flippin atomic structure revision
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
atom
smallest particles of matter made up of electrons orbiting a nucleus of protons and neutrons
molecue
two or more atoms chemically bonded to each other
particle
small unit of matter
element
a pure substance made of one type of atom
compound
a substance made up of two or more types of atoms bonded together in a fixed ratio and cannot be physically separated
mixture
a combination of two or more substance that are not chemically bonded
what is a periodic table
the periodic table organizes all discovered chemical elements in periods and columns according to their atomic number
subatomic particle
a particle smallar than an atom
electron
proton
neutron
isotopes
atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
half life
the time taken for half of a radioactive material to decay
radioactivity
the release of energy from the decay of the nucleus
benefits of using nuclear energy for medicine
nuclear energy can be used to both detect and treat cancers
benefits of using nuclear energy for industry
nuclear energy can generate electricity instead of using fossil fuels
problems of using nuclear energy medicine
patients are vulnerable to receiving high amounts of radiation if not used properly, harming their bodies even further
problems of using nuclear energy industry
handling nuclear energy can result in safety concerns and can lead to diseases
Ionise
to remove electrons from an atom or molecule
radioisotope
an isotope that emits radiation
ionising radiation
having enough radiation energy to remove the bond between an atom and electron which results in an ionized atom.
nucleus
the centre of an atom
electron shell
the space around the nucleus where electrons orbit
atomic number
the number of protons and electrons in an atom
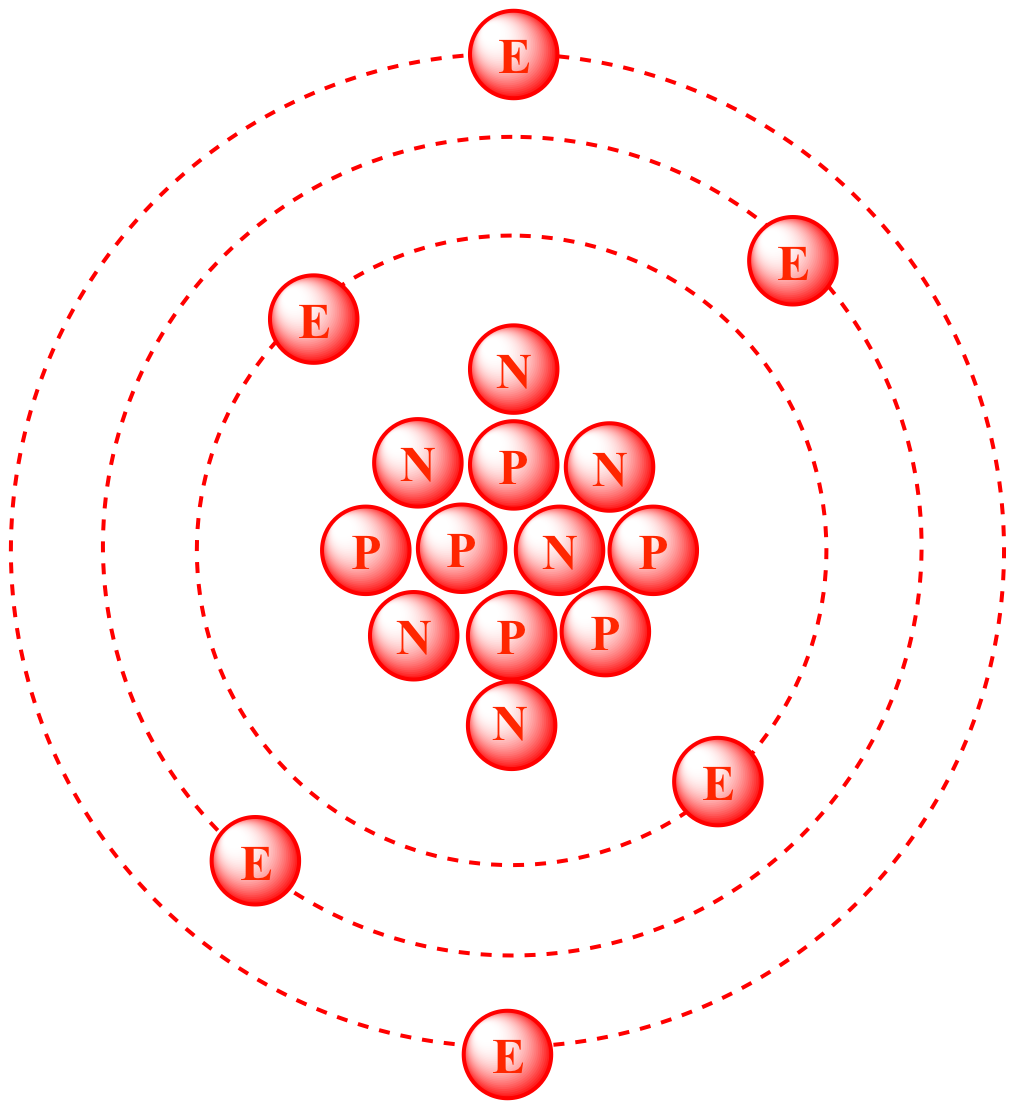
Carbon-12
6 nuetrons
6 elctrons
6 protons
Democritus discoveries
All substances are made of small INDIVISIBLE particles
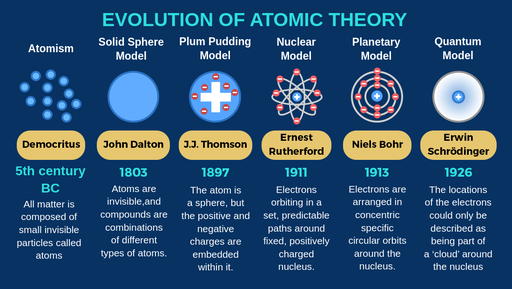
John Dalton discoveries
Atoms of different elements combine to form new substances and compounds
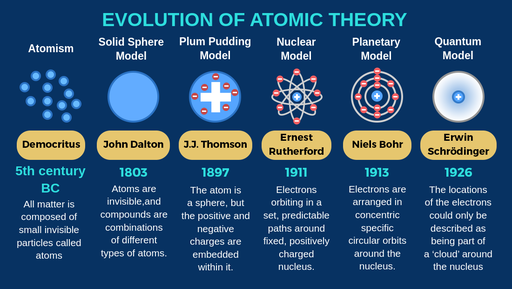
JJ Thomson discoveries
atoms are composed of electrons
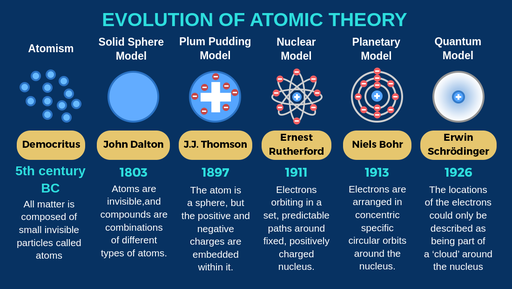
Ernest Rutherford discoveries
Atoms are mostly empty space
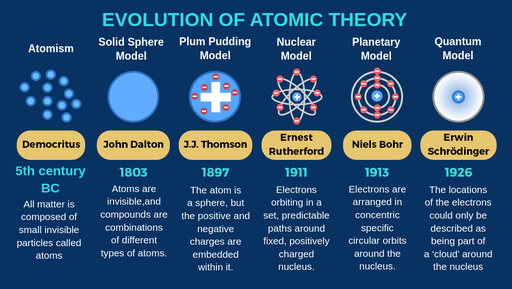
Niels Bohr discoveries
Proposed that electrons orbit around the nucleus
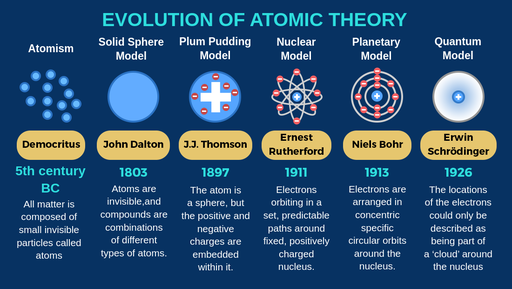
Erwin Schrodinger discoveries
Proposed that electrons move in wave, not set in paths around the nucleus
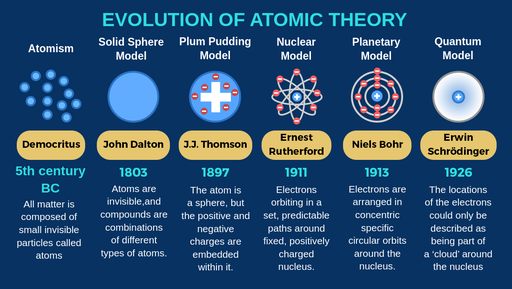
The modern atomic model states that:
most of the mass is concentratred in the centre of the atom
proton
definition: positively charged subatomic particle +
location: in the nucleus
electron
definition: negatively charged subatomic particle -
location: orbiting the nucleus
neutron
definition: neutrally charged subatomic particle =
location: in the nucleus
Alpha Radiation
Symbol: α
Composition: alpha particles
Charge: 2+
Relative penetrating power: low
Ionising power: strong
Beta Radiation
Symbol: β
Composition: beta particles
Charge: 1-
Relative penetrating power: medium
Ionising power: medium
Gamma Radiation
Symbol: γ
Composition: high-energy radiation
Charge: 0
Relative penetrating power: high
Ionising power: very weak