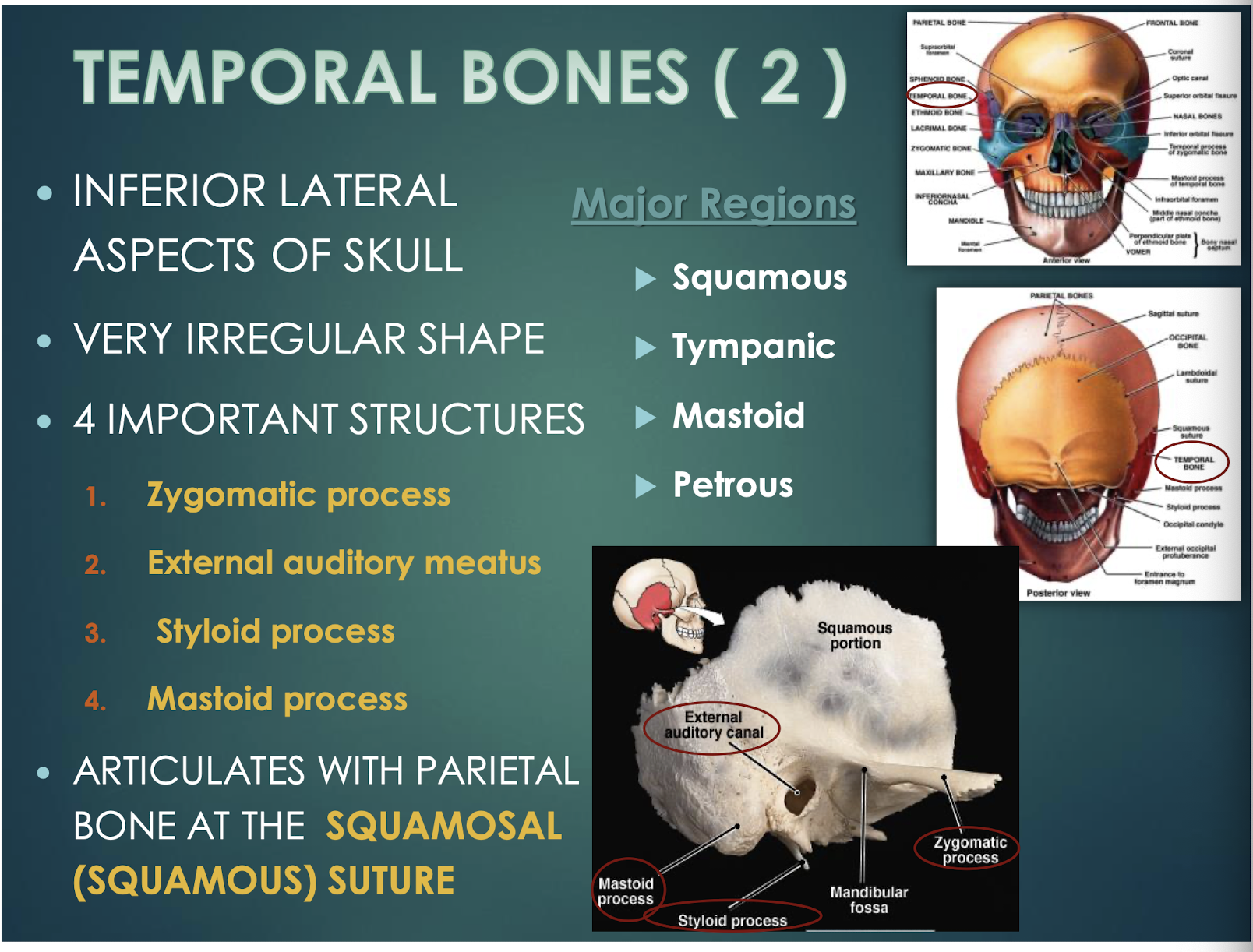
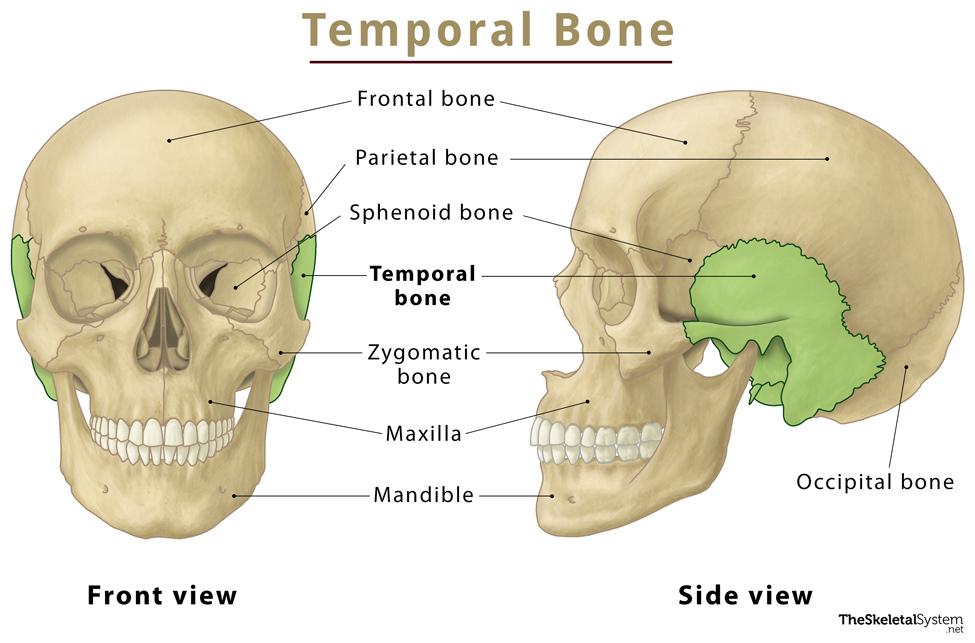
Temporal Bones
4 important structures, including the zygomatic process, external auditory meatus, styloid and mastoid processes, and meet the parietal bone at the squamous suture.
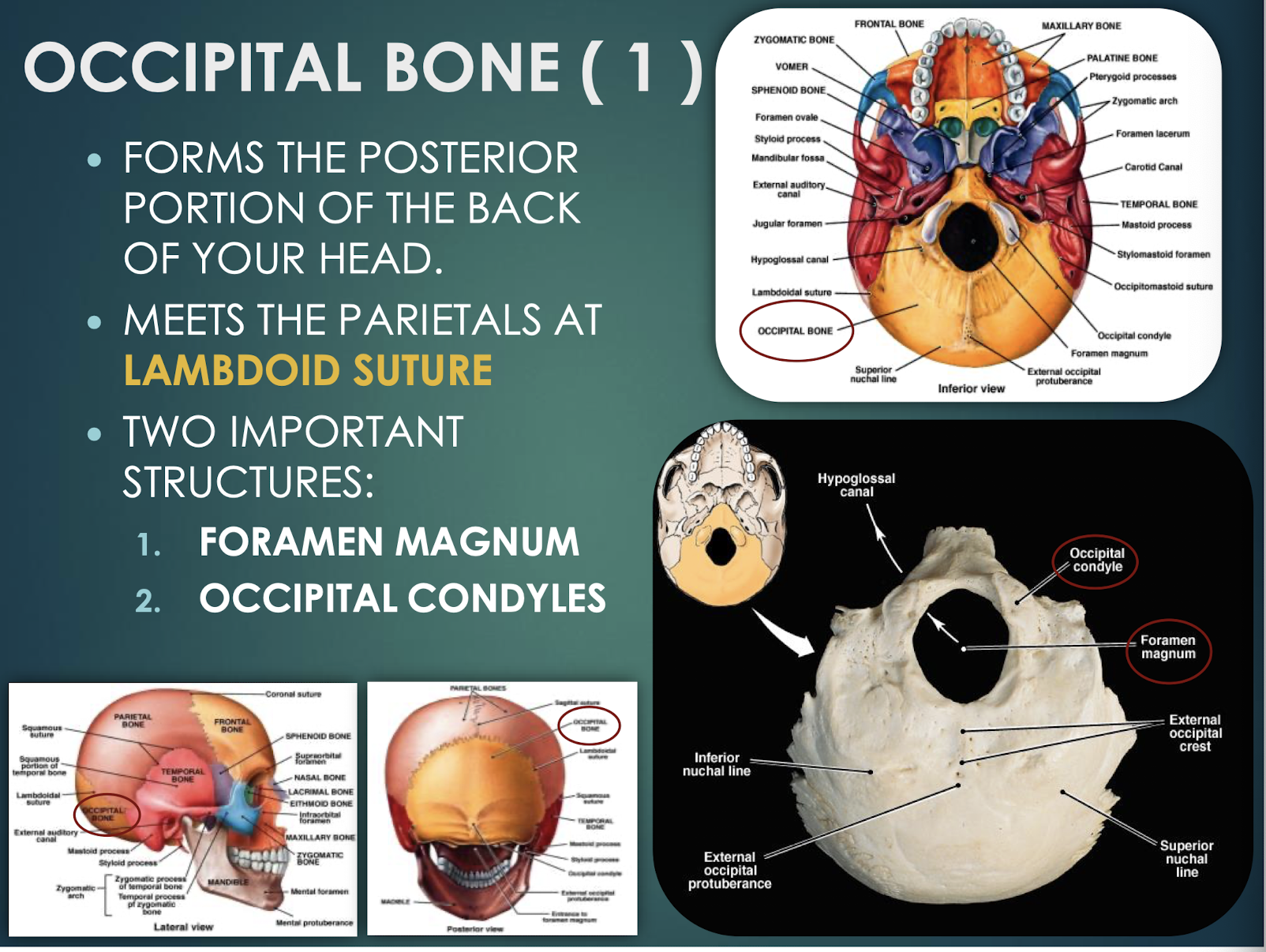
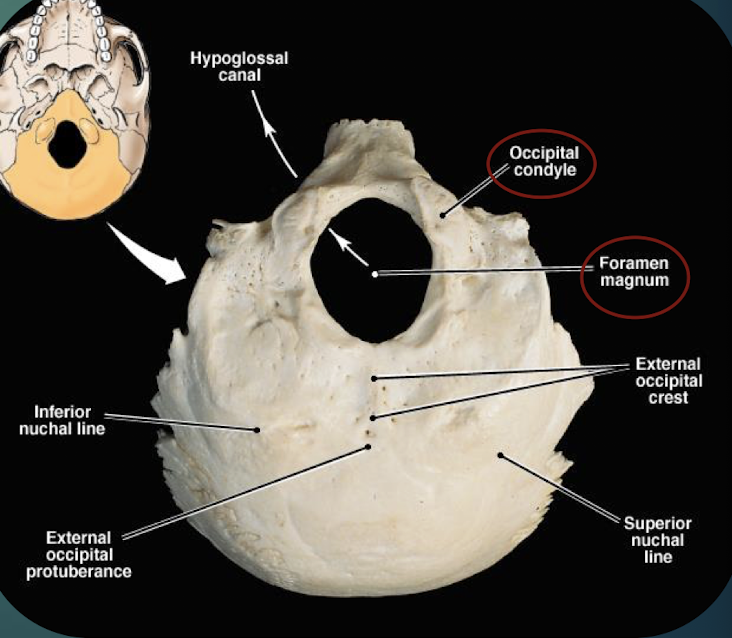
Occipital Bone
Posterior skull bone; contains foramen magnum & occipital condyles; meets parietals at lambdoid suture.
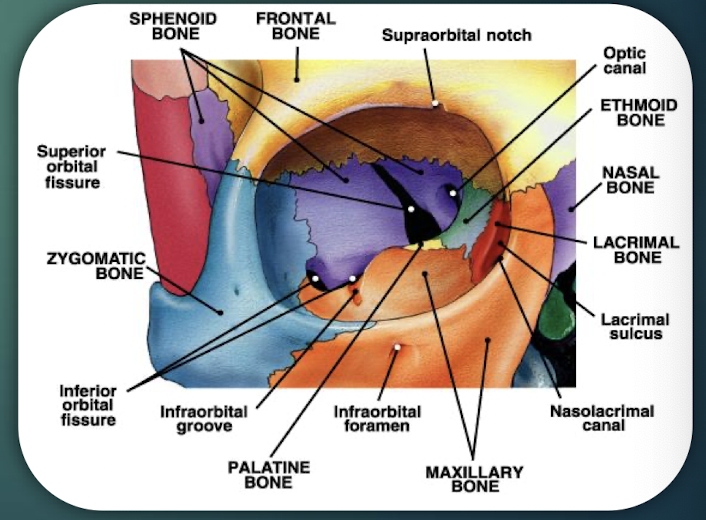
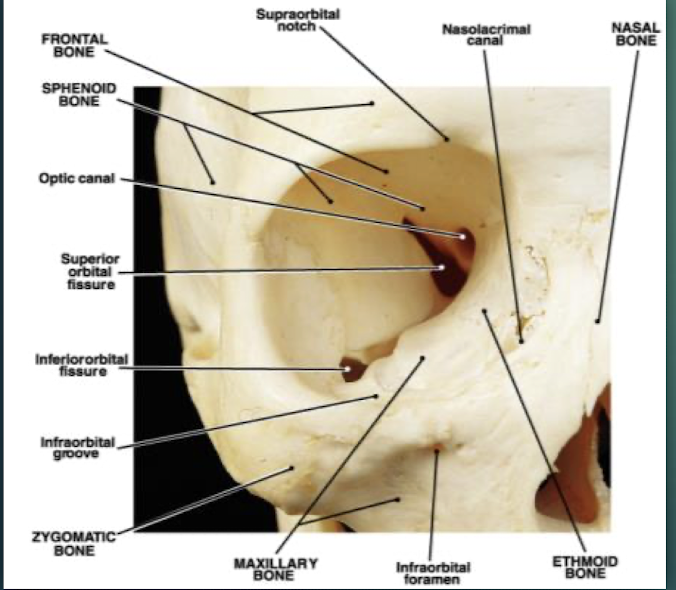
The Orbits
Cavities that encase eyes, attachment points for the eye muscles. Formed by 7 bones, including the Frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, maxilla, palatine, lacrimal, ethmoid bones.
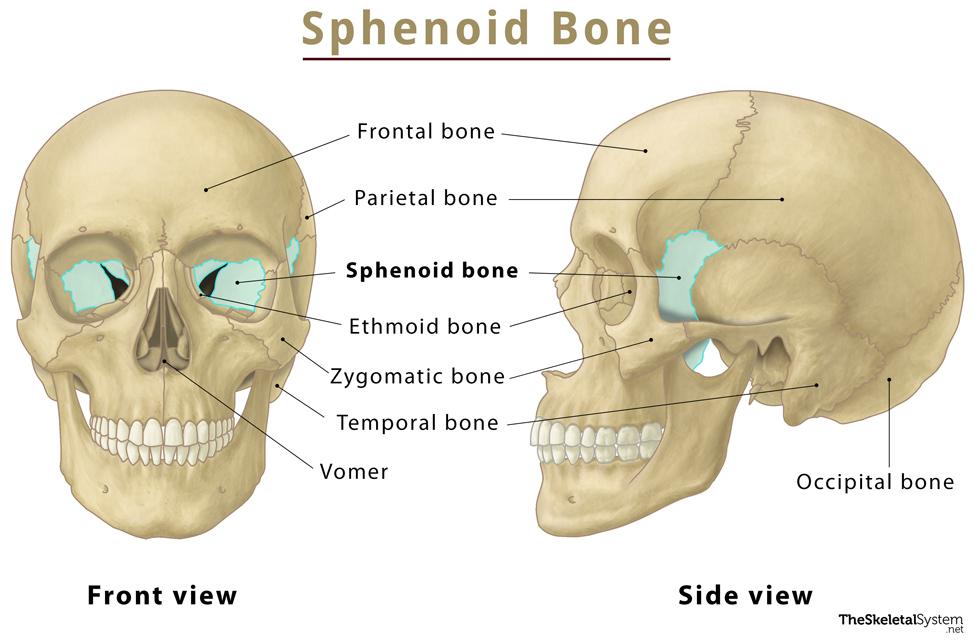
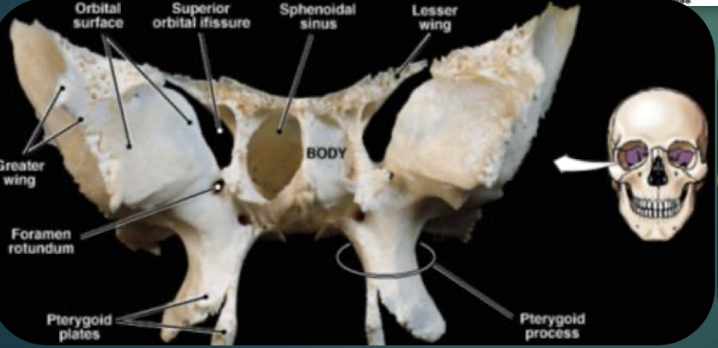
Sphenoid Bone
Bat-shaped keystone cranial bone articulating with all other cranial bones; has greater & lesser wings and pterygoid processes.
Zygomatic Bones
Paired cheek bones located below the orbits.
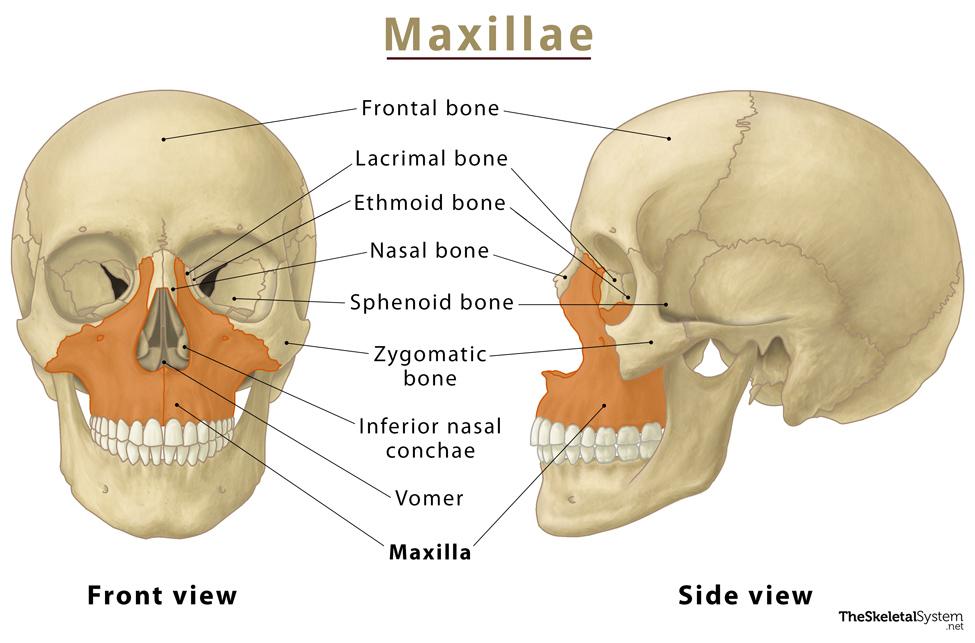
Maxillary Bones
Medially fused upper-jaw bones; keystone facial bones articulating with all others except mandible; house maxillary sinuses.
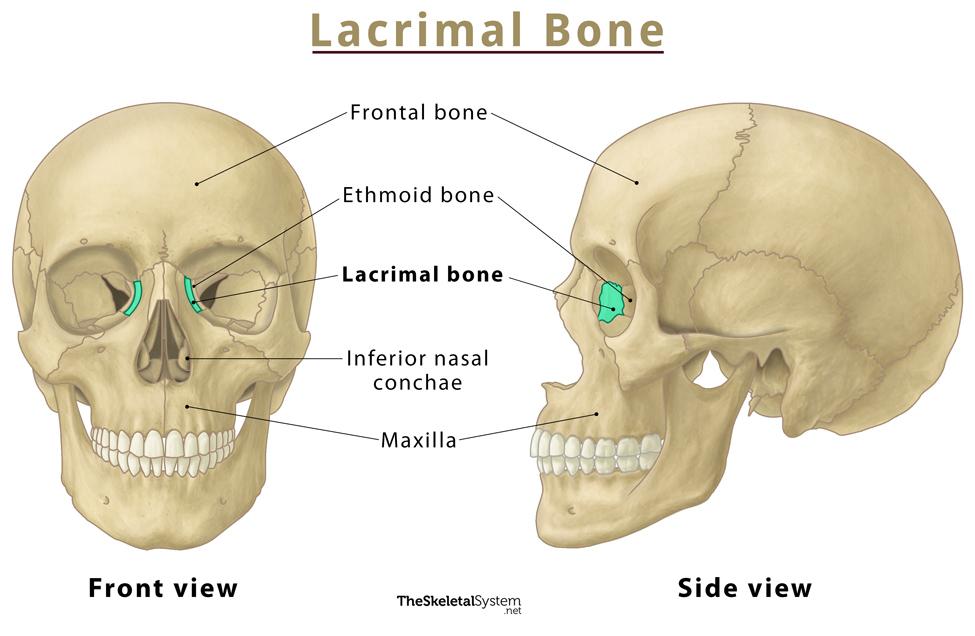
Lacrimal Bones
Small paired bones in medial orbit walls, lateral to each maxilla.
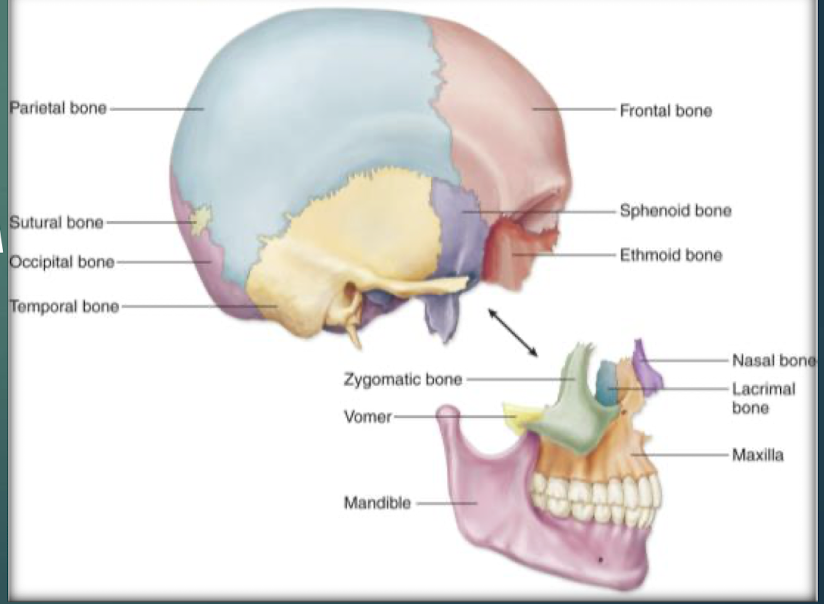
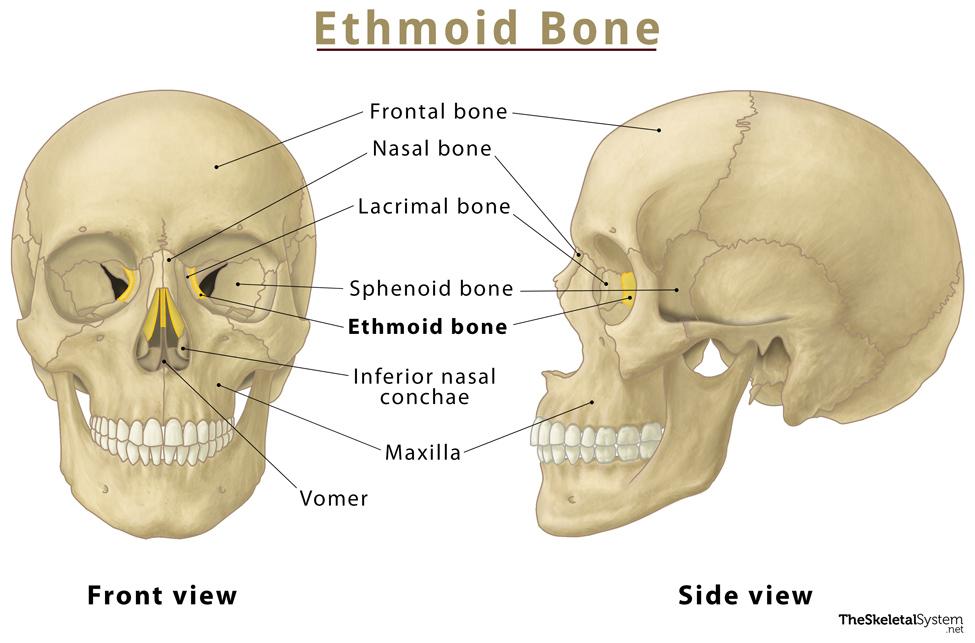
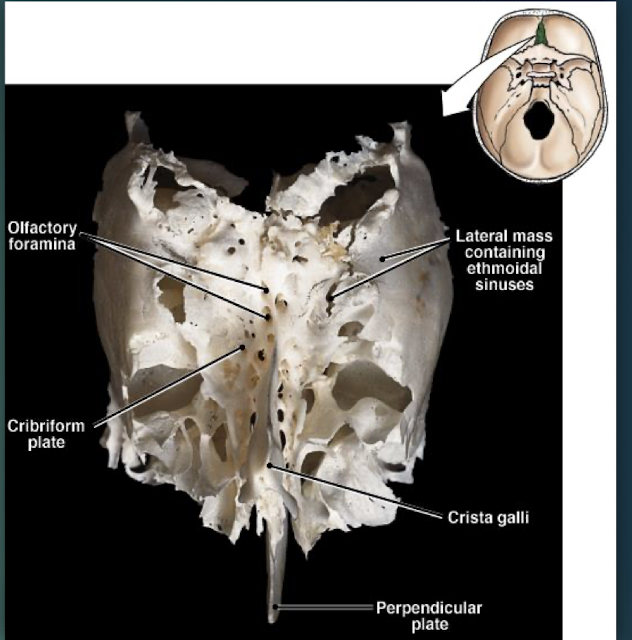
Ethmoid Bone
Deepest skull bone; forms superior nasal septum and medial orbit walls; cribriform plate with olfactory foramina and crista galli.
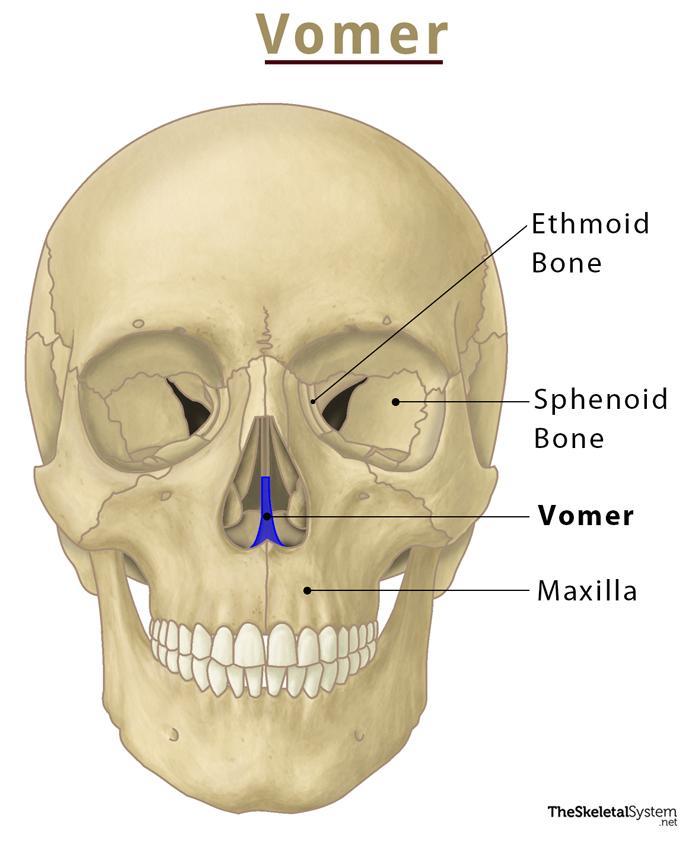
Vomer
Thin median bone forming inferior portion of nasal septumthat separates the left and right nasal cavities.
