Sheep abortion
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
List the zoonotic infectious causes of abortion in sheep
Chlamydia abortus (most common)
Toxoplasma gondii (2nd most common)
Campylobacter (3rd most common)
Listeria
Salmonella
List the non-infectious causes of abortion in sheep
Poor nutrition/BCS
Pregnancy toxaemia
Rough handling
Transport
Vaccinaton/foot trimming
Dog worry
Fluke/worms
When should abortion be investigated in a flock of sheep?
If abortion rates fall above 2%
What are important samples to take when investigating abortion in sheep
Placenta including cotyledons
Stomach content (or liver/lung)
Spleen/thymus
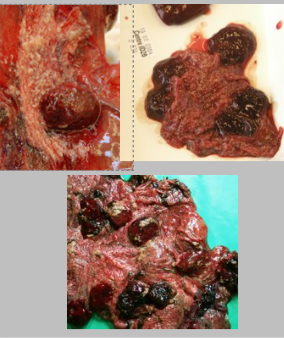
What is the likely causative agent of this abortion? Describe the pathology and pathophysiology.
Chlamydia abortus
Marked placentitis
inflamed cotyledons and intercotyledonary areas
thick fibrinopurulent or necrotic exudate (looks like custard)
Bacteria causes gradual reduction of nutrient/excretory exchange in foetus
Describe the patterns of abortion with enzootic abortion of ewes
(Chlamydia abortus)
Infection can be acquired previous season then abort next season
Infection can occur same season but takes 6 weeks to incubate
Diagnosis and treatment of Chlamydia abortus
MZN of placenta (or poorer sensitivity with stomach content)
Dam serology tests flock exposure
Treat abortion storms with long acting tetracycline
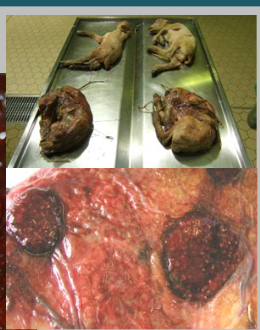
What is the likely causative agent of this abortion and describe the pathology.
Toxoplasma gondii
Spreads in cat faeces - 10 oocysts is an infective dose
Inflamed cotyledons with white miliary necrotic foci
Foetal pathology is non-specific, abortion can happen at any stage. Can be mummified or normal.
Causes poor scanning percentages
How is Toxoplasma gondii diagnosed?
PCR of cotyledons
Histopathology of brain
Dam serology to assess flock exposure
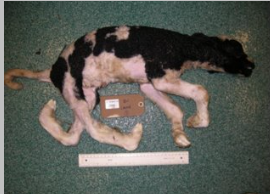
What is the likely cause of this abortion and describe the pathology.
Schmallenberg virus
transmitted by midges Culicoides, that peak in the late summer and early autumn
periodical re-emergence of disease
arthrogryposis
torticollis
scoliosis
brachygnathia inferior
hydranencephaly
cerebral hypoplasia/cerebellar aplasia
micromyelia
How is Schmallenberg diagnosed?
Fresh brain or brainstem PCR
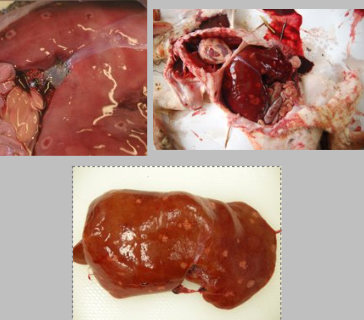
What is the likely cause of this abortion and describe the patholoy
Campylobacter (fetus fetus is most common)
Transmitted in faeces and vaginal fluids, and can be spread by wild birds and rodents
Associated with ground feeding and poor trough hygiene
Lambs have multifocal necrotizing hepatitis forming target-like lesions
Placenta has pale/small necrotic cotyledons
How is Campylobacter diagnosed?
Bacteriology of stomach content (or liver/lung if absent)
takes 4 days for initial bacterial identification