Ch. 21: The Immune System
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Can you label the cause of infection and some structures involved in fighting that infection?
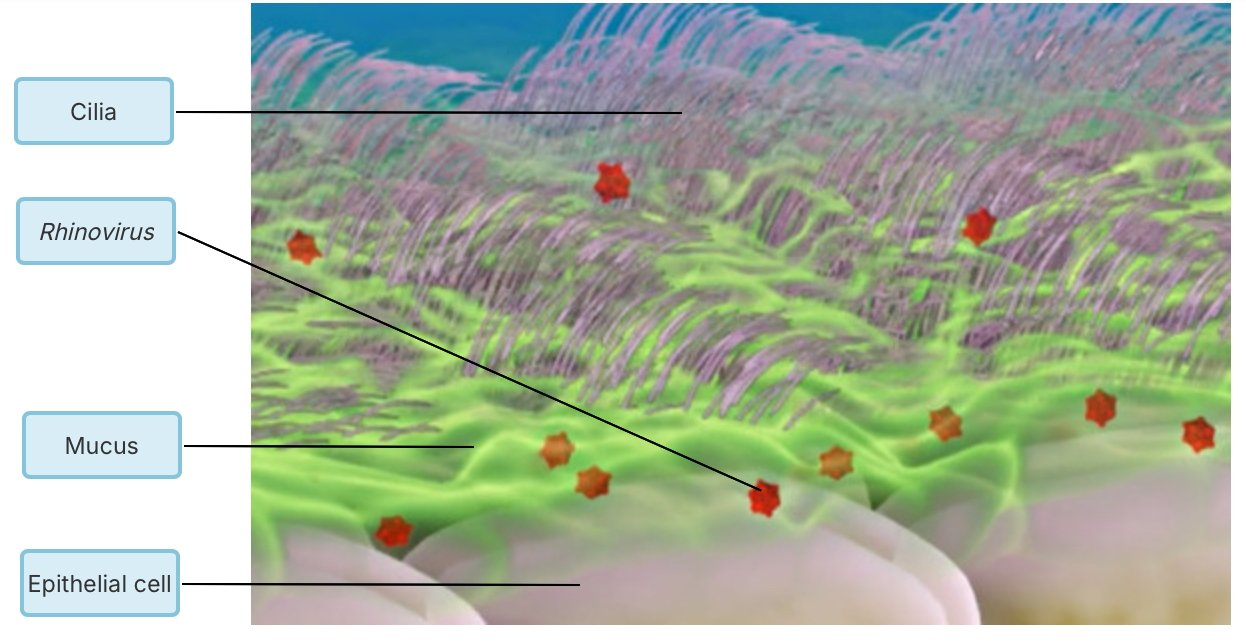
Discharge is one of the cardinal signs of Inflammation.
True
False
False
Which antimicrobial protein triggers inflammation?
histamine
pyrogen
interferon
lysozyme
Histamine
Which of the following is not an antigen-presenting cell (APC)?
macrophage
dendritic cell
B cell
T cell
T cell
Which molecules of the adaptive defense system provide humoral immunity by circulating freely in the blood and lymph, where they bind to extracellular antigens and inactivate them and mark them for destruction?
interferons
complement proteins
antibodies
antigens
Antibodies
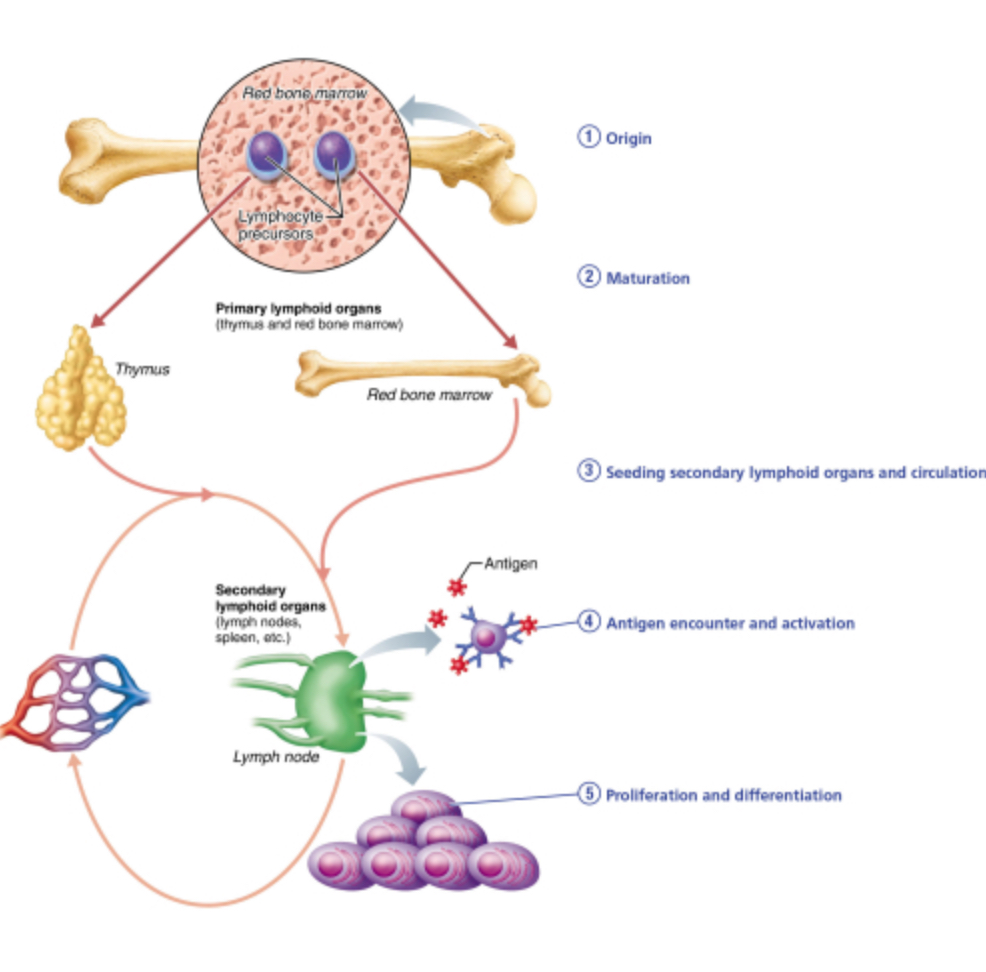
How does a lymphocyte exhibit immunocompetence?
by being relatively unresponsive to self-antigens so that they do not attack the body's own cells
by recognizing self-antigen
by being able to recognize their one specific antigen
by rapidly proliferating to form an army of cells exactly like themselves and bearing the same antigen-specific receptors
by being able to recognize their one specific antigen
Which of the following is an effect of complement activation?
