Protists and Prokaryotes: Key Features, Diversity, and Evolution
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the key characteristics of all eukaryotes?
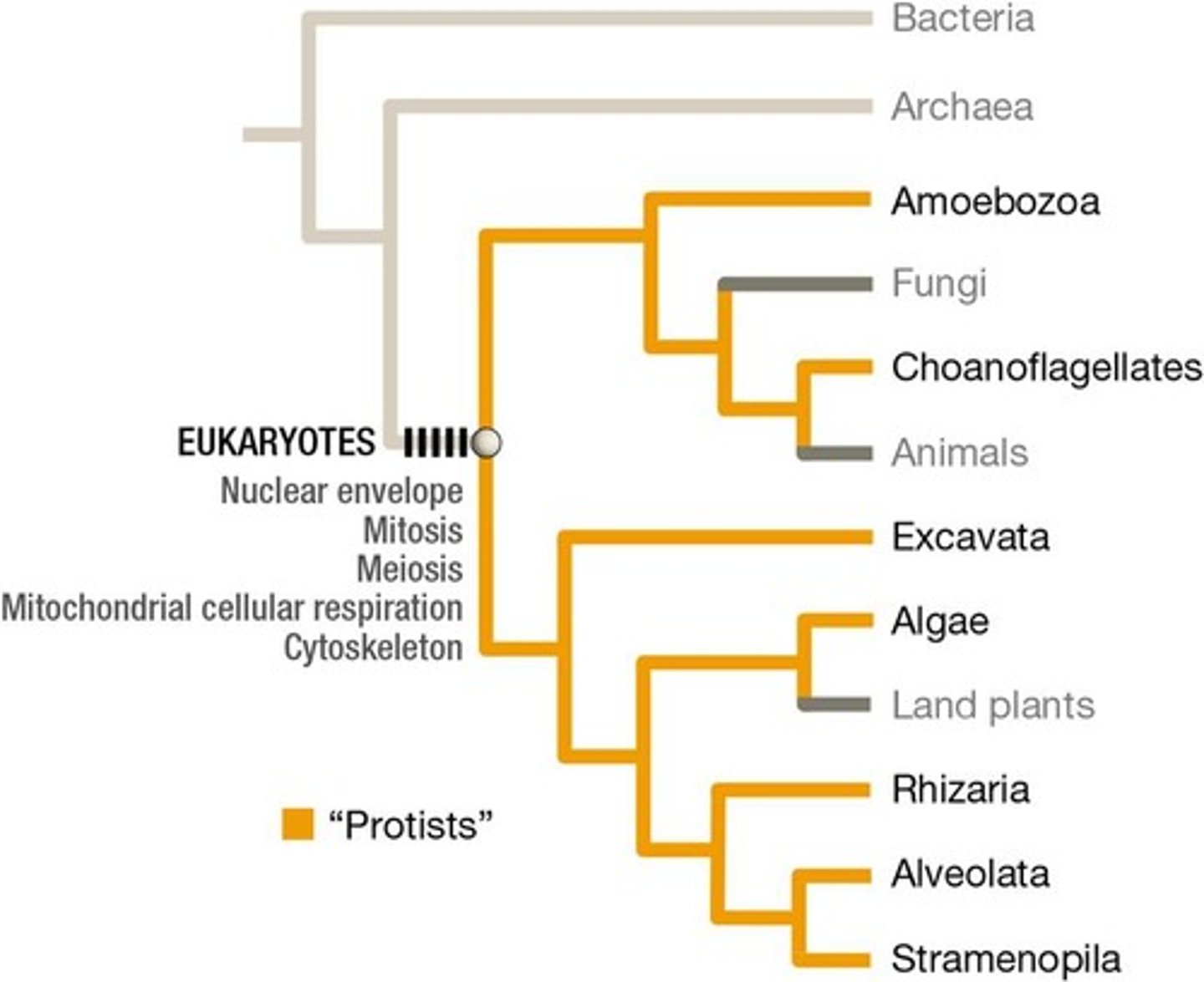
All eukaryotes have either mitochondria or genes normally found in mitochondria, a nucleus and endomembrane system, and a cytoskeleton.
