physics exam ( chp 2-10)law of inertia.
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Newton's first law of motion
Every object continues in a state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net force.

force
Any push or pull exerted on an object, measured in newtons
.
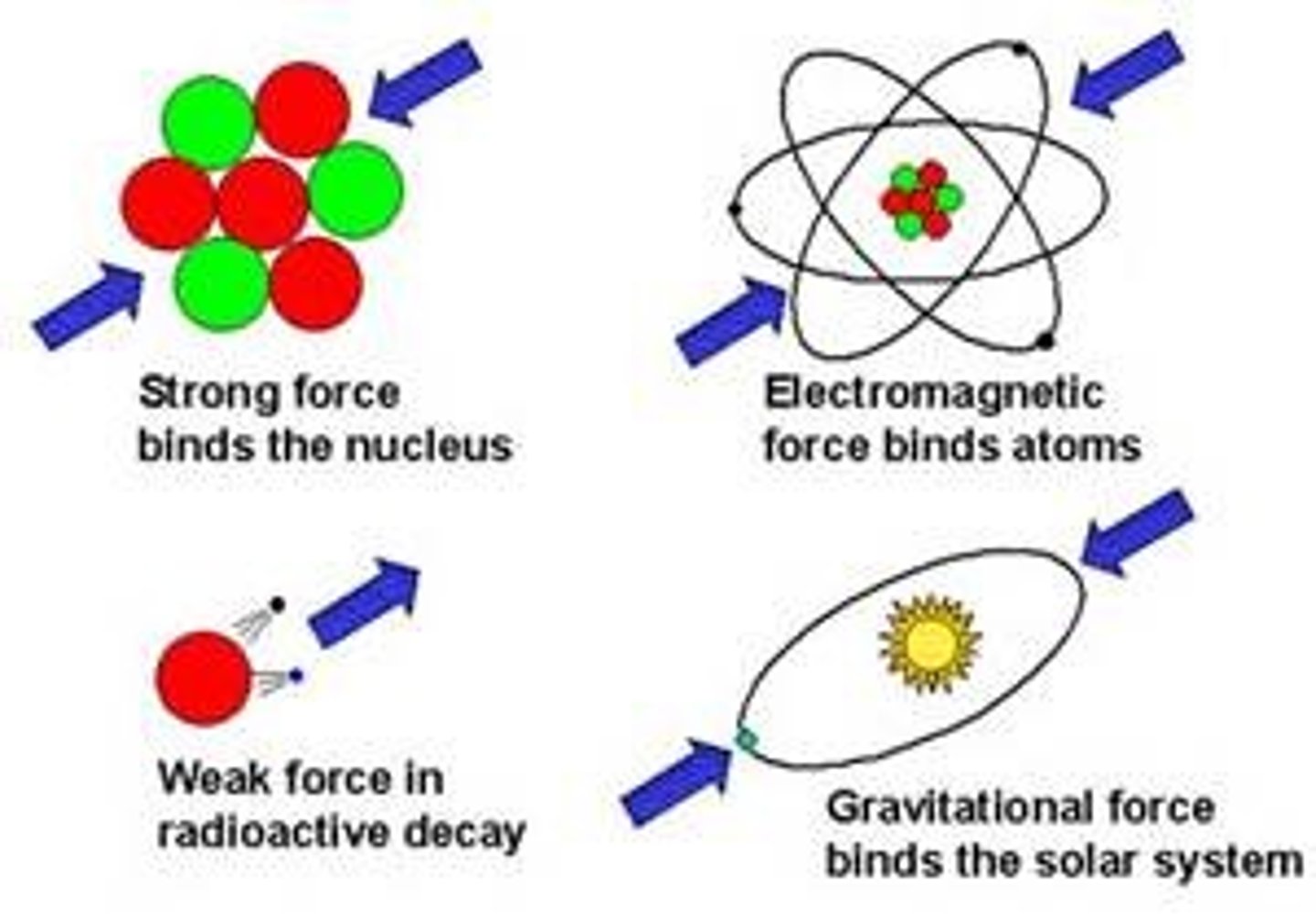
fundamental force
four basic forces acting in nature: strong force, electromagnetic force, weak force, gravitational force
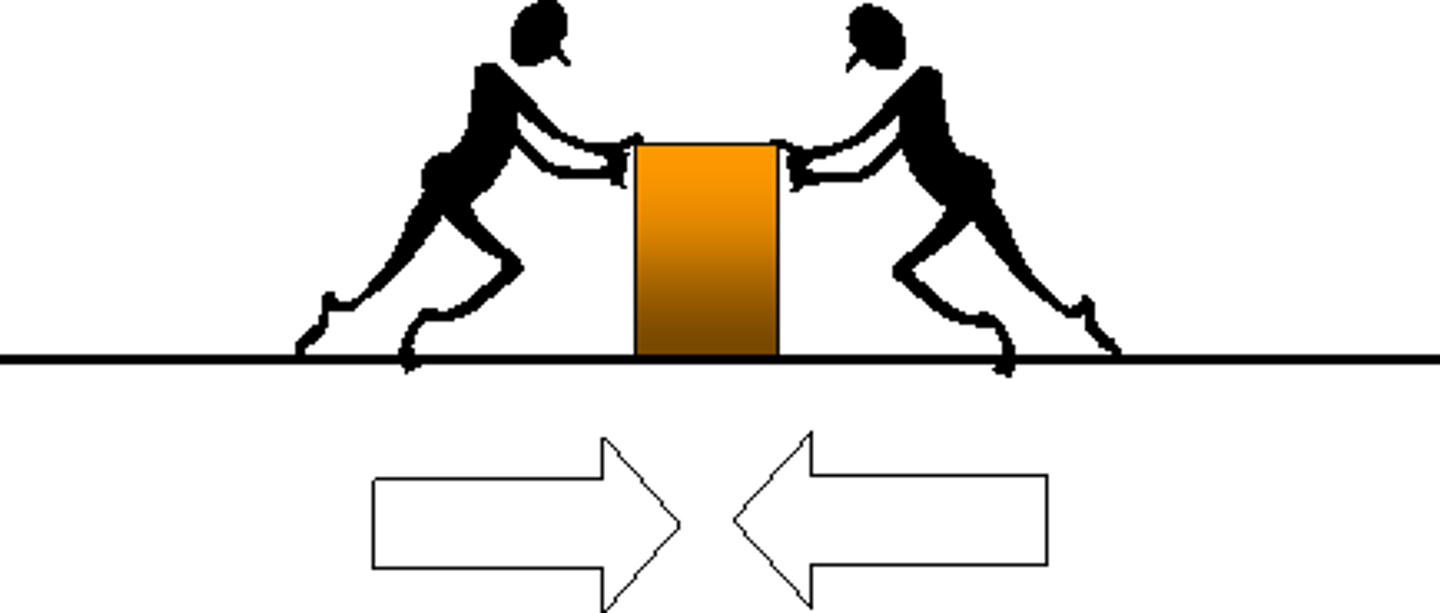
net force
The vector sum of forces that act on an object.
