Sustaining Ecosystems Flashcards
5.0(1)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:55 PM on 11/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
how is flora in the coral reef adapted
seagrasses have roots in sediments of the sea floor to keep sturdy against water flow and have flexible blades which move with the water
2
New cards
how is fauna in the coral reef adapted
butterfly fish have a thin shape which allow them to fit between small gaps and have long thin slightly rounded teeth for scraping at and eating shrimp worms and invertebrates
3
New cards
where are coral reefs found
in the tropical zones mainly on land borders where the ground is usually shallower than deep sea
4
New cards
what is the climate like in temperate forests
precipitation remains moderate all year round peaking in august. clear seasons meaning it is lifeless during the winter but hardwood trees grow leaves in the spring and shrubs grow too
5
New cards
what are grasslands
large areas of land covered in grass found in all continents except antarctica
6
New cards
where are tropical grasslands found
in hot humid areas stretching between tropics of cancer and capricorn
7
New cards
where are temperate grasslands found
in areas of earth with mild temperatures between the polar regions and the tropics
8
New cards
what is ecotourism
a form of tourism that preserves the culture of local communities ensuring they benefit from the industry while protecting the natural environment
9
New cards
why are deserts important
home to many plants and animals which can only survive there and they help promote the formation and concentration of important materials which are easily extractable and can benefit humans
10
New cards
what are the causes of deforestation in the Brazilian amazon rainforest
80% from logging 15% from architecture 3% from cattle ranching and 2% other
11
New cards
what are the conditions of a coral reef like
shallow water so sunlight can reach the coral and warm water between 20-32c and saltwater as coral extracts salt and uses it for a tough outer surface and clear clean water so sunlight can get through to the coral so it can be used for photosynthesis
12
New cards
what are goods
physical products we obtain from the ecosystem
13
New cards
what are services
jobs an ecosystem does to regulate the environment
14
New cards
where are temperate forests located
north and south of the tropics extending to 60 degrees north and south but most at around 30c north as that latitude creates seasons. account for large areas of the globe such as most of europe eastern asia and north america
15
New cards
why is there hardly any permanent life in antarctica
there is no shelter and it is freezing cold however the easiest place to survive is the ocean where it is warmest so there are some plants and phytoplankton
16
New cards
why is deforestation devastating for the nutrient cycle
less leaves are returned to the ground meaning there is less organic matter so the humus layer of the ground is not replaced and less nutrients are returned to the soil and there is also a rapid loss of nutrients by leaching meaning overall the soil is unproductive and ferallitic. this means there are fewer nutrients available for plant use and less oxygen is released to the air so there is less moisture in the air and precipitation and less evapotranspiration
17
New cards
why is antarctica classified as a desert
it is the largest desert in the world as it receives very little rainfall around 200mm annually
18
New cards
how is flora in antarctica adapted
antarctic hair grass is short protecting them from the wind but is wind self pollinating
19
New cards
how is fauna in antarctica adapted
penguins can camouflage against the sea as they have white stomachs camouflaging them with the top of the sea from underneath and black backs camouflaging them with the top of the sea from above. they have a thick layer of blubber to protect them from the cold
20
New cards
if rainforest soils are so poor, how can they support an incredibly productive ecosystem
the thin humus layer is very fertile and the only source of nutrients within the soil which depends on trees for protections and leaf litter to be recycled
21
New cards
what is climate like in polar regions
antarctica can reach -60c in the winter and -28.2c in the summer and the highest precipitation is in february with around 29mm
the arctic can reach -40c in the winter and 0c in the summer with the highest precipitation of 25mm in august
the arctic can reach -40c in the winter and 0c in the summer with the highest precipitation of 25mm in august
22
New cards
how does the rainforest soil profile work
overall it is up to 30m deep with the rapid recycling of nutrients at the top in the humus layer and then hydrated oxides making the soil red underneath and then decomposing clays underneath and then clays formed by intense chemical weathering underneath and then parent rock at the bottom
23
New cards
what is the difference between the arctic and antarctica
the arctic is a collection of ice covered ocean and land areas - sea surrounded by land such as the arctic ocean and alaska canada norway and sweden surrounding it however the antarctic is the southern most continent and is land surrounded by the antarctic ocean. it is colder than the arctic.
