Year 10 biology
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
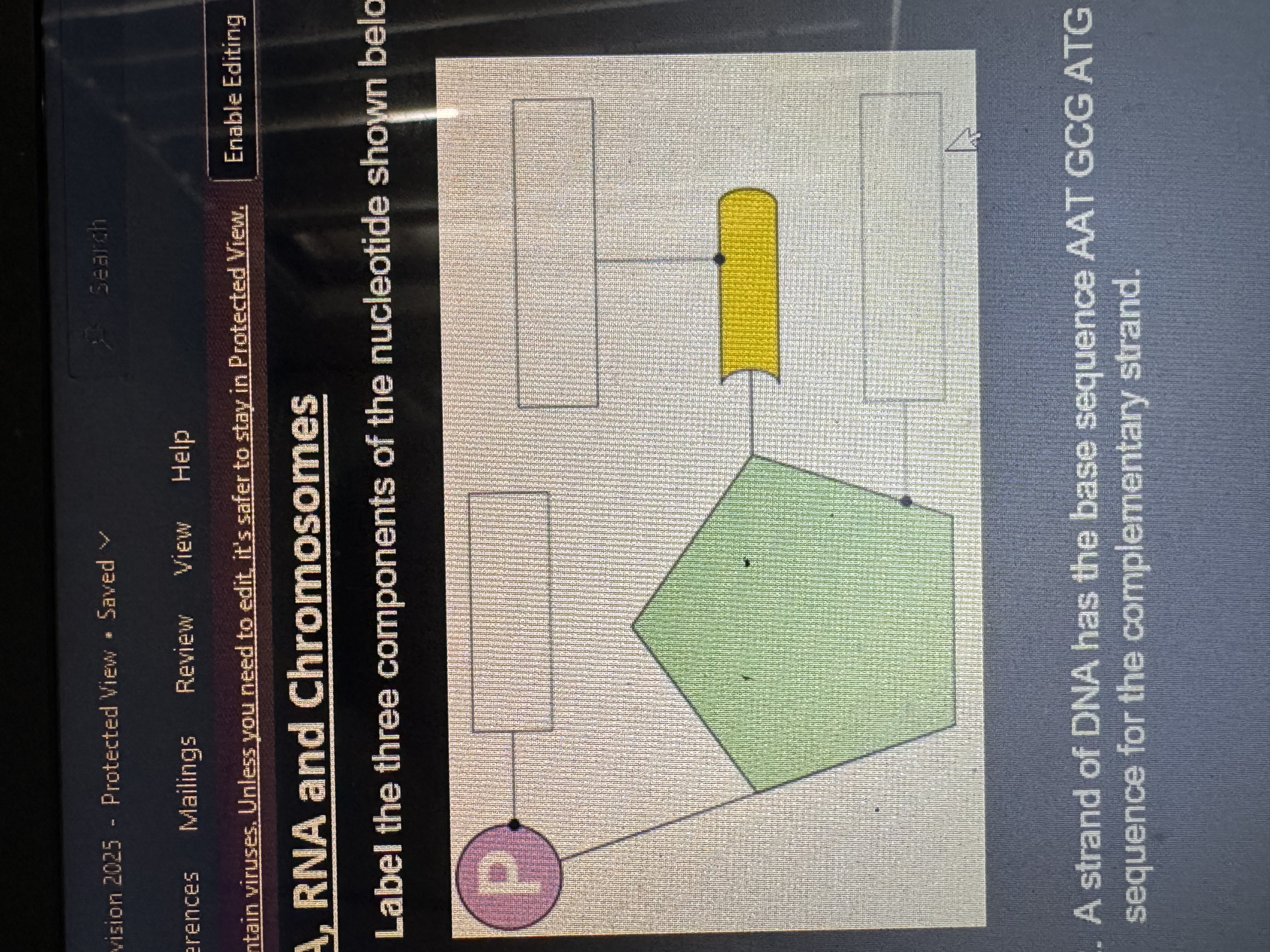
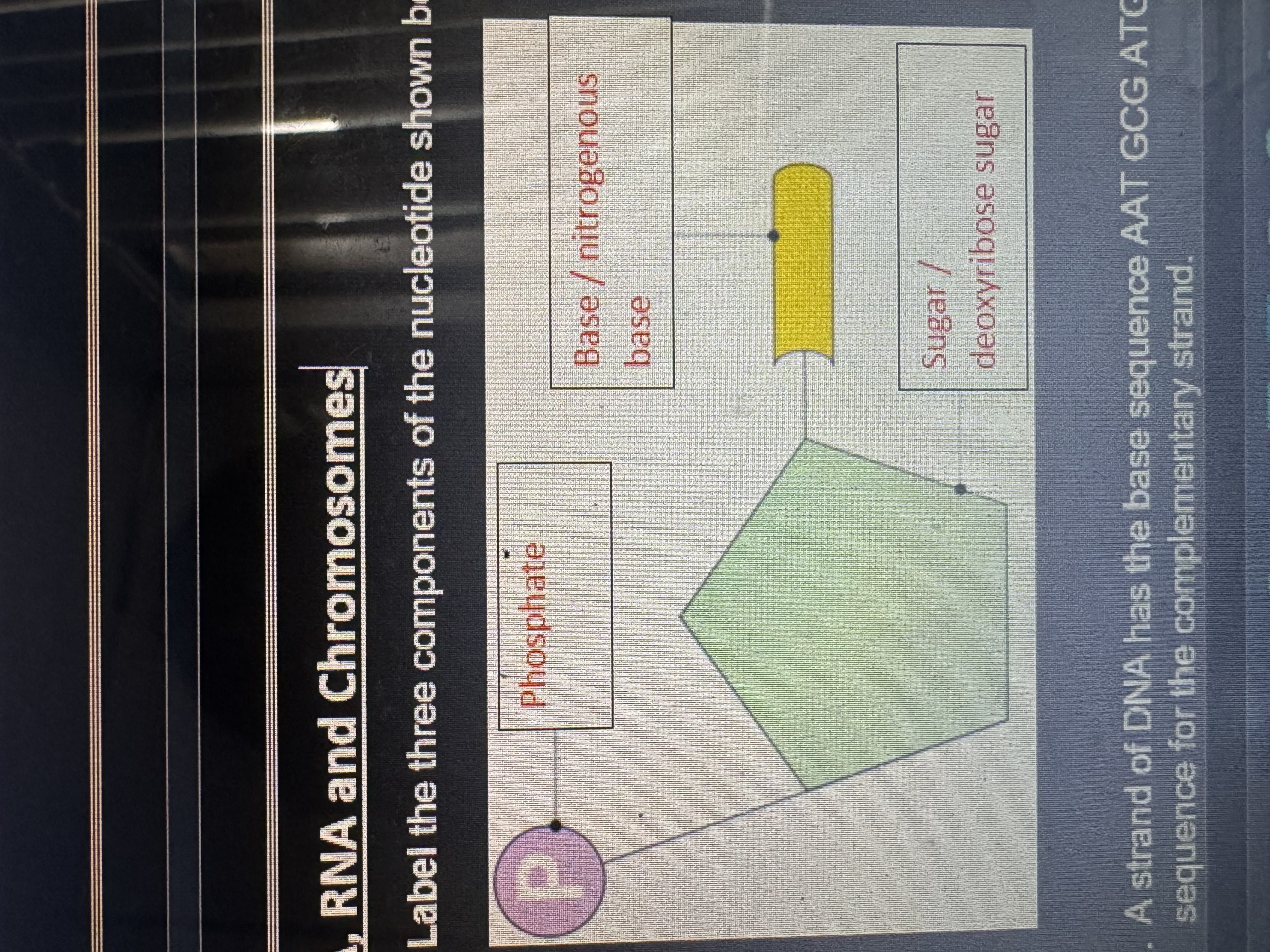
label the 3 components of the nucleotide shown below
phospate, nitrogenous base, deoxyribose sugar
a strand of DNW has the base sequence AAT GCG ATG CGA . state the base sequence for the complementary strand
TTA CGC TAC GCT
describe 4 differences between the structure or function of DNA and RNA
dna is double stranded, rna is single stranded
dna contains deoxyribose sugar, rna contains ribose sugar
dna has bases CGAT, rna has bases CGAU(rna has uracil instead of thymine)
dna is found in the nucleus and stays in the nucleus, rna can leave the nucleus and be found in the cytoplasm
explain the difference between a nitrogen base and a codon
a codon is a group of 3 nitrogenous bases
Explain whether a gene or a chromosome provides the most information about the genetic make-up of an individual
A single chromosome contains multiple genes. This means a chromosome provides a lot more information about the genetic make-up of an individual than a single gene.