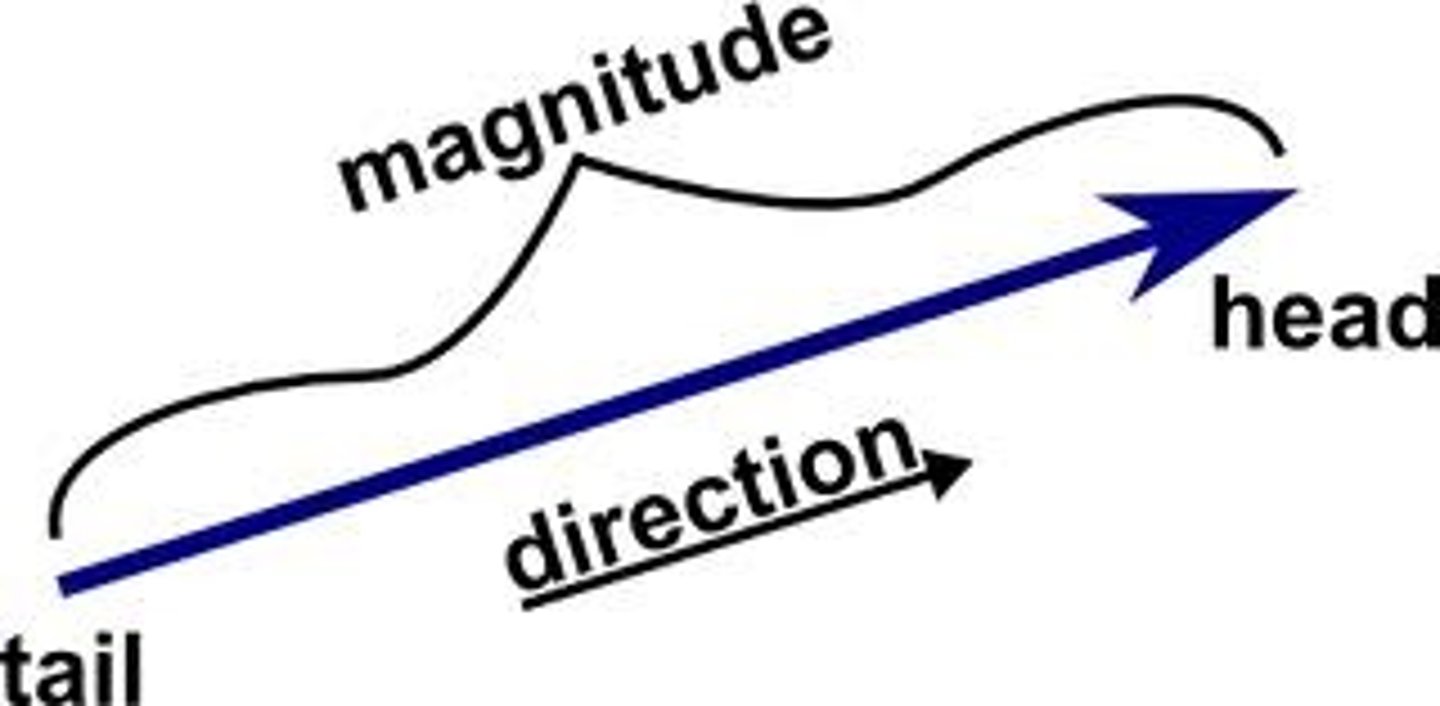
vector quantity
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as force.
vector
An arrow drawn to scale used to represent a vector quantity.
vector quantity example
velocity
scalar quantity
A quantity that has magnitude but not direction, such as mass and volume.
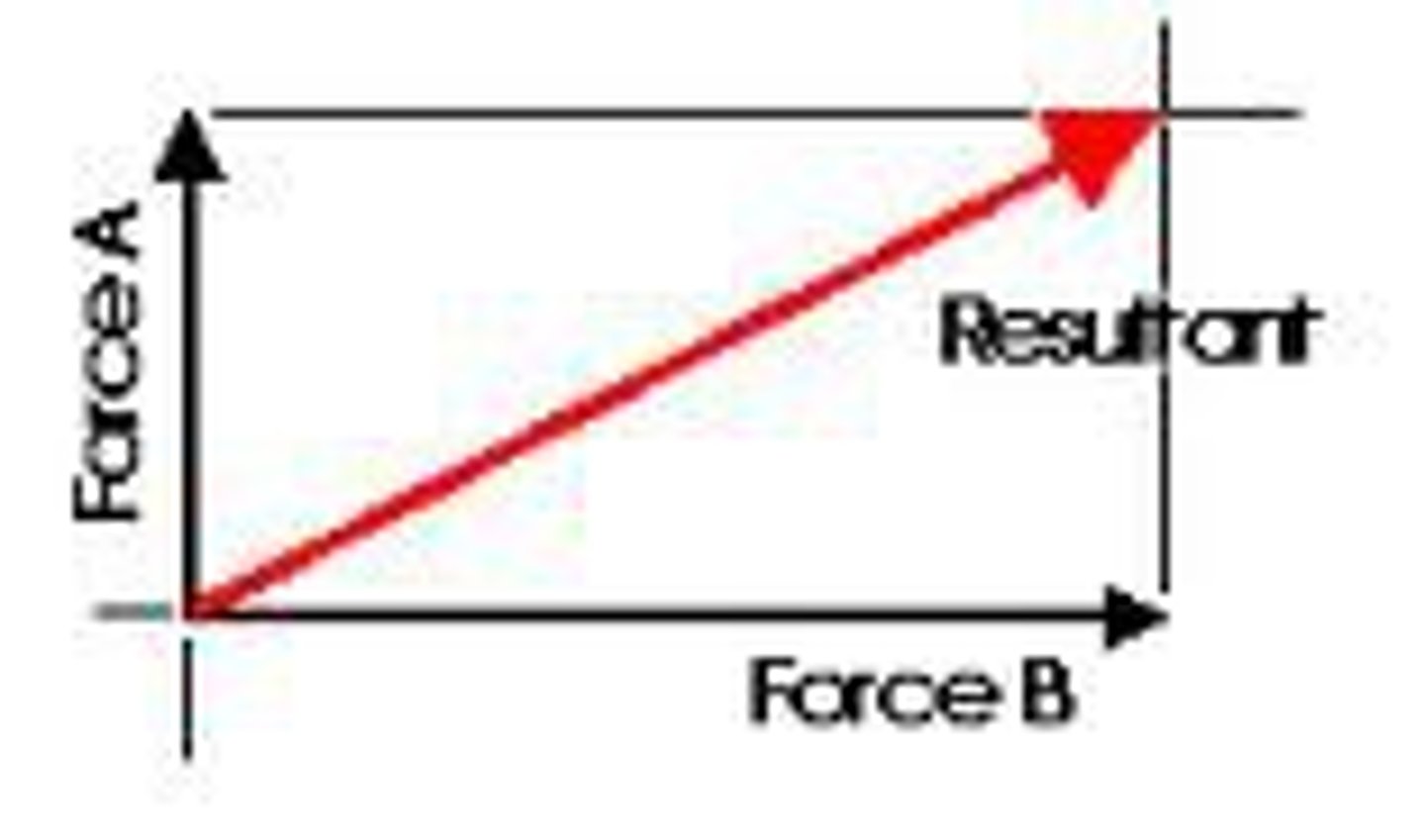
resultant
The net result of a combination of two or more vectors.
