BIOLOGY ALEVELS - cell structures
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.5 -2.6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
division of labour
each organelle has its functions and works togather to ensure cells success e.g. manufacturing and secretion of proteins
structure found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes
cell surface membrane
ribosomes
cytoplasm
DNA
define eukaryotes
contains membrane bound organelles and has a nucleus containing DNA
define prokaryotes
DNA is free in the cytoplasm and doesnt contain membrane bound organelles
common cell adaptation
folded membrane or microvilli increase SA for diffusion
many mitochondria - large amounts of ATP for active transport
walls one cell thick to reduce the diffusion pathway
difference from eukaryotes and prokaryotes
prokaryotes cells dont have a nucleus whereas a eukaryotes cell does
prokaryotes cells are less than 1-2 micrometer whereas eukaryotes are 10-100 micrometer
prokaryotes doesnt have membrane bound organelles whereas eukaryote does
Prokaryote contains circular DNA whereas eukaryotes contains linear DNA
Prokaryotes contains a pili whereas eukaryotes doesnt
function of flagella in bacteria
flagella is used for the movement of bacteria and locomotion
how fimbriae differs structurally and functionally from flagella
fimbraes are shorter and thinner than flagella and is used for attachement not movement like flagella
location and general composition of bacterial cell wall
made up of peptidoglycan and is based on top of the plasma membrane and underneath the slime capsule
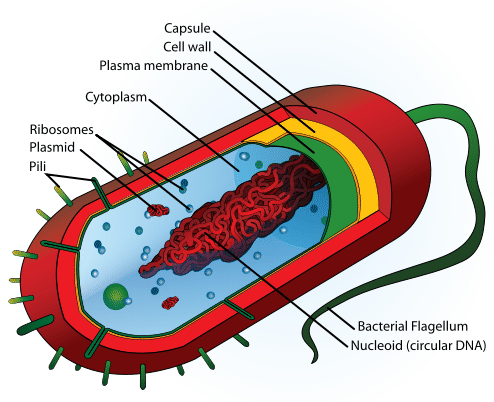
prokaryotes - bacteria components
ribosomes (70s) cytoplasm flagellum cell wall slime capsule plasmids plasma membrane nucleoid
eukaryotes - plant cell
cell wall cell membrane vacuole nucleus nucleolus nuclear membrane chloroplast mitochondria cytoplasm lysosomes centrioles RER SER ribosomes golgi apparatus
why the lack of membrane bound organelles doesnt stop prokaryotes from making proteins
prokaryotes contains ribosomes which can carry out protein synthesis and ribosomes are not membrane bound
some antibiotics kills bacteria by disrupting the formation of peptidoglycan molecules. explain why these kill bacteria but do not affect eukaryotes
eukaryotes dont have a peptidoglycan cell wall and these antibiotics do not damage any other cell components e.g. nucleus mitochondria
microfilament
two intertwined strands
mobility (pseudopodia)
has a diameter of 7 nm
