yum
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:17 PM on 1/12/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Bcr Abl
in frame fusion protein between chromosome 9 & 22
causes leukemia, treated wit Gleevec
causes leukemia, treated wit Gleevec
2
New cards
Rb
many signaling pathways converge to regulate phosphorylation of this protein, which controls the R point
tumour suppressor that causes retinoblastoma
tumour suppressor that causes retinoblastoma
3
New cards
driver mutations
cause expansion of unique subpopulations
4
New cards
R point
between G1 & S, decision to divide
convergence of many growth and inhibition pathways
convergence of many growth and inhibition pathways
5
New cards
cyclins
form complexes with Cdks to promote/regulate events of the cell cycle
6
New cards
cyclin dependent kinases CDKs
enzyme that regulates cell cycle progression and is activated by cyclin proteins
7
New cards
E2F
transcription factor that prevents transcription of Rb
bound when Rb is hy**po**phosphorylated
when released, drives transcription of cyclins
activates genes involved in progression from G1 to S phase
bound when Rb is hy**po**phosphorylated
when released, drives transcription of cyclins
activates genes involved in progression from G1 to S phase
8
New cards
p53
tumor suppressor responsible for cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, block of angiogenesis (blood vessel growth) and apoptosis
tetramer
tetramer
9
New cards
MDM2
ubiquitylates p53 for degradation
10
New cards
Scr
inhibited when bound to tyrosine 527
activated when tyrosine 416 is phosphorylated
non-receptor tyrosine kinase
activated when tyrosine 416 is phosphorylated
non-receptor tyrosine kinase
11
New cards
v Scr
viral oncogene caused by rous sarcoma virus (RSV)
causes increase in tyrosine phosphorylation
causes increase in tyrosine phosphorylation
12
New cards
western blot
detect specific proteins using specific antibodies
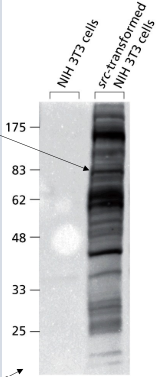
13
New cards
receptor tyrosine kinase RTK
respond to growth factors
enzyme coupled receptor, forms a dimer after ligand binding
Src and Kras are intracellular response to GF binding to receptor
have intracellular tyrosine kinase domains and variable extracellular domains
enzyme coupled receptor, forms a dimer after ligand binding
Src and Kras are intracellular response to GF binding to receptor
have intracellular tyrosine kinase domains and variable extracellular domains
14
New cards
epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR
transmembrane protein that is activated by dimerization upon growth factor binding
RTK that has cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain homologous to Src
RTK that has cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain homologous to Src
15
New cards
non receptor tyrosine kinase
do not have receptor activity but interact with proteins that do
ex - Src
ex - Src
16
New cards
GPCR
respond to GEFs by activating G proteins (large heterodimers)
7 helical transmembrane domains
7 helical transmembrane domains
17
New cards
large scaffold proteins
assemble groups of multiple downstream signaling components
18
New cards
PI3K
activates downstream of growth factor signal
converts PIP2 to PIP3
PIP3 recruits Atk which influences proliferation
converts PIP2 to PIP3
PIP3 recruits Atk which influences proliferation
19
New cards
PTEN
converts PIP3 to PIP2, inhibiting Akt and stopping cell proliferation
Loss (deletion/mutation) of this phosphatase increases Akt signaling in cancers
Loss (deletion/mutation) of this phosphatase increases Akt signaling in cancers
20
New cards
Ras
activated by GEF
stimulates pathways that promote tumour development and progression
stimulates pathways that promote tumour development and progression
21
New cards
MAPK
scaffold protein-mediated signaling cascade that promotes proliferation and is activated downstream of Ras
22
New cards
second messenger
influence activation/inhibition of proteins/pathways
generate in large amounts in response to signal activation to amplify that signal
ex - calcium ions
generate in large amounts in response to signal activation to amplify that signal
ex - calcium ions
23
New cards
Ku protein
ring shaped heterodimer protein used in nonhomologous end joining to fix double strand breaks
24
New cards
Akt
serine/threonine kinase that binds to PIP3
activation involves binding to a phosphoinositide
activation involves binding to a phosphoinositide
25
New cards
sporadic
cancers that are initiated by mutations in somatic cells that are not found in the germline
26
New cards
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
condition caused by inheriting a p53 mutation
27
New cards
phosphoinoditides
phosphorylated lipids in cell membranes, regulating signaling, membrane trafficking, and cellular processes.