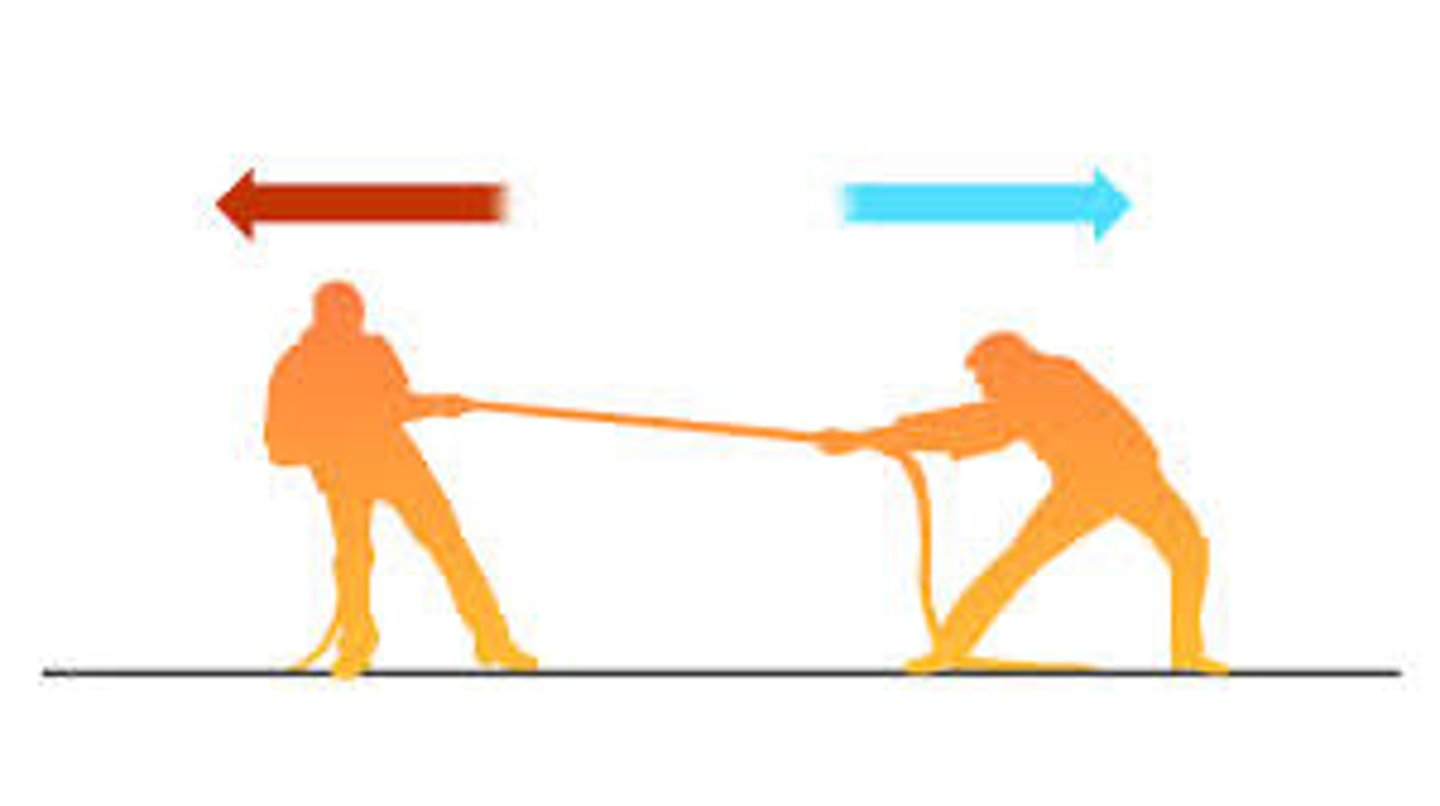
tension
stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object
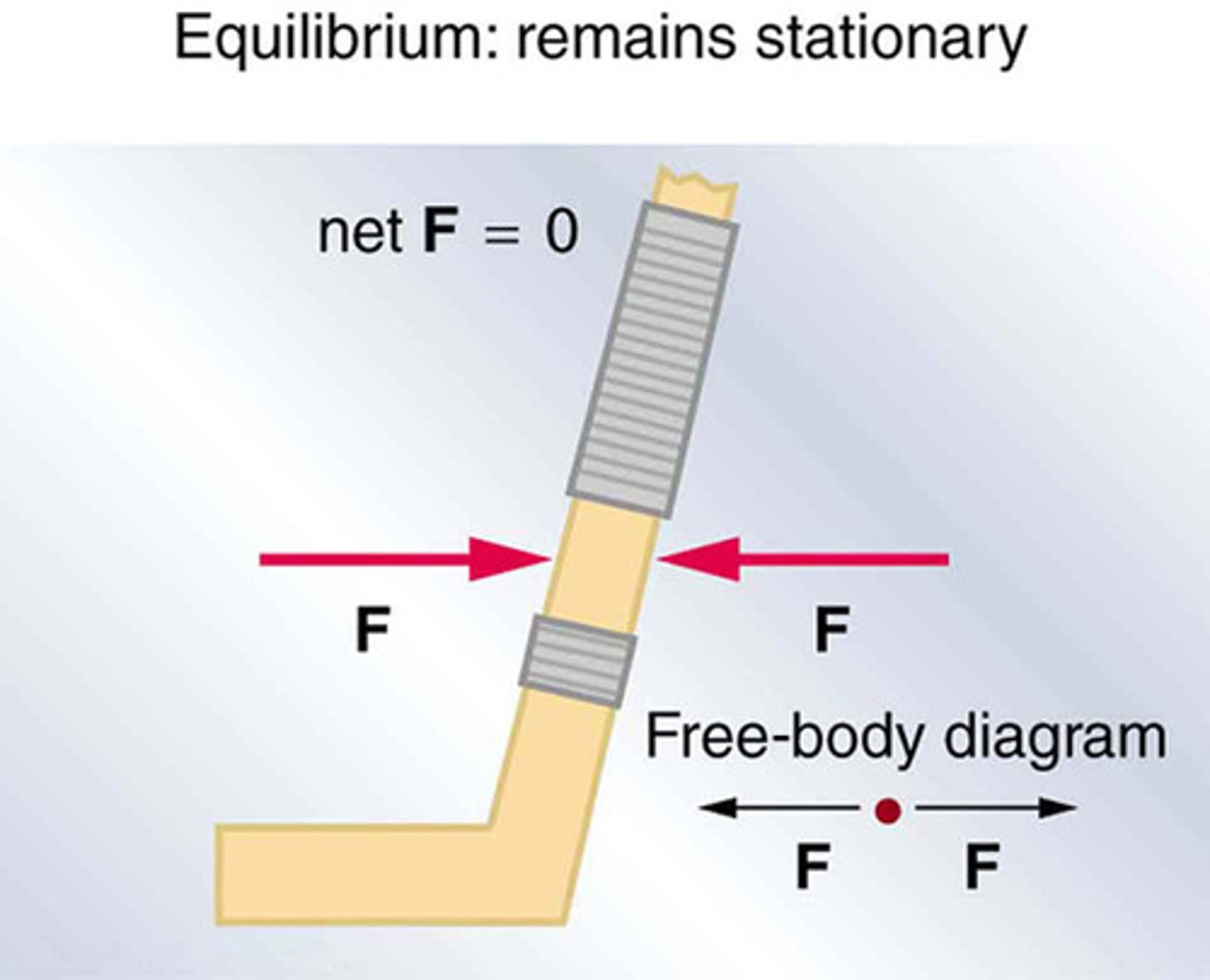
mechanical equilibrium.
The state of an object or system of objects for which there are no changes in motion. In accord with Newton's first law, if an object is at rest, the state of rest persists. If an object is moving, its motion continues without change.

equilibrium rule
For any object or system of objects in equilibrium, the sum of the forces acting equals zero. In equation form,ΣF = 0
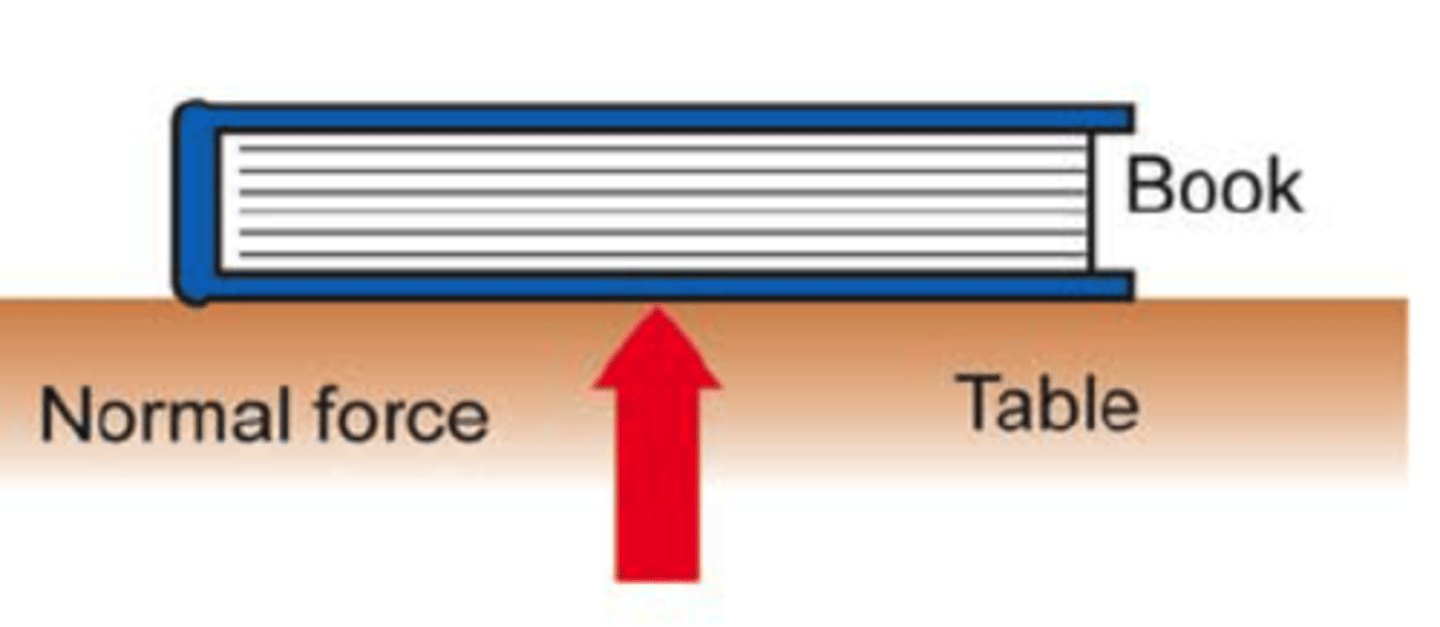
support force/ normal force
the upward force that balances the weight of an object on a surface
static equilibrium
A condition where there are no net external forces acting upon a particle or rigid body and the body remains at rest or continues at a constant velocity.
