Psychology Unit 5: mental and physical health
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
health psychology
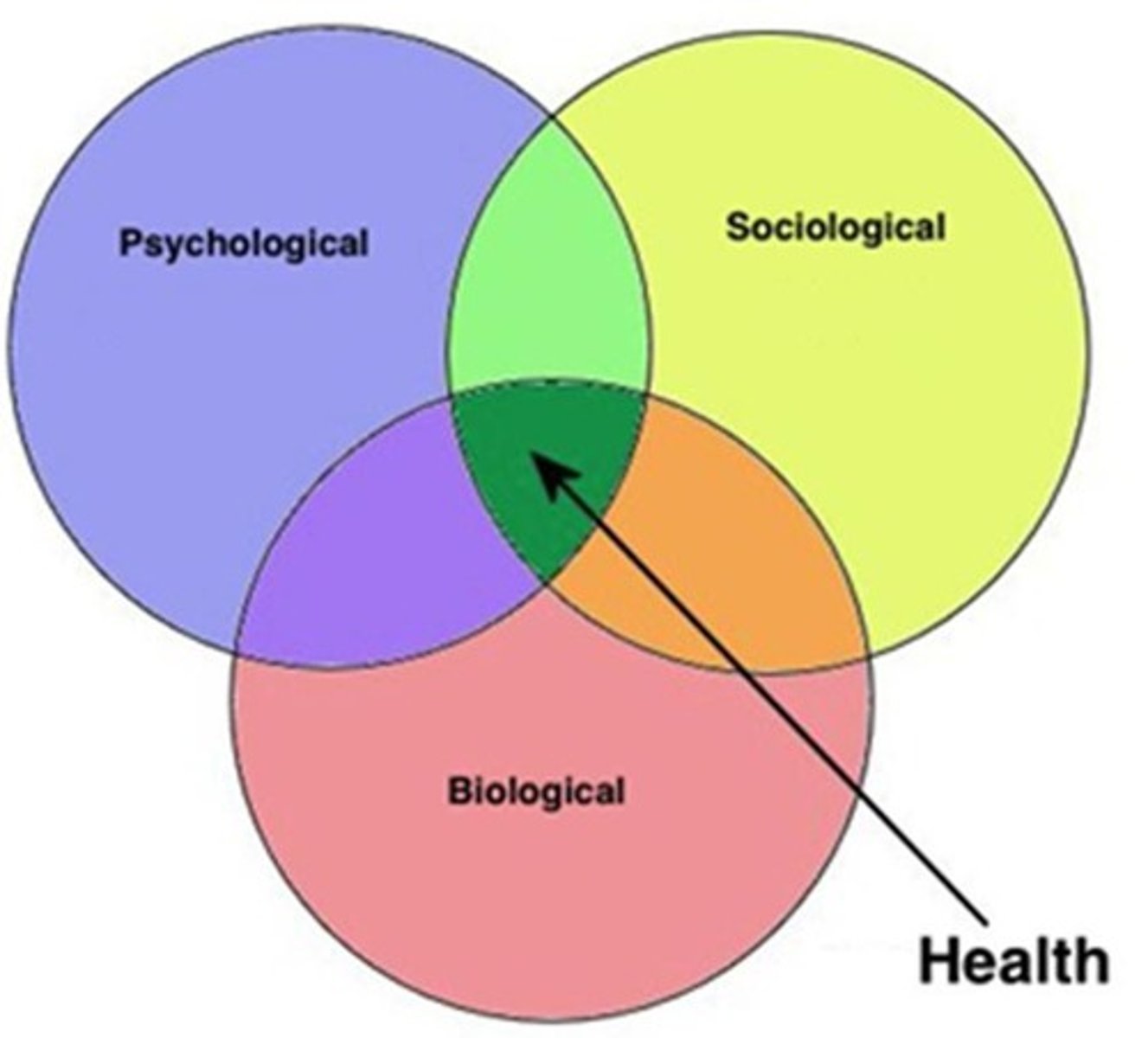
Domain of psych that uses biopsychosocial model to study how people stay healthy, why they become ill, and how they respond when they do become ill
Eustress
motivate us

Distress
deliberate us

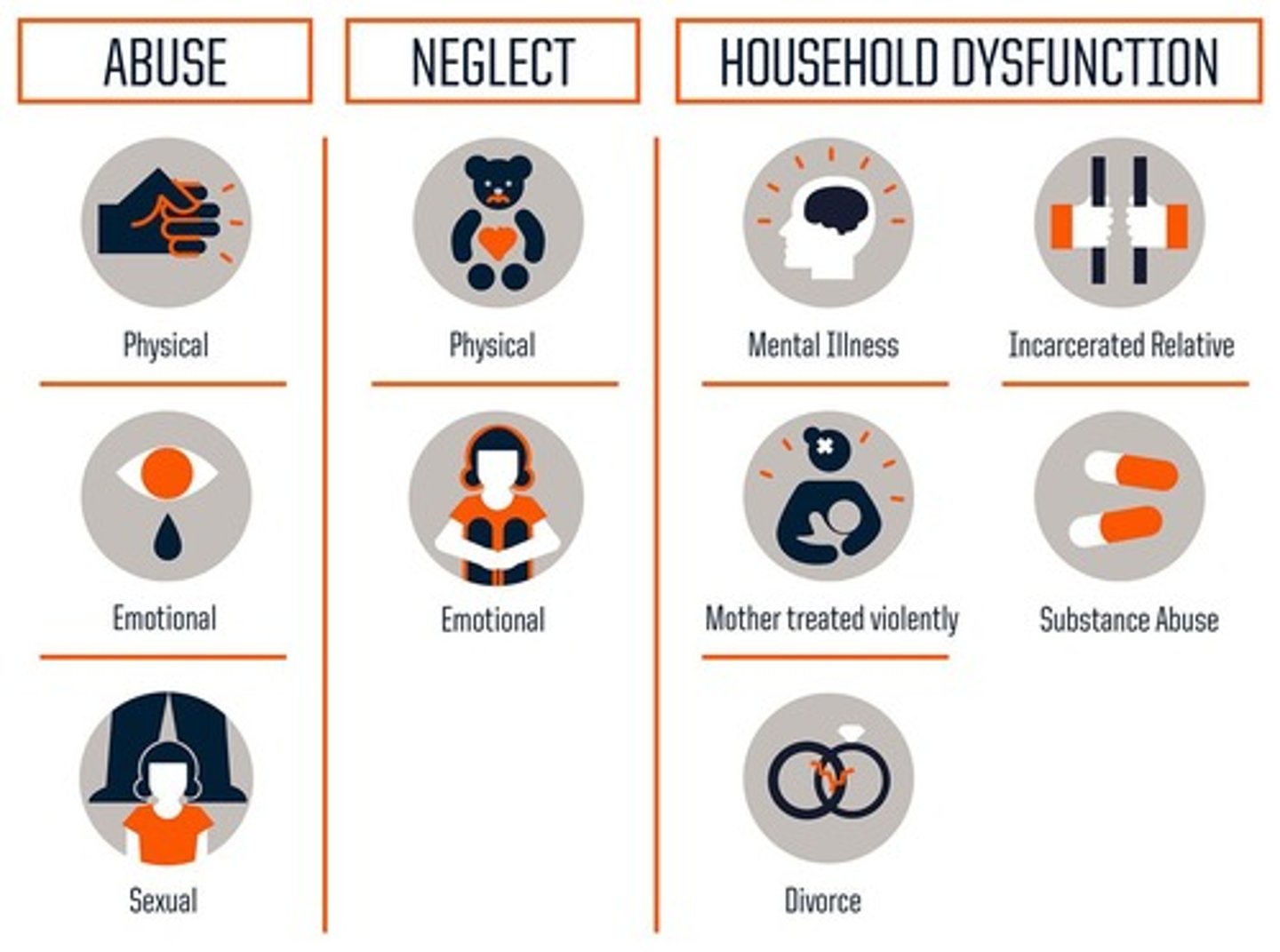
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
traumatic childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, violence exposure, or death of a parent, that are linked to mental and physical health problems later in life
resilience
the ability to adapt effectively in the face of threats

