P1.5 - Benign Bone Tumors
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Osteoclastoma
Another term for giant cell tumor
- 80%
- 20%
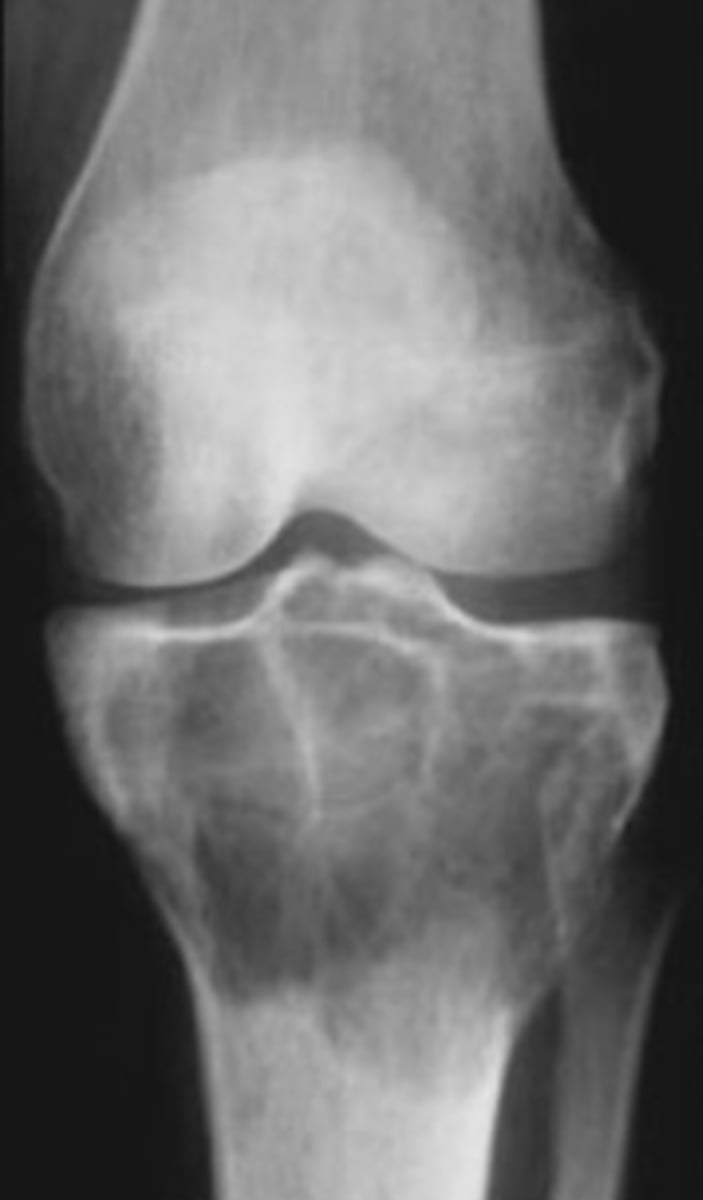
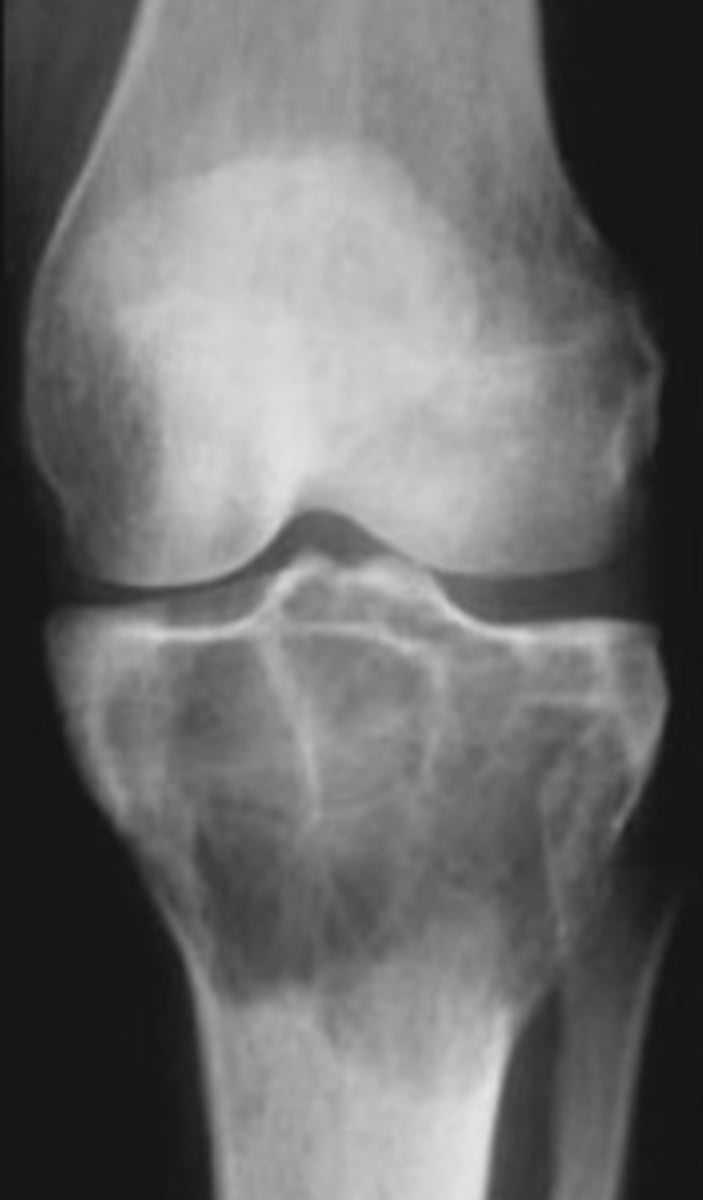
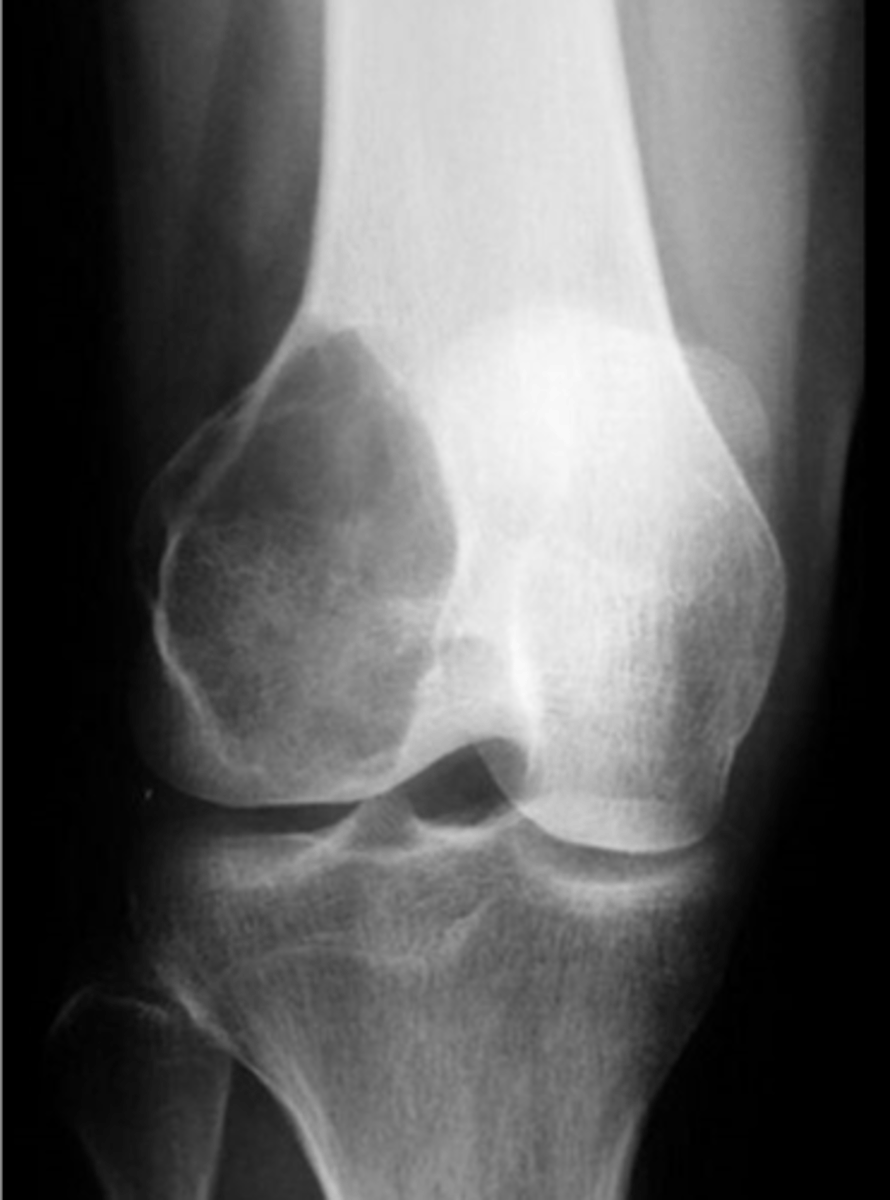
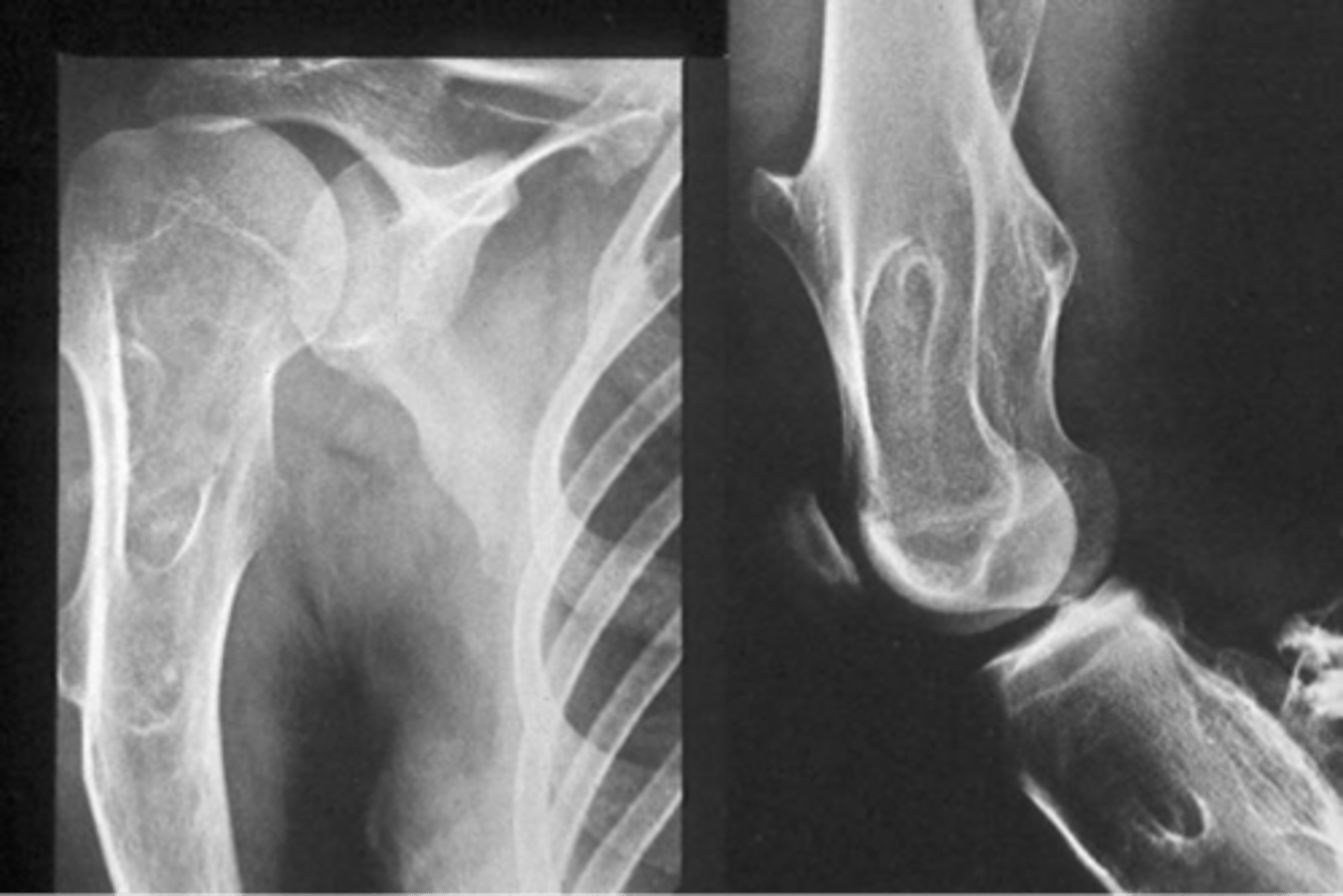
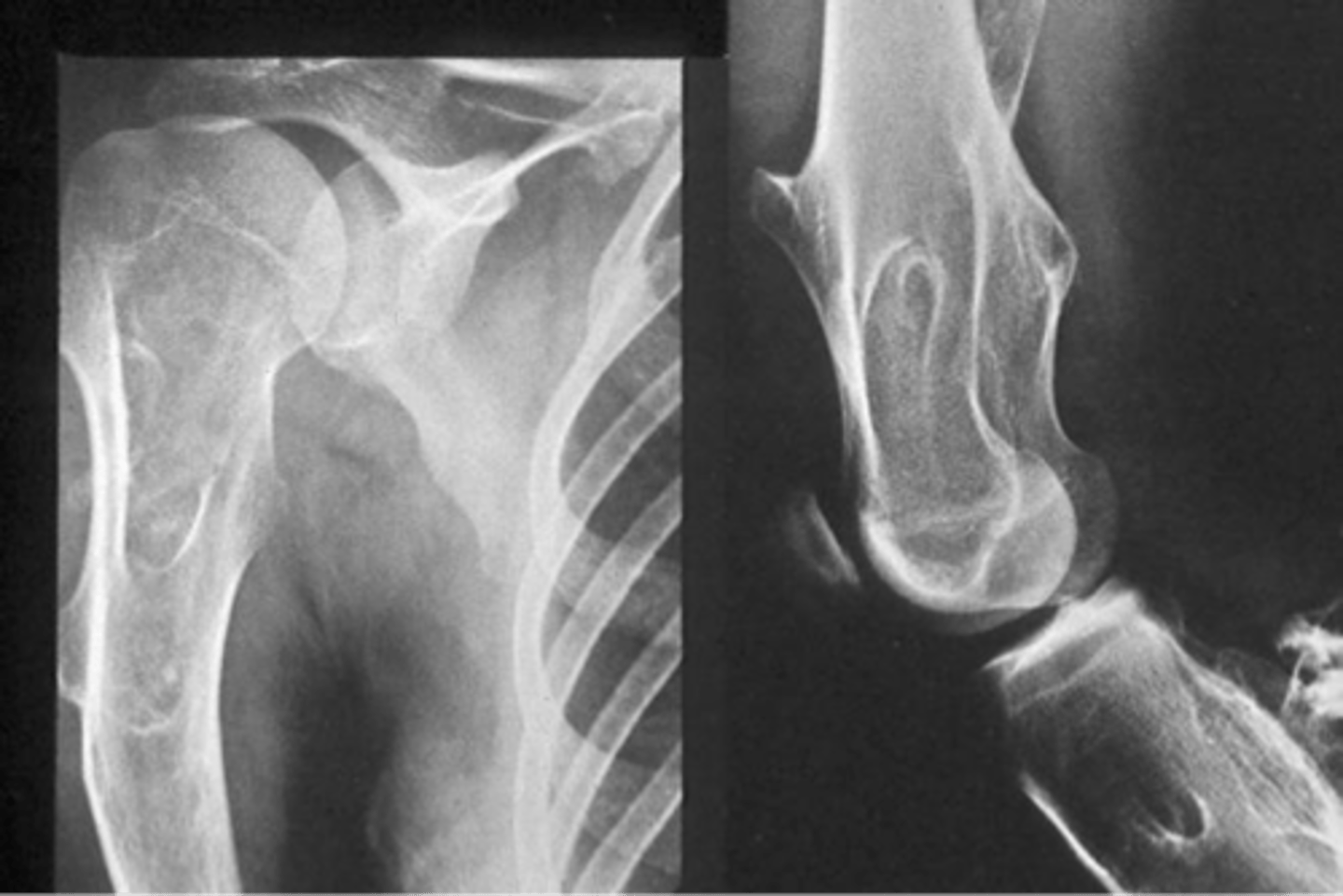
Giant cell tumor pathology:
- _____ benign (F:M, 3:2)
- _____ malignant (M:F, 3:1)
- 20-40 y.o.
- Knee (tibia and femur)
- Localized pain and aching
- Joint pain and restricted motion
State the clinical features of giant cell tumor
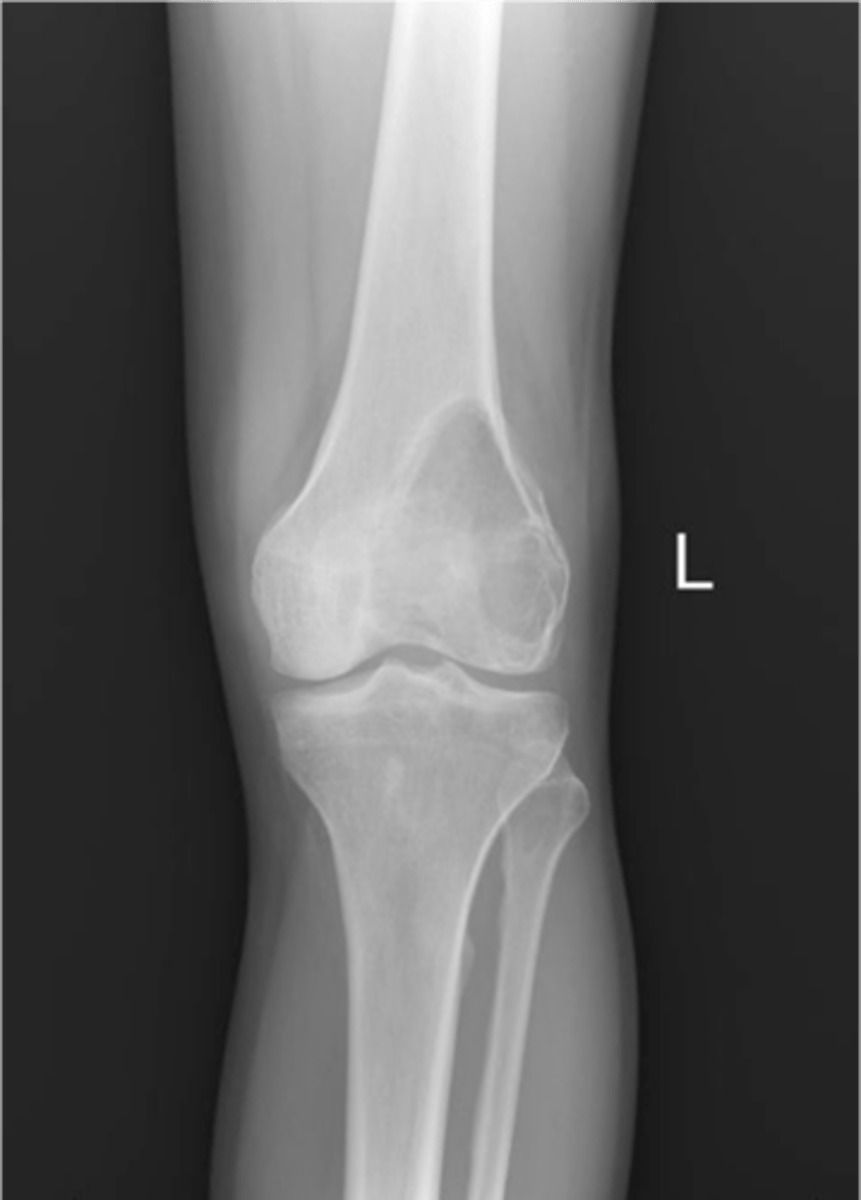
- Osteolytic
- Geographic
- Multiloculated and septated
- Begin in metaphysis
- Extend to subarticular bone
- Expansion
- Eccentric
- Quasi-malignant (can't tell benign from malignant)
State the imaging features of giant cell tumor
Biopsy
We need to do a _____ to tell if giant cell tumor is benign or malignant
Solitary osteochondroma
- Most common benign skeletal growth or tumor
- 50% of all benign bone tumors
- 10-15% of all primary bone tumors
- 75% <20 y.o.
- M:F, 2:1
- Malignant transformation <1%
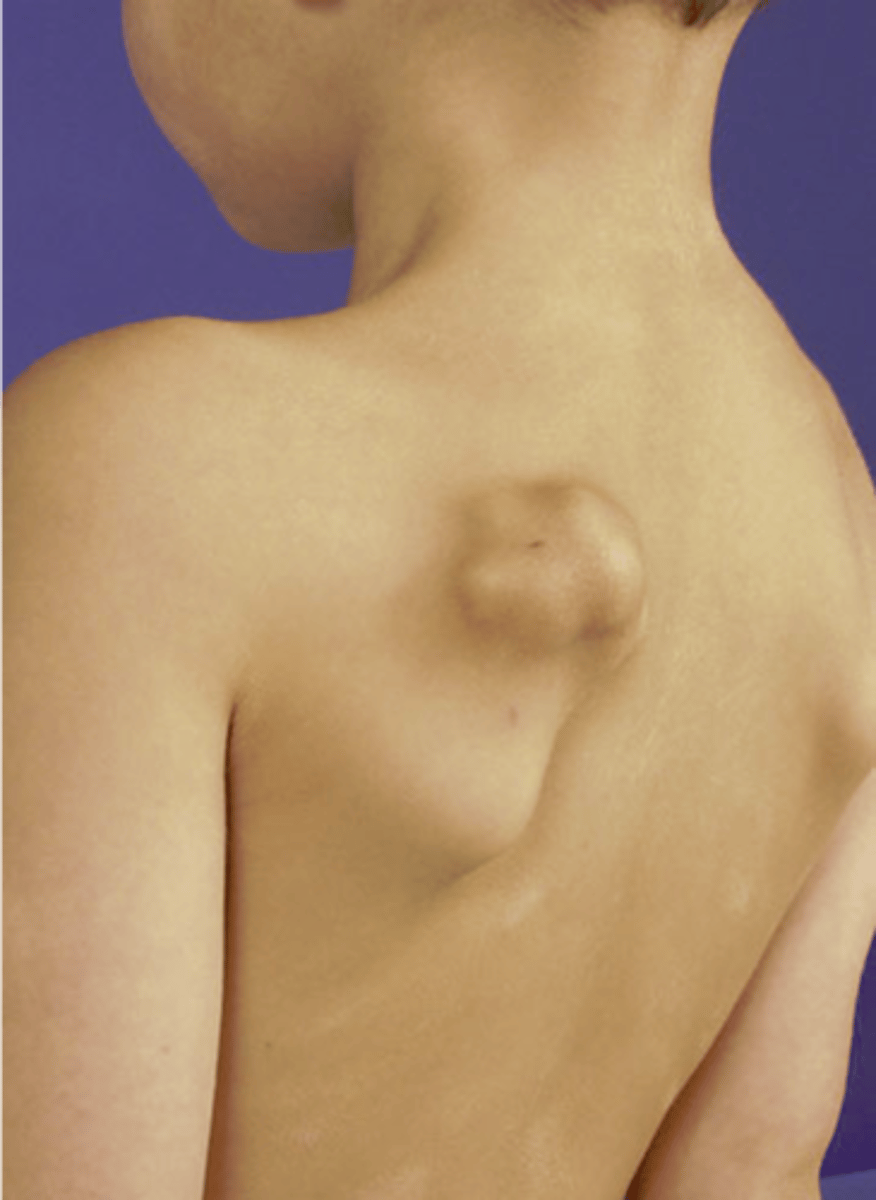
- Mostly asymptomatic
- Painless, hard mass
- Stalk may fracture
- Pain and rapid growth = malignant transformation
State the clinical features of solitary osteochondroma
Pedunculated
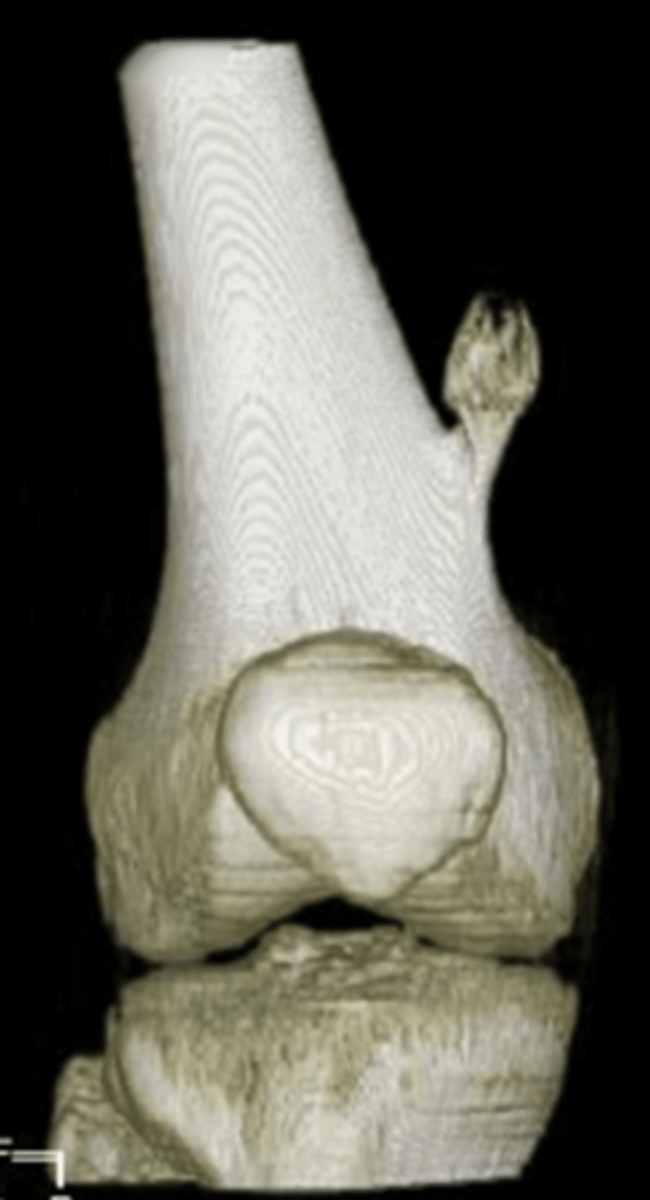
_____ solitary osteochondroma:
- Metaphyseal
- Thin, elongated stalk
- Cortex and medulla continuous
- Calcified cap
- Projects away from joint
- Lucent when en face (on end)
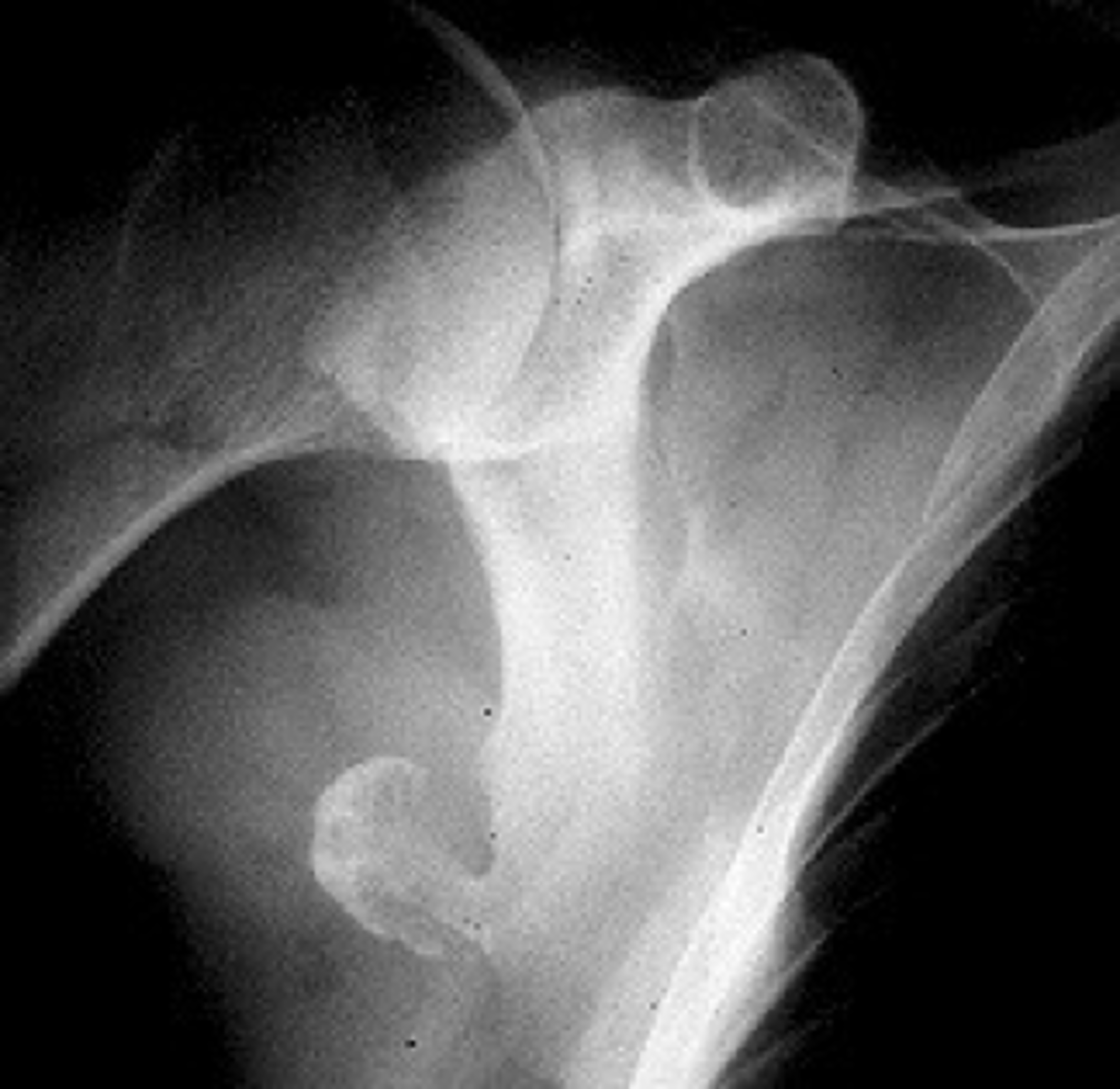
Sessile
_____ solitary osteochondroma:
- Broad-based
- Metaphyseal
- Wide, broad metaphysis
- Lucent when en face (on end)
- Cartilage cap uncommon
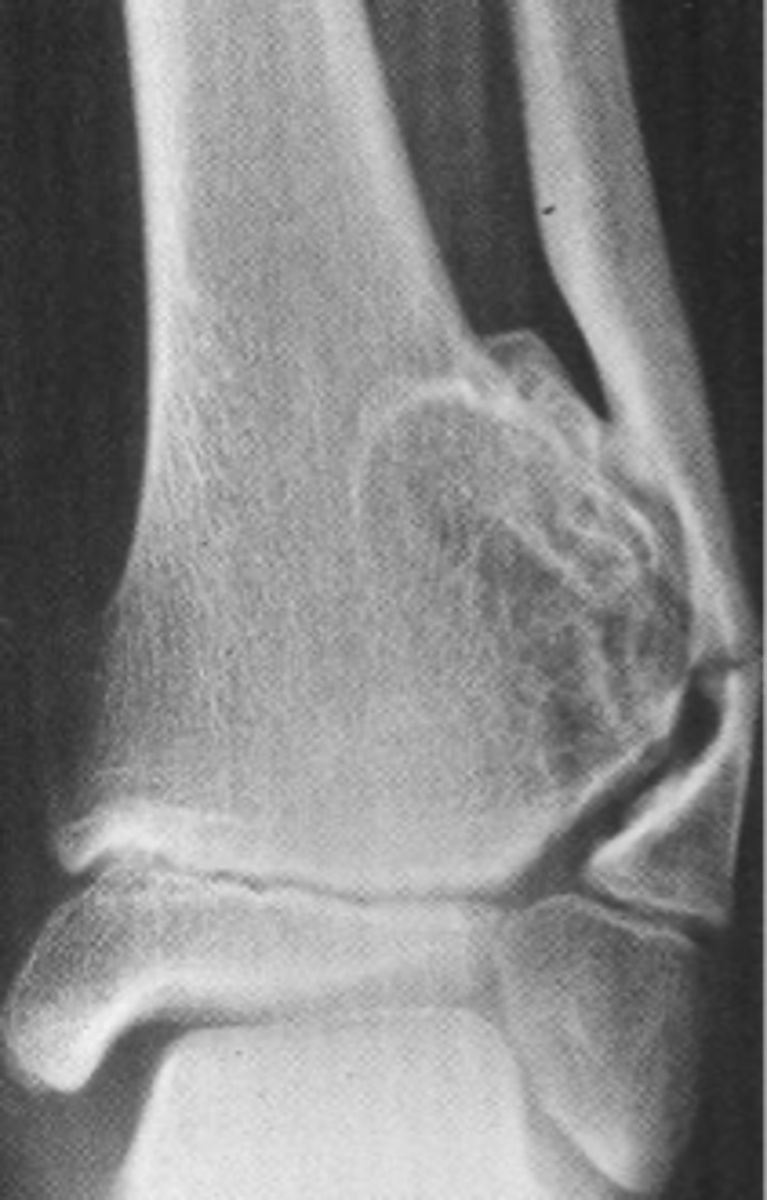
Cartilage cap
What is this?