What is the significance of morphological features in Protists?
Morphological features are useful for distinguishing groups of Protists and are primarily studied through microscopy.
How many monophyletic groups of Protists have been suggested?
Tentatively, there are 7 monophyletic groups of Protists, each sharing unique morphological characteristics.
What key innovations evolved in Protists?
Many key innovations, such as multicellularity and unique structures for support and protection, evolved in Protists.
What are mitochondria similar to, and how do they replicate?
Mitochondria are similar in size to α-proteobacteria, replicate by fission, and have their own ribosomes and genomes.

What is the primary endosymbiotic event associated with chloroplasts in Plantae?
The primary endosymbiotic event likely occurred in the common ancestor of Plantae, leading to chloroplasts with 2 membranes.
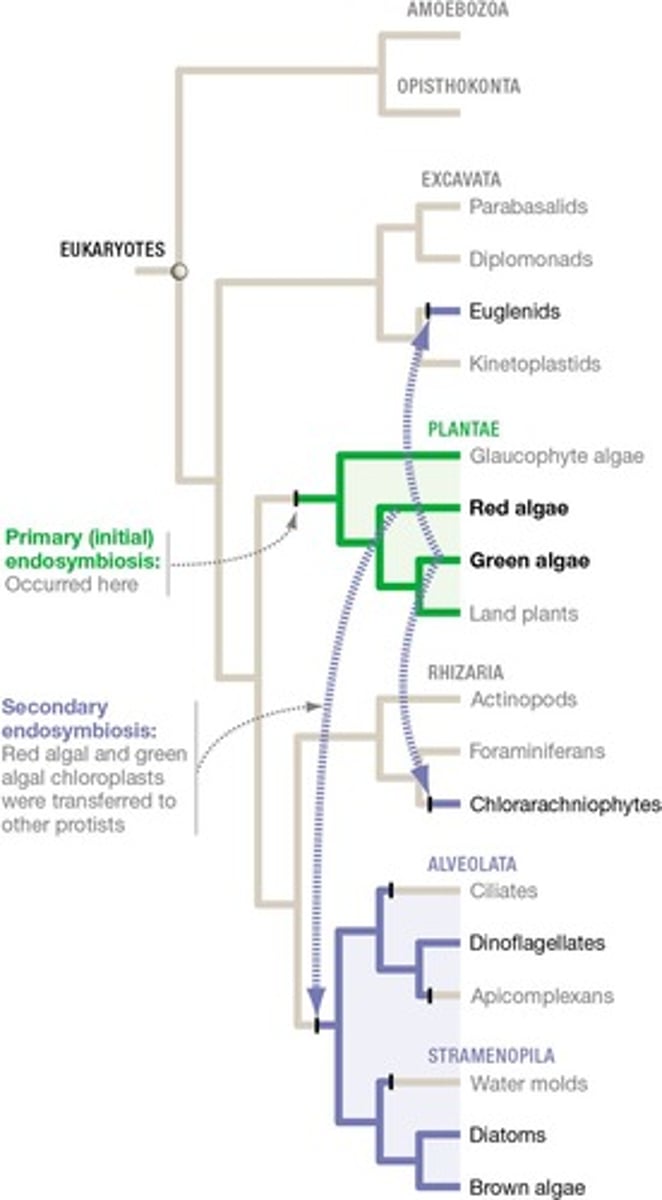
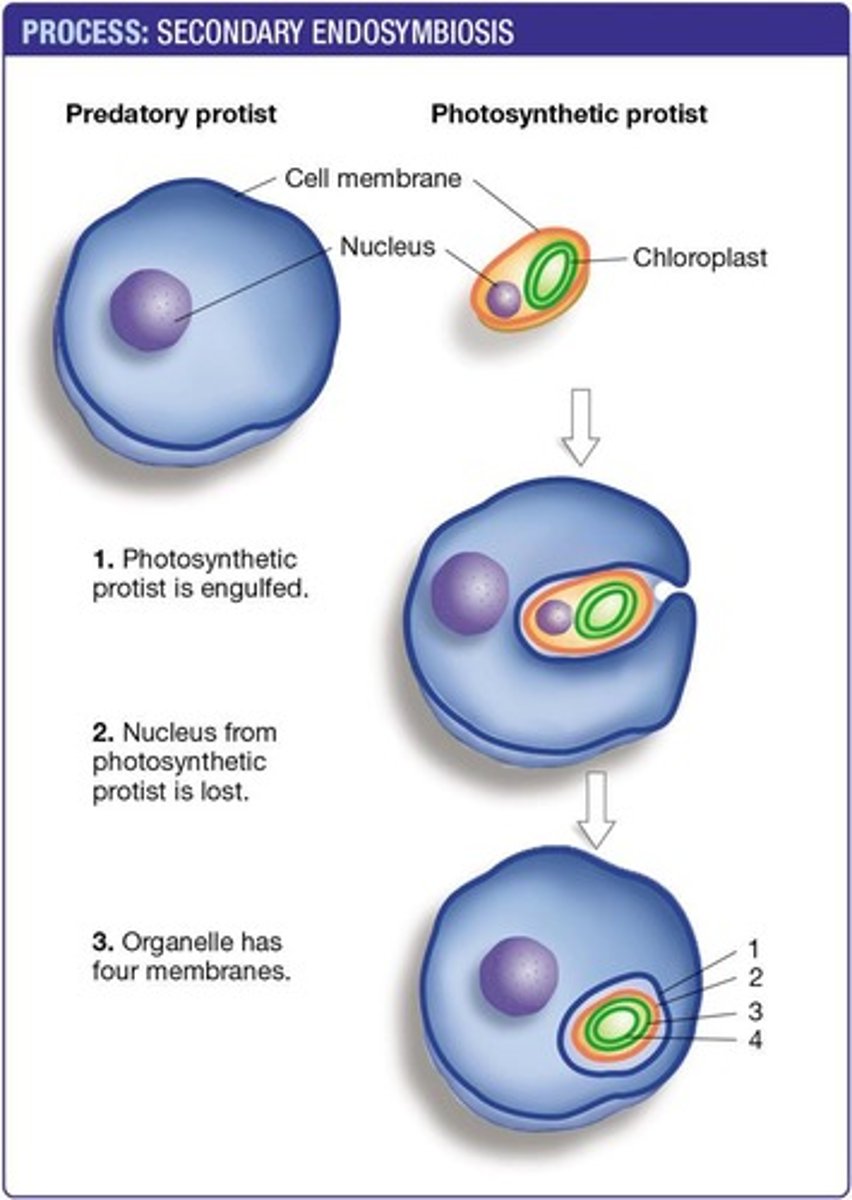
How did some Protists acquire chloroplasts?
Some Protists acquired chloroplasts by ingesting photosynthetic Protists that already had chloroplasts.
What types of reproduction can Protists undergo?
Protists can reproduce sexually, asexually, or both, with sexual reproduction being unique to Eukaryotes.
