Suspensions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Differences between dispersed system and solution
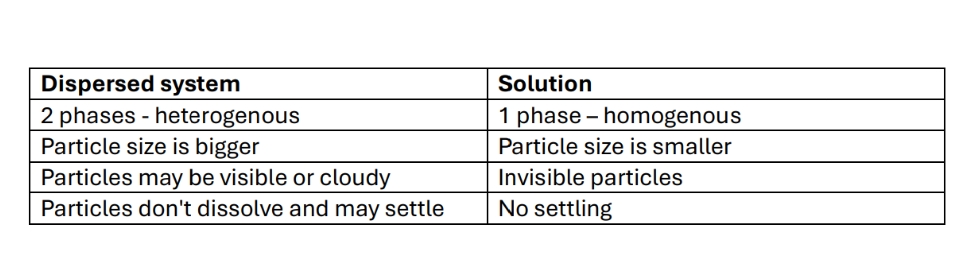
Dipersed system can be translucent = the dispersed particles are so small they can't be seen with naked eye
Types of biphasic systems and their continuous and dispersed phase

What is a surface

Why can water adpot a spherical shape

Force and length of forced applied to the surface = N/m
What is an interface

Why do substances adopt a spherical shape

What is laplace pressure

Work done equation

Detachment method

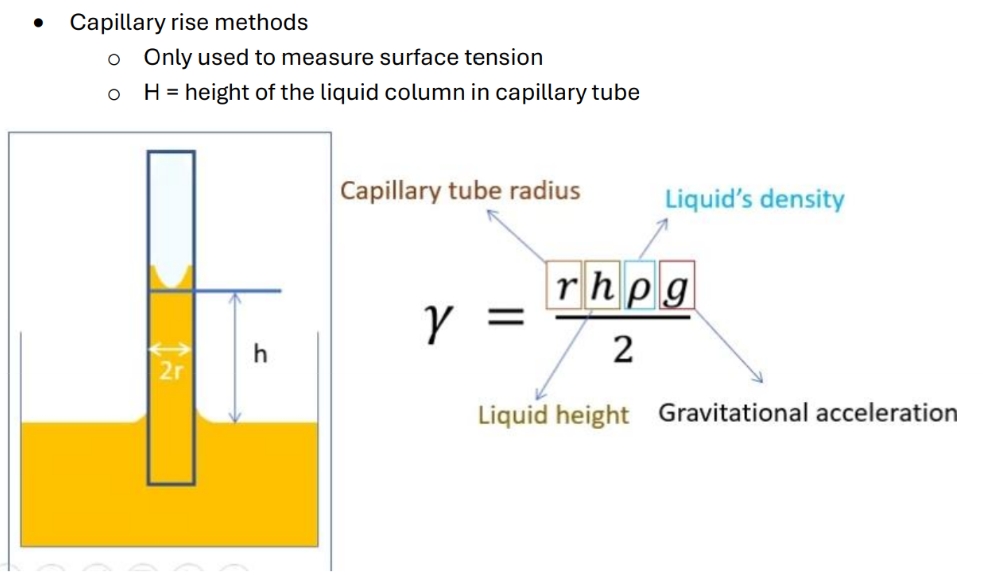
Capillary rise methods
wWhat is cohesion and adhesion
C = attraction between like molecules
A = different molecules
Balance of these predicts how a dispersed system behaves
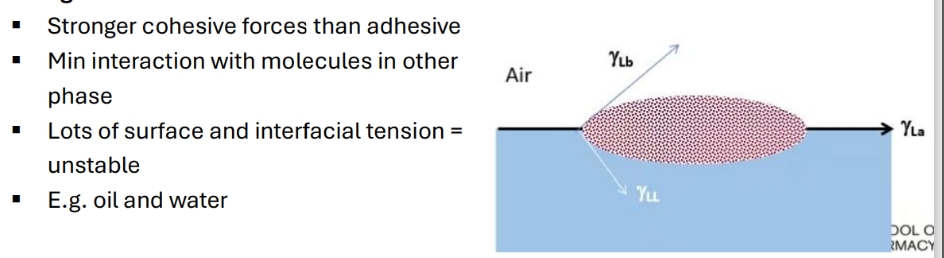
When does spreading occur
Consequences of spreading
Happens between 2 immiscible liwquid phases
Film formation
Lens or globule formation
Film formation
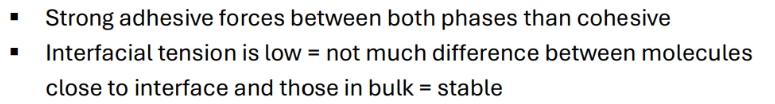
Lens or globule formation
When does wetting occur
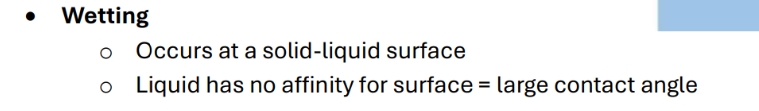
Contact angles
Advantages of suspensions