tissue repair
fever
T cell activation
opsonization
Opsonization
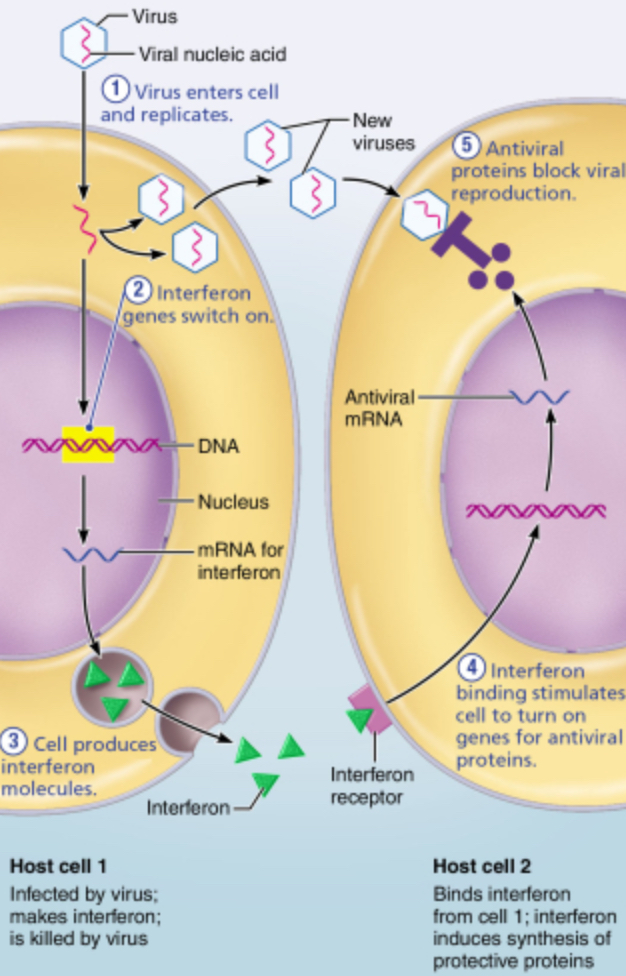
What protein can be released by infected cells to help protect cells that have not yet been infected?
pyrogens
complement
opsonins
interferon
Interferon
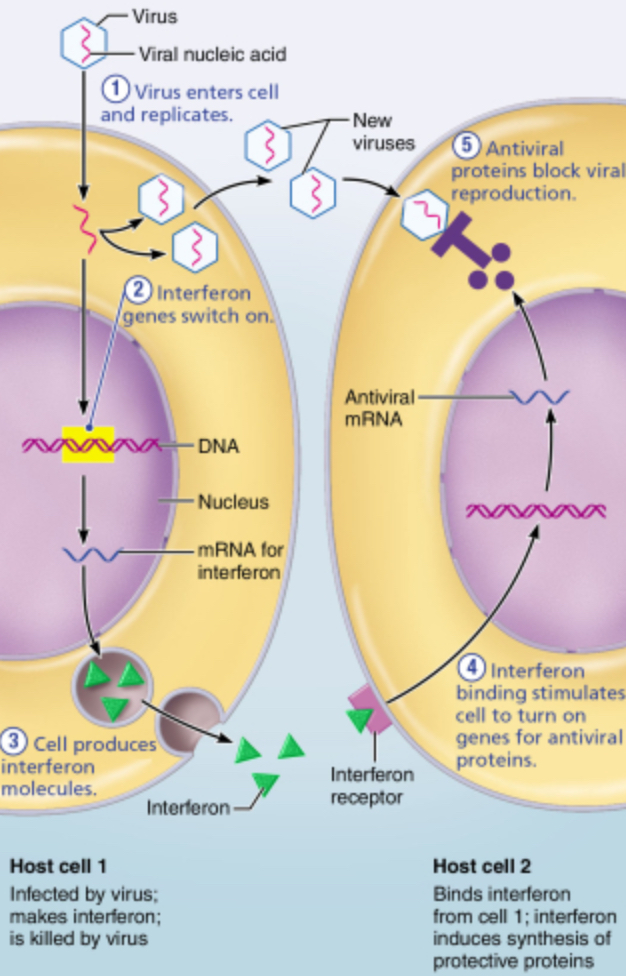
How do interferons protect against viral infection in healthy cells?
Interferons perform opsonization to coat microorganisms.
Interferons encourage the production of antiviral proteins.
Interferons promote fever, or an abnormally high body temperature.
Interferons activate complement.
Interferons encourage the production of antiviral proteins.
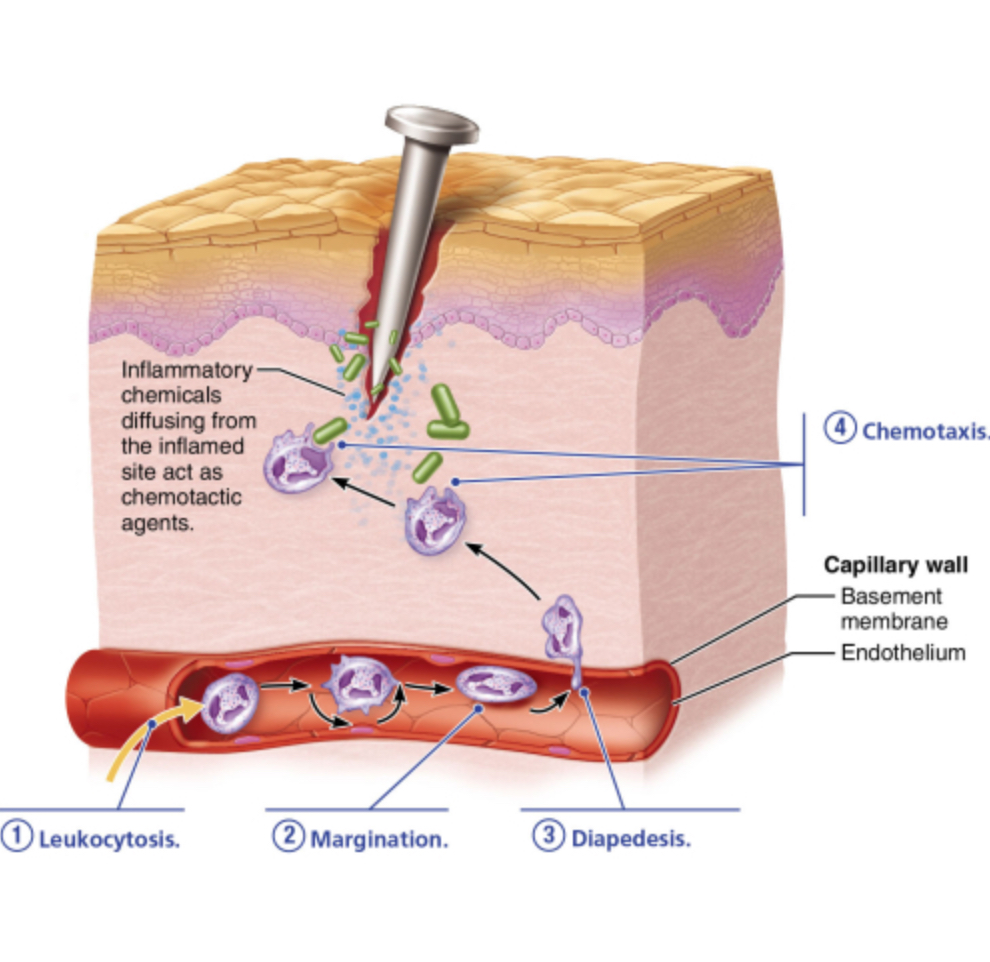
What characterizes the chemotaxis phase of phagocyte mobilization?
Neutrophils actively ingest bacteria.
Neutrophils cling to the inner walls of capillaries and postcapillary venules.
Neutrophils and other WBCs migrate up the gradient of chemotactic agents to the site of injury.
Neutrophils flatten to squeeze between the endothelial cells of the capillary walls.
Neutrophils and other WBCs migrate up the gradient of chemotactic agents to the site of injury.
Unless they are attached to protein carriers, haptens have immunogenicity but not reactivity.