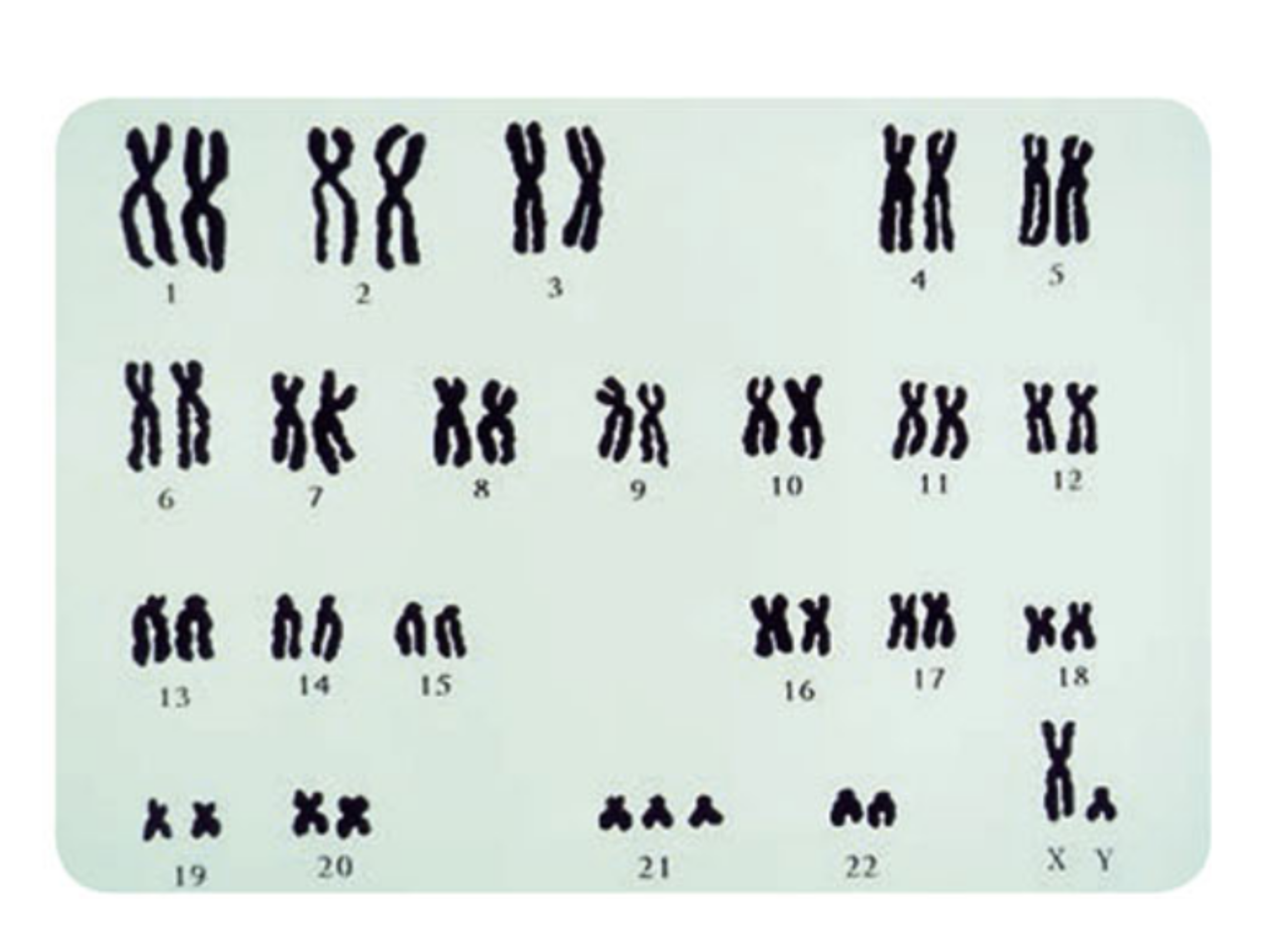
State the total number of chromosomes shown.