cytokinessis of cell division
maintains cells shape
contraction (muscles)
Actin
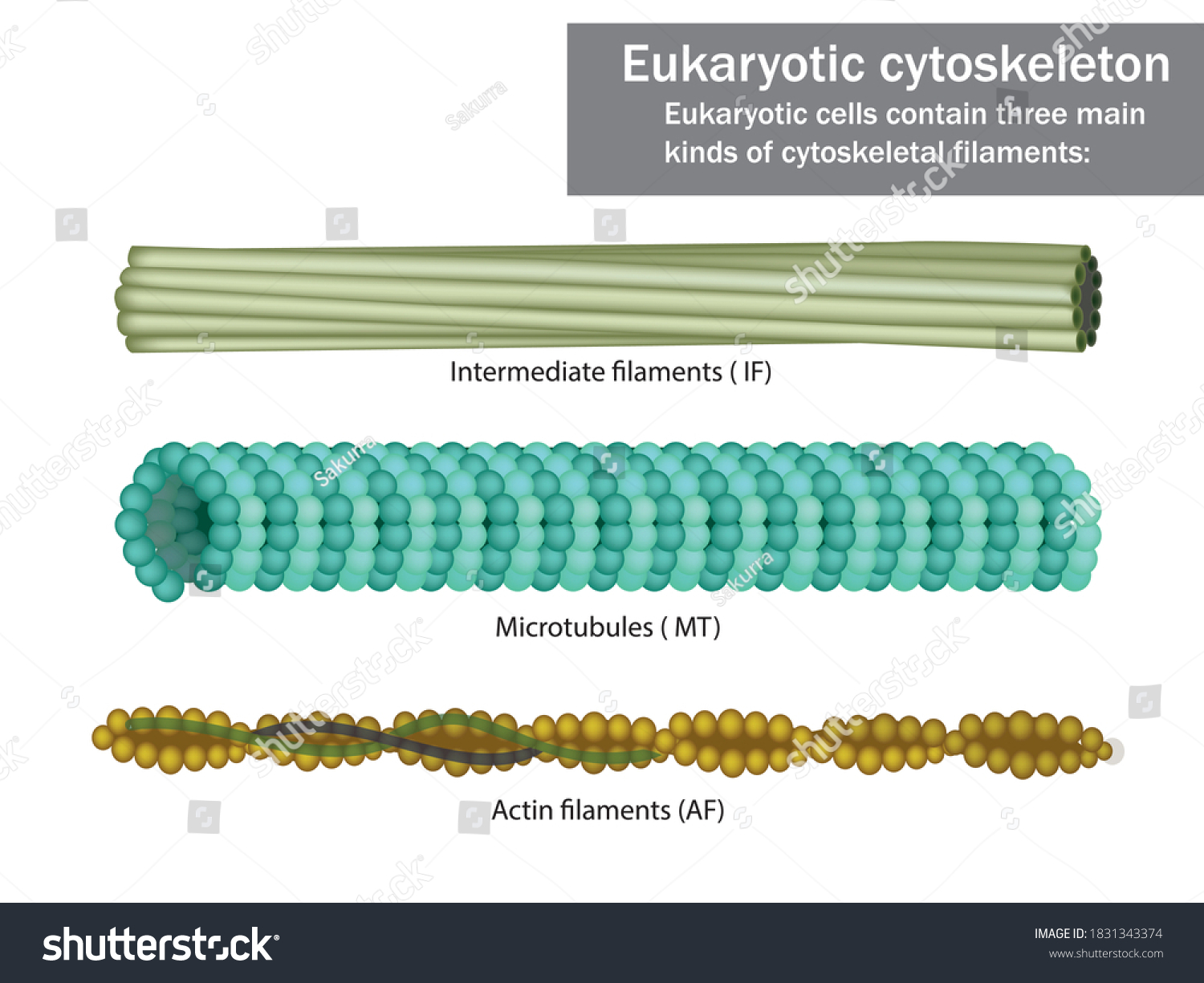
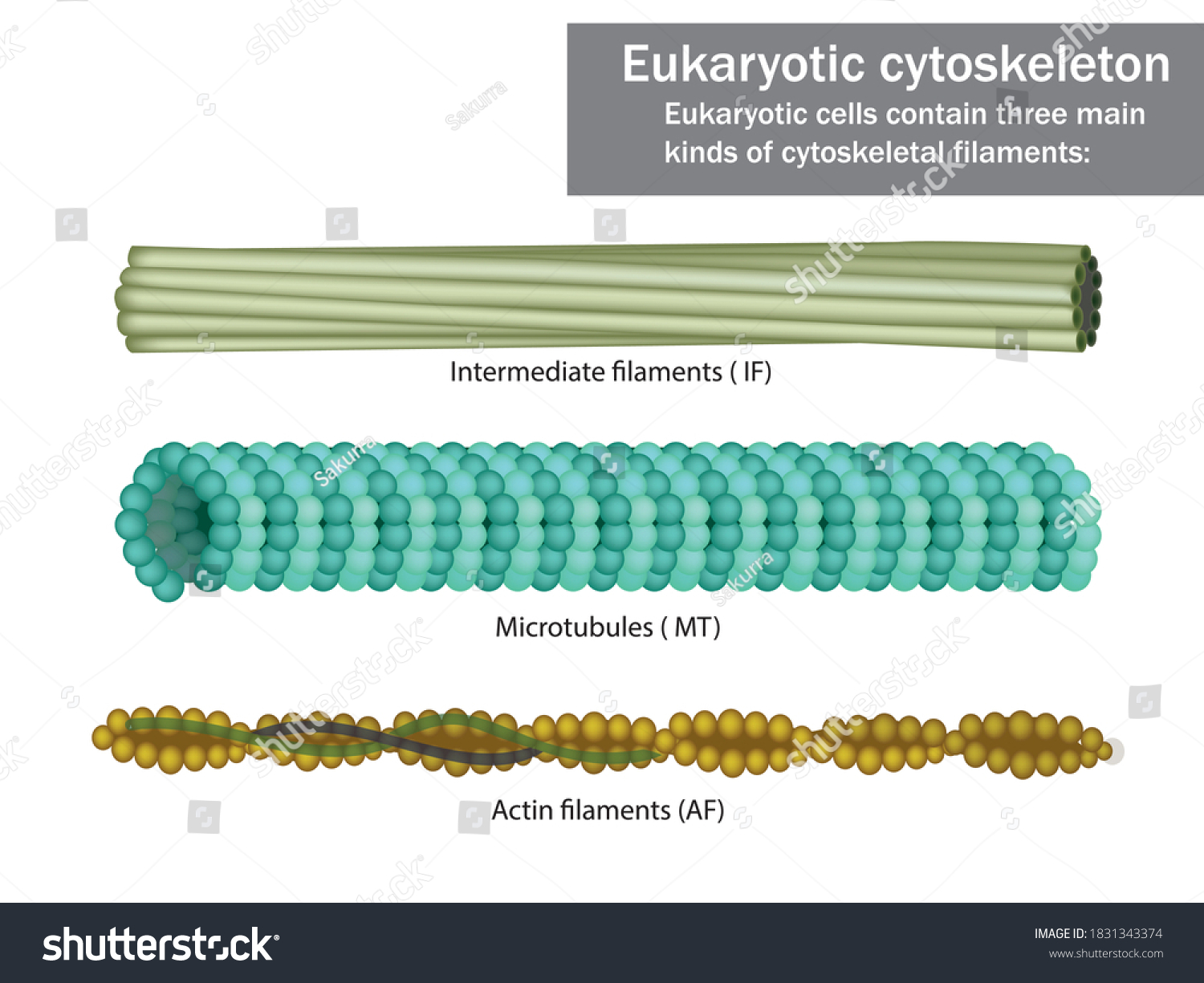
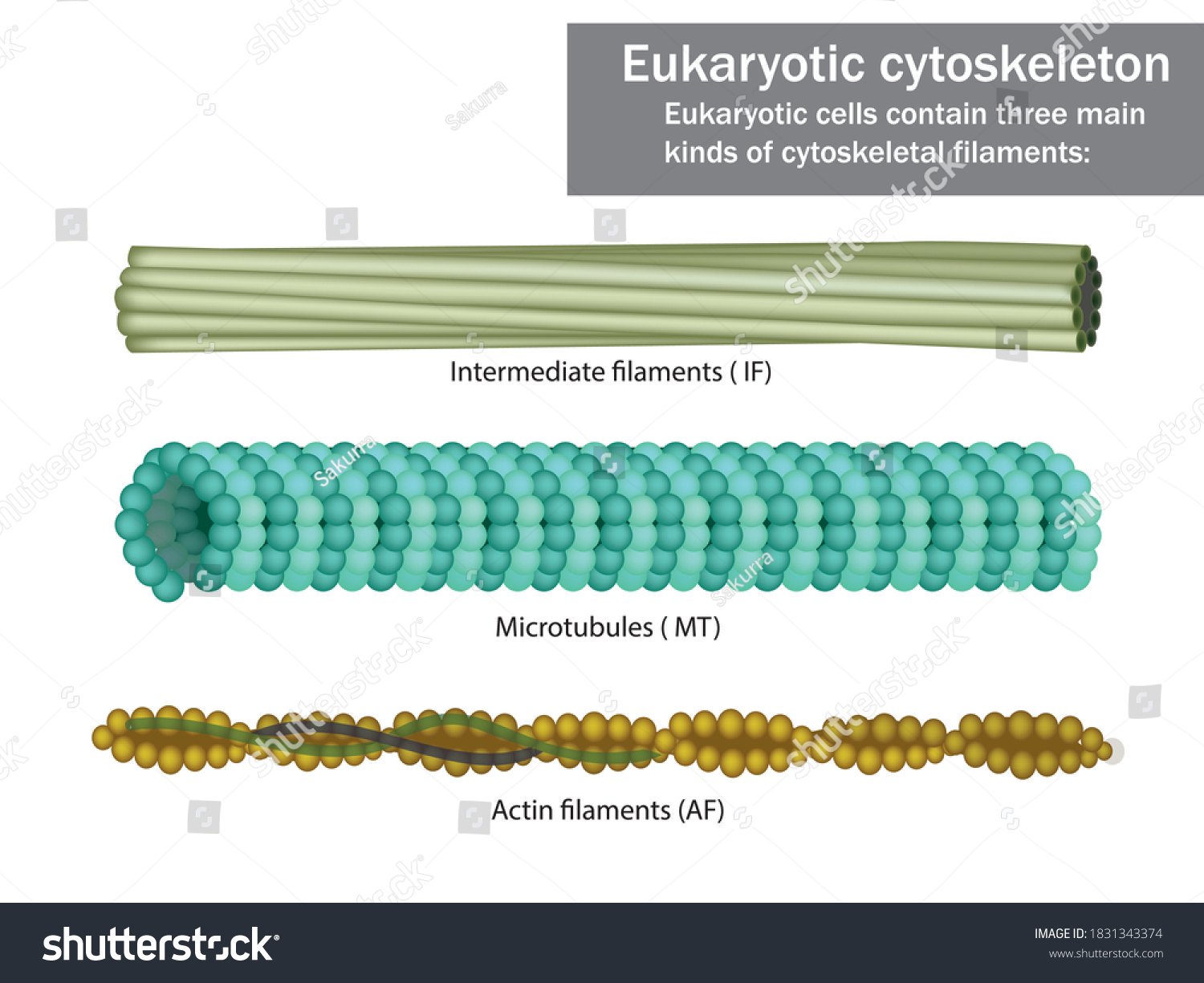
microtubules
hollow tubes
mobility (cilia and flagella)
move organelles
move chromosomes (spindle)
diameter: 25nm
maintains cell shape
intermediate filaments
fibres wound into thicker cables
maintains cell shape
anchor nucleus and organelles
fibrous proteins e.g. keratin
diameter: 8-12 nm
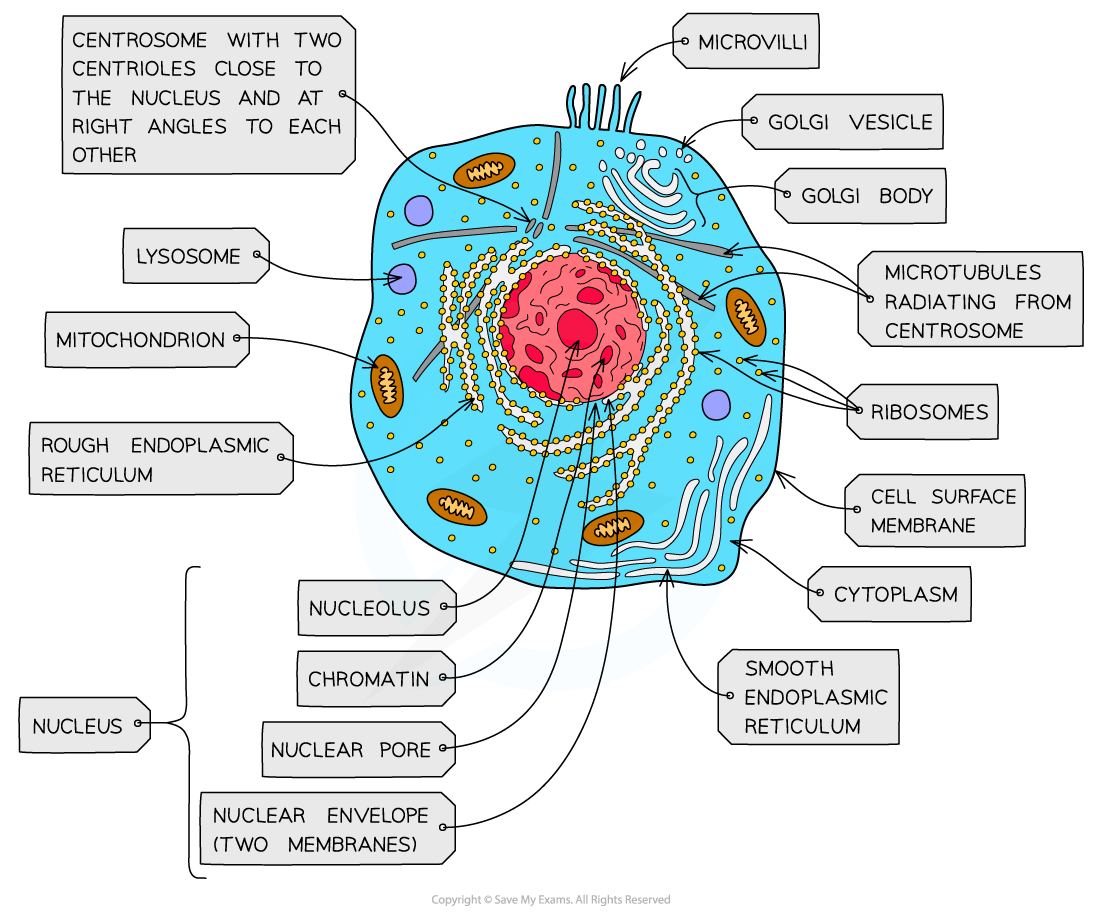
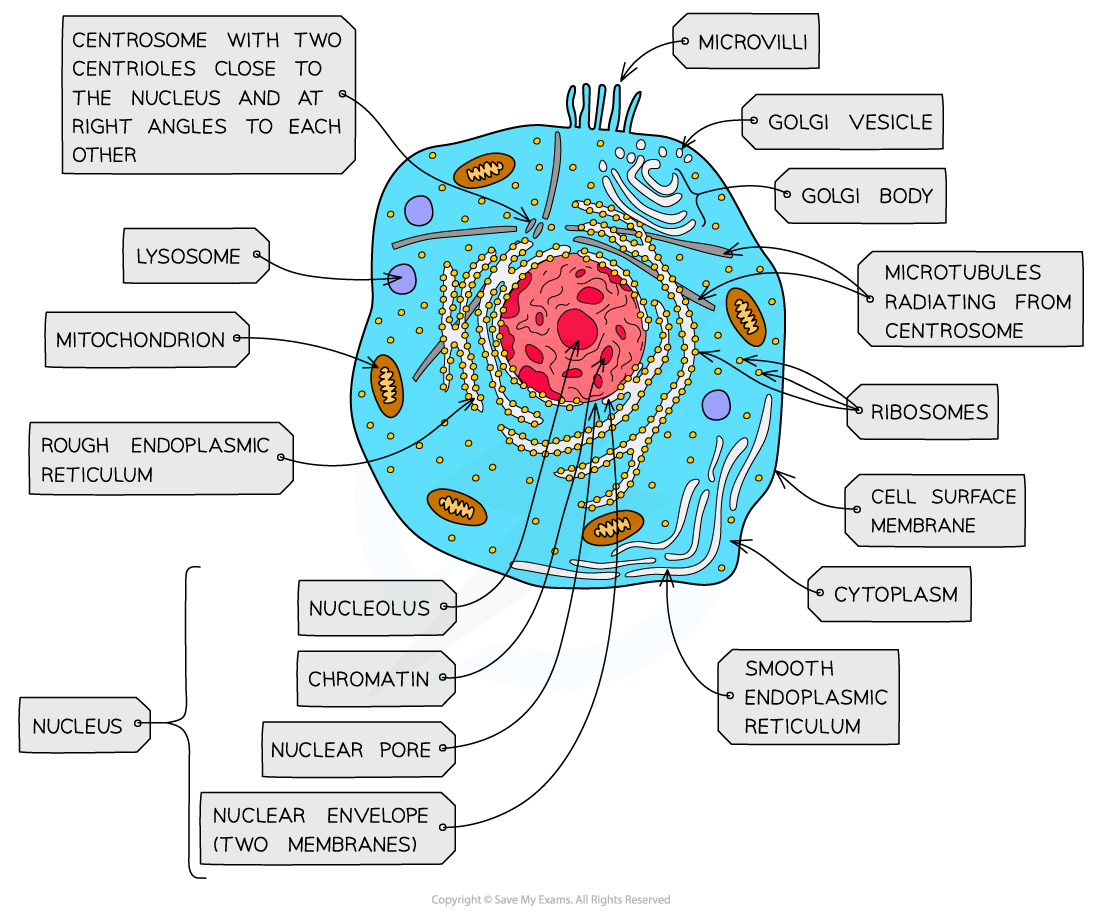
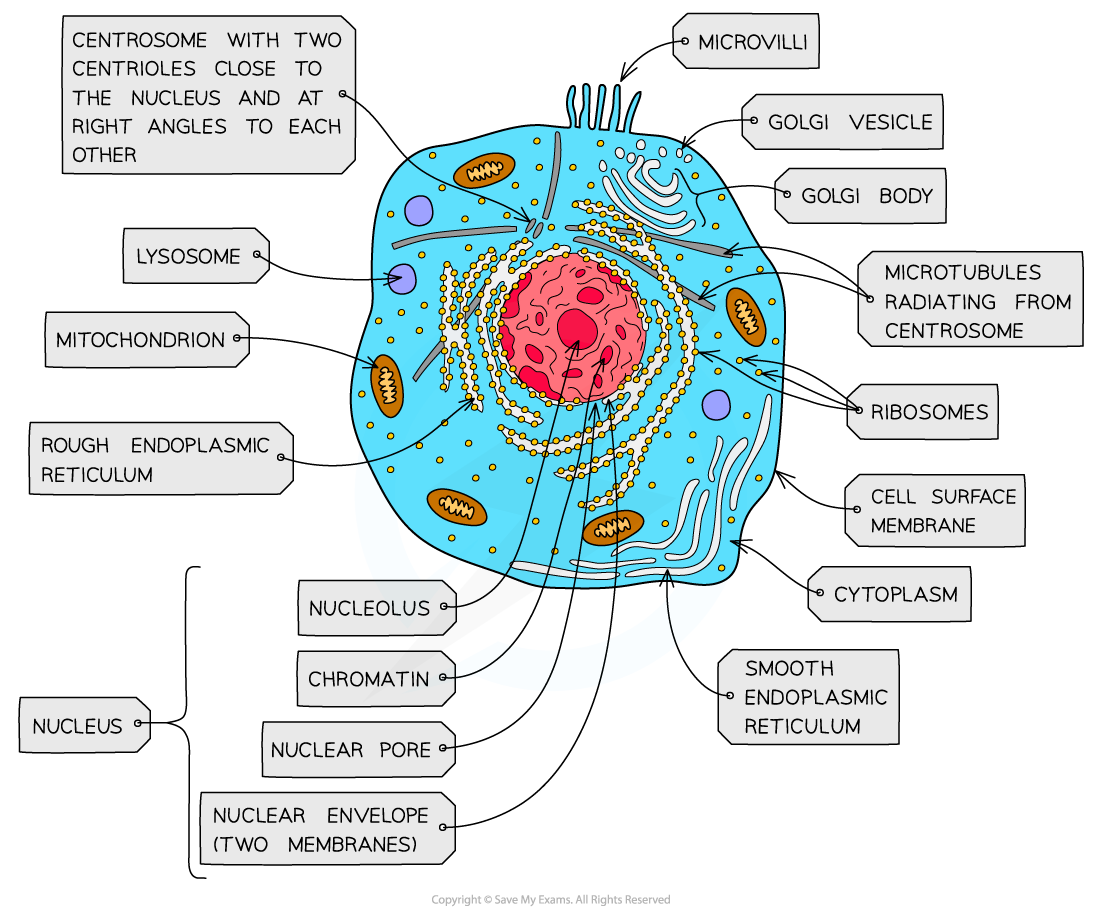
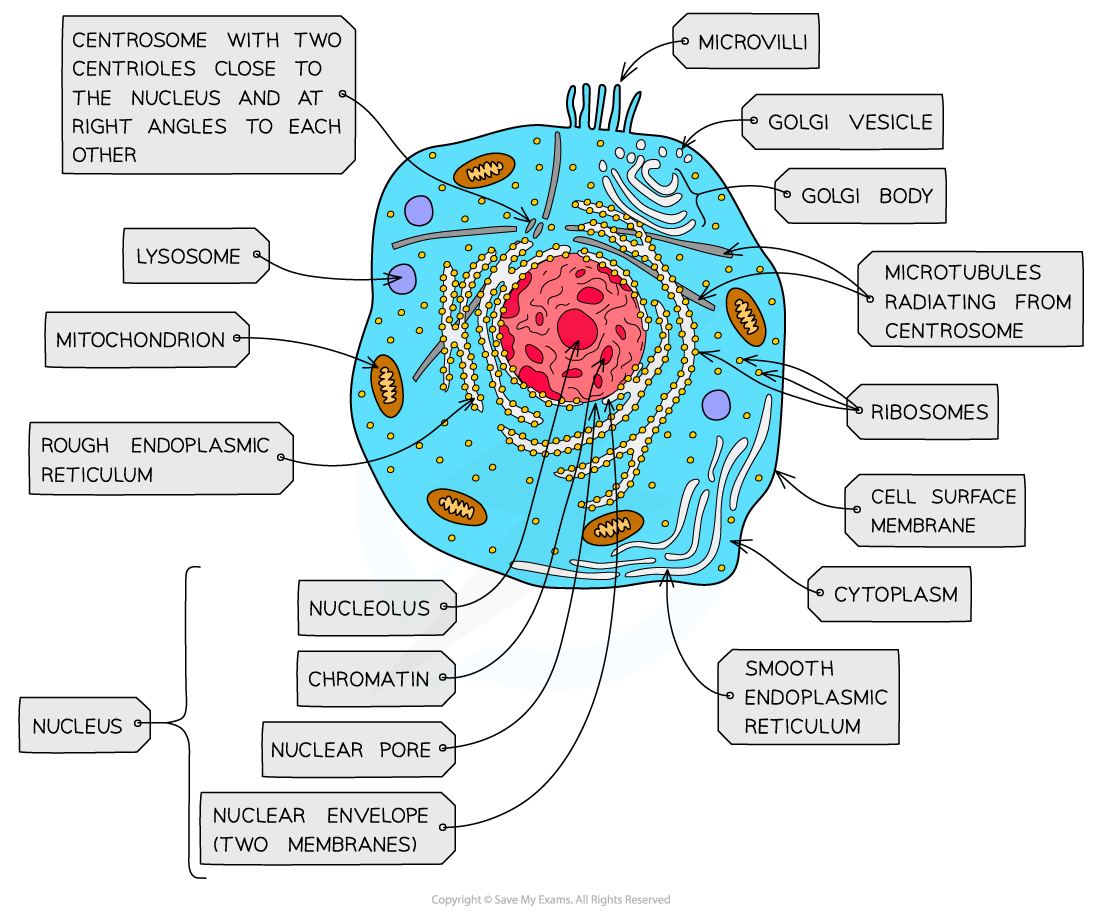
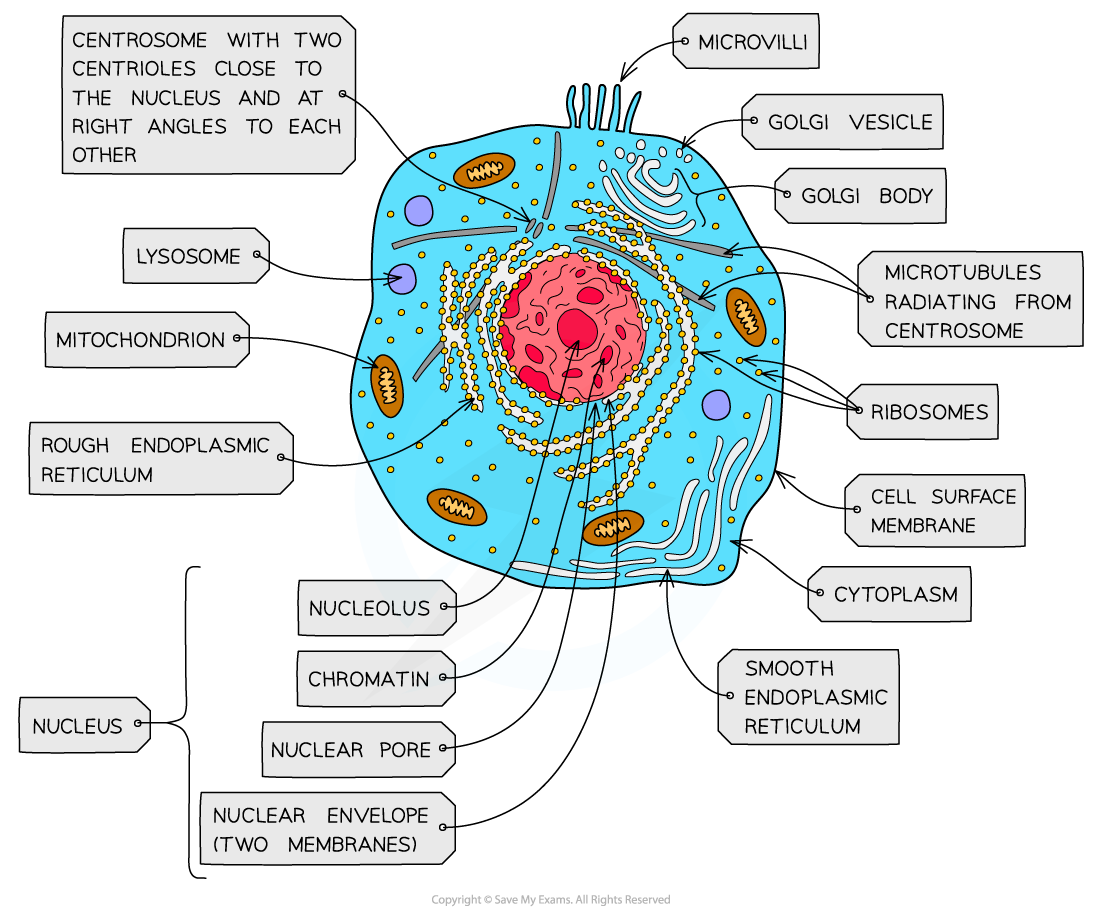
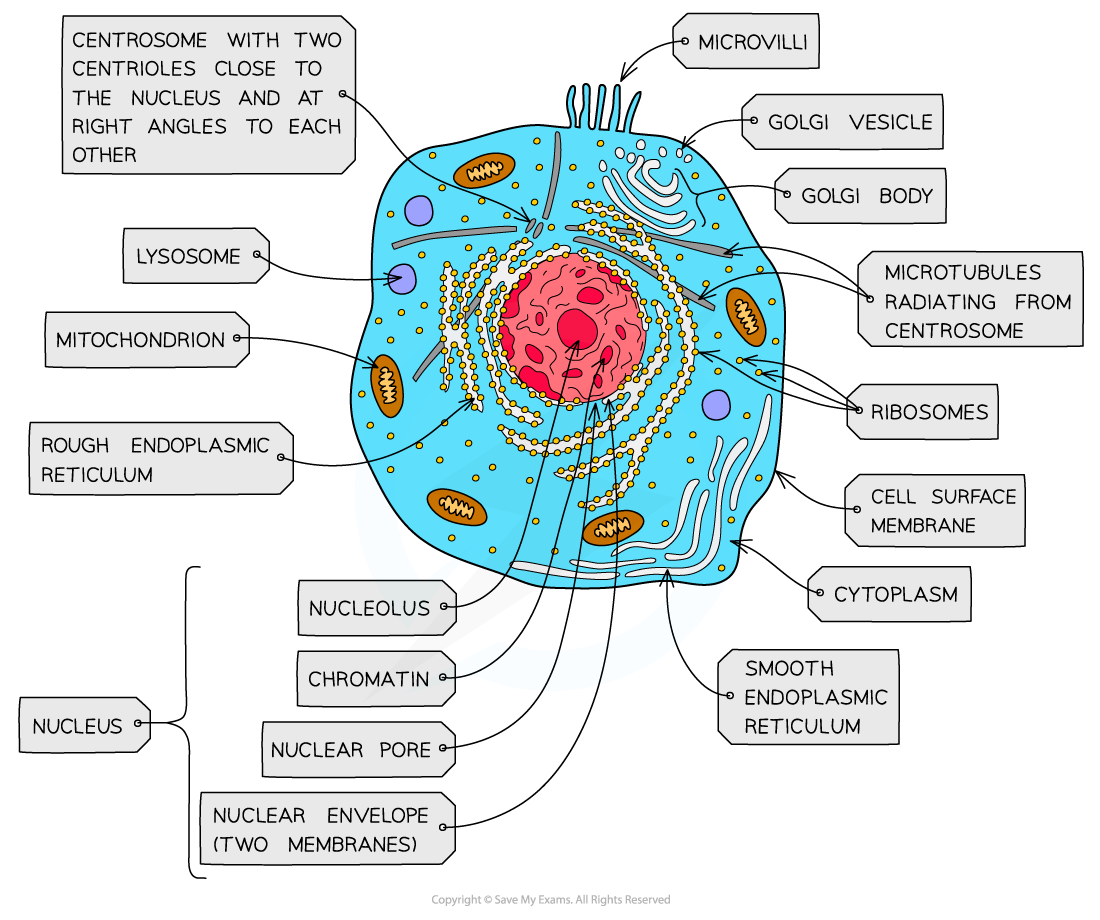
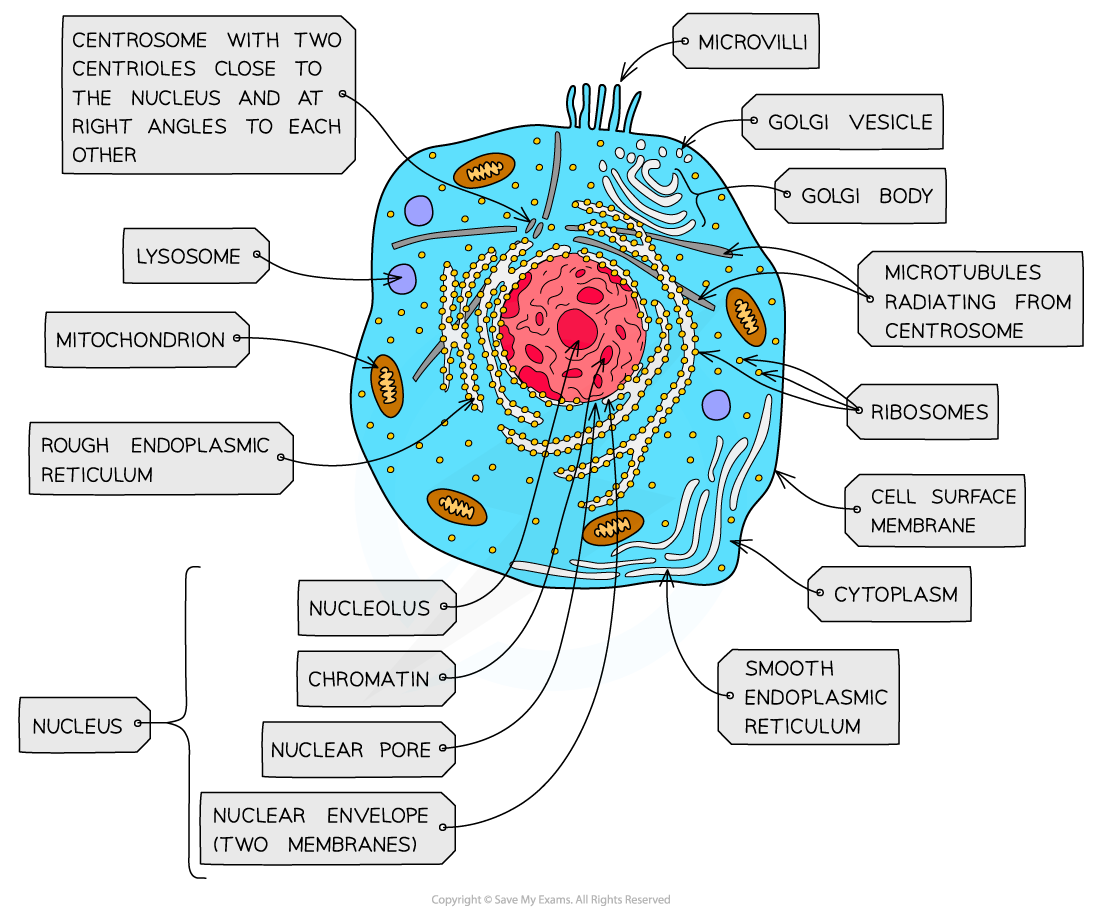
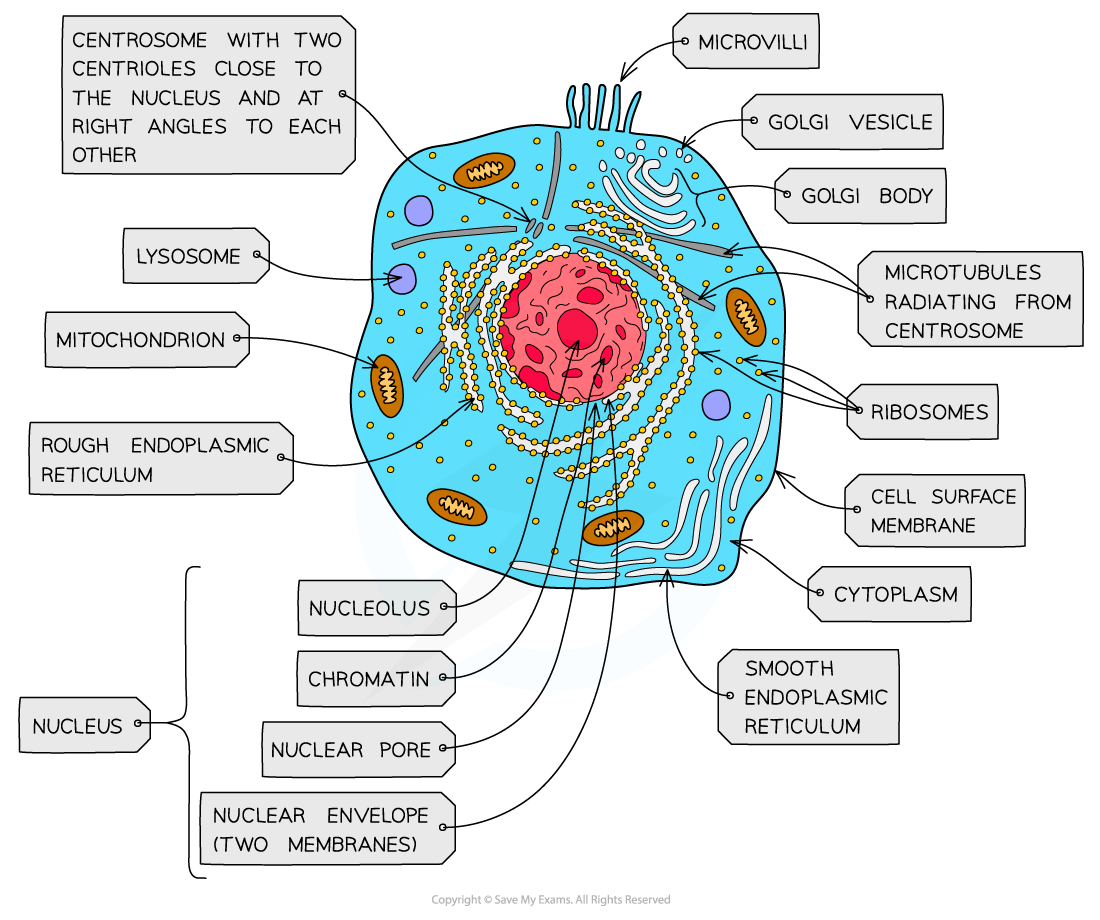
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) - structure
system of membrane enclosing a fluid filled space
large surface area
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) - function
synthesise, store and transport lipids and carbohydrates
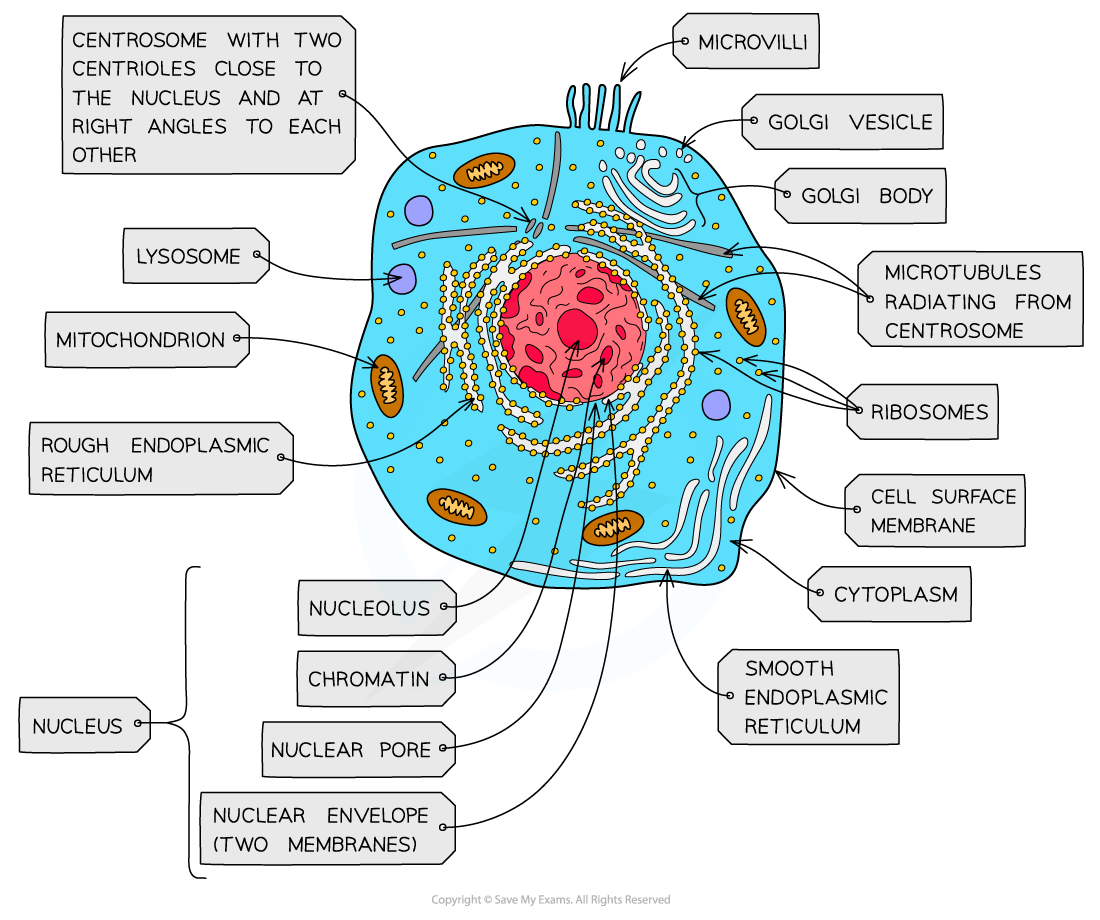
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) - structure
system enclosing a fluid filled space
has ribosomes on the outer surface