True
False
False
Why are children given vaccinations?
in order to see whether the immune system is capable of defense against disease
so that they will develop a primary immune response against various disease-causing pathogens
in order to activate the cell-mediated defense against pathogens
so that they will develop a mild case of a disease in order to prevent a more serious case of the disease later on
So that they will develop a primary immune response against various disease-causing pathogens
Vaccines provide what type of immunity?
naturally acquired passive
artificially acquired passive
artificially acquired active
naturally acquired active
Artificially acquired active
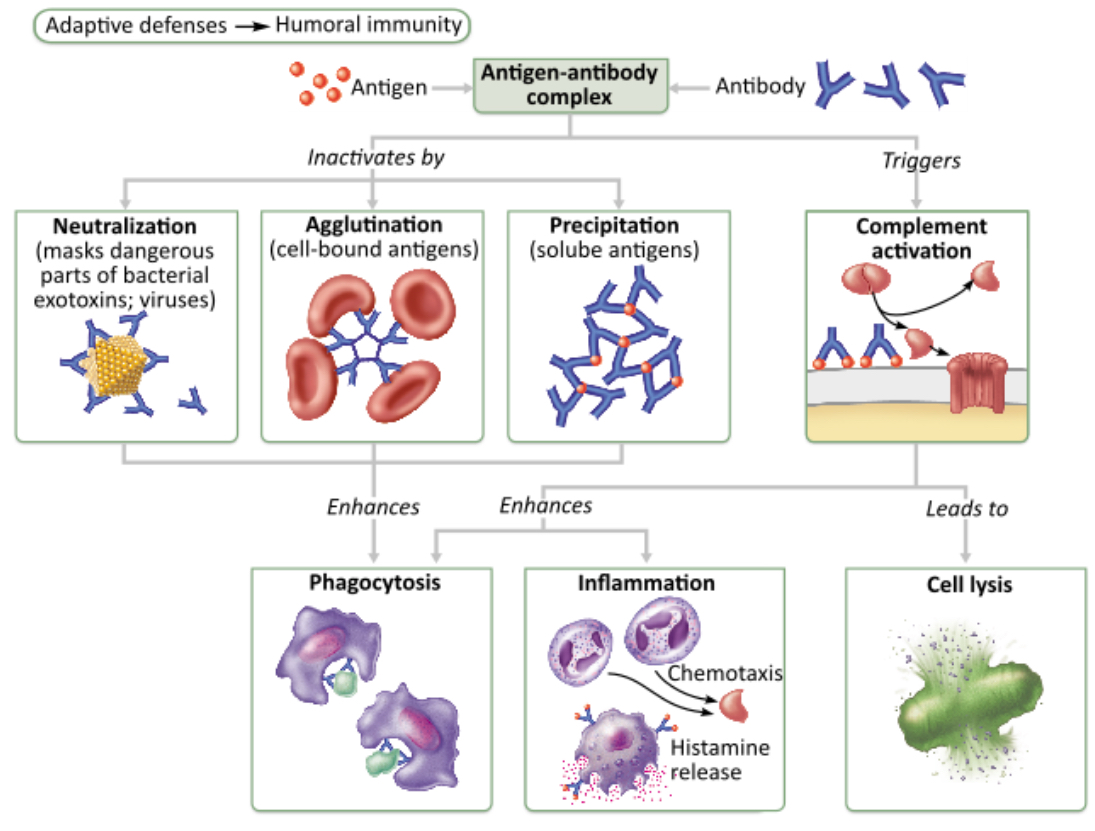
Which of the following occurs when antibodies block specific sites on viruses or bacterial exotoxins?
precipitation
agglutination
complement fixation and activation
neutralization
Neutralization
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Natural Killer (NK) cells?
NK cells recognize abnormal or cancer cells by a specific antigen on their cell membrane.
NK cells attack transplanted organs.
NK cells induce the target cell to undergo "apoptosis" (cell suicide).
NK cells attack infected or cancerous cells.
NK cells recognize abnormal or cancer cells by a specific antigen on their cell membrane.
Which of the following innate internal defenses work by interfering with viral
replication?
complement proteins
interferons
phagocytes
T lymphocytes
Interferons
How do phagocytes recognize foreign cells or bacteria?
The phagocytes recognize molecules on pathogens not normally found on body cells.
The phagocytes look for the absence of "self" proteins.
All the foreign cells or bacteria are marked with opsonins that the phagocytes recognize.
Phagocytes recognize a specific antigen on the cell surface.
The phagocytes recognize molecules on pathogens not normally found on body cells.
Which of the innate defense mechanisms can lyse bacteria and mark cells for
phagocytosis?
interferons
natural killer (NK) cells
complement proteins
cytokines
Complement proteins
Which of the following can act as opsonins on bacteria, thus enhancing phagocytosis?
natural killer (NK) cells
T cells
antibodies and complement proteins
interferons
Antibodies and complement proteins
Which of the following is NOT a chemical barrier that helps prevent infections?
the pH of the blood
mucus
pH of the urine
tears
The pH of the blood
Class II MHC proteins are found on which of the following cell types?
antigen-presenting cells
all nucleated cells
Antigen-presenting cells
Which class of MHC proteins presents exogenous antigens?
class II MHC proteins
class I MHC proteins
class II MHC proteins
Class I MHC proteins are recognized by which of the following cell types (that are destined to become T cells)?
CD4
CD8
CD8
Which of the following types of cells display protein fragments produced by the cancer within them?
dendritic cells
all nucleated cells
macrophages
B cells
All nucleated cells
Which major class of lymphocytes become cytotoxic T cells?
CD6 cells
CD8 cells
CD4 cells
CD8 cells
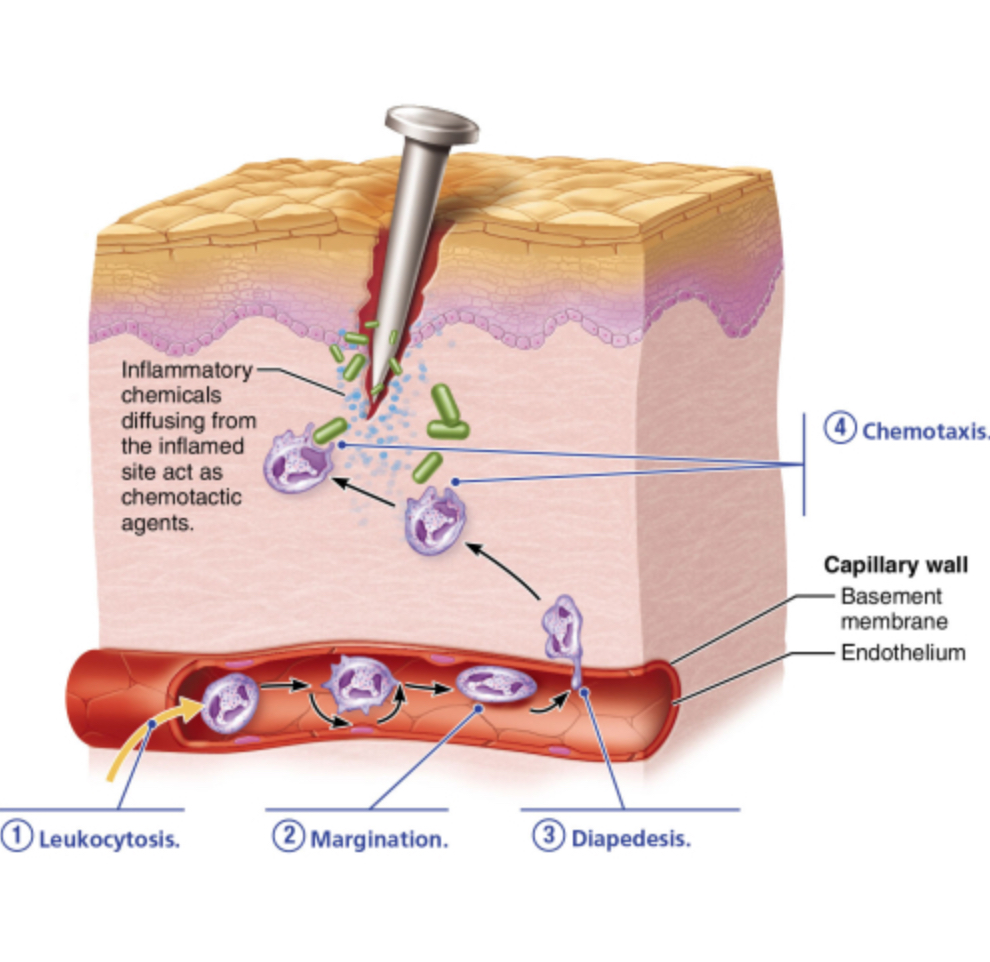
When do neutrophils enter the blood from the red bone marrow in response to leukocytosis-inducing factors?
