S 1.4 Neurological System
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the two system in Nervous System
System | Components | Function | Subdivisions |
|---|---|---|---|
Central Nervous System (CNS) | Brain, Spinal Cord | Processes information and controls responses; main integration center, regulate body mechanisms | None |
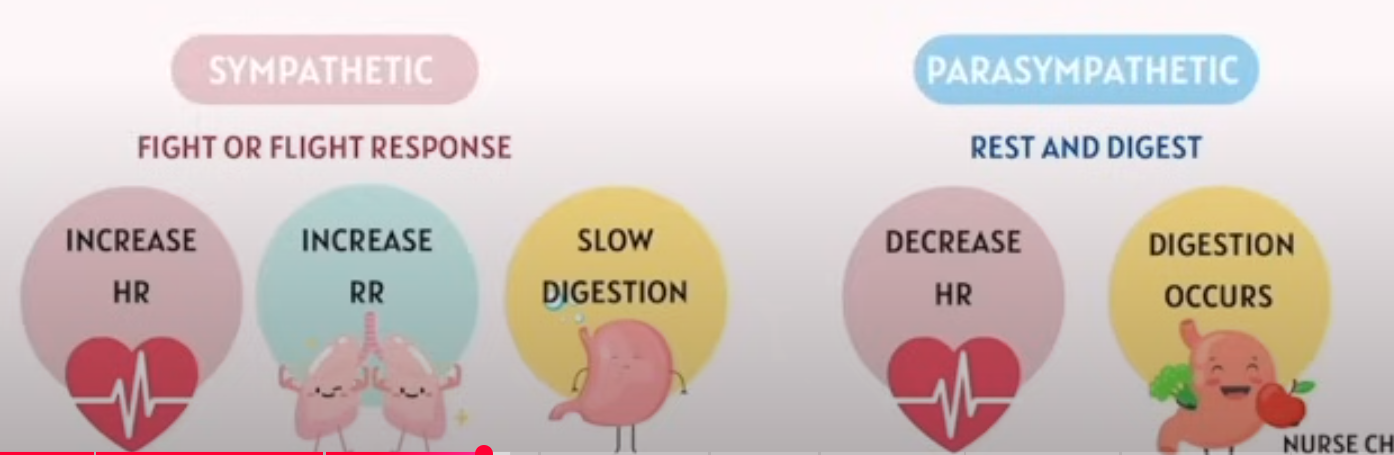
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) | All nerves outside CNS | Connects CNS to the body; carries messages to and from CNS | - Somatic Nervous System (voluntary control, e.g. skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary control, e.g. organs, glands) • Sympathetic (“fight or flight”) • Parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) |
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is the part of your peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary body functions, like:
Heart rate 💓
Breathing rate
Digestion 🍔➡💩
Pupil dilation 👁
Blood vessel constriction
What make up of the Brain (3 parts) (CNS)
Part of Brain | Main Components | Functions |
|---|---|---|
Forebrain | - Cerebrum- Thalamus- Hypothalamus | - Higher cognitive functions (thinking, memory, reasoning)- Sensory perception- Voluntary motor activities- Regulation of temperature, hunger, emotions |
Midbrain | - Tectum - Tegmentum | - Reflexes for vision and hearing- Controls eye movement- Relays motor signals |
Hindbrain | - Cerebellum- Pons - Medulla Oblongata | - Coordination of movement and balance (cerebellum)- Breathing and sleep regulation (pons)- Controls vital functions like heart rate, breathing, blood pressure (medulla oblongata) |

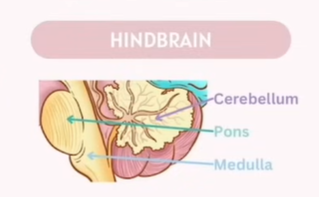
What make up of the Hindbrain (CNS)
Hindbrain | - Cerebellum - Pons - Medulla Oblongata | - Coordination of movement and balance (cerebellum)- Breathing and sleep regulation (pons)- Controls vital functions like heart rate, breathing, blood pressure (medulla oblongata) |
Part | Location | Functions |