large surface area
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) - function
synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins
provides pathway for materials to be transported throughout the cell especially proteins
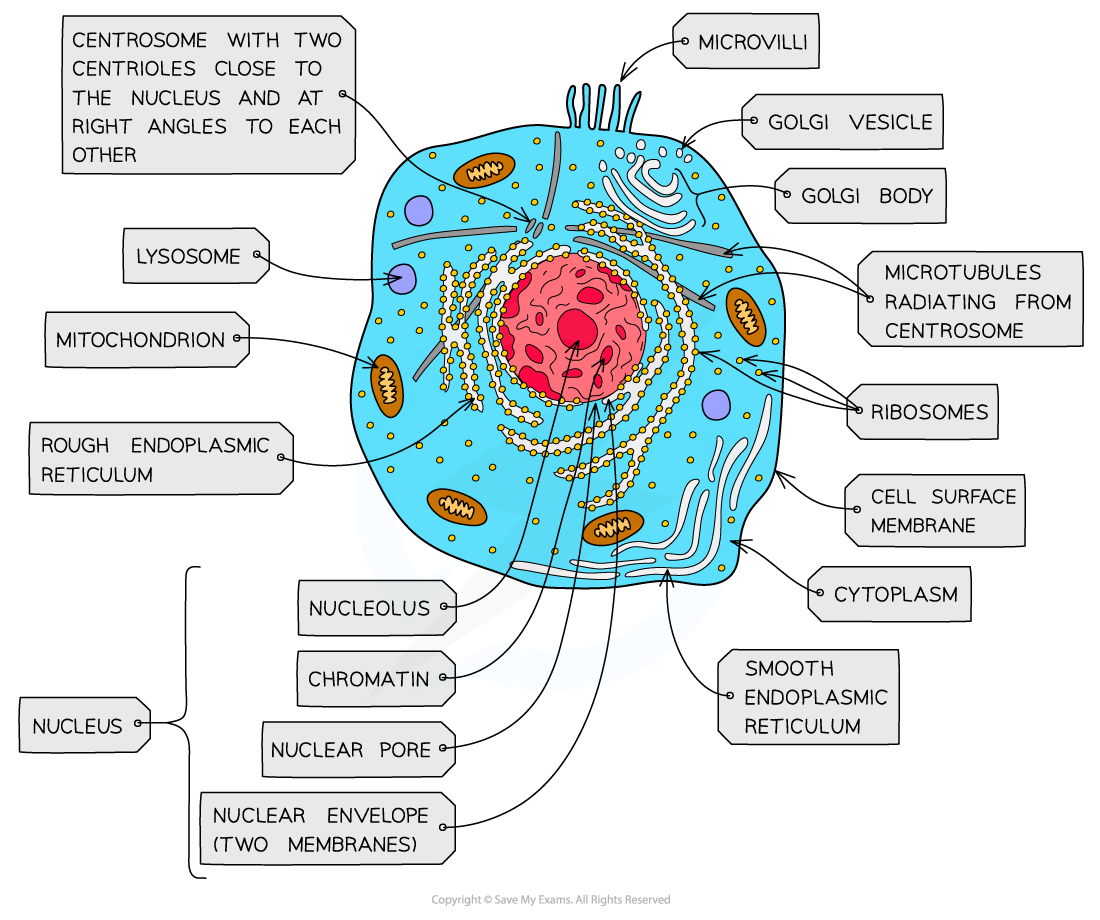
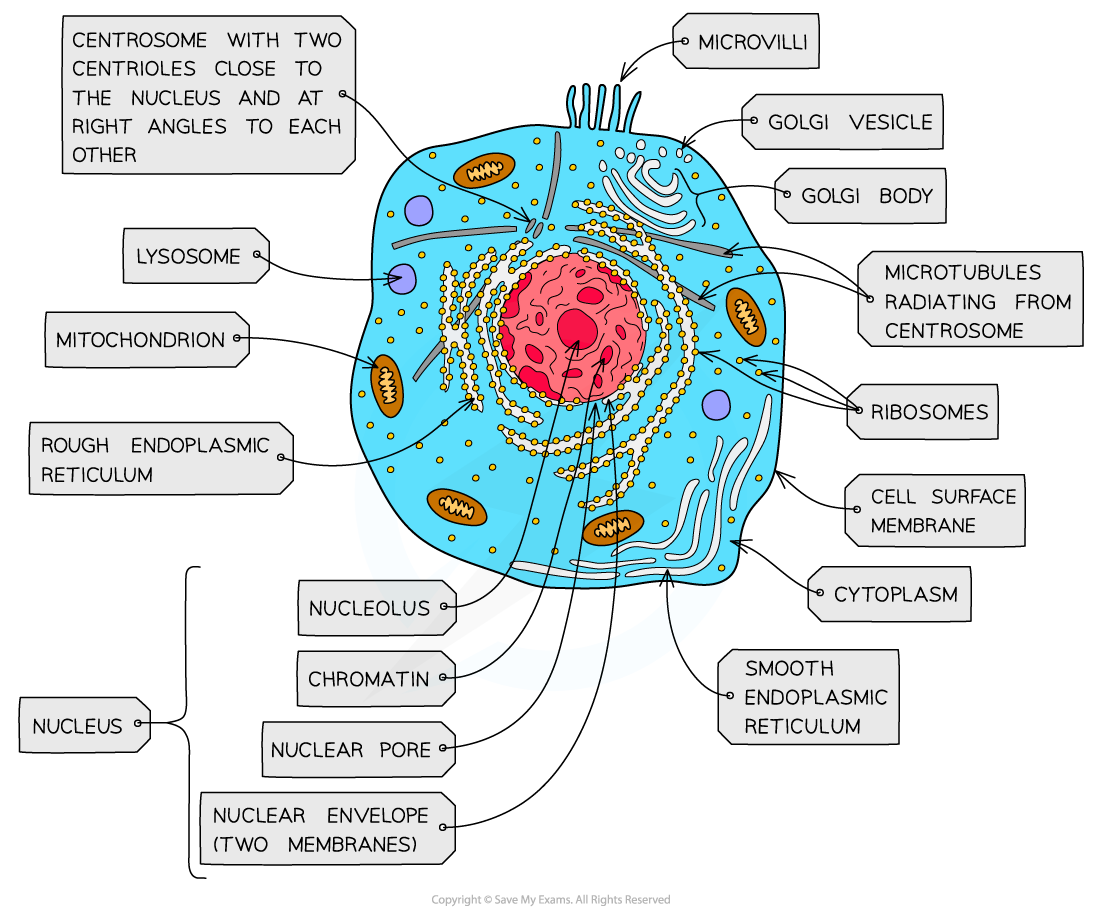
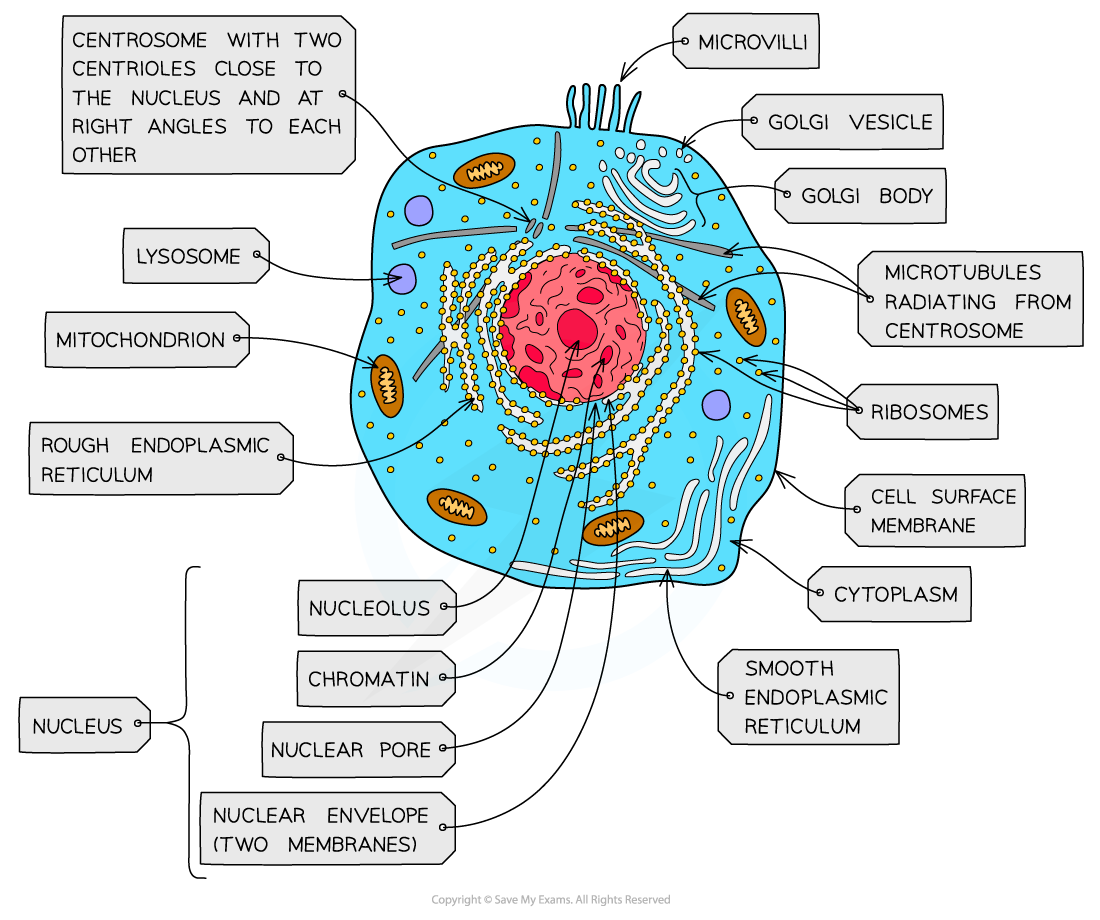
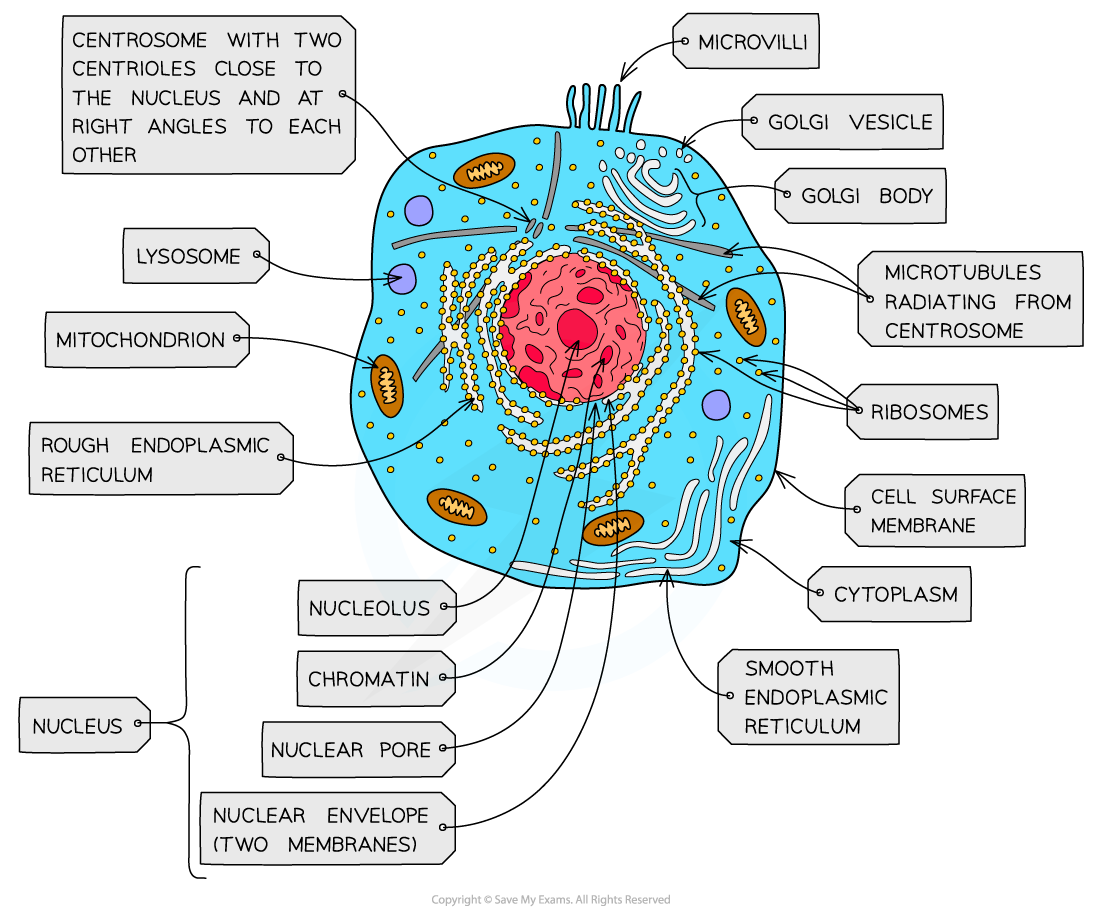
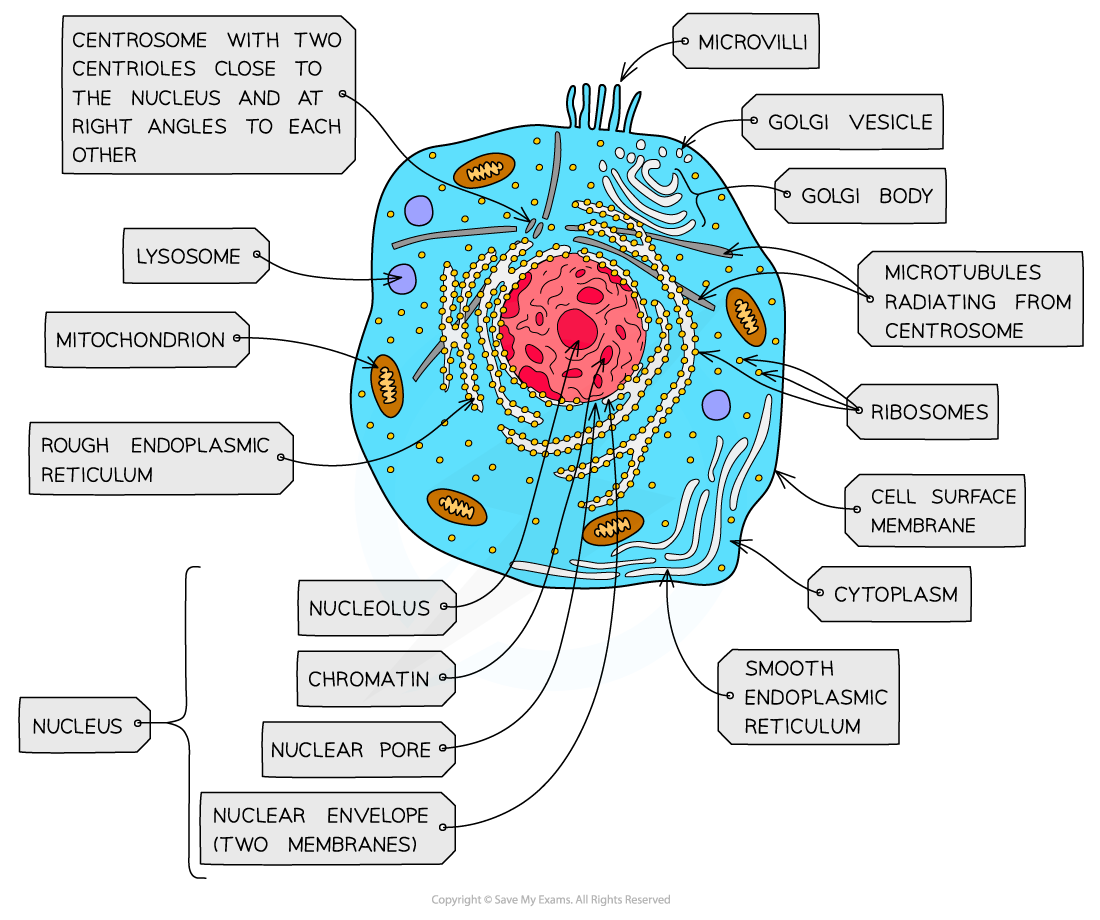
nucleus, nuclear membrane and nucleolus - structure
nuclear envelope - double membrane
nuclear pores - allows mRNA out
chromatin - made from proteins & DNA
nucleoplasm - jelly like substances
nucleolus - makes rRNA and ribosomes
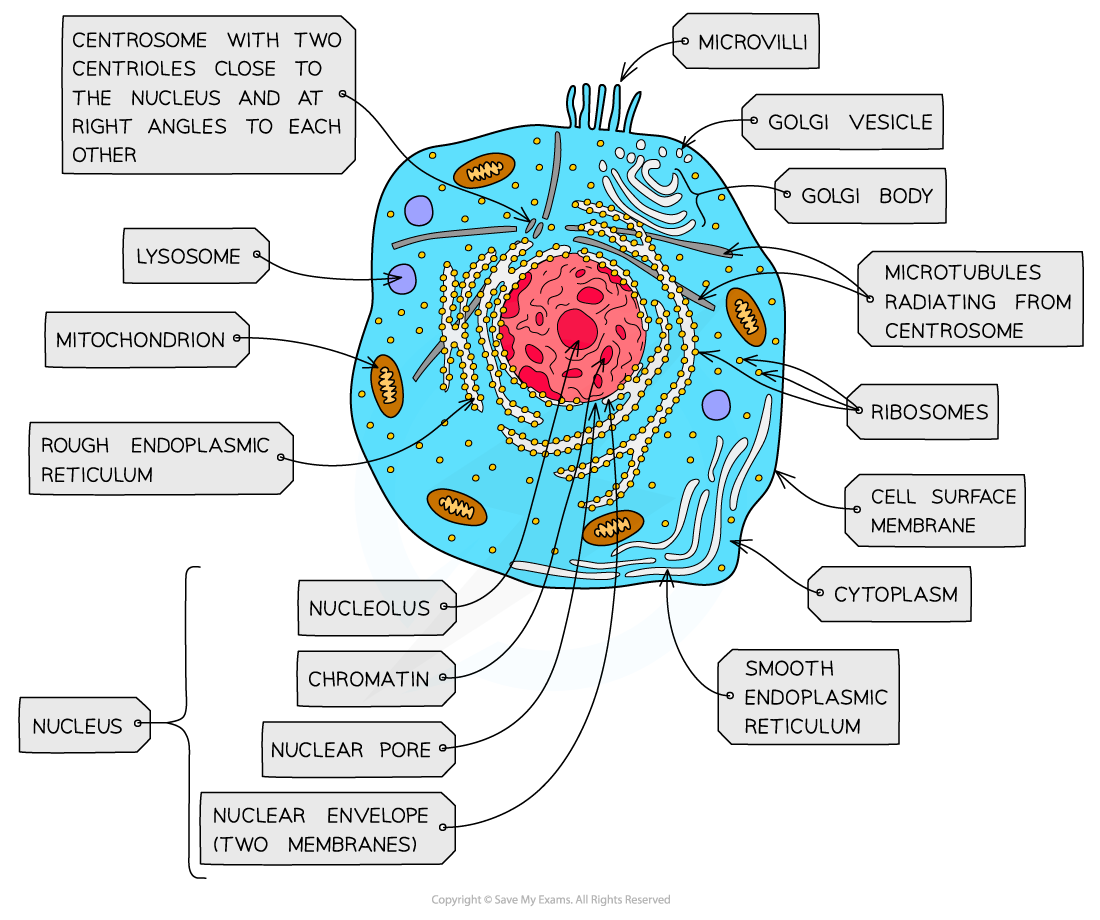
nucleus, nuclear membrane and nucleolus - function
acts as control centre for the cell by producing mRNA and hence protein synthesis
retain for the genetic material for the cell in the form of DNA or chromosomes
manufacture ribosomal RNA and ribsomes
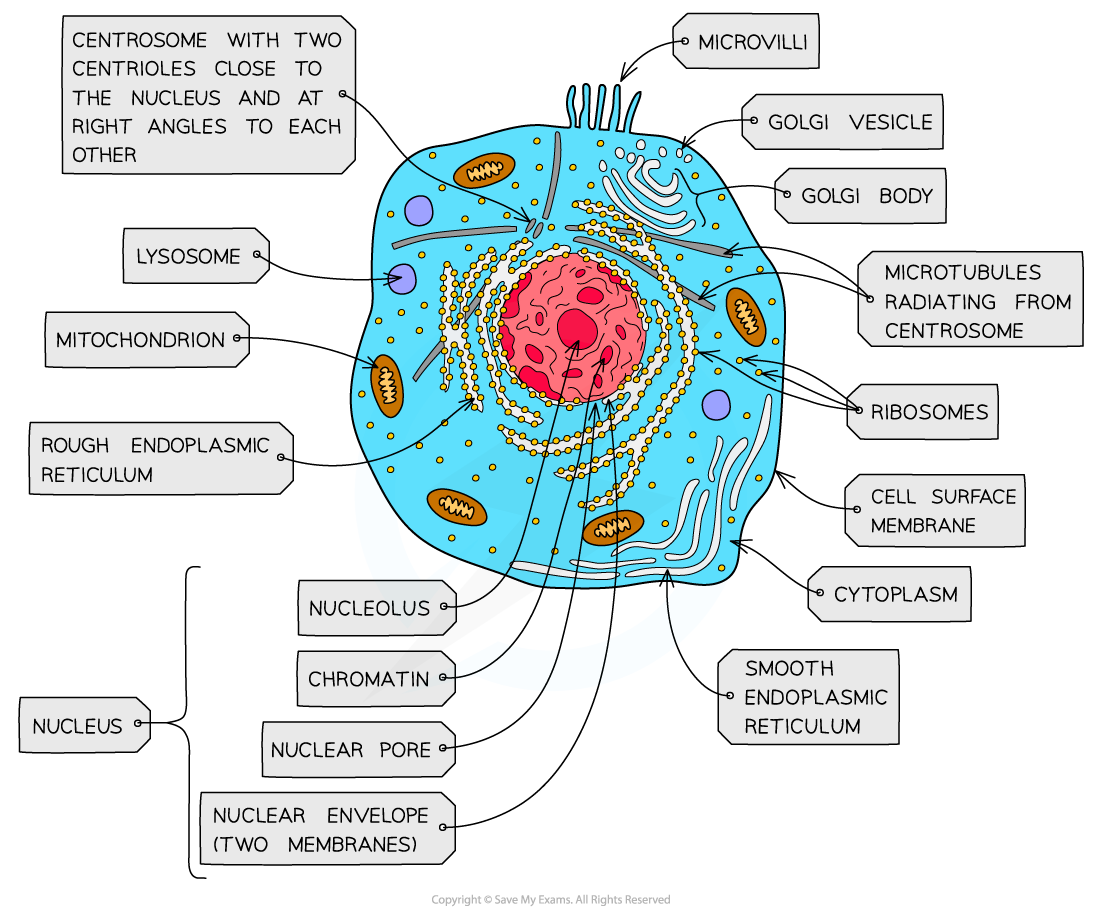
golgi apparatus - structure
Cisternae - a group of fluid filled flattened sacs
vesicles = small hollow structure
golgi apparatus - function
processing and packaging new lipids and proteins made by endoplasmic reticulum (often adds carbohydrates) which are then transported by vesicles