State if child is male or female and justify answer
As the geneticist, advice the parents in the health of the baby
47
Male since ir has an X and a Y chromosome
The child has 3 copies of chromosome 21, so does have a genetic condition. In this case, the condition would be Down Syndrome
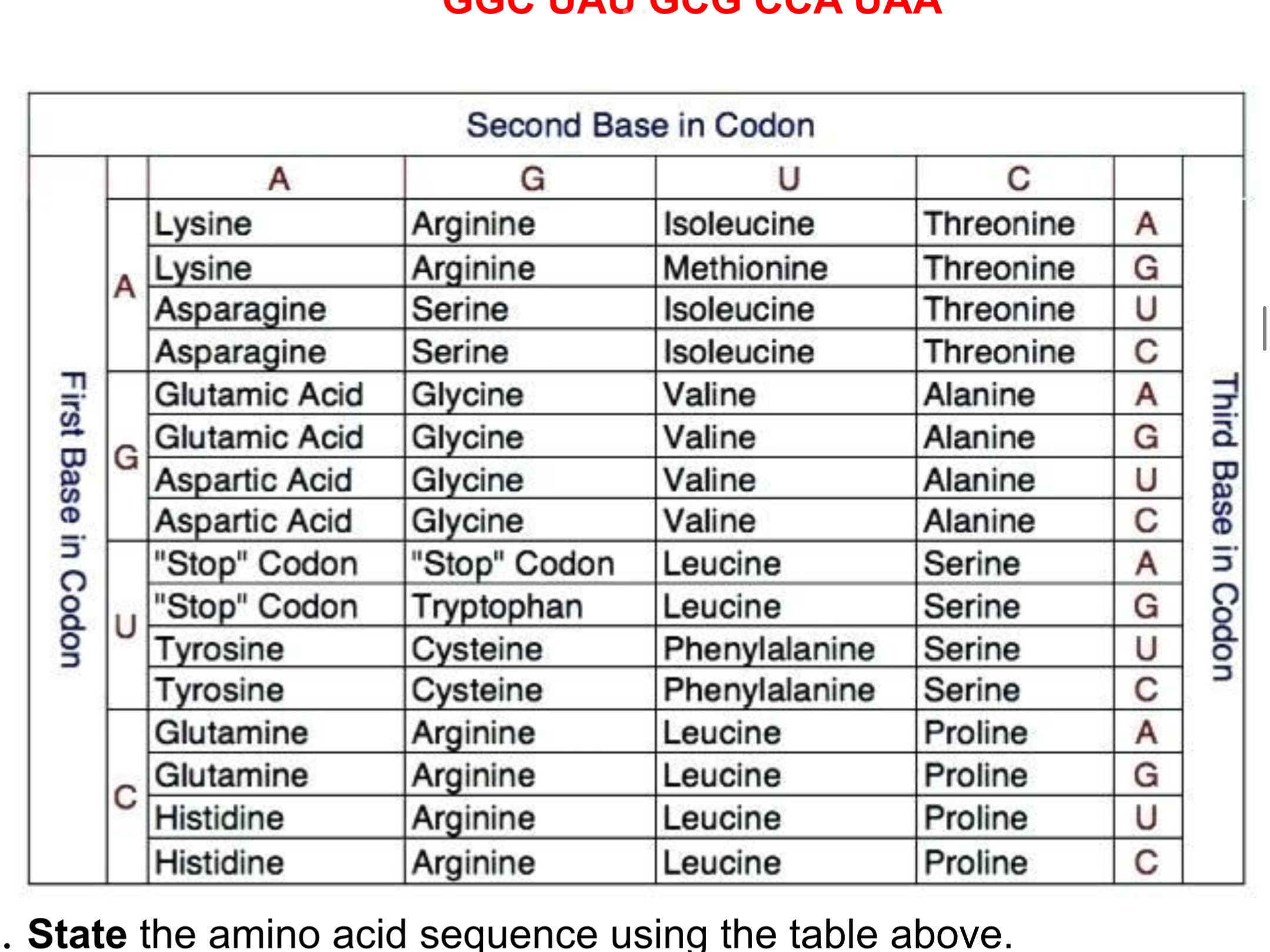
Convert the following dna sequence into an rna sequence: CCG ATA CGC GGT ATT
State the amino acid sequence using the table above
Predict the effect on the protein strand if the SECOND A in the DNA sequence was misread as a T
GGC UAU GCG UAA
Glycine - Tyrosine - Alanine - Proline - “Stop” codon
This changes the RNA strand to UAA, which is a “stop” codon. This stops amino acid production at this point, reducing the length of the protein and possible affecting its function.
State the difference between transcription and translation
Transcription is the process of turning DNA into RNA (transcribing / copying it).
Translation is the process of forming amino acids from the RNA strand (translating bases into amino acids)
a. What Statement below is not a function of mitosis
A . Replenishing the epithelial cells of the small intestine that are shed daily.
B. Forming new red blood cells to replace those that are worn out.
C. Forming cells for sexual reproduction.
D. Repairing cuts and abrasions of the skin.
b. State the name given to the process responsible for the function u selected in (a)
c. Propose a reason why this process is not a function of mitosis. Consider what would happen if mitosis was responsible for this function
A. C
B. Meiosis
C. Mitosis produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent, so have 2 sets of chromosomes. If sex cells are produced by mitosis, when fertilisation occurs the zygote will have 4 sets of chromosomes (for a total of 92). This would continue to double each generation.
State the difference between a halploid cell and a diploid cell
a haploid cell contains one set of chromosomes (n=1). sex cells r haploid cells.
a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes (n=2). body cells are all diploid cells