|---|---|---|
Cerebellum 小脑 ( Balance and Movement Coordination) | Behind the brainstem, below the cerebrum | - Coordinates voluntary movements - Maintains posture and balance - Fine motor control |
Pons (Transmits signals btw Forebrain and Cerebellum) | Above the medulla, below the midbrain (part of brainstem) | - Connects cerebrum and cerebellum - Controls breathing rhythm - Involved in sleep and arousal |
Medulla Oblongata (Regulation of ) | Lowest part of brainstem, continuous with spinal cord | - Controls vital involuntary functions (heart rate, breathing, blood pressure) - Reflex actions like swallowing, coughing, sneezing |
Tips to memorize:
Medulla Manages
Pons Passes
Cerebellum Coordinates
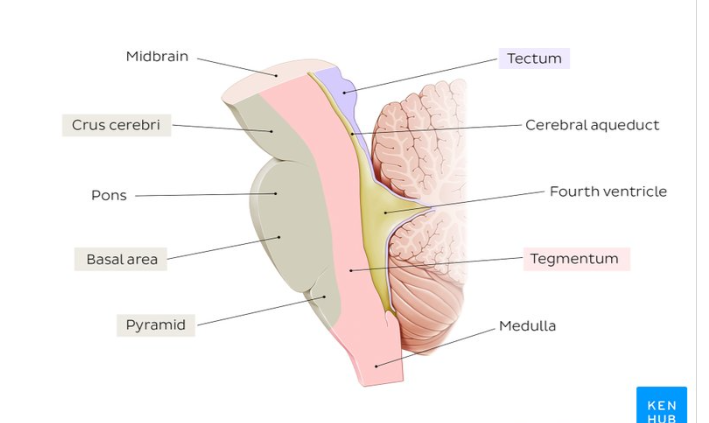
what make up of Midbrain (2 parts)(CNS)
Part | Location (in Midbrain) | Main Components | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
Tectum | Dorsal (back) part of midbrain | - Superior colliculi- Inferior colliculi | - Superior colliculi: visual reflexes, tracking moving objects- Inferior colliculi: auditory reflexes |
Tegmentum | Ventral (front) part of midbrain | - Red nucleus- Substantia nigra- Reticular formation | - Controls motor functions - Regulates awareness and attention - Contains pathways for voluntary movement (substantia nigra linked to Parkinson’s disease) |
Function: Alertness, Sleep/Wake cycle, Motor activities
Midbrain - MID
M - Movement (Especially Eye Movements)
I - Involuntary (Sleep/Wake Cycle)
D - Detection of Auditory and Visual Reflexes
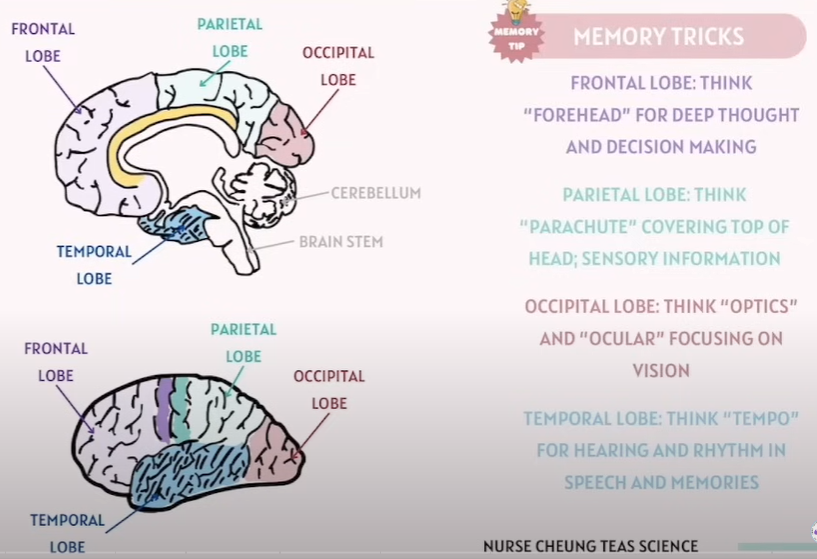
(CNS)What make up of the Forebrain
🧠 Forebrain Structures & Their Functions
Brain Part | 中文 | Function(s) |
|---|---|---|
Cerebrum | 大脑 | - Higher cognitive functions (thinking, memory, reasoning) |
Thalamus | 丘脑 | - Sensory relay (directs sensory info to the cortex) |
Hypothalamus | 下丘脑 | - Regulation of temperature, hunger, thirst, and emotions |
🧠 Mnemonic to Remember It (in English)
"Cool Thinking Helps Survive."