it makes lysosomes
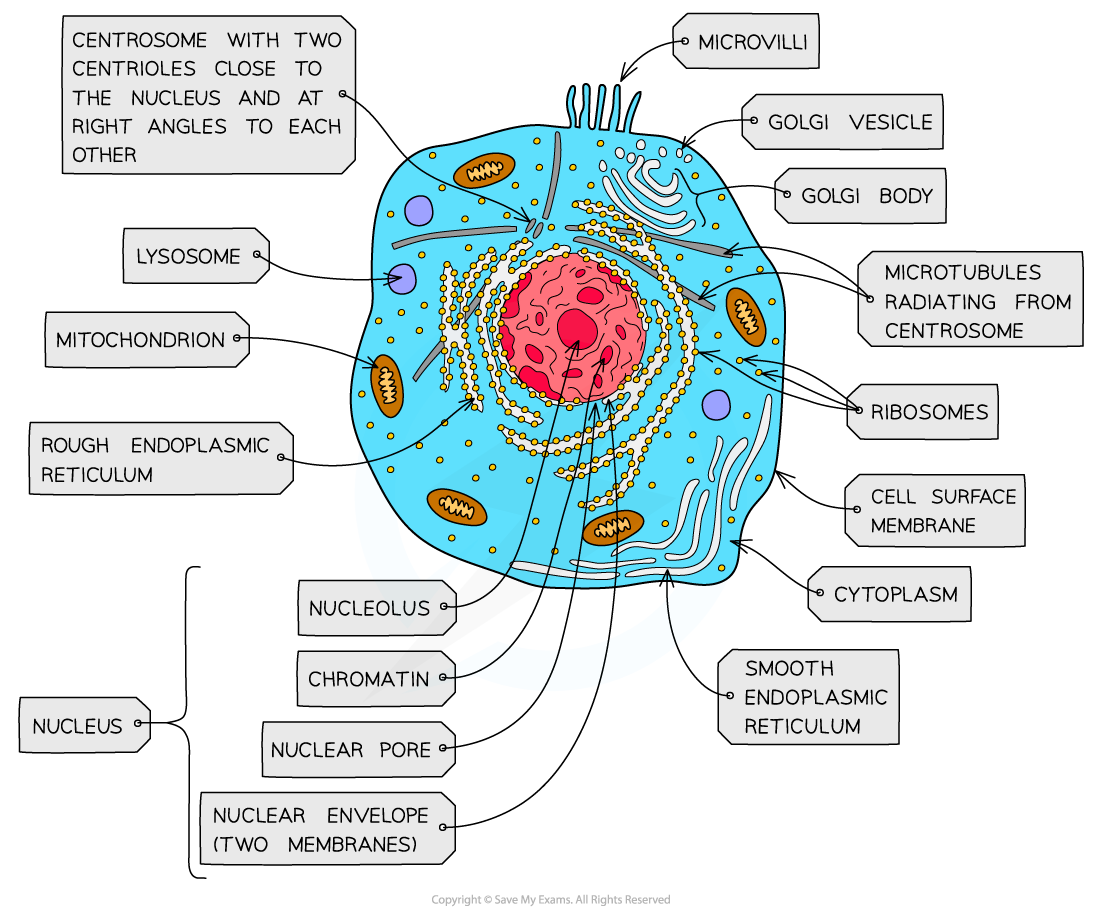
ribosomes - structure
contains ribosomal RNA and proteins
2 sub units
floats freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the membrane of the RER
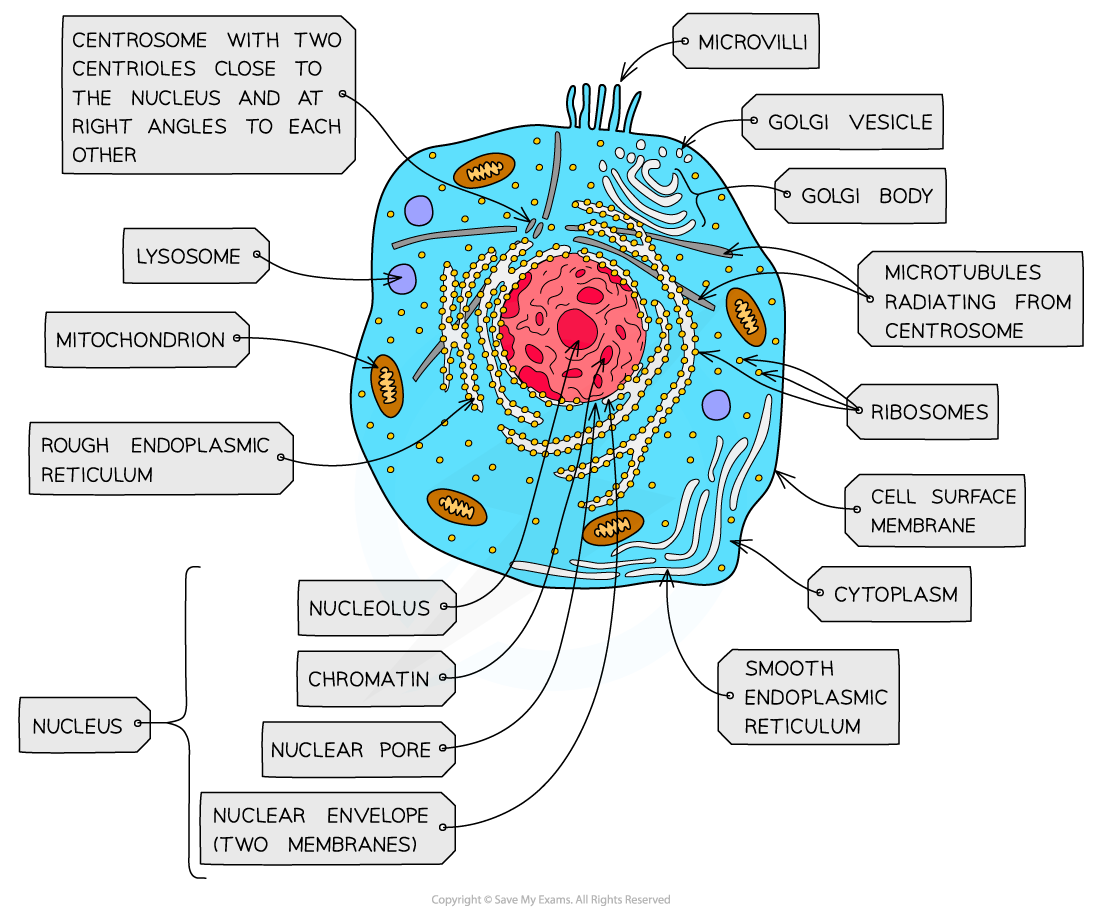
ribosomes - function
protein synthesis
80s = eukaryotes
70s = prokaryotes
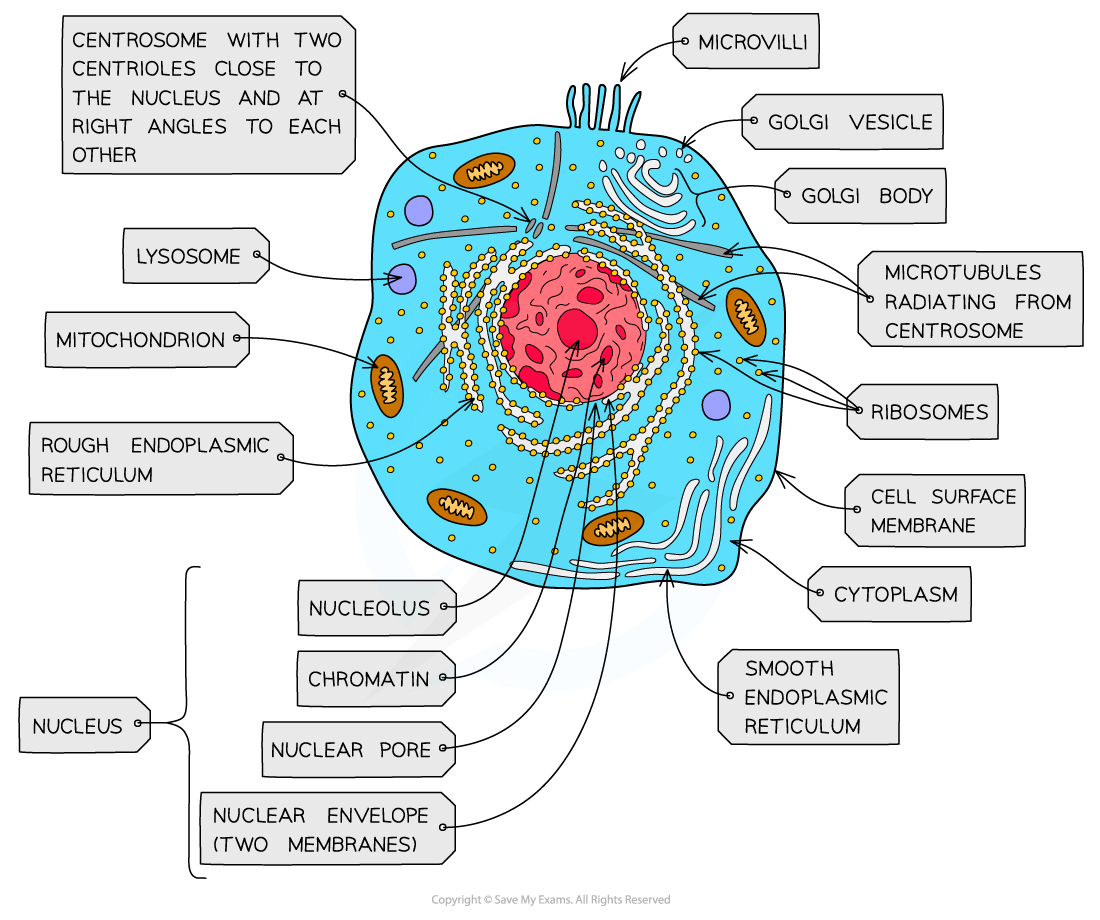
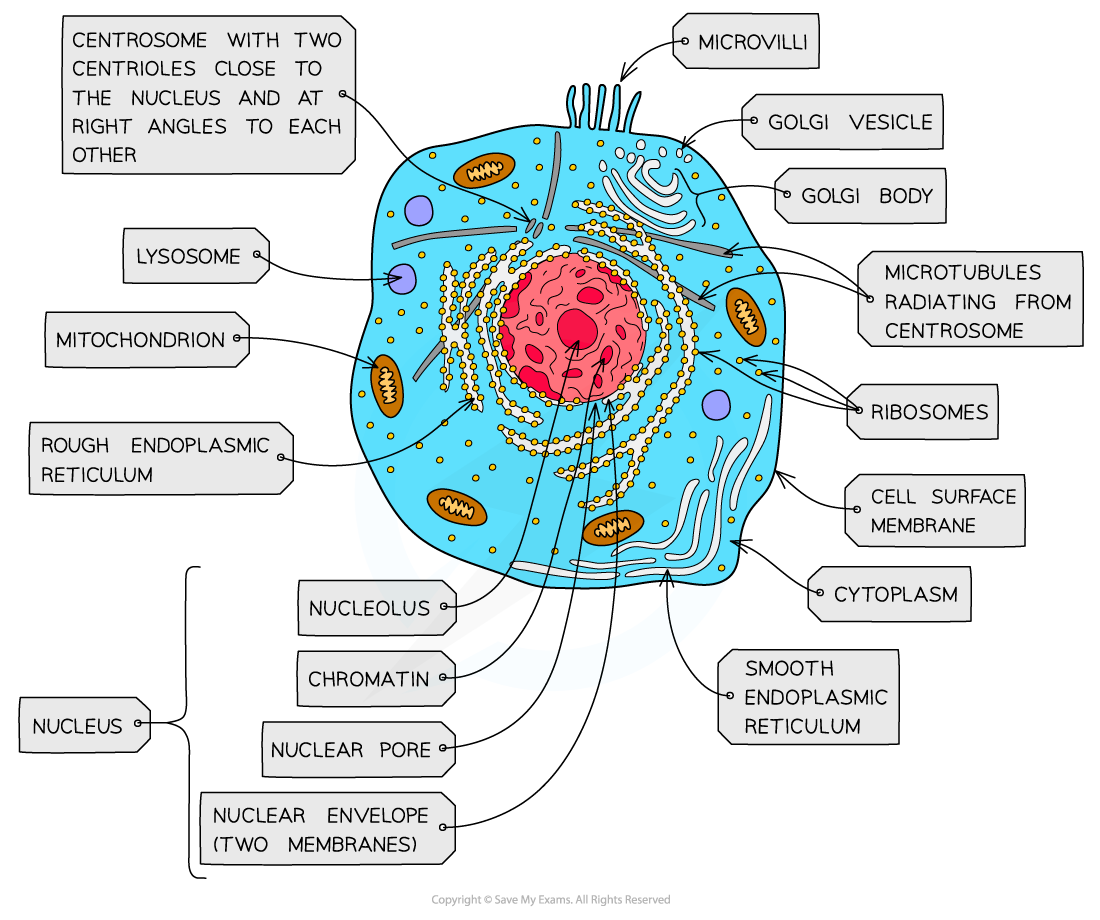
Mitochondria - structure
has double membrane controls entry and exit of materials
cristae - folded extensions on the inner membrane provide large SA, for enzyme reaction
matrix - semi rigid material containing enzymes involved in respiration
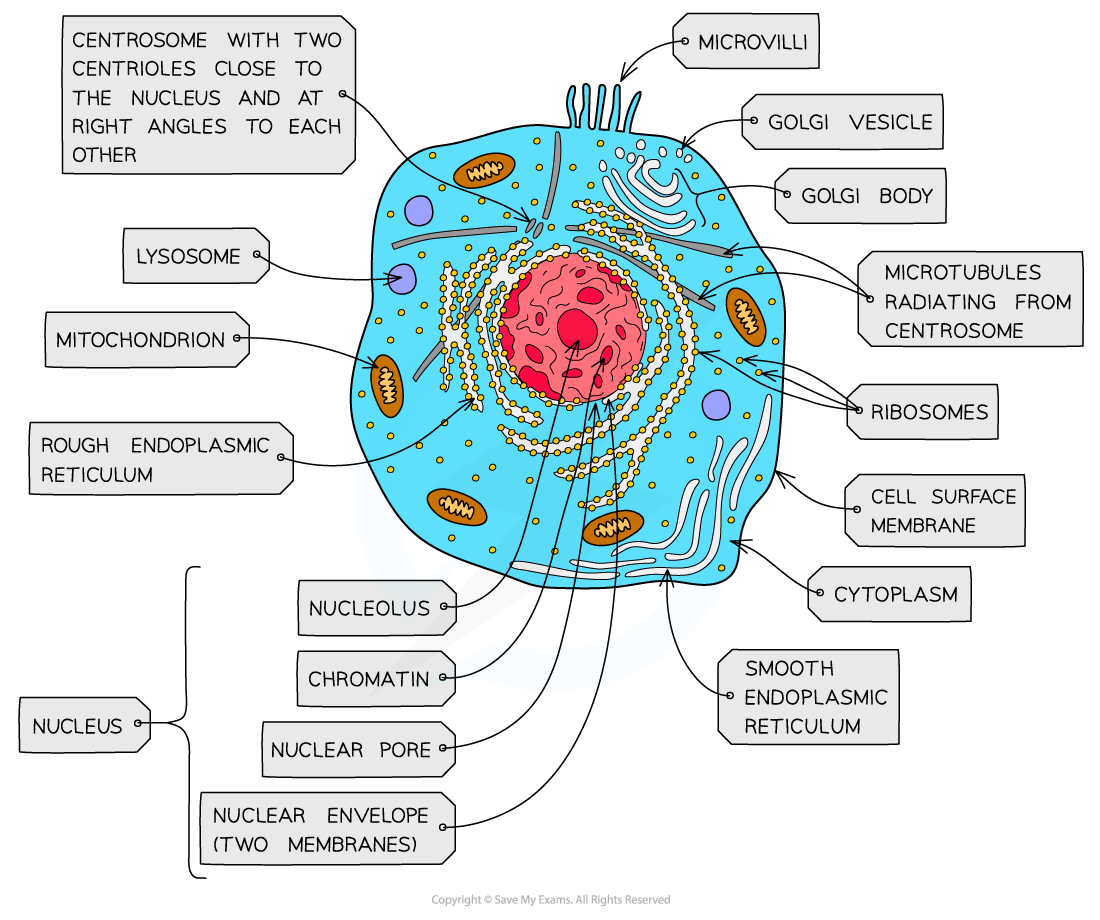
mitochondria - function
site of aerobic respiration
(krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation) to produce ATP
they are found in large numbers in muscles and epithilial
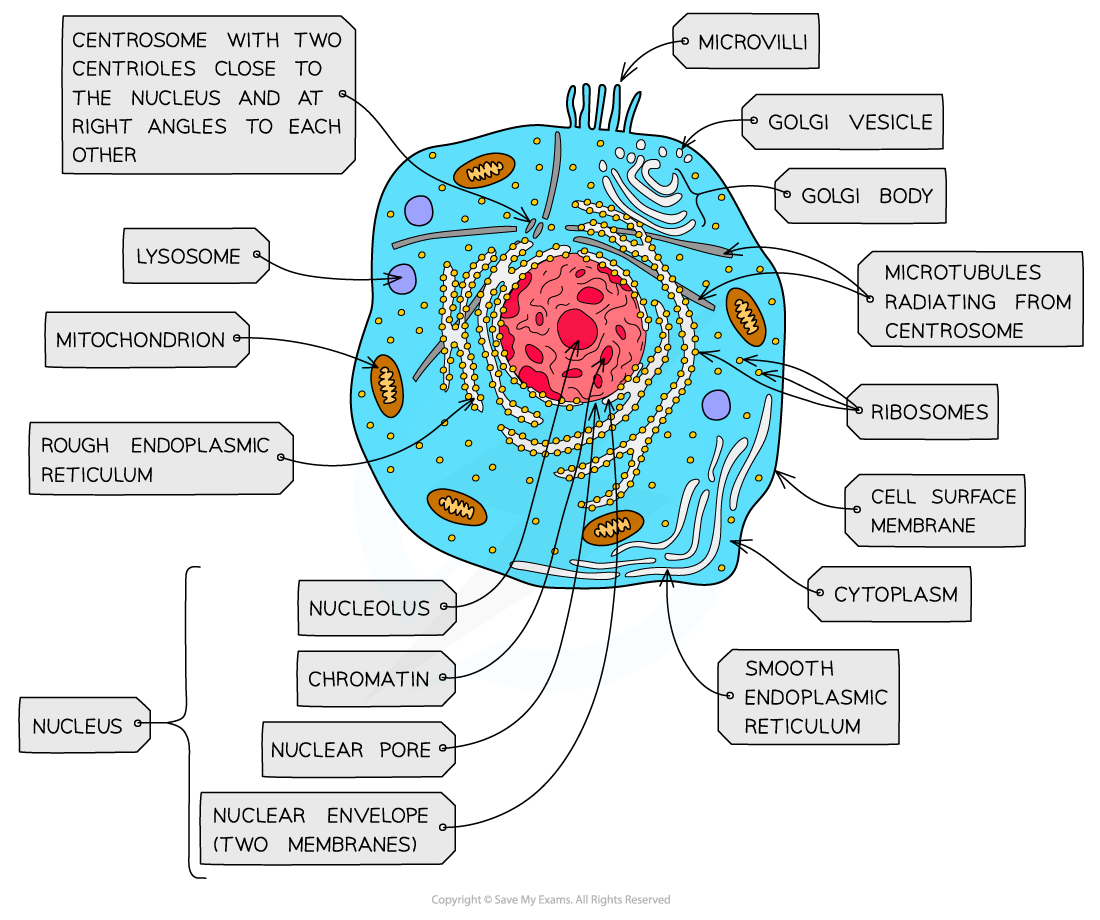
lysosomes - structure
double membrane
contains enzymes such as protease and lipase
lysosomes - function
breaks down materials ingested by phagocytes
release enzymes to the outside of the cell to destroy material around the cell
digest worn out organelles to reuse useful chemicals that are made up of
