protein structure
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms

structure of an amino acid
carboxylic group
amino group
r group
how do two aa’s form a dipeptide ?
they condense tg
two aa ‘s line up losing a water molecule to form a peptide bond (first aa loses OH from COOH grp while second loses H frm NH2 grp )
polypeptide
single molecule, made up of a long chain of aas covalently linked by peptide bonds
each pp is encoded for by a single gene
protein
fully folded functional molecule
contains all subunits, prosthetic groups, cofactors/coenzymes
e.g. haemoglobin protein contains 2 α and 2 β subunits each with a haem prosthetic group
how many haemoglobin genes must there be ?
2
haemoglobin A codes for alpha polypeptide while B codes for beta polypeptide
what makes amino acids soluble
many OH or NH groups in their R groups as they can form H bonds or r groups that can be ionised
primary structure
order of aa’s in a polypeptide chain
secondary structure
folding of pp chain due to formation of h bonds into two specific 3D shapes:
alpha helix- each aa forms h bonds w/ the aa 4 units along
beta pleated sheet - 2 parts of the pp chain lay side by side and h bonds form between them
polypeptide bond
covalent bond linking two aas
what 4 bonds form between aas in the tertiary structure
h bonds
ionic
disulphide bridge
hydrophobic interactions
as these form the pp chain folds into a complex 3d shape
ionic bonds
can form between ionised amino and carboxylic grps
disulfide bridges
covalent bonds that form between the sulfur atoms of 2 cysteines
hydrophobic interactions
form between non polar R grps
Quaternary structure
final, 3D shape of the proteins formed from more than one polypeptide chain
conjugated protein
contain non protein prosthetic grps
prosthetic grp
molecule/ ion that is tightly bound to proteins and required for biological function can be organic or inorganic but never another aa
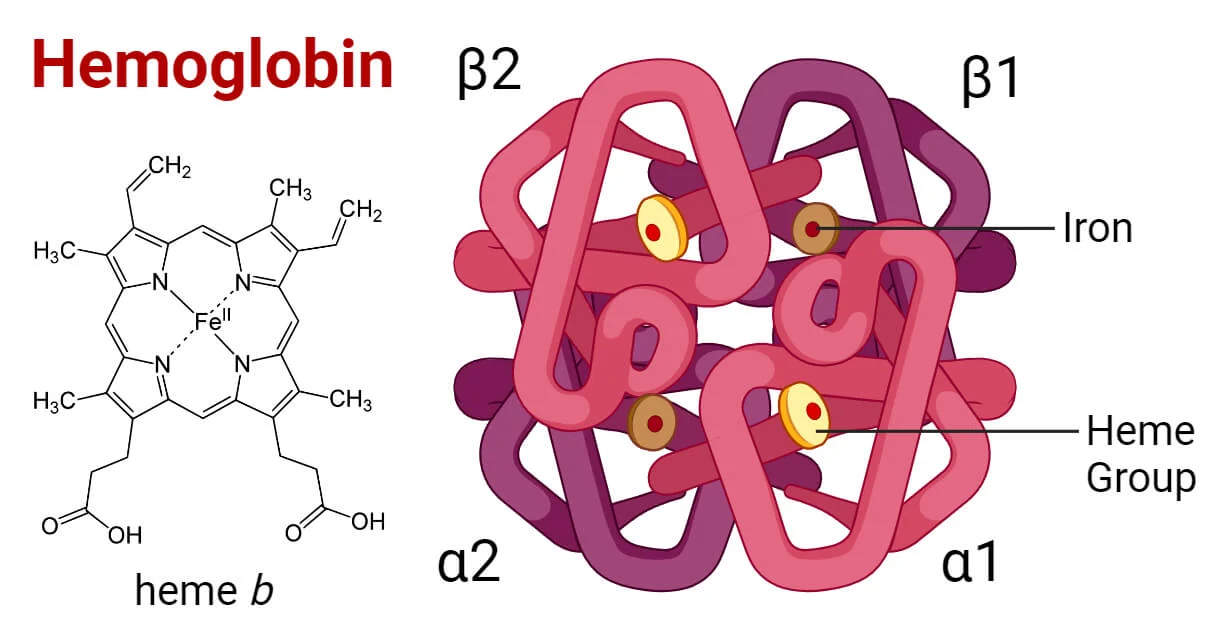
haemoglobin
globular protein so it folds into a spherical shape
soluble
haem prosthetic grp which O2 binds to also has iron
4 pps ( 1 haem for each )
2 alpha 2 beta subunits
quaternary
haemoglobin function
transport 02 +CO2 in blood
globular proteins
spherical proteins
soluble bcs hydrophilic R groups found on outside of protein/ hydrophobic R groups cluster in the centre
denature easily/sensitive to temperature/ pH because shape is critical to function
may be conjugated or require cofactor/ coenzymes
fibrous proteins
INSULIN
hormone (peptide)
synthesised by b-cells of pancreas
reduces blood glucose - stimulates uptake of glucose & conversion into glycogen
globular protein
carbonic anhydrase
enzyme
CO2 transport
reacts CO2 + H2O to form carbonic acid (CO2 transported as hydrogencarbonate ions in plasma )
globular protein
(salivary a) amylase
enzyme
hydrolyses starch into maltose/ dextrins
globular protein
insulin structure
synthesised as single polypeptide from one gene (Tertiary structure)
contains 3 disulphide bonds
post-translation modification
- hydrolysed into 2 chains by peptidases & stored in secretory vesicles
carbonic anhydrase structure
Zn2+ ion = prosthetic group
forms part of active site – takes part in reaction
held in position by 3 histidines
synthesised as single polypeptide from one gene (Tertiary structure)
salivary amylase structure
synthesised as single polypeptide from one gene (Tertiary structure)
metalloenzyme – requires 2 ions:
Cl- needed as cofactor to help starch bind to active site
Ca2+ stabilises enzyme
Fibrous proteins
form structures, e.g. connective tissues: bone, cartilage….
fibrous proteins properties
linear unbranched and insoluble - primary structure contains repeated sequence of hydrophobic amino acids
so insufficient OH groups to form intramolecular H bonds, so do not coil into helix
high tensile strength - extensive cross-links (between pps)
collagen – structure:
3 collagen polypeptides form intermolecular H bonds causing them to form a rope-like triple helix
covalent bonds form between triple helices to form microfibrils
Extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins
form a complex scaffold around cells, providing structural support – they include collagen (for tensile strength), elastin (for elasticity)
tendons
transmit pulling force of muscle to bone
they require high tensile strength
consist mainly of collagen
ligaments
connect bones/ stabilise joints
they require tensile strength and some elasticity
consist of collagen and elastin
denaturation
process of disrupting protein structure by breaking bonds
always causes loss of function and is irreversible