"Cool Thinking Helps Survive."
C = Cerebrum → Cognition, Control, Consciousness
T = Thalamus → Traffic director for sensory info
H = Hypothalamus → Homeostasis (temperature, hunger, emotions)
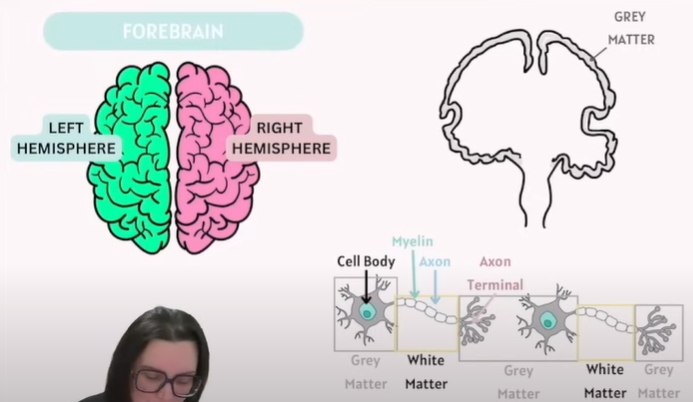
What is White and Grey Matter(CNS)
Type | What it is | Composition | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
White Matter | The part of the nervous system that looks white due to myelin | Mainly myelinated axons (nerve fibres) | - Inner part of brain- Outer part of spinal cord | Carries nerve impulses between neurons, connecting different parts of grey matter |
Grey Matter | The darker part containing neuron cell bodies | Mainly neuron cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, glial cells, synapses | - Outer part of brain (cerebral cortex)- Inner part of spinal cord | Processes information – where synapses occur, signals are integrated and processed |
Grey matter = processing and integration (cell bodies).
White matter = communication pathways (myelinated axons).
Note: (Check Screenshot)
Axon in white matter is covered in Myelin ( Make up of fats and Lipids)
Axon Terminal connects to the next Cell body
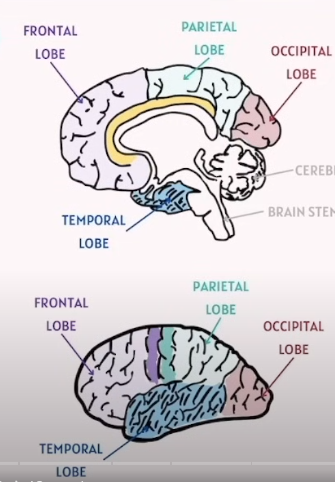
Identify the Four Lobes in Brain(CNS)
Lobe | Location | Main Functions |
|---|---|---|
Frontal Lobe | Front part of cerebrum | - Voluntary movement (motor cortex)- Planning, reasoning, problem-solving- Emotions, personality, speech production (Broca’s area) |
Parietal Lobe | Behind frontal lobe, top middle of brain | - Sensory perception and integration (touch, temperature, pain)- Spatial awareness |
Temporal Lobe | Side of brain, near ears | - Hearing (auditory cortex)- Memory- Language comprehension (Wernicke’s area) |
Occipital Lobe | Back of brain | - Visual processing (interpreting visual information) |
Tips to memorize:
Lobe |
|---|
Frontal Lobe - Think Forehead for Deep Thought and Decision Making |