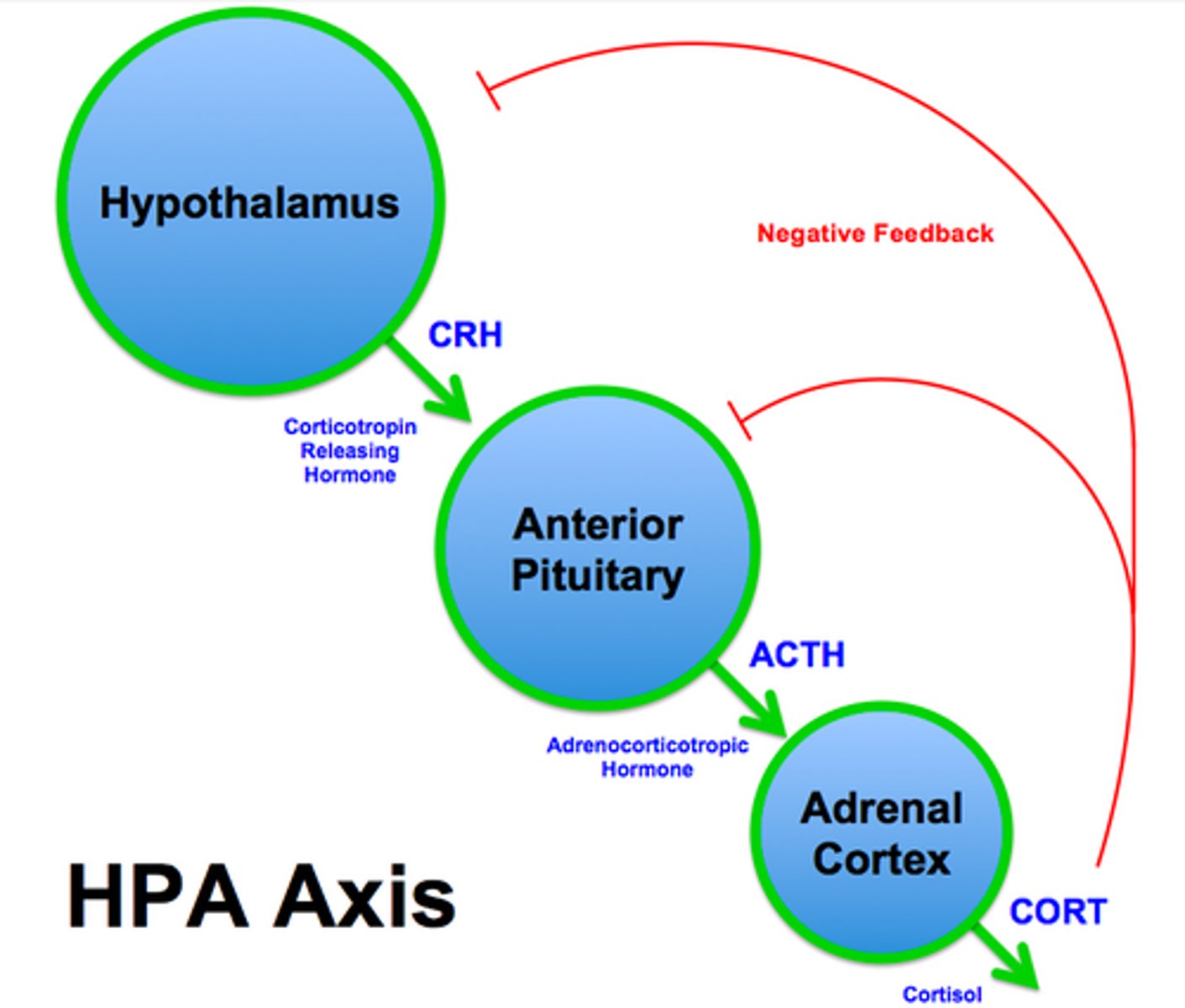
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system
a major neuroendocrine pathway relevant to the stress response involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the adrenal cortex
general adaption syndrome (GAS)
the body's adaptive response to stress in three states - alarm, resistance, exhaustion
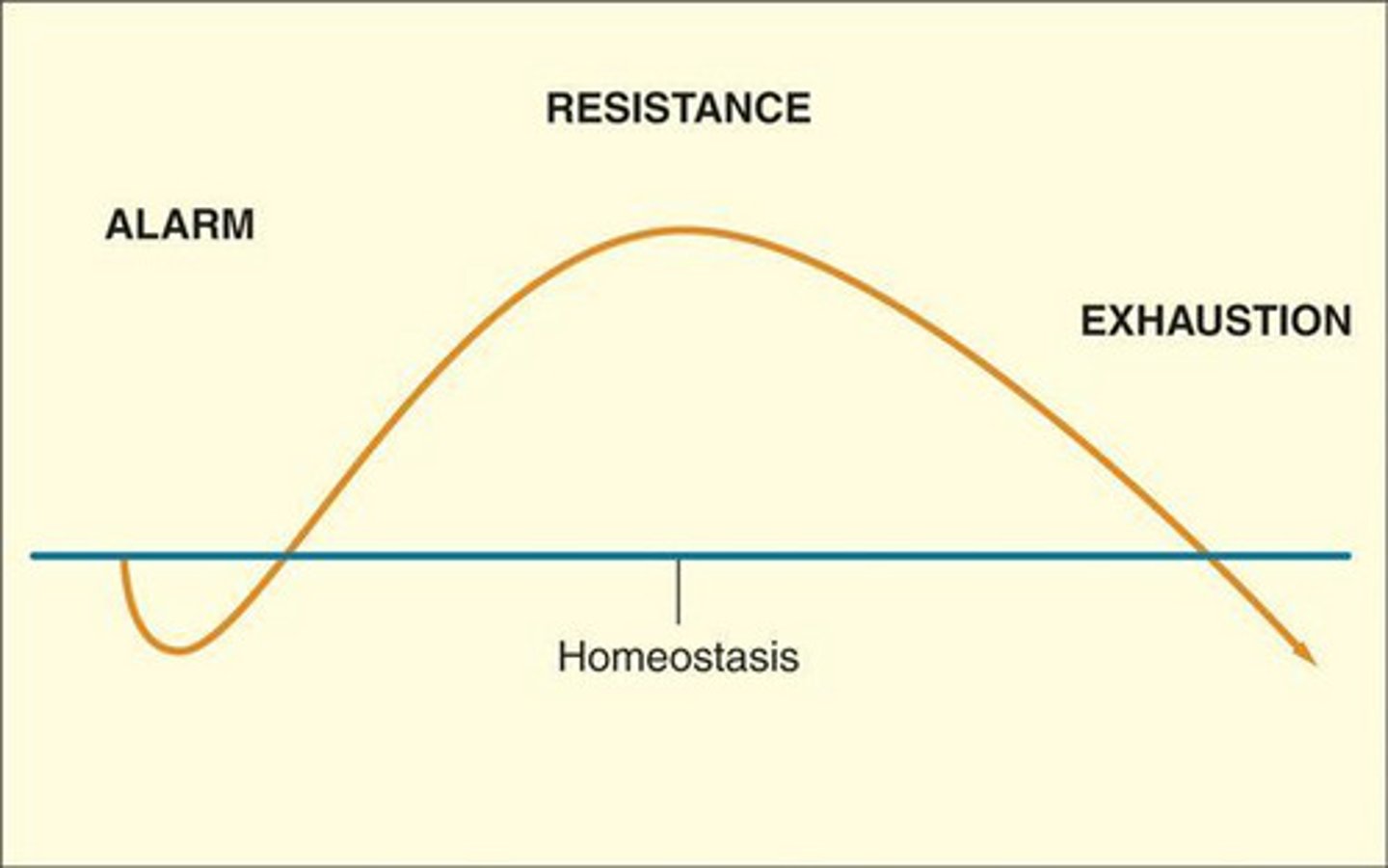
general adaption syndrome (GAS) leads to
physiological issues like hypertensions, headaches and immune suppression in the exhaustion stage of GAS since the alarm stage takes up too many resources)
tend and befriend
under stress, people (especially women) often provide support to others (tend) and bond with and seek support from others (befriend)
Coping
dealing with problems and troubles in an effective way

types of coping
problem focused and emotion focused
problem-focused coping
a type of coping in which people take direct steps to confront or minimize a stressor

emotion-focused coping
a type of coping in which people try to prevent having an emotional response to a stressor

learned helplessness
the tendency to fail to act to escape from a situation because of a history of repeated failures in the past

positive psychology
Identifies factors that lead to well-being, resilience, positive emotions, and psychological health