How can suspension be administered

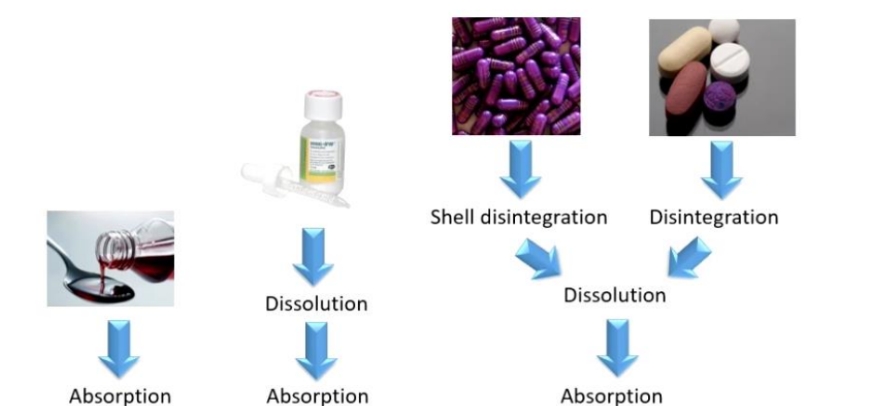
Processes before absorption can occur for solutions, susnsions, capsules, tablets
What does the ideal suspension look like

What is settling and stokes' law
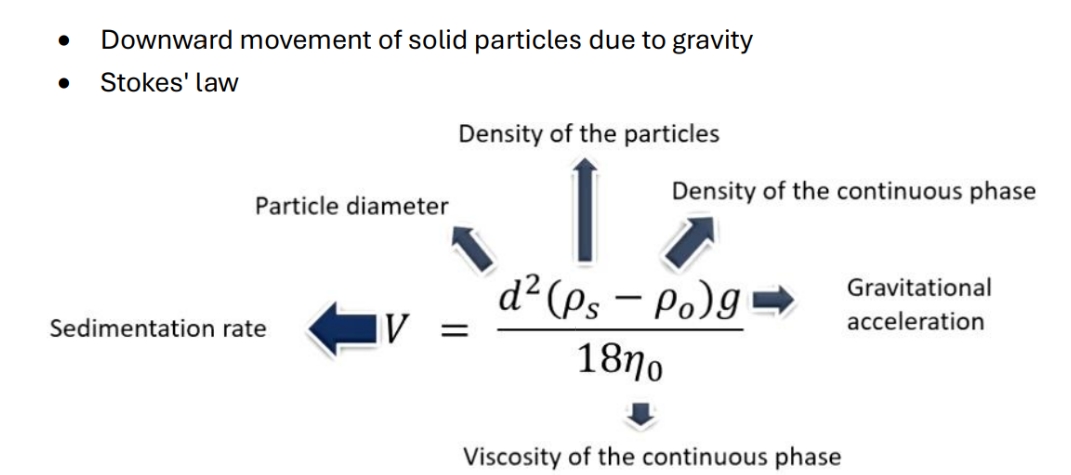
Limitations of stokes' law
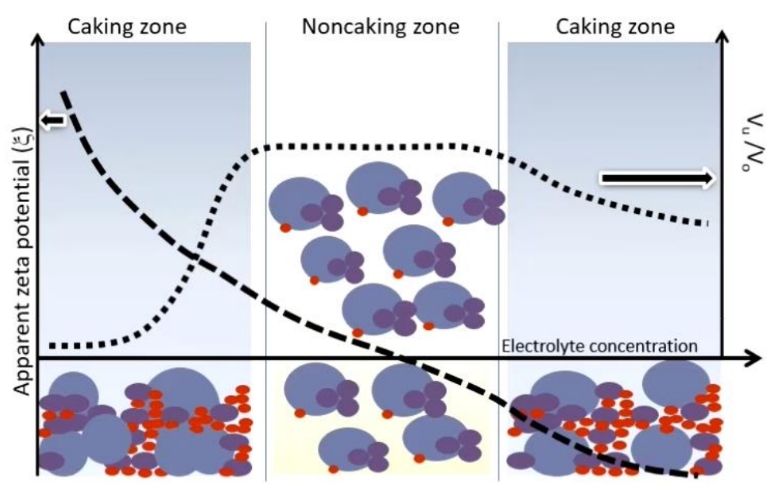
What is caking