during leukocytosis
during chemotaxis
during diapedesis
during margination
During leukocytosis
Which of the following is NOT one of the effects produced by the release of inflammatory chemicals?
redness
vasoconstriction
increased access of clotting chemicals
attraction of neutrophils
Vasoconstriction
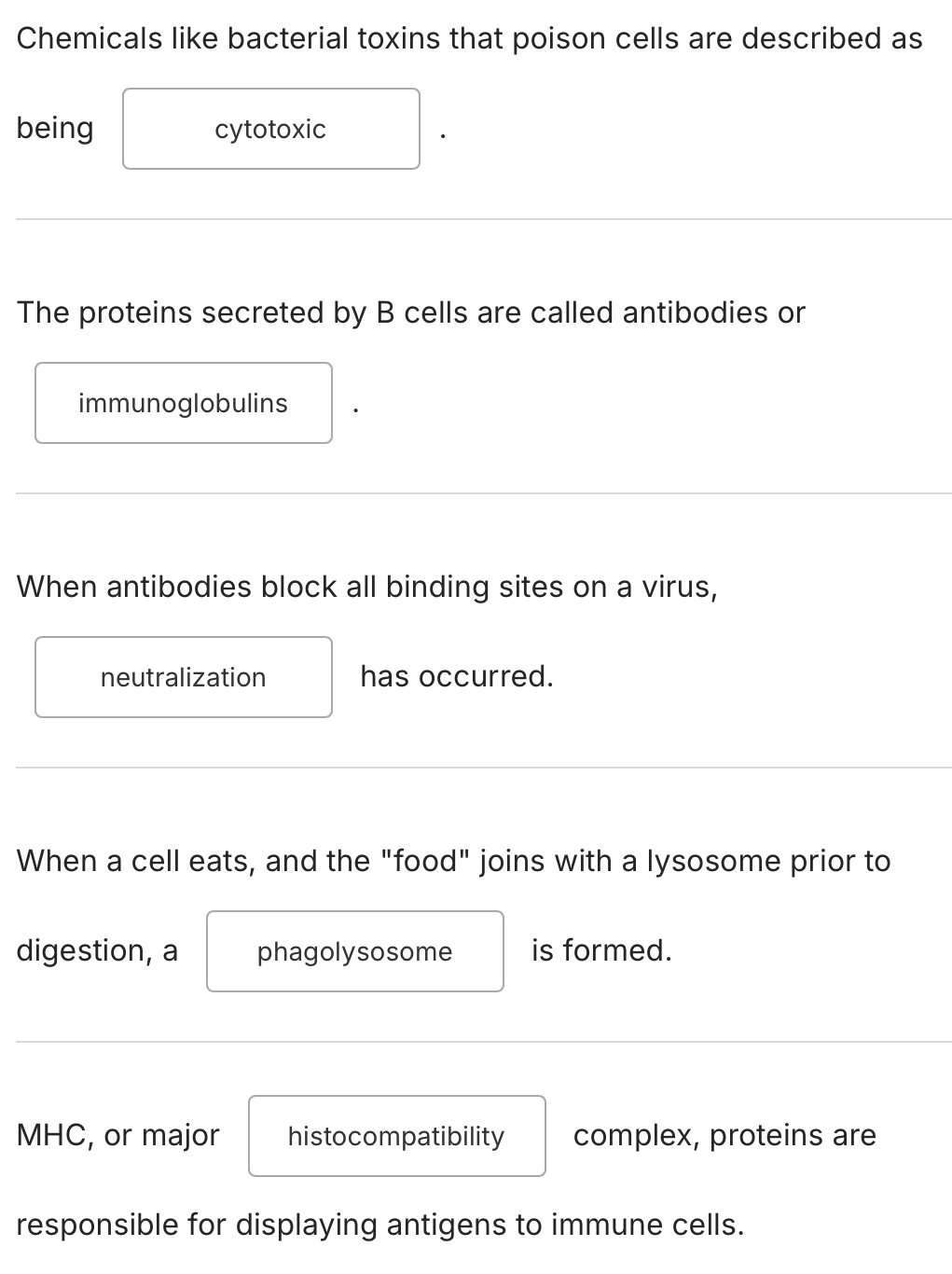
Which cells secrete histamines that trigger inflammatory pathways?
neutrophils
mast cells
NK cells
macrophages
Mast cells
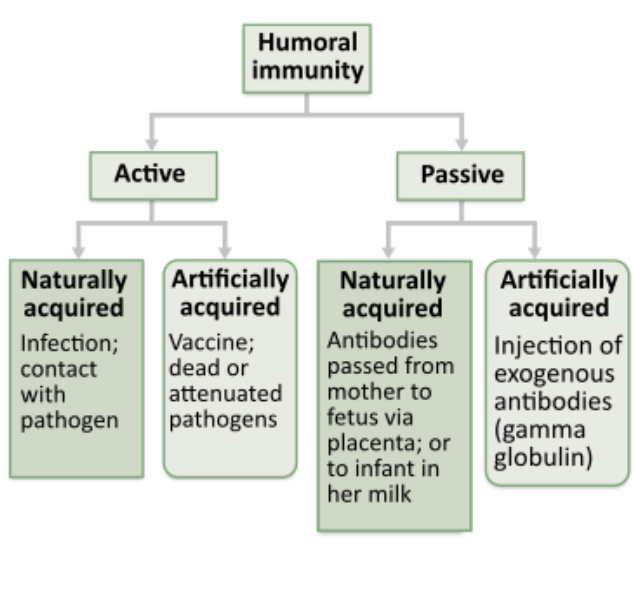
Which of the following best illustrates artificially acquired active humoral immunity?
antivenoms
antibodies received in breast milk
infection
vaccines
Vaccines
What part of the antibody's structure determines its class?
constant (C) region
variable (V) region
light (L) chain
heavy (H) chain
Constant (C) region
Which of the following phases involves white blood cells leaving capillaries?