completely breaks down dead cells (autolysis)
chloroplasts - structure
contains double membrane structure
fluid enclosed in the chloroplast = stroma
internal network of membrane, forming flattened sacs called thykaloid
grana joined by membranes - lamelae
large SA
chloroplast - function
responsible for photosynthesis
can make own protein
starch is produced by photosynthesis and is presented as starch grains
centrioles - structure
composed of microtubules
componants of cytoskeleton
2 associated centrioles forms centrosome
centrioles - functions
centrosomes = involved in the assembly and organisation of the spindle fibres during cell division
flagella and cilia - structure
flagella = whip like
cilia = hair like
flagella = longer than cilia
cilia = present in greater numbers
cilia = 2 central microtubules (black circles) with 9 pairs of microtubules arranged in a wheel
flagella and cilia - function
flagella = enables cell motivity and sometimes sensory organelles detecting chemical changes
cilia = mobile/stationary stationary cilia is on the surface of the cell which is important in sensory organs e.g. nose
mobile cilia beats in rythmic pattern and creates a current which causes fluid to move in the trachea which moves the mucus along
plasma membrane - structure
made up of lipids and salts
plasma membrane - function
controls movement of substances in and out of cells
cell wall - structure
made up of cellulose carbohydrate
freely permeable - substances passes in and out of cells
cell wall gives its shape
cell wall - function
allows turgidity
keeps the plant upright
prevents cell from bursting
making a protein process
the nucleus is the site of ribosomes and mRNA manufacture (copy the protein gene)
ribosomes on the RER makes proteins to be secreted (free ribosomes make proteins to stay in cells)
The proteins are transported from RER to golgi apparatus by vesicles
golgi body further processess proteins (may add sugar chains)
vesicles contains proteins and move towards the plasma membrane
exocytosis
the cytoskeleton - function
microtubules, microfilaments and intermediate fibres helps to support the cells organelles
they help cell to maintain its shape
they transport organelles and materials within the cell (e.g. mitosis)
this can cause the cell to move
light microscope use
uses light rays to observe object
light microscope - advantage
can observe living things
does not use harsh chemical
easy to set up and use
cheap and portable
light microscope - disadvantage
low magnification (up to 2000 times)
low resolution
transmission EM - use
uses focused beams of electrons through sections of tissues
transmission EM - advantage
very high resolution image - very detailed image or cell organelles (upto 5000000 times)
high resolutions
can see details inside cells
scanning EM - use
uses focused beams of electrons reflected off the tissue
scanning EM - advantage
SEM can produce 3D images of a speciman
high magnifaction (upto 5000000 times)
high resolution
can see details of the surface of the structure
transmission and scanning EM - disadvantages
TEM can be used for thin tissues and must be performed on very thin specimen as thick specimen easily absorb the electrons and therefore do not produce good image
expensive
can only see dead materials
harsh materials/chemicals used in preparation which can cause artefact
laser scanning confocal - use
uses laser beam of light to illuminate chemical stains within the specimen. these then fluoresce
laser scanning confocal - advantage
can see living cells
can observe cell processes by tracking molecules
higher resolution than light microscope
laser scanning confocal - disadvantage
more expensive than light microscope
more complex than light microscope