ex - PIP2, PIP3
ex - PIP2, PIP3
28
New cards
anoikis
cell death when detached from extracellular matrix
29
New cards
endocrine
signaling factors that travel long distances in blood
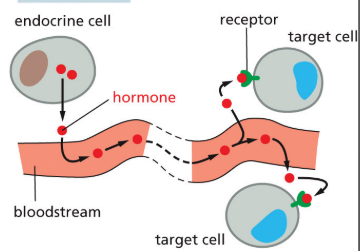
30
New cards
paracrine
signaling involves secreted factors with a limited range (signal within a localized region)
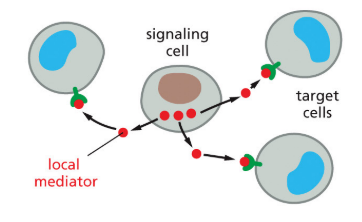
31
New cards
juxtracrine
signaling is mediated by contact diffusible factors
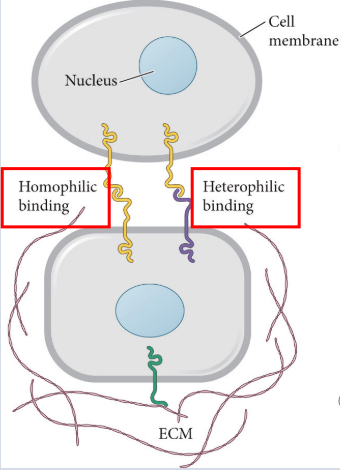
32
New cards
autocrine
cell producing the signal is the same type as the cell receiving the signal
33
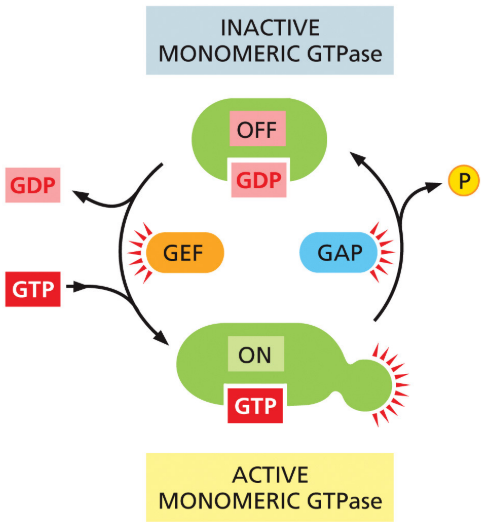
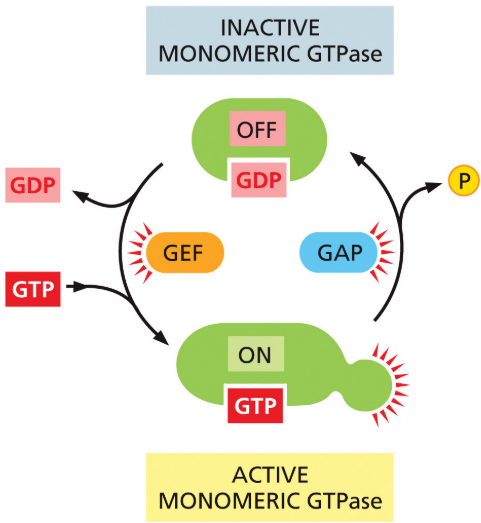
New cards
GAPs
promote GTP hydrolysis
34
New cards
GEFs
stimulate release of GDP so GTP can bind
35
New cards
iPSCs
pluripotent cells derived from the somatic cells of a patient's own body
36
New cards
master regulator
transcription factor with a key role in directing cell fate
37
New cards
lncRNA
have regulatory roles, usually to decrease gene expression
RNA molecules that can act in cis or trans to influence transcription
RNA molecules that can act in cis or trans to influence transcription
38
New cards
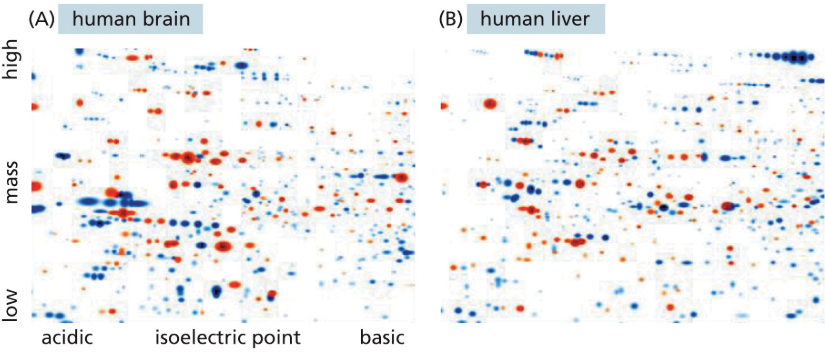
2D gel electrophoresis
separates proteins by mass and charge to create an array of dots that reflect the proteome of the cell type analyzed
39
New cards
40
New cards
in situ hybridization
uses an RNA probe to identify where a particular mRNA is expressed
41
New cards
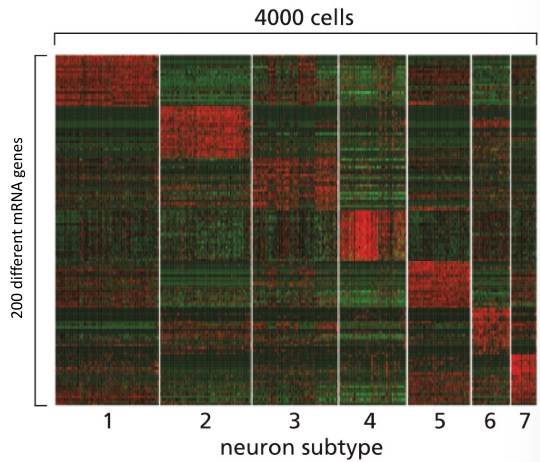
heatmap
uses different colors to indicate high and low expression to display gene expression data
42
New cards
reporter gene assay
to characterize the effects of any enhancers that could be present in a segment of DNA, that sequence of DNA is fused to a green florescent protein (GFP) gene
43
New cards
ChIP-Seq
can be used to identify the DNA sequences that a particular insulator protein binds to