dynamic equilibrium
condition of continuous, random movement of particles but no overall change in concentration of materials

speed
How fast an object moves; the distance traveled per unit of time.
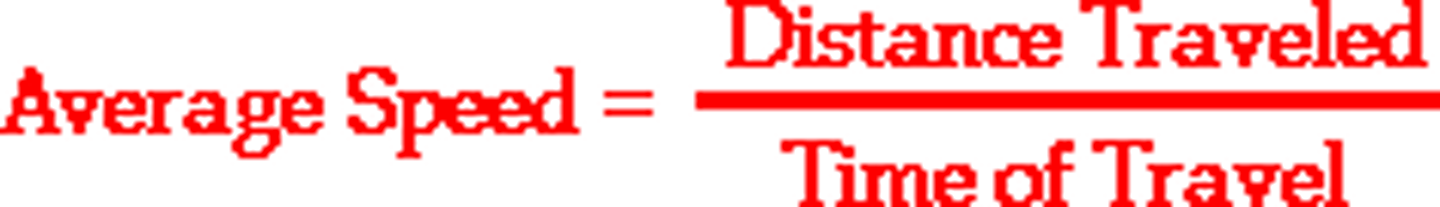
instanteous speed
the speed at any instant

average speed
the total distance traveled divided by the time it takes to travel that distance
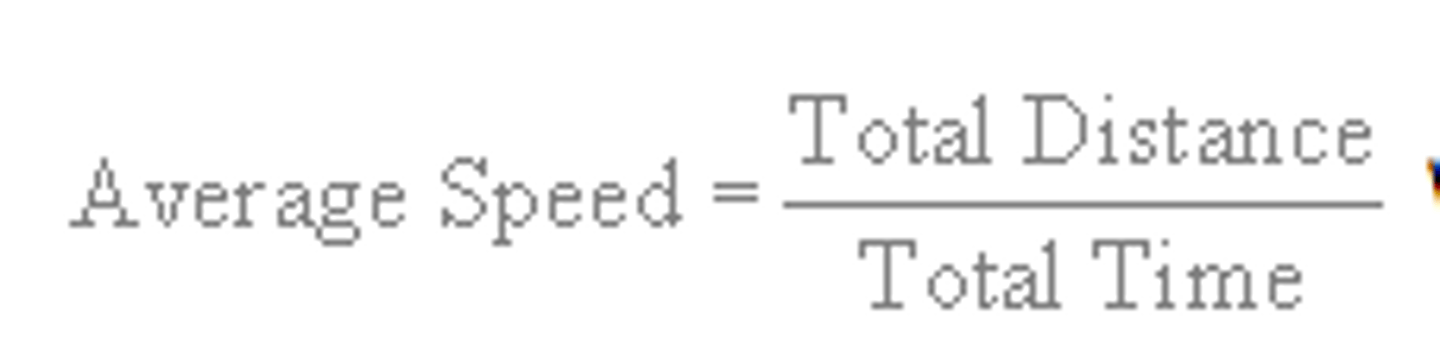
velocity
an object's speed and direction of motion
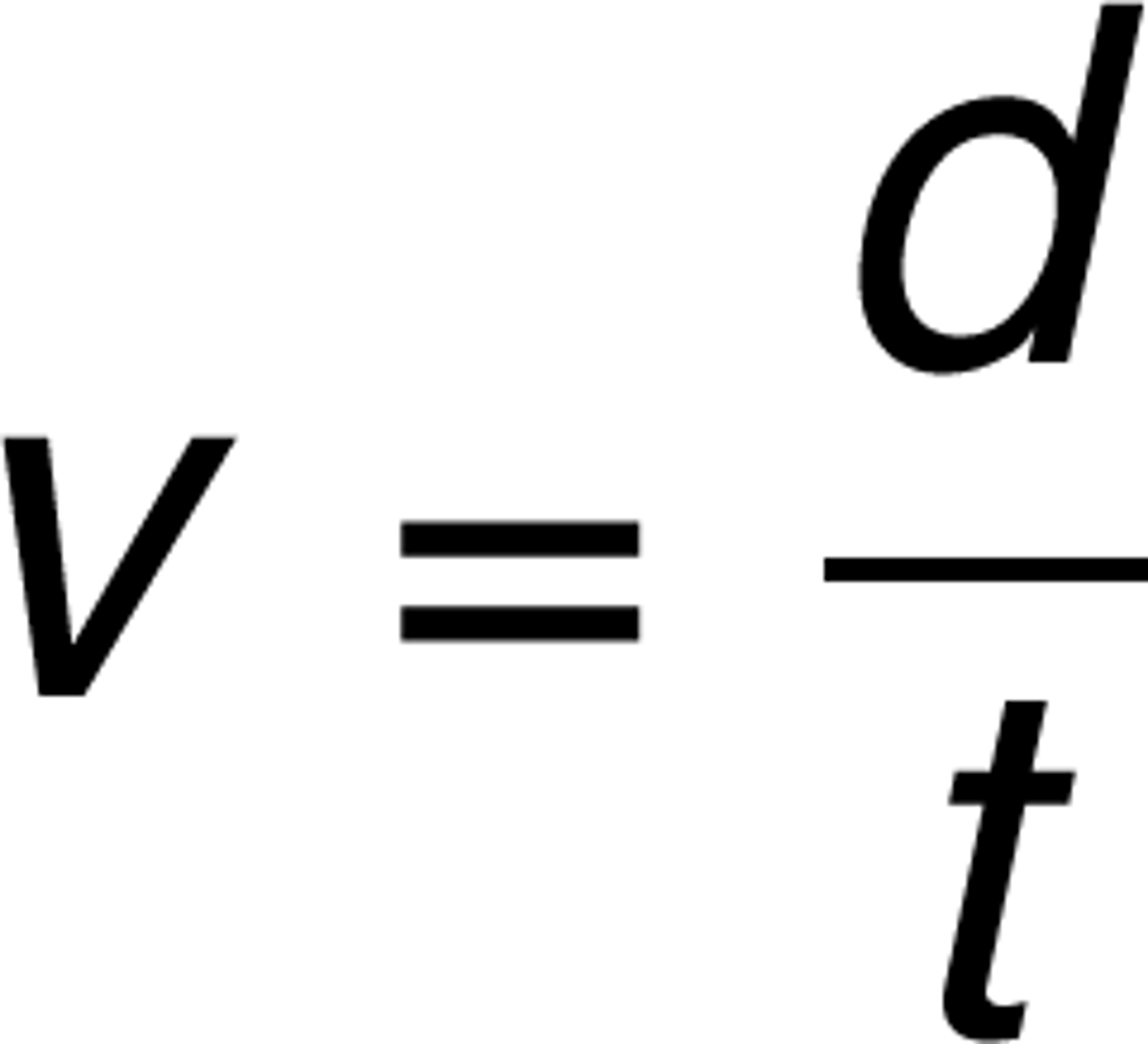
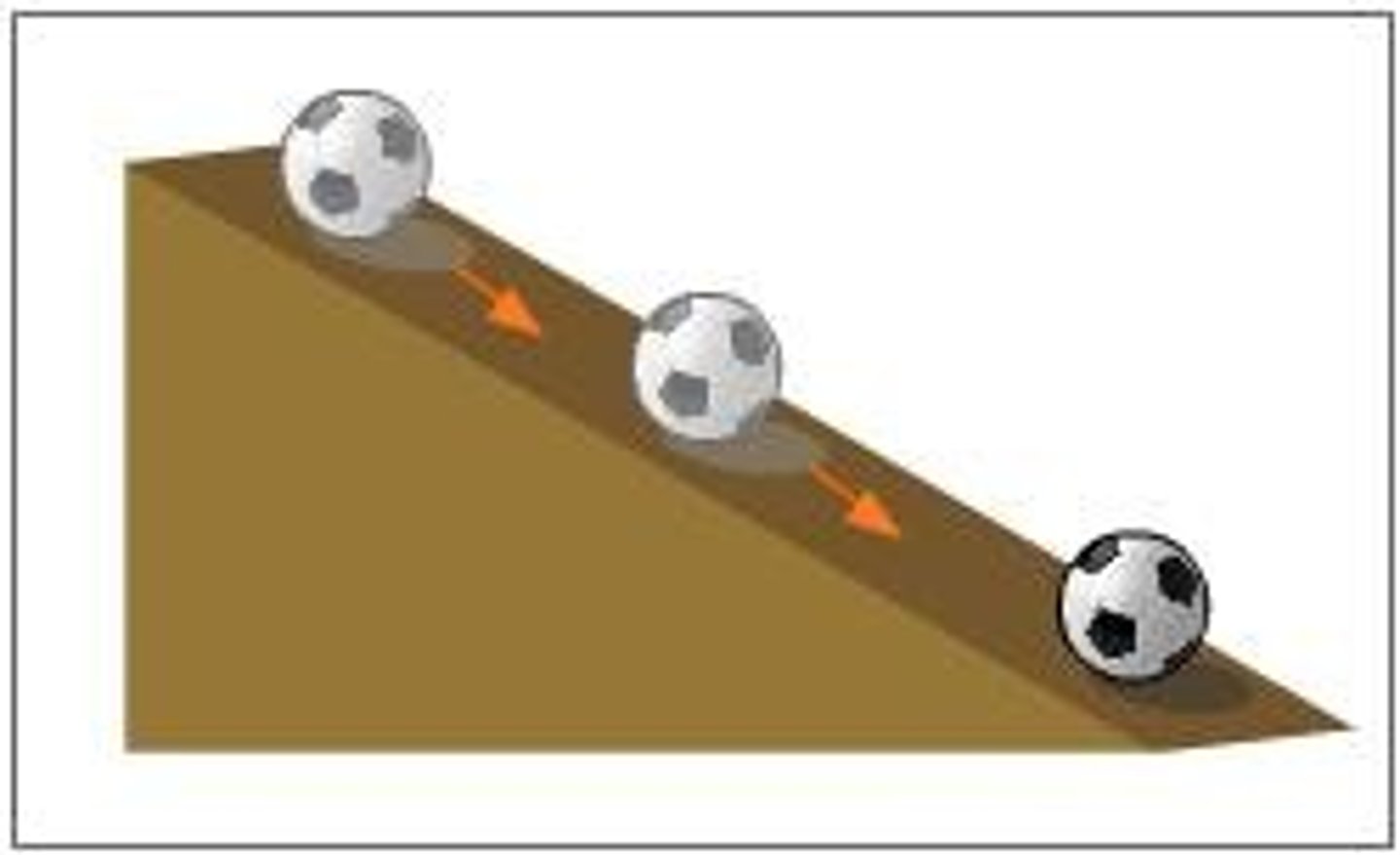
acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes with time; the change in velocity may be in magnitude, or direction, or both.
friction
The resistive force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object either past another object with which it is in contact or through a fluid.
static friction