diapedesis
leukocytosis
chemotaxis
margination
Diapedesis
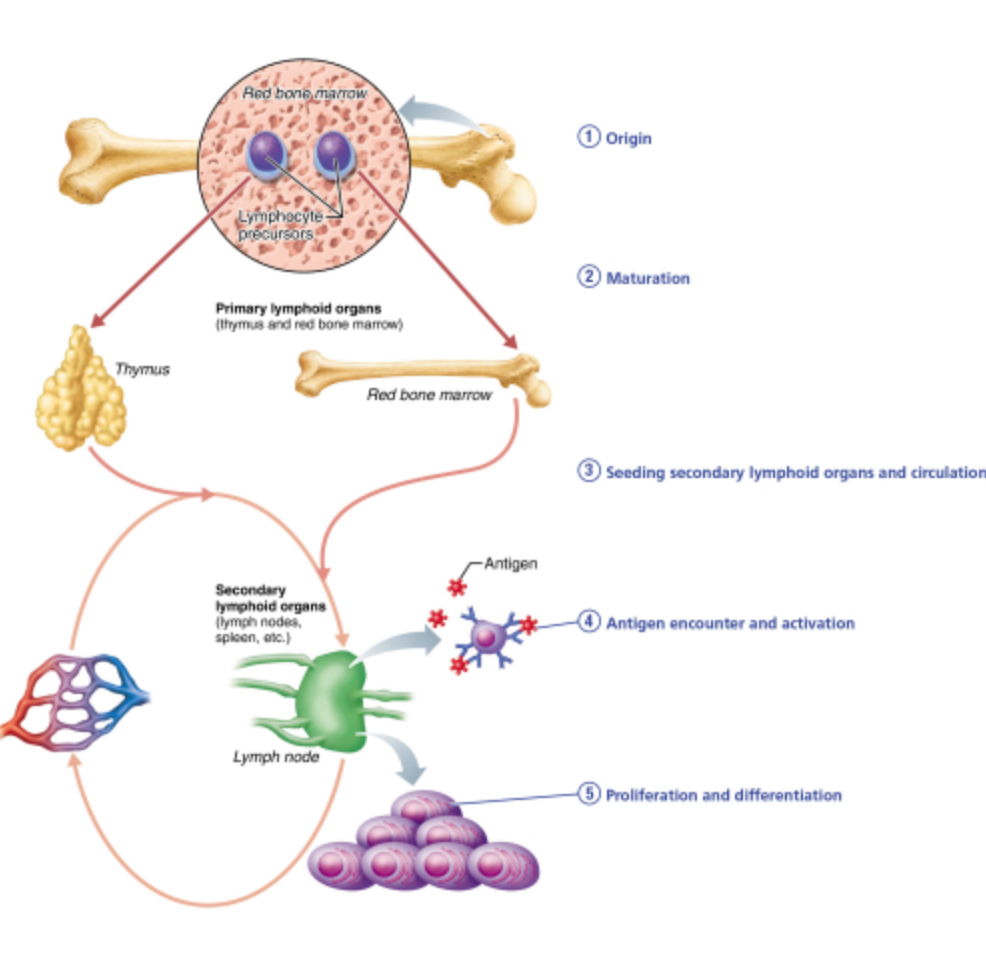
Which of the areas seen the figure must be occupied by T lymphocytes, at least for a while, but is NOT required for the production of B lymphocytes?
the thymus
the bone marrow
the general circulation
lymph nodes
The thymus
Which of the following inflammatory chemicals is/are released by mast cells?
histamine
kinins
prostaglandins
complement
Histamine
Which of the following provides a first line of defense against pathogens?
skin and mucous membranes
inflammation
antimicrobial proteins
complement
Skin and mucous membranes
In certain classes of antibody, the monomeric versions join to form dimers. What portions of the molecules adhere to each other to form these dimers?
the stem regions
variable regions of the light chain
variable regions of the heavy chain
the hinge regions
The stem regions
With what does our immune system coat pathogens to facilitate their capture and accelerate phagocytosis?
defensins
histamine
mucin
opsonins
Opsonins
Which of the following are properly matched?
IgA: first antibody released during primary immune response
IgM: secreted in tears
IgG: most abundant antibody
IgE: main antibody of the secondary immune response
IgG: most abundant antibody
Which of the following cells engulf antigens by phagocytosis and present fragments of them on their own surfaces for recognition?
NK cells
T lymphocytes
plasma cells
dendritic cells
Dendritic cells
Which of the following chemicals do NOT directly trigger Inflammation?
prostaglandins
kinins
antibodies
histamines
Antibodies
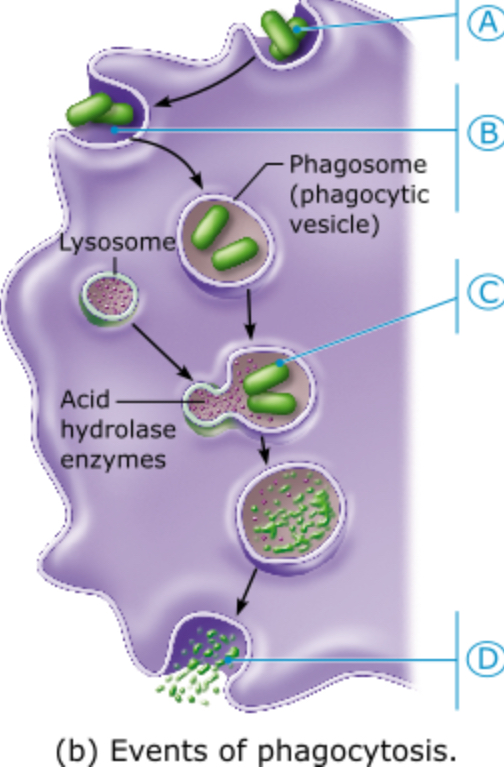
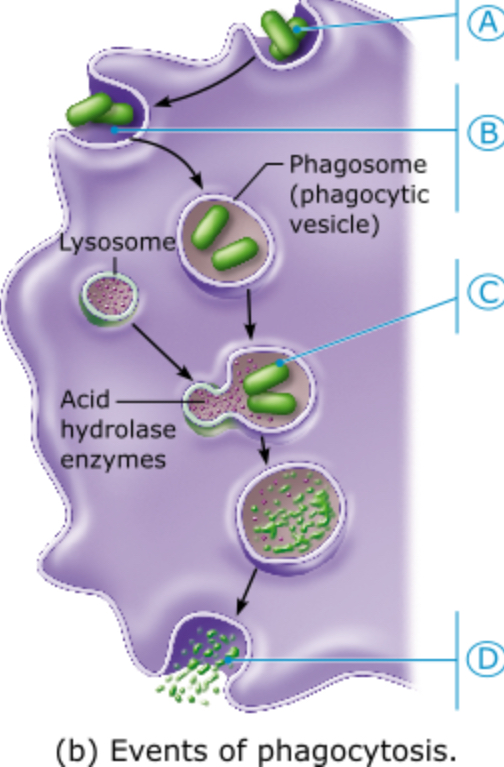
Which letter represents the formation of a phagolysosome resulting from the fusion of a lysosome with the phagocytic vesicle?
A
B
C
D
C
Which type of chemical induces fever?
antibodies
pyrogens
interferon
complement
Pyrogens
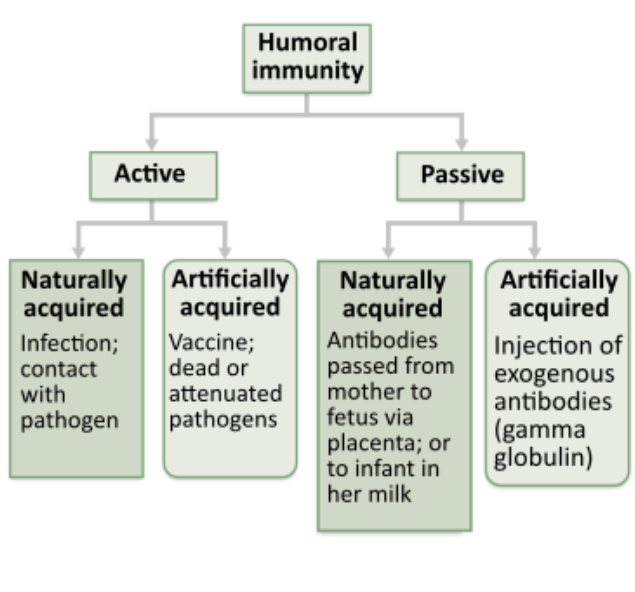
The antivenom used to treat a venomous snake bite is an antibody produced in an animal such as a horse. Suppose these antibodies are injected into a patient who was bitten by a venomous snake. How would you classify the resulting humoral immunity?
active immunity, naturally acquired
passive immunity, artificially acquired
active immunity, artificially acquired
passive immunity, naturally acquired
Passive immunity, artificially acquired
Which of the following statements regarding the primary versus the secondary immune response is true?
A primary response occurs faster than a secondary response.
A primary response results when naïve lymphocytes are activated, while a secondary response is a result of activating memory cells.