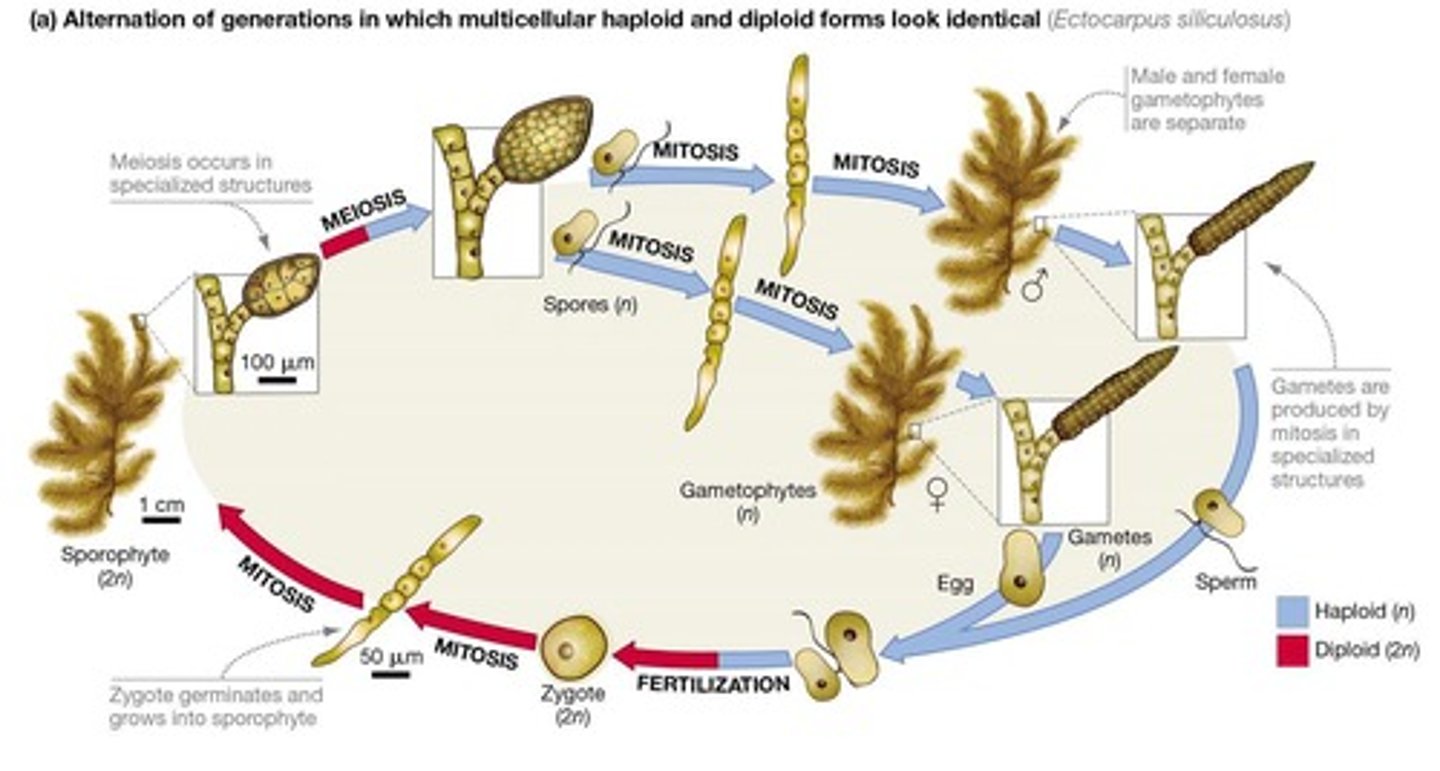
What is alternation of generations in multicellular Protists?
Multicellular Protists can have multicellular haploid and diploid forms, demonstrating alternation of generations.
What historical event was caused by a protist?
The worst crop failure in history was caused by a protist.
What disease is caused by the genus Plasmodium?
Malaria is caused by 5 species of Plasmodium.