a friction force that acts on objects that are not moving
sliding friction
friction that occurs when one solid surface slides over another
air resistance
Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air
mass
The quantity of matter in an object. It is also the measure of the inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, or change its state of motion in any way.
weight
Usually the force upon an object due to gravity.
kilogram
fundamental SI unit of mass. One kilogram (symbol kg) is the mass of 1 liter (1 L) of water at 4°C.
Newton
The SI unit of force. One newton (symbol N) is the force that will give an object of mass 1 kg an acceleration of 1 m/s2.
volume
the quantity of space an object occupies
newtons second law of motion
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
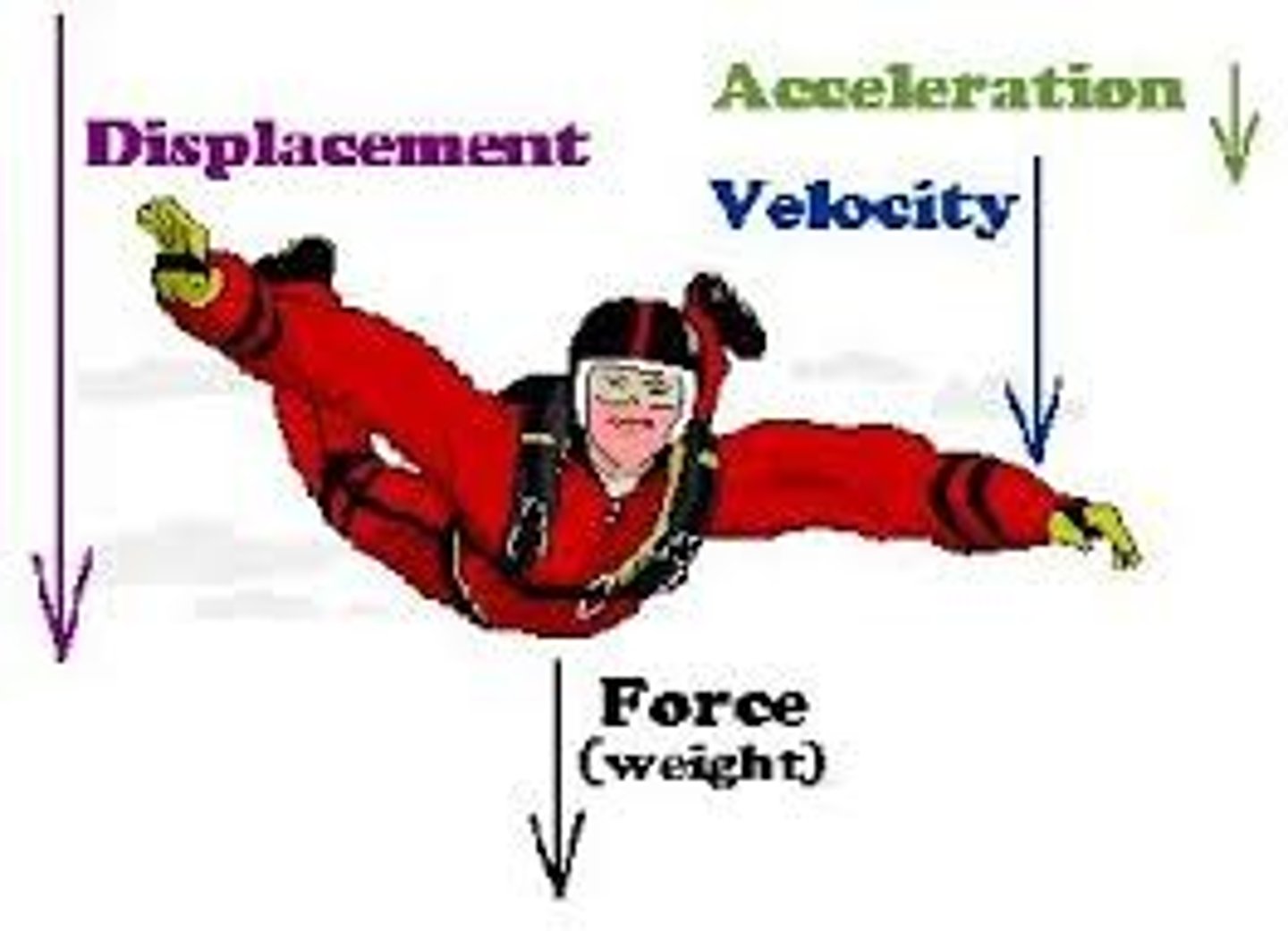
Free Fall
Motion under the influence of gravitational pull only.