24
New cards
what is a soil profile
cross section of different layers of soil in a location revealing all the soil horizons e.g. organic material at the top with surface top soil underneath then subsoil underneath then substratum underneath then bedrock at the bottom
25
New cards
what is the rainforest nutrient cycle like
(between biomass litter and soil)
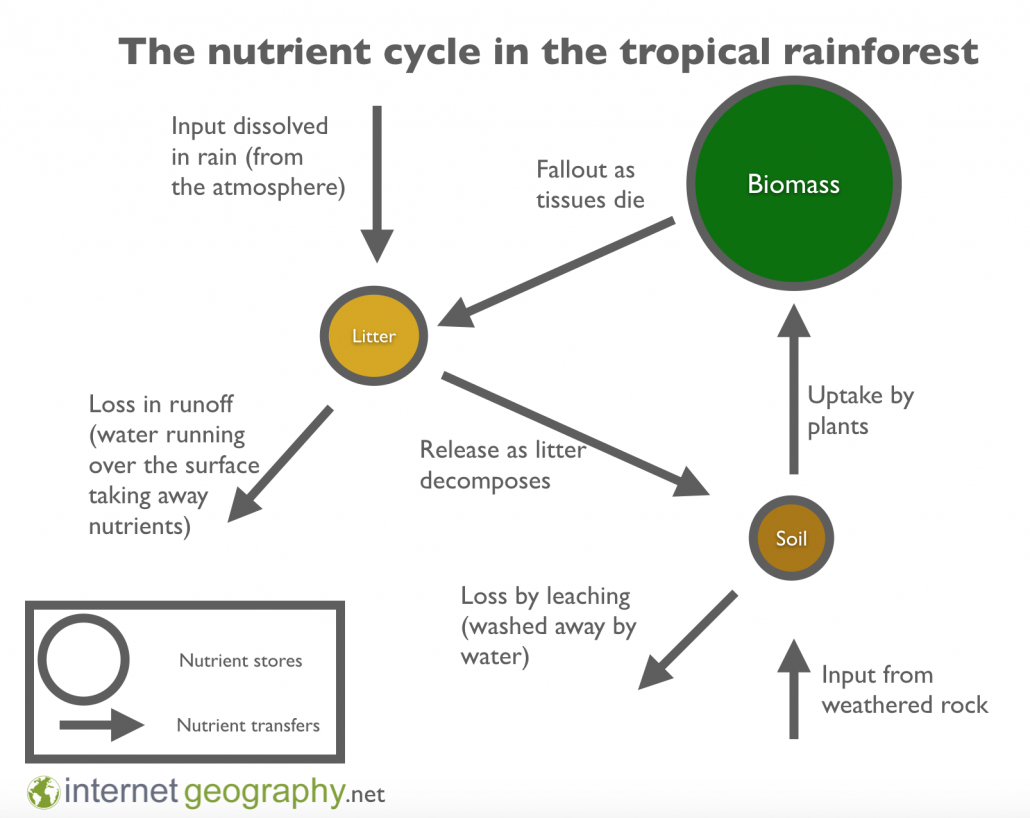
26
New cards
what is a coral reef
underwater ecosystem formed by colonies of coral polyps that form reefs with calcium carbonate
27
New cards
what are tropical grasslands (savannas) like
they have fairly infertile red soil with lots of iron in it and high temperatures letting organic matter decay quickly and wet seasons have heavy rainfall and lush vegetations whereas the dry seasons bring droughts. the further from the equator they are the drier they are
28
New cards
how have plants adapted to tropical rainforests
trees don’t become dormant or lose their leaves or change colour during the year
29
New cards
what is life like for coral
they form when polyps separate from parents to create a new colony and attach themselves to rock. they are home to algae and algae photosynthesise to produce energy and sugars for the coral. at night they come out of their skeletons and stretch out to catch zooplankton to eat
30
New cards
what is climate in tropical rainforests like
hot all year with a total annual rainfall of 2082 in Mannaus brazil
31
New cards
how is flora in deserts adapted
cacti have thick waxy skin to reduce water loss and reflect heat and have thorns and thin spiky glossy leaves or spikes to protect them from animals stealing water from them. they also have deep roots to tap into groundwater
32
New cards
how is fauna in deserts adapted
camels have long eyelashes and hairy ears and closing nostrils to keep out sand and they have wide feet so they don’t sink into sand and can drink gallons of water in one go to store in their bloodstream and store fat in humps so they can go months without it food. their fur keeps them well camouflaged and warm at night
33
New cards
how does the vegetations of rainforests affect rainfall
the cycle of convectional rainfall happens because of trees as rain is intercepted by leaves on trees and water is absorbed by the roots and stored in trees. the intense sunlight causes transpiration and water is released to the atmosphere as water vapour which forms clouds causing rain
34
New cards
how are there rain and clouds in such as hot place as the rainforest
sun heats the ground causing warm air there which rises and as it rises it cools and condenses forming clouds at the dew point. these are cumolo nimbus clouds which accumulate water droplets until they let rain fall due to gravity
35
New cards
what does the rainforest nutrient cycle look like
trees shed leaves all year and decaying vegetation decomposes rapidly so nutrients enter the soil and shallow roots of trees take up these nutrients causing the trees to grow rapidly and then shed leaves