what is each stage of mitosis
interphase
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
cytokinesis
describe each stage of mitosis
interphase: chromosomes duplicate and the cell builds extra organelles. the normal life of a cell
prophase: the chromosomes duplicate to form bivalent chromosomes and chromosomes become visible. chromosomes appear, nucleus membrane disappears, spindle forms
metaphase: nuclear membrane disappears, and spindle fibres attach to chromosomes which line up at the equator. the chromosomes line up in a single line across the centre of cell
anaphase: the bivalent chromosomes split into sister chromatids, which r each pulled to the opposite side of the cell by spindle fibres. each side receives one chromatid per pair and a set of organelles.
telophase: the cell begins splitting into two new cells, each containing 46 chromosomes. nuclear membranes re-form
cytokinesis: the new cell wall forms, separating the two new cells from each other. cytoplasm divides; two daughter cells are produced
describe the difference between autosome and sex chromosome
sex chrosomed determine the sex of an individual. autosomes r all the chromosomes that aren’t sex chromosomes
determine the different between a gene and allele
an allele is a variation/possible version of a gene
describe the difference between heterozygous and homozygous
an individual is heterozygous for a trait if they have two different alleles for a trait. an individual is homozygous for a trait if they have two of the same alleles for a trait
define a genotype and provide an example
the allele combination an individual carries for a trait, for example Rr
define phenotype and provide an example of each
the observable characteristics of a trait, for example can roll tongue
patate the conditions under which dominant traits r expressed. contrast this to the conditions under which recessive traits r expressed.
dominant traits wil be expressed whenever there’s at least one copy of the dominant allele present.