terminal speed
The speed at which the acceleration of a falling object terminates because air resistance balances gravitational force.
terminal velocity
Terminal speed with direction specified.
gravity
acceleration due to gravity, 9.8 m/s2 (the
unit of force is
Newton
unit of mass
kilogram (kg)
acceleration equation
final velocity-initial velocity/time
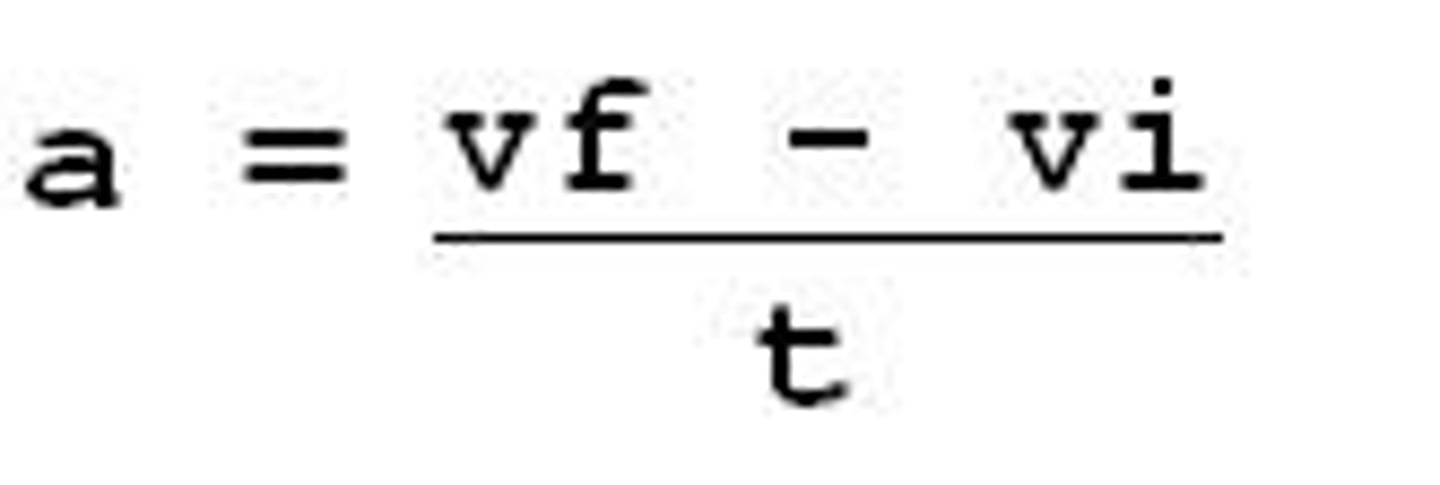
the greater the mass of the object
the greater its inertia
the greater the gravitational force
The greater the mass of an object,
gravity equation
F = Gm1m2/r^2
force equation
Force = mass x acceleration
newton's third law of motion
Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first.

components
Mutually perpendicular vectors, usually horizontal and vertical, whose vector sum is a given vector.
momentum equation
momentum = mass x velocity
impulse equation
impulse = force x time
impulse= changes in momentum
Ft = D(mv)
no net force or net impulse acts on a system,
the momentum of that system cannot change.
elastic collision equation
m1v1+m2v2=m1v1+m2v2
momentum conservation equation
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
momentum
The product of the mass of an object and its velocity.
impulse
The product of the force acting on an object and the time during which it acts.
Impulse-momentum relationship
Impulse is equal to the change in the momentum of the object that the impulse acts upon. In symbolic notation, Ft = D mv
Law of conservation of momentum
In the absence of an external force, the momentum of a system remains unchanged. Hence, the momentum before an event involving only internal forces is equal to the momentum after the event: mv(before event) = mv(after event)
elastic collision
A collision in which objects rebound without lasting deformation or the generation of heat.
inelastic collision
a collision in which objects become distorted, generate heat, and possibly stick together.
work
The product of the force and the distance moved by the force: W = Fd
Power
The time rate of work:
Power = work done / time interval
Energy
The property of a system that enables it to do work.
mechanical energy
Energy due to the position of something or the movement of something.
potential energy
energy that something possesses because of its position
Potential energy equation
PE=mgh
kinetic energy
Energy that something possesses because of its motion, quantified by the relationship Kinetic energy = 1/2 mv2
kinetic energy equation
KE=1/2mv^2
work energy theorem
The work done on an object equals the change in the kinetic energy of the object: W=ΔKE
work energy theorem equation
W=ΔE, W=ΔKE
law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes.
machine
A device, such as a lever or pulley, that increases (or decreases) a force or simply changes the direction of a force.
conservation of energy
The work output of any machine cannot exceed the work input. In an ideal machine, where no energy is transformed into thermal energy, workinput = workoutput; (Fd )input = (Fd )output.
conservation of energy equation
workinput = workoutput; (Fd )input = (Fd )output.
lever
A simple machine consisting of a rigid rod pivoted at a fixed point called the fulcrum.
Efficiency
The percentage of the work put into a machine that is converted into useful work output. (More generally, useful energy output divided by total energy input.)
Tangential speed
The linear speed tangent to a curved path, such as in circular motion.
Rotational speed
The number of rotations or revolutions per unit of time; often measured in rotations or revolutions per second or per minute. (Scientists usually measure it in radians per second.)
Rotational inertia
The property of an object to resist any change in its state of rotation: If at rest, the body tends to remain at rest; if rotating, it tends to remain rotating and will continue to do so unless acted upon by an external net torque.
Torque
The product of force and lever-arm distance, which tends to produce or change rotation:
Torque equation
Torque = lever arm * force
Center of Mass(CM)
The average position of the mass of an object. The CM moves as if all the external forces acted at this point.
Center of gravity (CG)
.
The average position of weight or the single point associated with an object where the force of gravity can be considered to act.
Equilibrium(torque)
The state of an object in which it is not acted upon by a net force or a net torque.
Centripetal force
A force directed toward a fixed point, usually the cause of circular motion: F = mv2 /r
centrefugal force
An outward force apparent in a rotating frame of reference. It is apparent (fictitious) in the sense that it is not part of an interaction but is a result of rotation—with no reaction-force counterpart.
linear momentum
The product of the mass of an object and its linear velocity.
angular momentum
The product of a body's rotational inertia and rotational velocity about a particular axis. For an object that is small compared with the radial distance, angular momentum can be expressed as the product of mass, speed, and radial distance of rotation.
conservation of angular momentum
When no external torque acts on an object or a system of objects, no change of angular momentum can occur. Hence, the angular momentum before an event involving only internal torques or no torques is equal to the angular momentum after the event.
law of universal gravitation
Every body in the universe attracts every other body with a force that, for two bodies, is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers:
law of universal gravitation equation
F=G m1m2/d2
inverse square law
A law that relates the intensity of an effect to the inverse square of the distance from the cause. Gravity follows an inverse-square law, as do the effects of electric, magnetic, light, sound, and radiation phenomena.