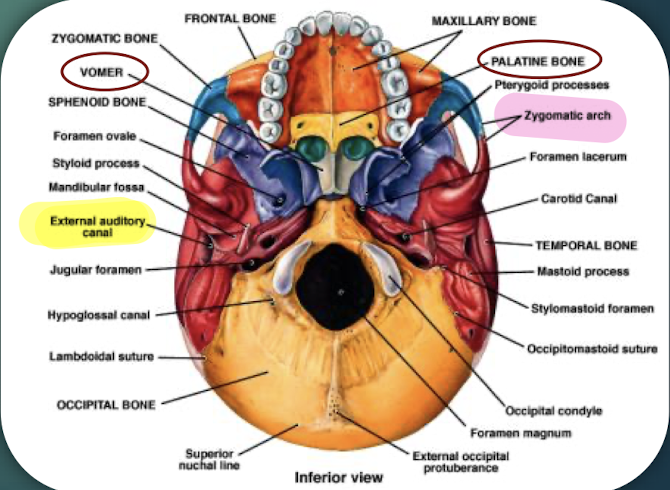

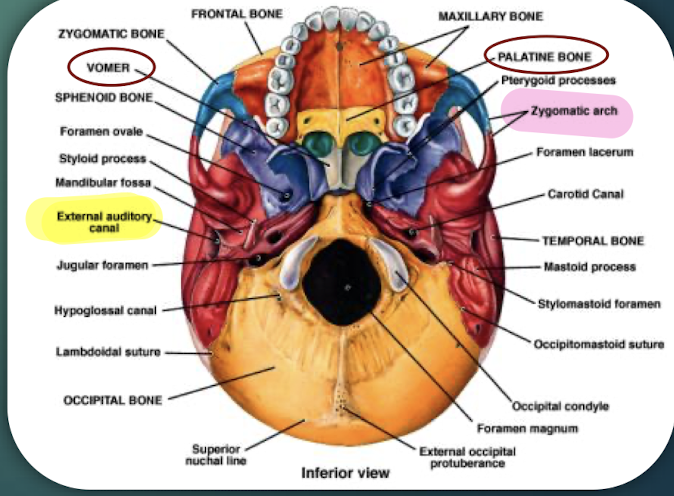
Palatine Bones
Paired bones forming posterior hard palate and part of nasal cavity; visible on skull’s inferior view.
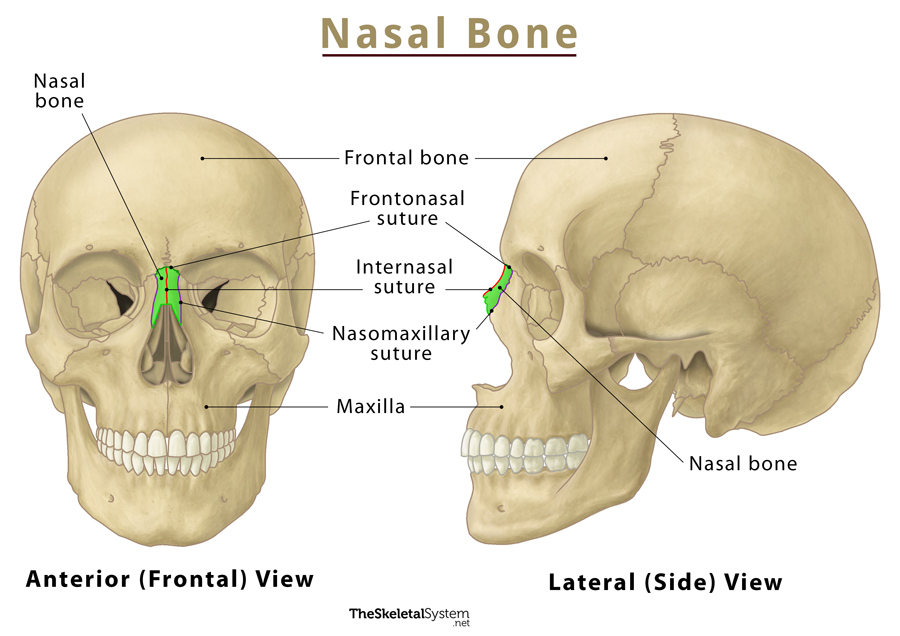
Nasal Bones
Small paired bones forming the bridge of the nose.
Inferior Nasal Conchae
Paired shelves of bone forming the lower nasal cavity walls.
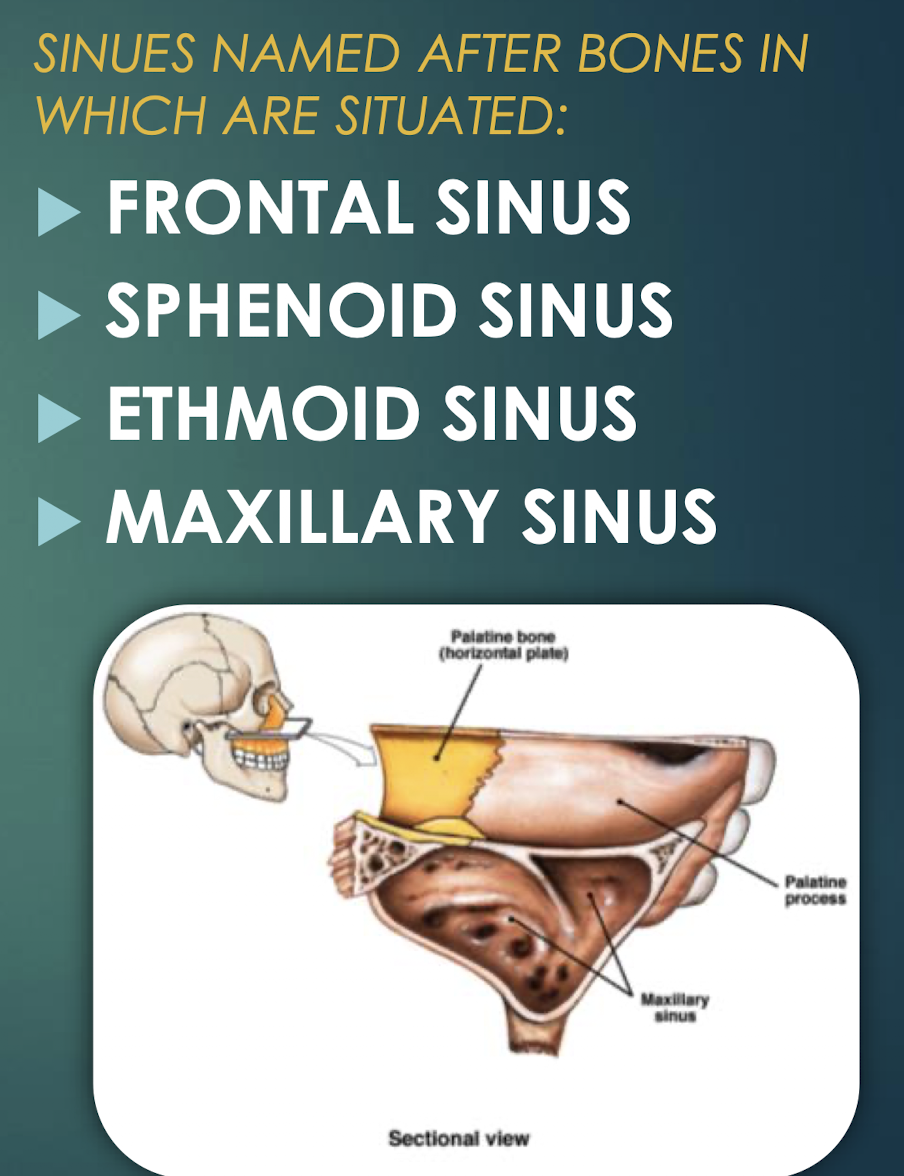
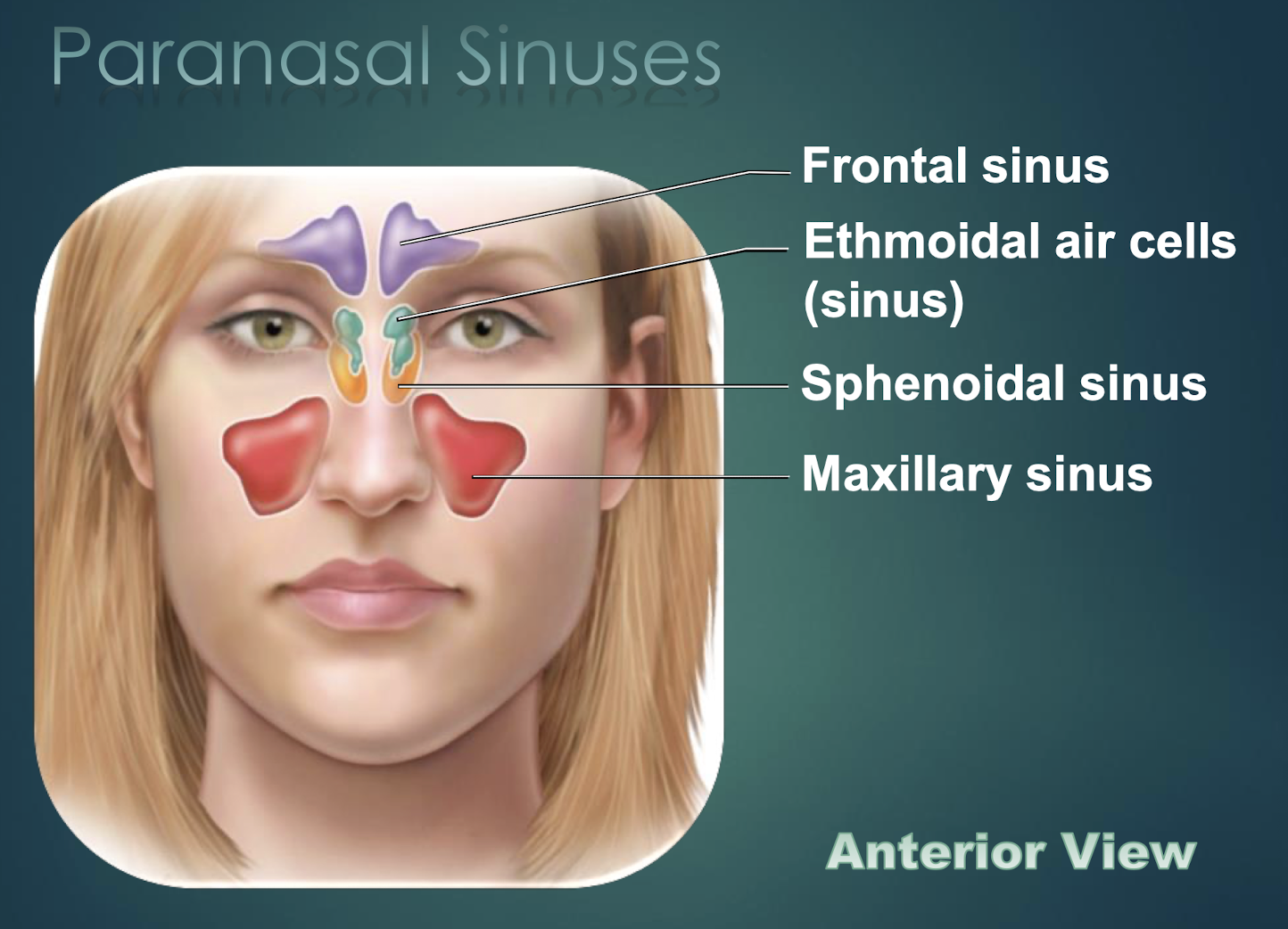
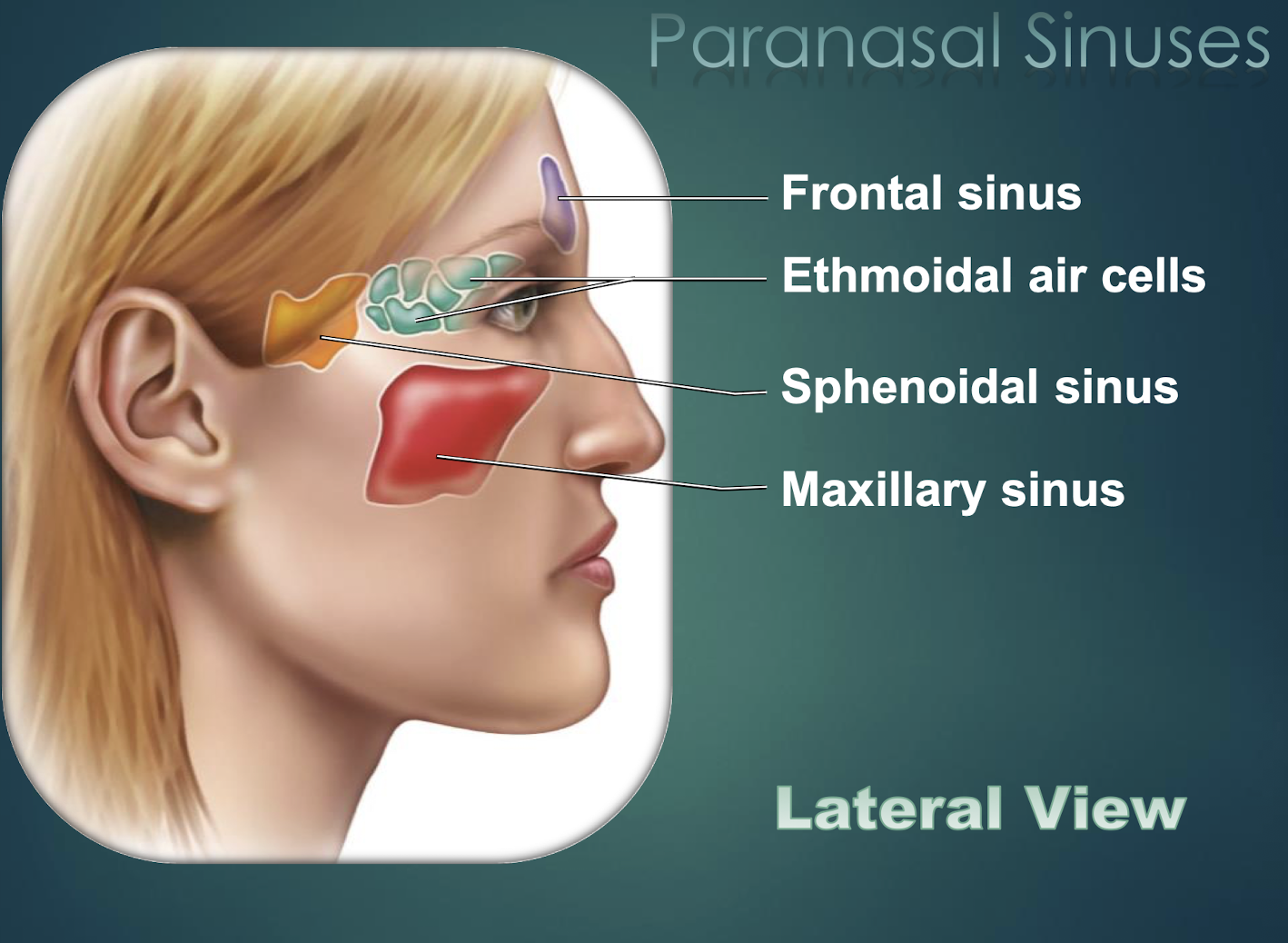
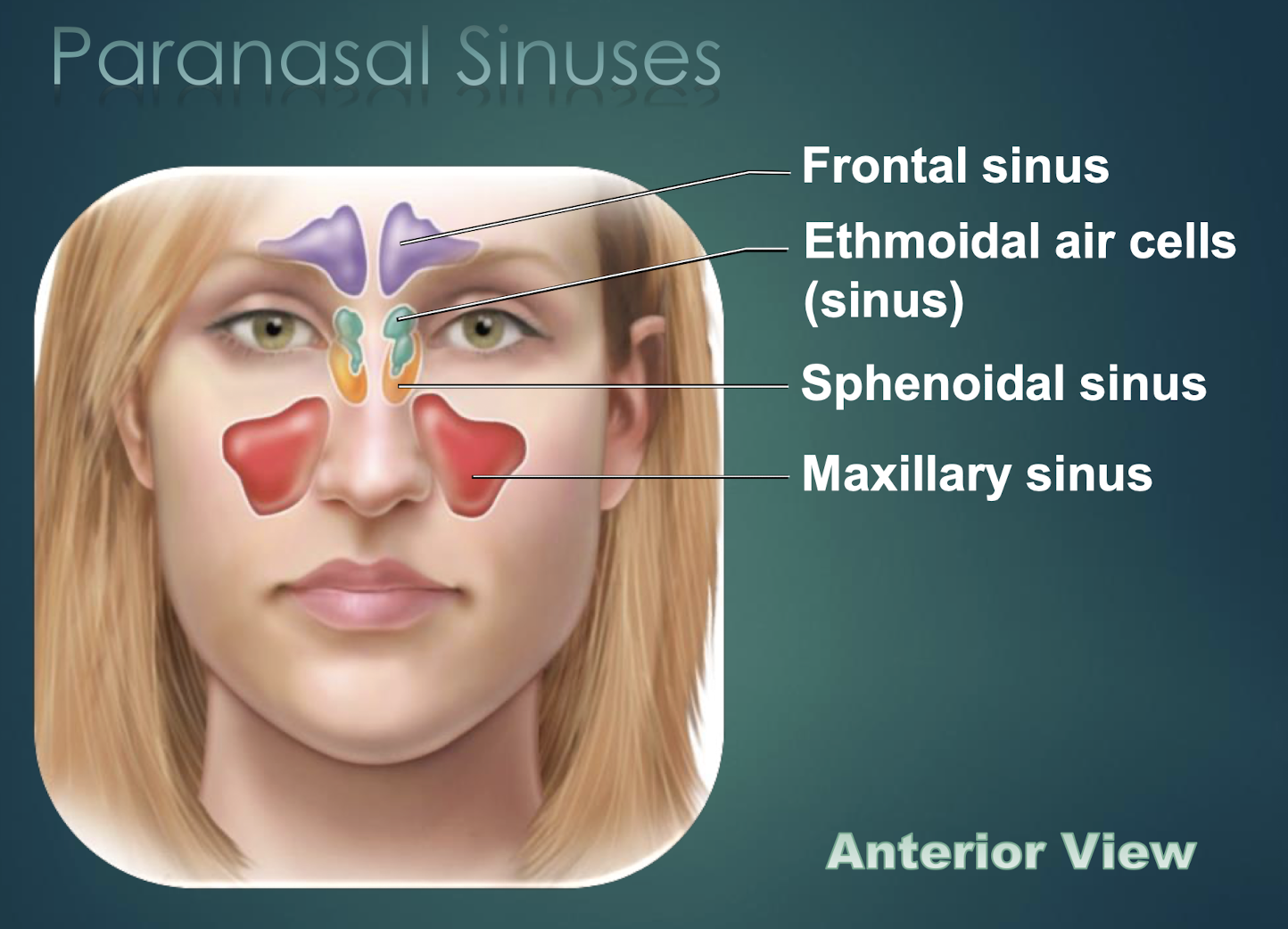
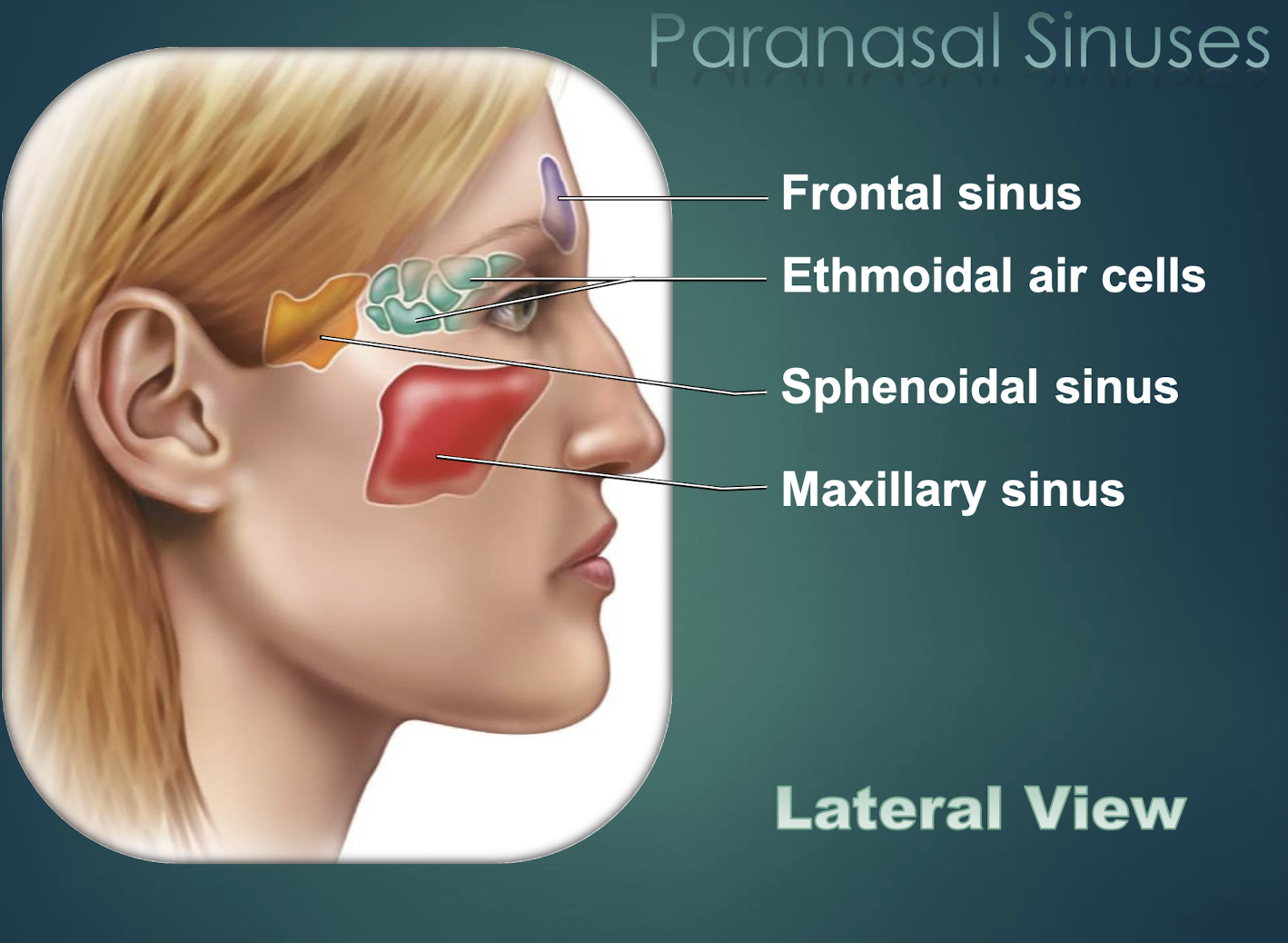
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled cavities within skull bones that lighten skull and connect to nasal cavity.
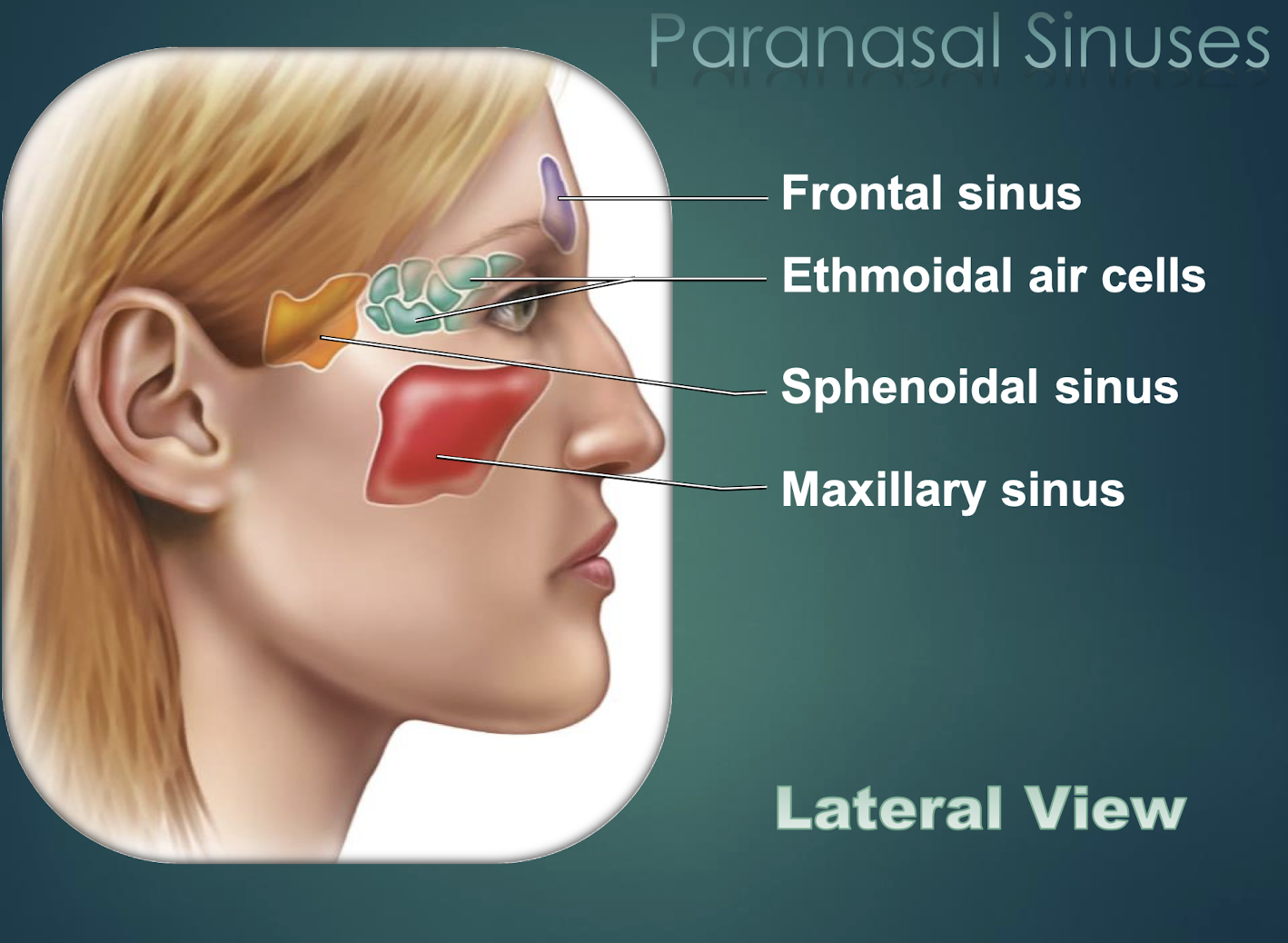
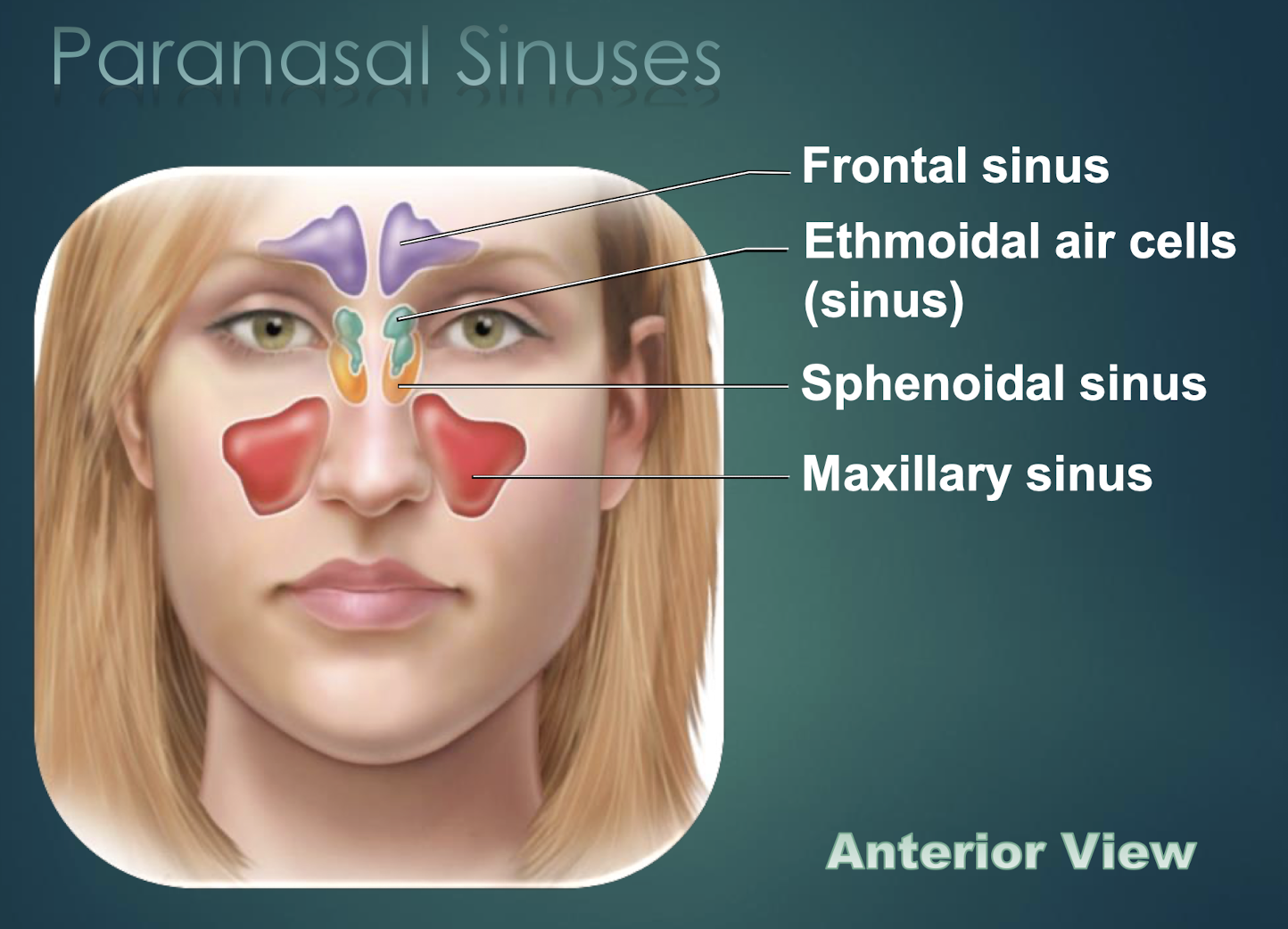
Frontal Sinus
Paranasal sinus located within the frontal bone.
