CSF CH 10A: Lipid Bilayer
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What properties do amphipathic lipids have that allow them to become bilayers, micelles, and liposomes
-nonpolar tail and polar head
-associate in “like” environments
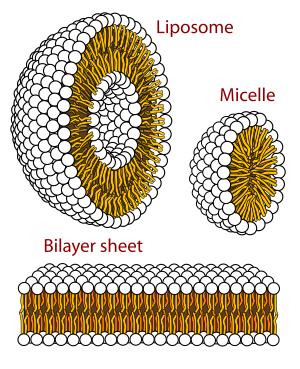
hydrophobic portion of lipid
any part that has nonpolar bonds
hydroohilic portion of a lipid
bonds with large EN differences
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)=internal
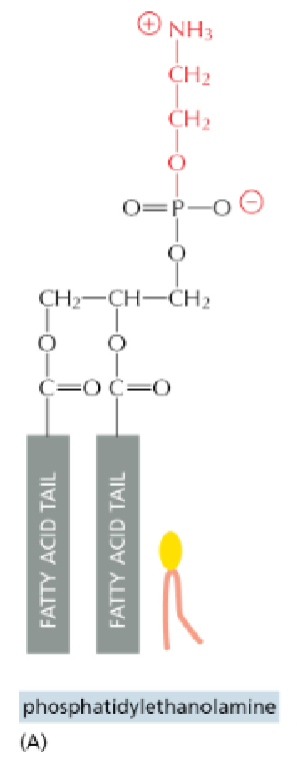
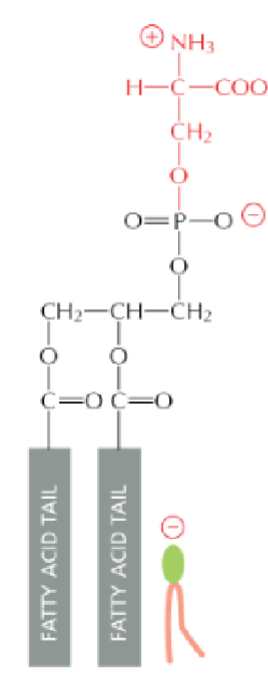
Phosphatidylserine (PS)= internal,negatively charged
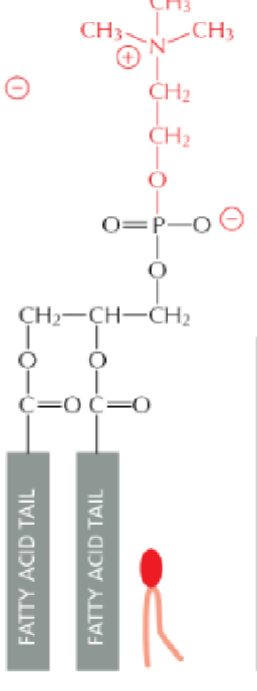
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)= external
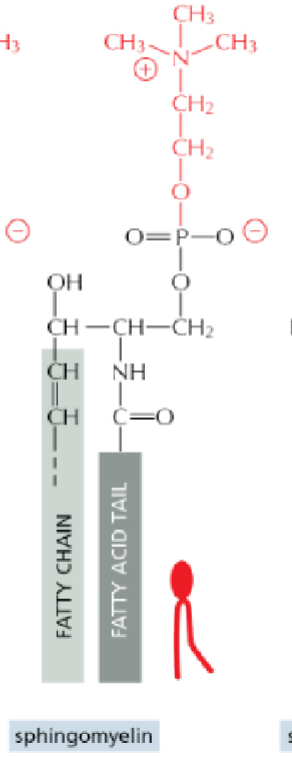
Sphingomyelin= external
3 factors that affect membrane fluidity
composition
length: short chains more fluid
temp: high temp more fluid
membrane composition 3 factors
cholesterol makes membraned more stiff; less fluid
sat. fatty acids make less fluid
unsat. fatty acids make more fluid
Lateral diffusion
movement within the plane of the leaflet
flexion
tails can flex and move
rotation
lipids can rotate
flip-flop
lipids switch to diff leaflet sides (need help of flippases, scramblases, and phospholipid translocases)
2 reasons asymmetry matters
membrane change: PS presense on extracellular side causes cell death
cell signaling: PS and PI (also on cytosolic side) bind intracellular signaling proteins
lipid aggregation/lipid rafts
-rafts form in areas of greater fluidity (more sat. lipids)
-attract transmembrane proteins with linger hydrophobic transmembrane signaling
-important for cell signaling
components of lipid rafts
-cholesterol
-sat hydrocarbons
-glycolipids
(carbohydrate groups always on non-cytosolic side of membrane)
lipid droplet formation from interleaflet space of ER membrane
lipid droplet: storage for excess lipid where they can be retrived as building blocks for membrane sysnthesis or a food source fueling metabolic energy generation
-surrounded by phospholipid bilayer