well-being
Feeling good about one's life

adaption-level phenomenon
our tendency to form judgements relative to a neutral level defined by our prior experience
relative deprivation
the perception that we are worse off relative to those with whom we compare ourselves
broaden and build theory
theory proposing that happiness predisposes us to think more openly
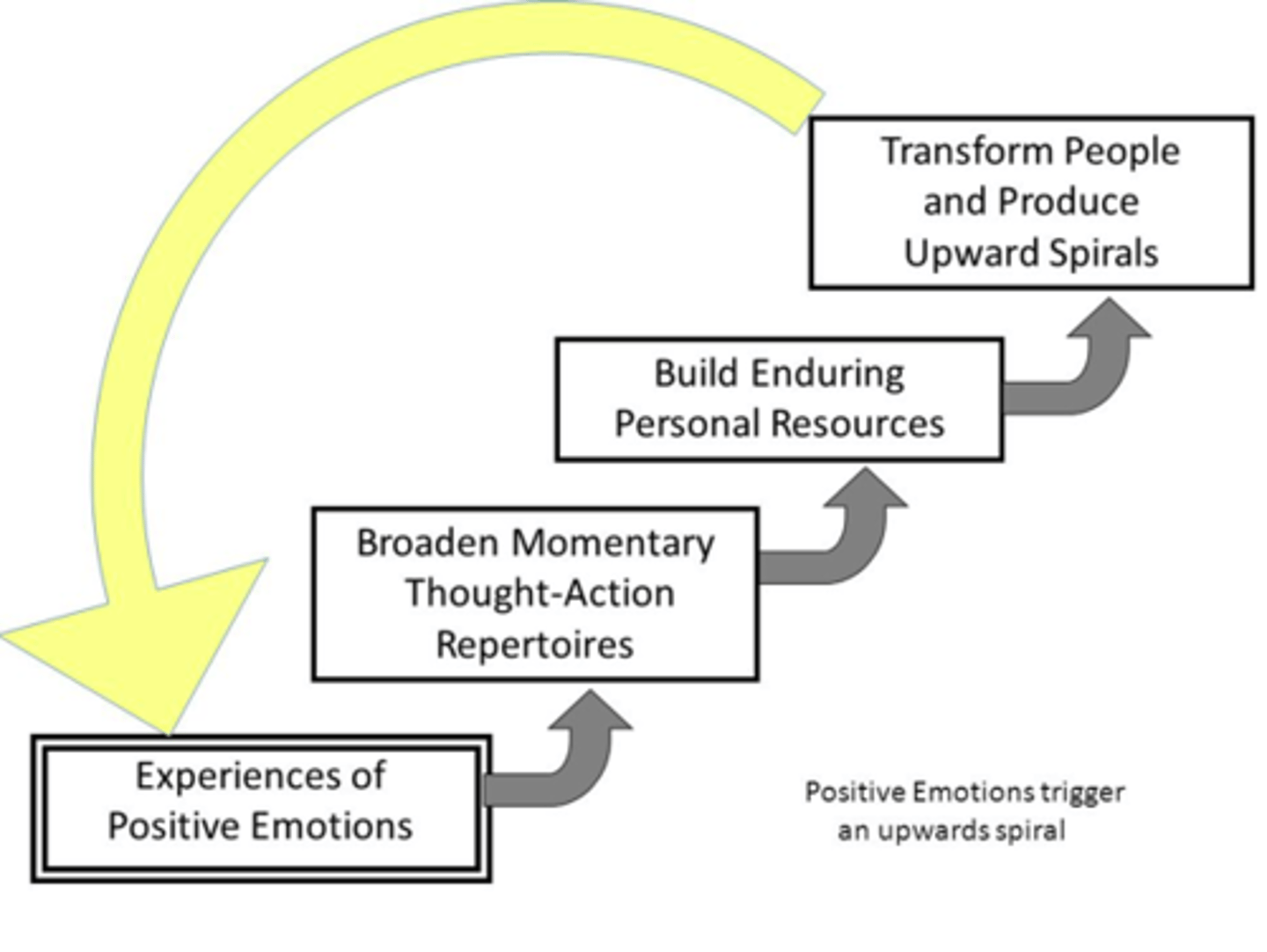
Signature Strengths & Virtues
Character strengths and virtues that are personally fulfilling, intrinsic to one's identity, and contribute to the collective well-being.

post-traumatic growth
positive psychological changes as a result of struggling with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises

critera used to evalute if behaviors/mental processes are a psychological disorder
-Level of dysfunction
-Level of distress
-Deviation of socail norm
Rosenhan Study
study in which healthy individuals were admitted into mental hospitals after saying they were hearing voices. Once in, they acted normally and still were not labeled as impostors.
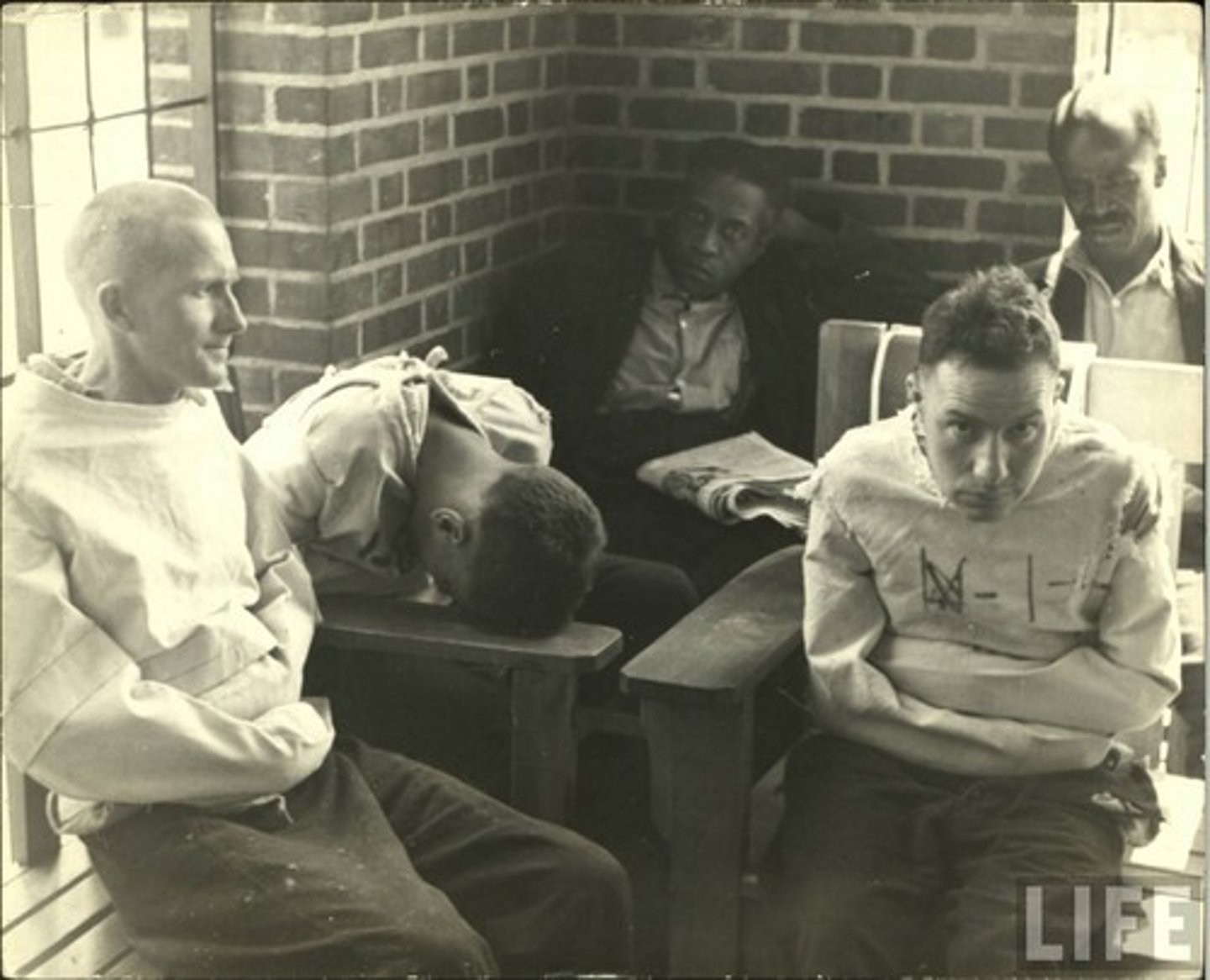

Rosenhan effect
Once someone is given a mental illness label, it's hard for others to see them differently, and therapists might stick to that label instead of seeing how the person changes or improves.

Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
Where disorders are classified by symptoms and described (provides diagnosis not treatment or explanations)

International classification of mental disorders (ICD)
used by the international health organization which is updated regularly to respond to new research and advances in practice