What is flocculation

What are flocculating agents

Sedimentation voume equation
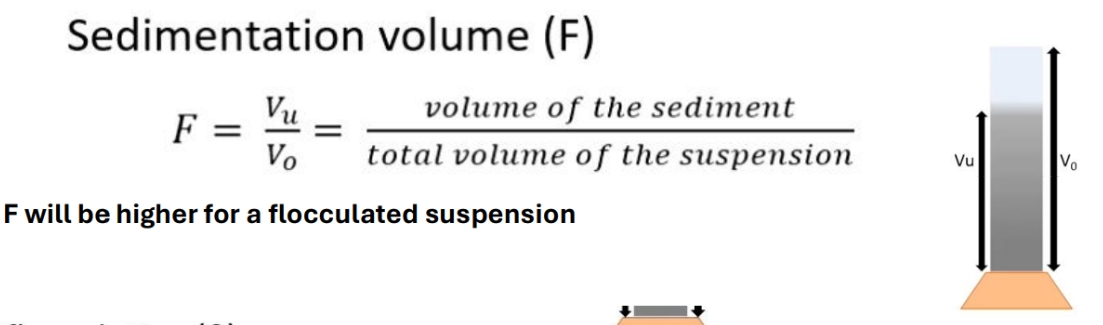
Degree of flocculation equation

How does zeta potential and sedimentation volume change with increasing electrolyte concentration
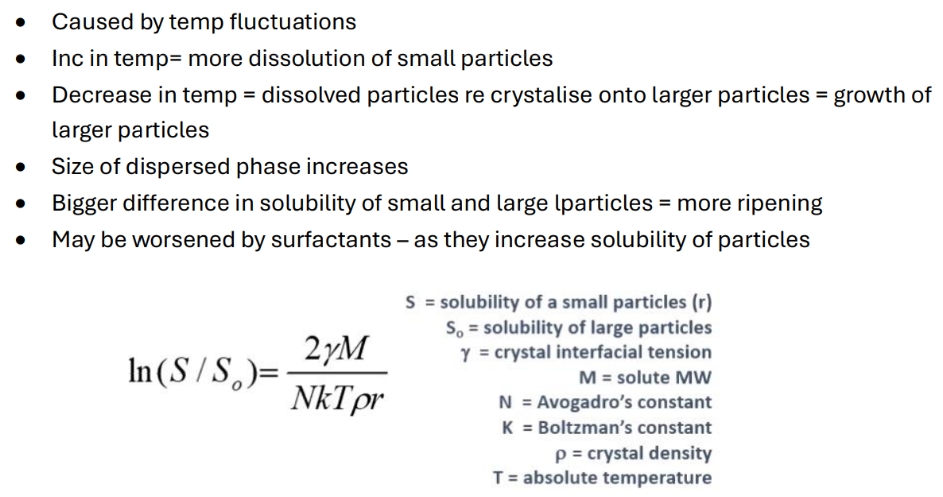
What is ostwald ripening g