44
New cards
RNA-Seq
can be used to discover which RNA are expressed in a particular cell type
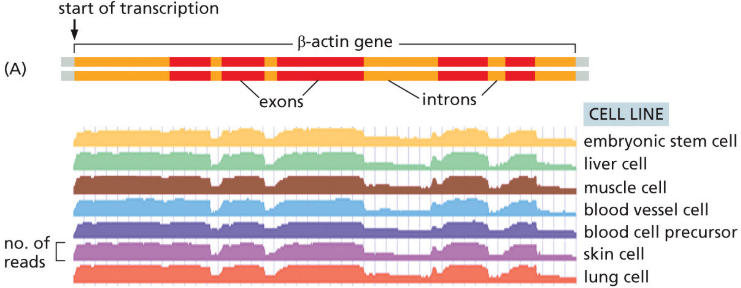
45
New cards
transcriptome
complete set of RNA molecules present in a cell, tissue, or organism at a specific point in time
46
New cards
cis regulatory elements
regulatory DNA sequences located adjacent to gene they regulate
generally sequences encoded on the same chromosome as the gene they affect
ex - promoters, enhancers, silencers
generally sequences encoded on the same chromosome as the gene they affect
ex - promoters, enhancers, silencers
47
New cards
trans regulatory elements
bind to cis elements, can regulate multiple genes and can be expressed from any chromosome
ex - transcription factors, microRNA
ex - transcription factors, microRNA
48
New cards
activators
bind to enhancer DNA elements
cause change to chromatin structure
cause change to chromatin structure
49
New cards
repressors
bind to silence DNA elements
50
New cards
insulators
alter 3D arrangement of chromatin to divide DNA into looped regions
51
New cards
operon
polycistronic cluster of genes that share a cis-regulatory element
in prokaryotes
in prokaryotes
52
New cards
operator
cis regulatory element that words on a polycistronic cluster of genes
53
New cards
tryptophan repressor
binds to operator when tryptophan is present to inhibit further transcription
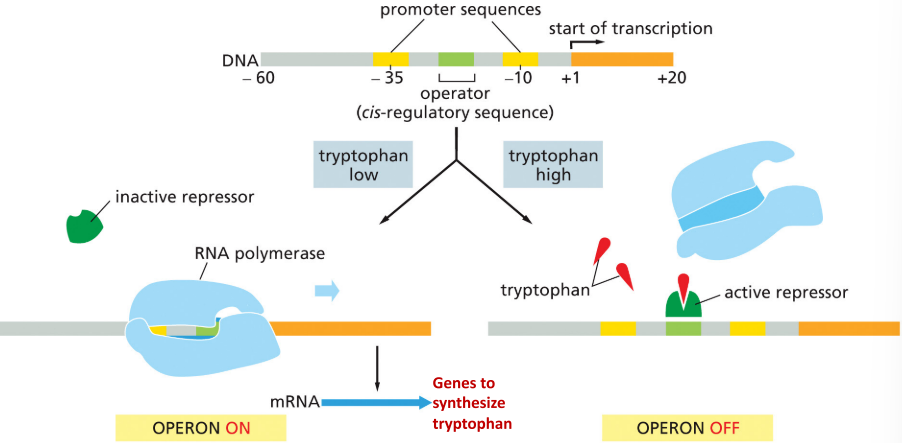
54
New cards
lac repressor
binds when there is enough glucose, enough energy, or no lactose in the bacteria
releases when there is low energy (cAMP) and high lactose
releases when there is low energy (cAMP) and high lactose
55
New cards
negative splicing control
prevents access to splice site
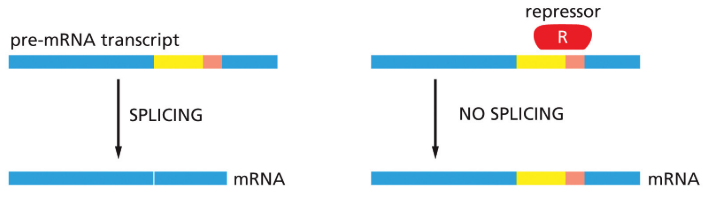
56
New cards
positive splicing control
directs splicing machinery to splice site that would otherwise not be used
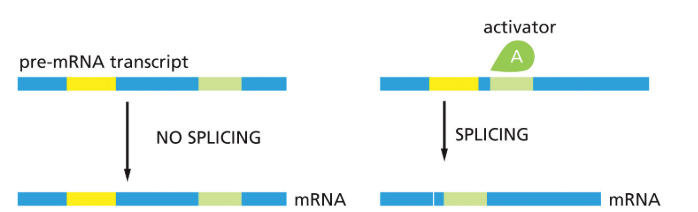