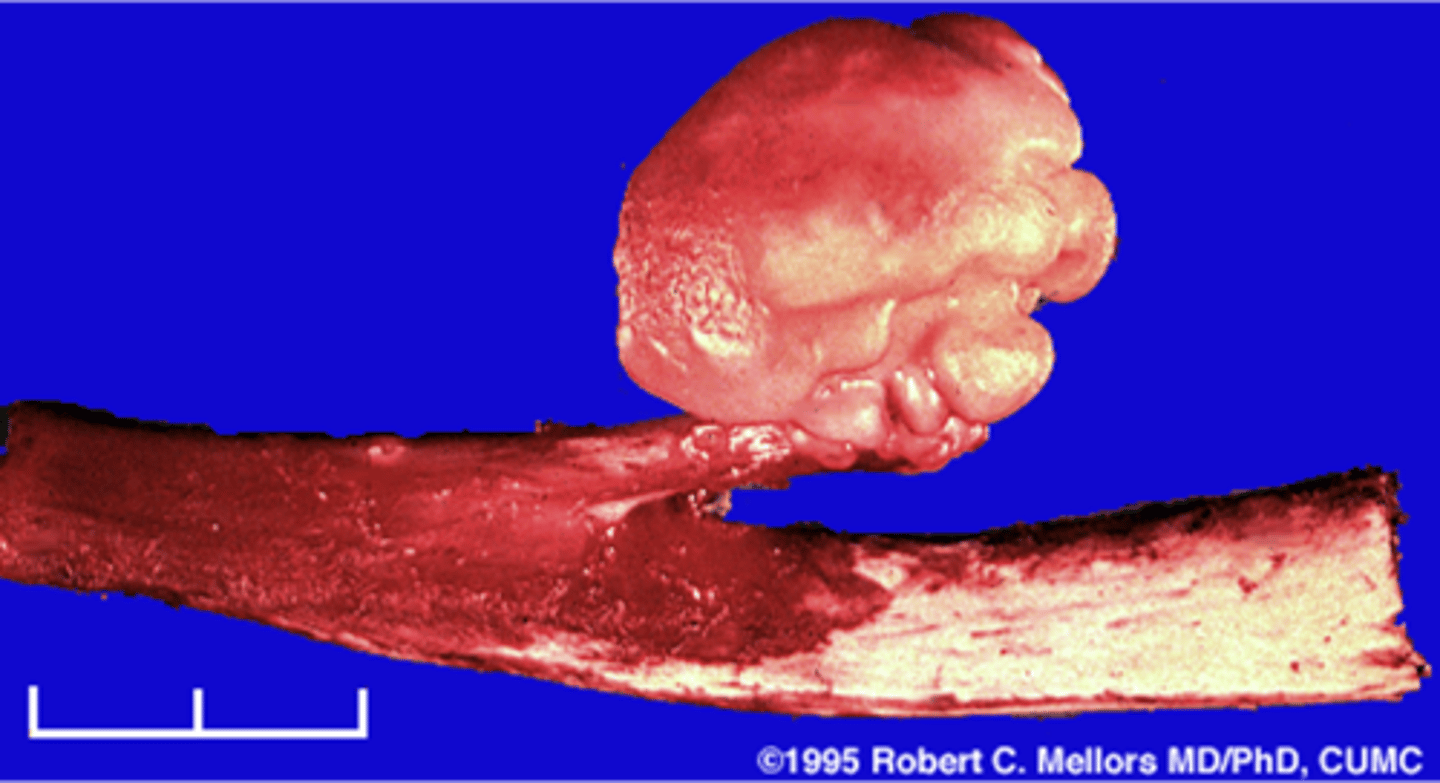
- Usually leave it alone
- Surgical removal if symptomatic
State osteochondroma treatments
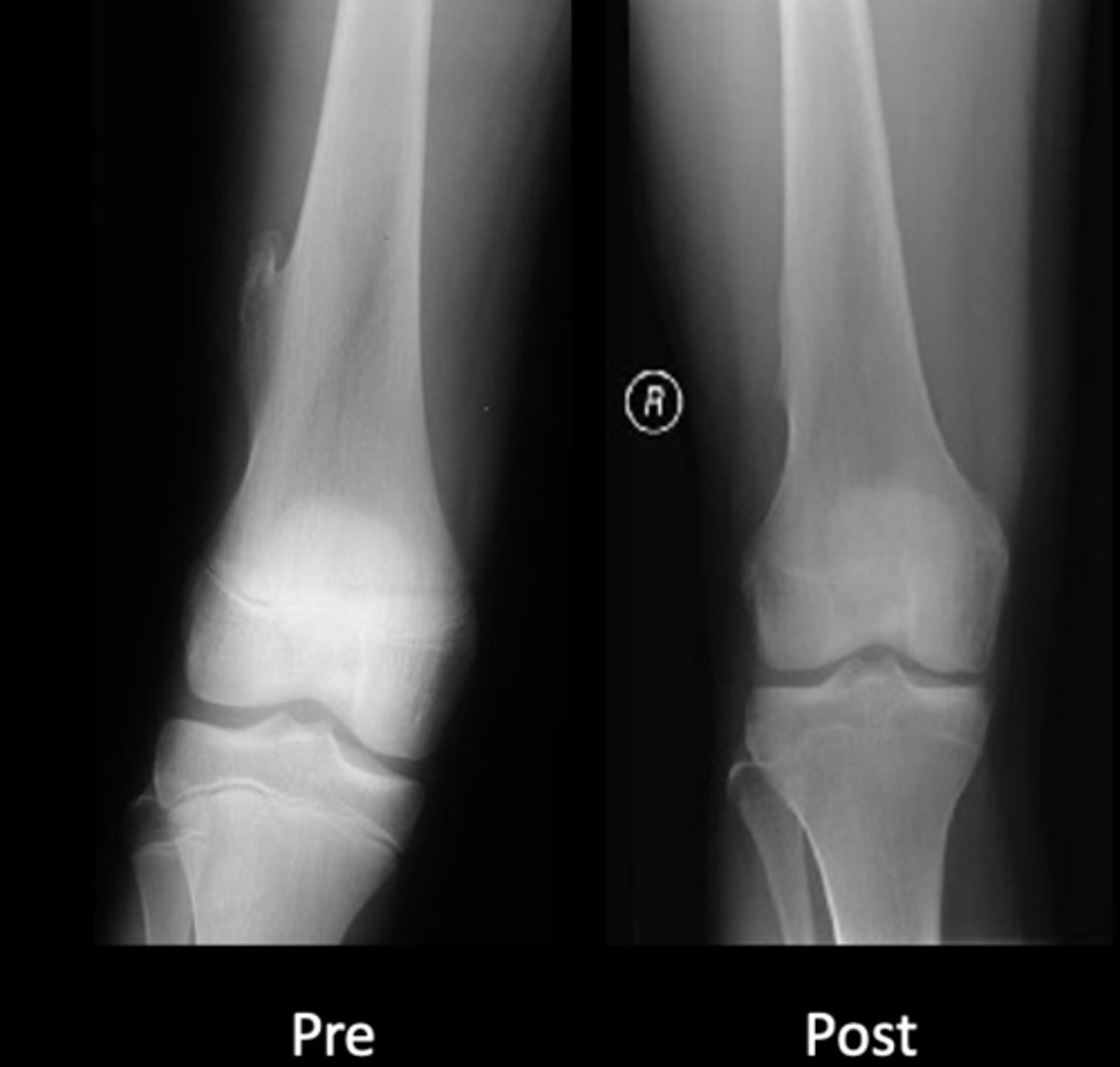
Patient will live
State osteochondroma prognosis
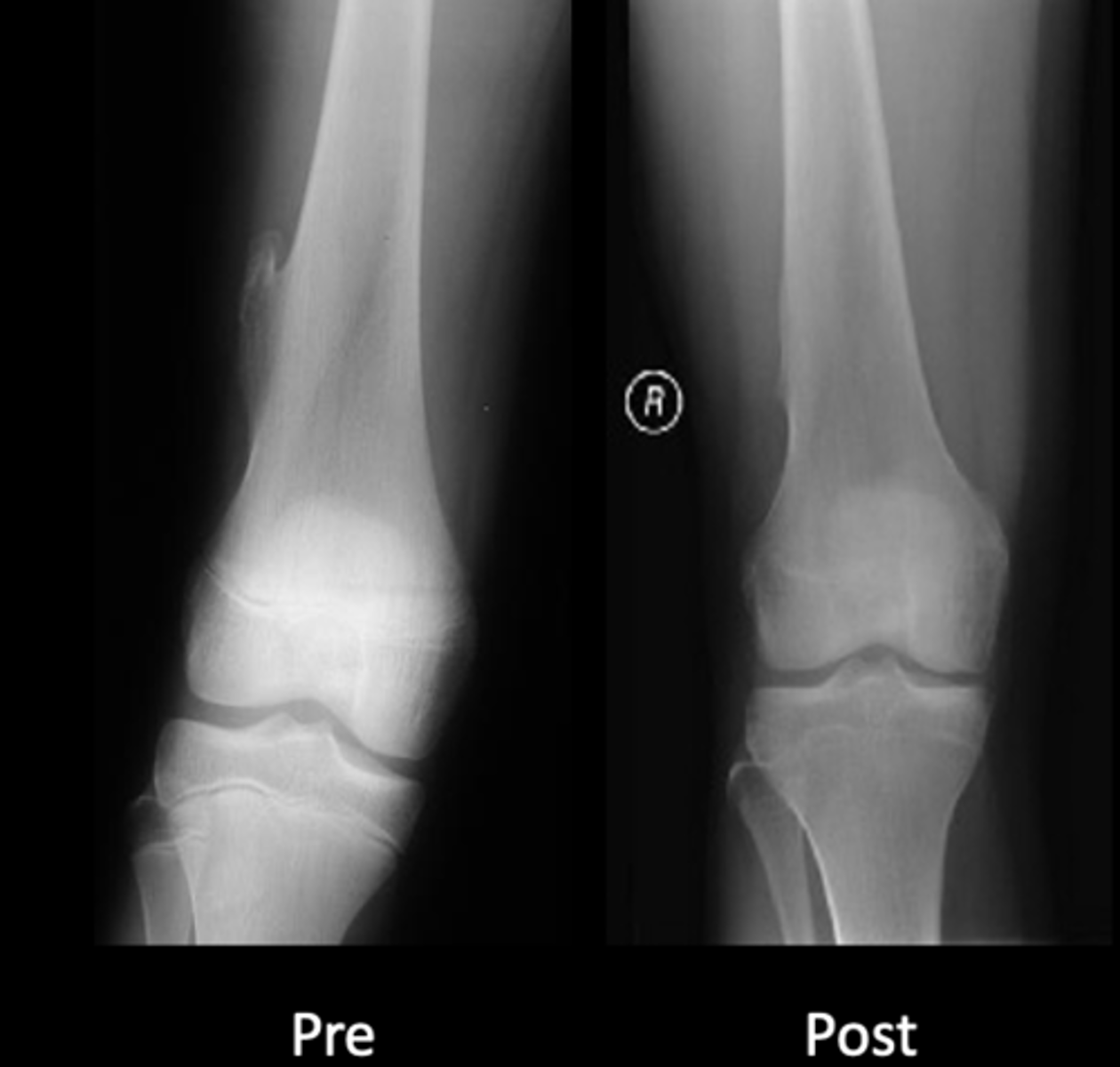
Hereditary multiple exostoses
- Inherited metaphyseal overgrowth
- Multiple painless osteochondromas
- Identical to solitary
- Discovered 2-10 y.o.
- Knee, ankle, shoulder, wrist
5-25%
Hereditary multiple exostoses malignant transformation rate
Bone island
- Any age
- Adults > children
- Asymptomatic
- Usually solitary
- Any bone (except skull)
Enostoma/enostosis
Normal tissue in an abnormal area
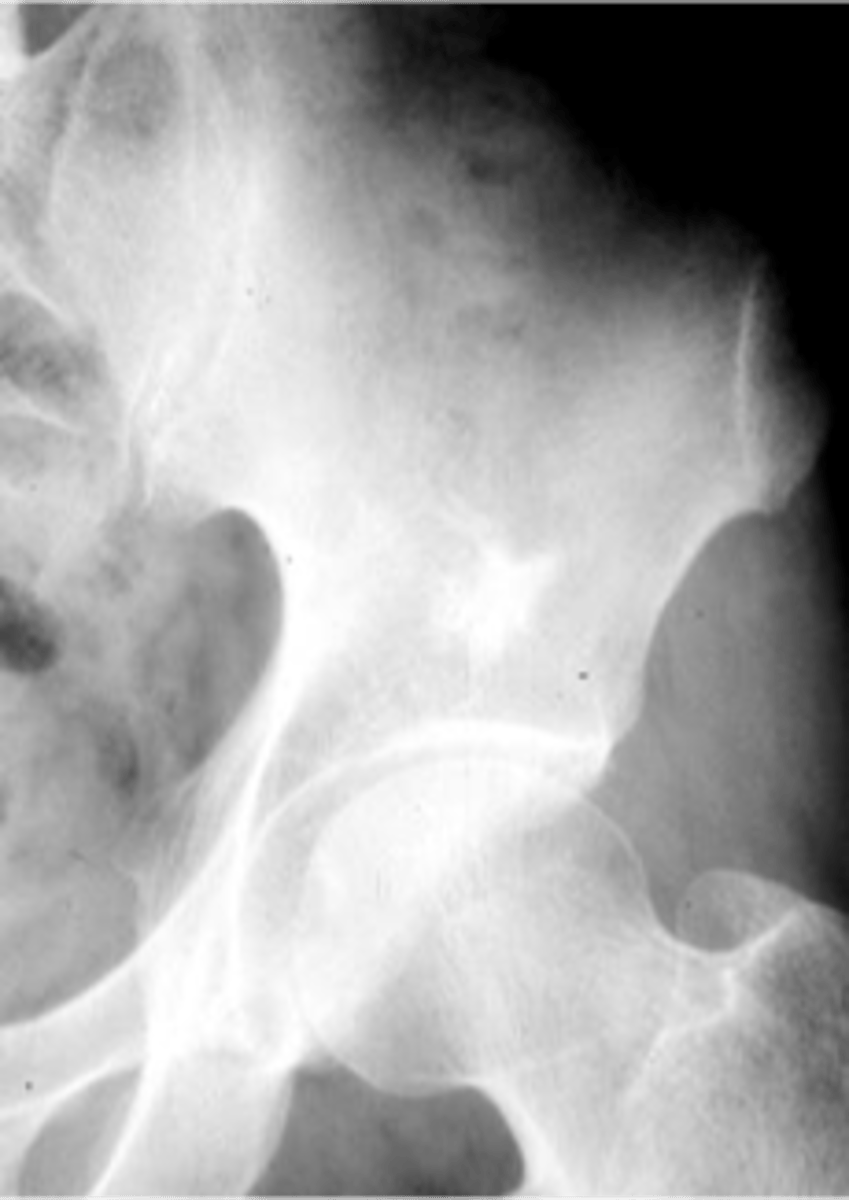
- Epiphyseal, metaphyseal
- Medullary
- Round/oval
- Radiating border ("brush border")
- Radiodense
- May change size
- May be warm on bone scan
State the radiologic features of a bone island (enostoma/enostosis)
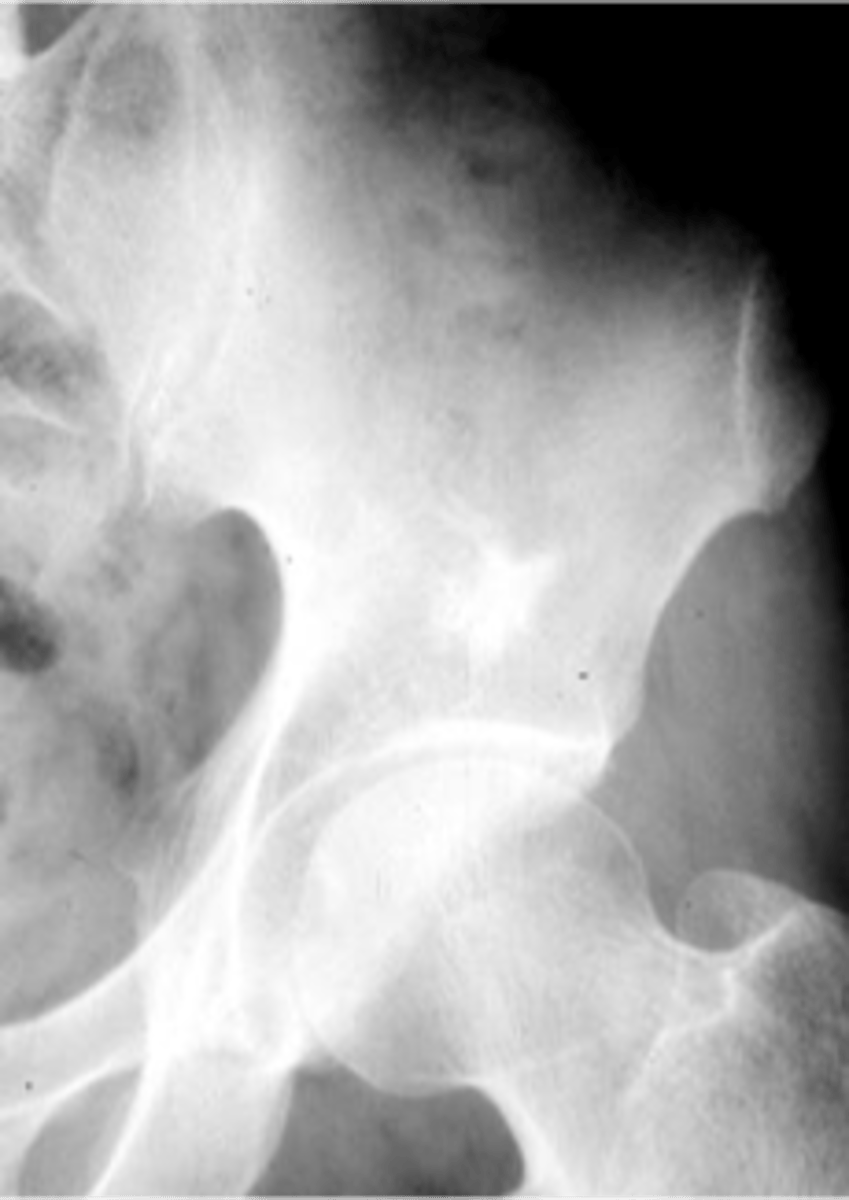
- Ischium
- Ilium
- Sacrum
- Proximal femur
- Humerus
- Vertebra
- Talus
- Scaphoid
State the locations for a bone island
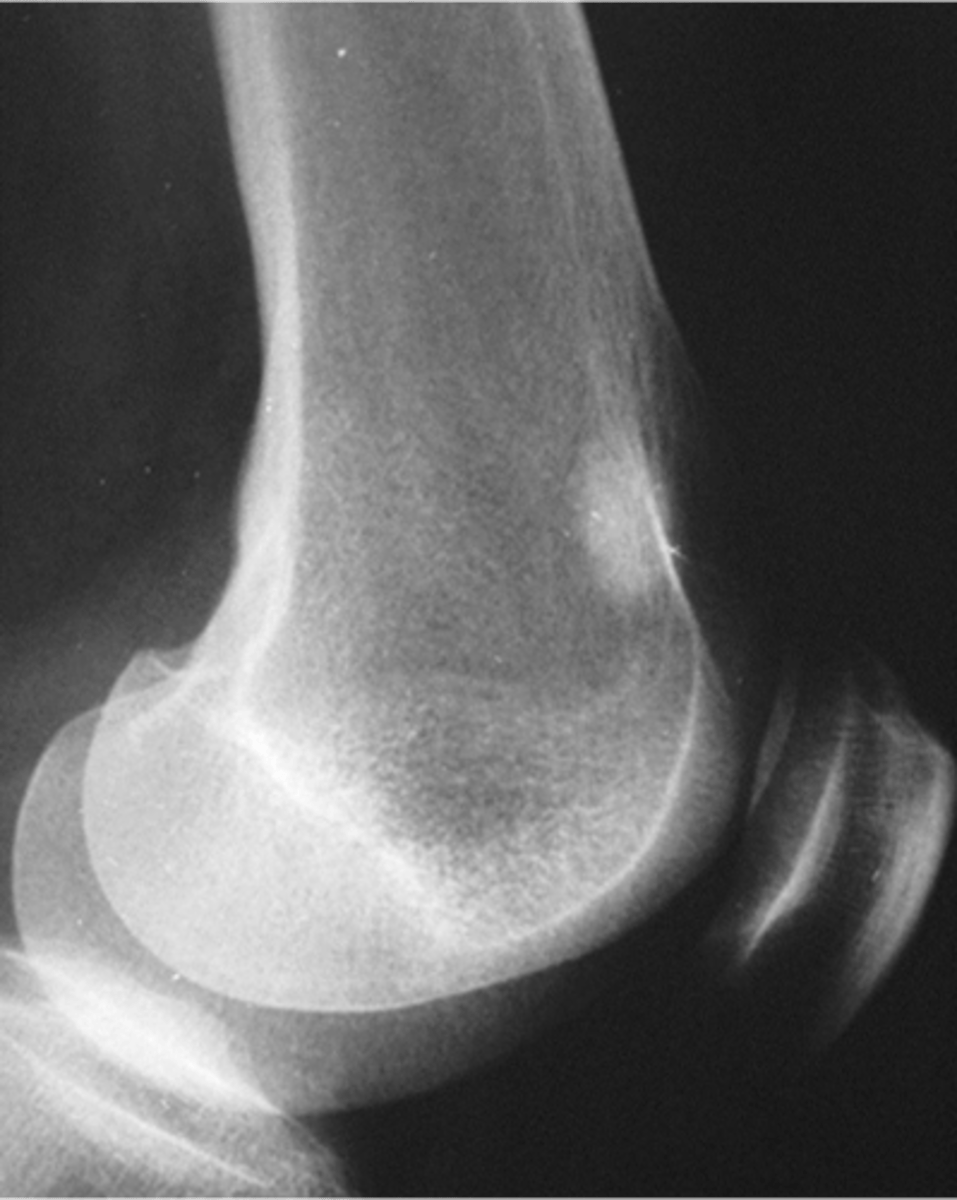
No
Bone island pain
Solitary
Bone island number
Warm
Bone island bone scan
Any
Bone island age
Occasionally
Bone island change in size
Yes
Osteoblastic metastasis pain
Multiple
Osteoblastic metastasis number
Hot
Osteoblastic metastasis bone scan
>45
Osteoblastic metastasis age
Yes
Osteoblastic metastasis change in size
Giant bone islands
ID
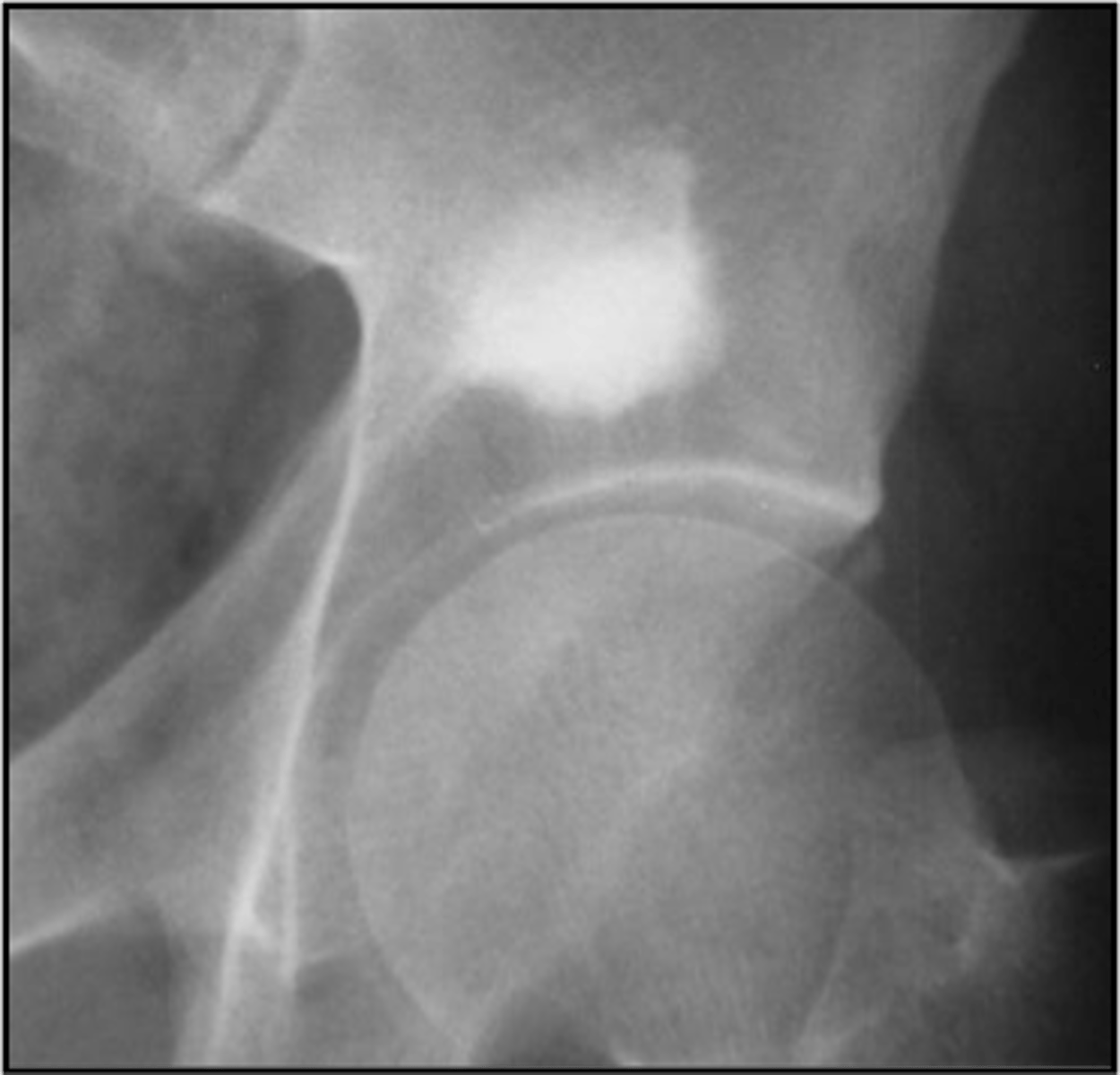
- Bone island
- Kidney stone*
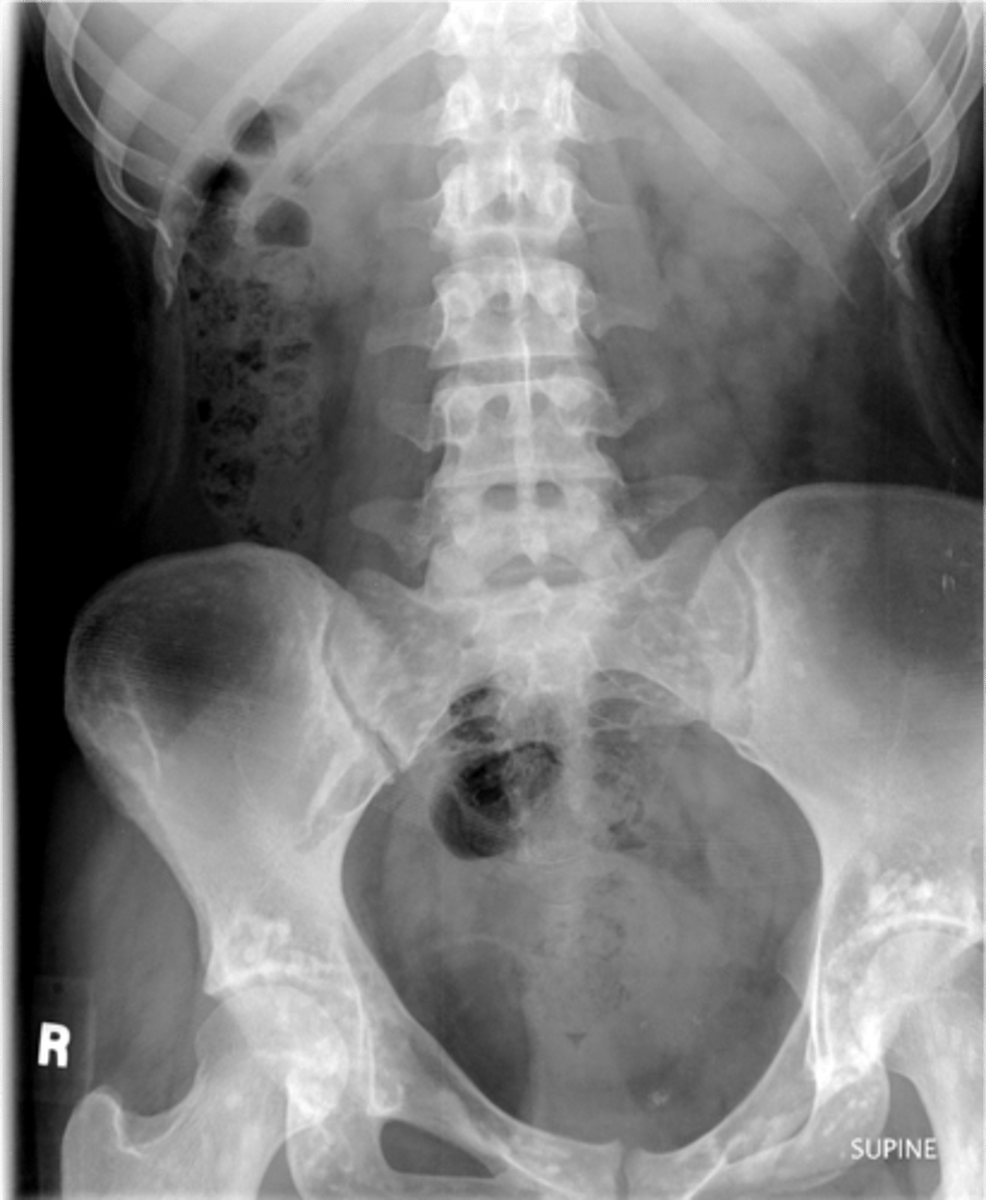
22 y.o. male with L/S pain, post motor vehicle accident
- Differential diagnosis?