recessive traits will only be expressed if they’re the only allele present
attached earlobes (E) is dominant to unattached earlobes. write the possible genotypes for
a. attached earlobes
b. unattached earlobes
c. carriers
a. EE and Ee
b. ee
c. Ee
long eyelashes (L) r dominant to short eyelashes. a woman and man, both with long lashes, have 2 children. the daughter has long lashes and the son has short. write the possible genotypes for each individual.
woman:
man:
daughter:
son:
Ll
Ll
LL or Ll
ll
state how a sex linked trait is different to an autosomal trait
a sex linked trait is found in the sex chromosome instead of an autosome
list 4 conditions that r sex linked
haemophilia, red green colour blindness, high blood pressure, muscular dystrophy
what’s a square, circle, coloured square, coloured circle
male, female, affected male, affected female
if affected children always have affected parents, what’s the pattern of inheritance of the characteristic
sex-linked dominant
mendels laws of inheritance
law of segregation: traits exist in pairs which must be separated before they’re passed onto offspring
law of independent assortment: traits r inherited separately from eachother
law of dominance: where an organism has 2 alternative forms of a gene, the dominant one will always be expressed
define genome
entire dna code of an individual
define dna
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid. a molecule that carries the genetic instructions essential for life
define nucleotides
basic units of dna made from sugar phosphate group and one nitrogenous base
define nitrogenous base
organic, nitrogen containing molecules in dna that pair in specific ways
describe what a dna molecule looks like

what r bivalent chromosomes
they have 2 identical strands. they’re formed during dna replication. each strand is called a chromatid, the 2 chromatically r bind at the centromere (middle of x chromosome)
how many chromosomes does humans have
46(unless abnormality) half from each parent
define protein
complex molecule essential for cellular functions and the foundation of genetic traits
define amino acid
a building block of proteins
define codon
sequences of 3 nucleotides
shape, location, nucleotides, and role of DNA
shape: deoxyribose sugar backbone, double stranded helix
location: nucleus
nucleotides: A T G C
role: stores genetic info as instructions to be copied into mRNA and actioned