The antibodies produced in a primary response bind to antigens more efficiently than the antibodies produced in a secondary immune response.
A primary response leads to higher levels of antibodies than does a secondary response.
A primary response results when naïve lymphocytes are activated, while a secondary response is a result of activating memory cells.
Which leukocytes are sometimes referred to as "housekeeping" phagocytes because of their role in clearing (cleaning up) cell debris?
basophils
macrophages
lymphocytes
megakaryocytes
Macrophages
What is the most important reason you should not try draining an abscess by pressing on it?
too painful a process to perform
may result in a permanent scar
may spread infection to deeper tissue
releases large amounts of pus/debris
May spread infection to deeper tissue
Four (or five) cardinal signs indicate inflammation. What specific sign of inflammation is the result of exudate in the tissue spaces?
edema (swelling)
heat
pain
impaired function
Edema (swelling)
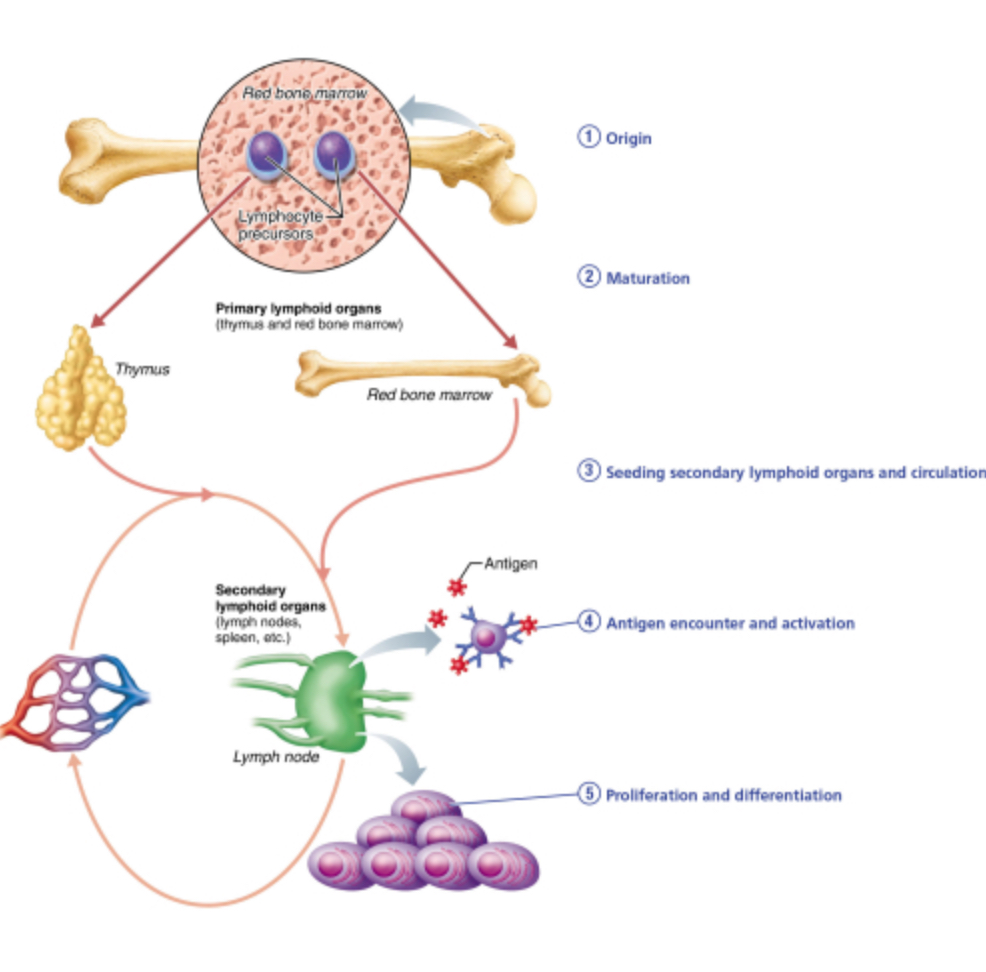
Proliferation of lymphocytes occurs immediately after which of these events?
activation
seeding of secondary lymphoid organs
entering the circulation
release from the bone marrow
Activation
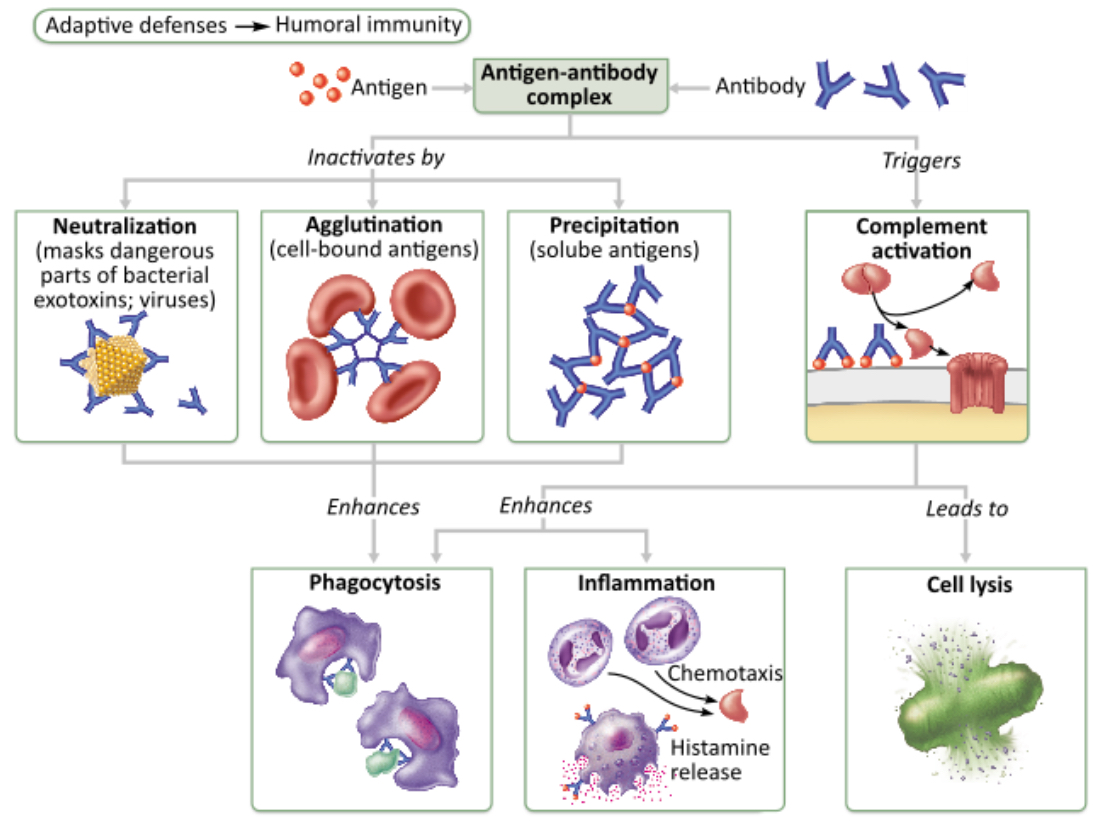
Which mechanism(s) of antibody action result(s) in cell lysis?