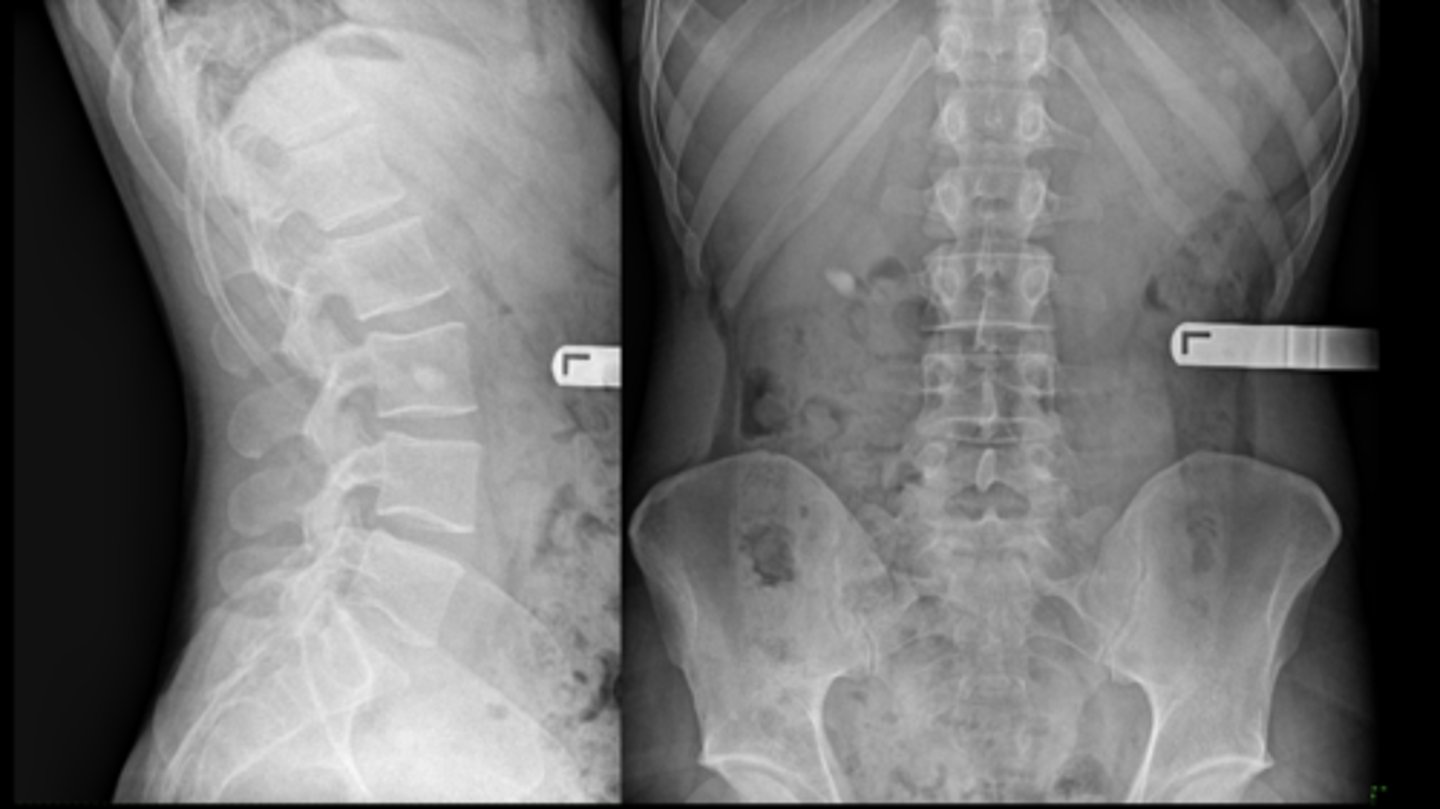
Osteopoikilosis
Diagnosis?
Osteoid osteoma
- 11% of all benign bone tumors
- M:F, 2:1
- 10-25 y.o.
- Severe pain (worse at night)
- 50% femur and tibia
- 10% spine (neural arch)
Aspirin
The severe pain caused by osteoid osteoma is relieved by _____
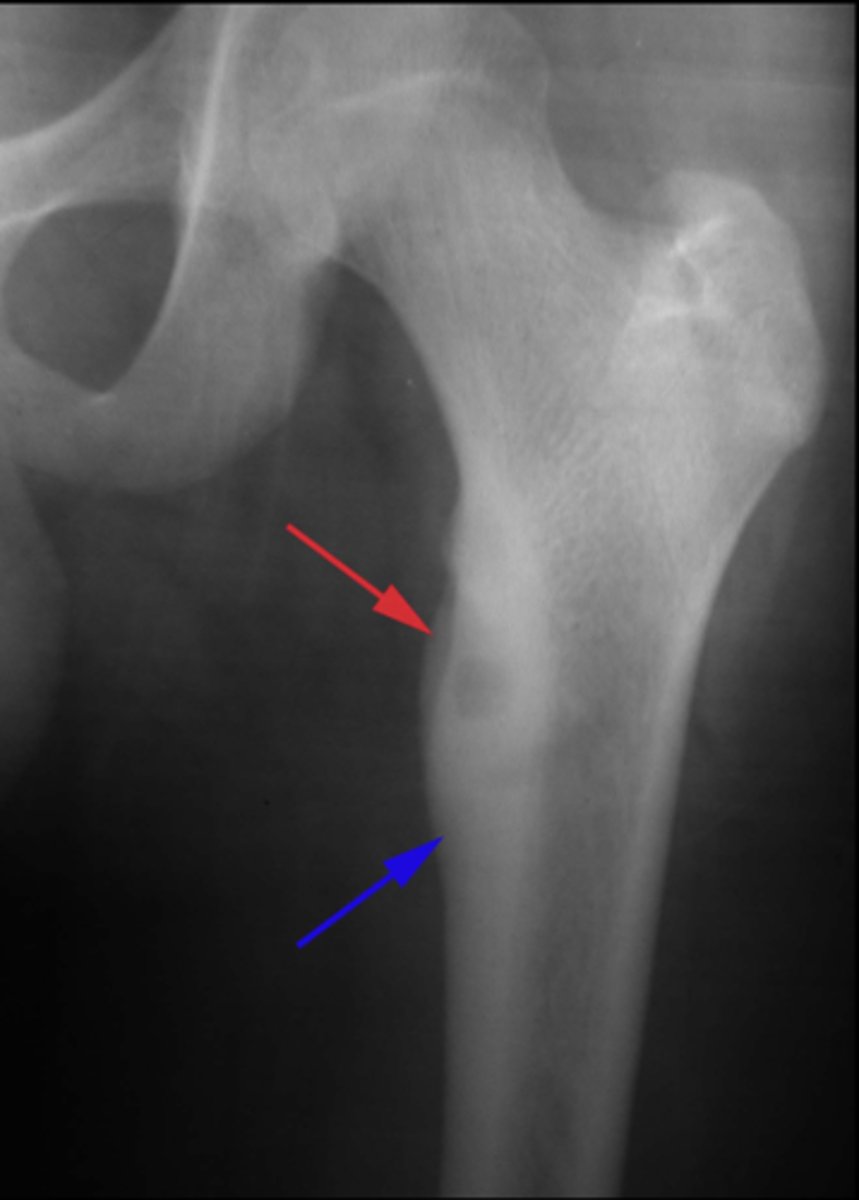
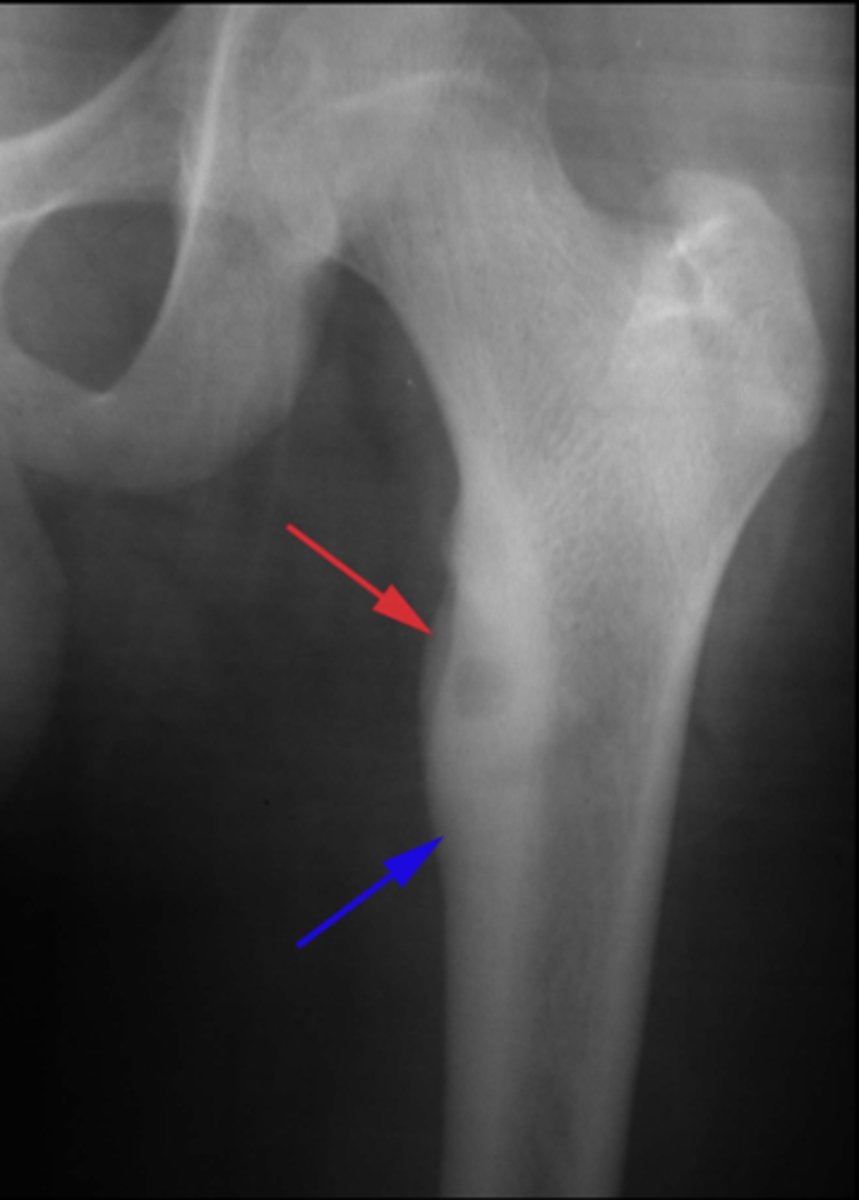
- Central radiolucent nidus <1 cm
- Surrounding sclerosis
- Central calcific fleck
- Metaphyseal and diaphyseal
- Positive bone scan
State the radiologic features of osteoid osteoma

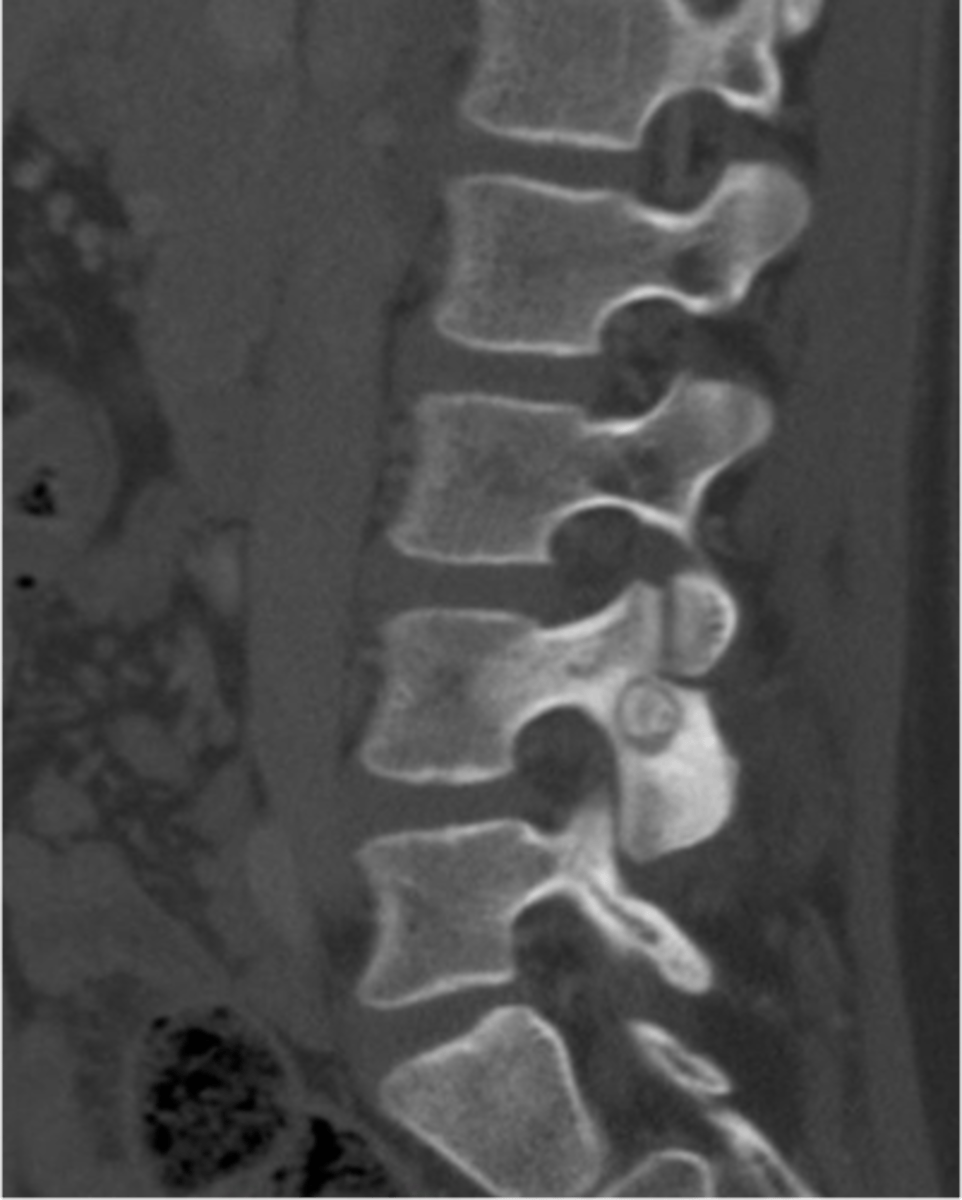
- 10% in spine
- Neural arch
- Painful scoliosis
- Dense
• Pedicle
• Lamina
• Facet
- Lesion on concave side
State the spinal radiologic features of osteoid osteoma
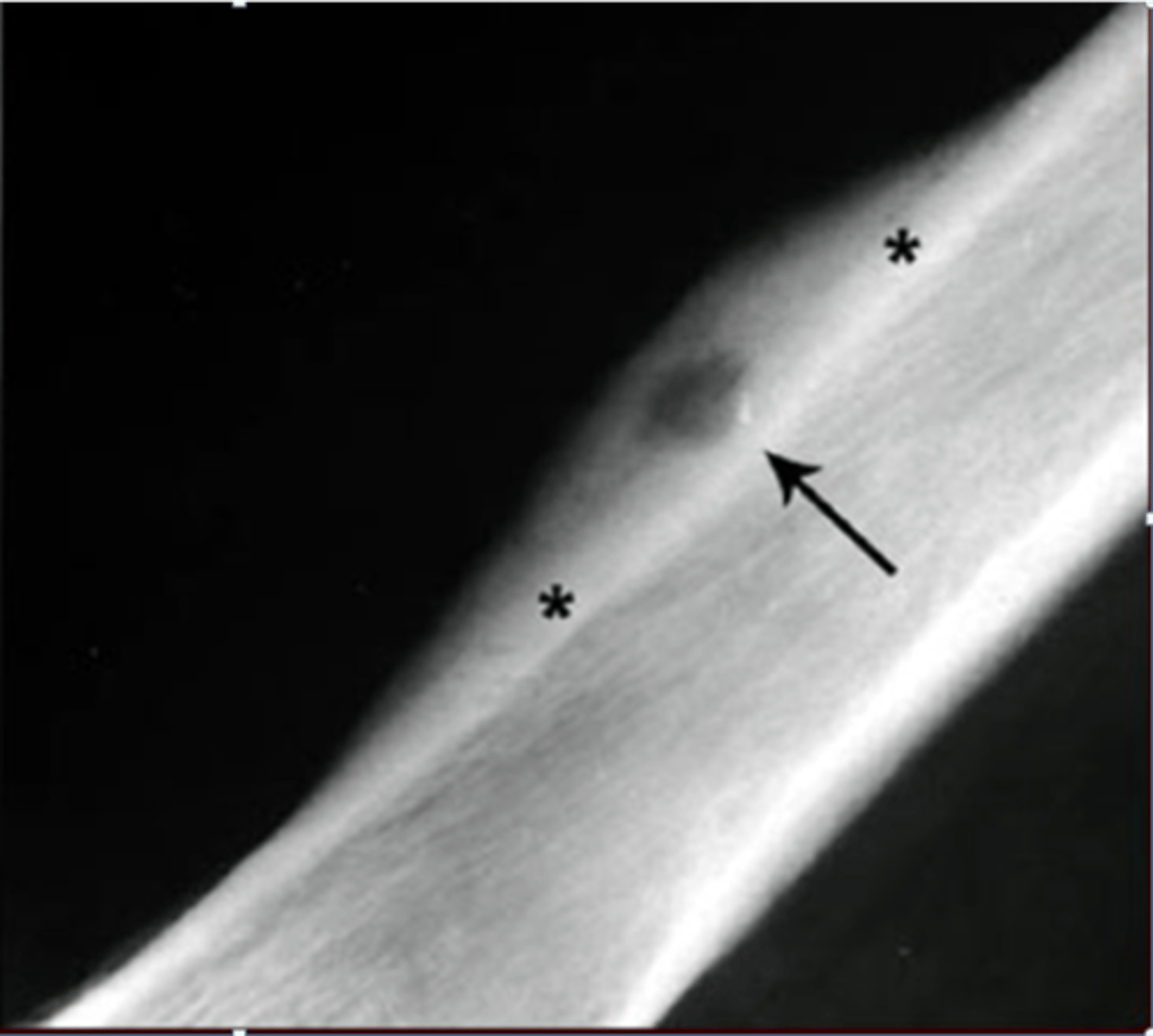
50%
_____ of osteoid osteoma occurs in the tibia or femur
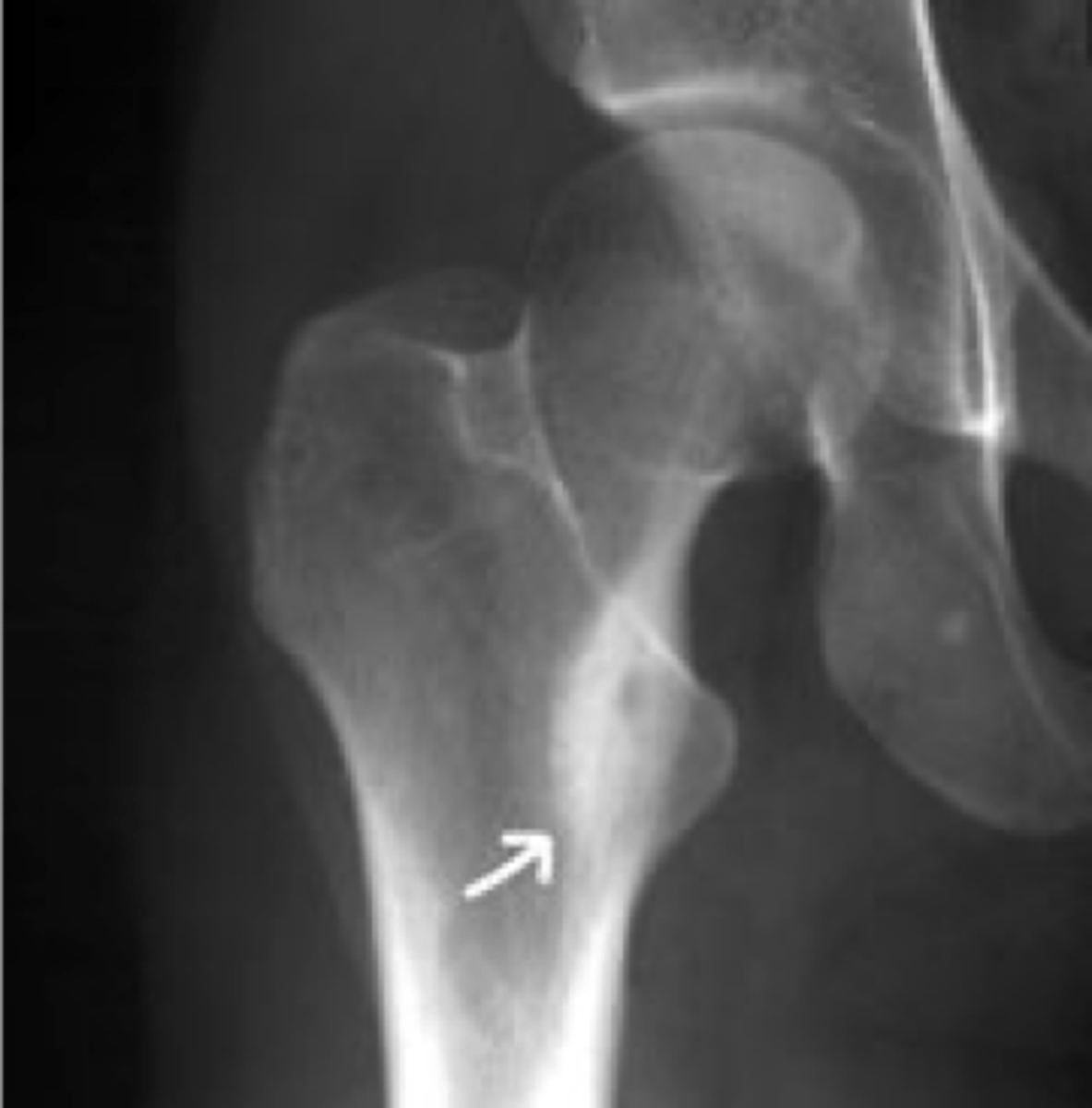
Nidus
ID radiographic feature of osteoid osteoma
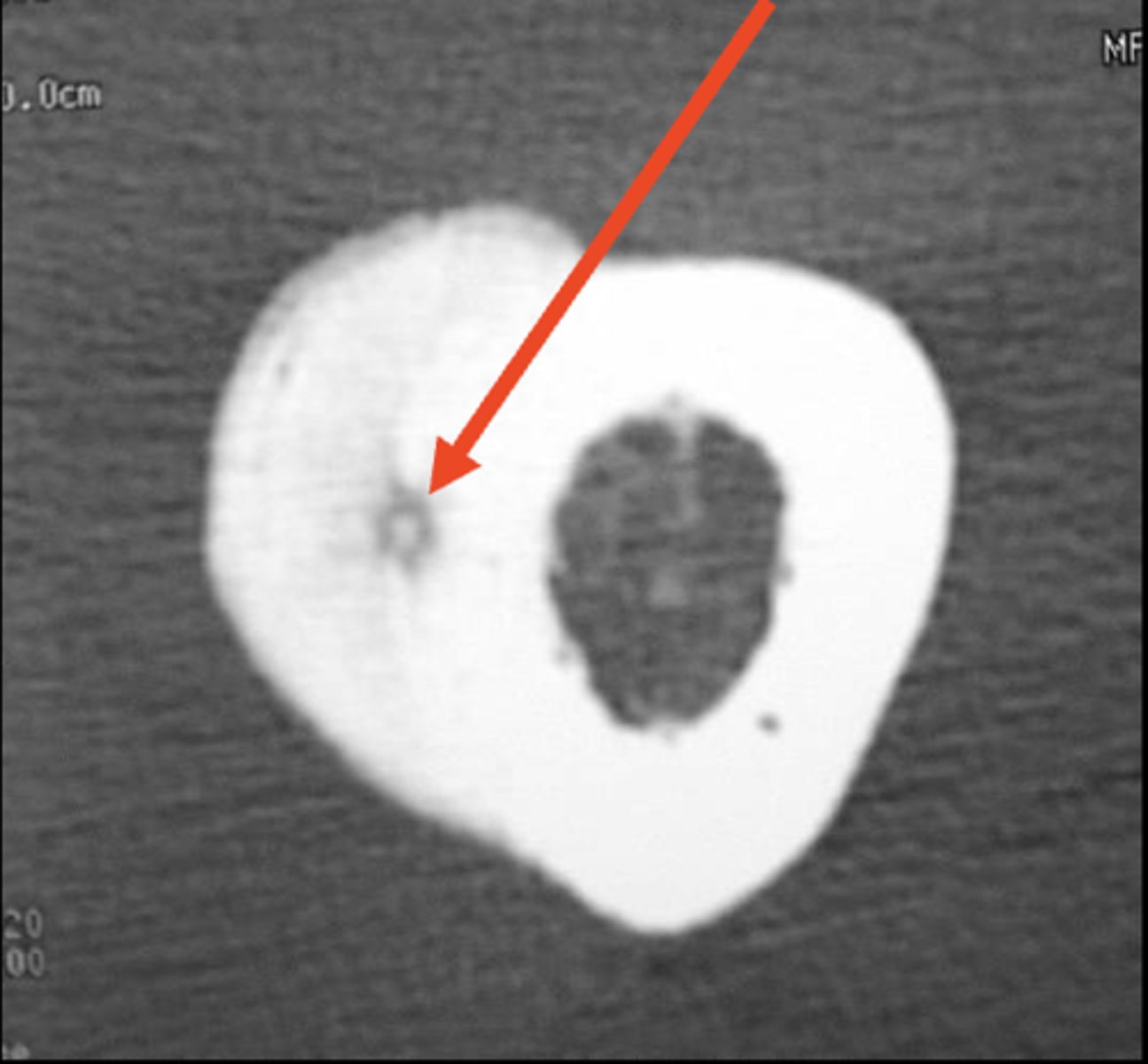
- CT
- Orthopedic referral
Osteoid osteoma follow-up:
- _____ demonstrates nidus
- _____
• Radiofrequency ablation
• Resection
• Watch and wait?