shape, location, nucleotides. and role of mRNA
shape: ribose sugar backbone, single strand of nucleotide codons
location: nucleus
nucleotides: A, uracil(U), G , C
role: messenger, carries info from dna gene code to ribosomes
shape location nucleotides and role of tRNA
shape: cloverleaf with anticodon , amino acid attached
location: cytoplasm
nucleotides: U,A,G,C
role: transfer, transfers amino acids to ribosome so they can be added to the protein chain in order
define mitosis
process of cell division to provide growth or repair
define meiosis
the process rhag results in the formation of gamete’s with half the genetic material of the parent cell
define gamete
sex cell(sperm or egg/ova) that has the genetic material of the parent cell
draw a labelled diagram of mitosis
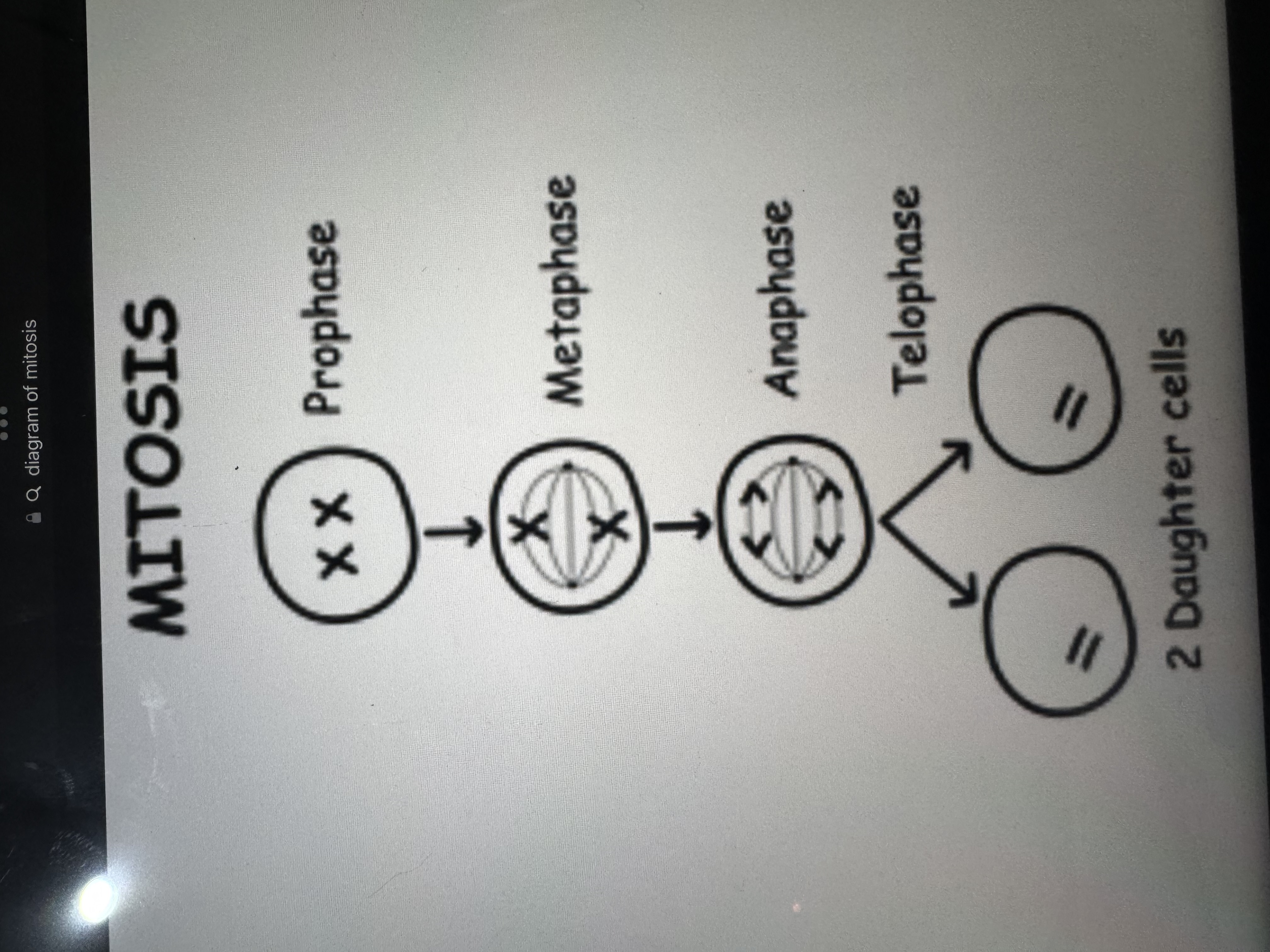
define alleles
a version of a gene
define autosome
a non sex chromosome (1-22)
define sec chromosome
directly involved with determining sex. X and Y in humans
7 features of mitosis
produces w des
undergoes PMAT phases
dna replication occurs prior to division
cytokinesis separates new cells
one cell division occurs
two identical daughter cells
formation of diploid somatic cells
7 featurez of meiosis
produces new cells
undergoes PMAT phases
dna replication occurs prior to division
cytokinesis separates new cells
two cell divisions occur
four genetically difference daughter cells
formation of haploid gamete cells
state the 4 patterns of inheritance
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, x linked dominant, x linked recessive
describe autosomal dominant
typically appears in every gen
unaffected individuals don’t transmit the trait; affected individuals must have at least one affected parent
make and female equally likely to inherit trait
describe autosomal recessive
trait often skips a gen
unaffected individuals may transmit trait; affected individuals don’t have to have an affected parent
x linked/ sex linked recessive
trait can skip a generation
more common in males
affected father can’t pass trait to son
only females can be carriers
x linked / sex linked dominant
affected males pass trait to all daughters but no sons
affected females can pass trait to both sexes with: one allele 50% chance (heterozygous), two alleles 100% chance (homozygous)
appears in every generation
how many chromosomes does a human gamete have
they’re haploid cells thag contain 23 chromosomes