57
New cards
exon junction complexes EJC
mark a complete splice
58
New cards
RNA editing
post transcription modification that changes base pairs
adenosine can become inosine (A→I)
cytosine can become uracil (C→U)
adenosine can become inosine (A→I)
cytosine can become uracil (C→U)
59
New cards
5’UTR
capping region of mature mRNA that does not encode for proteins
60
New cards
3’UTR
polyA and cleavage region of mature mRNA that does not encode for proteins
61
New cards
untranslated regions UTRs
mRNA stability (how long mRNA is present)
mRNA translation (when, how often)
mRNA localization (where in cell)
mRNA translation (when, how often)
mRNA localization (where in cell)
62
New cards
endonuclease site
when exposed, allows for mRNA degradation
found at 3’UTR
found at 3’UTR
63
New cards
maternal contributions
proteins and RNA that are stored in the egg until they are needed to orchestrate early development
64
New cards
Xist
lncRNA that triggers X-inactivation
65
New cards
RNA interference RNAi
small non-coding RNA recognize targets by complementary base-pairing and regulate a large number of eukaryotic genes
ex - siRNA, piRNA, & miRNA
ex - siRNA, piRNA, & miRNA
66
New cards
miRNA
hairpin after transcription
target RISC complex to particular mRNA based on complementary pairing
cleaved in nucleus and cytoplasm
target RISC complex to particular mRNA based on complementary pairing
cleaved in nucleus and cytoplasm
67
New cards
siRNA
double stranded RNA from endogenous source
transfected into cells to knockdown expression of target mRNA
transfected into cells to knockdown expression of target mRNA
68
New cards
argonaute protein
associated with RISC complex
69
New cards
RISC complex
RNA-Induced Silencing Complex
associated with Argonaute proteins
guides the small RNAs to target mRNAs resulting in degradation or repression
associated with Argonaute proteins
guides the small RNAs to target mRNAs resulting in degradation or repression