Osteoma
- Asymptomatic (can have headaches)
- Most common benign bone tumor of the nose and paranasal sinuses
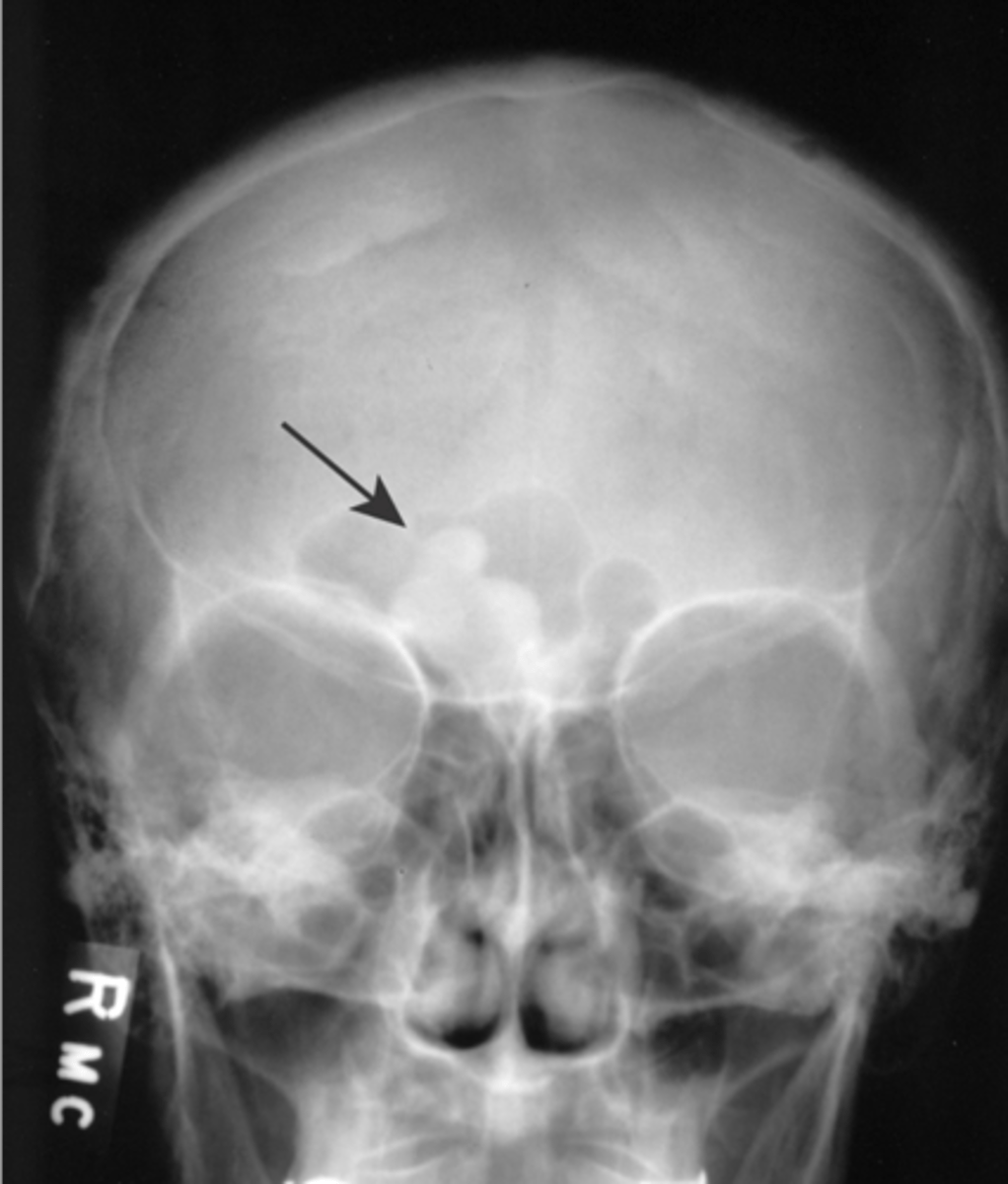
Osteoblastoma
- 10-20 y.o. (3-78 y.o. reported)
- M:F, 2:1
- Spine
• Painful scoliosis
• Posterior elements
- Femur, foot, ankle
• Nidus >2cm
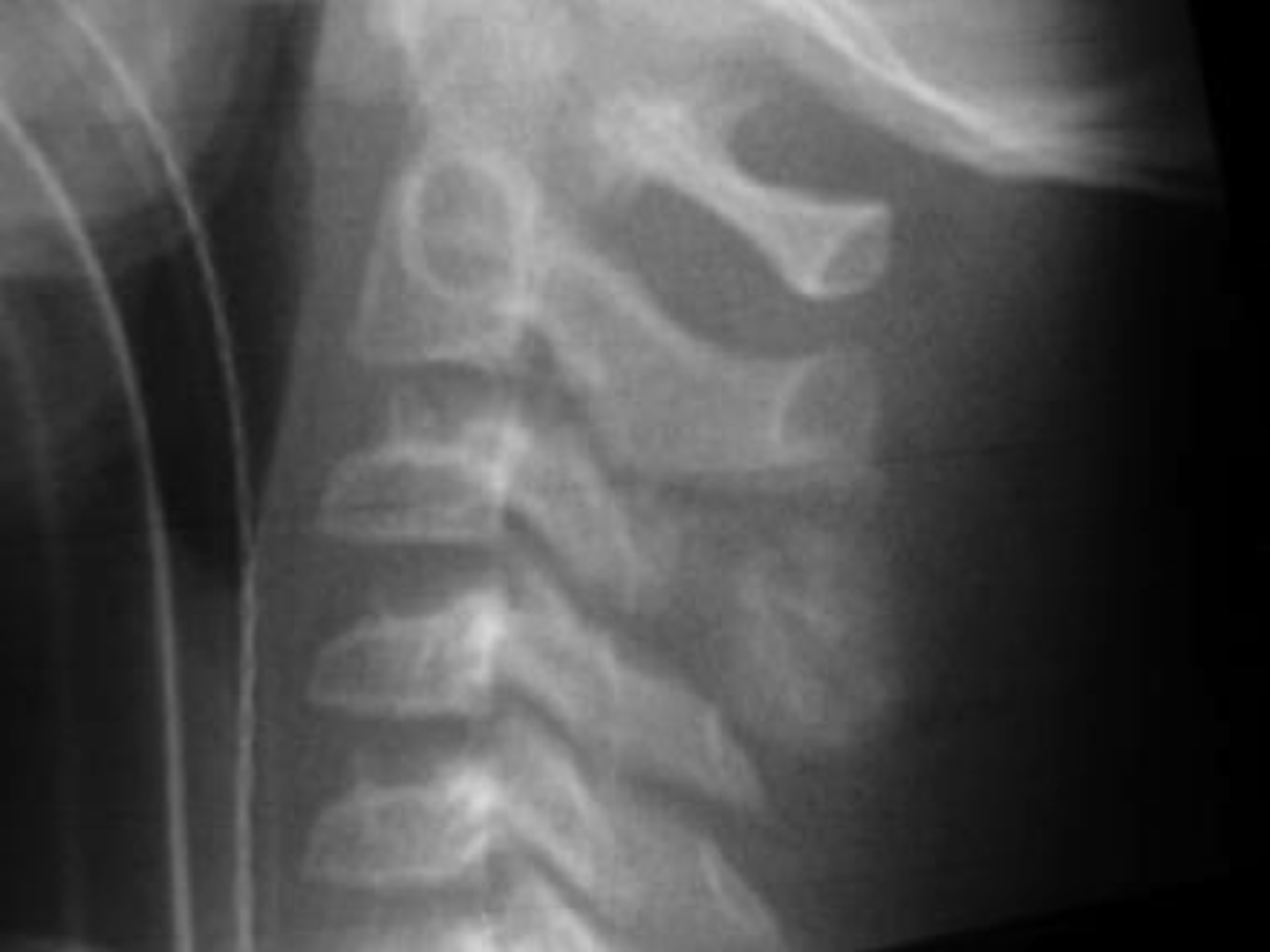
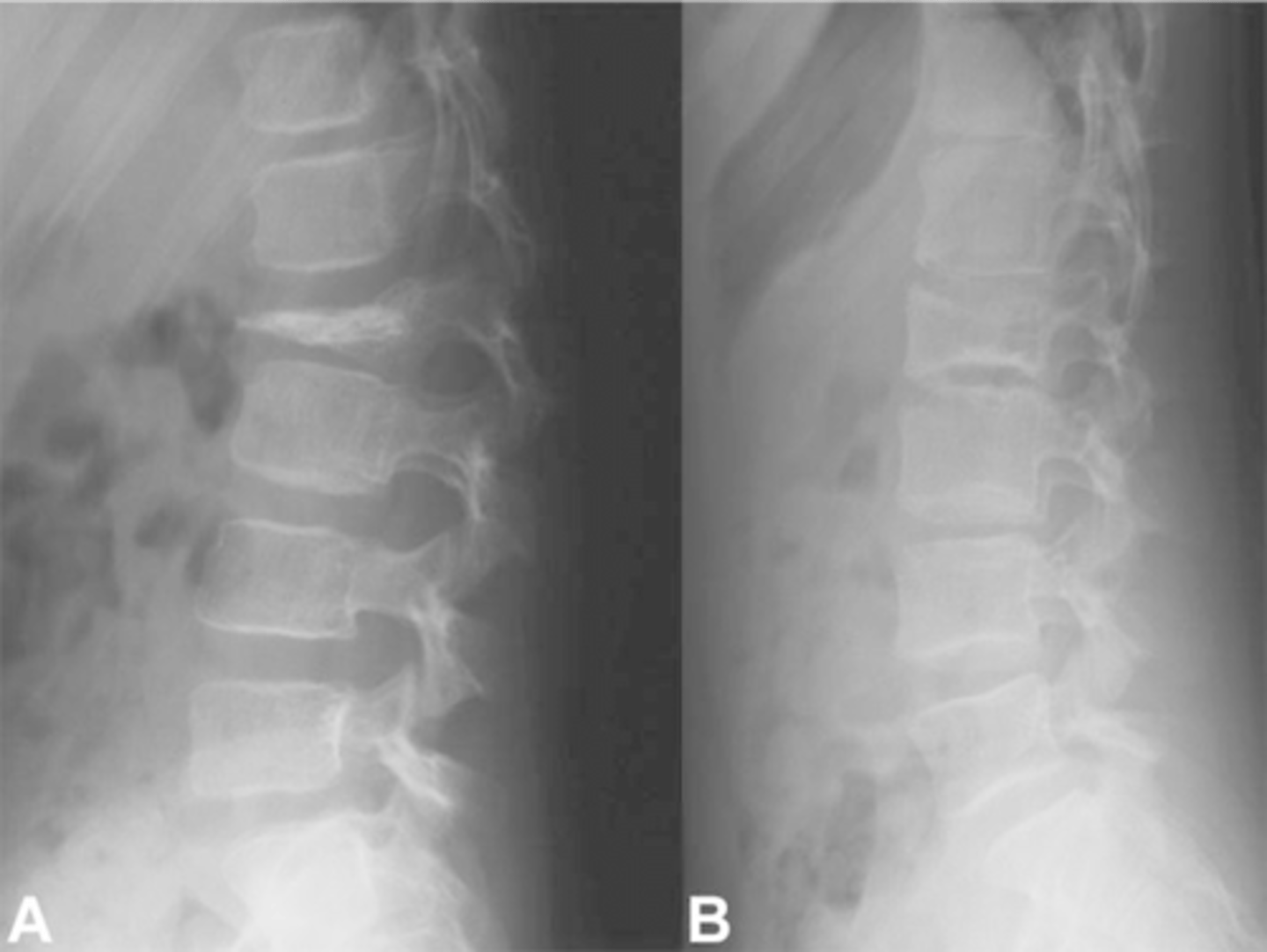
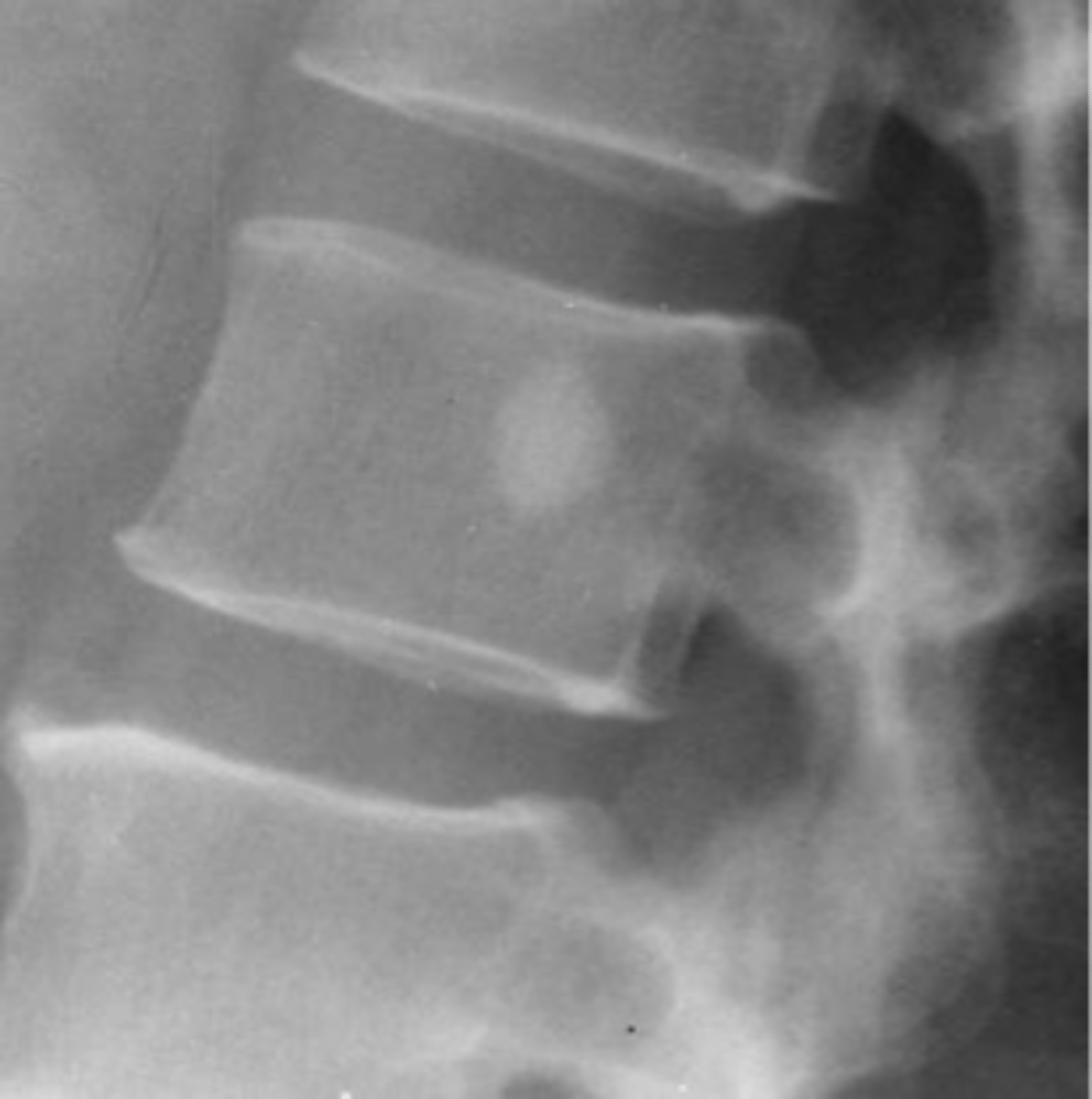
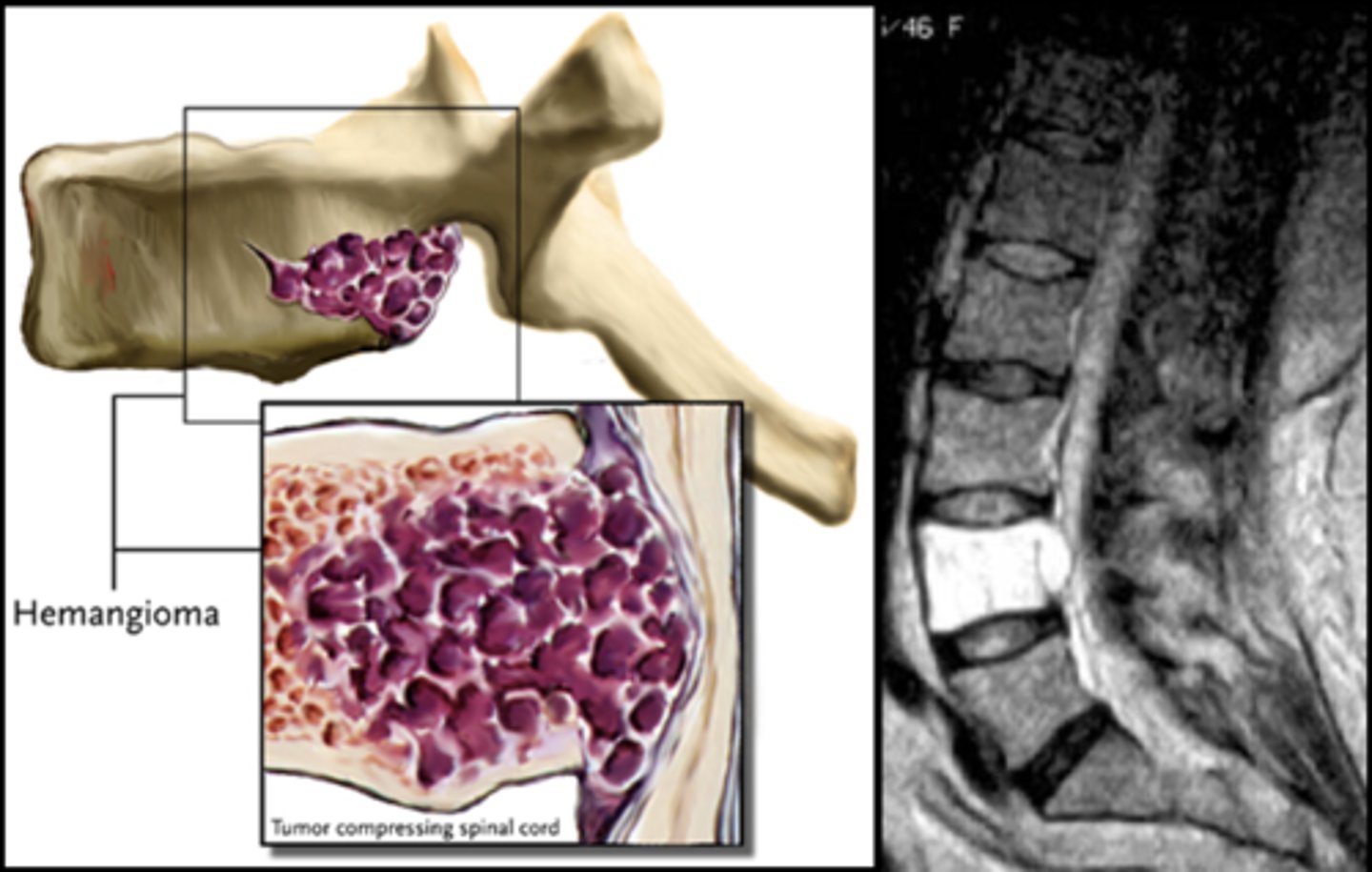
Vertebral hemangioma
- Solitary vascular neoplasm
- Slow growing
- 2-3% of all spine tumors (radiographs)
- 11% of all spines (autopsy)
- Most common benign tumor of the spine
State the incidence of vertebral hemangioma
- First seen over 40 y.o.