Parietal Lobe - Think Plates (Satellite) Covering top of the head, Sensory Information |
Temporal Lobe - Think Tempo, For hearing and Rhythm in Speech and Memories |
Occipital Lobe - Think Optics and Ocular . Focusing on Vision |
PNS
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
- Somatic Nervous System (voluntary control, e.g. skeletal muscles)
- Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary control, e.g. organs, glands) Two division~
• Sympathetic (“fight or flight”)
• Parasympathetic (“rest and digest”)
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System)
What make up for PNS
Everything outside of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Autonomic Nervous System
Responsibility:
Internal Temperature
Regulating GI functions
Excretory and Endocrine System
Cardiac Activities
Sympathetic: Fight or Flight
Parasympathetic: Rest and Digest
Somatic Nervous System
Responsibility:
Motor function of skeletal muscle (Voluntary)
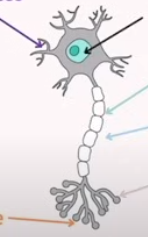
Identify what on the graph.
Neuron: (Comes in many types, this is the general one)
Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
Dendrite | Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and carry them toward the cell body. |
Cell Body | Also called soma; contains the nucleus and most of the cell’s organelles, maintaining neuron health and integrating incoming signals. |
Myelin | A fatty insulating layer covering some axons, which increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission. |
Axon | A long, slender projection that carries electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles. |
Synapse | The small gap between neurons where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals to the next cell. |
Axon Terminal | The endpoint of an axon where neurotransmitters are stored and released into the synapse to communicate with other cells. |
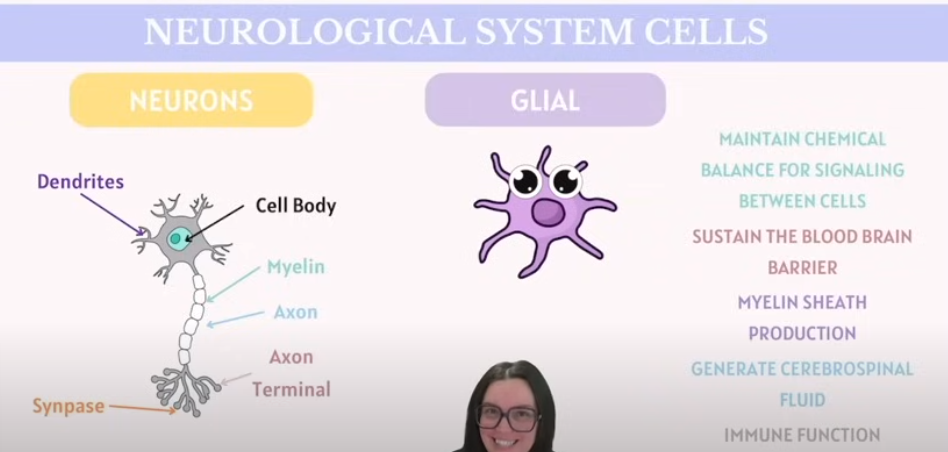
What is a Glial Cell?
What do they do?
Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
Glial (Glial Cells / Neuroglia) | Supporting cells in the nervous system that do not conduct nerve impulses. They provide structural support, nourishment, insulation (e.g. forming myelin), and protection for neurons. Types include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, and ependymal cells. |

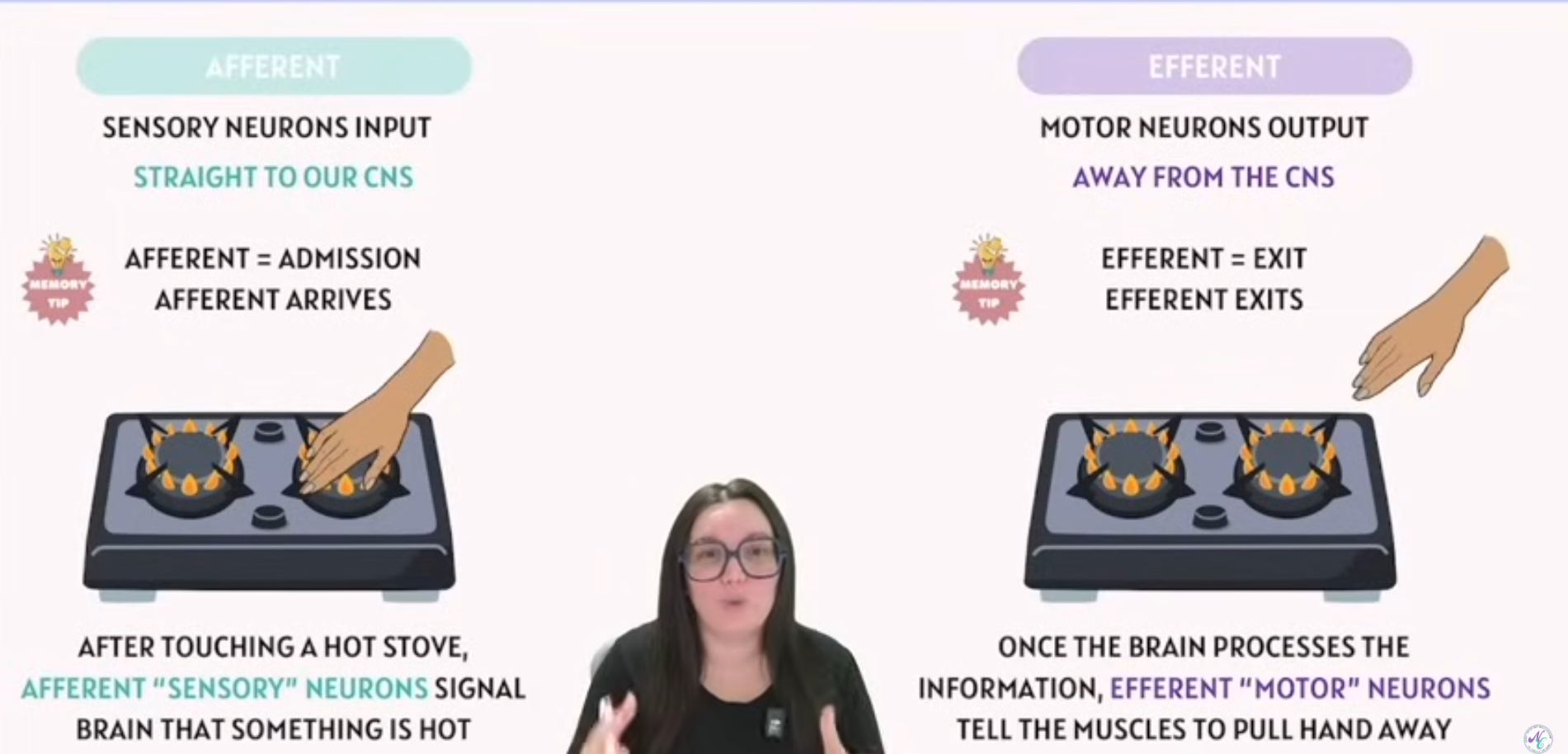
What is Afferent and Efferent in Nervous System
What type of neurons are they( they’re diff)
Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
Afferent | Refers to sensory neurons that carry information from the body to the central nervous system (CNS). For example, feeling heat from a stove sends signals via afferent pathways to the brain. |
Efferent | Refers to motor neurons that carry commands from the CNS to the body, such as muscles or glands. For example, your brain sends efferent signals to move your hand away from the hot stove. |
Mnemonic Tips:
Afferent = Arrives
Efferent = Exit