70
New cards
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
CRISPR
CRISPR
use a gene-specific guide RNA sequence to direct the Cas9 nuclease to a specific site
71
New cards
p bodies
\
membrane-less regions of the cytoplasm where RNA can accumulate
membrane-less regions of the cytoplasm where RNA can accumulate
72
New cards
snRNA
removes lariant from pre-mRNA, forms spliceosome
ex - U1, U2, U4, U5, U6
ex - U1, U2, U4, U5, U6
73
New cards
snoRNA
small nucle__o__lar RNAs
small nucle__o__lar RNAs
modify rRNAs
74
New cards
spliceosome
large assembly of RNA and protein molecules (snRNPs) that performs pre-mRNA splicing in eukaryotic cells
ribozyme
ribozyme
75
New cards
release factors
bind to vacant A site and catalyze addition of water instead of amino acid to free the C-terminus to end translation
76
New cards
EF-Tu
helps with checking accuracy of codon/anti-codon interaction
77
New cards
eIF4G
connects the 5' cap and 3' polyA tail of the mRNA to create a circular message in eukaryotic translation initiation
78
New cards
20
there are # different amino acids
79
New cards
shine dalgarno sequence
in prokaryotes
complementary to sequence near 3’ end of 16S rRNA
positions small ribosomal subunit in the correct spot
complementary to sequence near 3’ end of 16S rRNA
positions small ribosomal subunit in the correct spot

80
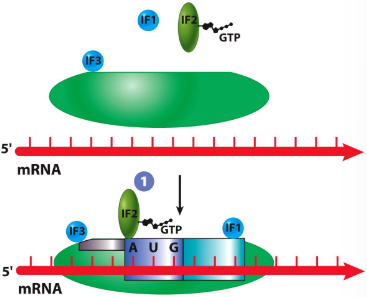
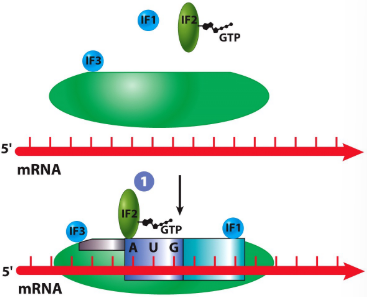
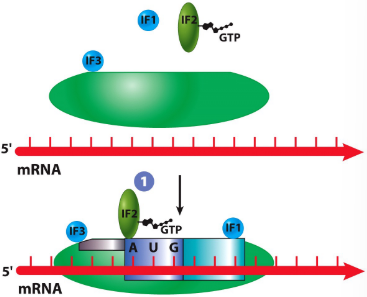
New cards
IF1
helps with attachment to mRNA
translation initiation in prokaryotes
translation initiation in prokaryotes
81
New cards
IF2
GTP-binding protein that is required for attachment of first AA-tRNA
translation initiation in prokaryotes
translation initiation in prokaryotes
82
New cards
IF3
prevents premature attachment of large subunit
translation initiation in prokaryotes
translation initiation in prokaryotes
83