- F>M
- Most asymptomatic
- 75% in spine and skull
- Lower thoracic and upper lumbar
- Vertebral body
• Extension into vertebral arch (10-15%)
State the clinical features of vertebral hemangioma
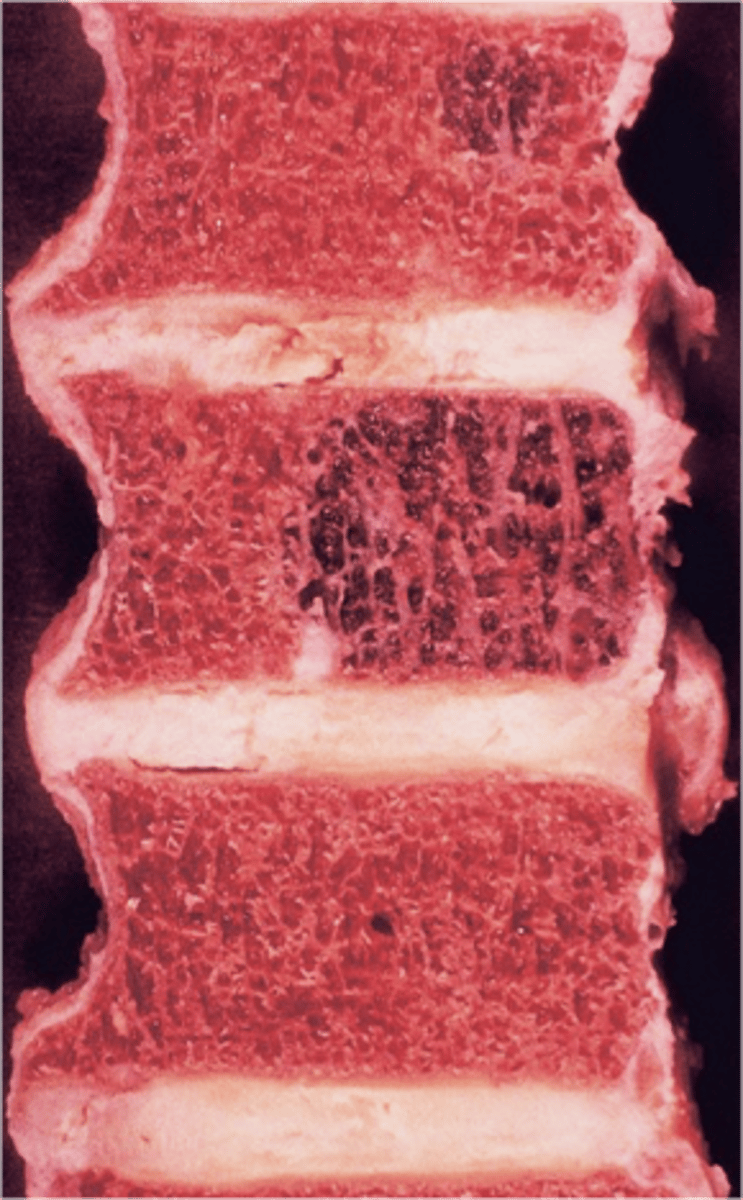
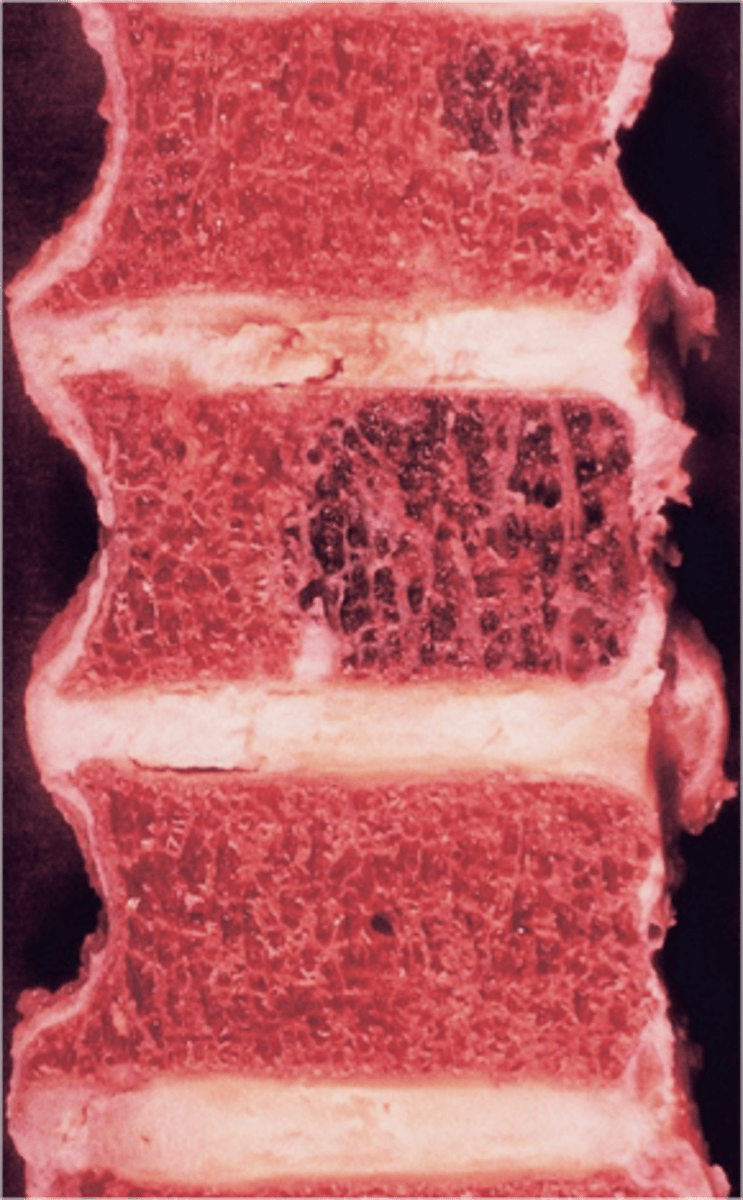
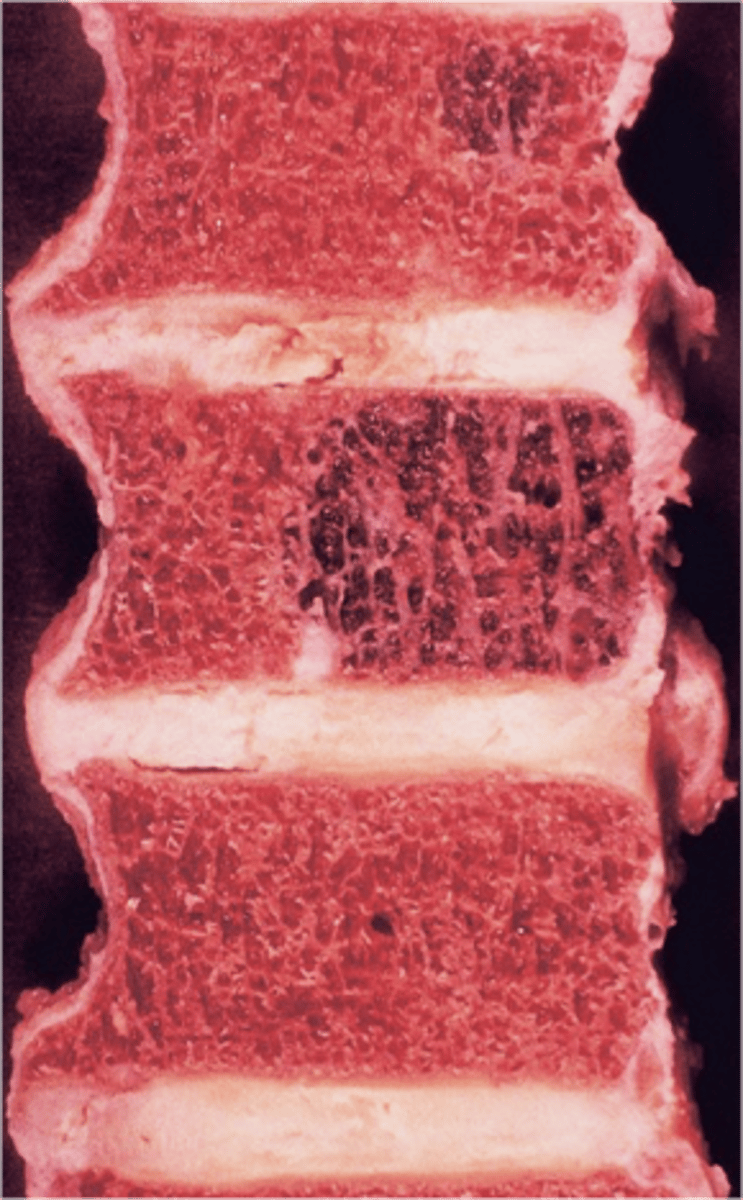
- Vertical striations (corduroy cloth)
- Expansion (rare) may result in neurologic findings
- Skull ("sand dollar")
- Paravertebral swelling
State the radiographic features of vertebral hemangioma
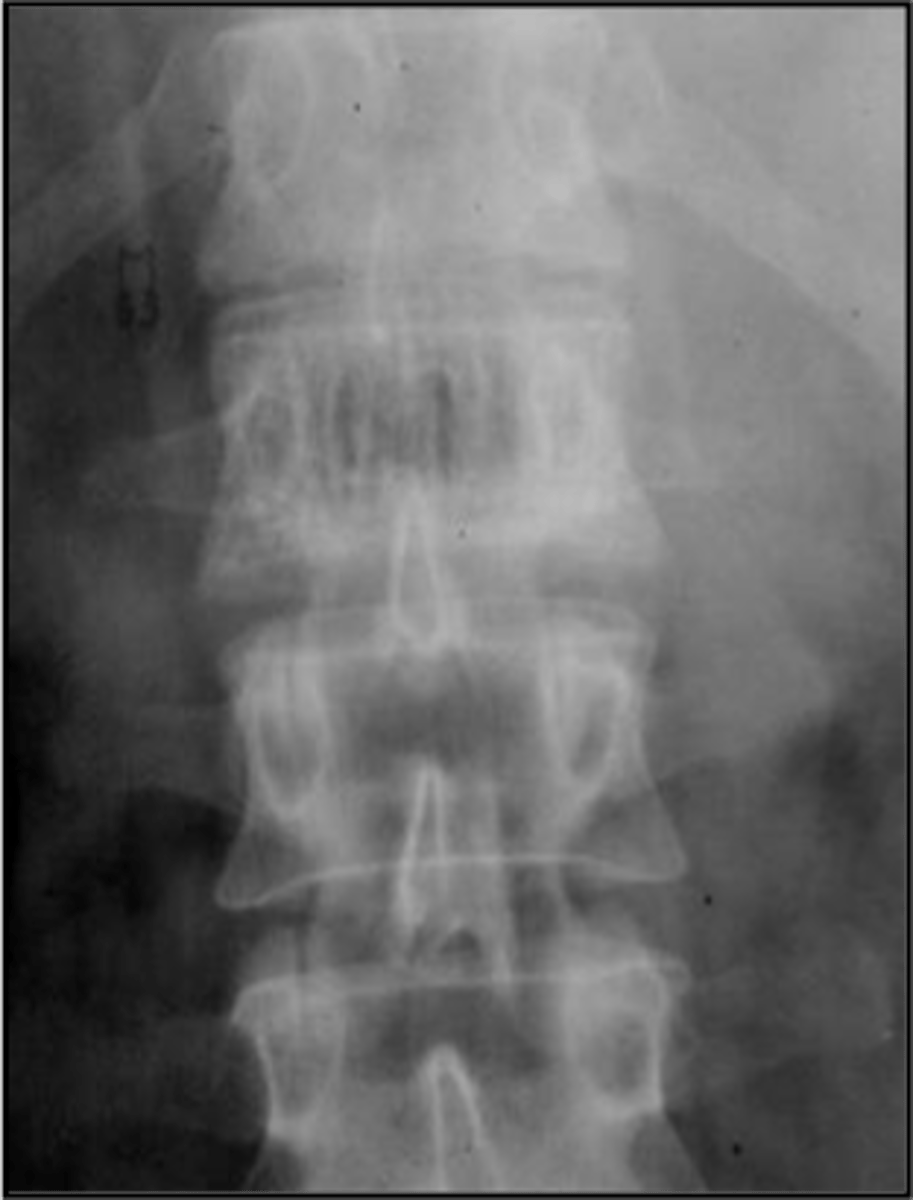
Expansile
_____ vertebral hemangioma
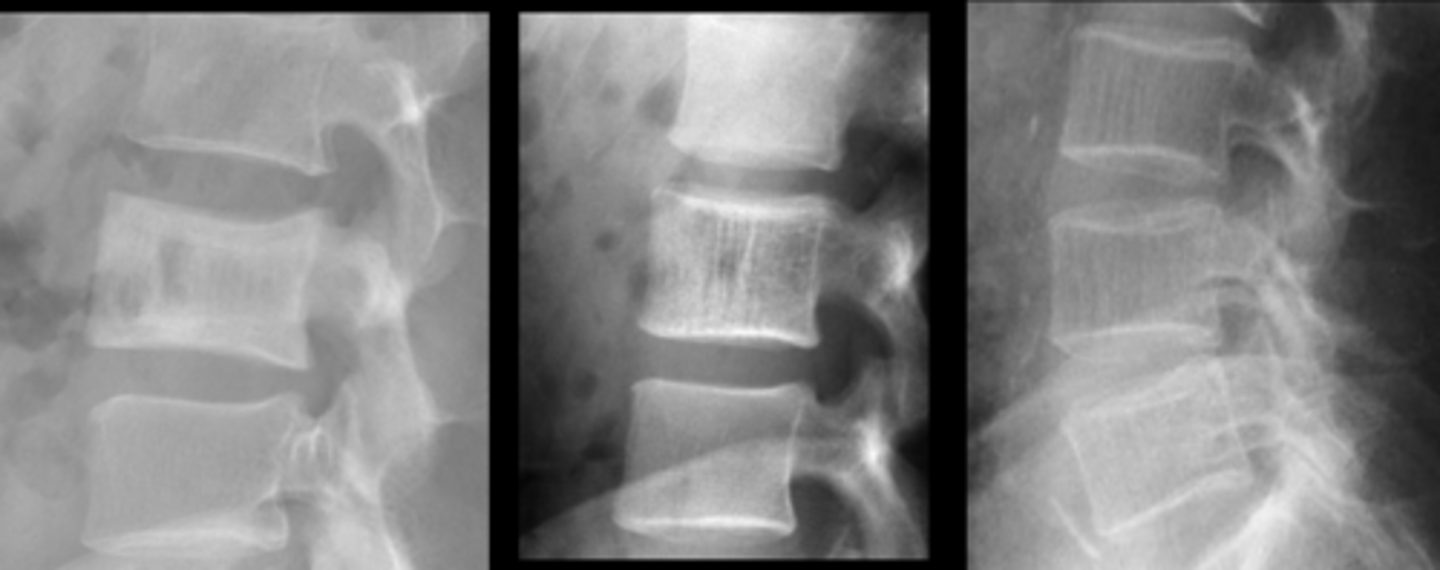
- Left: Paget Disease
- Middle: Vertebral hemangioma
- Right: Osteoporosis
Complete the DDx for vertebral hemangioma
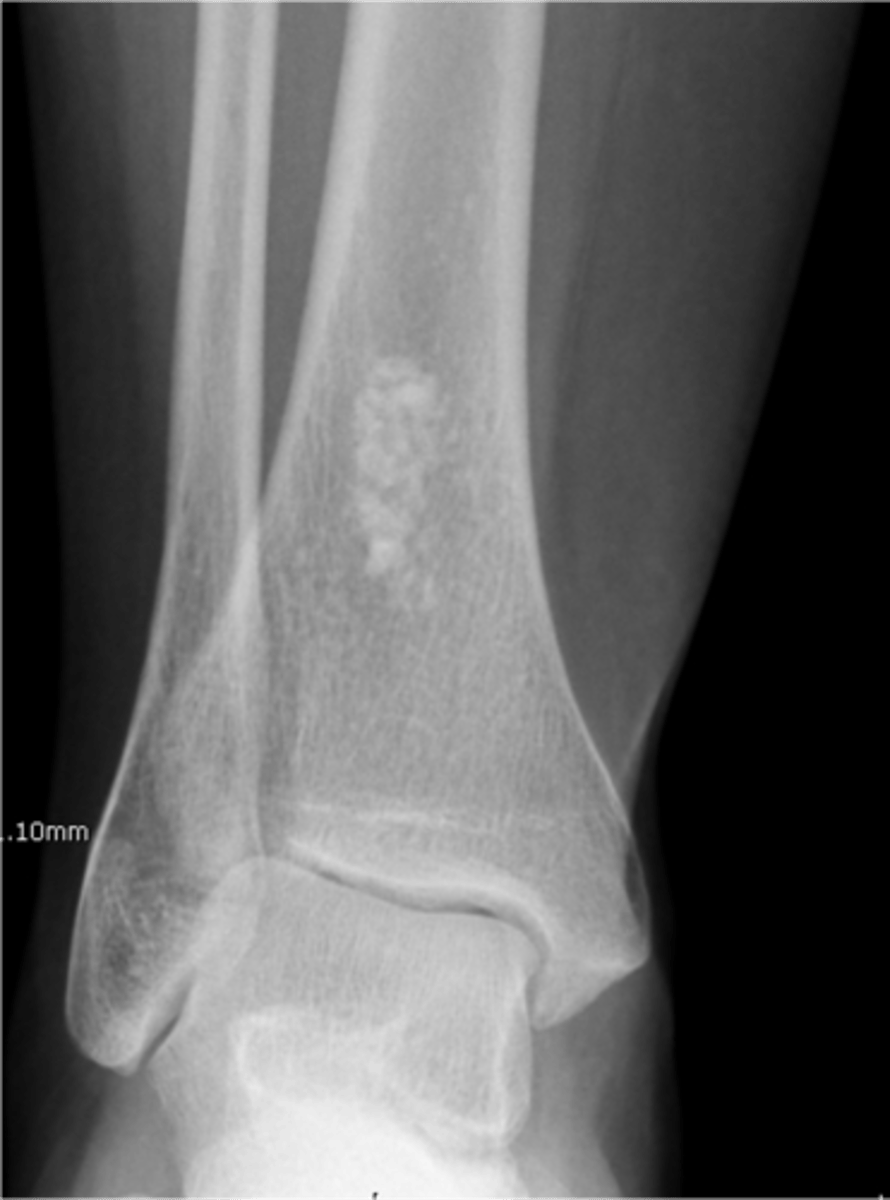
- M=F
- 10-30 y.o.
- Hands and feet
- Usually painless
- Most common benign tumor of hand
- 10% of all benign bone tumors
- <1% malignant transformation
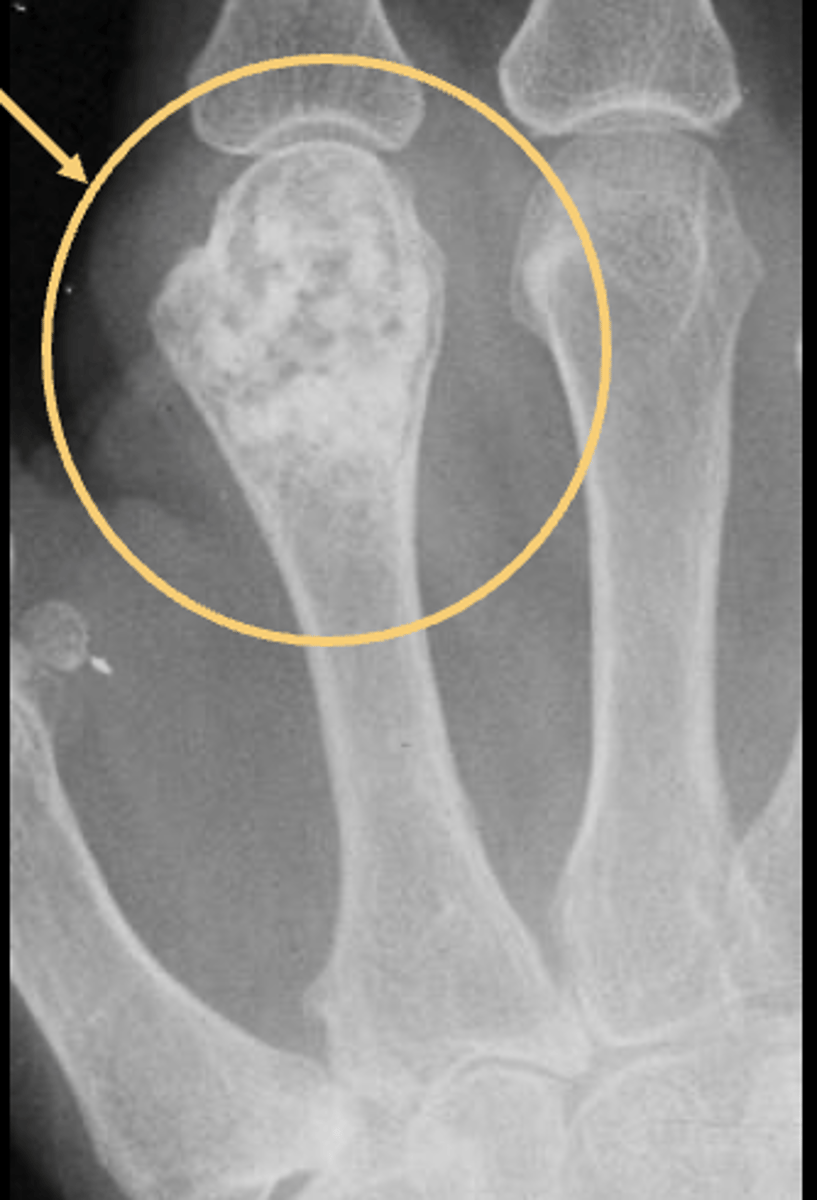
State the clinical features of solitary enchondroma
- Central
- Geographic
- Metaphyseal and diaphyseal
- Endosteal scalloping
- Cortical thinning/expansion
- Stippled calcification (50%)
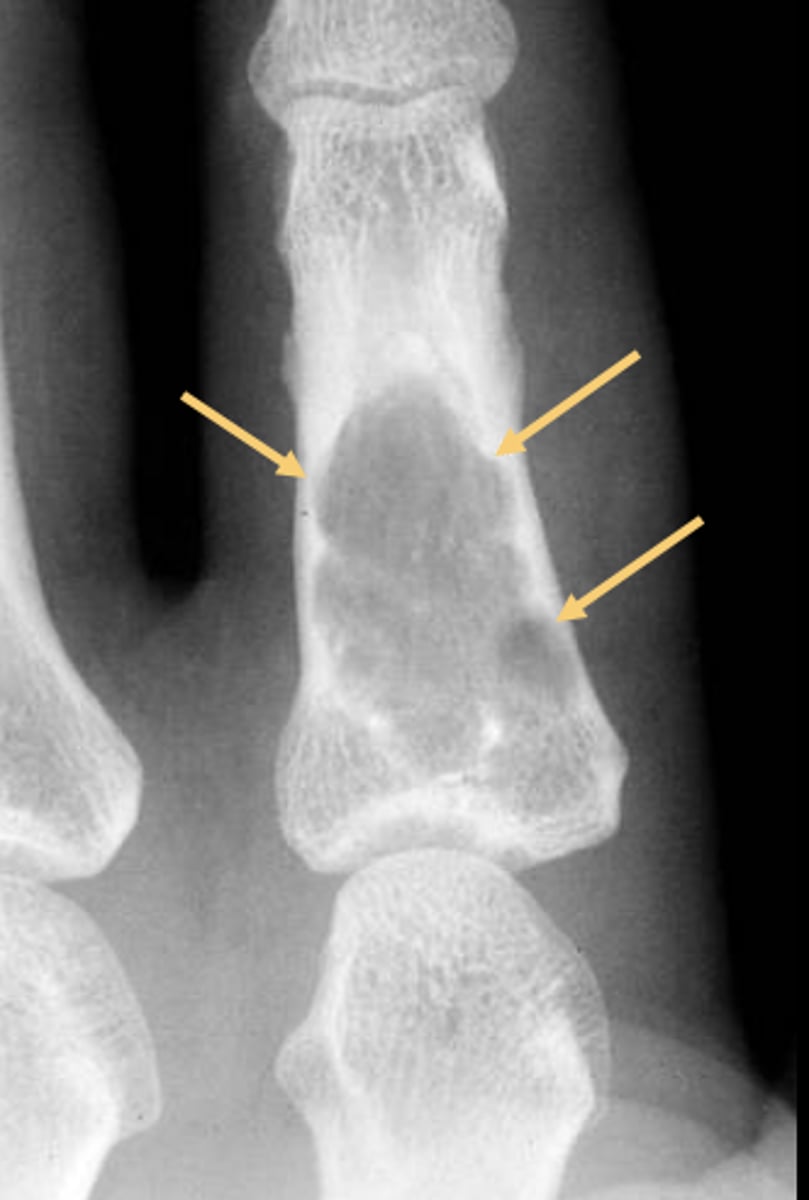
State the radiographic features of solitary enchondroma
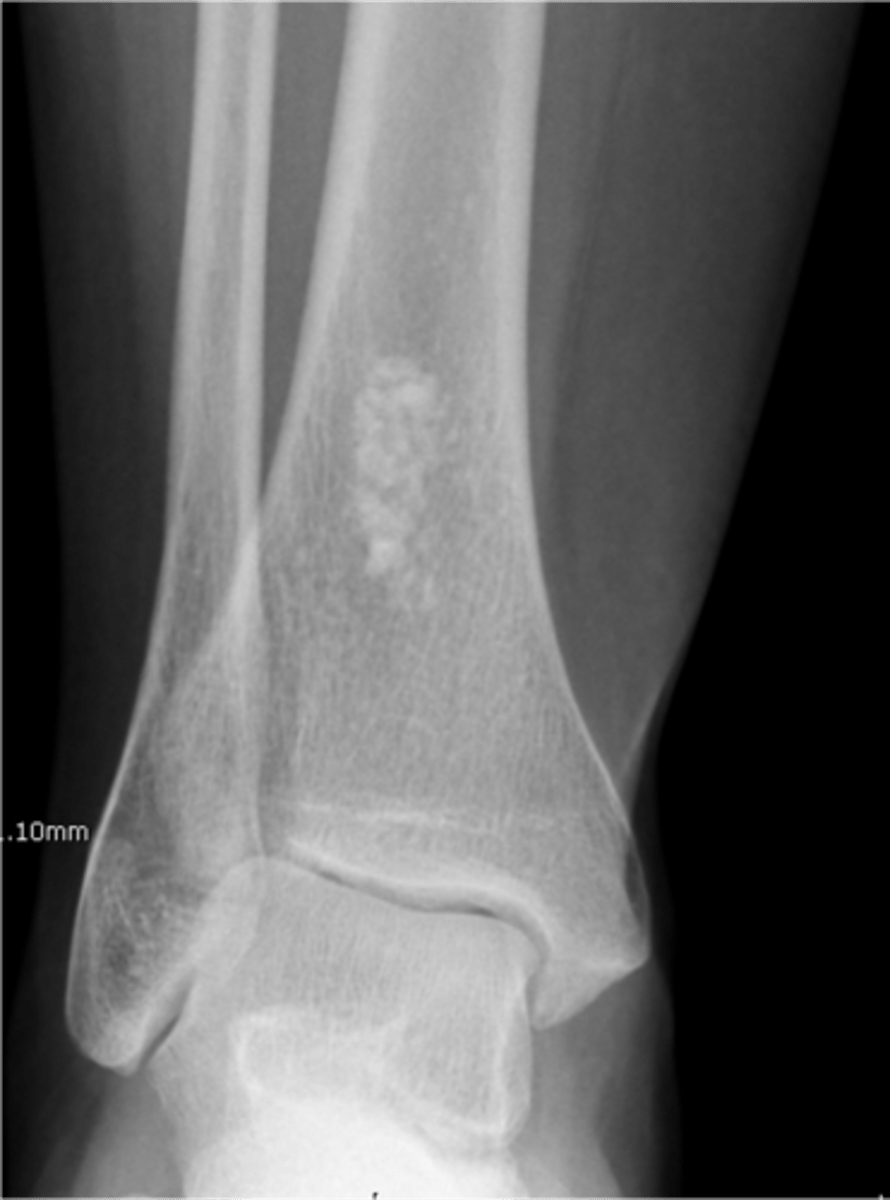
Matrix calcification
ID feature of solitary enchondroma
Endosteal scalloping
ID feature of solitary enchondroma
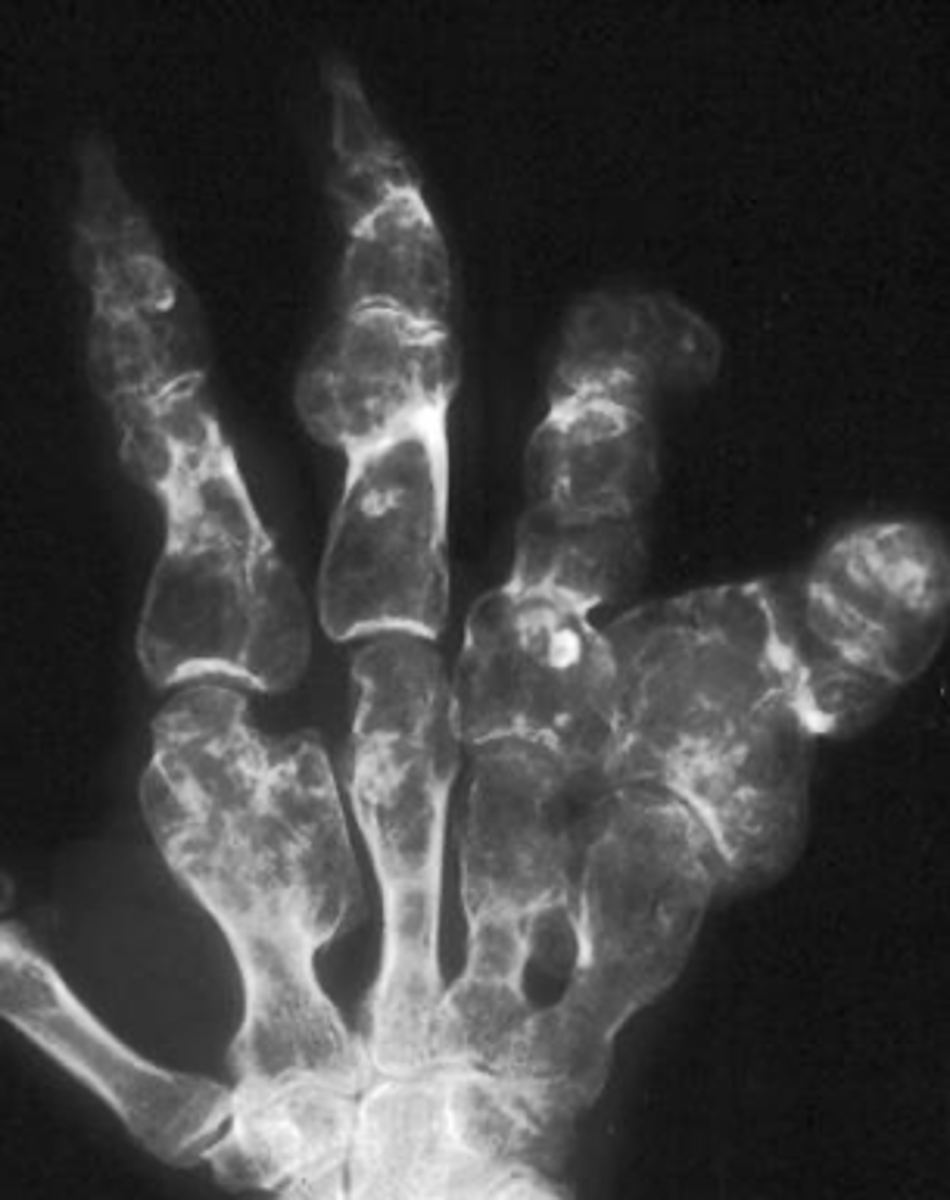