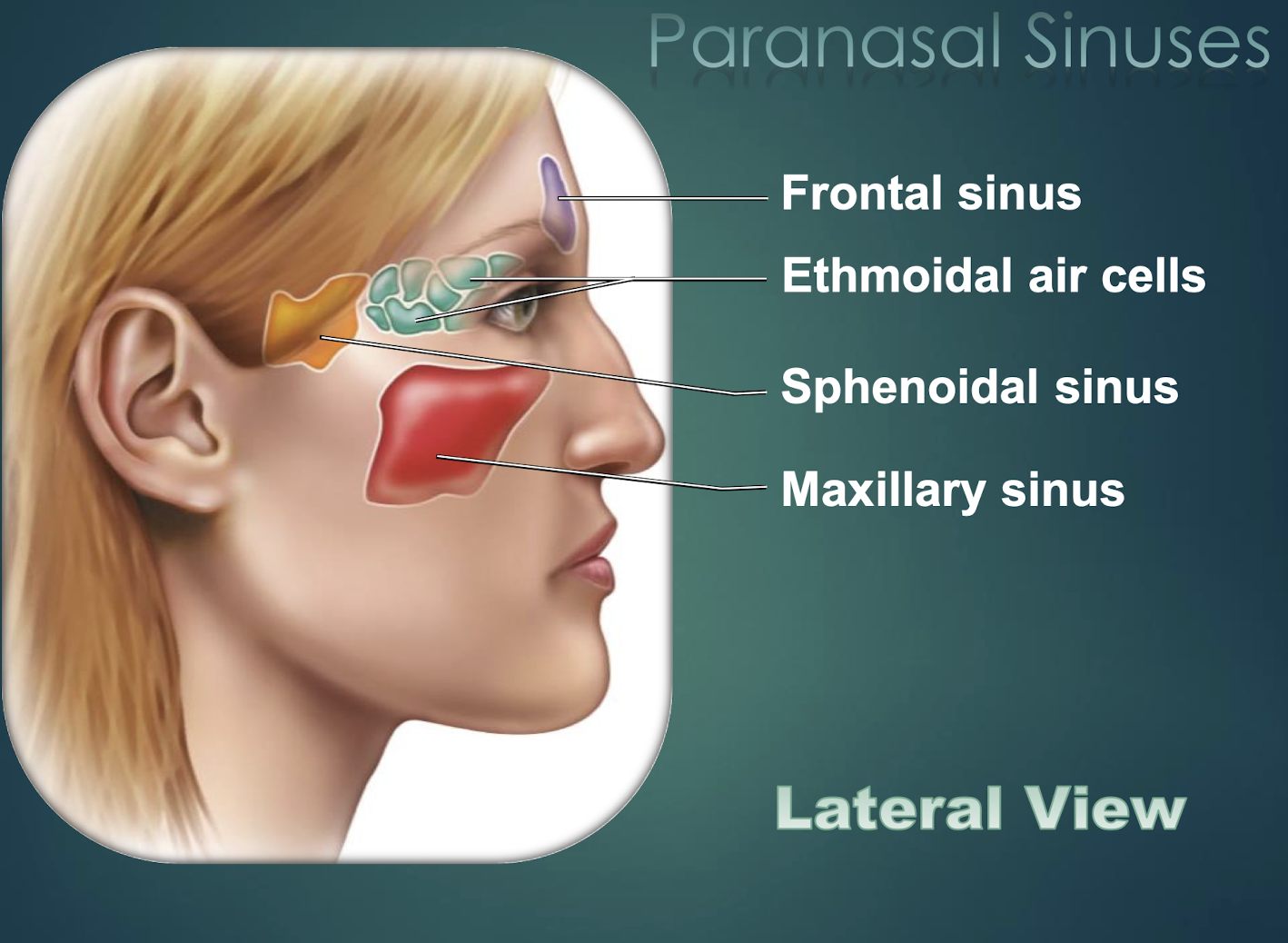
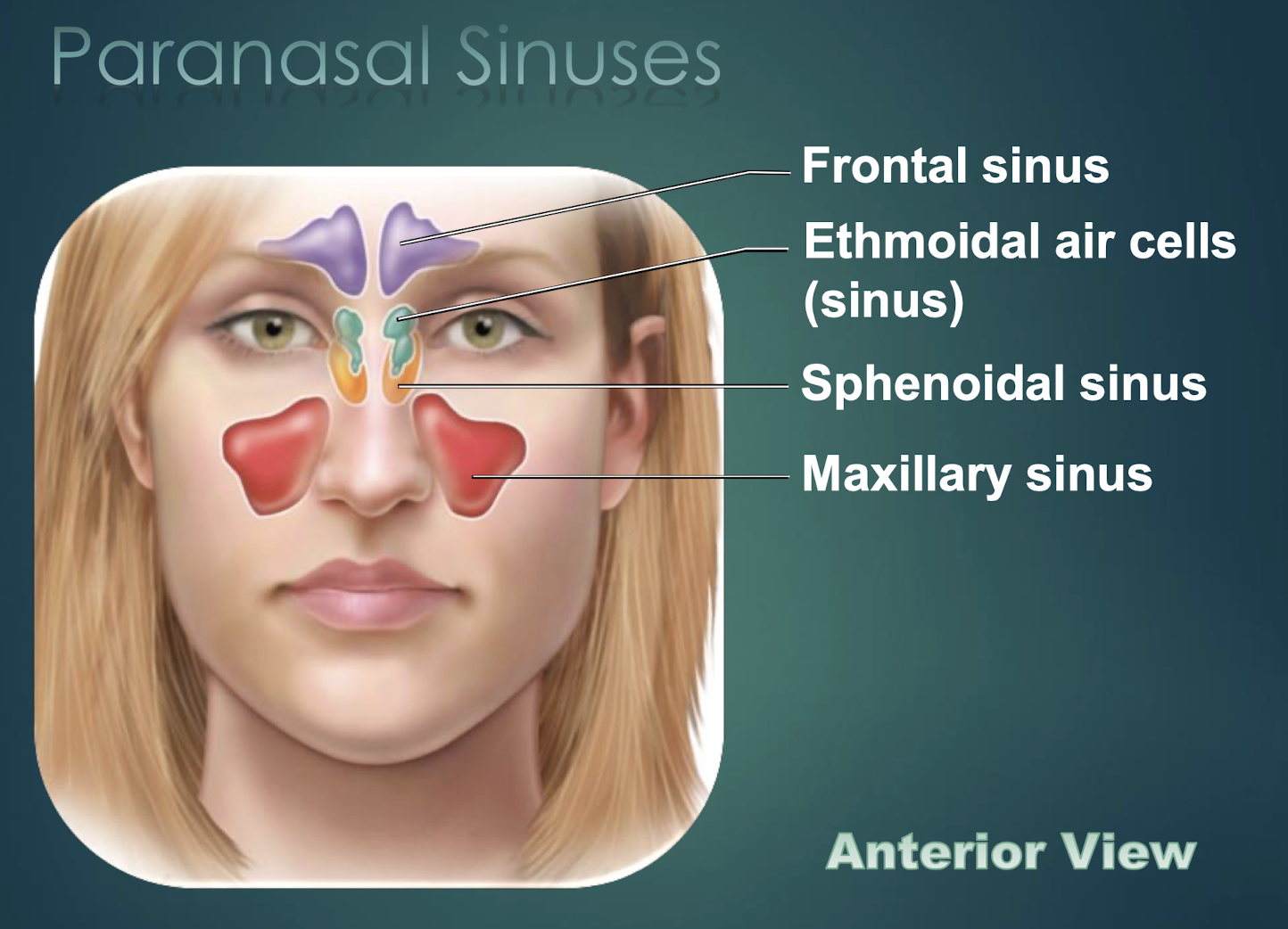
Sphenoid Sinus
Paranasal cavity housed in sphenoid bone.
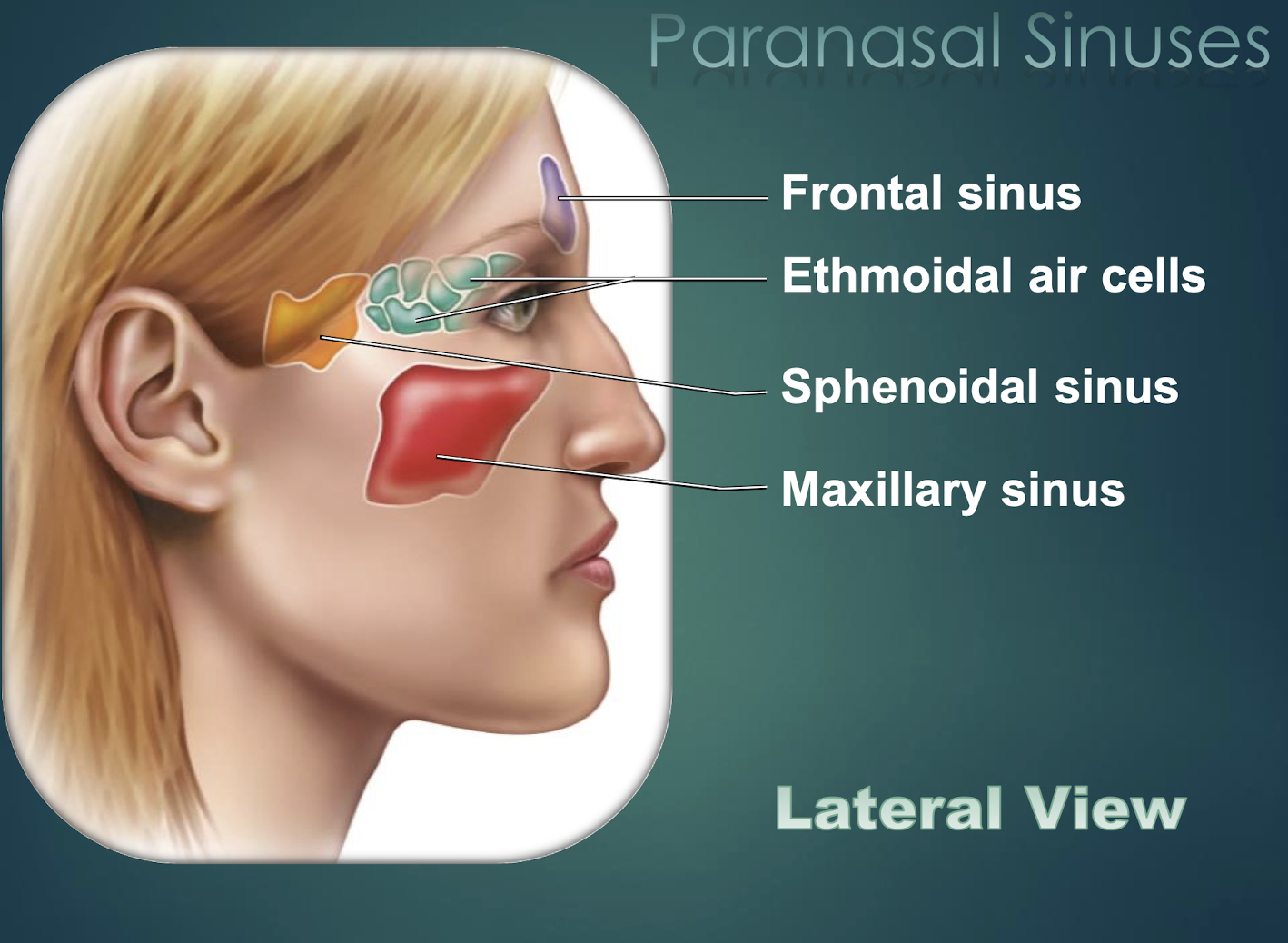
Ethmoid Sinus
Multiple small cavities within the ethmoid bone.
Maxillary Sinus
Largest paranasal sinus, located in each maxilla.
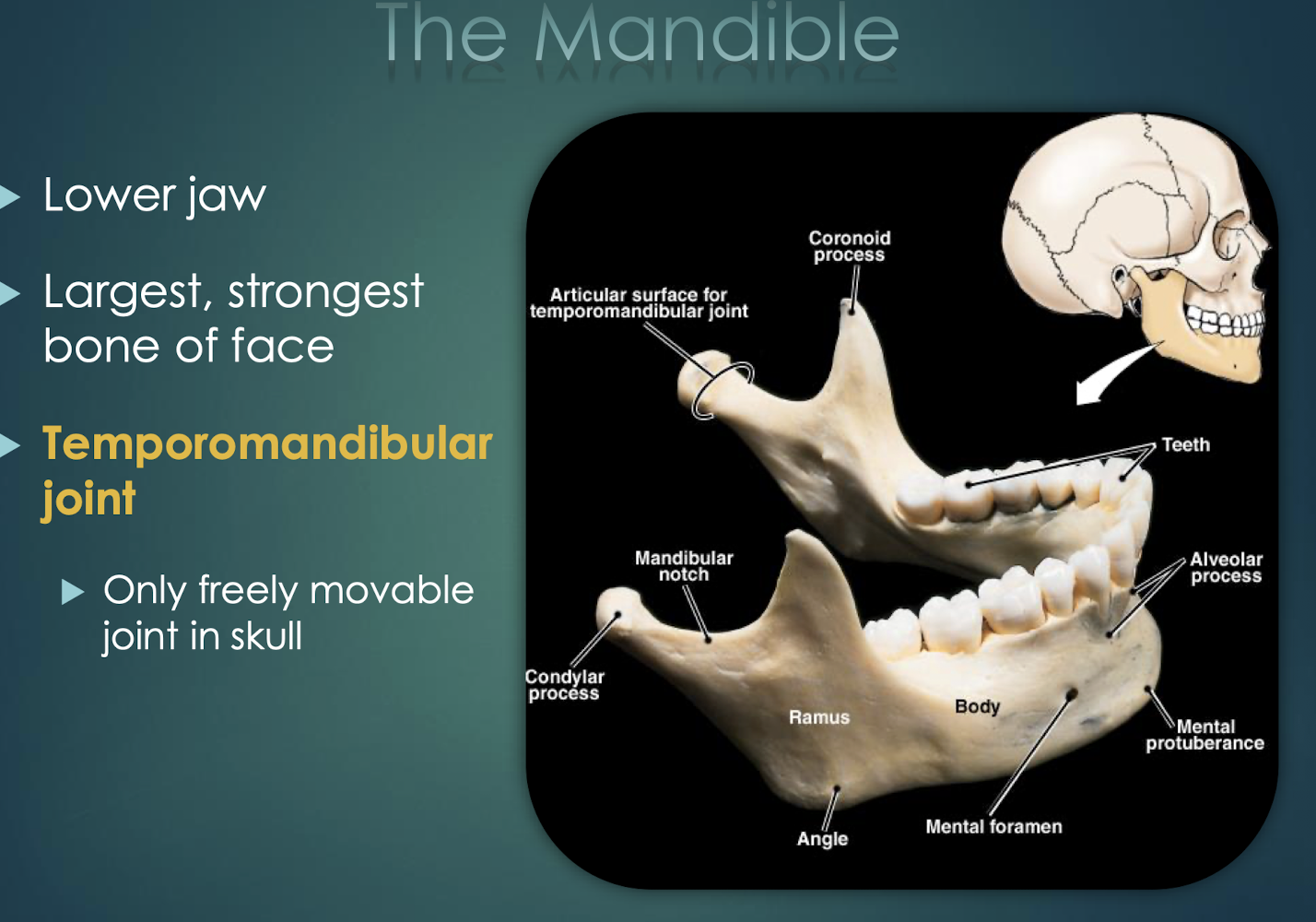
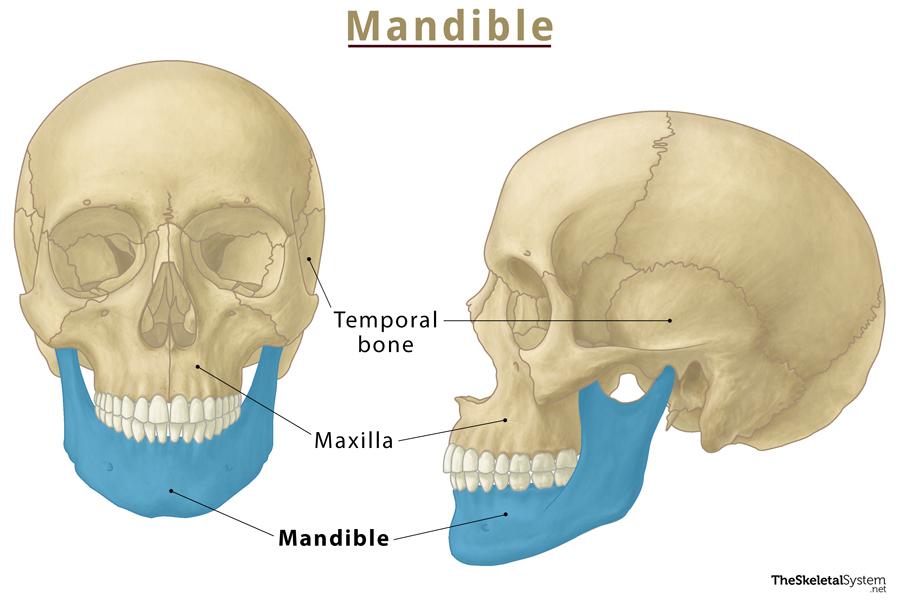
Mandible
Lower jaw; only movable skull bone.
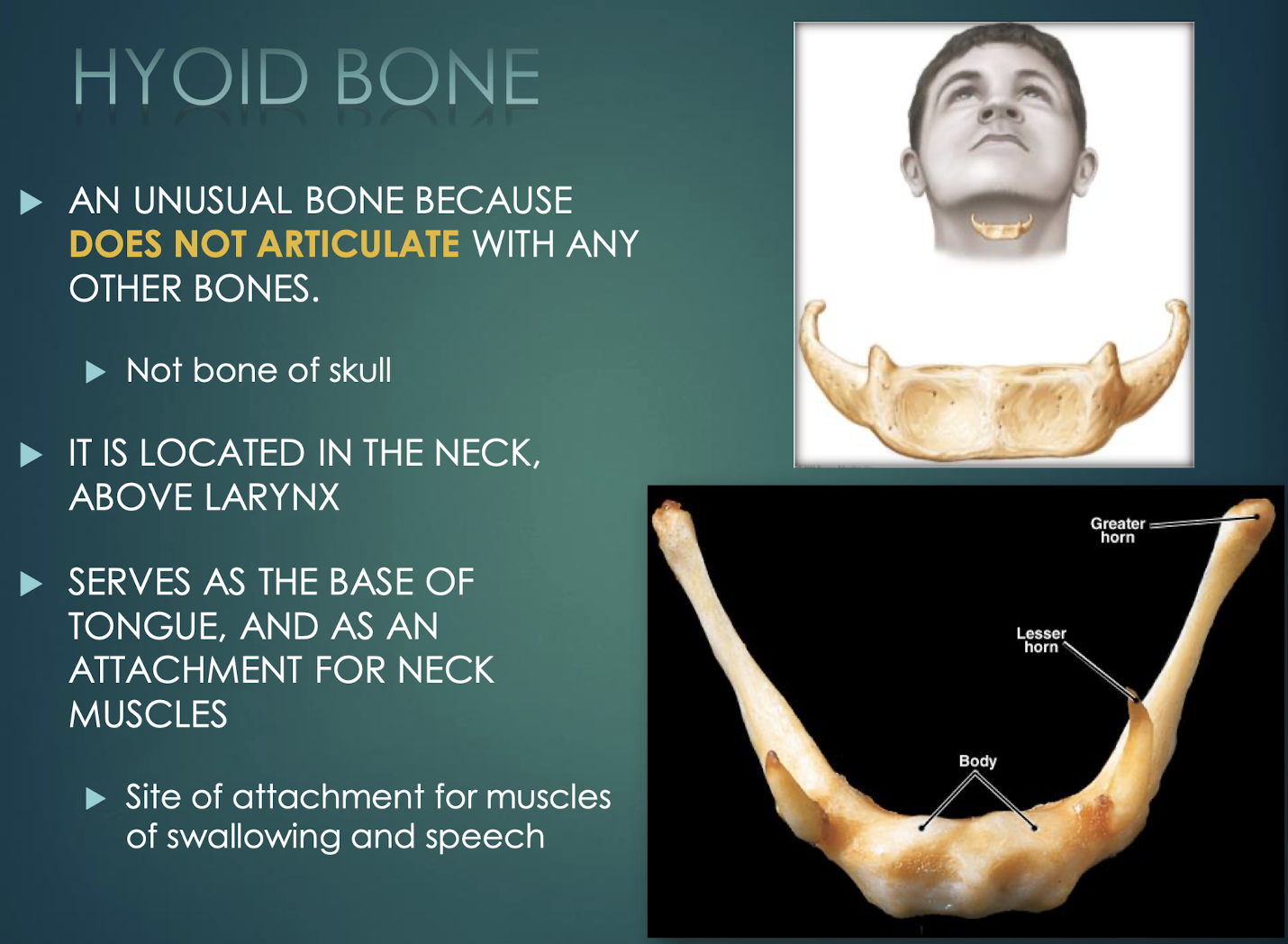
Hyoid Bone
U-shaped neck bone that does not articulate with others; attachment for tongue and swallowing muscles.
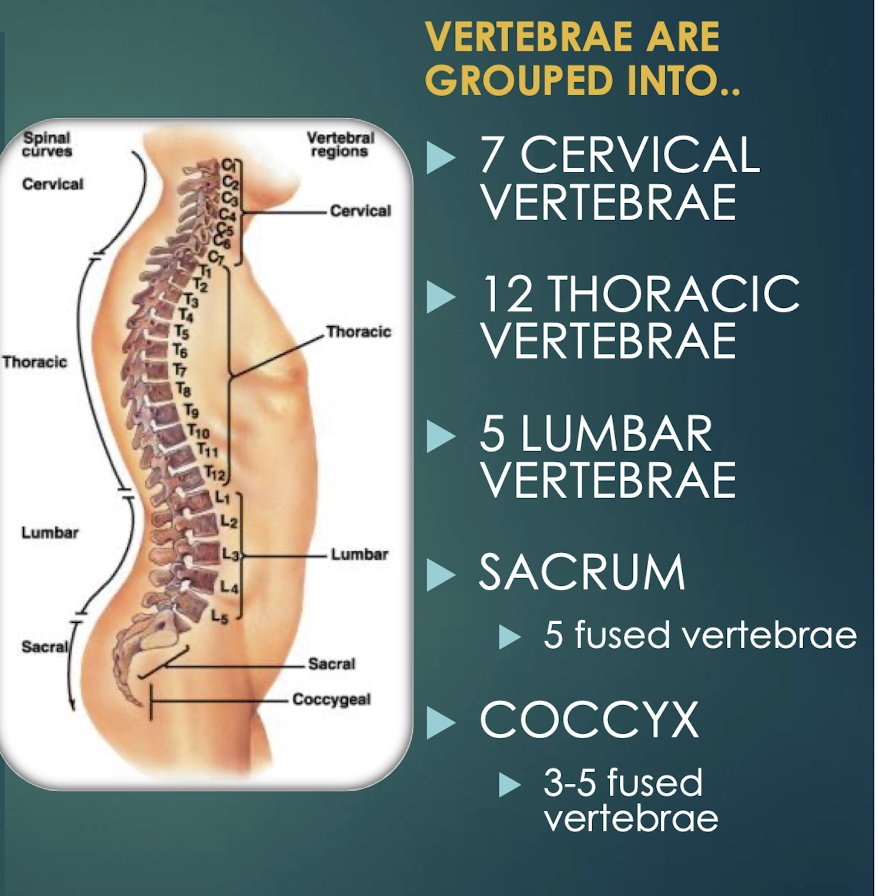
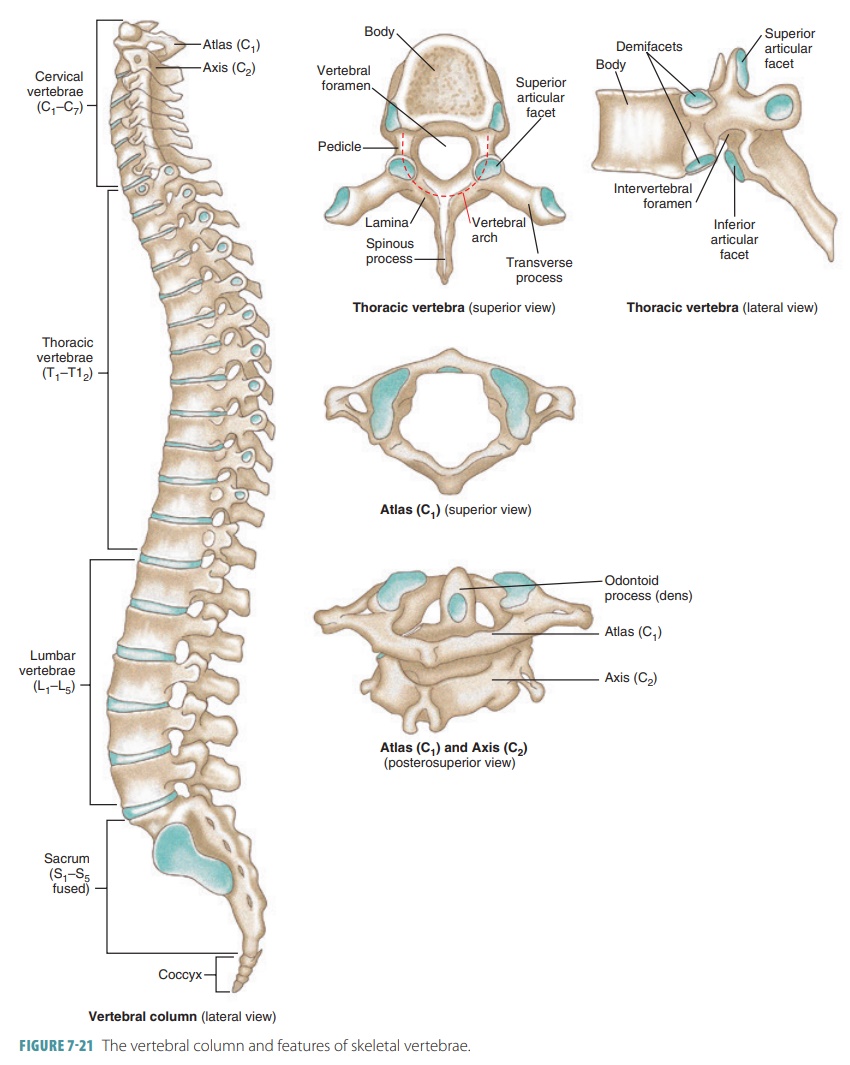
Vertebral Column
Flexible protective column of 33 vertebrae connected by ligaments; articulates with skull, ribs, and pelvis.