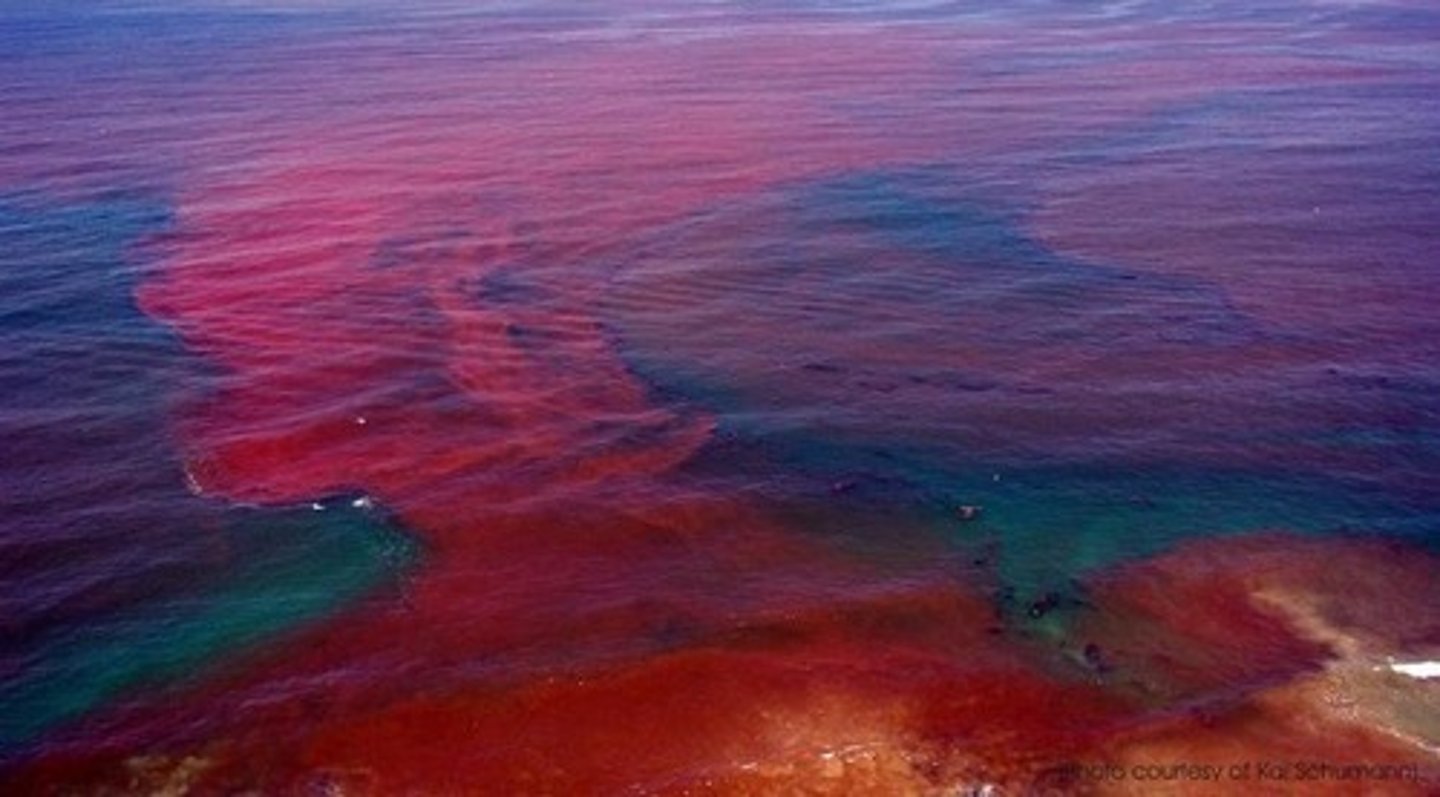
What are harmful algal blooms and what can cause them?
Harmful algal blooms can be caused by dinoflagellates.

What was the previously accepted major division among organisms?
Biologists previously thought the major division was between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
What did Woese propose regarding the tree of life?
Woese proposed the now accepted 3 domain tree of life.
Where can prokaryotes be found?
Prokaryotes can be found almost everywhere, including extreme environments like oxygen-free mud and hot springs.
What are extremophiles?
Extremophiles are organisms that live in extreme environments.
What are pathogens?
Pathogens are bacteria that cause disease.
What are Koch's Postulates?
Koch's Postulates are criteria to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease.
What is virulence?
Virulence is the ability to cause disease and is heritable among individuals in a population.
What is a unique feature of some pathogenic bacteria?
Some pathogenic bacteria produce resistant endospores, which are tough, dormant structures formed during environmental stress.
What are the two main groups of bacteria based on cell-wall composition?
Bacteria can be distinguished into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups.
What are the three metabolic strategies exhibited by prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes exhibit cellular respiration, fermentation, and photosynthesis.