Weight( chp 9)
The force that an object exerts on a supporting surface (or, if suspended, on a supporting rope), which is often, but not always, due to the force of gravity.
Weightless
Being without a support force, as in free fall.
Spring tides
High or low tides that occur when the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are all lined up so that the tides due to the Sun and the Moon coincide, making the high tides higher than average and the low tides lower than average.
Neap tides
Tides that occur when the Moon is midway between new and full, in either direction. Tides due to the Sun and the Moon partly cancel, making the high tides lower than average and the low tides higher than average.
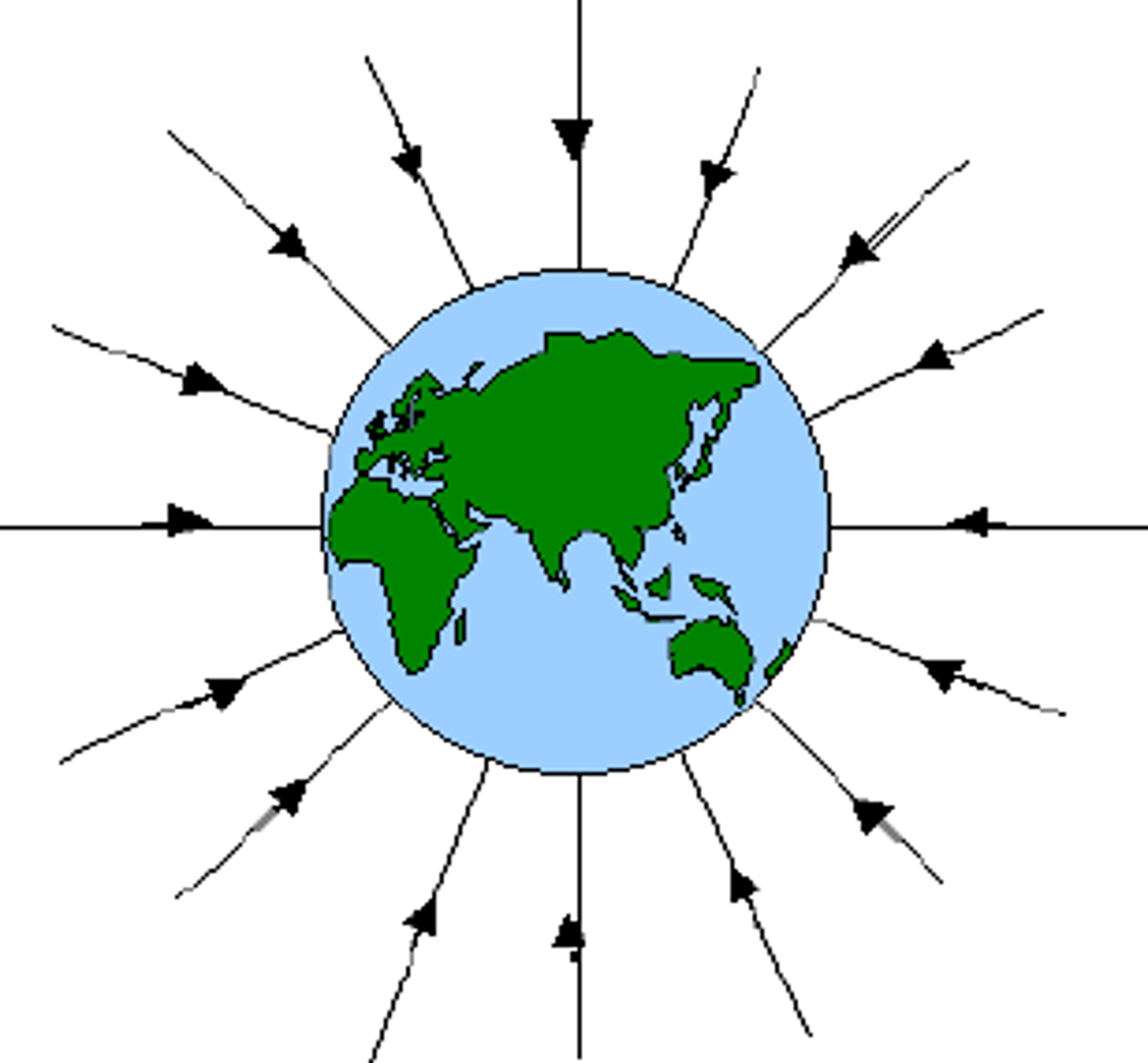
Gravitational field
The influence that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body, It is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg).
Black hole
A concentration of mass that results from gravitational collapse, near which gravity is so intense that not even light can escape.

projectile
Any object that moves through the air or through space under the influence of gravity.
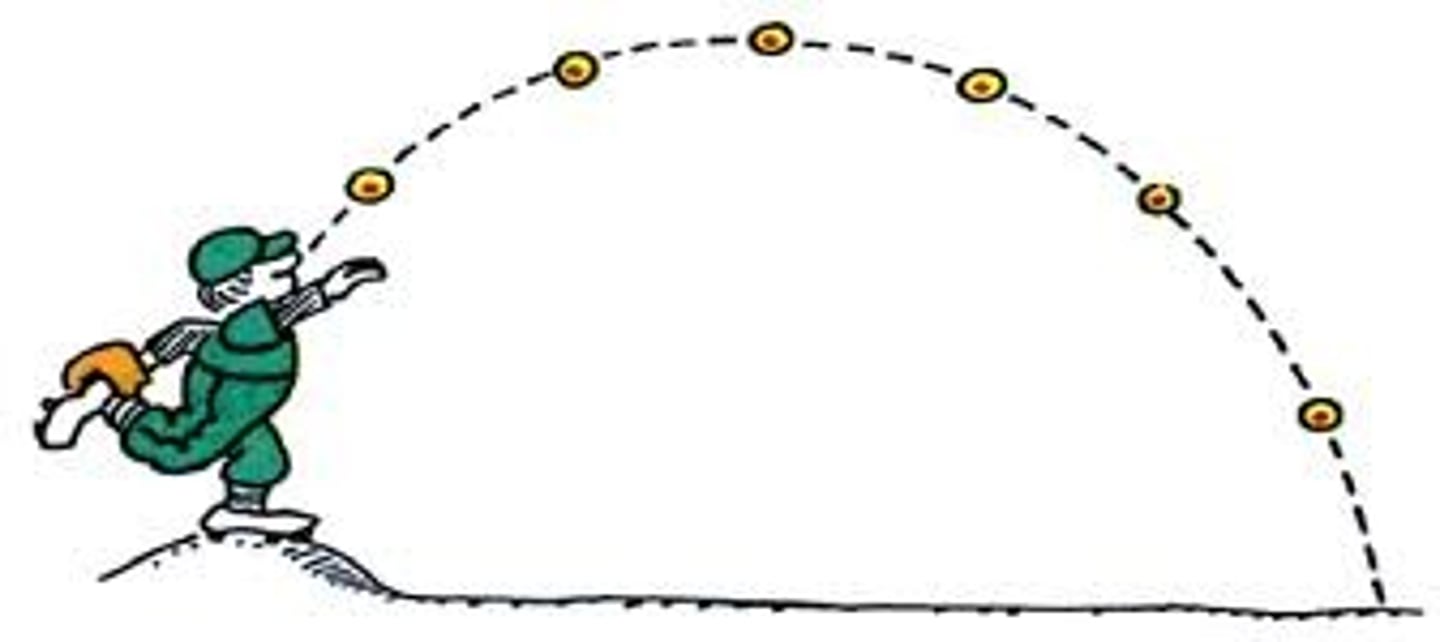
parabola
The curved path followed by a projectile under the influence of only constant gravity
satellite
A projectile or small celestial body that orbits a larger celestial body.
Ellipse
The oval shaped path followed by a satellite. The sum of the distances from any point on the path to two points called foci is a constant. When the foci are together at one point, the ellipse is a circle. As the foci get farther apart, the ellipse becomes more "eccentric."