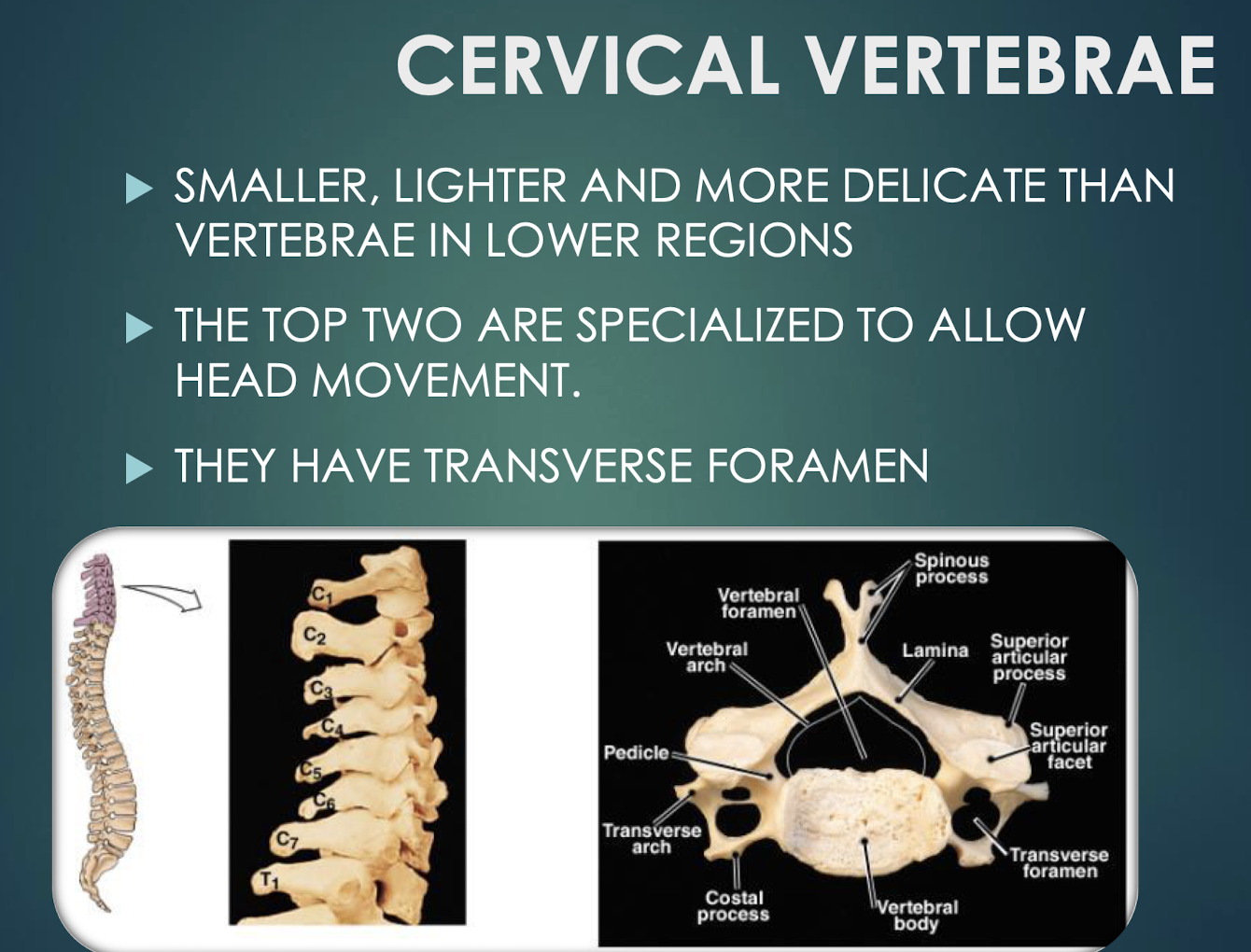
Cervical Vertebrae
Seven smallest vertebrae (C1–C7); have transverse foramina; C1 atlas and C2 axis specialized for head movement.
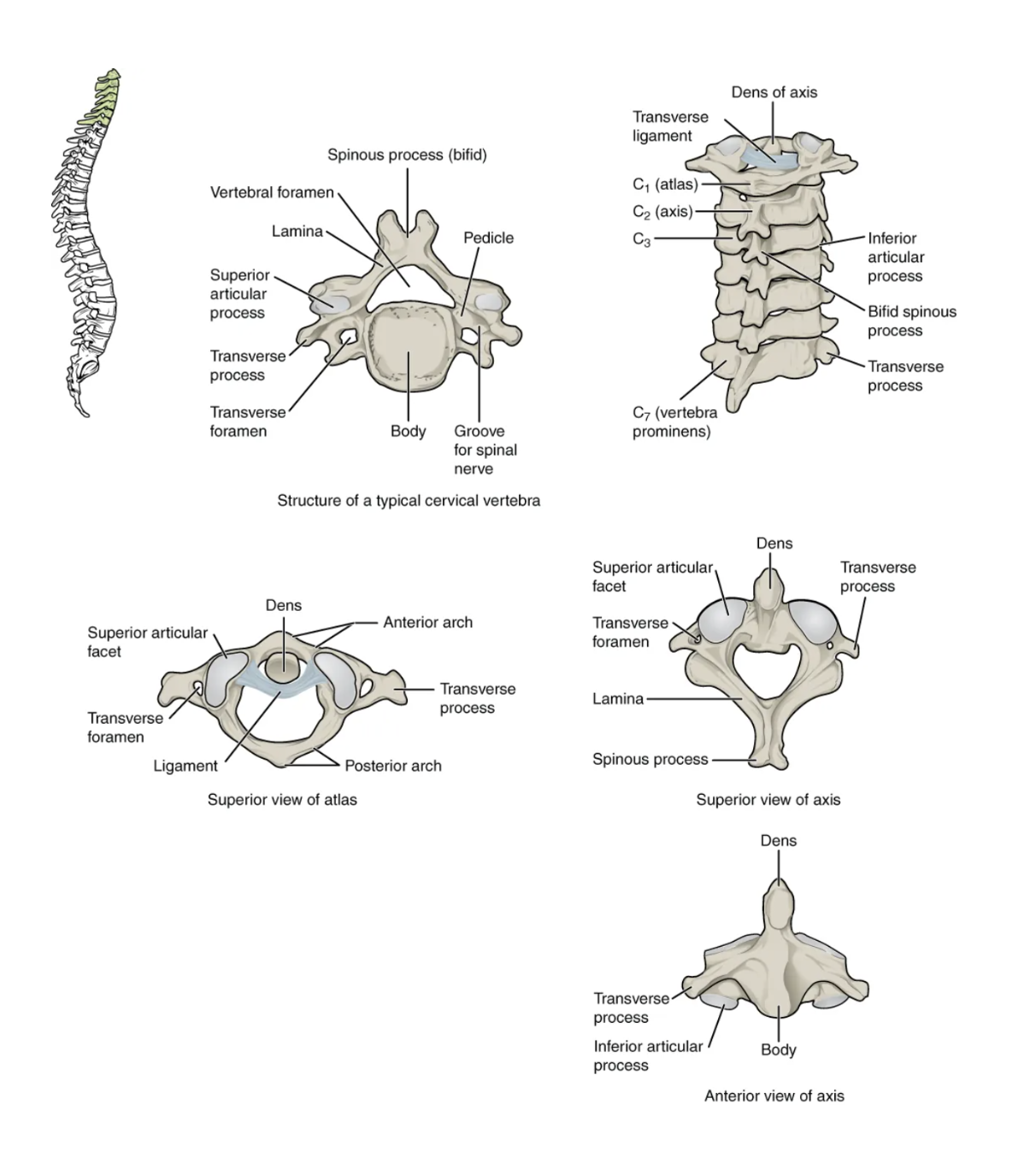
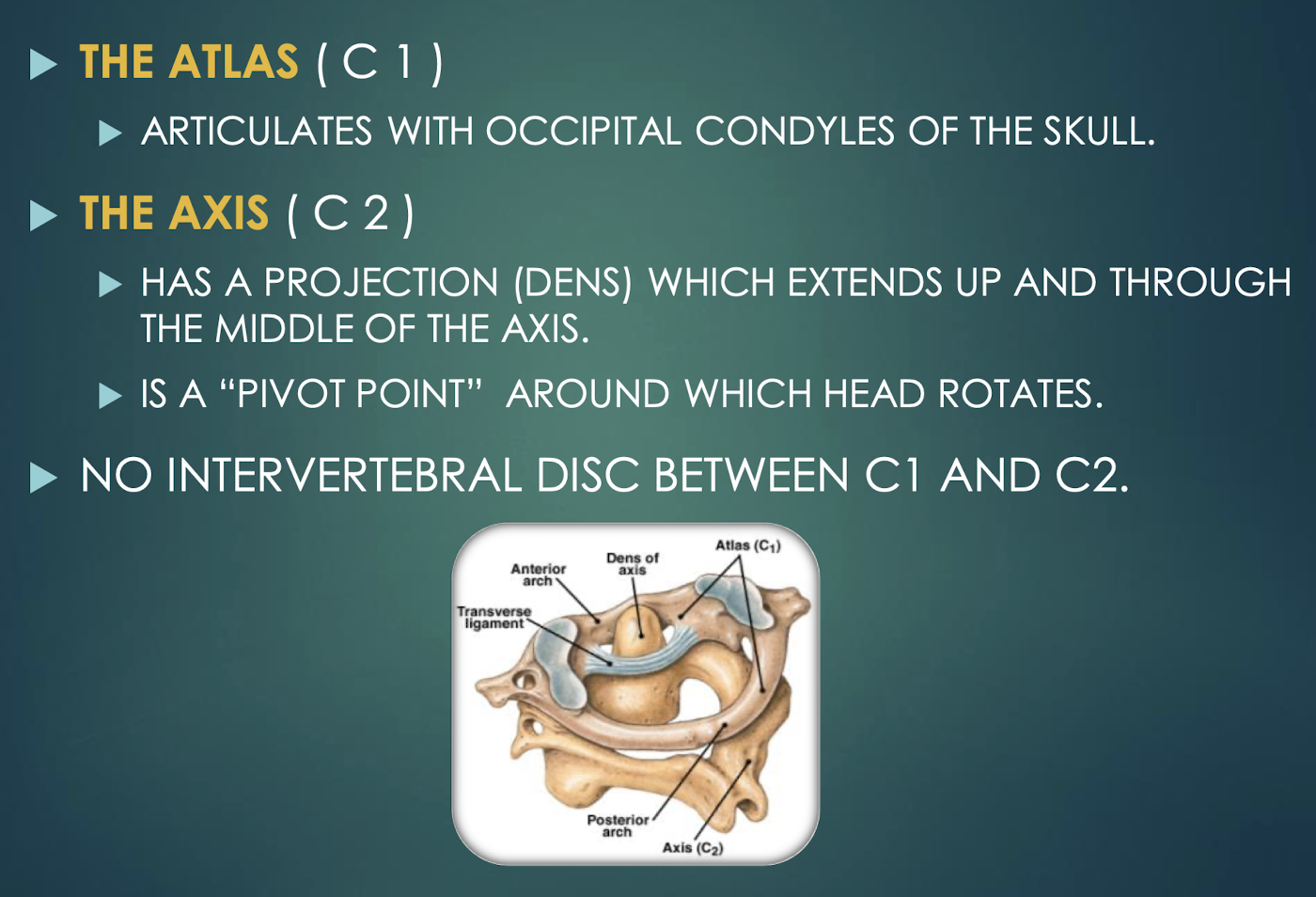
Atlas (C1)
First cervical vertebra that articulates with occipital condyles; supports the head.
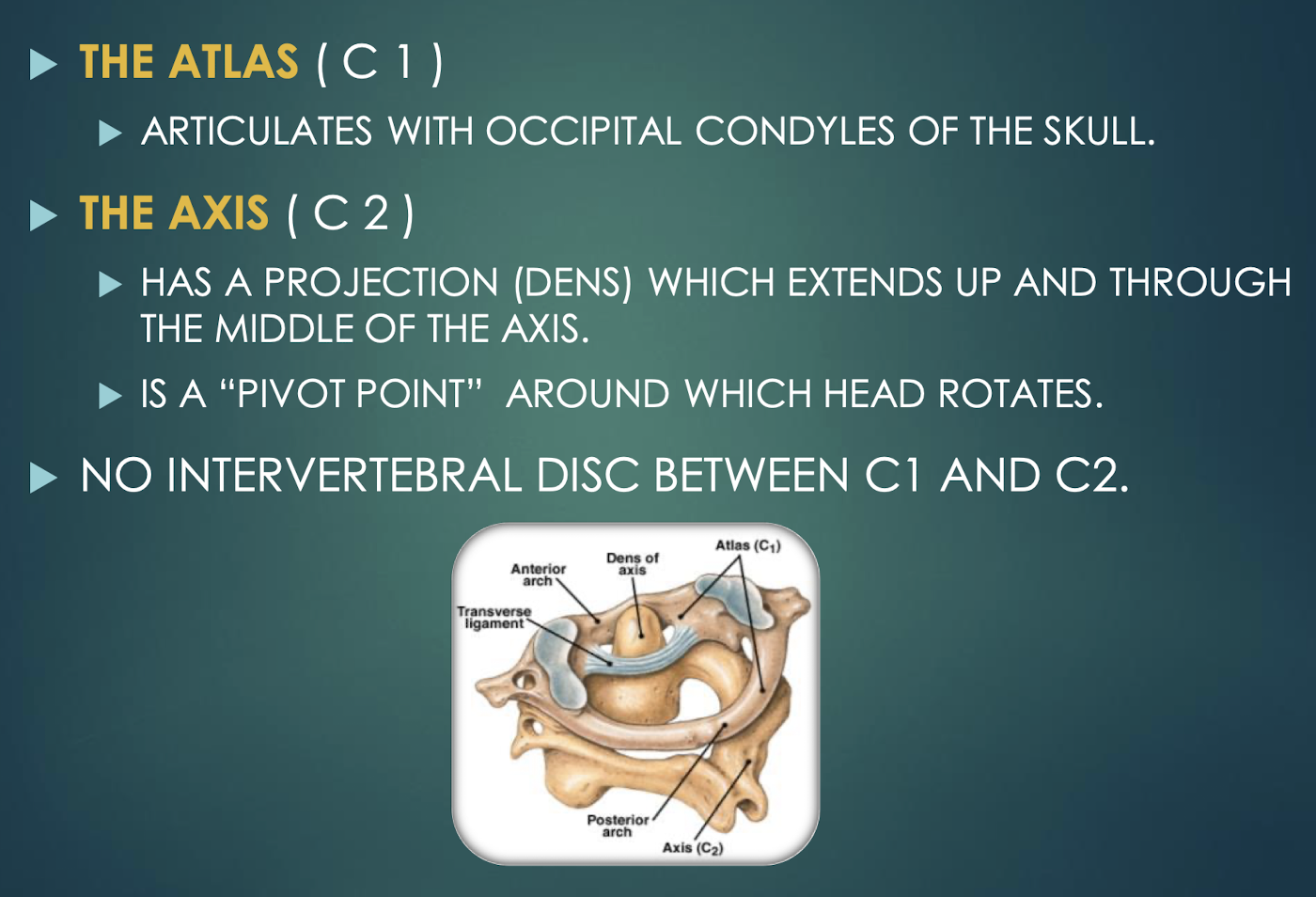
Axis (C2)
Second cervical vertebra featuring the dens, a pivot for head rotation.
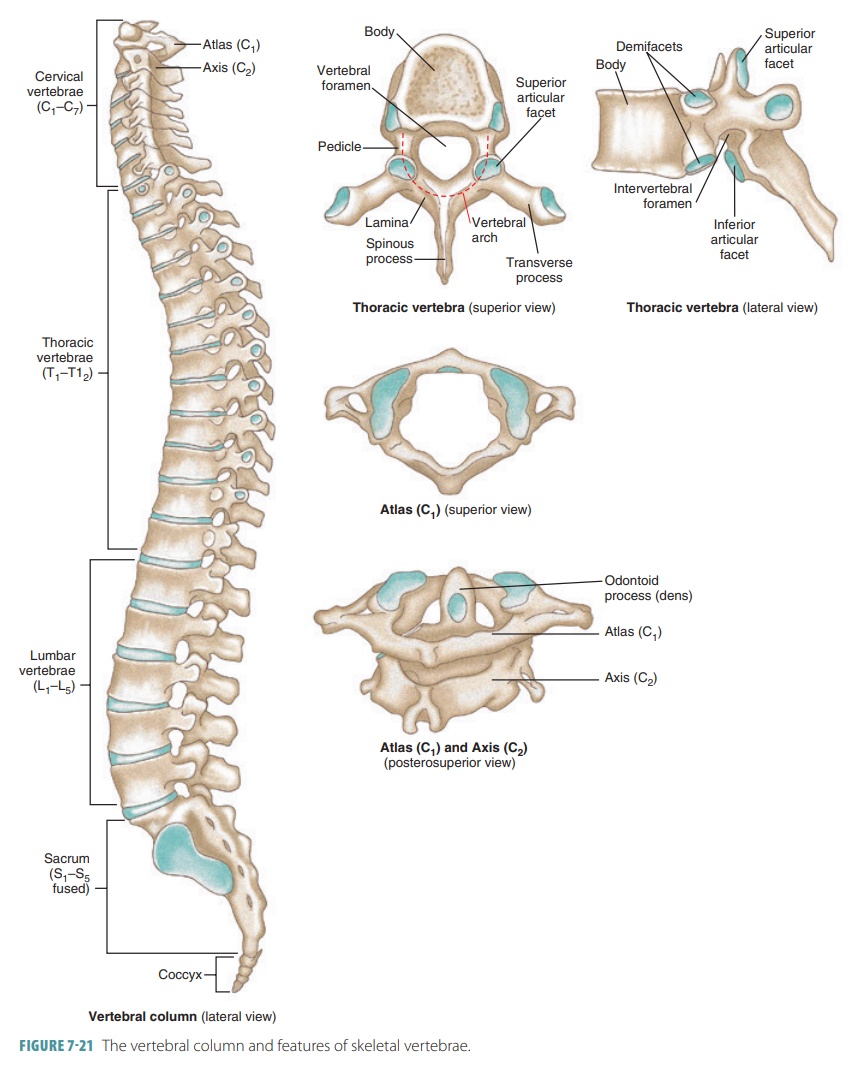
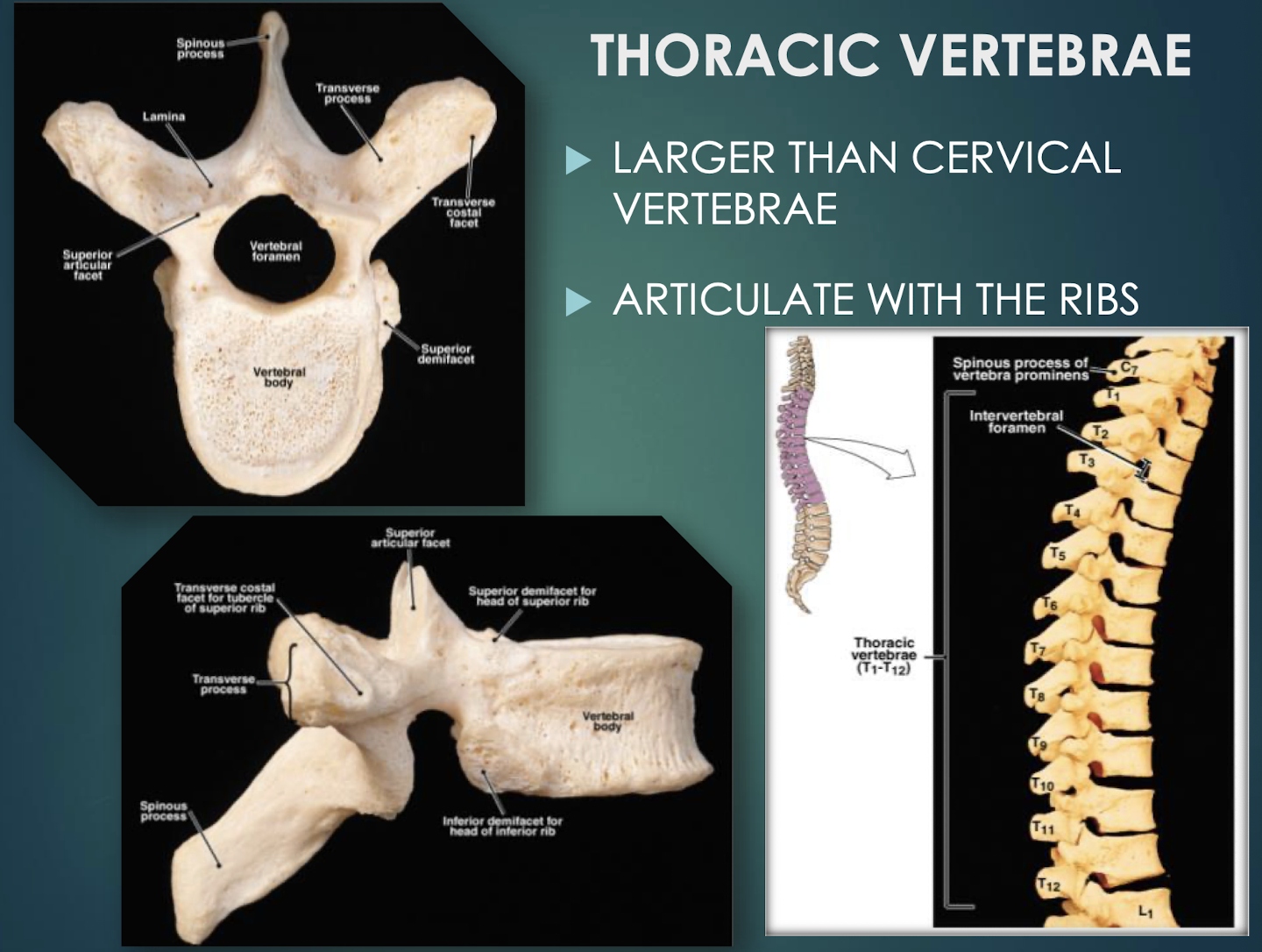
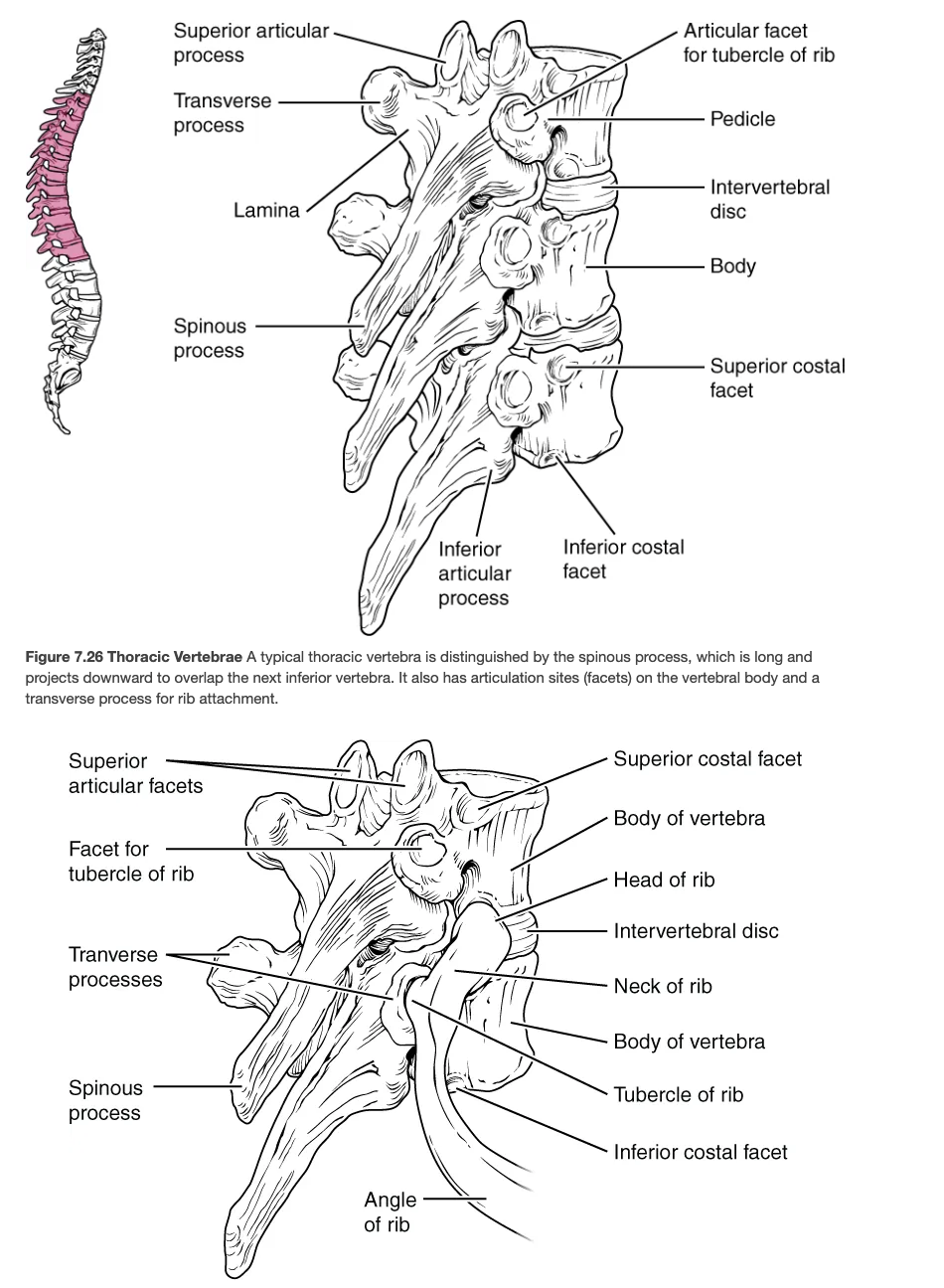
Thoracic Vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae (T1–T12) that articulate with ribs.