New cards
eIF4E
binds to 5’ cap of mRNA in eukaryotic translation initiation
84
New cards
Kozak sequence
small ribosomal subunit along with eIFs and initiator tRNA finds 5’ end of mRNA and scans along until reaches a _________ ___________
85
New cards
constitutive expression
protein present in all cells all the time
ex - beta actin
ex - beta actin
86
New cards
U1
binds to 5’ splice site
in splicing
in splicing
87
New cards
snRNP
snRNA complex with proteins that form the spliceosome
88
New cards
U2
binds the branch point site causing adenosine to budge out
in splicing
in splicing
89
New cards
U6
replaces U1 at the 5’ splice site
pairs with U4 originally
pairs with U4 originally
90
New cards
cryptic site
exon skipping due to similarity to a splice site consensus sequence
91
New cards
RNA exosome
degrade RNA in the nucleus unless proteins are bound
92
New cards
nucleoli
ribosomal DNA clusters that come together during interphase
93
New cards
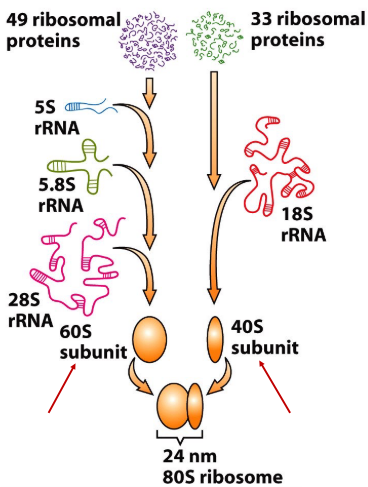
s value
Svedberg unit
Svedberg unit
measure of the sedimentation rate during centrifugation affected by both mass and shape
the larger the molecule, the larger the S value, the faster the sedimentation
the larger the molecule, the larger the S value, the faster the sedimentation
94
New cards
40S
s value for small ribosomal subunit
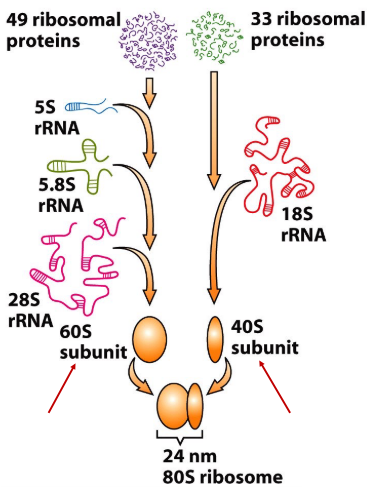
95
New cards
60S
s value for large ribosomal subunit
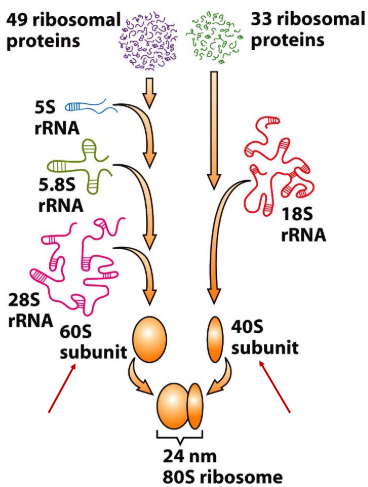
96
New cards
rho factor
bacterial protein for transcription termination
97
New cards
RNA pol I
transcribes 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNA genes
98
New cards
RNA pol II
transcribes all protein coding genes, snoRNA genes, miRNA genes, siRNA genes, licRNA genes, and most snRNA genes
99
New cards
RNA pol III
transcribes tRNA genes, 5S rRNA genes, some snRNA genes, and other small RNAs
100
New cards
TFIID
recognizes and binds the TATA box