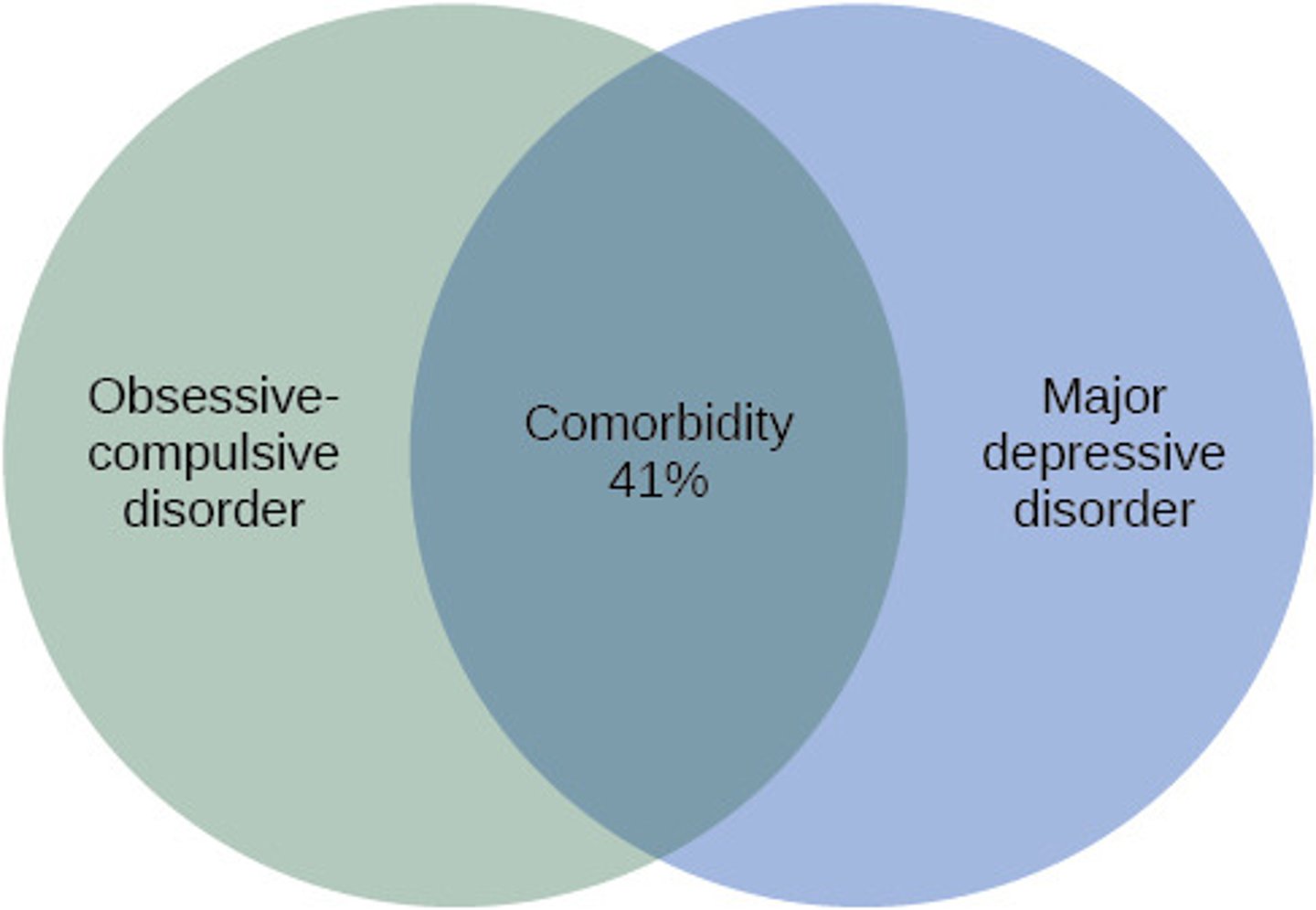
Comorbidity
The coexistence of two or more disorders.
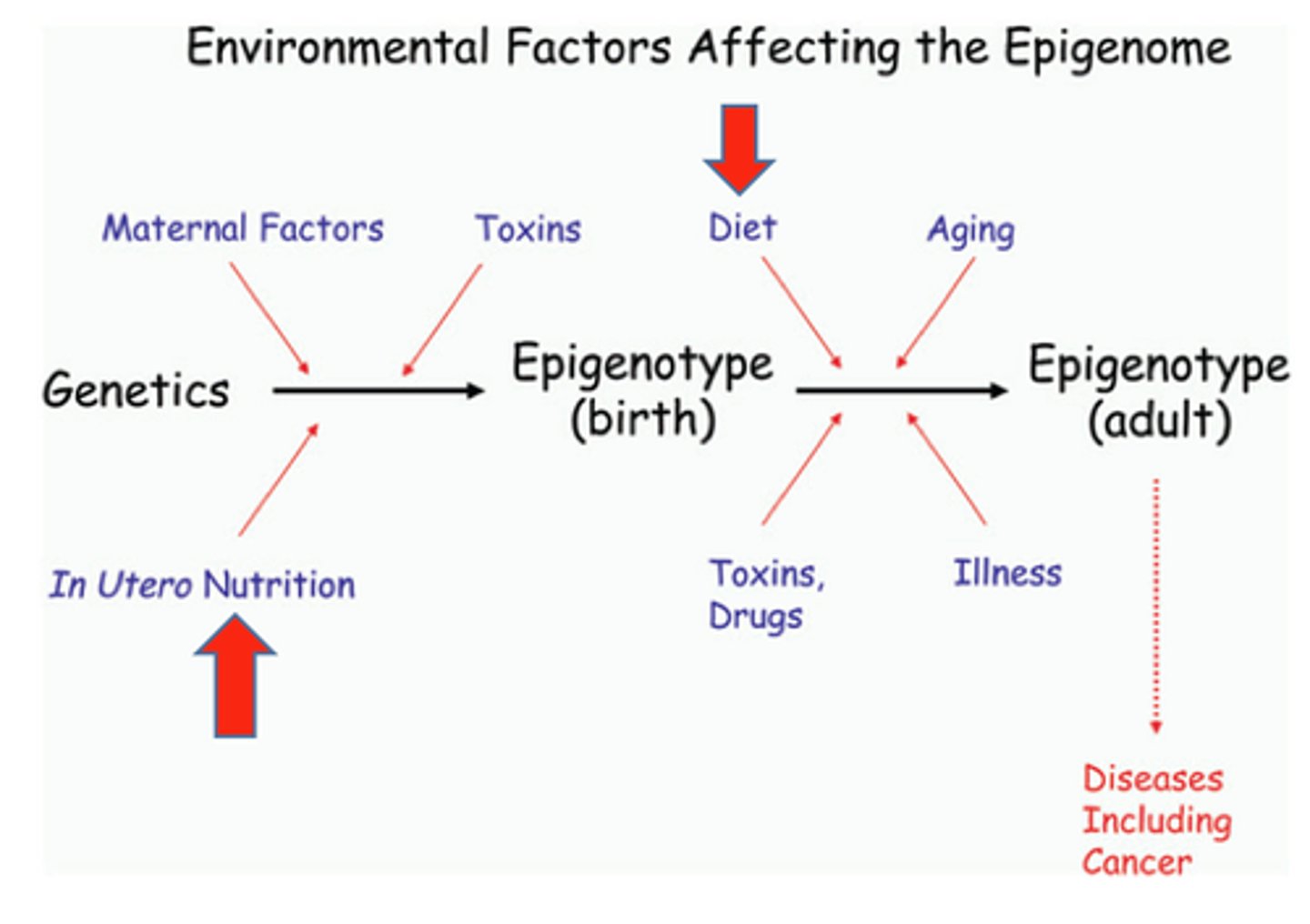
Epigenetics
Chemical marks on your DNA express how much a gene is expressed. The environment affects those marks
Prevalence
fraction of a population having a specific disease at a given time

eclectic approach
an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client's individual problems, uses techniques from a blend of different approaches