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Law 1: The path of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
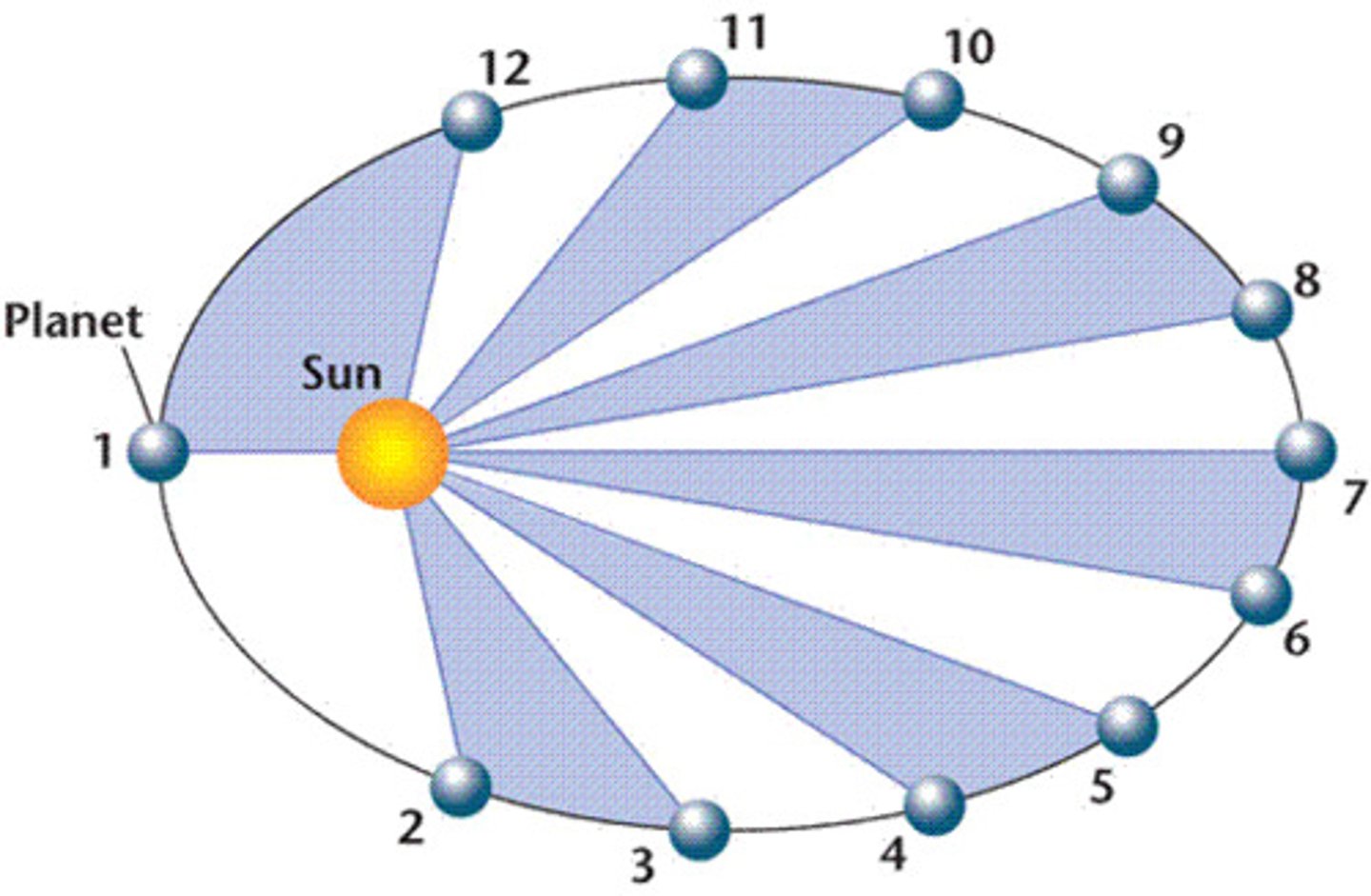
Law 2: The line from the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas of space in equal time intervals.
Law 3: The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the average distance of the planet from the Sun (T 2 ∼ r 3 for all planets).
Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion
The path of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
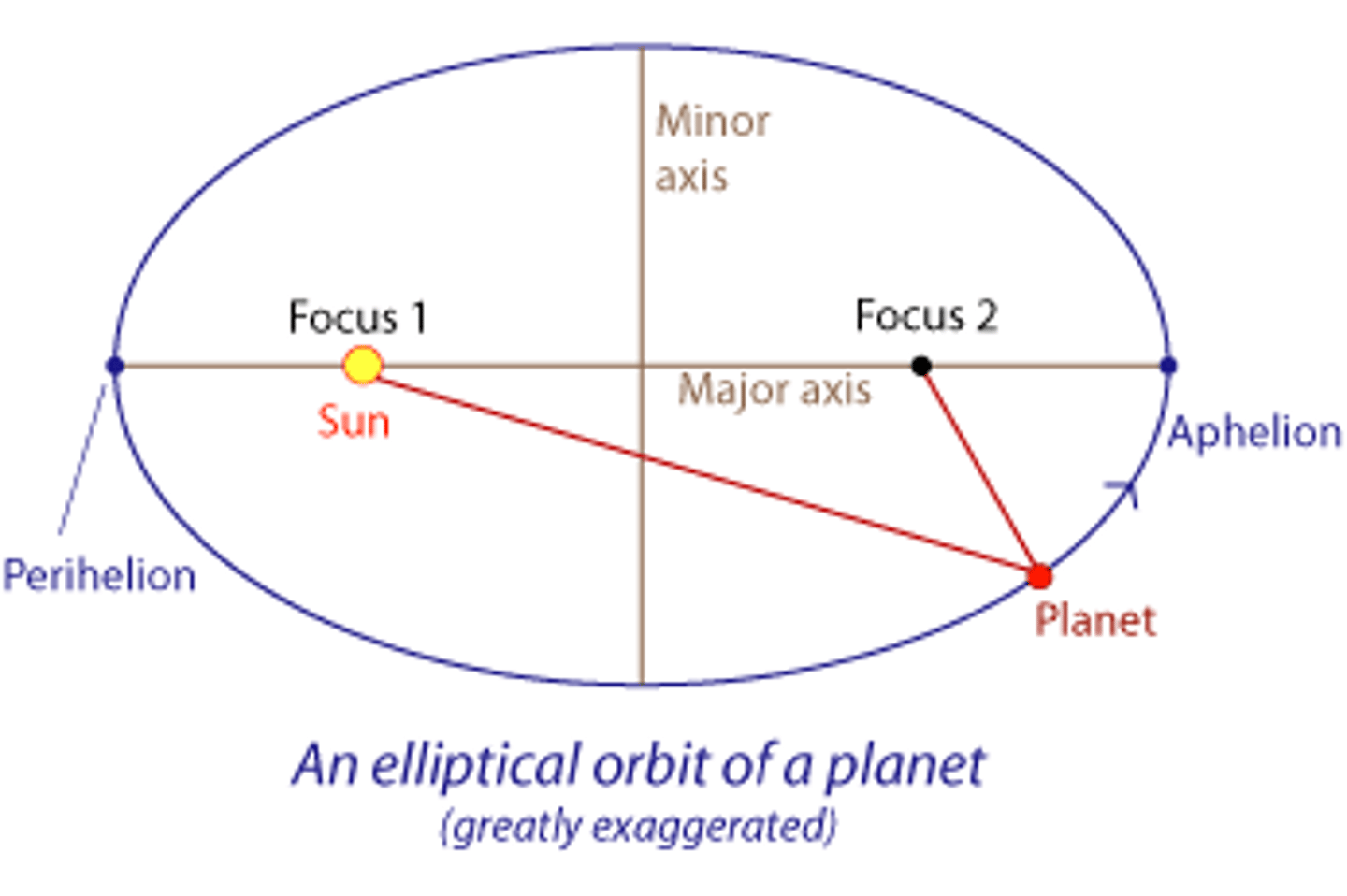
Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
The line from the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas of space in equal time intervals