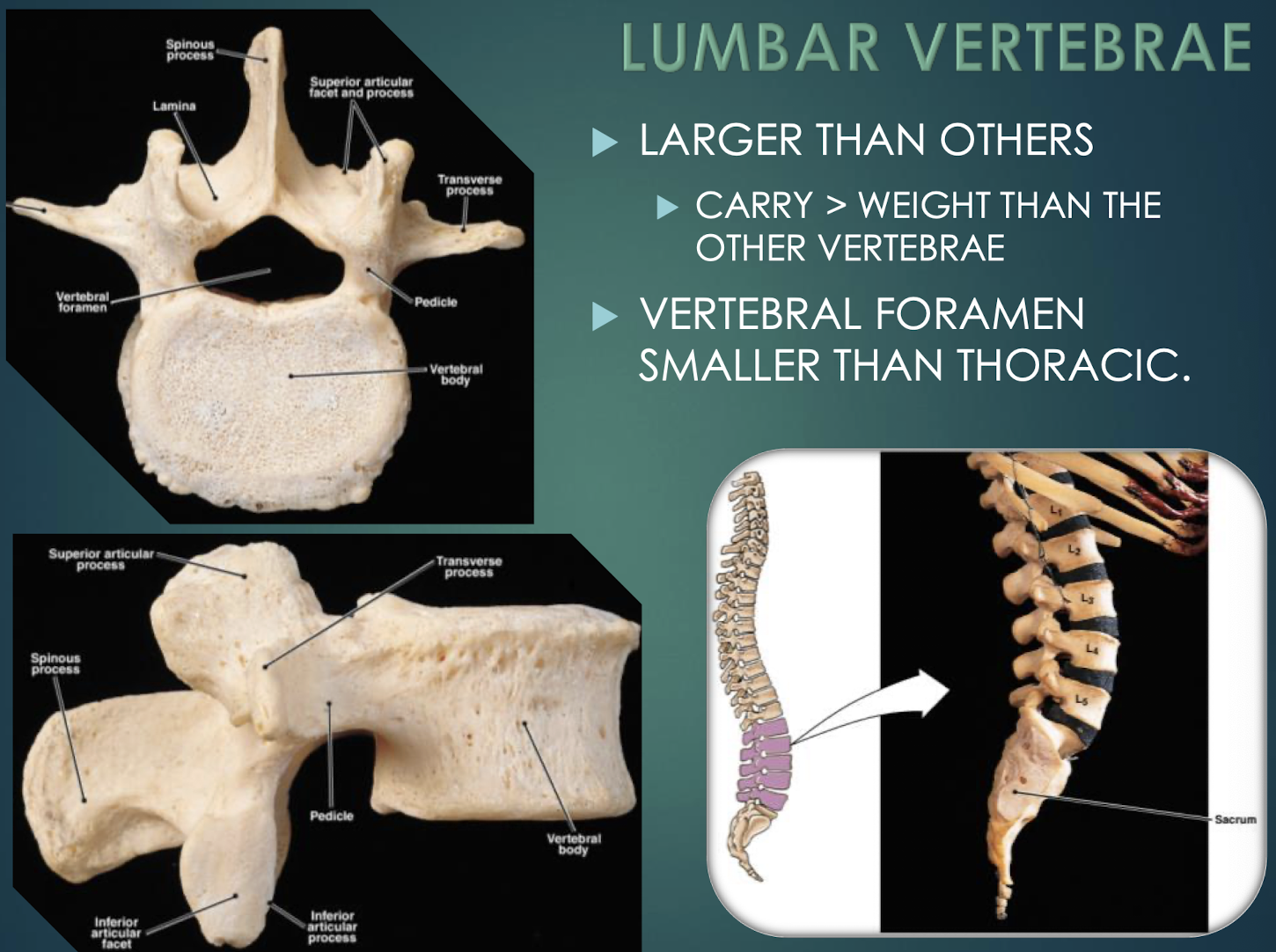
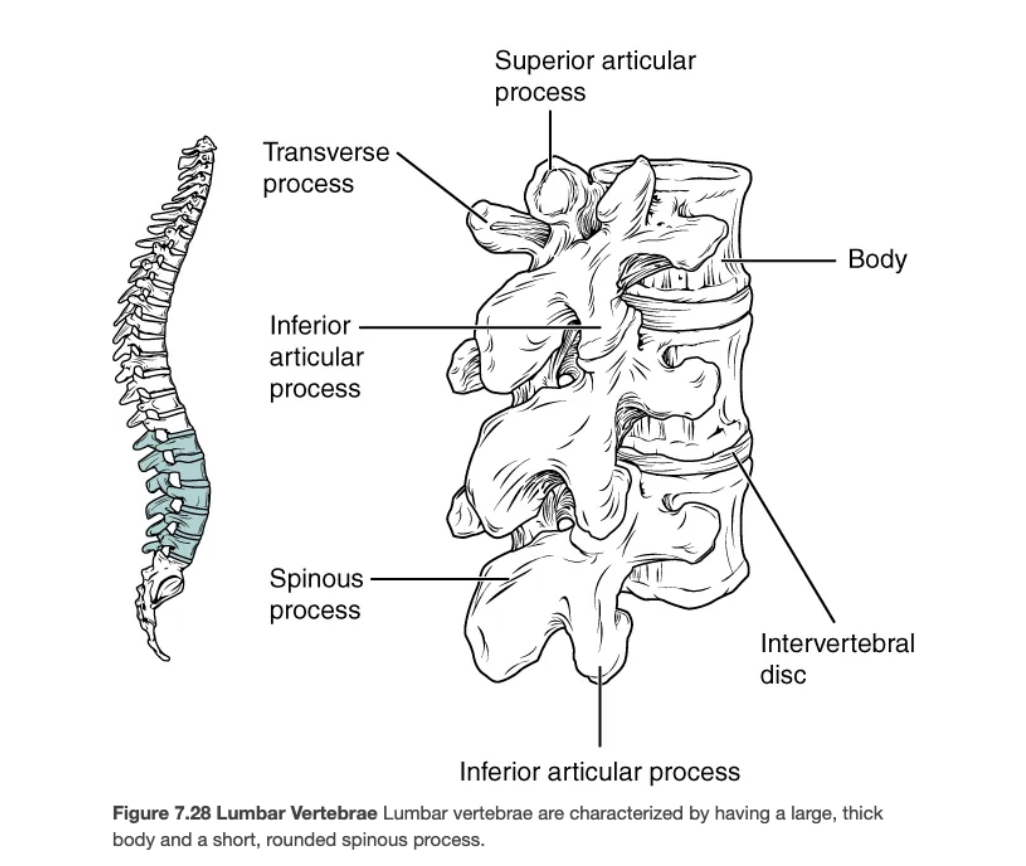
Lumbar Vertebrae
Five massive vertebrae (L1–L5) bearing greatest body weight; have smaller vertebral foramina.
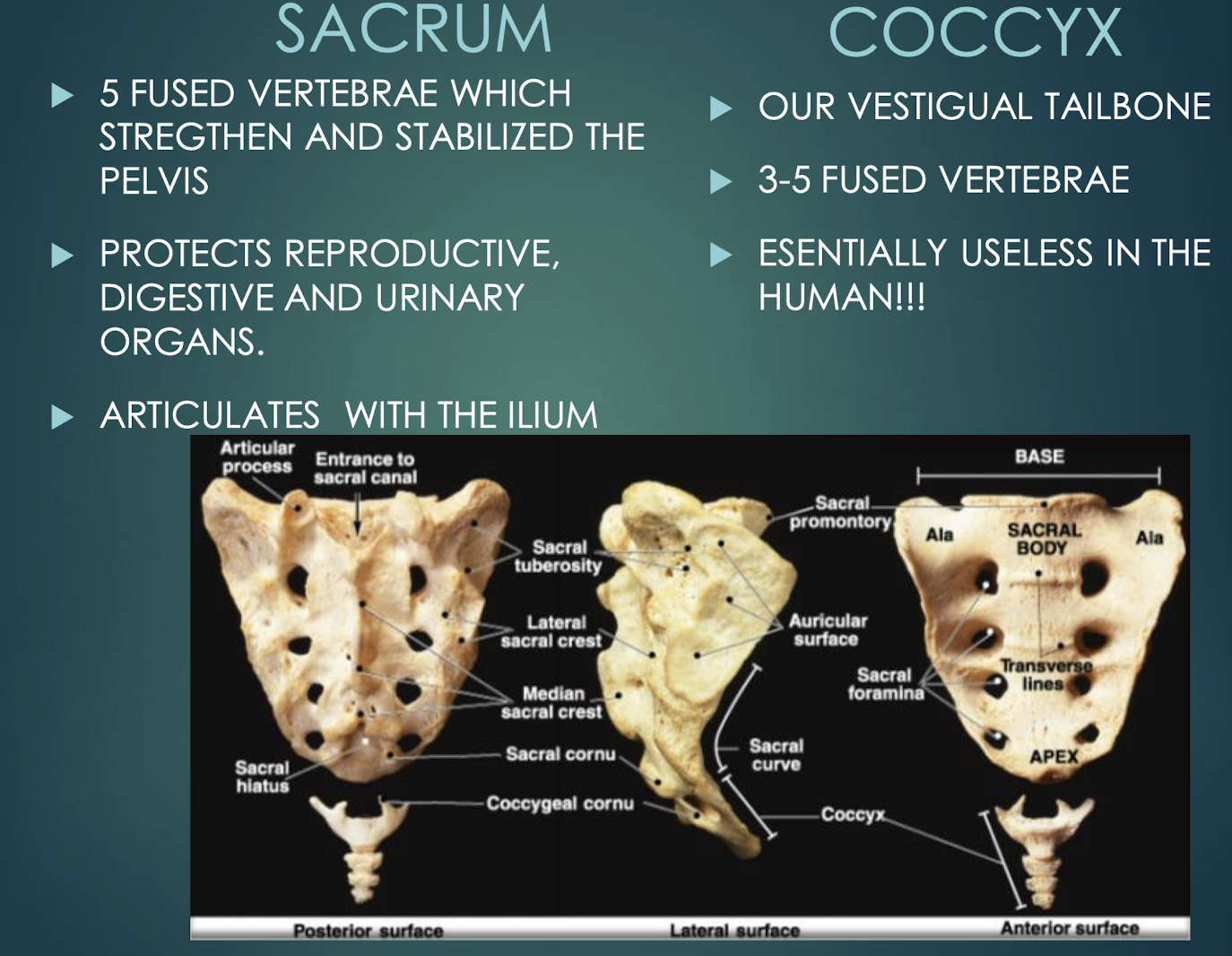
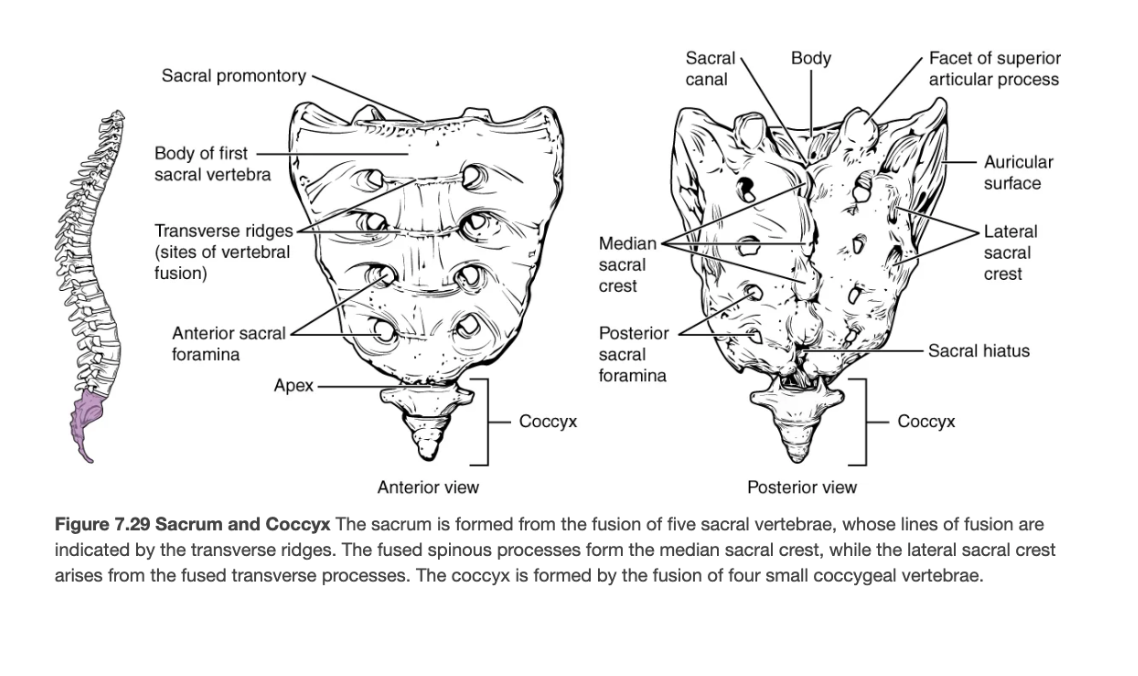
Sacrum
Single bone formed by fusion of five vertebrae; strengthens pelvis and protects pelvic organs.
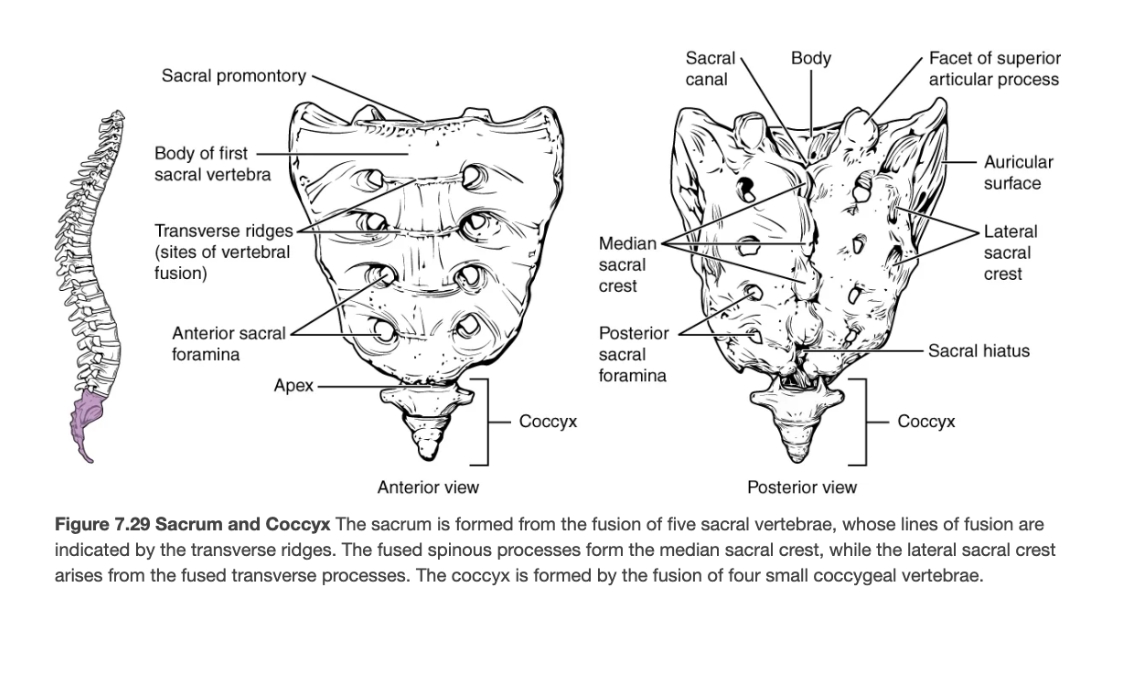
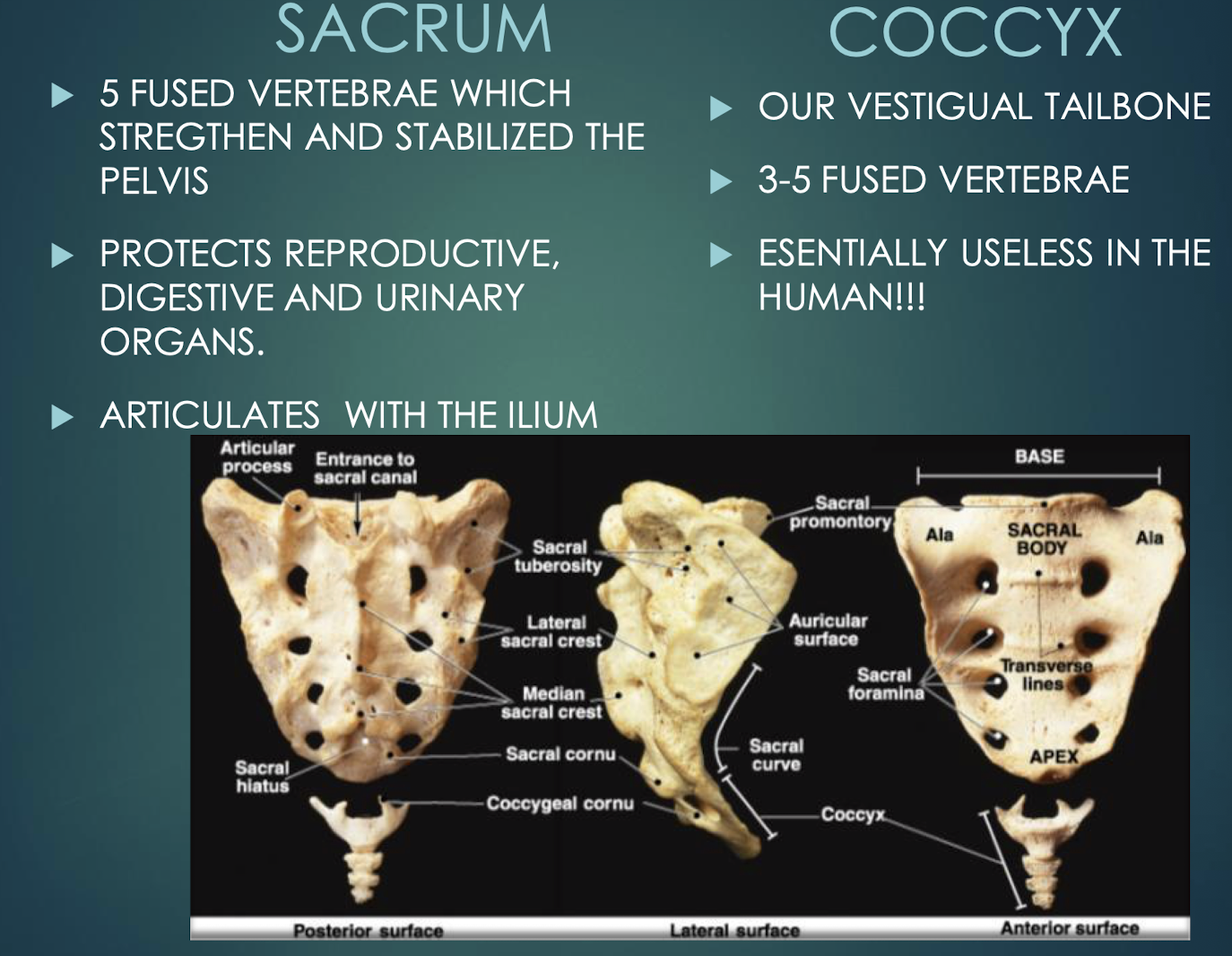
Coccyx
Vestigial tailbone of 3–5 fused vertebrae.
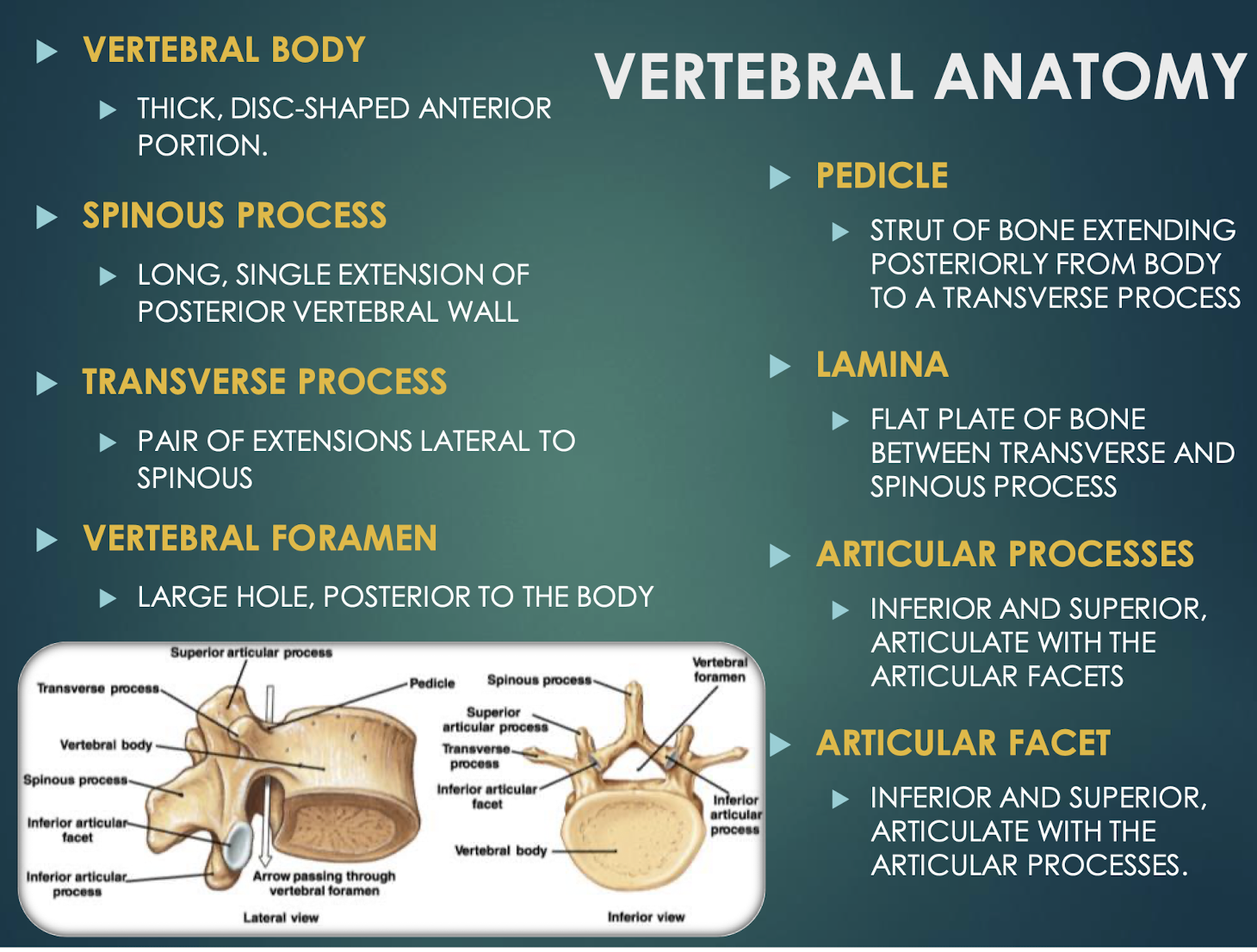
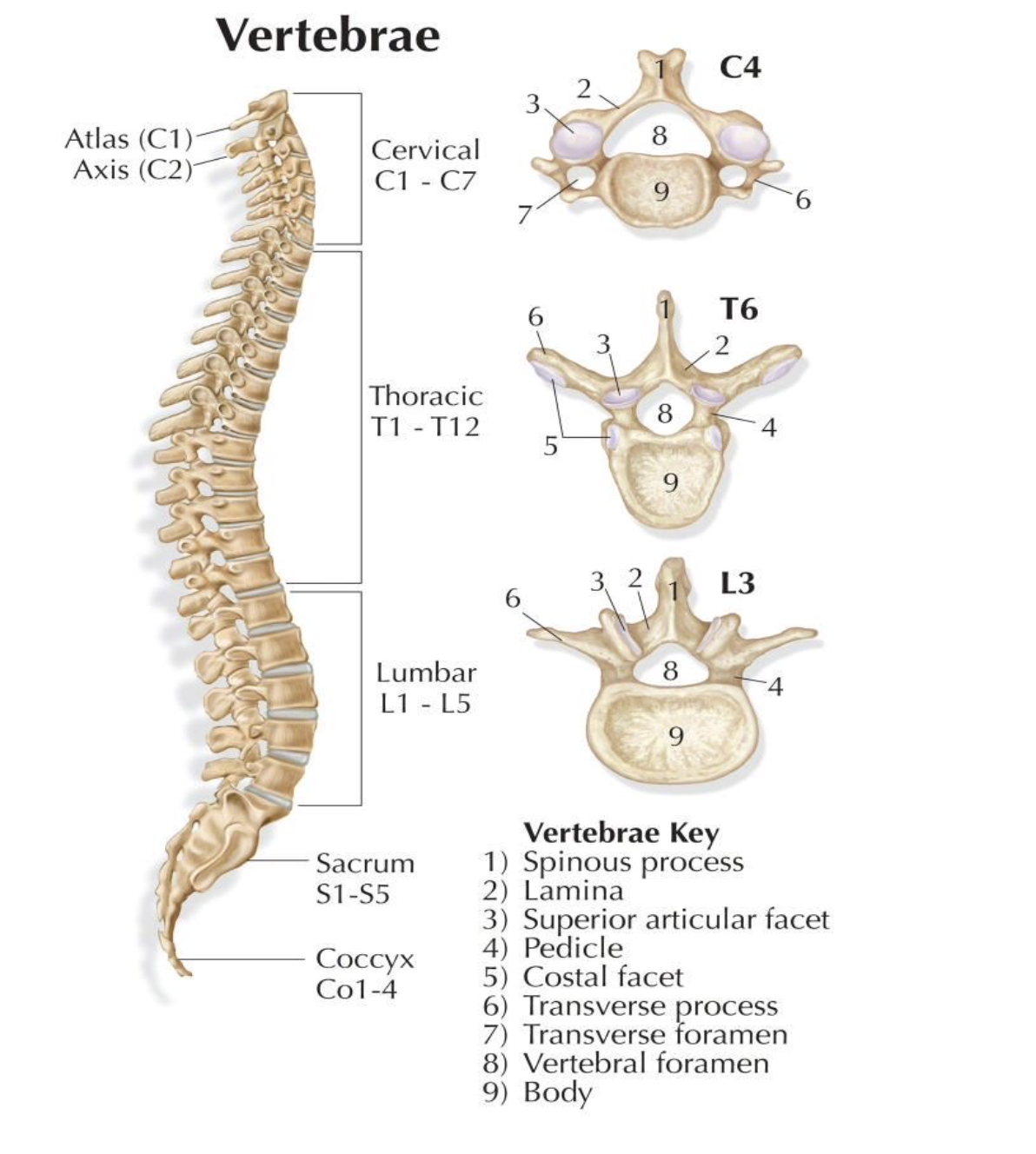
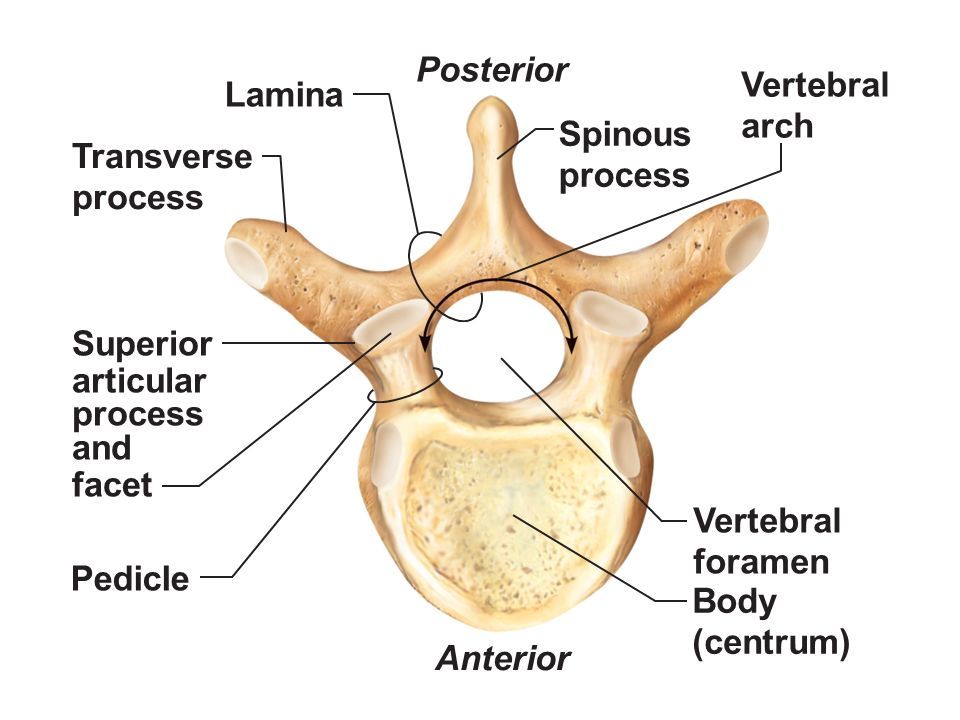
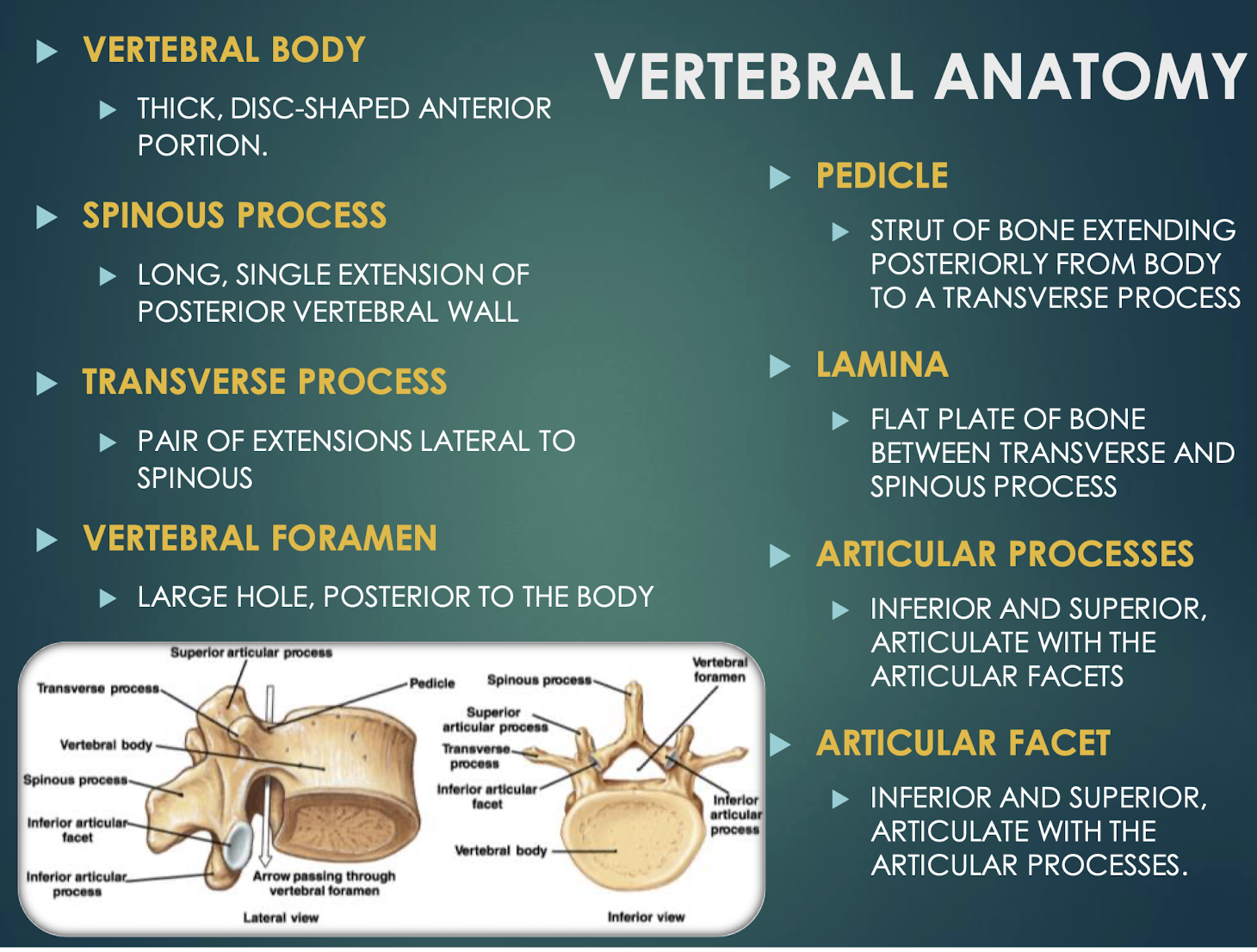
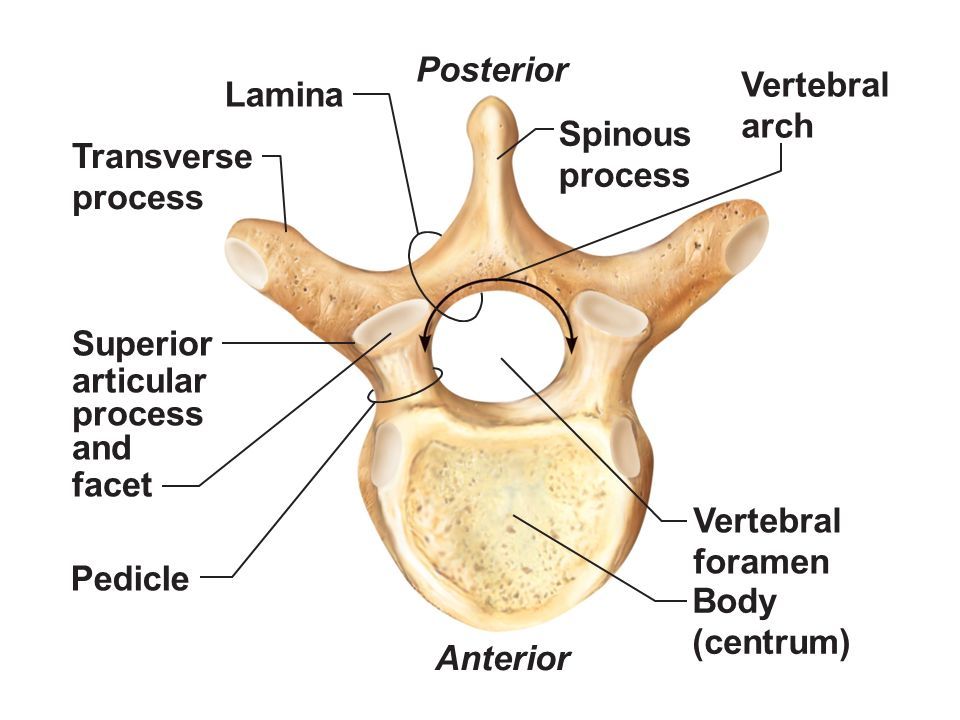
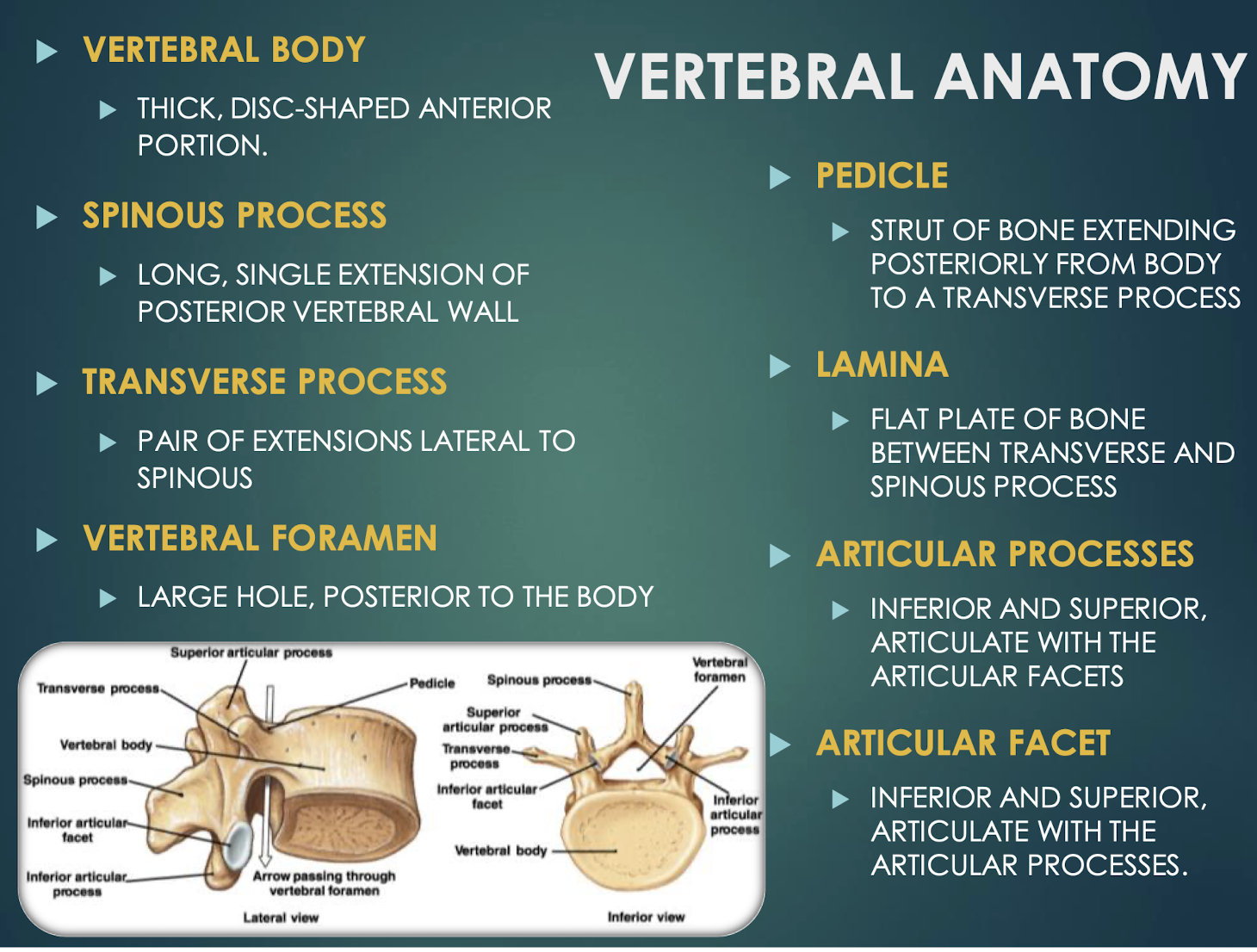
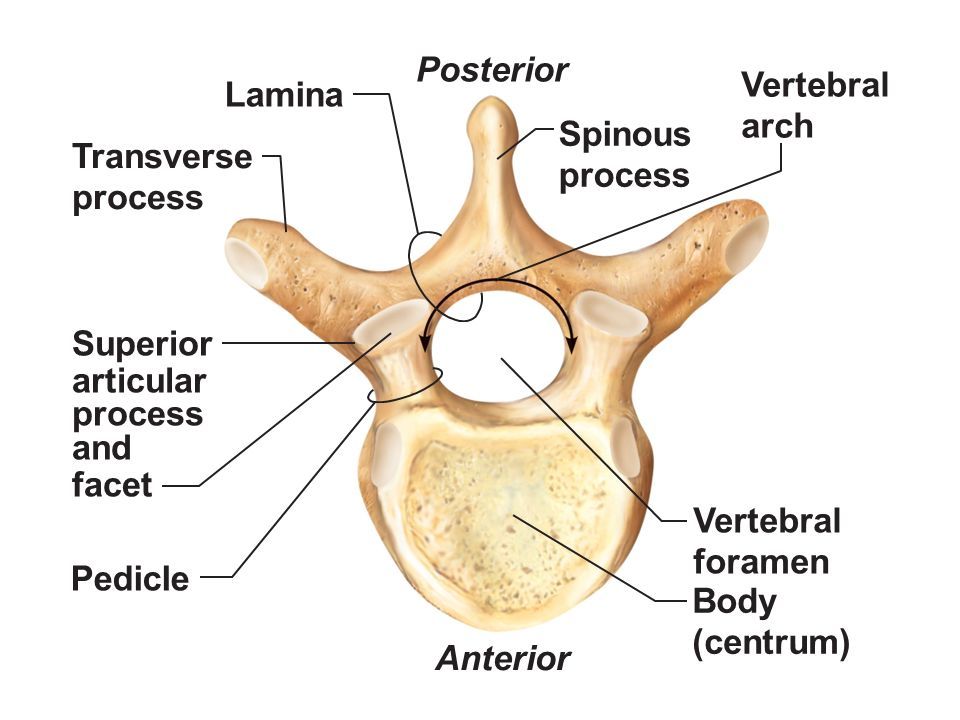
Vertebral Body