Multiple enchondromas
ID benign tumor
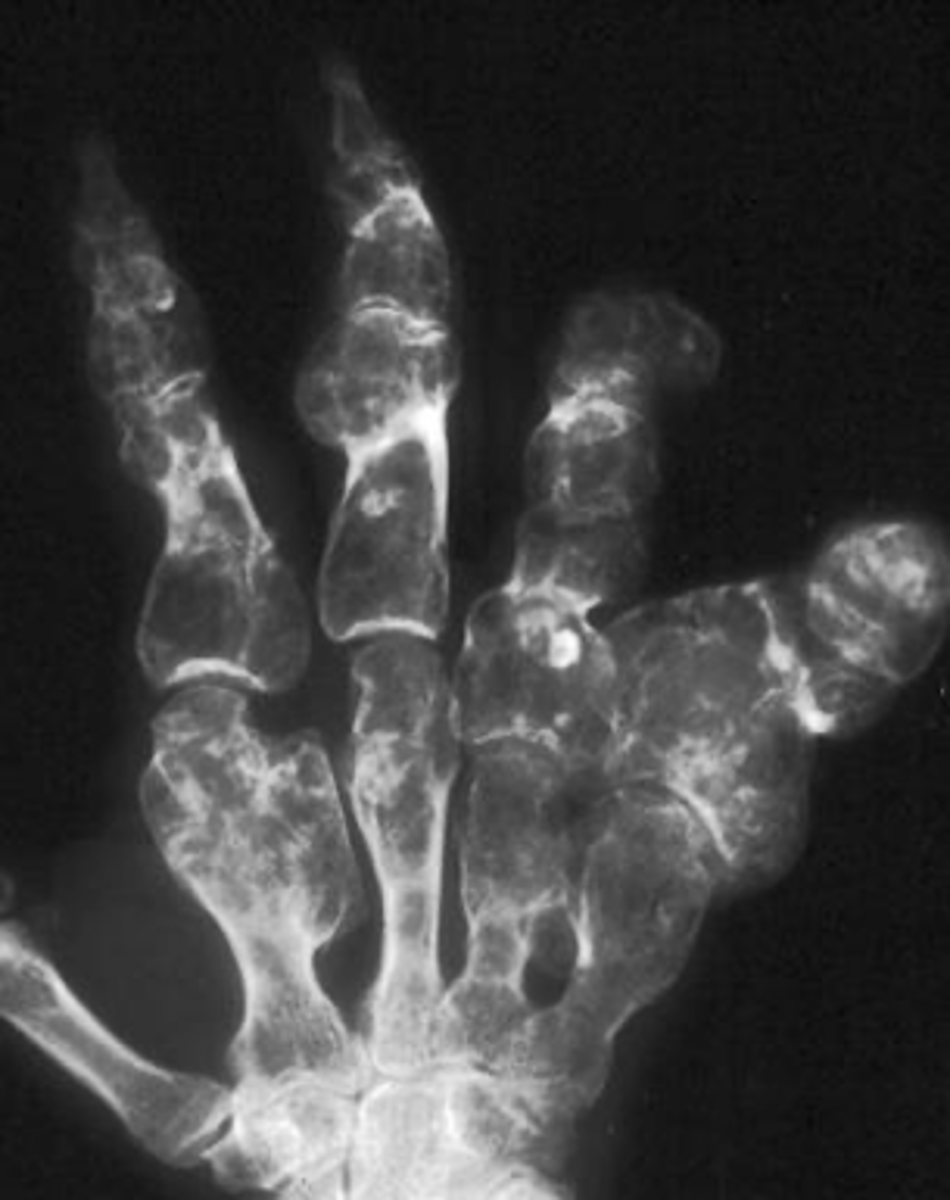
Ollier's disease
- Multiple enchondromas
- Malignant transformation (10-50%)
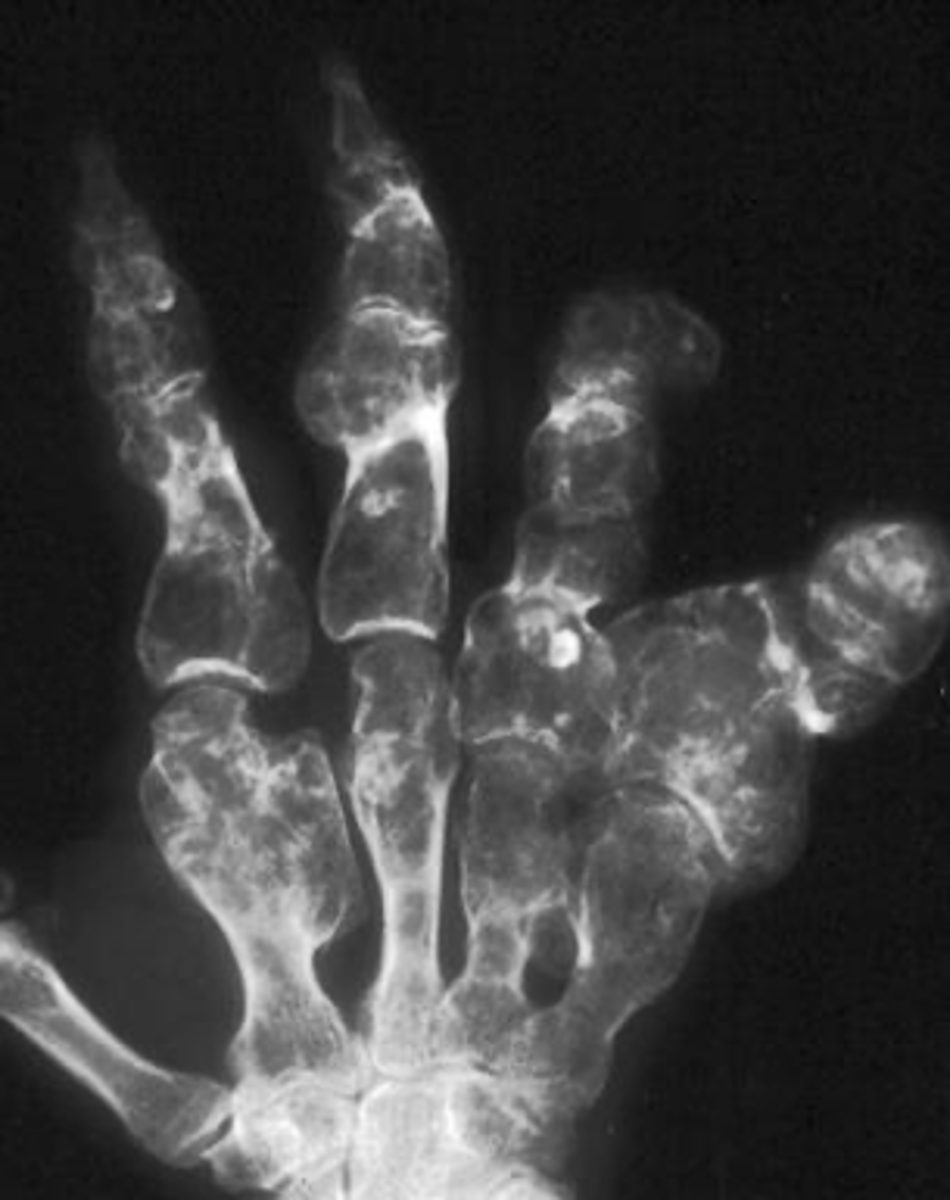
Maffucci's syndrome
- Rare
- Multiple enchondromas
- Soft tissue hemangiomas
- Malignant transformation (25-50%)
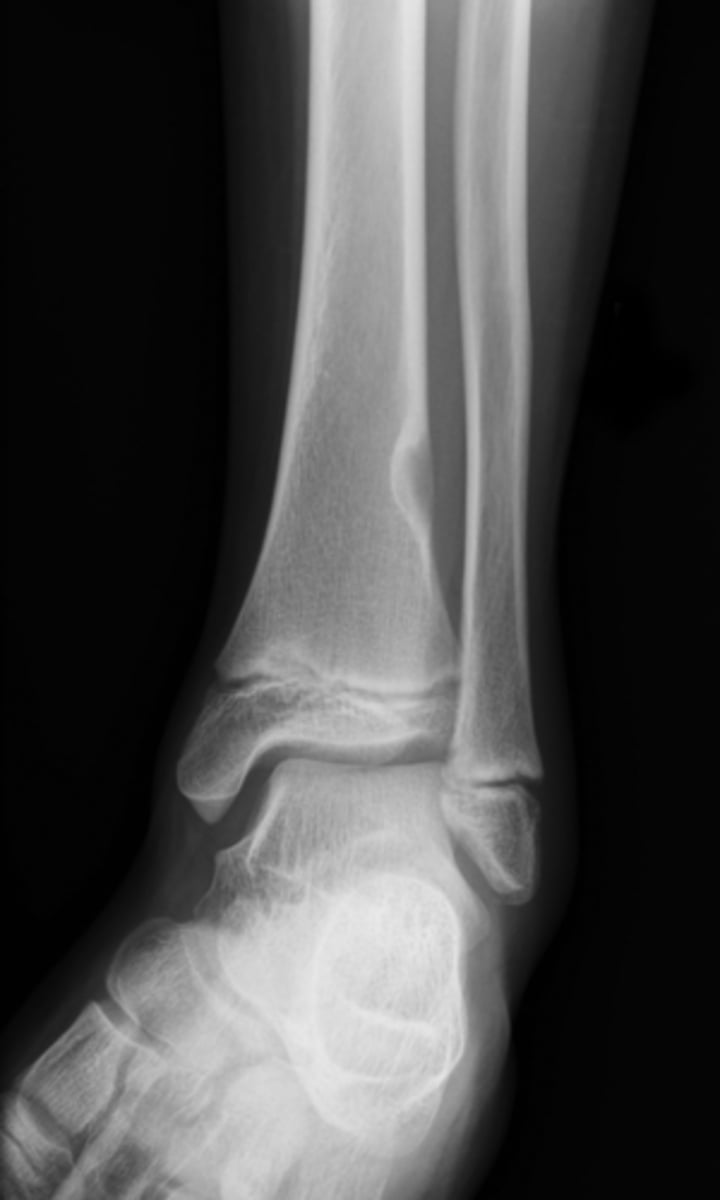
Non-ossifying fibroma
- Kids (<20 y.o.)
• Fibrous cortical defect (older term)
• Younger patient and smaller <2-3 cm
- M:F, 2:1
- Lower extremities
- Present in 30-40% of normal children
- Most asymptomatic (unless pathologic fracture)
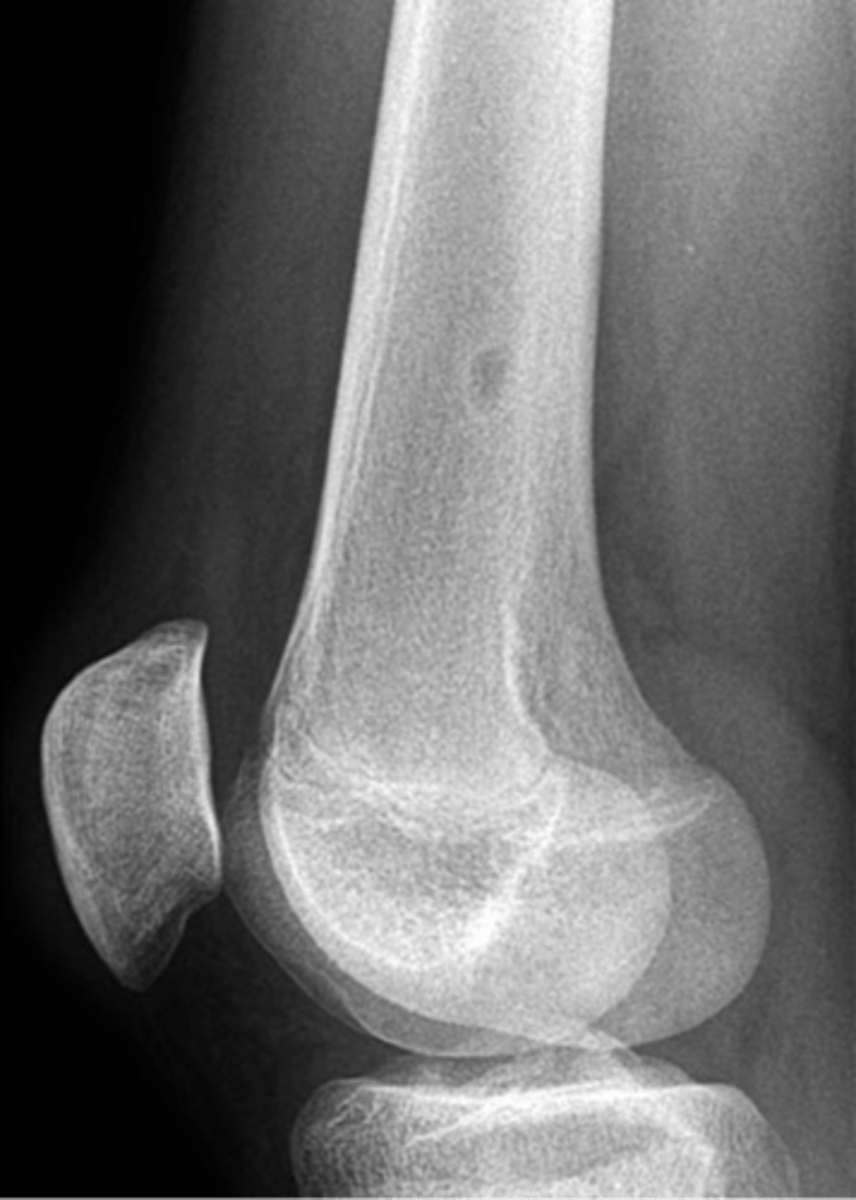
8 cm
Larger non-ossifying fibroma lesions >_____ may fracture
- Distal tibia
- Distal femur
- Proximal tibia
- Humerus
- Fibula
- Bones of the lower extremity (80-90%)
State the common locations for non-ossifying fibroma
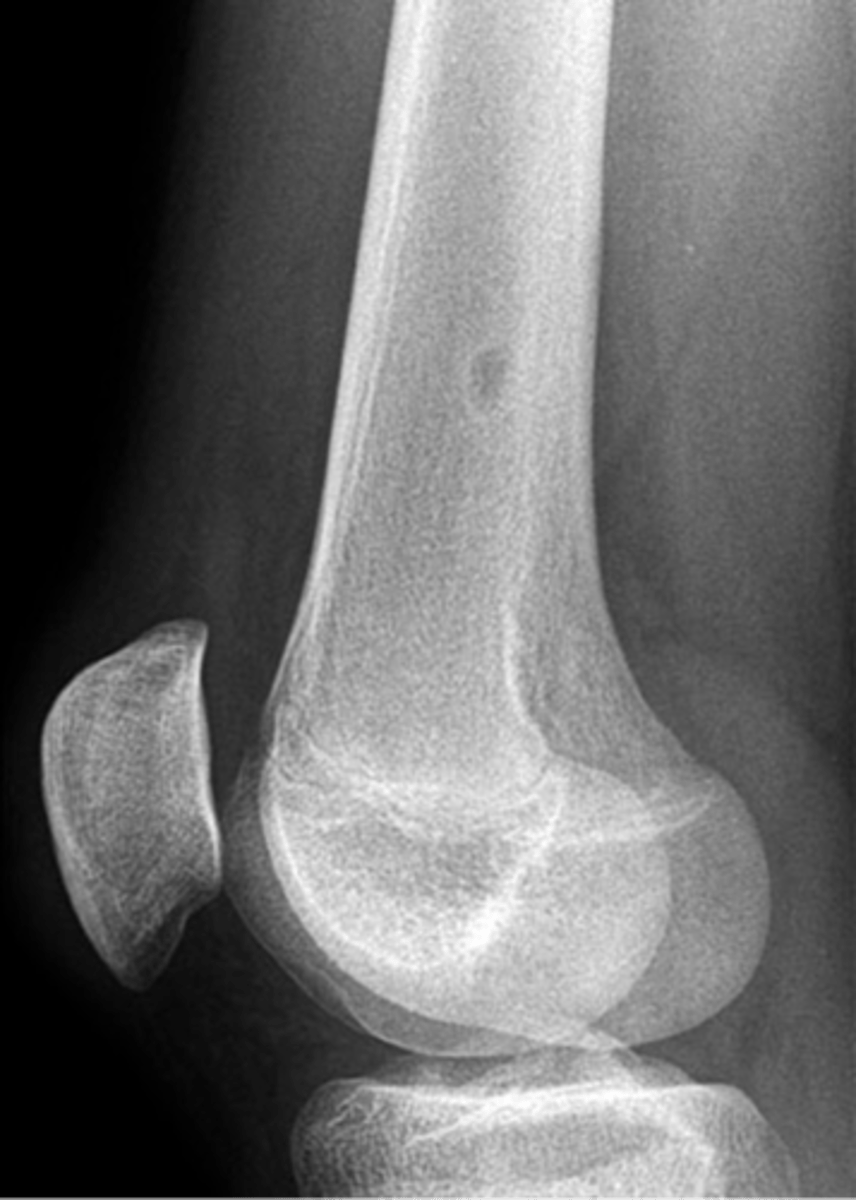
- Solitary
- Eccentric
- Geographic
- Multiloculated
- No malignant transformation
State the radiographic features of non-ossifying fibroma
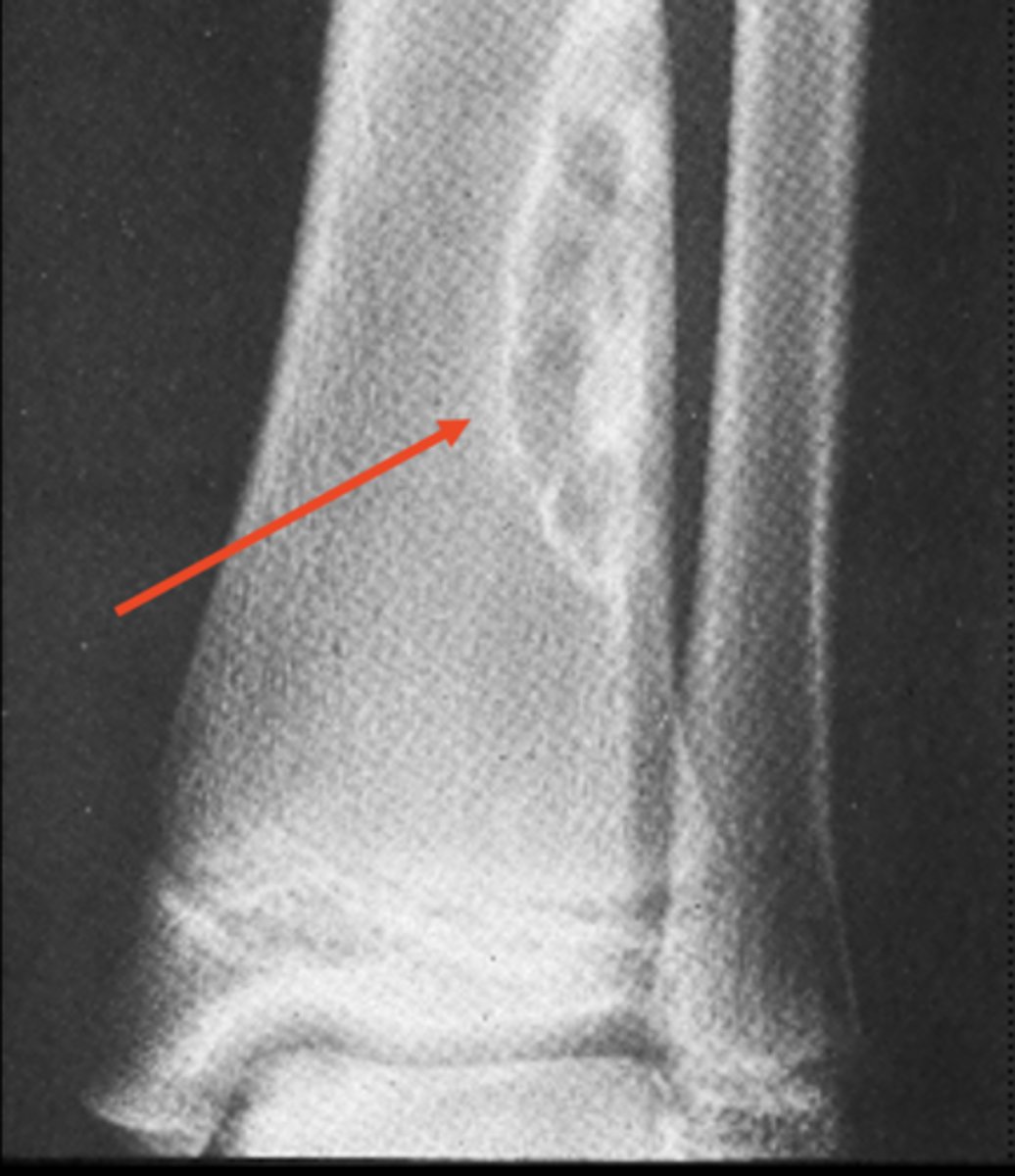
Geographic bone blister
ID radiographic feature of non-ossifying fibroma indicated by top arrow
Septations
ID radiographic feature of non-ossifying fibroma indicated by bottom arrow
Pathologic fracture
Non-ossifying fibroma with _____
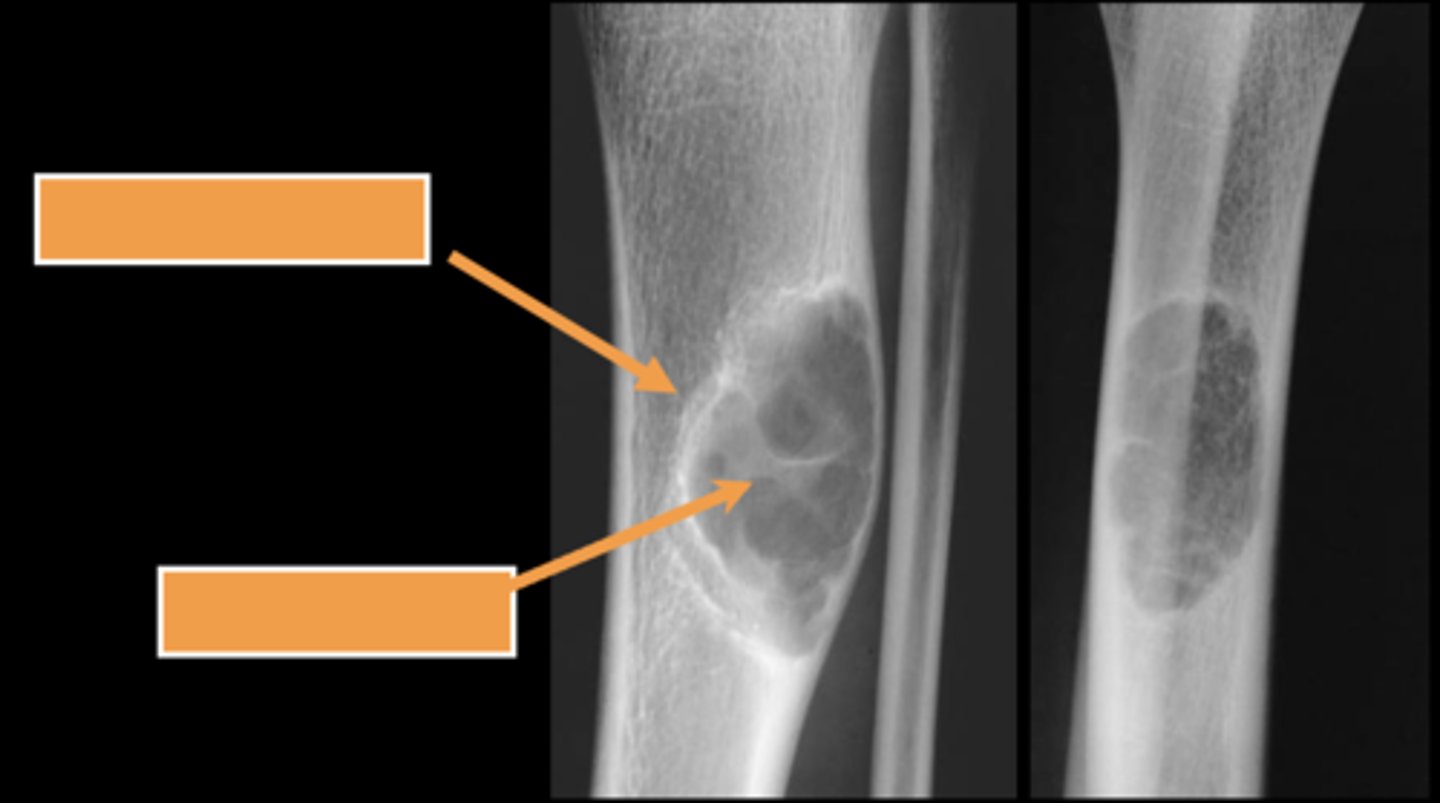
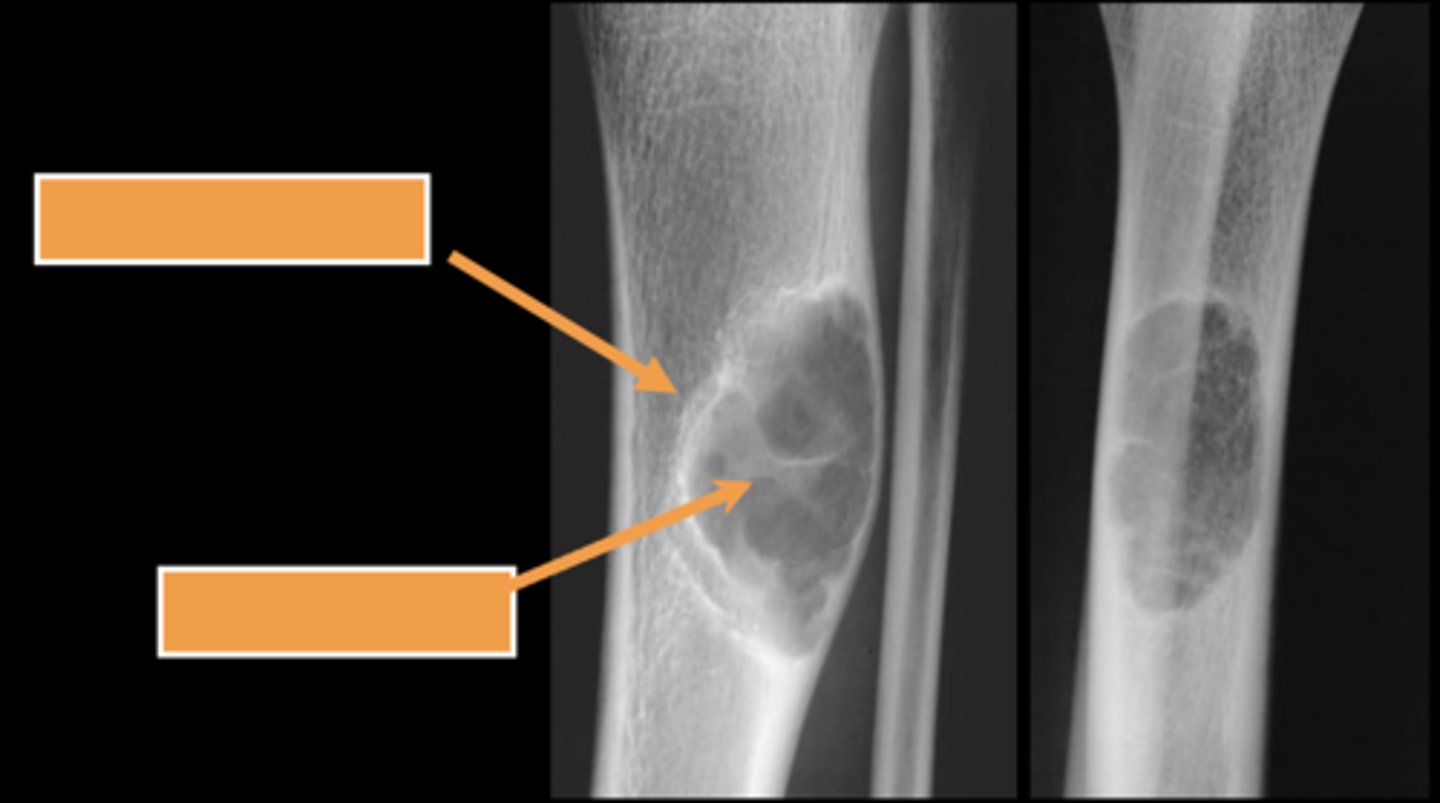
Simple bone cyst
- M:F, 2:1
- 3-14 y.o.