neutralization
precipitation
complement activation
agglutination
Complement activation
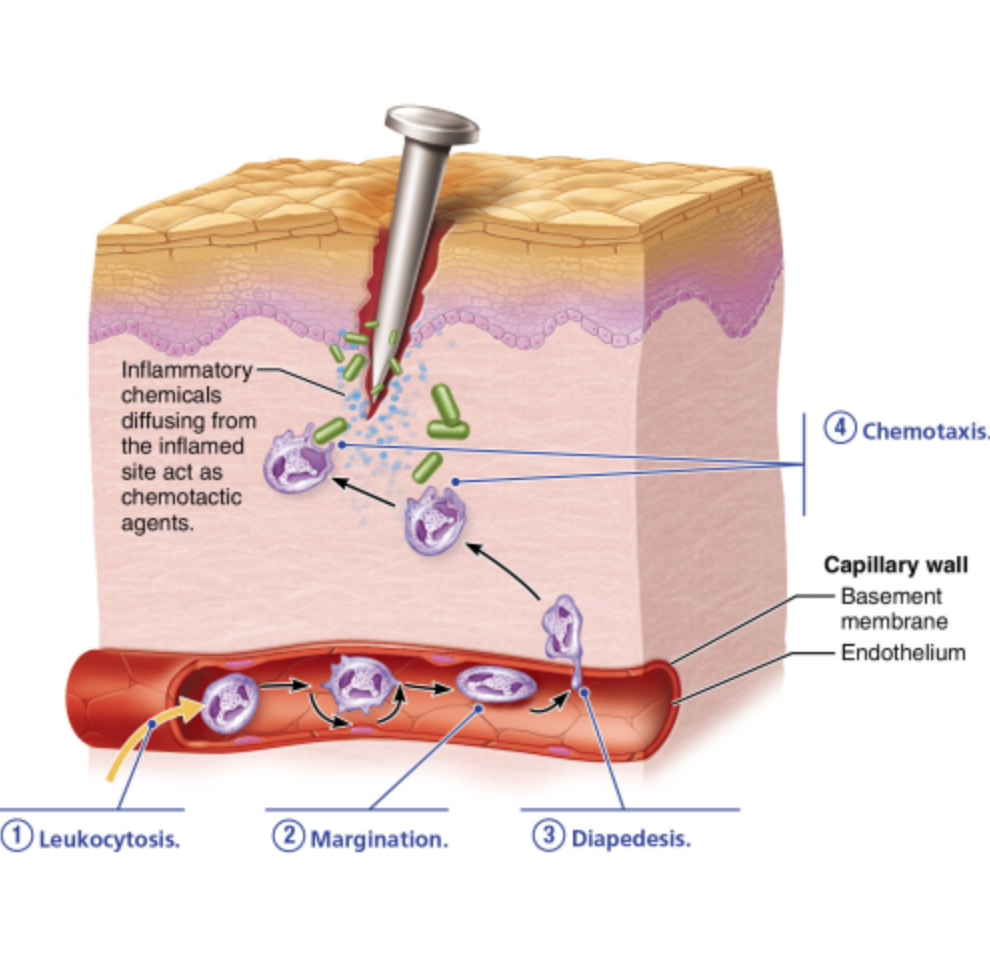
What characterizes flattening of neutrophils to squeeze between the endothelial cells of the capillary walls?
diapedesis
leukocytosis
chemotaxis
margination
Diapedesis
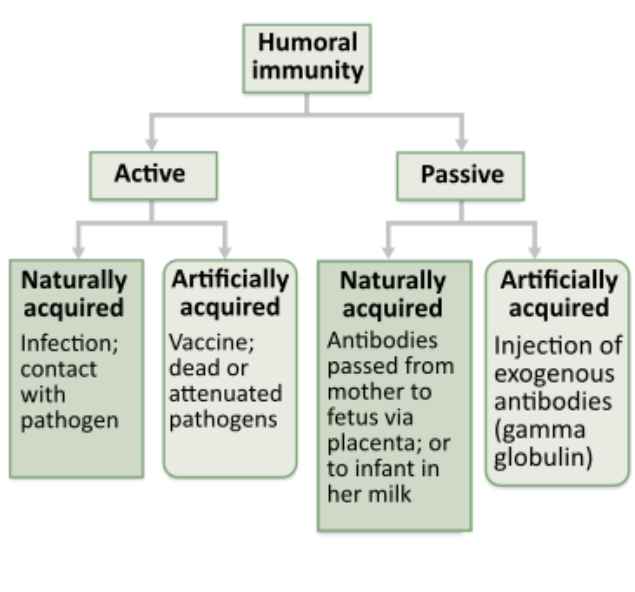
Which of the following should produce naturally acquired active immunity?
drinking breast milk
injections of antibodies produced by a goat
recovering from the chicken pox
getting a flu vaccine
Recovering from the chicken pox
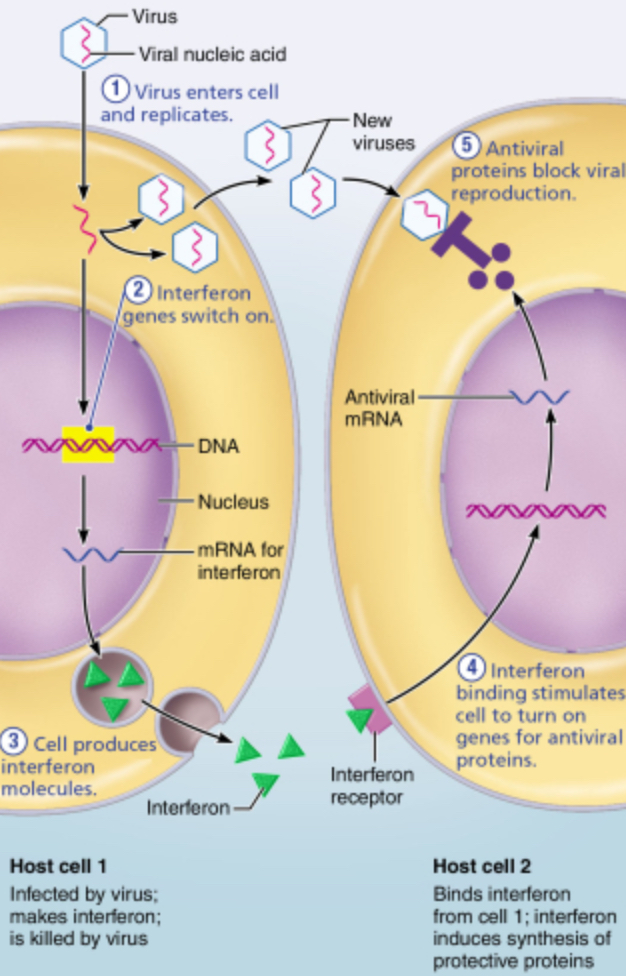
What is/are the specific target(s) of interferons?
the DNA of the cell making the interferon
the DNA of healthy cells
the membrane receptors on healthy cells
the immature viruses in infected cells
The membrane receptors on healthy cells
What type of cell is the precursor to the helper T cell?