Thick anterior weight-bearing portion of a vertebrathat provides support and stability to the spine.
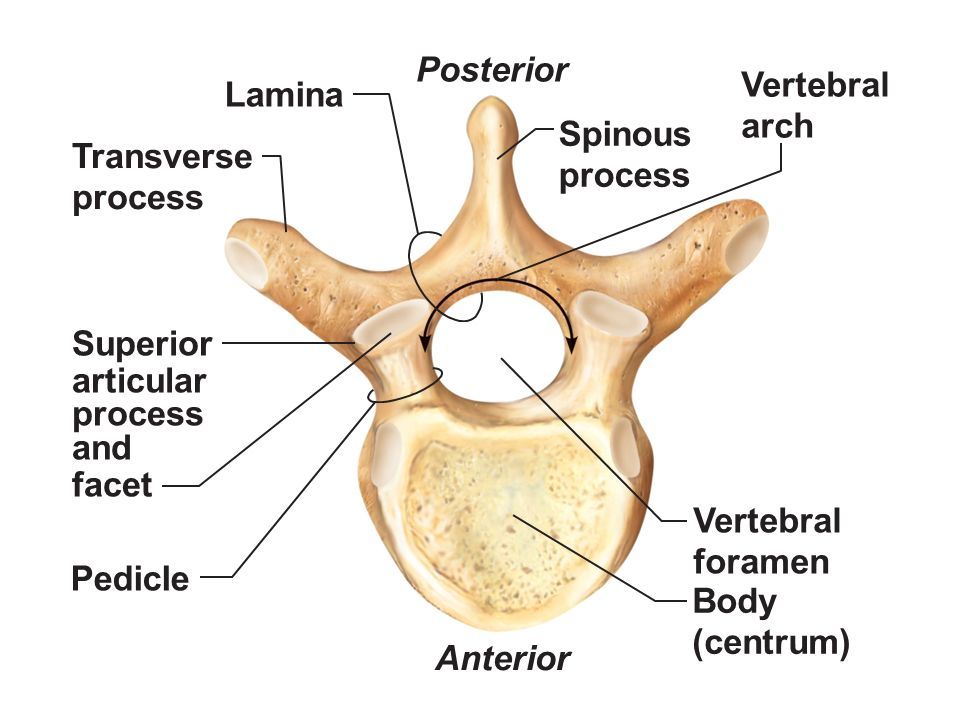
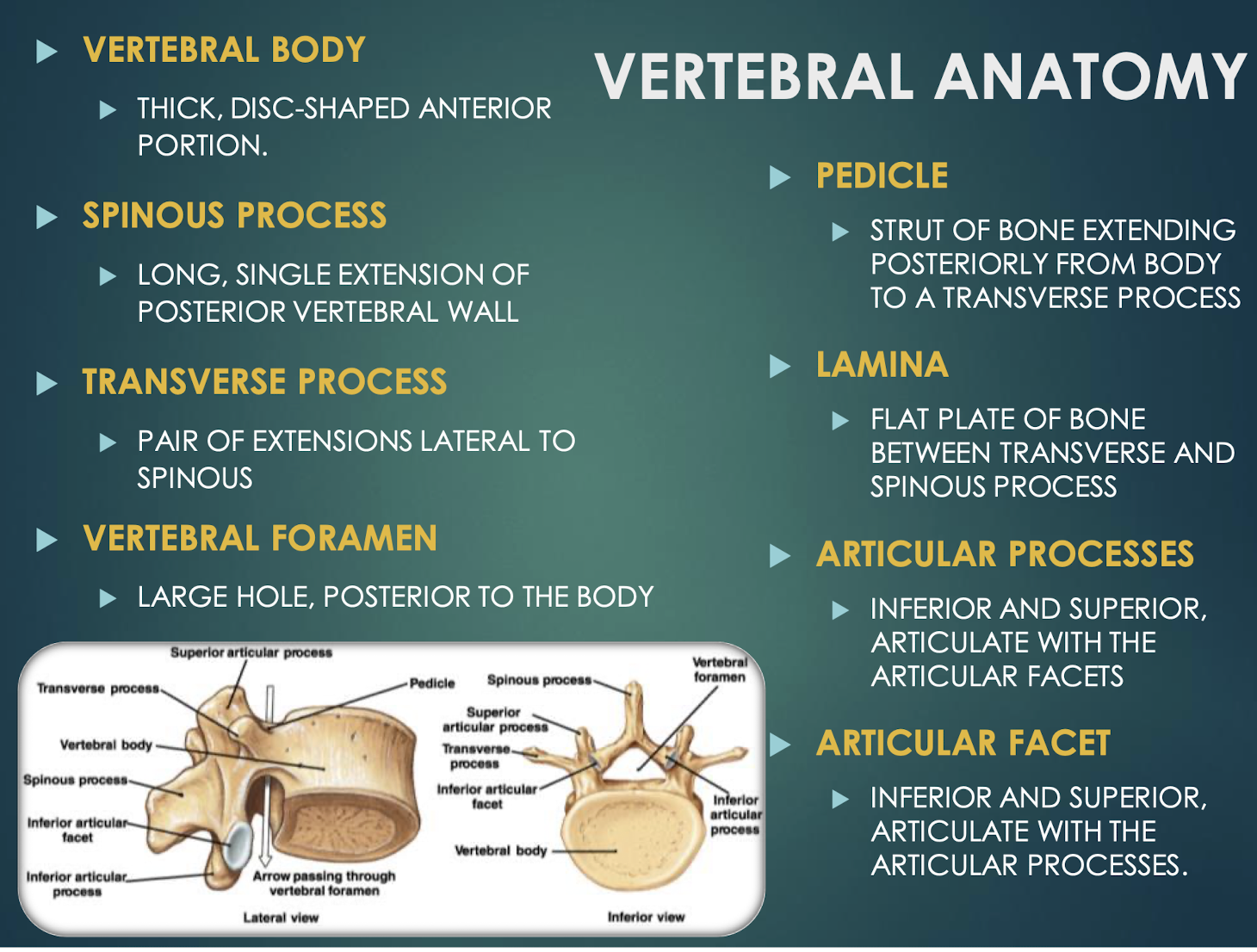
Spinous Process
Posterior midline projection from vertebral arch
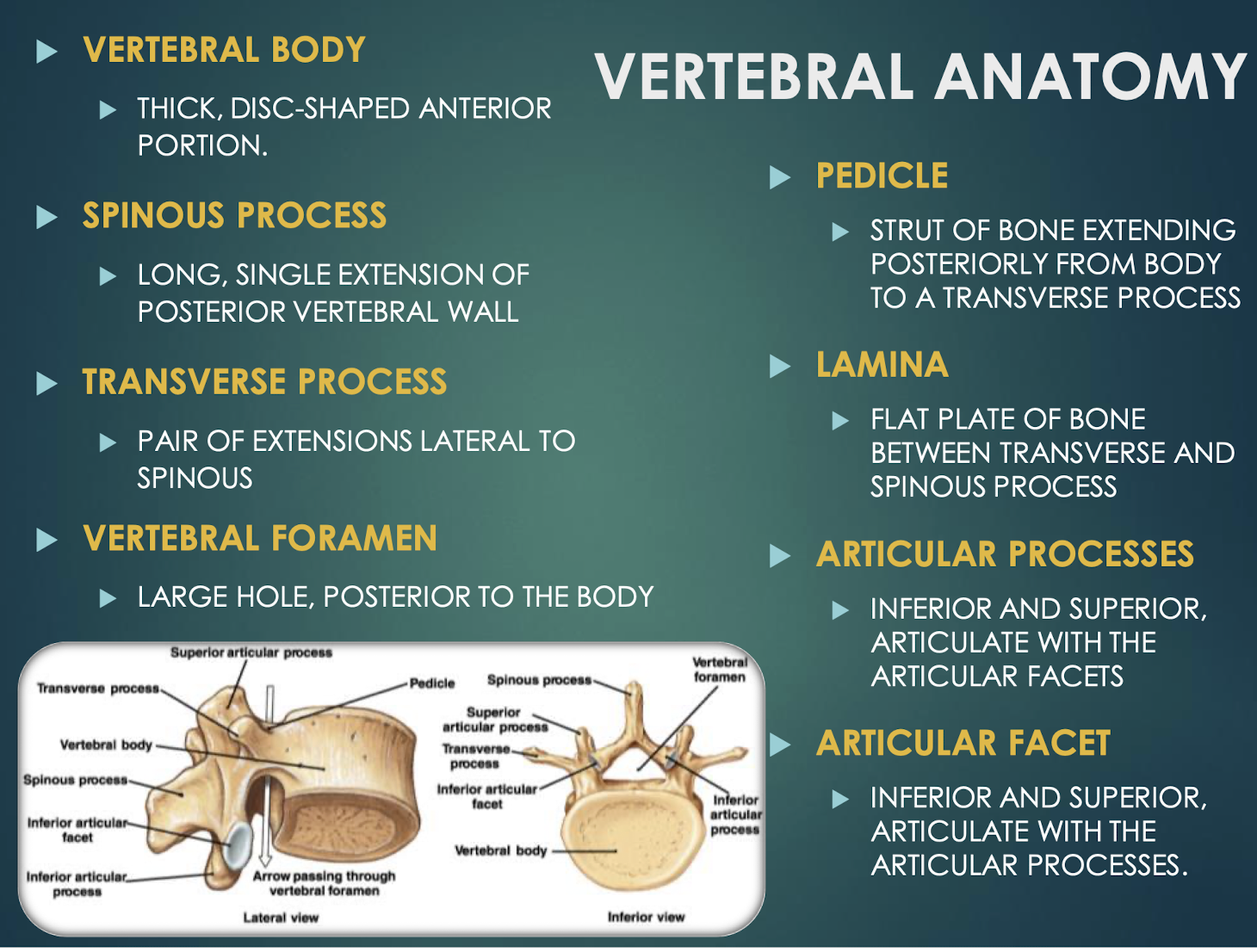
Transverse Process
Paired lateral projections from a vertebrathat extend outwards from the vertebral arch and serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
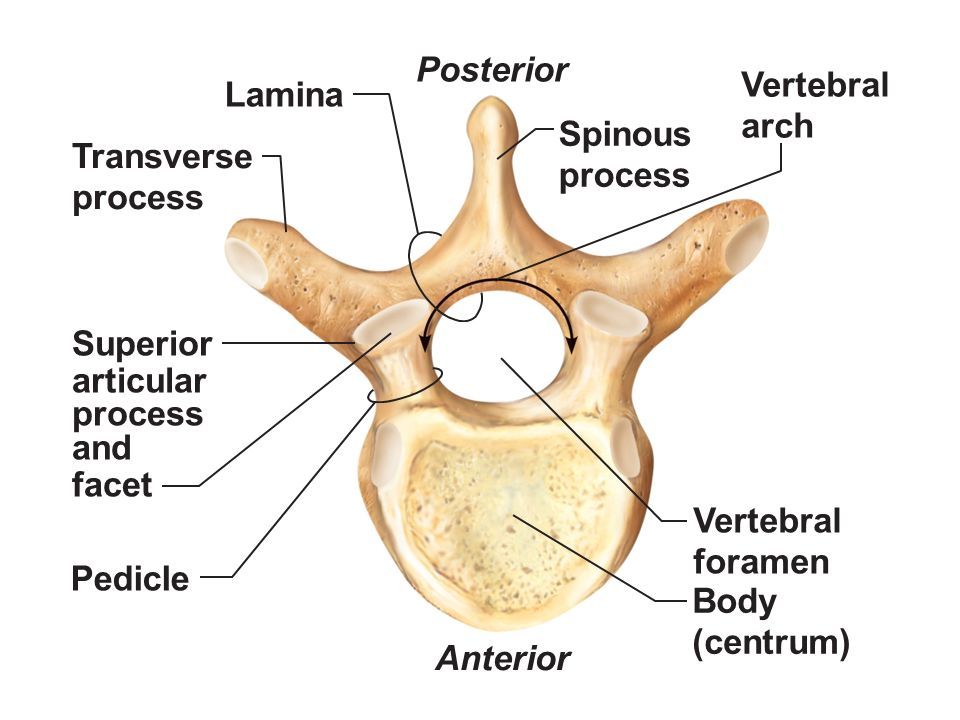
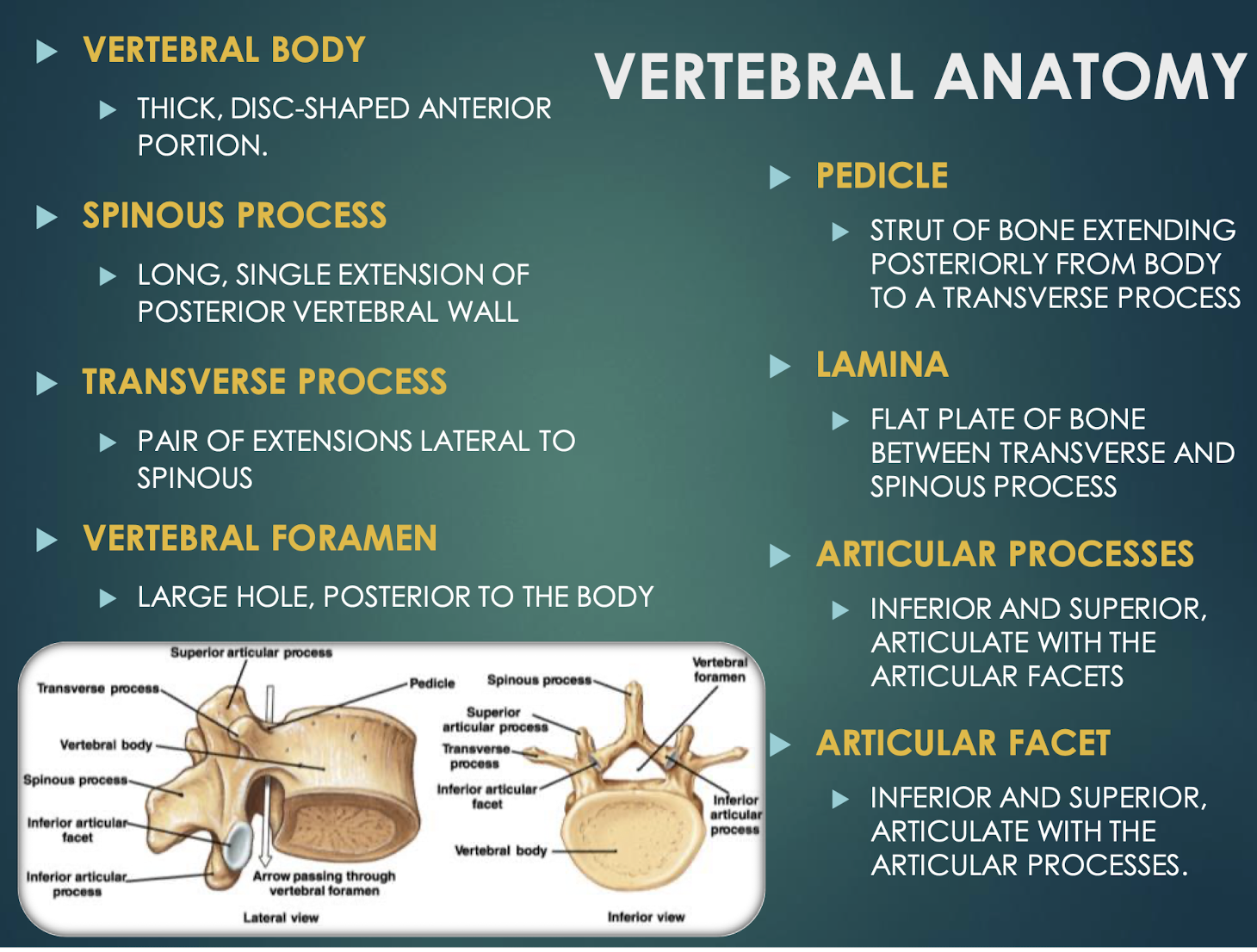
Vertebral Foramen
Large central opening posterior to body; houses spinal cordand surrounding protective tissues.
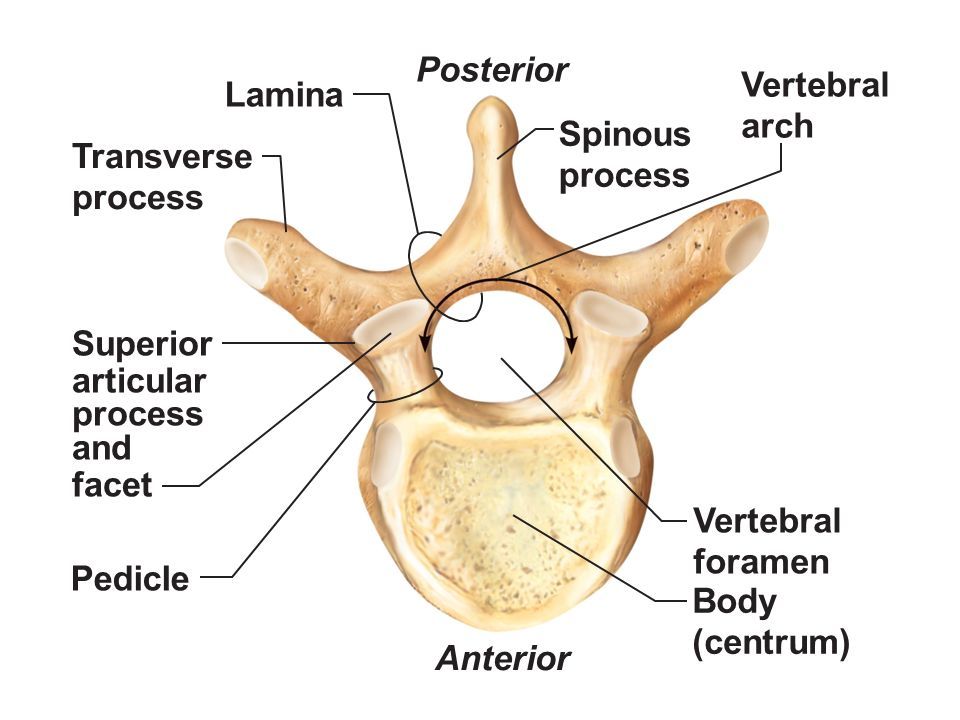
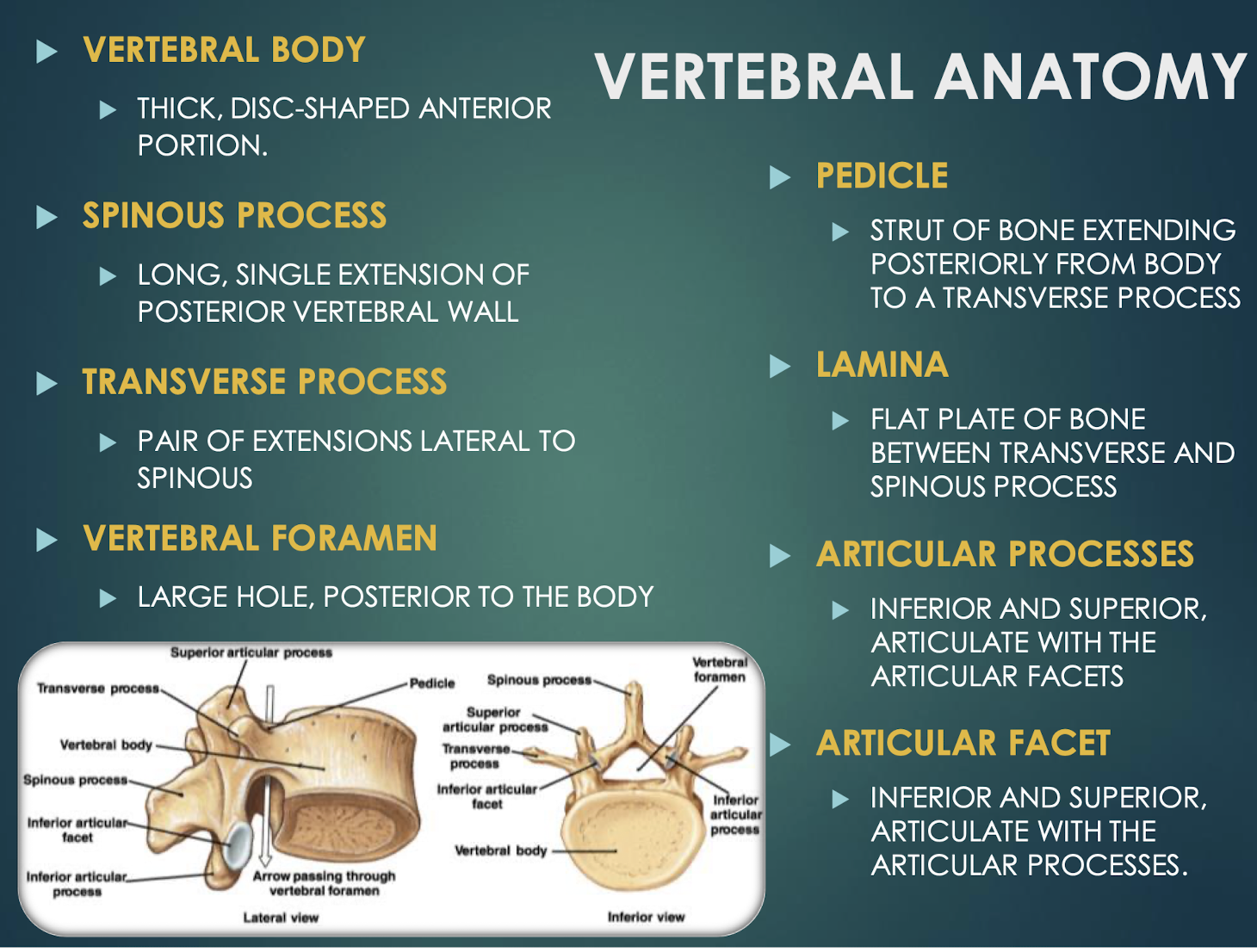
Pedicle
Short bony pillar connecting vertebral body to transverse processthat helps to support the vertebra and protect the spinal cord.