- Asymptomatic until fracture
- Proximal humerus (50%)
- Proximal femur (25%)
- Metaphyseal
- Migrate from physis with growth
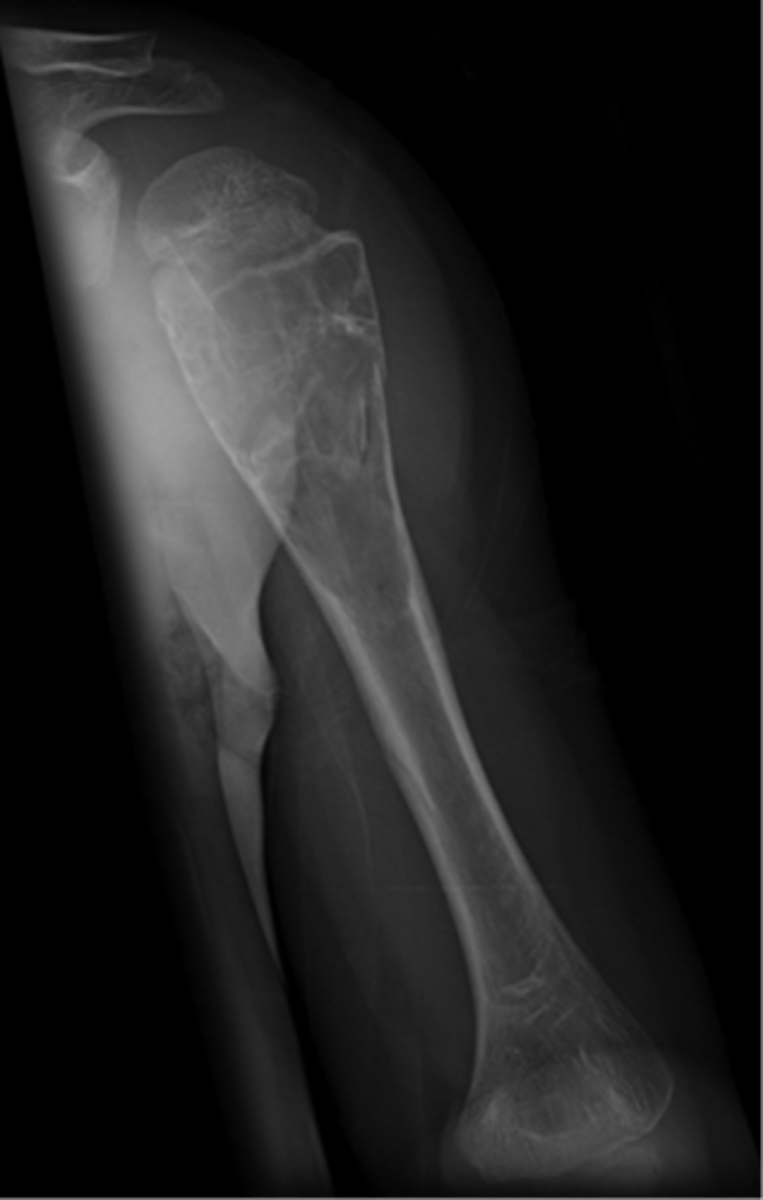
- Mildly expansile
- Geographic
- Pseudoloculated
- Metaphyseal
- Central
- 30-40% recurrence
State the radiographic features of simple bone cyst
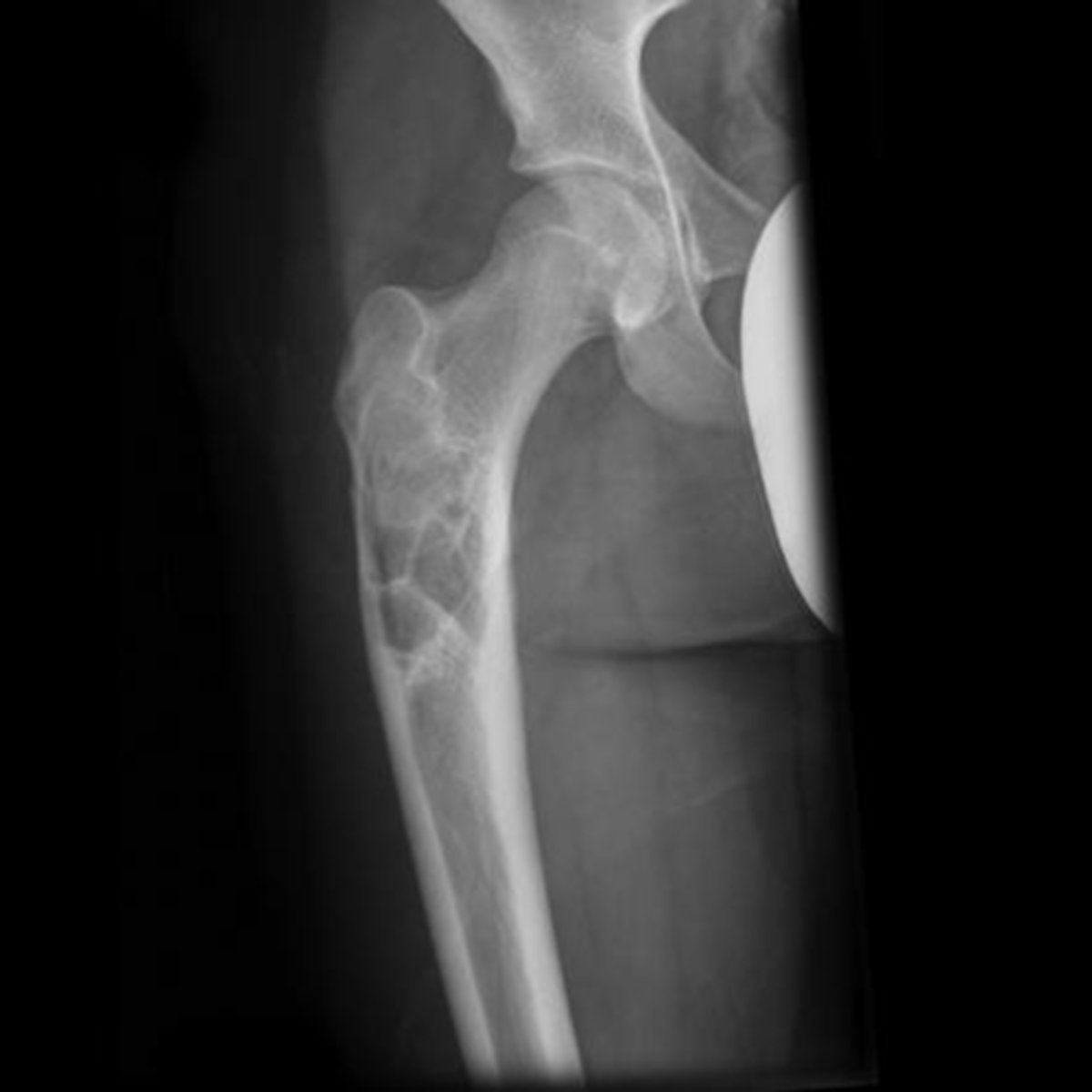
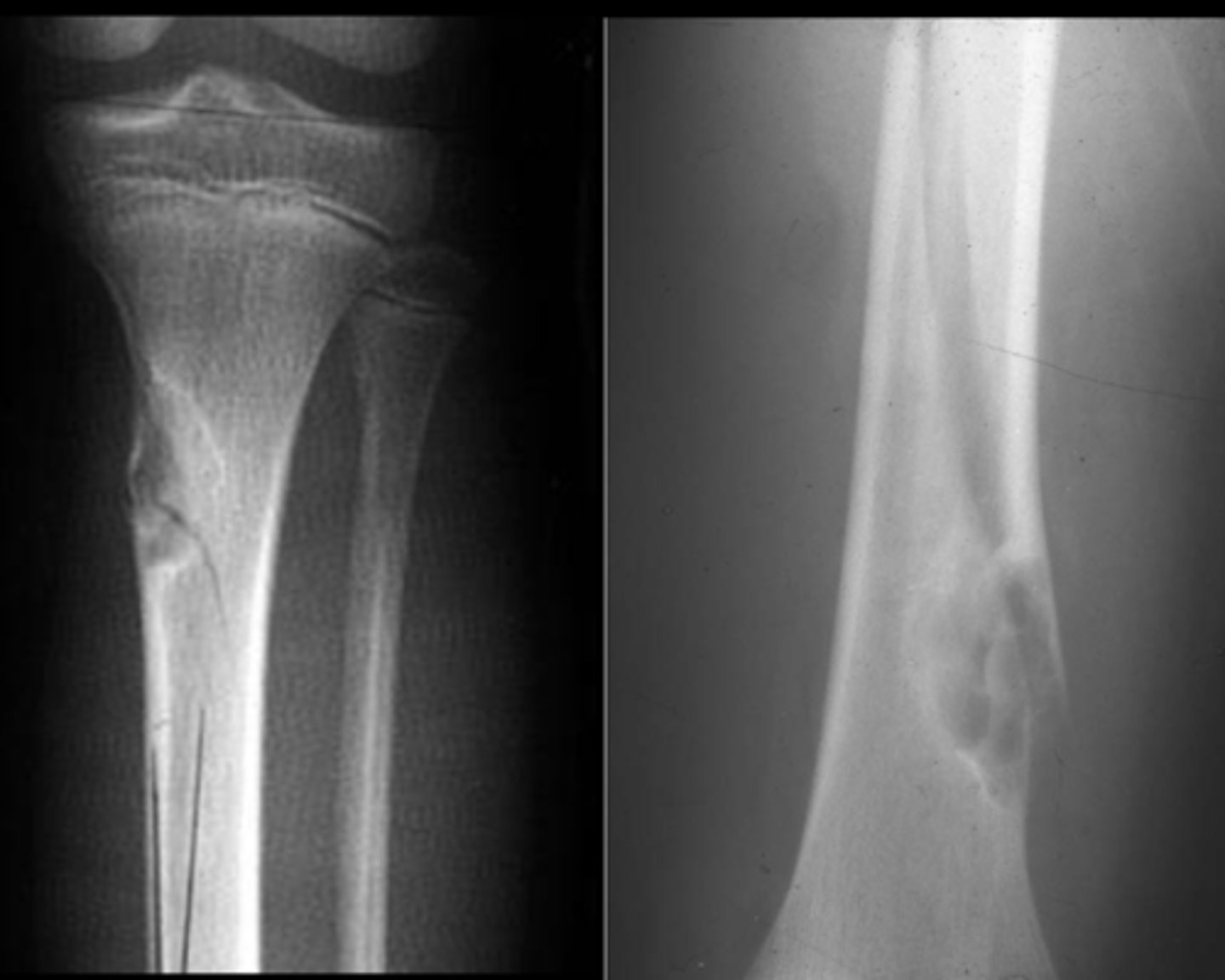
Pathologic fracture
ID radiographic feature of simple bone cyst indicated by the top arrow
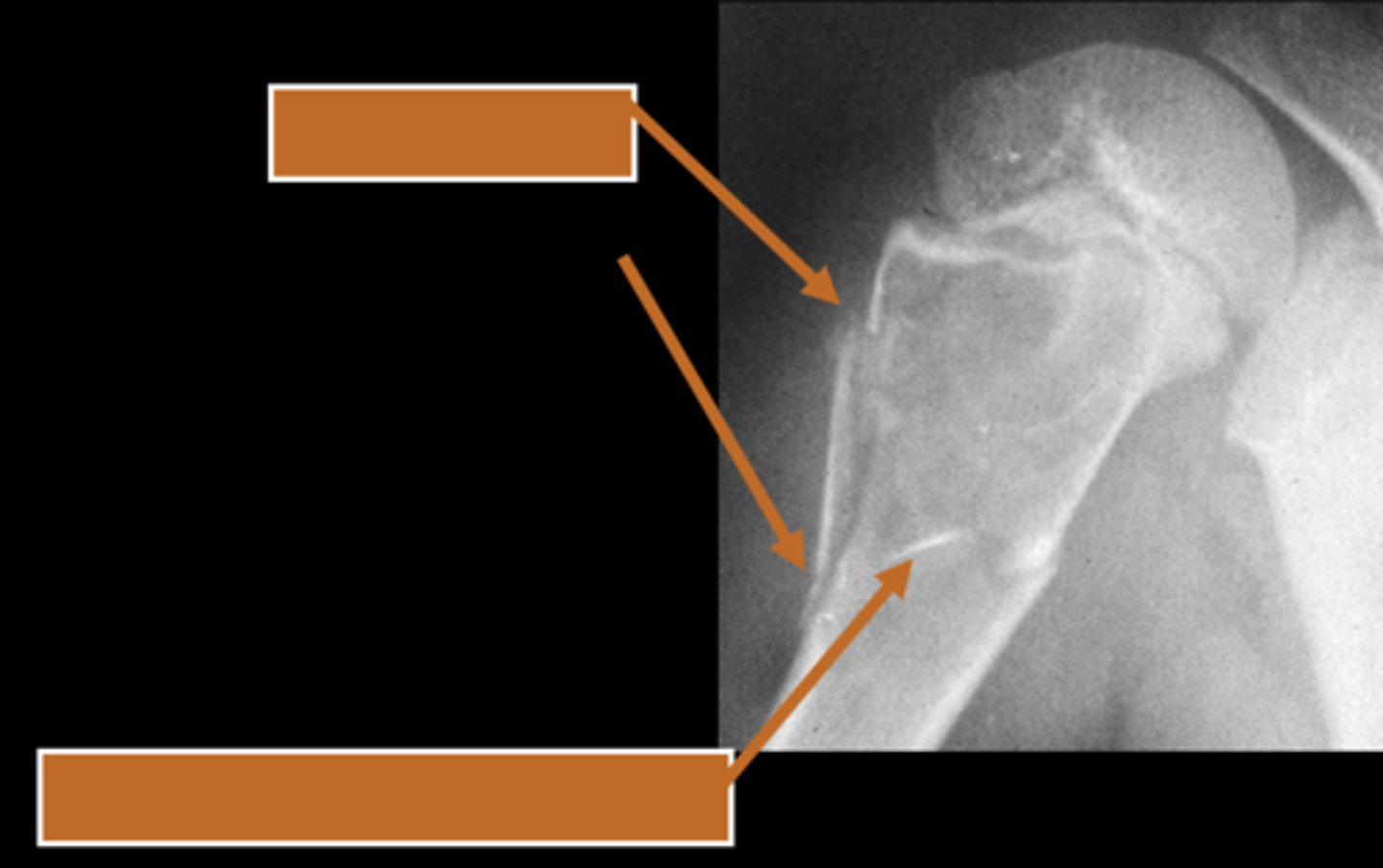
Fallen fragment sign
ID radiographic feature of simple bone cyst indicated by the bottom arrow
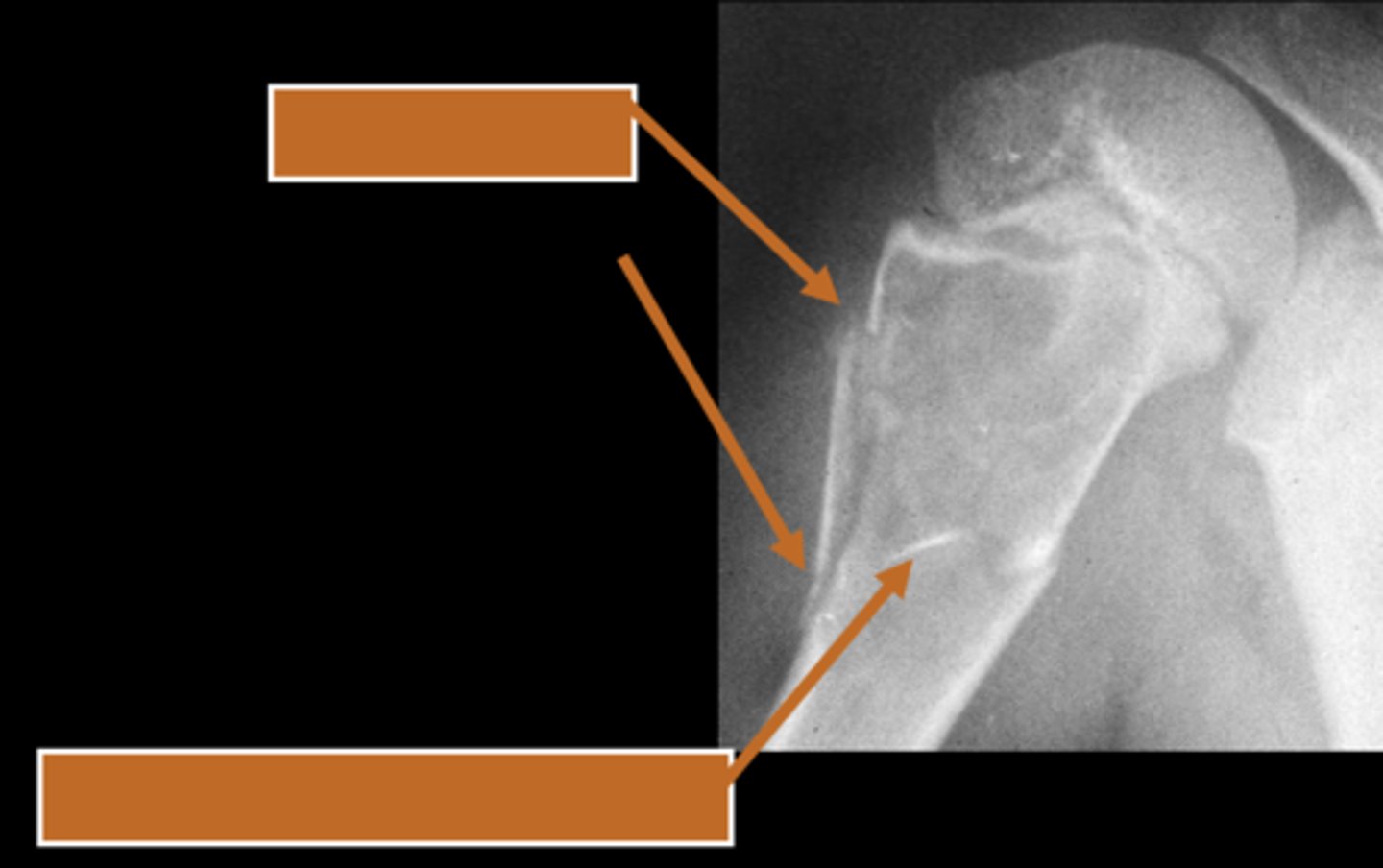
Fallen fragment sign (10%)
- Cortex broke off
- Pathognomonic
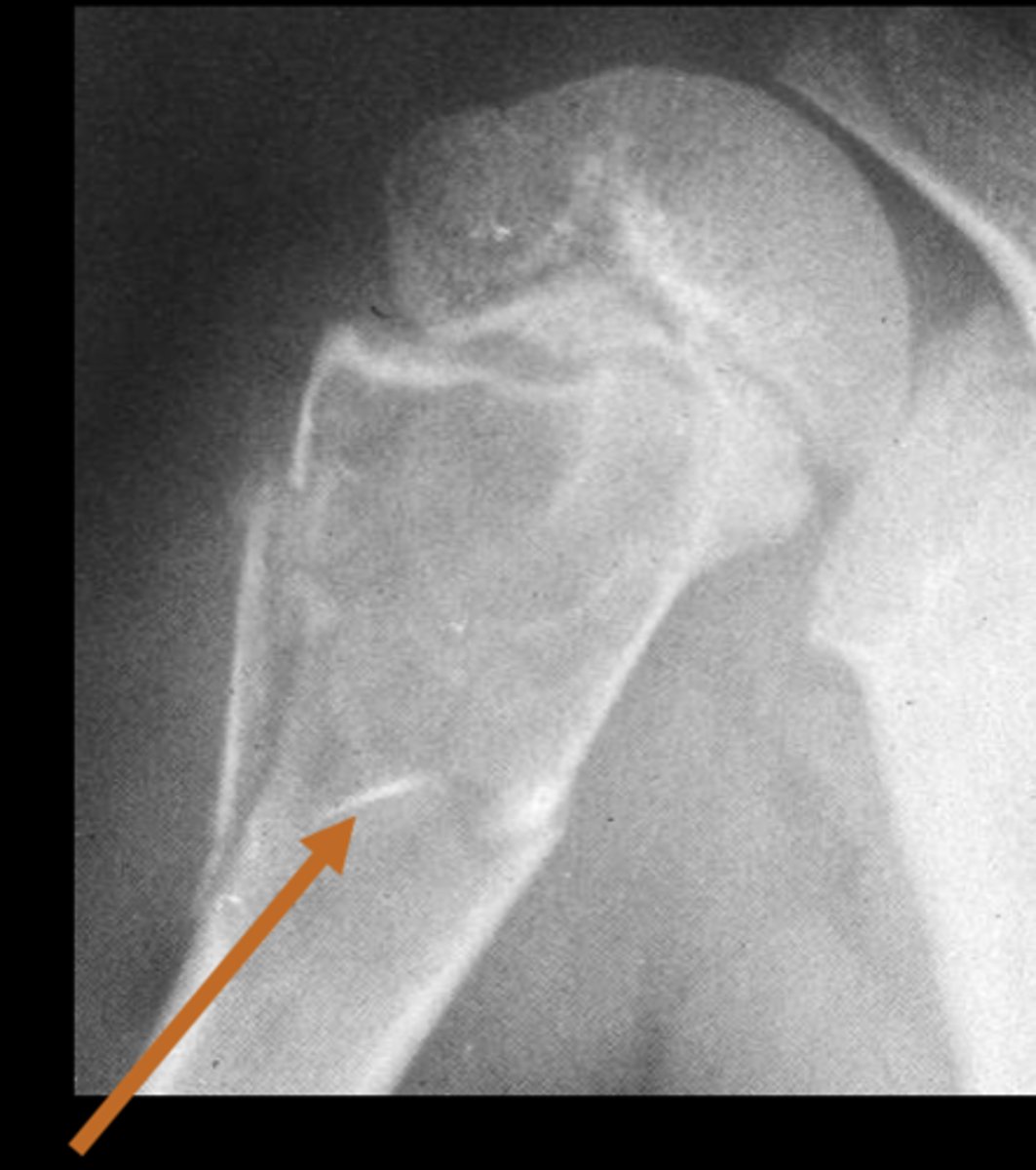
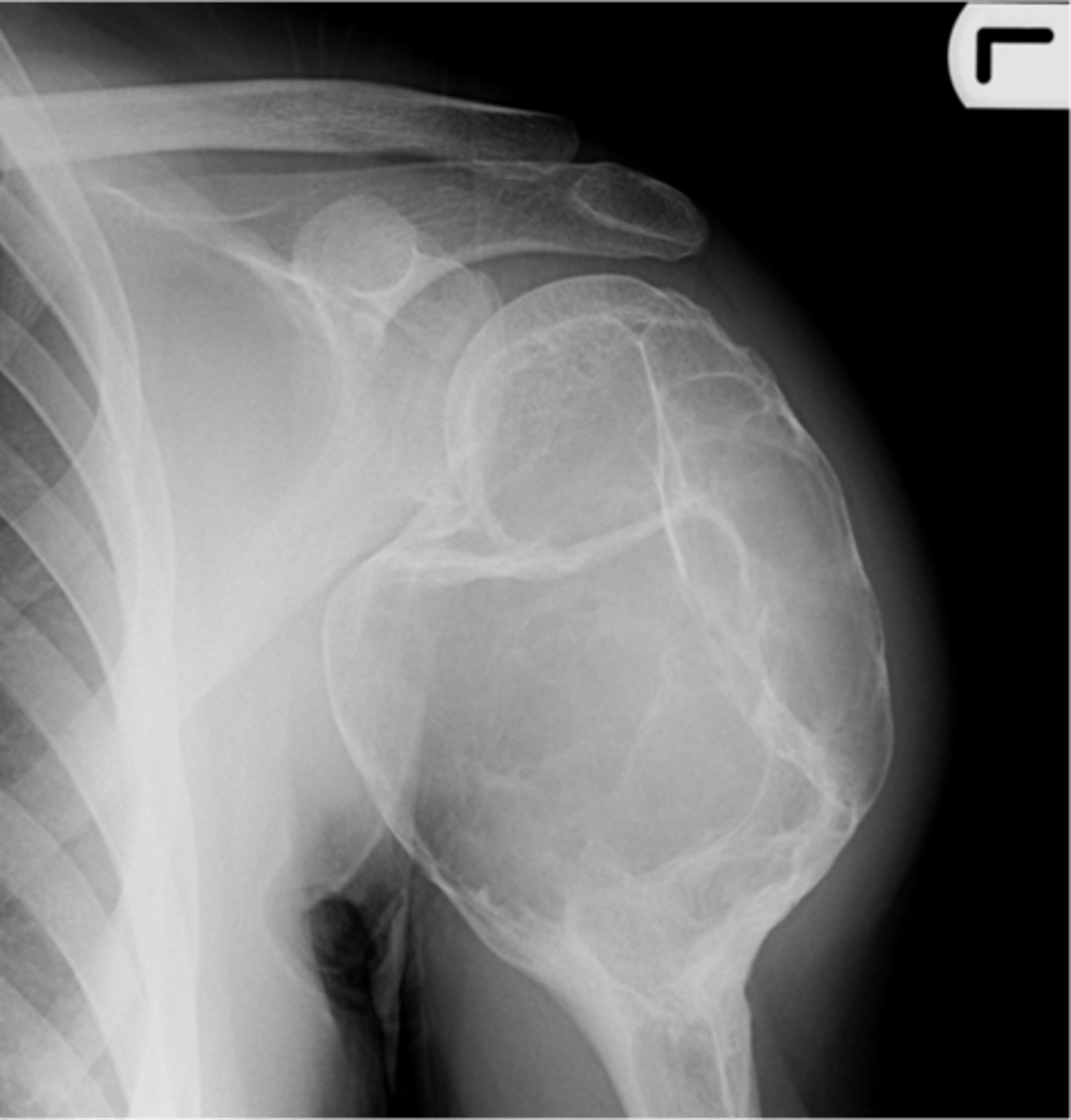
Aneurysmal bone cyst
- 1% of biopsied primary bone tumors
- M:F, 2:3
- 5-20 y.o.