Psychological Perspectives
biological, behavioral, cognitive, evolutionary, humanistic, psychodynamic, sociocultural
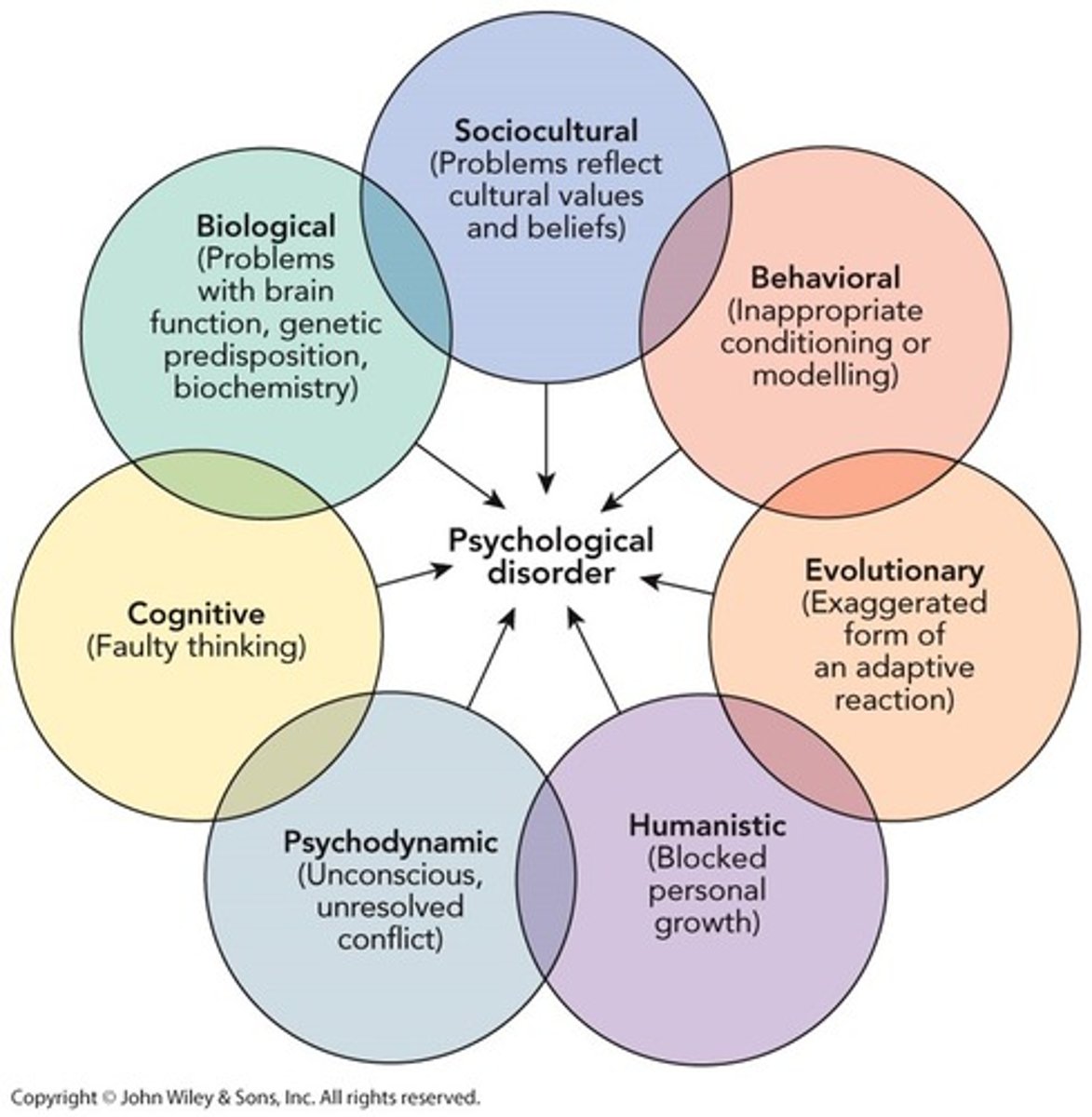
Psychodynamic perspective
Intrapsychic conflict, caused by repressed trauma, thoughts, ect (esp from 1-5 yrs) - distress happens when they try to break from the unconscious
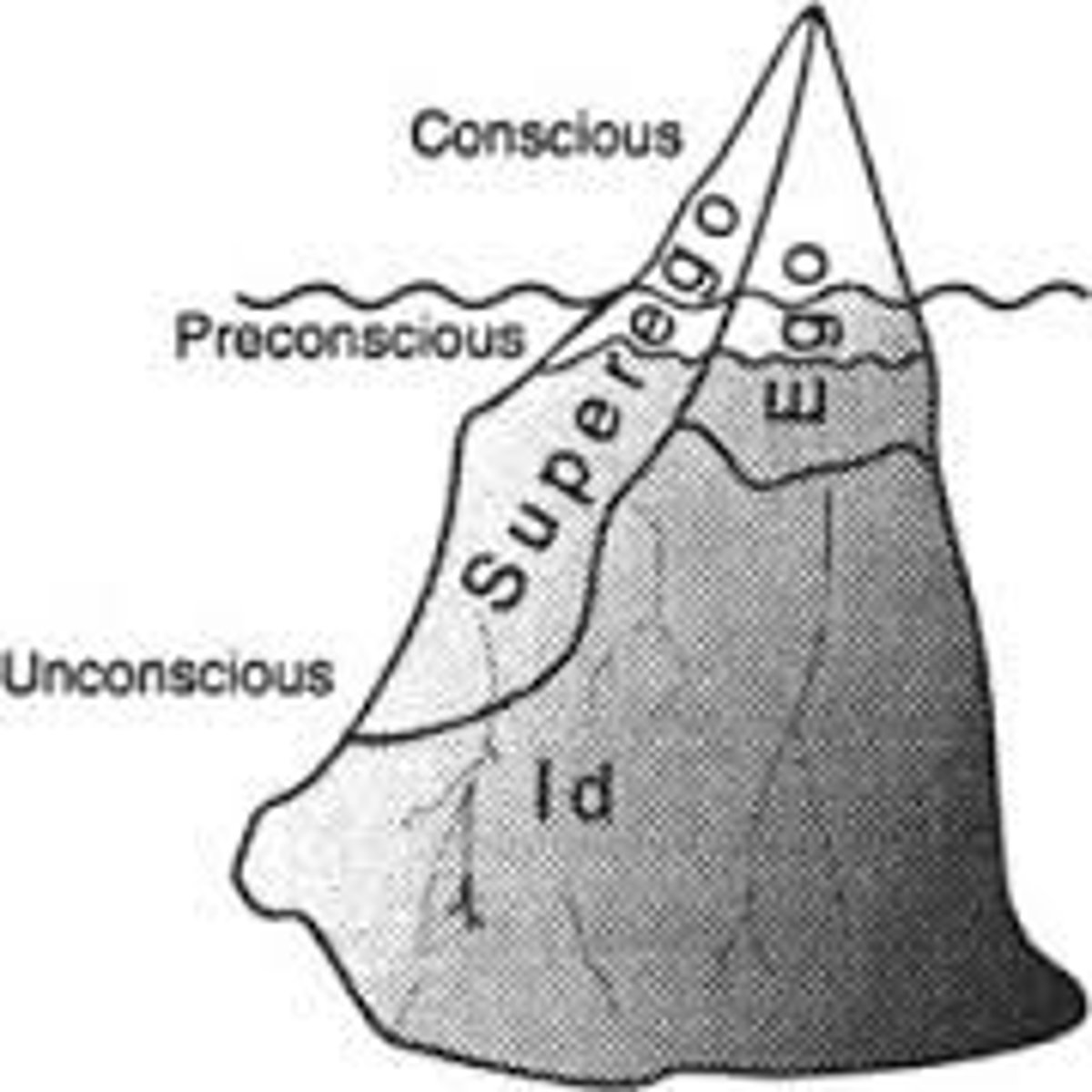
Behavioral perspective
Disordered behaviors are learned (were classically conditioned or are being reinforced)
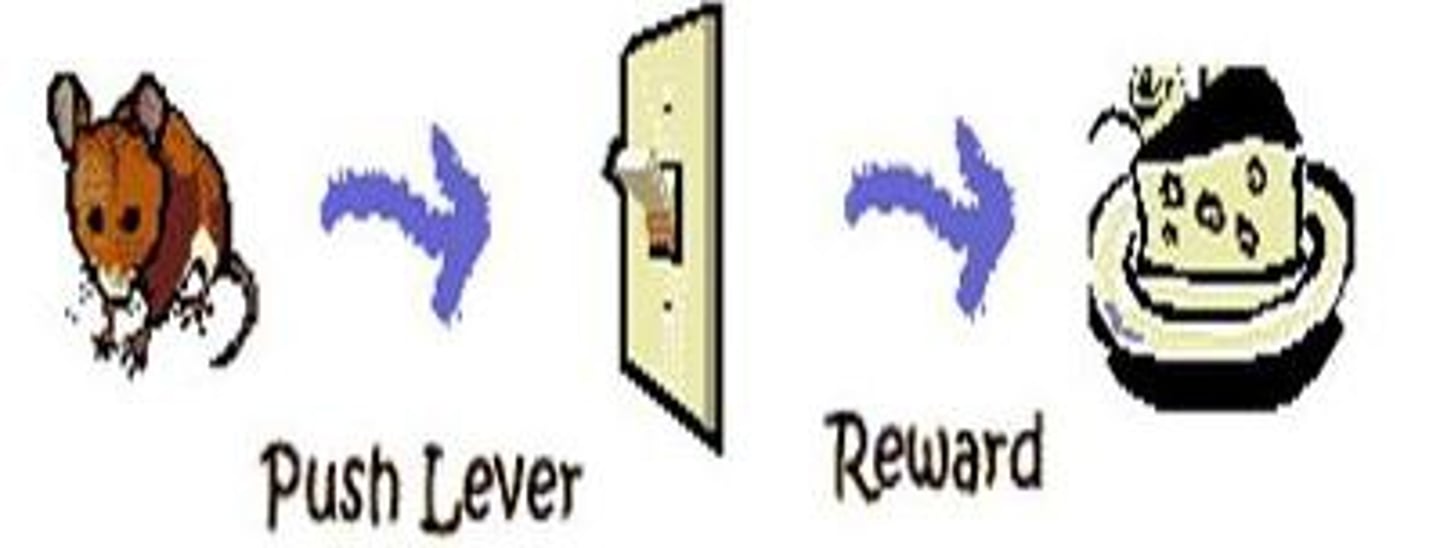
Cognitive perspective
faulty/ illogical thoughts, maladaptive thinking