Lamina
Flat plate connecting transverse and spinous processesof a vertebra that helps to form the vertebral arch and provides protection for the spinal cord.
Articular Processes
Superior & inferior projections bearing facets for vertebral articulationthat allow for movement and stability between adjacent vertebrae.
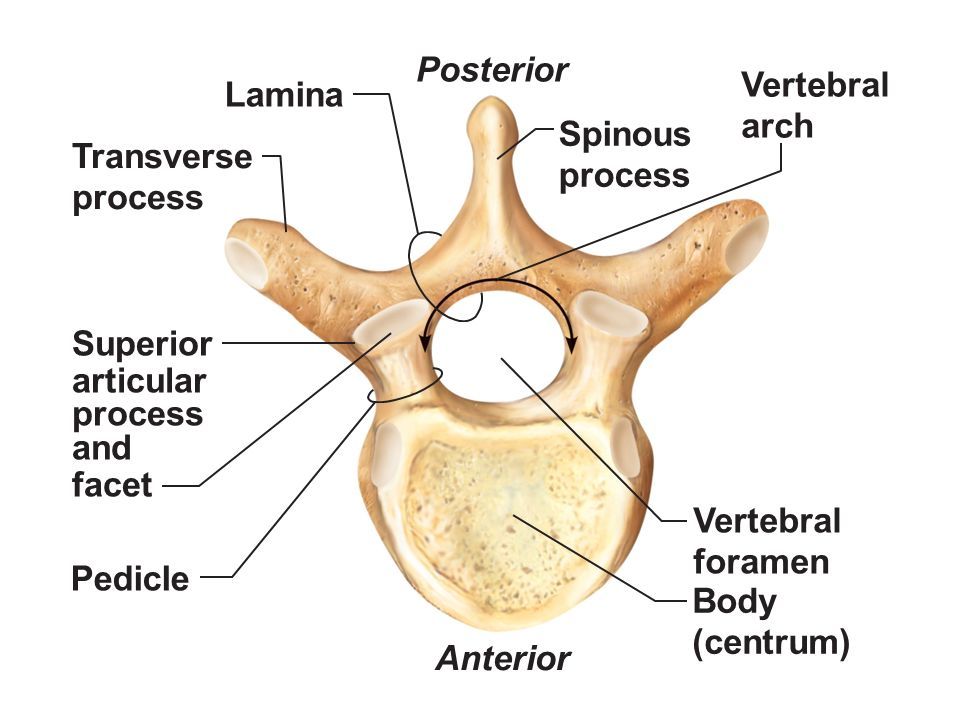
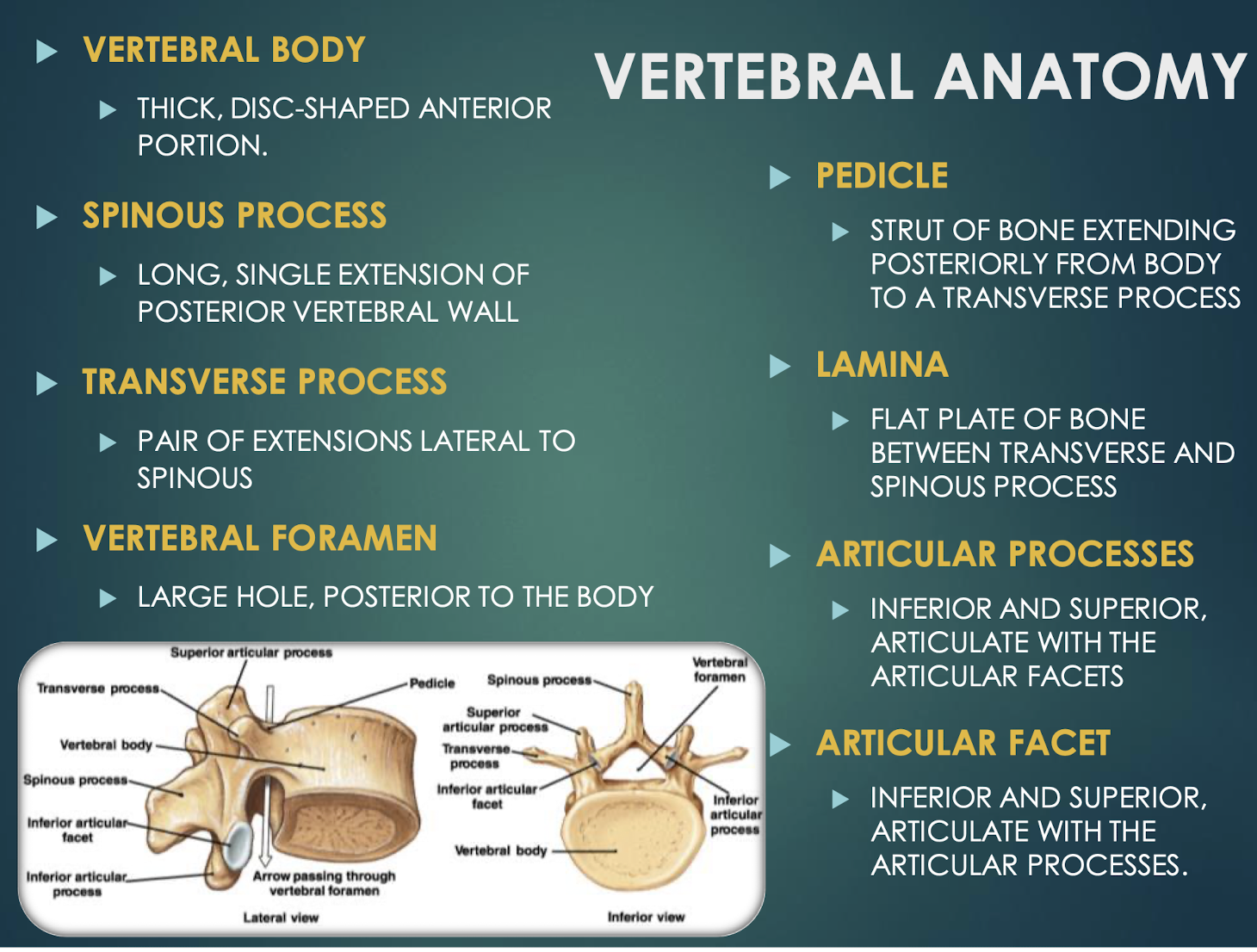
Articular Facet
Smooth surface on articular process that forms joints between vertebrae, allowing for flexibility and movement in the spine.
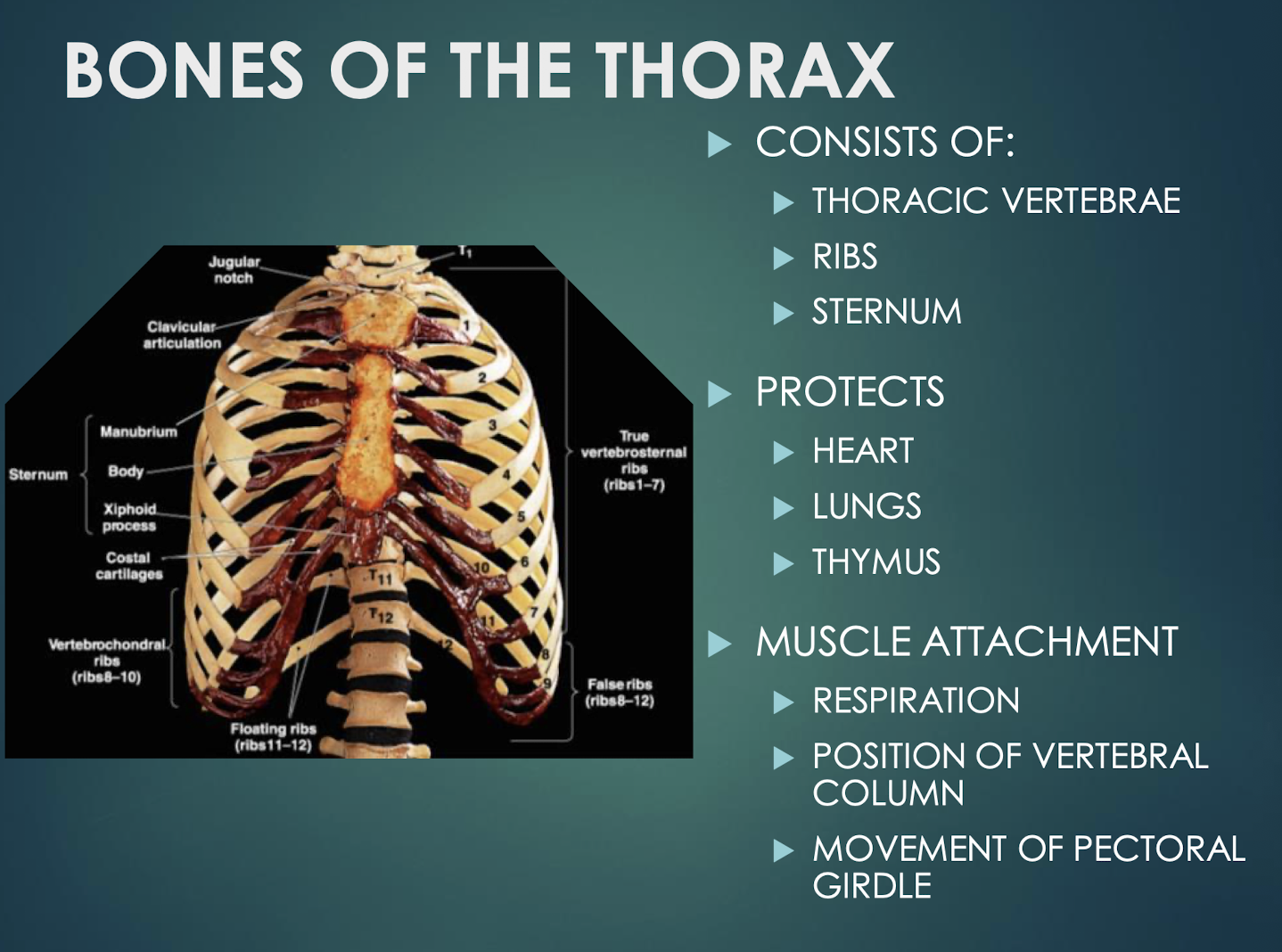
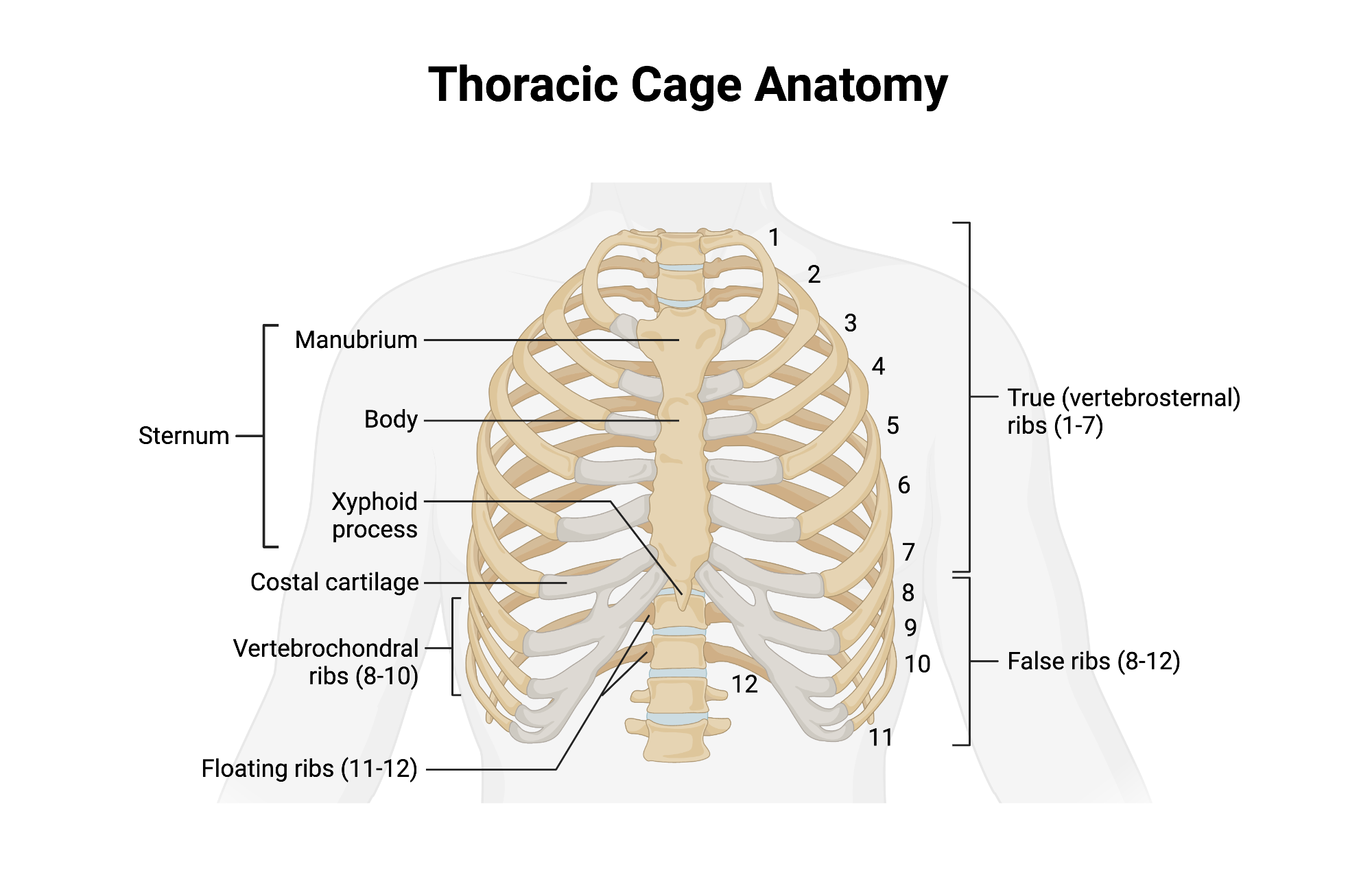
Thorax
Skeletal cage of thoracic vertebrae, ribs, and sternum that protects heart, lungs, and thymus.
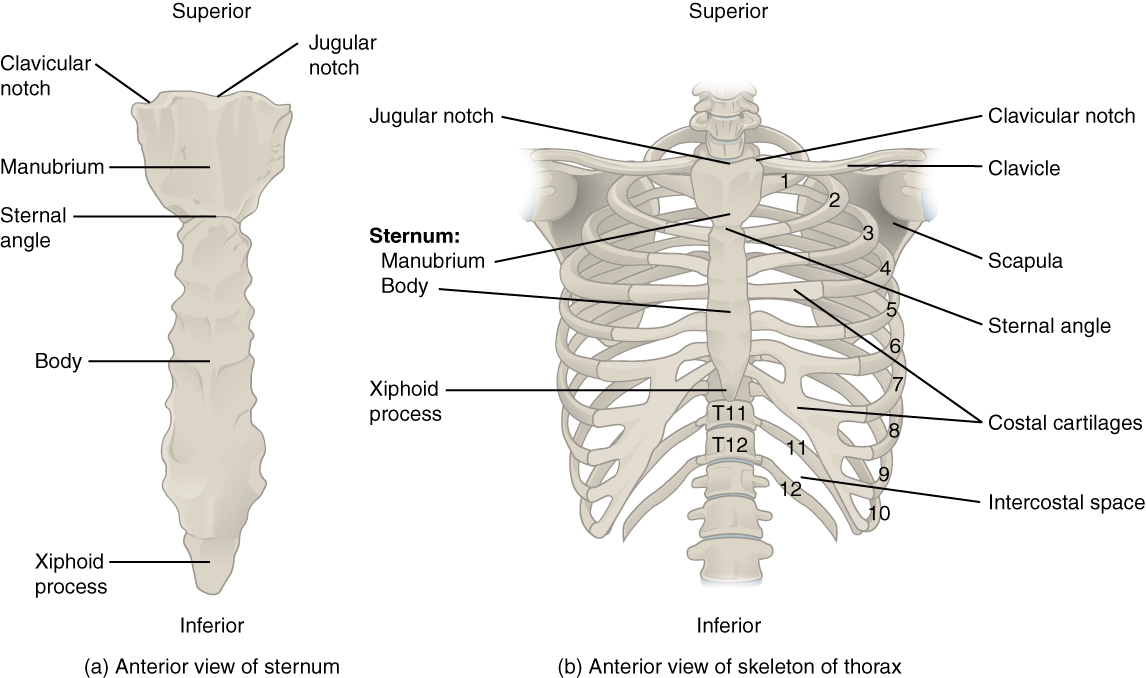
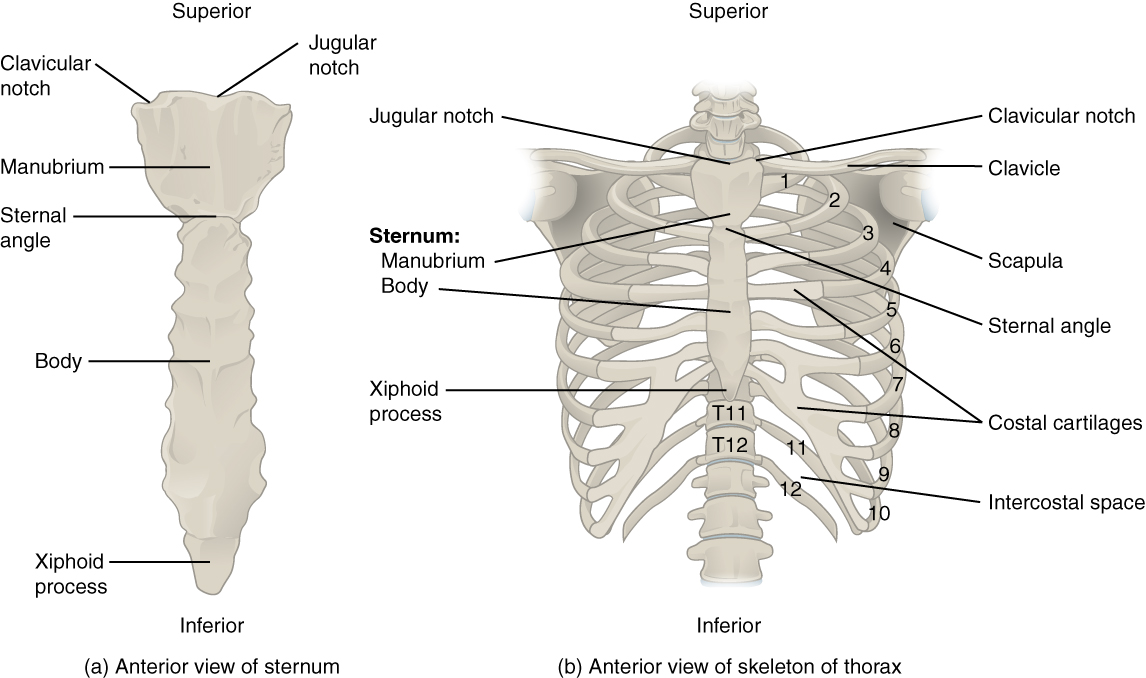
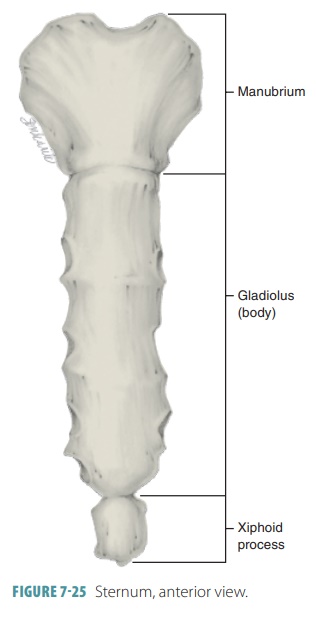
Sternum
Flat bone in anterior thorax composed of manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
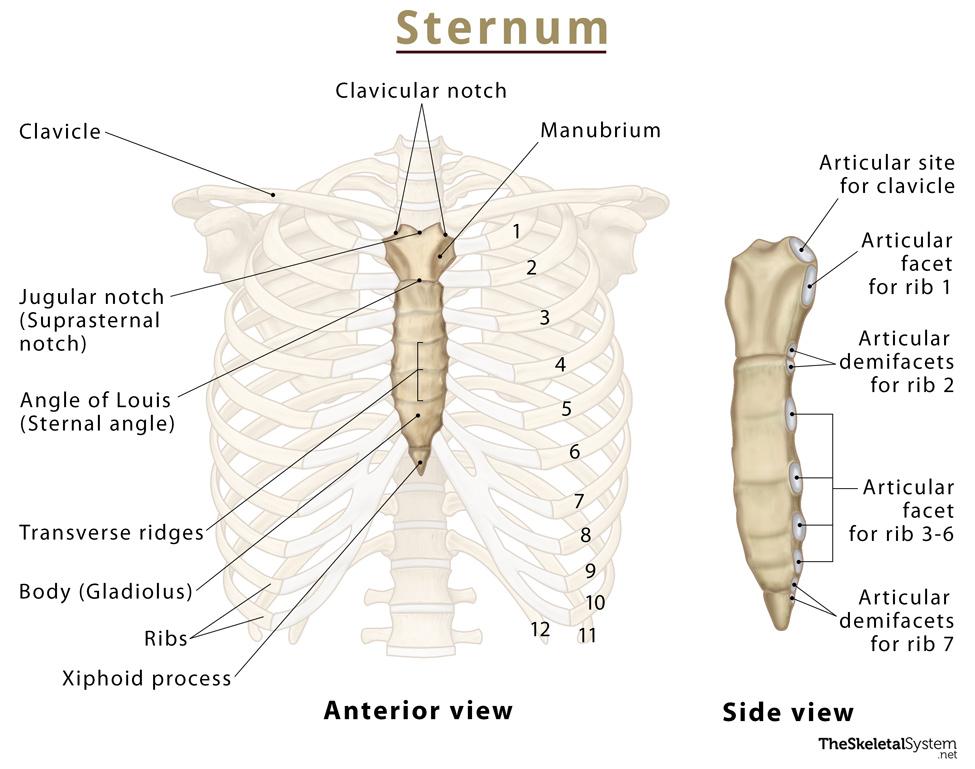
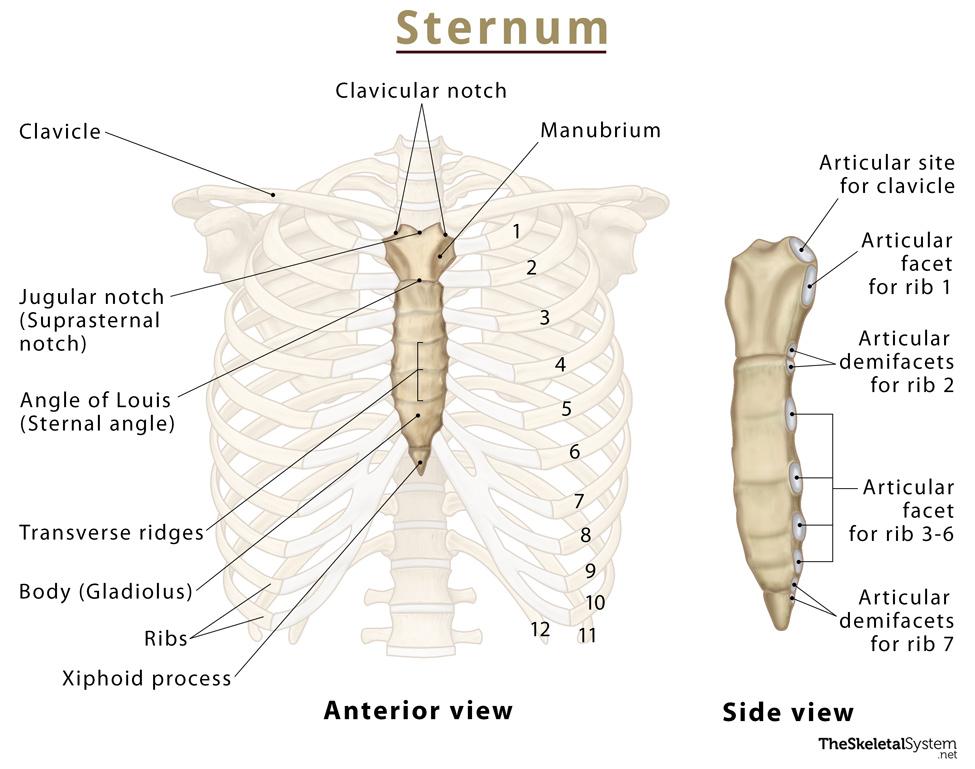
Manubrium
Superior sternum part; articulates with clavicles and first rib cartilage.