regulatory T cell
CD8 cell
memory T cell
CD4 cell
CD4 cell

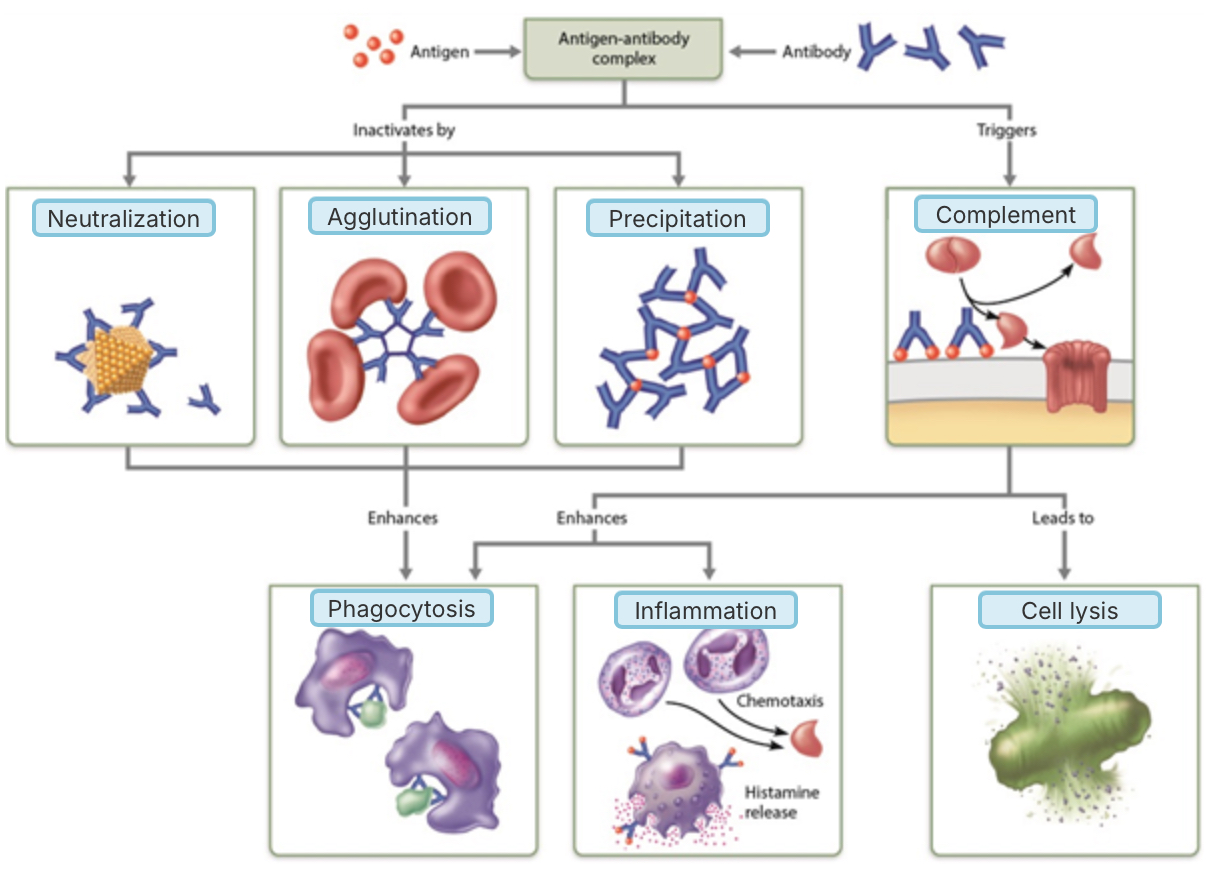
How many sites on this antibody molecule have potential to bind to a non-self molecule?
1
2
3
4
2
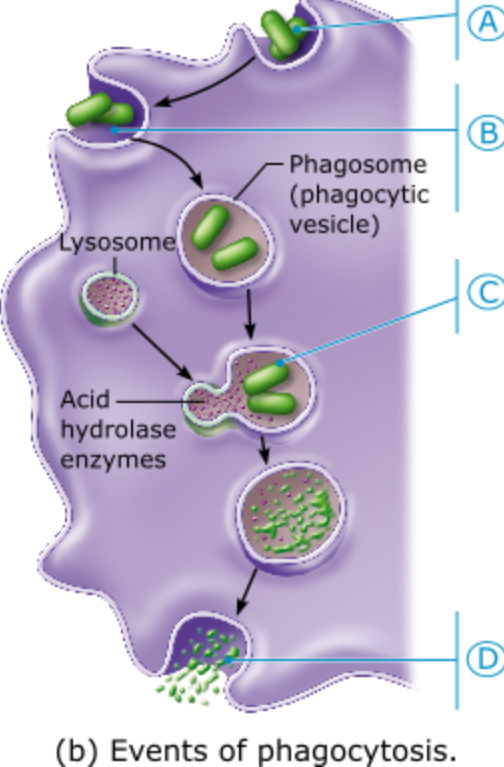
What type of immune system cell performs the most phagocytosis in the
body?
macrophages
B lymphocytes
natural killer, or NK, cells
neutrophils
Macrophages
Health workers working with diphtheria commonly receive a serum with antibodies against the pathogen. What type of immunity would this be?
passive, artificial immunity
passive, natural immunity
active, artificial immunity
active, natural immunity
Passive, artificial immunity
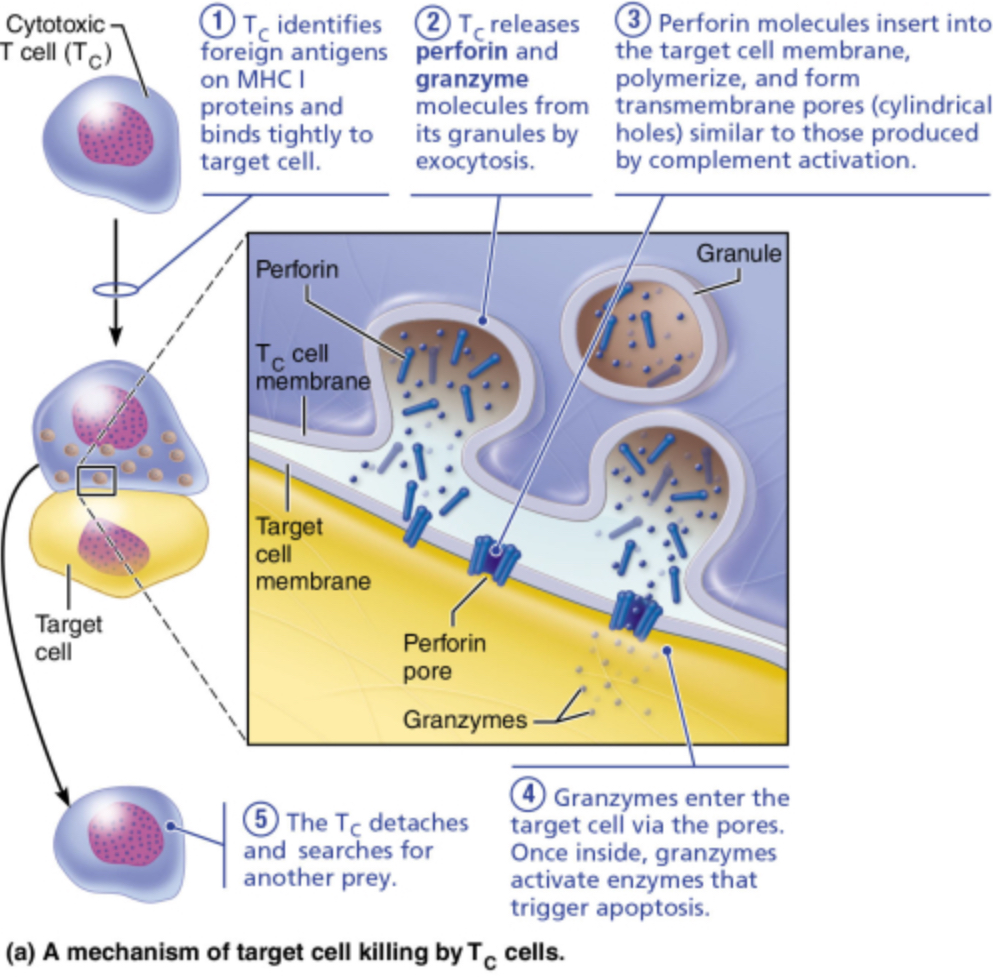
Which of these mechanisms do cytotoxic T (TC) cells use to destroy a target--that is, to deliver a lethal hit?
producing antibodies
agglutination of target cells
perforation of the membrane
opsonization
Perforation of the membrane
Which of the following statements does not describe the adaptive immune response?
It occurs immediately after the body is challenged by foreign material.
It is systemic.
It has memory.
It is specific.
It occurs immediately after the body is challenged by foreign material.