Biological perspective
Organic cause; structural or chemical abnormalities in the brain, hormonal or neuro transmitter imbalances, genetic predisposition (focus of psychiatrists)
sociocultural perspective
Acceptable behavior is defined by society and culture so going against them labels you as abnormal

medical model
the concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and, in most cases, cured.
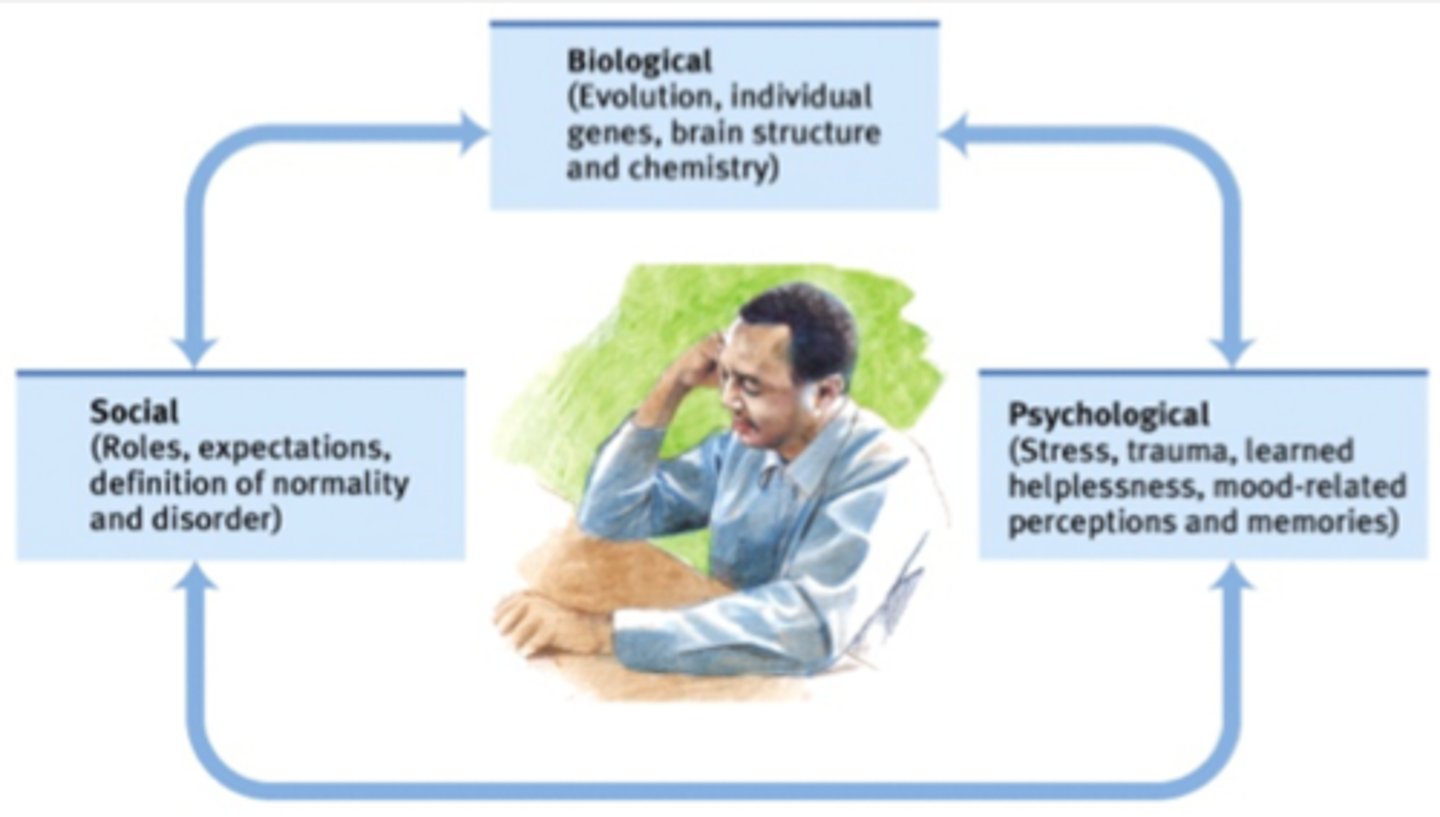
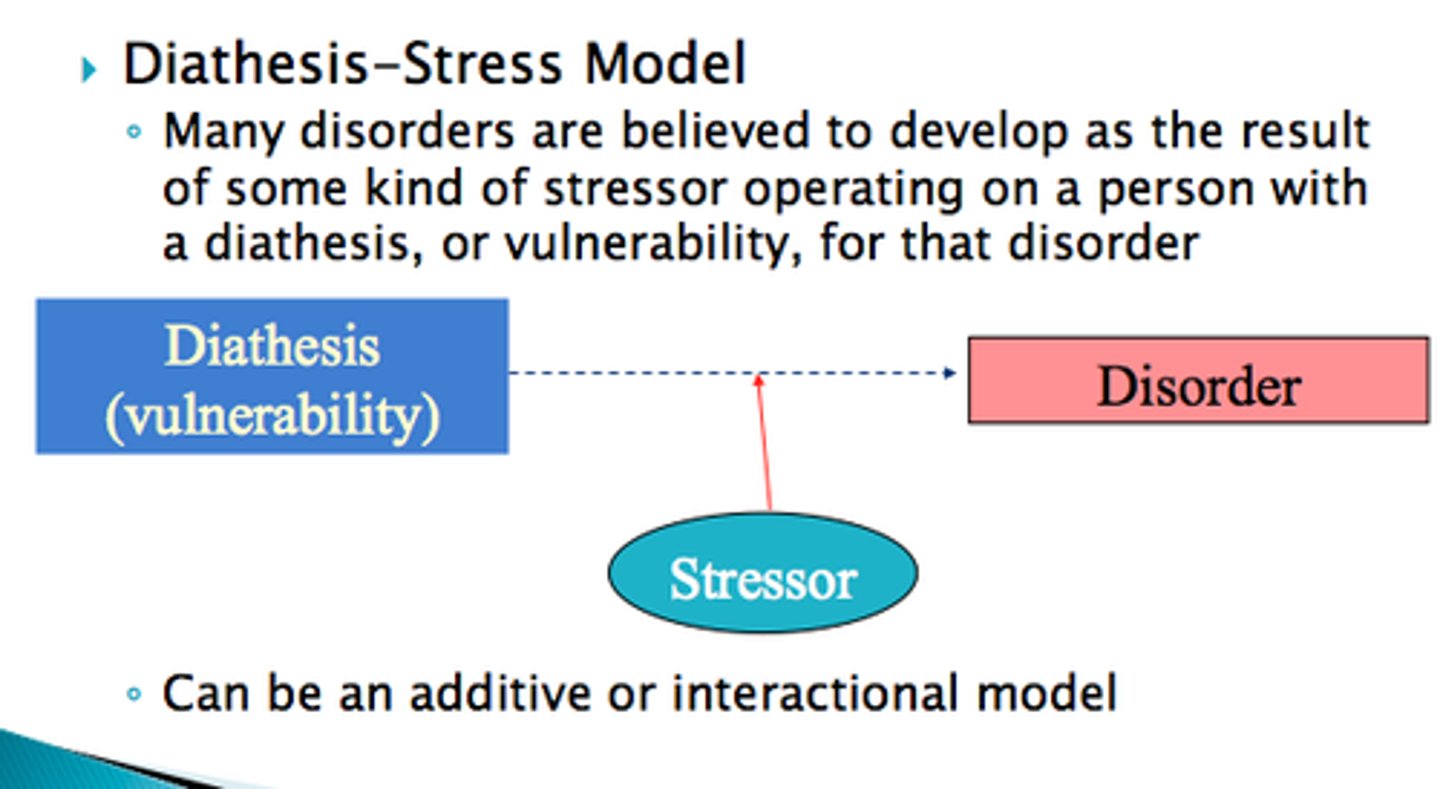
interaction models include...
biopsychosocial and diathesis-stress model
bio-psycho-social perspective
a contemporary perspective which assumes that biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors combine and interact to produce psychological disorders
diathesis-stress model
vulnerability to mental illness in nature (diathesis) and nurture (stress) combined - protective and risk factors mediate between them
Neuro-developmental Disorders
Attention deficit/ Hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)

Attention deficit/ Hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
a psychological disorder marked by extreme inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity

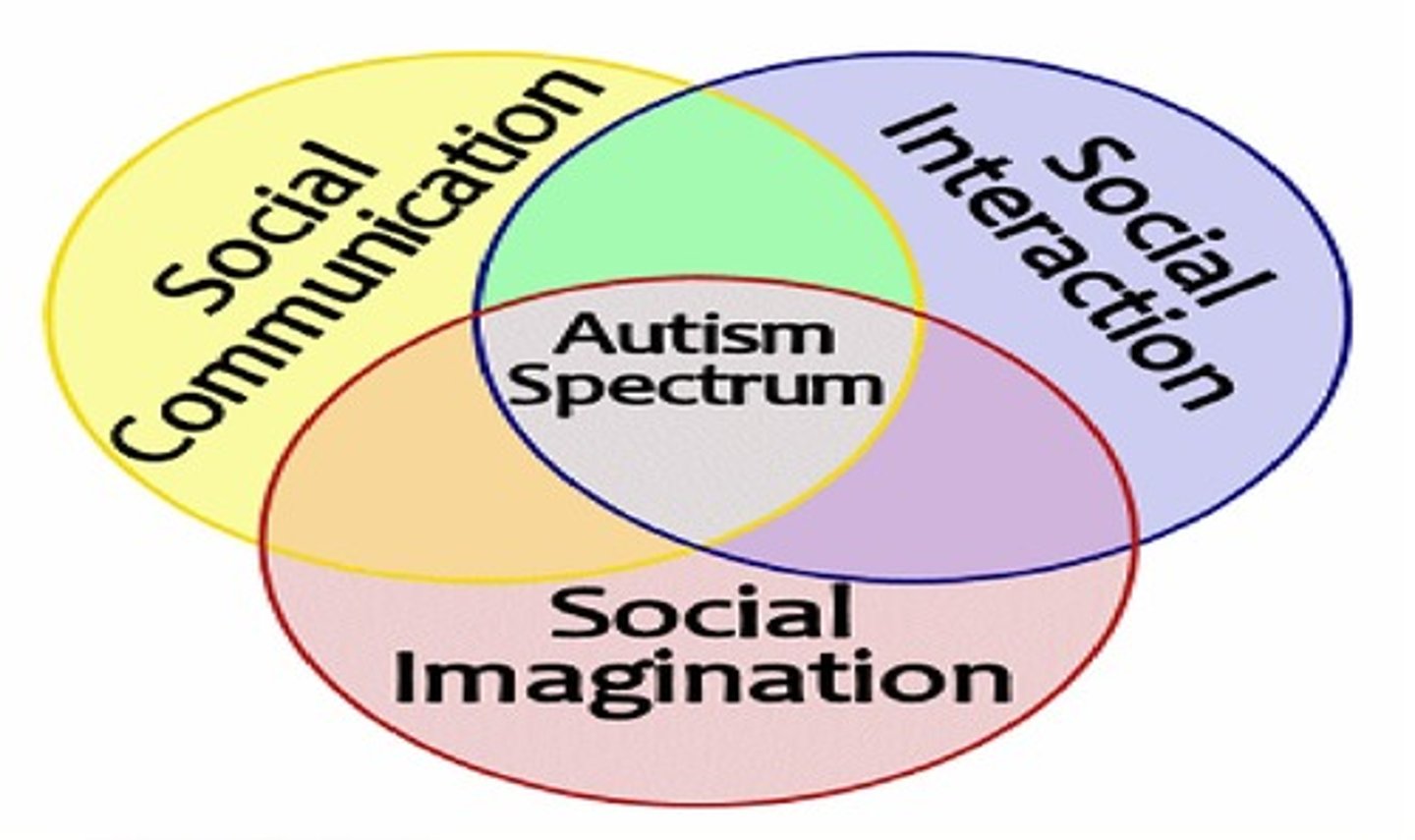
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
A disorder characterized by deficits in social relatedness and communication skills that are often accompanied by repetitive, ritualistic behavior.
Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder
Spectrum of thought and behavior that feature the breakdown of integrated personality and distributed/ inappropriate emotional responses to environmental stimuli