- Acute pain
- Previous trauma
- 80% tubular bones and spine
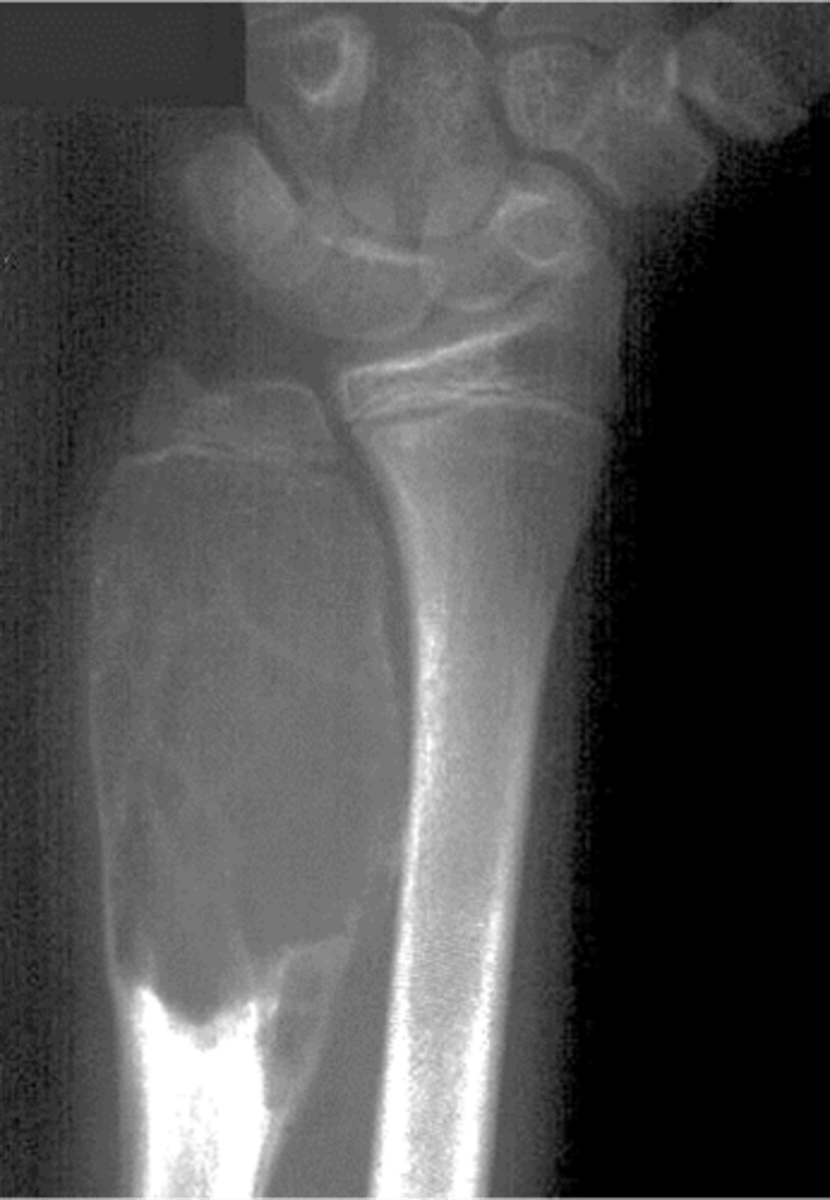
- Eccentric
- Metaphyseal
- Osteolytic with fine trabeculae
- Saccular ballooning of cortex
- May cross epiphysis
- Periosteal buttressing
State the radiographic features of aneurysmal bone cyst in tubular bones
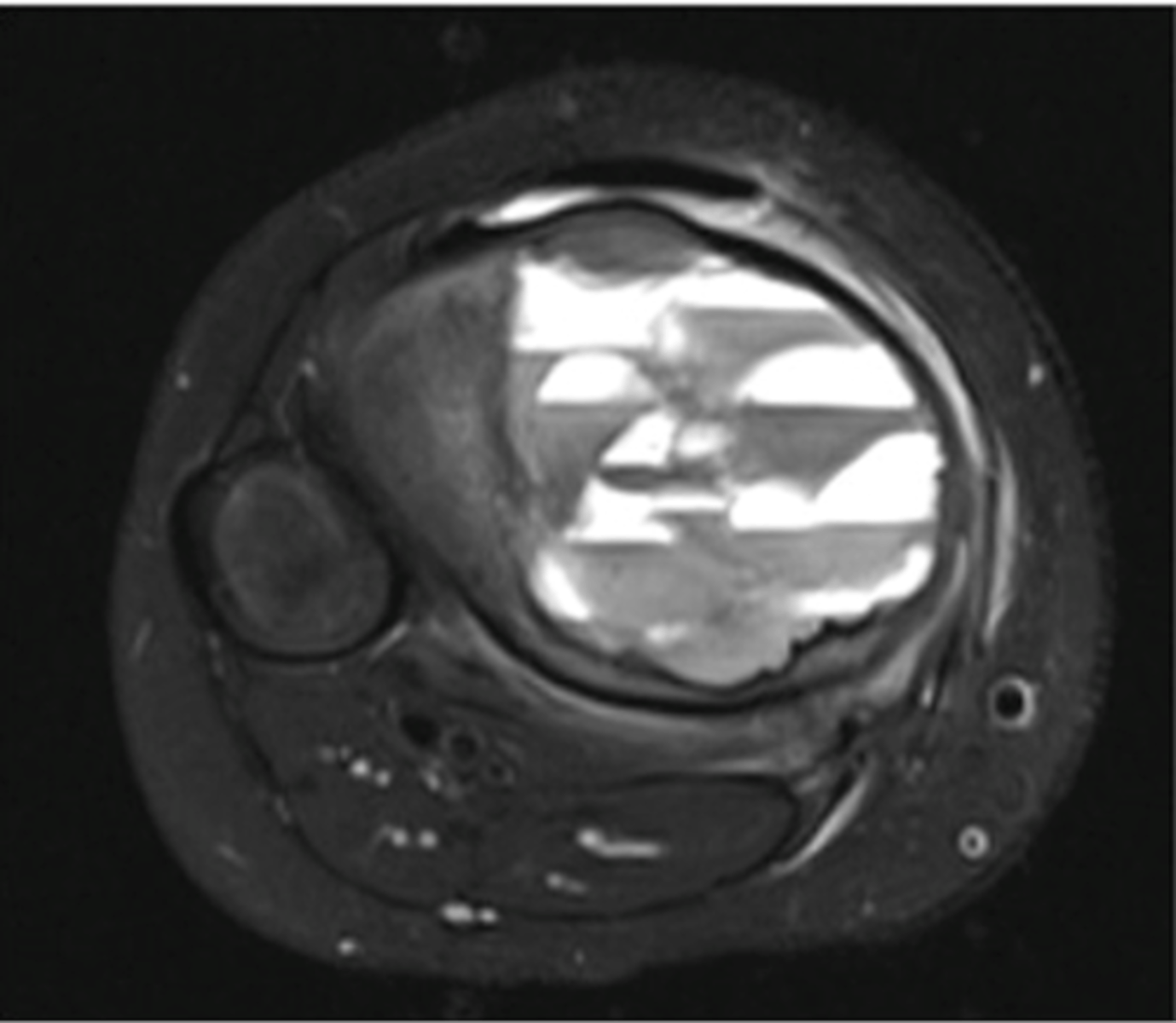
Fluid-Fluid Levels
- Most compatible with aneurysmal bone cyst
- Also seen in giant cell tumors, simple bone cysts, and telangiectatic osteosarcoma
Intraosseous lipoma
- M=F
- 5-70 y.o.
- Asymptomatic
- Central target sequestrum
- Calcaneus
- Tibial metaphysis
- Fibular metaphysis
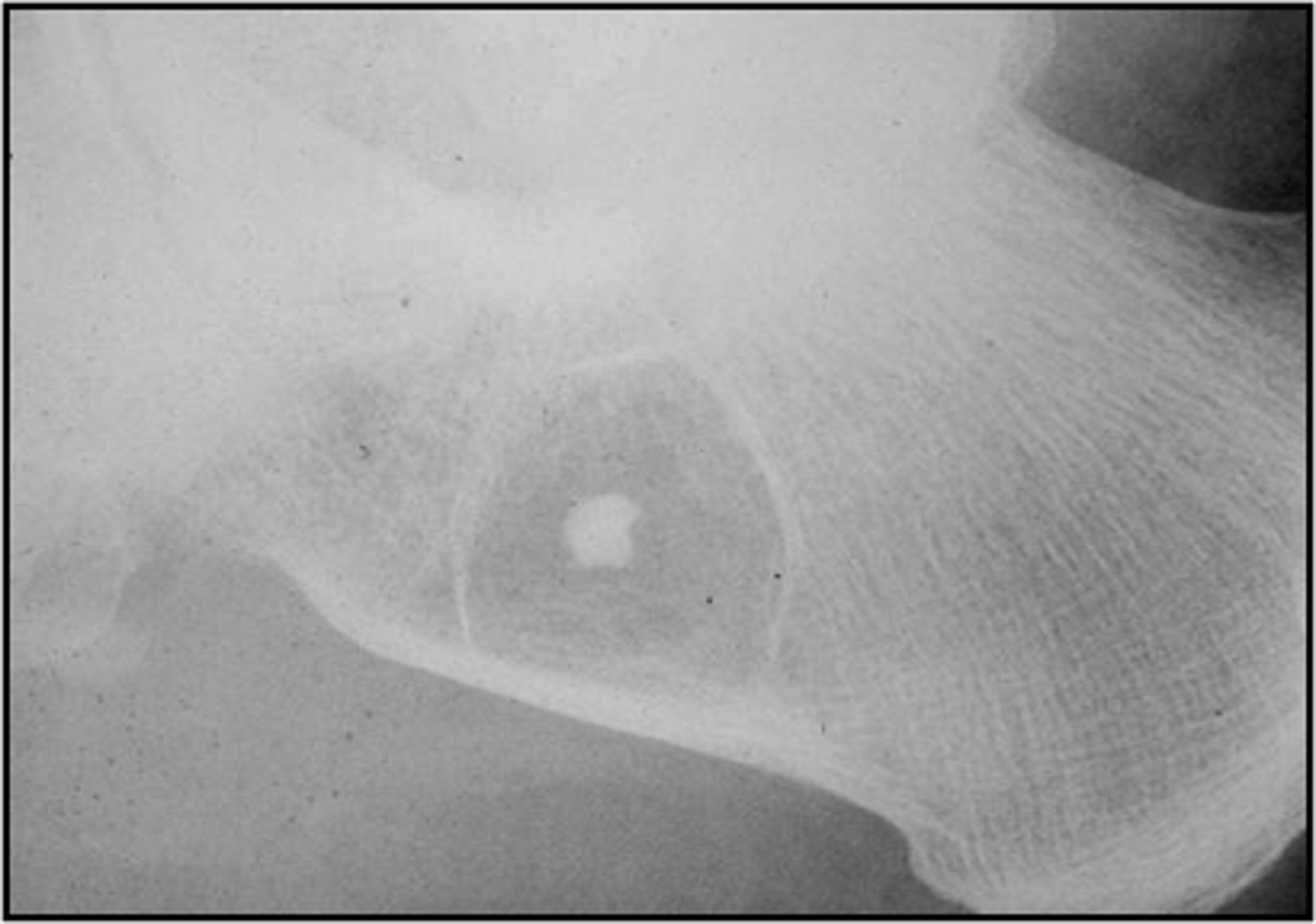
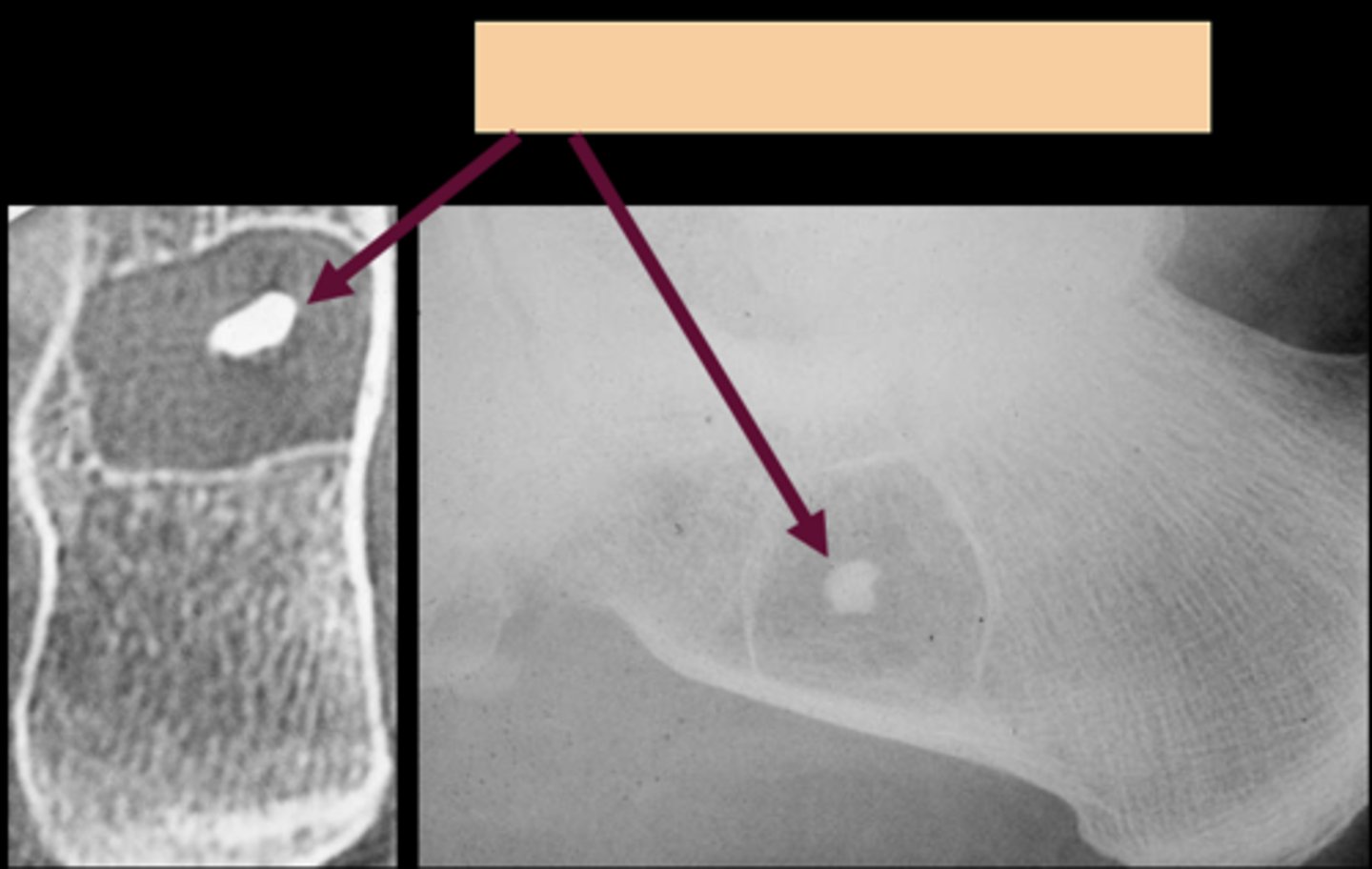
Target sequestrum
ID sign of intraosseous lipoma
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Eosinophilic granuloma is a type of _____
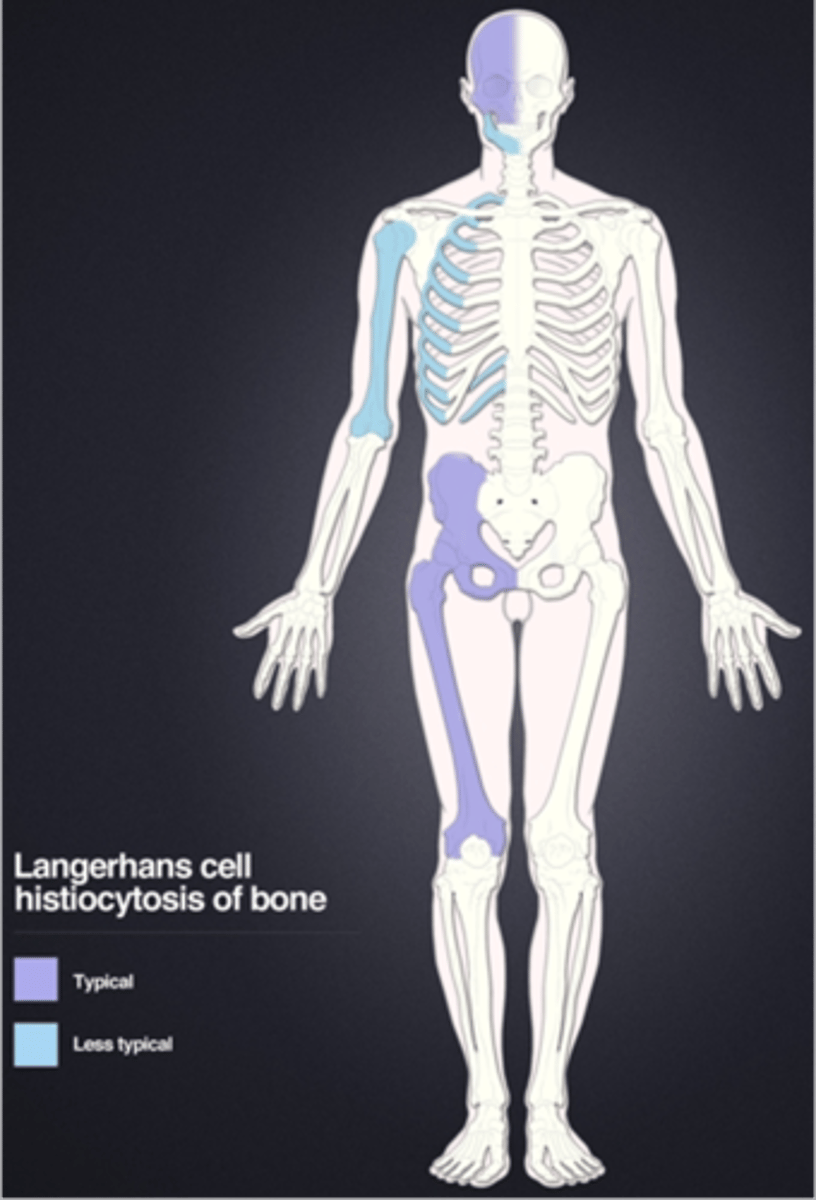
Eosinophilic granuloma
- <20 y.o. (peak 5-10 y.o.)
- Skull, mandible, pelvis, spine
- Monostotic > polyostotic
Beveled edge
ID radiographic feature of eosinophilic granuloma in the skull
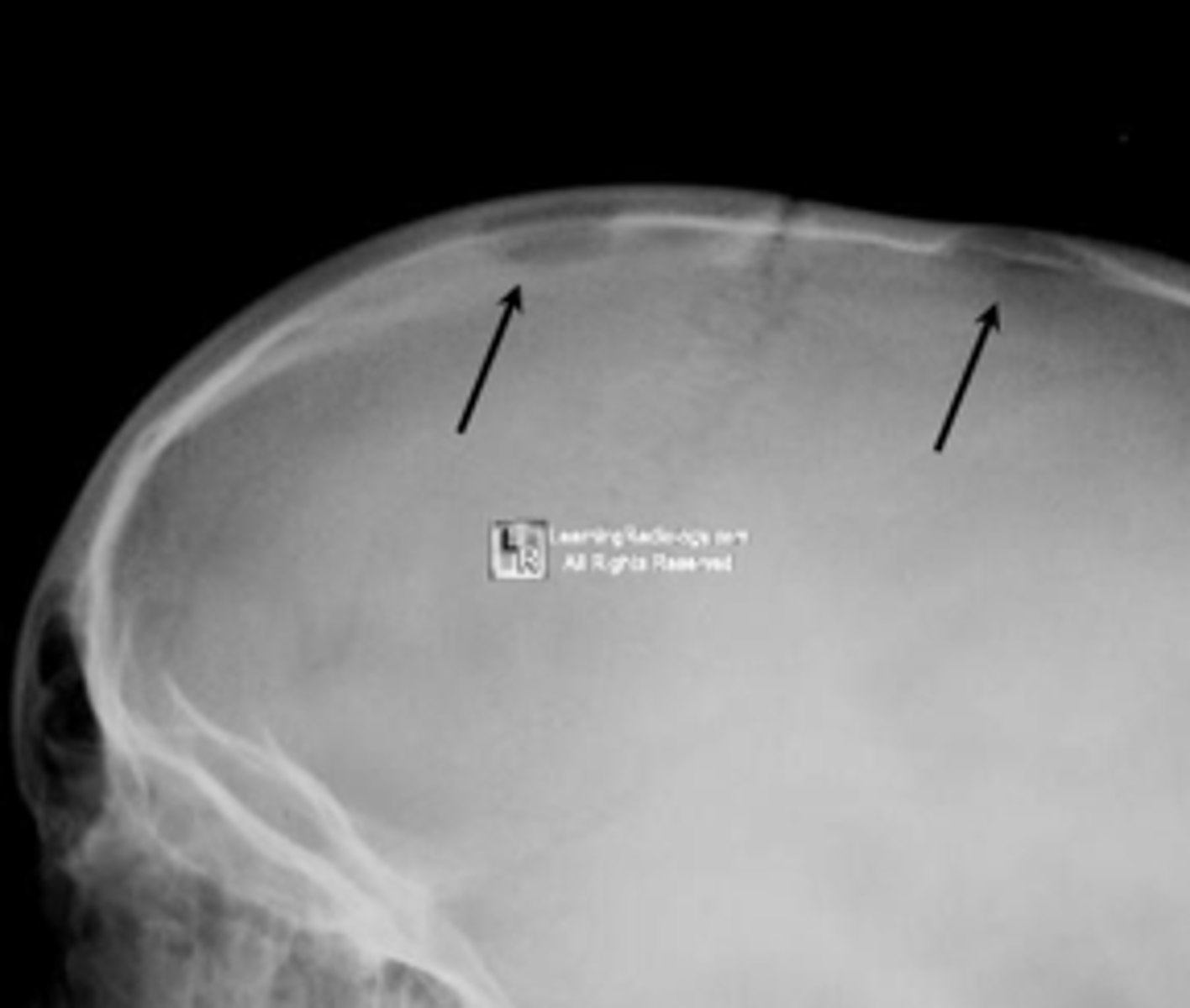
Button sequestrum
ID radiographic feature of eosinophilic granuloma in the skull
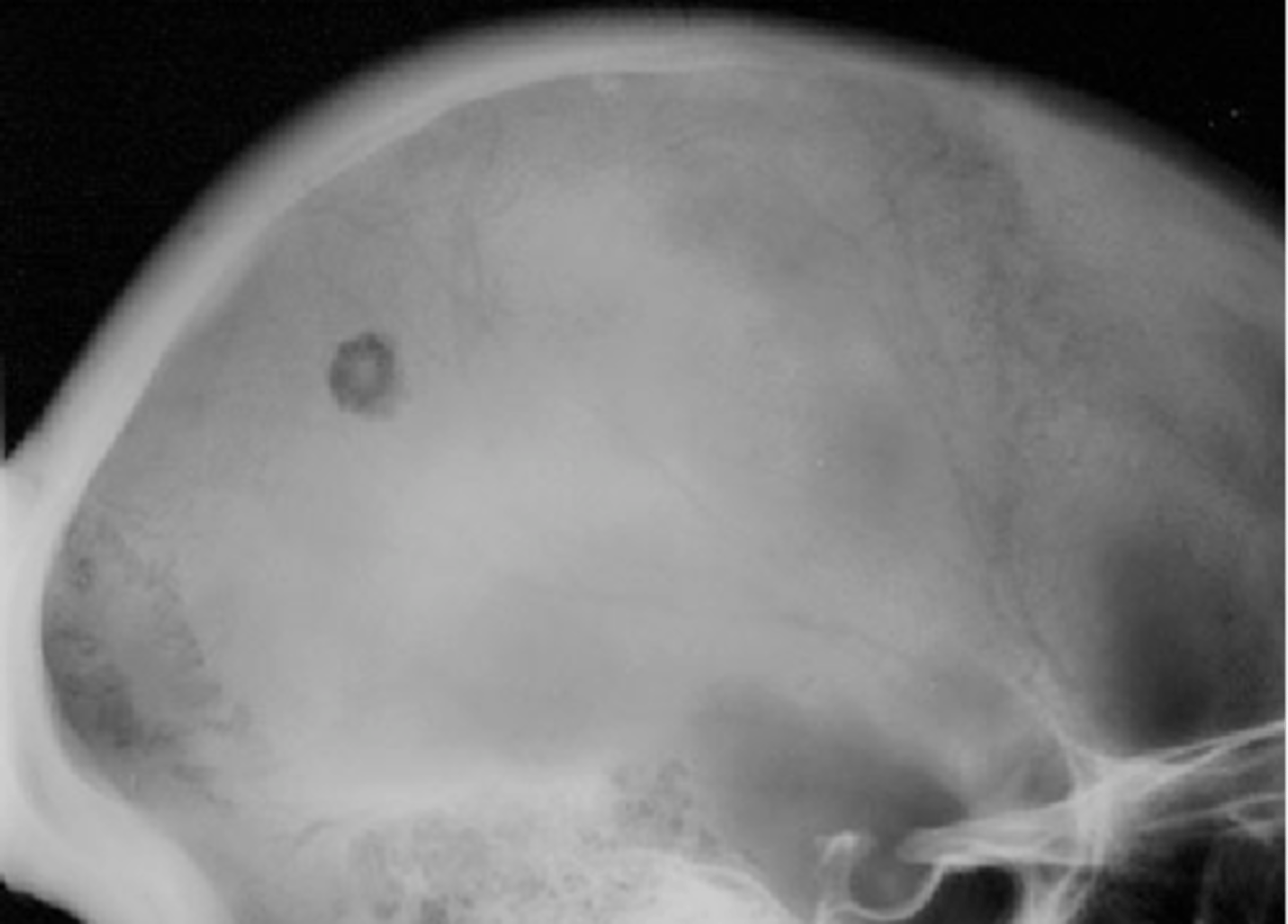
Eosinophilic granuloma in the spine
ID benign tumor