36
New cards
what does the rainforest water cycle look like
when there is heavy daily convectional rain the trees intercept the rain however some rain reaches the ground and the trees roots take up this water and then the water evaporates from the trees through transpiration and forms clouds which lead to heavy daily convectional rainfall
37
New cards
where are grasslands located
where there is too little rain for a forest to grow and too much for a desert to form such as in southern america and the african savannas and the russian steppe
38
New cards
what are temperate grasslands (pampas) like
large areas of grass sparsely populated with trees with around 30 inches of rain annually mostly in snow form and have summer temperatures exceeding 30c but winter temperatures below 15c
39
New cards
what are hot deserts like
places that mostly lie between 20 degrees north and 35 degrees south of the equator which receive less than 250mm of rain annually and have two distinct seasons of summer 35-40c and winter 20-30c
40
New cards
why are temperate forests important
have lots of biodiversity and immense natural beauty which increases tourism. they provide possibly life saving medicine ingredients and wood for the manufacturing industry and are carbon sinks and release oxygen for animals
41
New cards
how is flora in temperate forests adapted
beach trees have a long lifespan of 40 years and have a thick canopy of leaves which develops in the spring after losing leaves in the winter which protects them from being damaged by strong winds
42
New cards
how is fauna in temperate forests adapted
black bears have a heavy coat with lots of layers of fur to cope in the cold. they can climb trees with long paws and have exceptional hearing to find prey
43
New cards
how is fauna in the arctic adapted
arctic fox fur changes colour each season and they have muzzle to minimise heat loss
44
New cards
how is flora in the arctic adapted
the pasque flower is short to protect itself from strong winds and each flower is covered in lots of tiny silky hairs which help insulate it
45
New cards
how is flora in grasslands adapted
the baobab tree can survive without leaves for most of the year and has a thick trunk to store water in case of long droughts. its bark is slick and shiny to reflect light to moderate temperature
46
New cards
how is fauna in grasslands adapted
prairie dogs have sharp incisors to help them consume tough grassland plants and can make a barking sound to alert their colony when danger arises
47
New cards
how do tropical rainforests provide valuable services
they are a habitat for lots of flora and fauna which are adapted to living in rainforest conditions and they are also carbon sinks and release oxygen for animals and humans to respire and they help regulate global temperatures and reduce flood risk as water is taken up by trees and are good for the farming industry