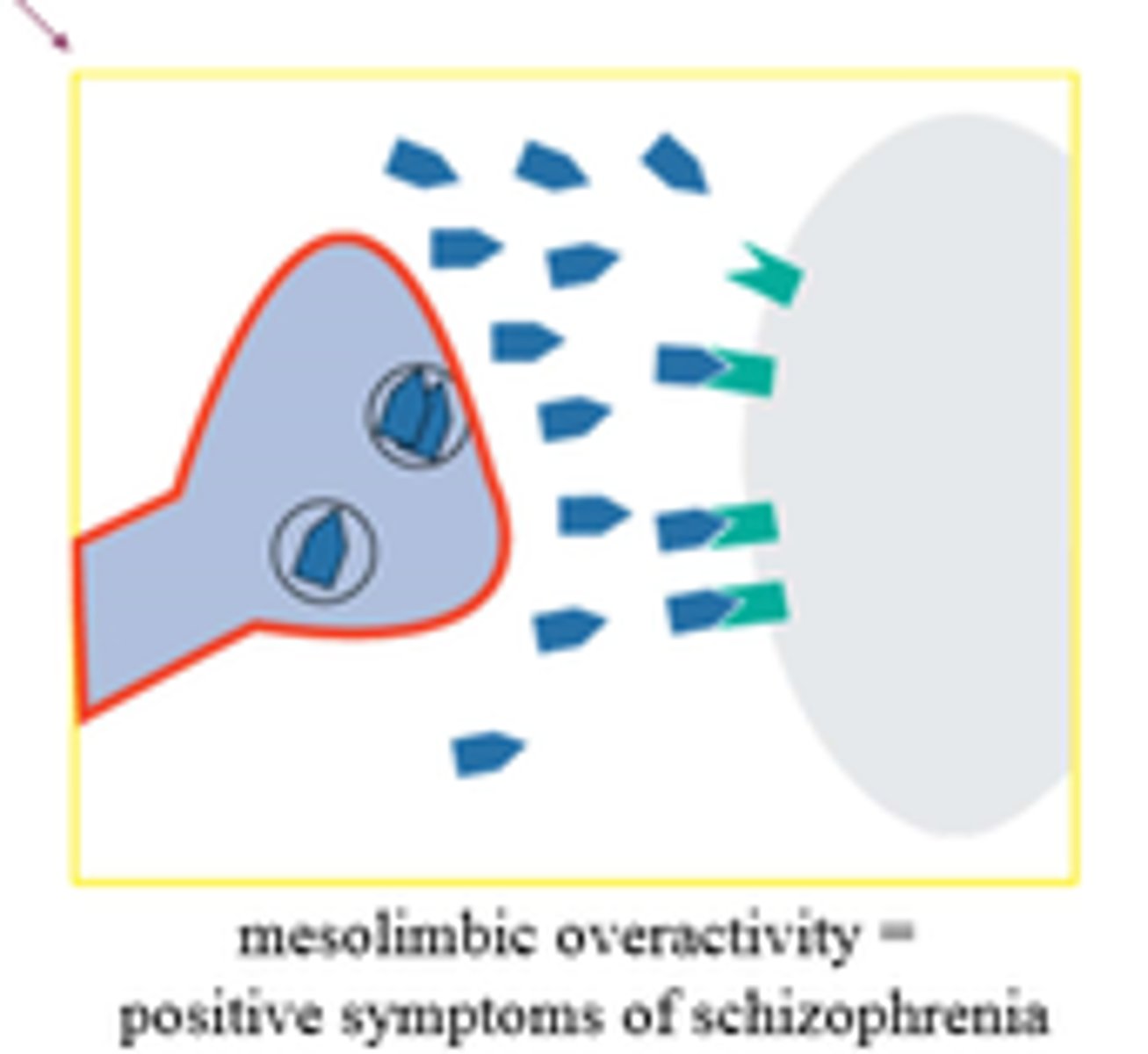
postitive symptoms of schizophrenia
unexpected symptom

negative symptoms of schizophrenia
something is missing that you would expect

Schizophrenia symptoms
Delusions
hallucinations
disorganized thinking or speech (ex: word salad)
disorganized motor behavior (ex: catatonia)
lack of typical behavior (ex: flat affect or catatonic stupor)
Delusions
Positive schizophrenia symptom- false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur

Hallucinations
Positive schizophrenia symptom- sensory perception but no stimulus

Word salad
Positive schizophrenia symptom- non sensical string of words
catatonia
Excessive or bizarre movements, like repetitive gestures or strange postures

catatonic stupor
Complete lack of movement or speech

flat affect
a lack of emotional responsiveness

dopamine hypothesis
schizophrenia is linked to an imbalance of dopamine
Depressive disorder
sad, empty, or irritable moods along with cognitive and physical changes that interfere with the ability to function

Types of Depressive Disorders
major depressive disorder and persistent depressive disorder

major depressive disorder
a mood disorder in which a person feels sad and hopeless for weeks or months

presistant depressive disorder
Less intense but long-lasting depression — symptoms last for 2 years or more, more like a constant low mood.
are men or women more likely to get diagnosed with depression?
women
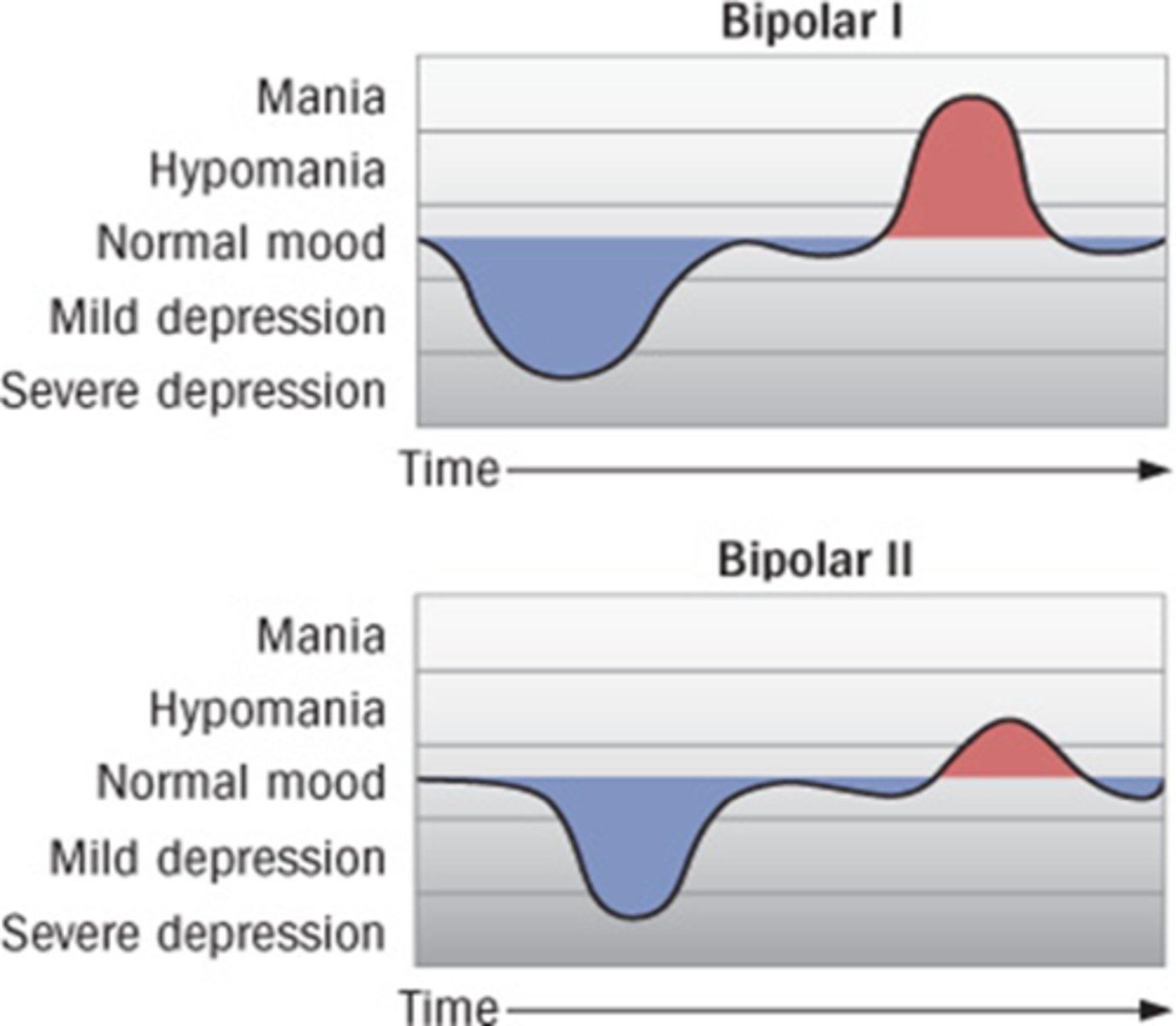
bipolar disorder
Characterized by manic (may include delusions/ hallucinations) and depressive episodes.