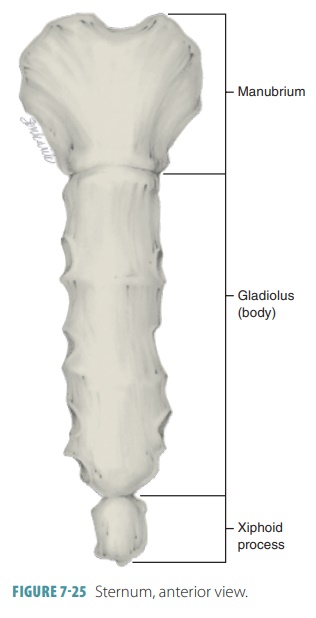
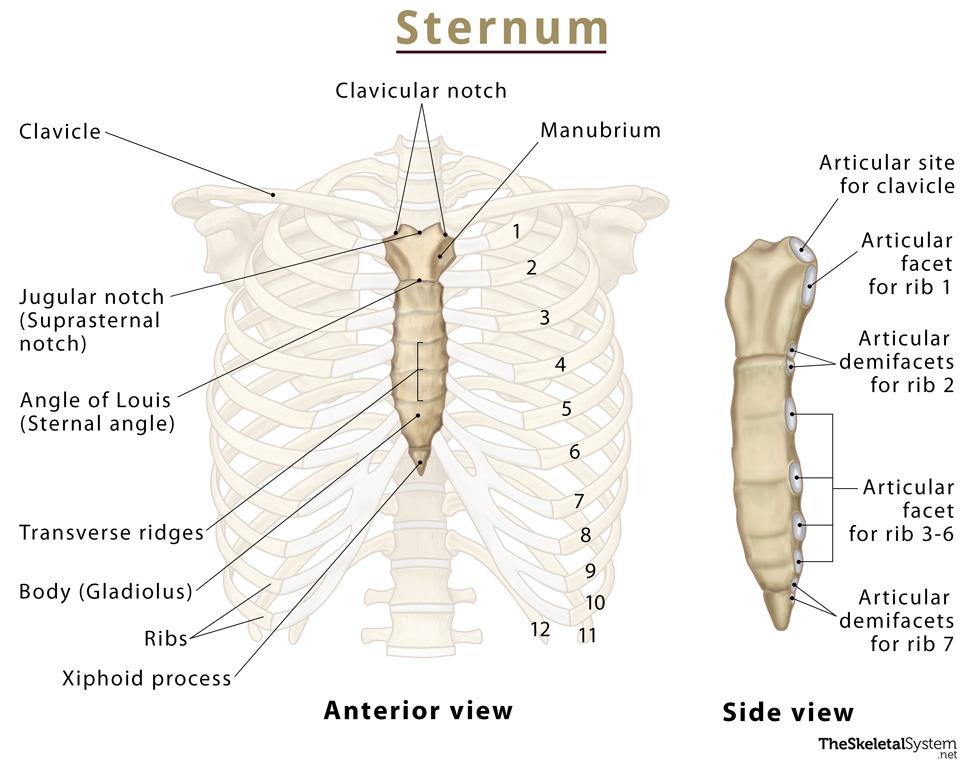
Body of Sternum
Middle, longest part where costal cartilages of ribs 2–7 attach.
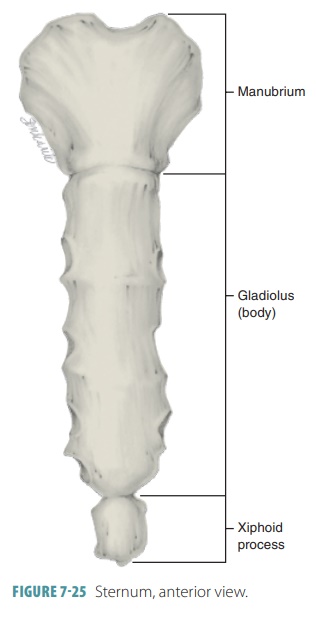
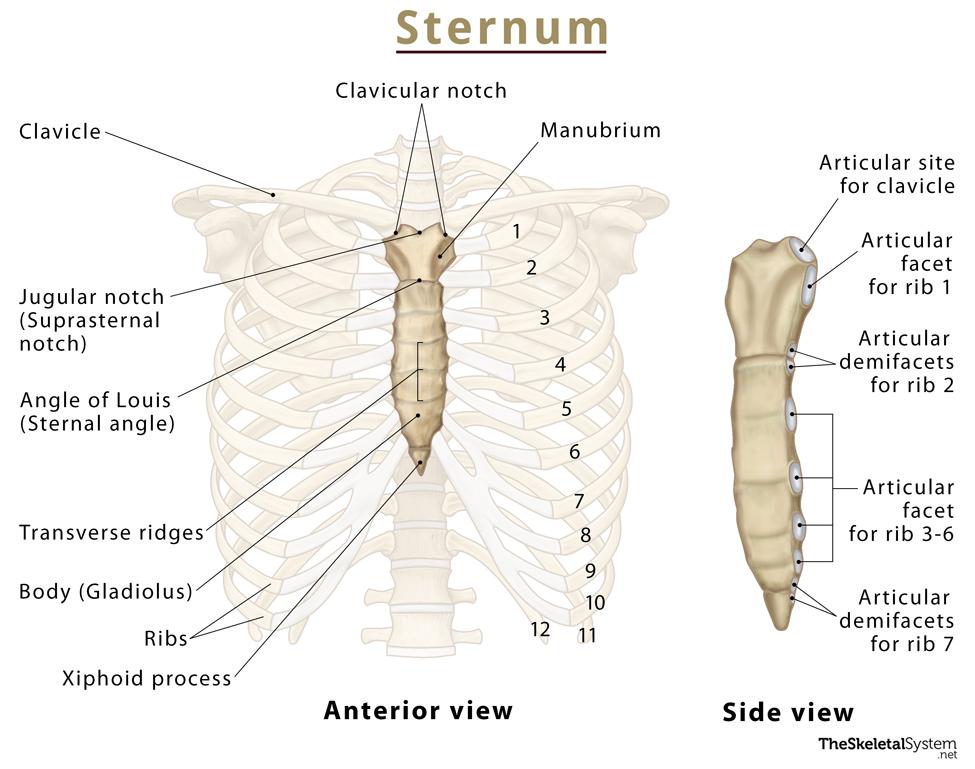
Xiphoid Process
Small inferior sternum part; attachment for diaphragm and rectus abdominismuscle. It is cartilaginous in youth and ossifies with age.
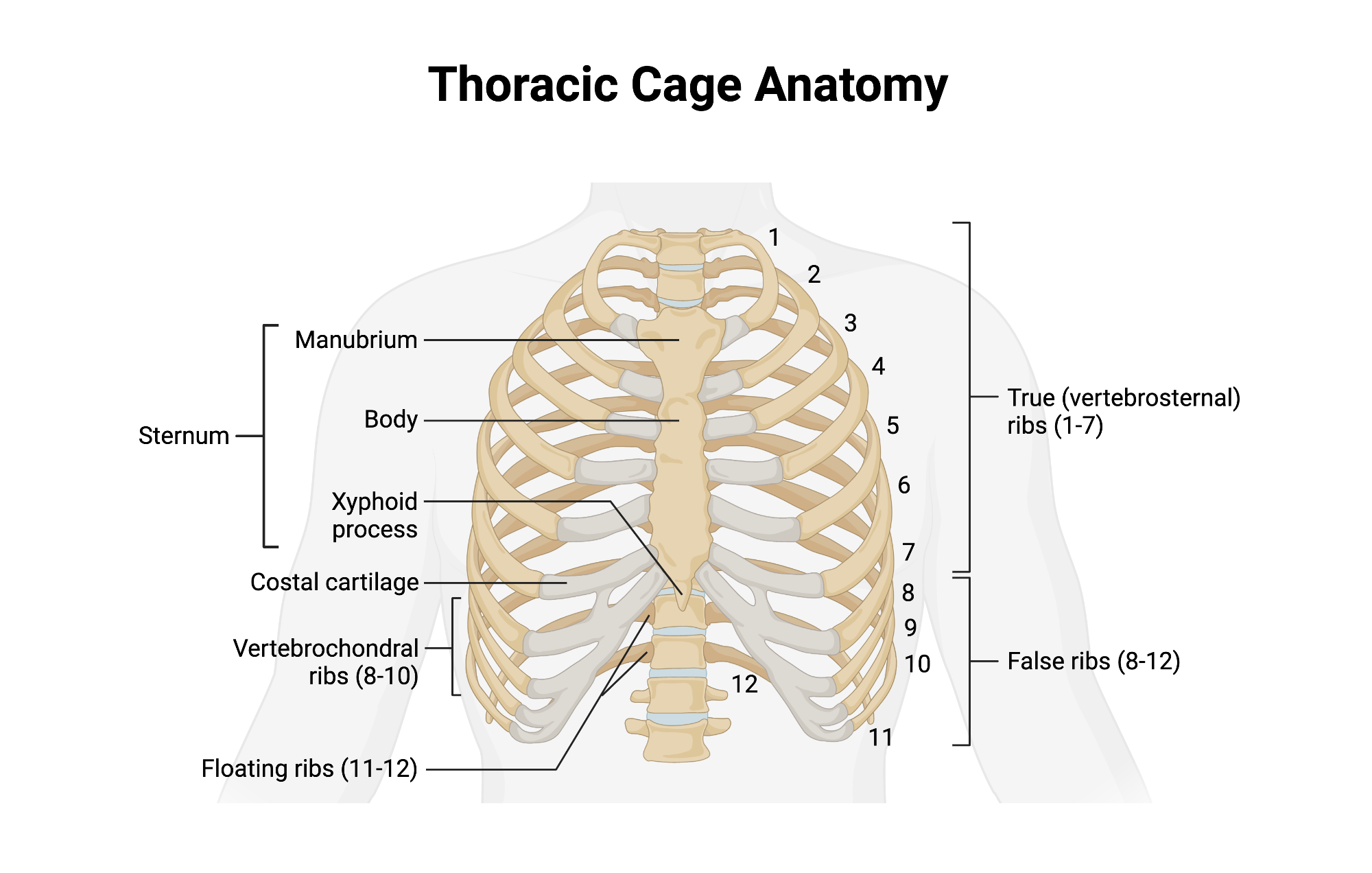
Ribs - 24 (12 pairs)
Twelve pairs of curved bones (costae) protecting thoracic organs and aiding respiration.

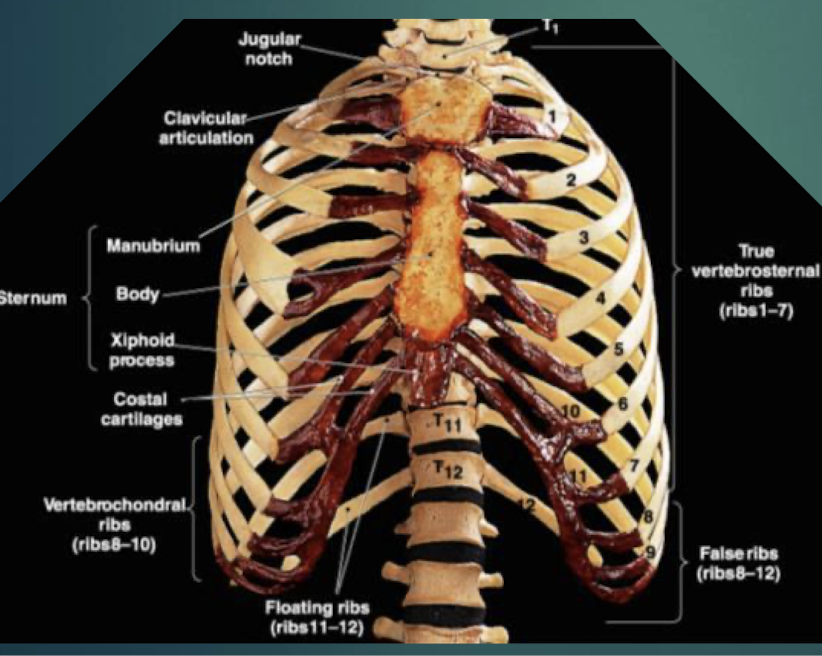
True Ribs
Vertebrosternal ribs 1–7 that attach directly to sternum via individual costal cartilages.
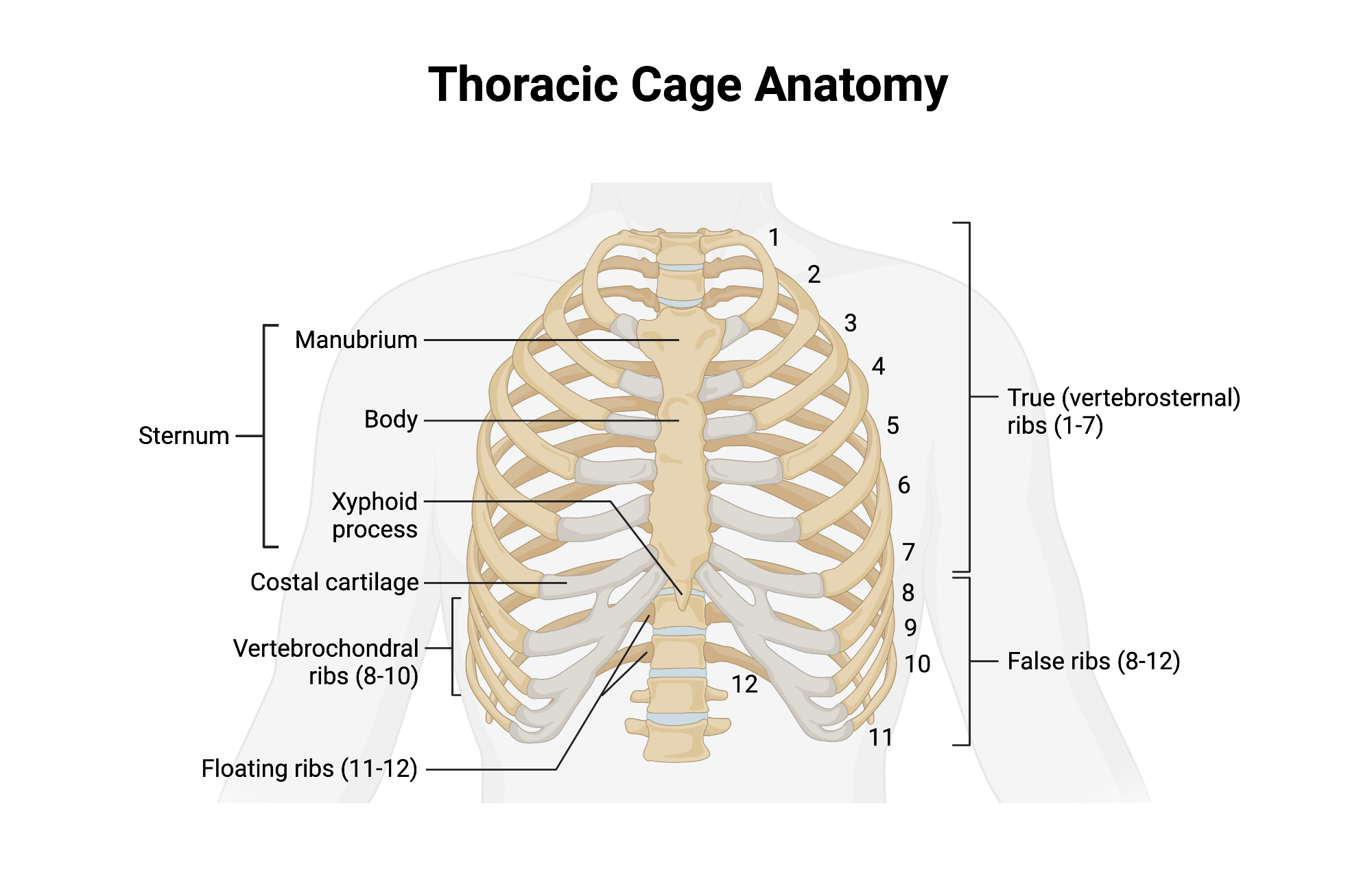
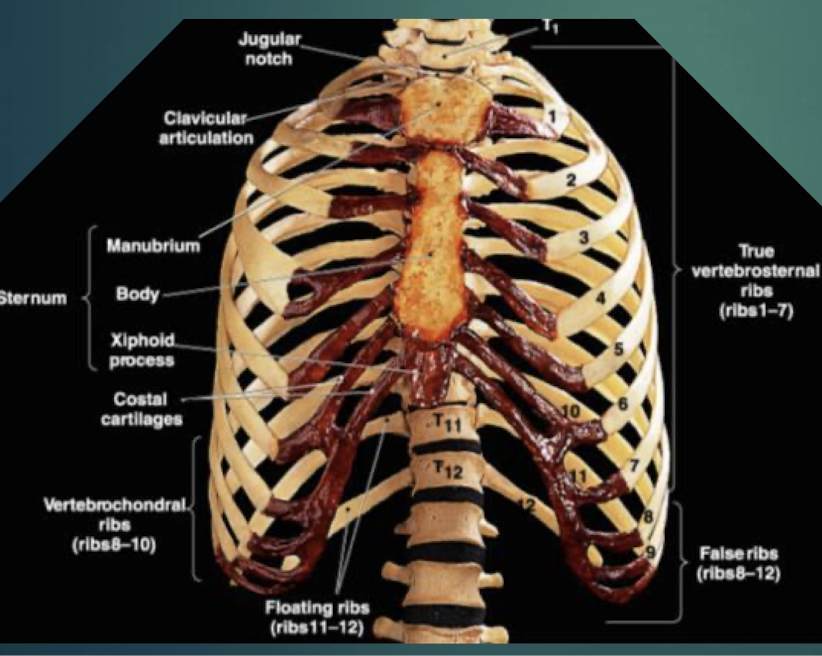
False Ribs
Vertebrochondral ribs 8–10; cartilage joins cartilage of rib 7 before reaching sternum. Ribs 11 and 12 are considered floating ribs as they do not attach to the sternum at all.
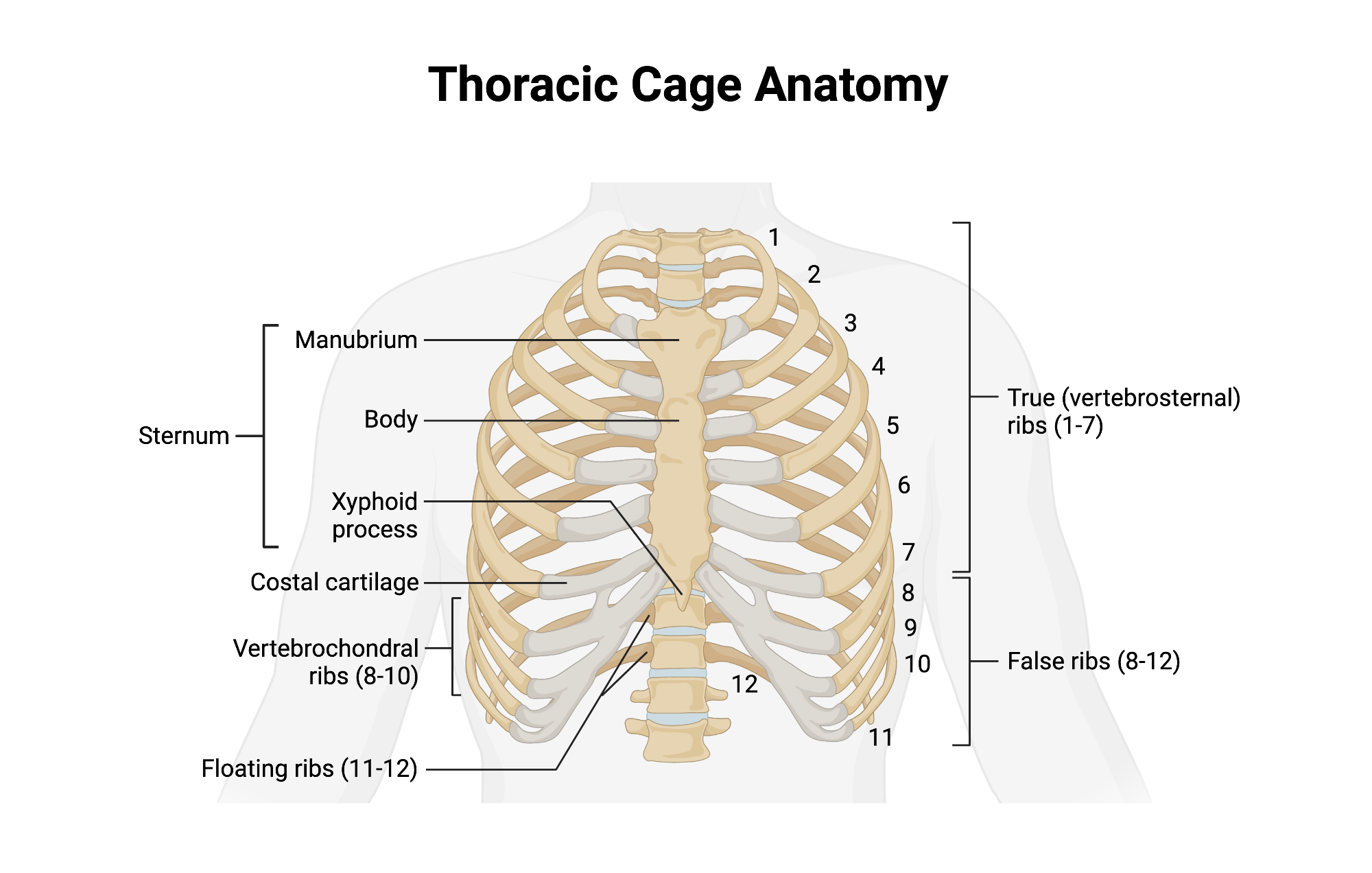
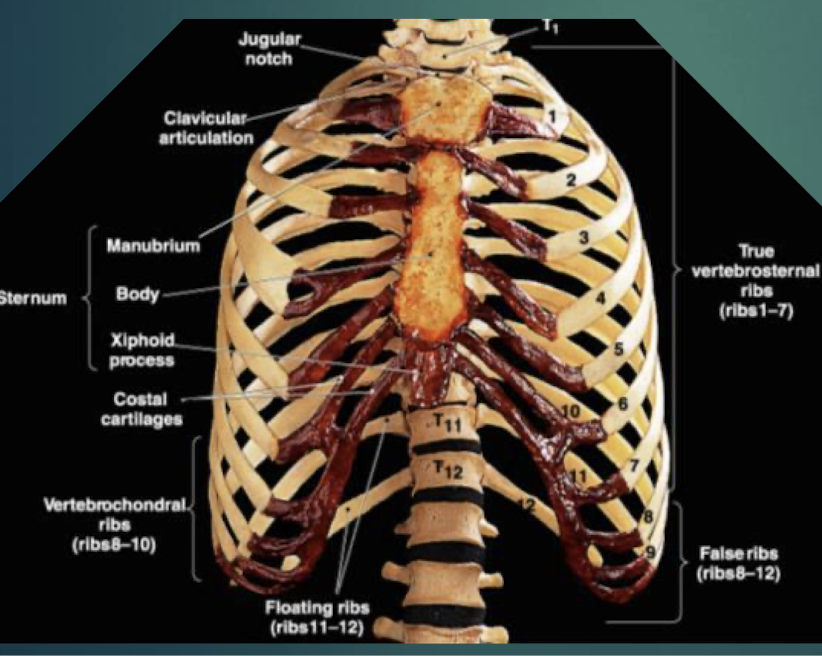
Floating Ribs
Pairs 11–12; do not connect to sternum, only to vertebrae.
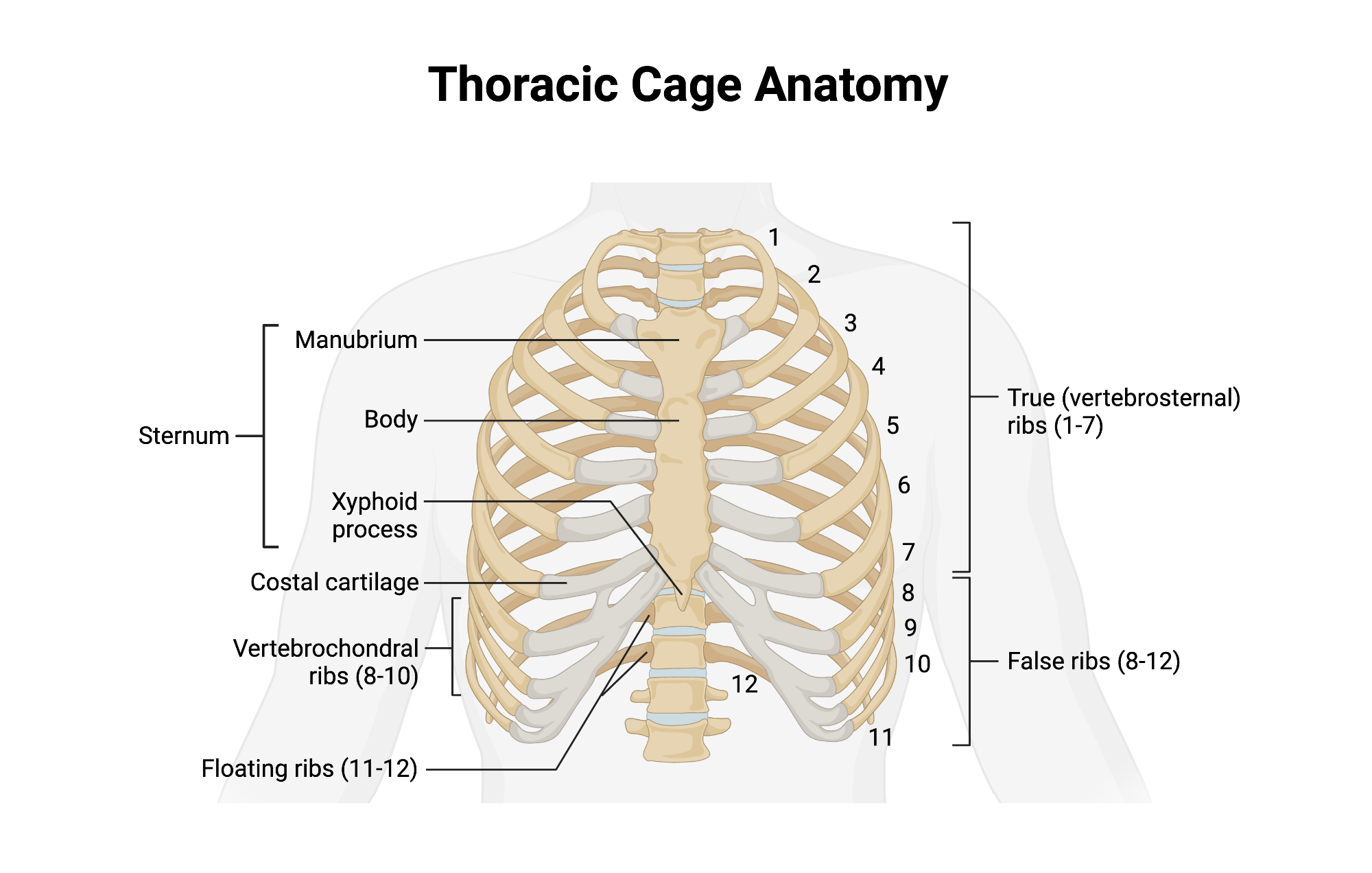
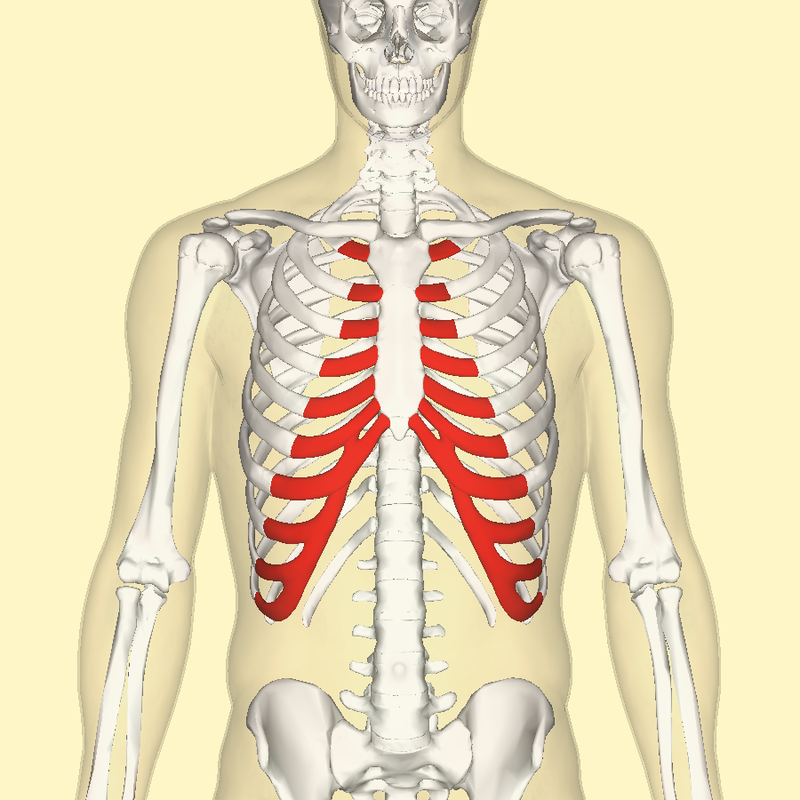
Costal Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage bars that connect ribs to sternum and provide flexibilityto the rib cage during breathing.