Types of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar I
Bipolar II
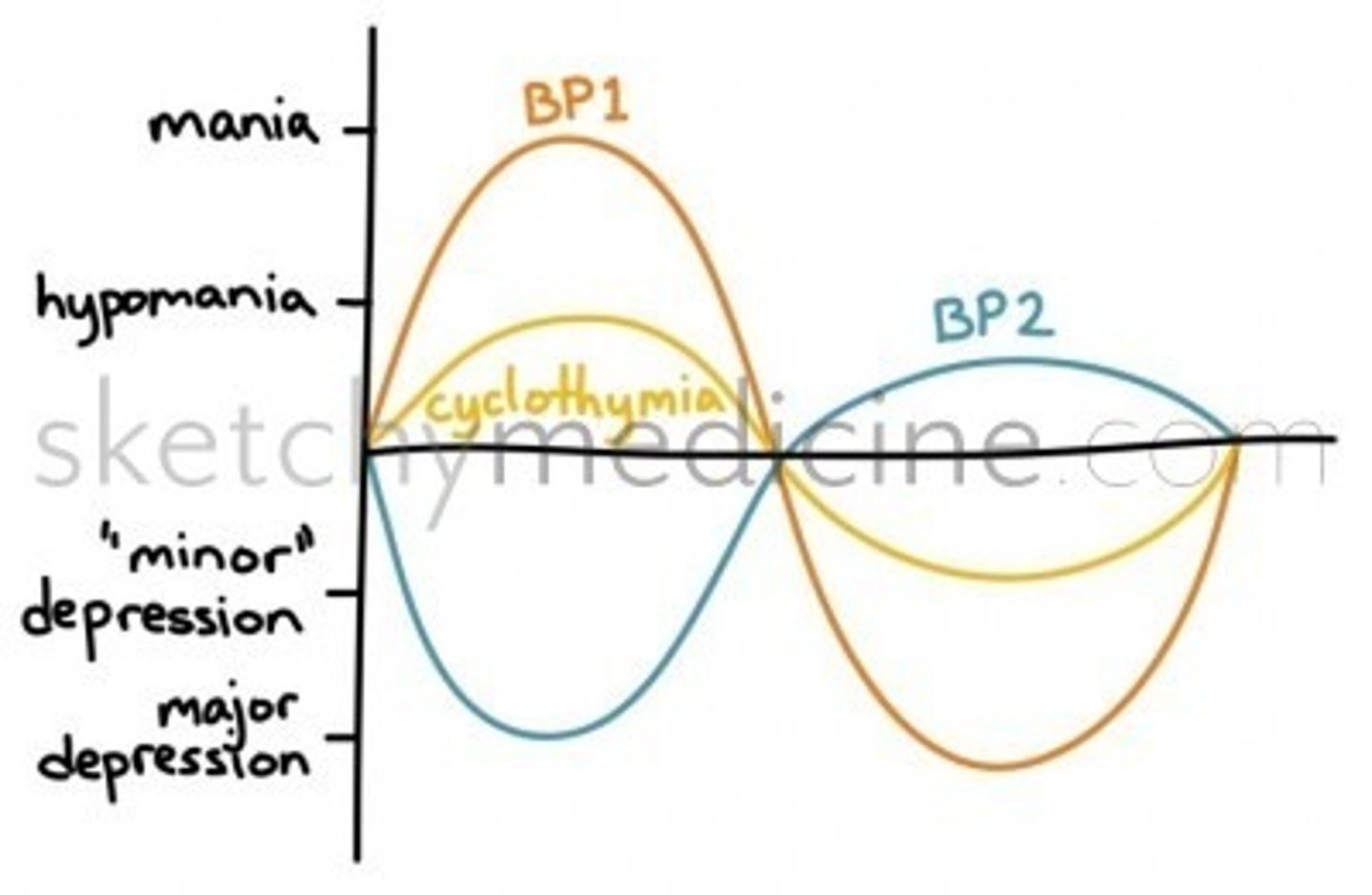
type 1 bipolar disorder
at least one full manic episode (very high energy, risky behavior, possibly delusions). Depression may also happen, but mania is the key feature

type 2 bipolar disorder
hypomania (not as severe as mania) and severe depression
mania
high norepinephrine
Does bipolar disorder have genetic vulnerability?
Yes
Anxiety disorders
Fear response is out of proportion to the actual danger present, with created disturbance to behavior

specific phobia
a severe and persistent fear of a specific object or situation

2 examples of specific phobias
Acrophobia and Arachnophobia
acrophobia
fear of heights

arachnophobia
fear of spiders

agoraphobia
most common phobia
fear of social situations like public transport, open spaces, enclosed spaces, standing in line, alone out of home

panic disorder
an anxiety disorder that consists of sudden, acute, overwhelming attacks of terror

panic attack
brief, intense episode of extreme fear characterized by sweating, dizziness, light-headedness, racing heartbeat, and feelings of impending death or going crazy

Ataque de nervios
A cultural syndrome primarily seen in Latin Americans, involving symptoms of intense emotional upset, acute anxiety, fear, or anger.

social anxiety disorder
intense fear of being judged in social situations, leading to avoidance of such

Taijin Kyofusho
A Japanese culture-specific syndrome characterized by an intense fear that one's body, body parts, or bodily functions give others a negative impression.

generalized anxiety disorder
a diffuse state of constant anxiety not associated with any specific object or event
Obsessive compulsive disorders
characterized by Obsessions (intrusive thoughts) and compulsions (intrusive, oftenrepetitive behaviors)
Hoarding Disorder
Persistent collection of useless or trivial items, resistance to discarding them, and anxiety if asked to

dissociative disorders
Disorders that involve dysfunction of memory (amnesia)and/or change in identity - a separation in the psyche from some parts of consciousness, emotions, body representation, motor control, or behavior (response to trauma or stress)

dissociative amnesia
Dissociative disorder characterized by the sudden and extensive inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature.

Fugue
Sudden and complete loss of identity and person "runs away"

dissosiative identity disorder
Presence in one individual of two or more distinct personality states that take control of a person's behavior (usually considered the result of severe childhood abuse

post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
caused by trauma or stress
symptoms may involve hypervigilance, severe anxiety, flashbacks, insomnia, emotional detachment, and hostility

Types of feeding and eating disorders
anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder in which an irrational fear of weight gain leads people to starve themselves

bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise

personality disorders
psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning

Cluster A personality disorders
odd/eccentric
paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal

Cluster B personality disorders
dramatic, emotional
antisocial, borderline, histrionic, narcissistic

Cluster C personality disorders
Anxious, fearful
avoidant, dependent, obsessive compulsive

Paranoid
Cluster A
suspicious, hypersensitive, secretive

schizoid
Cluster A
Seclusive, indifferent, passive

Schizotypal
Cluster A
Odd in thinking, bizarre fantasy, peculiar language

histronic
Cluster B
attention seeker, flamboyant, provocative
border line
Cluster B
impulsive, self mutilative, manipulative
narcissistic
Cluster B
exessive self-admiration, egocentric
anti social
Cluster B
rule breaker, aggressive, abusive

avoidant
Cluster C
fears criticism, overly serious, withdrawn

dependent
Cluster C
clingy, indecisive, submissive
